Get your patient on Orencia (Abatacept)
Orencia prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Orencia patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Intravenous Use for Adult RA (2.1) and Adult PsA (2.3)
- Administer at 0, 2, and 4 weeks, and every 4 weeks thereafter, as a 30-minute infusion
| Body Weight of Patient | Dose | Number of Vials |
|---|---|---|
Less than 60 kg | 500 mg | 2 |
60 to 100 kg | 750 mg | 3 |
More than 100 kg | 1,000 mg | 4 |
Subcutaneous Use for Adult RA (2.1)
- Prior to the first subcutaneous dose, may administer an optional loading dose as a single intravenous infusion as per body weight categories above.
- Administer 125 mg by subcutaneous injection once weekly (within a day of the intravenous infusion if infusion given).
- Patients switching from intravenous use to subcutaneous use, administer first subcutaneous dose instead of next scheduled intravenous dose.
Intravenous Use for pJIA in Pediatric Patients ≥6 Years Old (2.2)
- Pediatric patients weighing <75 kg administer 10 mg/kg intravenously and those weighing ≥75 kg administer the adult intravenous dosing regimen (not to exceed a maximum dose of 1,000 mg), as a 30-minute infusion.
- Subsequently administer infusions at 2 and 4 weeks and every 4 weeks thereafter.
Subcutaneous Use for pJIA and PsA in Pediatric Patients ≥2 Years Old (2.2)
- Administer subcutaneously without an intravenous loading dose
| Body Weight of Pediatric Patient | Dose (once weekly) |
|---|---|
10 kg to less than 25 kg | 50 mg |
25 kg to less than 50 kg | 87.5 mg |
50 kg or more | 125 mg |
Subcutaneous Use for Adult PsA (2.3 )
- Administer 125 mg by subcutaneous injection once weekly without an intravenous loading dose.
- Patients switching from intravenous use to subcutaneous use, administer first subcutaneous dose instead of next scheduled intravenous dose.
Intravenous Use for Prophylaxis of aGVHD (2.4)
- For patients 6 years and older, administer at a 10 mg/kg dose (maximum dose 1,000 mg) as a 60-minute infusion on the day before transplantation, followed by a dose on Day 5, 14, and 28 after transplant.
- For patients 2 to less than 6 years old, administer a 15 mg/kg dose as a 60-minute infusion on the day before transplantation, followed by a 12 mg/kg dose as a 60-minute infusion on Day 5, 14, and 28 after transplant.
Preparation and Administration Instructions (2.5 , 2.6 )
- Administer as a 30-minute intravenous infusion for RA, pJIA, and adult PsA. (2.5)
- Administer as a 60-minute intravenous infusion for aGVHD prophylaxis. (2.5)
- See the Full Prescribing Information for preparation and administration instructions for intravenous infusion and recommendations for subcutaneous use. (2.5, 2.6) Prepare ORENCIA using only the silicone-free disposable syringe. (2.5)
Dosage in Adult Rheumatoid Arthritis
For adult patients with RA, administer as an intravenous infusion or as a subcutaneous injection. ORENCIA may be used as monotherapy or concomitantly with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) other than JAK inhibitors or bDMARDs (e.g., TNF antagonists).
Intravenous Dosage
Reconstitute ORENCIA lyophilized powder and administer after dilution [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) ] as a 30-minute intravenous infusion utilizing the weight range-based dosing recommended in Table 1. Following the initial intravenous infusion, administer as an intravenous infusion at 2 and 4 weeks and every 4 weeks thereafter.
| Body Weight of Adult Patient | Dose | Number of Vials a |
|---|---|---|
| a Each vial provides 250 mg of abatacept for administration. | ||
Less than 60 kg | 500 mg | 2 |
60 to 100 kg | 750 mg | 3 |
More than 100 kg | 1,000 mg | 4 |
Subcutaneous Dosage
Prior to the first subcutaneous dose, an optional loading dose may be administered as a single intravenous infusion (as per body weight categories in Table 1). If an intravenous loading dose is used, administer the first subcutaneous injection within one day of the infusion. Administer ORENCIA 125 mg in prefilled syringes or in ORENCIA ClickJect™ autoinjector by subcutaneous injection once weekly [see Dosage and Administration (2.6) ] .
For patients switching from ORENCIA intravenous therapy to subcutaneous administration, administer the first subcutaneous dose instead of the next scheduled intravenous dose.
Dosage in Polyarticular Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
For pediatric patients with pJIA, either administer ORENCIA as an intravenous infusion (only patients 6 years of age and older) or as a subcutaneous injection (only patients 2 years of age and older) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4) ] . ORENCIA may be used as monotherapy or concomitantly with methotrexate.
Intravenous Dosage
Administer ORENCIA as a 30-minute intravenous infusion based on body weight [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) ] :
- For body weight less than 75 kg, administer a dose of 10 mg/kg.
- For body weight of 75 kg or greater, administer as per the recommendations in Table 1 (follow the adult intravenous dosing regimen), not to exceed a maximum dose of 1,000 mg.
Following the initial intravenous infusion, administer infusions at 2 and 4 weeks and every 4 weeks thereafter. Immediately discard any unused portion in the vials.
Subcutaneous Dosage
Administer ORENCIA for subcutaneous injection, without an intravenous loading dose, utilizing the weight range-based dosing as recommended in Table 2 [see Dosage and Administration (2.6) ] . Subsequently administer once weekly.
| Body Weight of Pediatric Patient | Dose (once weekly) |
|---|---|
10 to less than 25 kg | 50 mg |
25 to less than 50 kg | 87.5 mg |
50 kg or more | 125 mg |
Patients with pJIA may self-inject with ORENCIA or the patient’s caregiver may administer ORENCIA if both the healthcare practitioner and the parent/legal guardian determine it is appropriate. The ability of pediatric patients to self-inject with the autoinjector has not been tested.
Dosage in Psoriatic Arthritis
Adult Patients
For adult patients with psoriatic arthritis, administer as an intravenous infusion or a subcutaneous injection.
ORENCIA may be used with or without non-biologic DMARDs.
Intravenous Dosage
Administer ORENCIA as a 30-minute intravenous infusion utilizing the weight range-based dosing specified in Table 1. Following the initial intravenous administration, administer an intravenous infusion at 2 and 4 weeks and every 4 weeks thereafter.
Subcutaneous Dosage
Administer 125 mg of ORENCIA subcutaneously once weekly (no intravenous loading dose is needed) [see Dosage and Administration (2.6) ] .
For patients switching from ORENCIA intravenous infusions to subcutaneous administration, administer the first subcutaneous dose instead of the next scheduled intravenous dose.
Pediatric Patients
Administer ORENCIA as a subcutaneous injection in pediatric patients 2 years of age and older with psoriatic arthritis [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4) ] . ORENCIA may be used as monotherapy or concomitantly with methotrexate. Intravenous administration is not approved for pediatric patients with psoriatic arthritis.
Subcutaneous Dosage
Administer ORENCIA for subcutaneous injection weekly, utilizing the weight range-based dosage as recommended in Table 3 [see Dosage and Administration (2.6) ] .
Body Weight of Pediatric Patient | Dose (once weekly) |
10 to less than 25 kg | 50 mg |
25 to less than 50 kg | 87.5 mg |
50 kg or more | 125 mg |
Pediatric patients with psoriatic arthritis may self-inject with ORENCIA or the patient’s caregiver may administer ORENCIA if both the healthcare practitioner and the parent/legal guardian determine it is appropriate. The ability of pediatric patients to self-inject with the autoinjector has not been tested.
Dosage in Prophylaxis of Acute Graft versus Host Disease in Adults and Pediatric Patients Aged 2 Years and Older
Antiviral Prophylactic Treatment
Before administering ORENCIA, administer recommended antiviral prophylactic treatment for Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) reactivation, and continue for six months following HSCT. In addition, consider prophylactic antivirals for Cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection/reactivation during treatment and for six months following HSCT [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ].
Intravenous Dosing Regimen
For patients 6 years and older, administer ORENCIA 10 mg/kg (maximum dose of 1,000 mg) as an intravenous infusion over 60 minutes on the day before transplantation (Day -1), followed by administration on Days 5, 14, and 28 after transplantation.
For patients 2 to less than 6 years old, administer ORENCIA 15 mg/kg as an intravenous infusion over 60 minutes on the day before transplantation (Day -1), followed by 12 mg/kg as an intravenous infusion over 60 minutes on Days 5, 14, and 28 after transplantation.
Preparation and Administration Instructions for Intravenous Infusion
Calculate the ORENCIA dose, the total volume of reconstituted solution required, and the number of ORENCIA vials needed. For a full dose, less than the full contents of one vial or more than one vial may be needed. Using aseptic technique, reconstitute, dilute, and then administer ORENCIA as follows:
Reconstitution
- Use the vial only if the vacuum is present.
- Reconstitute each vial of supplied ORENCIA lyophilized powder (each vial supplies 250 mg of abatacept) with 10 mL of Sterile Water for Injection, USP (direct the stream toward the inside wall of the vial) to obtain a concentration of 25 mg/mL. Use only the provided silicone-free syringe with an 18- to 21-gauge needle:
- If the ORENCIA lyophilized powder is accidently reconstituted using a siliconized syringe, the solution may develop a few translucent particles (discard any solutions prepared using siliconized syringes).
- If the silicone-free disposable syringe is dropped or becomes contaminated, use a new silicone-free disposable syringe. To obtain new silicone-free syringes, contact Bristol-Myers Squibb at 1-800-ORENCIA.
- Gently swirl the vial to minimize foam formation, until the contents are completely dissolved. Do not shake. Avoid prolonged or vigorous agitation.
- Upon complete dissolution of the lyophilized powder, vent the vial with a needle to dissipate any foam that may be present.
- Visually inspect the reconstituted solution (the solution should be clear and colorless to pale yellow). Do not use if opaque particles, discoloration, or other foreign particles are present.
- Repeat steps 2) through 5) if two, three, or four vials are needed for a dose (see Table 1).
Dilution
- Must further dilute the reconstituted ORENCIA solution to 100 mL as follows:
- From a 100 mL infusion bag or bottle of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, withdraw a volume equal to the volume of the reconstituted ORENCIA solution required for the patient’s dose.
- Slowly add the reconstituted ORENCIA solution(s) into the infusion bag or bottle using the silicone-free disposable syringe provided with each vial .
- Gently mix. Do not shake the bag or bottle . The final concentration of abatacept in the bag or bottle will depend upon the amount of abatacept added, but will be no more than 10 mg/mL. Immediately discard any unused portion in the ORENCIA vial.
Administration
- Prior to administration, visually inspect the ORENCIA diluted solution for particulate matter and discoloration. Discard the diluted solution if any particulate matter or discoloration is observed.
- Using an infusion set and a sterile, non-pyrogenic, low-protein-binding filter (pore size of 0.2 μm to 1.2 μm), administer the entire diluted ORENCIA solution over:
- 30 minutes for RA, pJIA, and adults with PsA
- 60 minutes for aGVHD prophylaxis
- Must complete the infusion of the diluted ORENCIA solution within 24 hours of reconstitution of the ORENCIA vials.
Do not infuse ORENCIA concomitantly in the same intravenous line with other agents. No physical or biochemical compatibility studies have been conducted to evaluate the coadministration of ORENCIA with other drugs.
Storage of Diluted ORENCIA Solution
May store the diluted ORENCIA solution at room temperature or refrigerate at 2ºC to 8ºC (36ºF to 46ºF) up to 24 hours before use. Discard the diluted solution if not administered within 24 hours.
Recommendations for Subcutaneous Administration
ORENCIA prefilled syringes and ORENCIA ClickJect autoinjectors are intended for:
- Subcutaneous use only and are not intended for intravenous infusion.
- Use under the guidance of a healthcare practitioner.
After proper training in subcutaneous injection technique, a patient or the patient’s caregiver may administer a subcutaneous injection of ORENCIA (ClickJect autoinjector or prefilled syringe) if a healthcare practitioner determines that it is appropriate. Instruct patients and/or caregivers to follow the directions provided in the Instructions for Use for additional details on administration. Specifically instruct them to inject the full amount (which provides the proper dose of ORENCIA), rotate injection sites, and to avoid injections into areas where the skin is tender, bruised, red, or hard.
Visually inspect for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. Do not use ORENCIA prefilled syringes or ORENCIA ClickJect autoinjectors exhibiting particulate matter or discoloration. ORENCIA should be clear to slightly opalescent and colorless to pale yellow.

Orencia prescribing information
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ORENCIA is a selective T cell costimulation modulator indicated for:
- the treatment of adult patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis (RA). (1.1)
- the treatment of patients 2 years of age and older with moderately to severely active polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis (pJIA). (1.2)
- the treatment of patients 2 years of age and older with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA). (1.3)
- the prophylaxis of acute graft versus host disease (aGVHD), in combination with a calcineurin inhibitor and methotrexate, in adults and pediatric patients 2 years of age and older undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) from a matched or 1 allele-mismatched unrelated donor. (1.4)
Limitations of Use:
Concomitant use of ORENCIA with other immunosuppressives [e.g., biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDS), Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors] is not recommended. (1.5 , 5.1)
Adult Rheumatoid Arthritis
ORENCIA ® is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Polyarticular Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
ORENCIA is indicated for the treatment of patients 2 years of age and older with moderately to severely active polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis (pJIA).
Psoriatic Arthritis
ORENCIA is indicated for the treatment of patients 2 years of age and older with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Prophylaxis for Acute Graft versus Host Disease
ORENCIA is indicated for the prophylaxis of acute graft versus host disease (aGVHD), in combination with a calcineurin inhibitor and methotrexate, in adults and pediatric patients 2 years of age and older undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) from a matched or 1 allele-mismatched unrelated-donor.
Limitations of Use
The concomitant use of ORENCIA with other potent immunosuppressants [e.g., biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs), Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors] is not recommended.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Intravenous Use for Adult RA (2.1) and Adult PsA (2.3)
- Administer at 0, 2, and 4 weeks, and every 4 weeks thereafter, as a 30-minute infusion
| Body Weight of Patient | Dose | Number of Vials |
|---|---|---|
Less than 60 kg | 500 mg | 2 |
60 to 100 kg | 750 mg | 3 |
More than 100 kg | 1,000 mg | 4 |
Subcutaneous Use for Adult RA (2.1)
- Prior to the first subcutaneous dose, may administer an optional loading dose as a single intravenous infusion as per body weight categories above.
- Administer 125 mg by subcutaneous injection once weekly (within a day of the intravenous infusion if infusion given).
- Patients switching from intravenous use to subcutaneous use, administer first subcutaneous dose instead of next scheduled intravenous dose.
Intravenous Use for pJIA in Pediatric Patients ≥6 Years Old (2.2)
- Pediatric patients weighing <75 kg administer 10 mg/kg intravenously and those weighing ≥75 kg administer the adult intravenous dosing regimen (not to exceed a maximum dose of 1,000 mg), as a 30-minute infusion.
- Subsequently administer infusions at 2 and 4 weeks and every 4 weeks thereafter.
Subcutaneous Use for pJIA and PsA in Pediatric Patients ≥2 Years Old (2.2)
- Administer subcutaneously without an intravenous loading dose
| Body Weight of Pediatric Patient | Dose (once weekly) |
|---|---|
10 kg to less than 25 kg | 50 mg |
25 kg to less than 50 kg | 87.5 mg |
50 kg or more | 125 mg |
Subcutaneous Use for Adult PsA (2.3 )
- Administer 125 mg by subcutaneous injection once weekly without an intravenous loading dose.
- Patients switching from intravenous use to subcutaneous use, administer first subcutaneous dose instead of next scheduled intravenous dose.
Intravenous Use for Prophylaxis of aGVHD (2.4)
- For patients 6 years and older, administer at a 10 mg/kg dose (maximum dose 1,000 mg) as a 60-minute infusion on the day before transplantation, followed by a dose on Day 5, 14, and 28 after transplant.
- For patients 2 to less than 6 years old, administer a 15 mg/kg dose as a 60-minute infusion on the day before transplantation, followed by a 12 mg/kg dose as a 60-minute infusion on Day 5, 14, and 28 after transplant.
Preparation and Administration Instructions (2.5 , 2.6 )
- Administer as a 30-minute intravenous infusion for RA, pJIA, and adult PsA. (2.5)
- Administer as a 60-minute intravenous infusion for aGVHD prophylaxis. (2.5)
- See the Full Prescribing Information for preparation and administration instructions for intravenous infusion and recommendations for subcutaneous use. (2.5, 2.6) Prepare ORENCIA using only the silicone-free disposable syringe. (2.5)
Dosage in Adult Rheumatoid Arthritis
For adult patients with RA, administer as an intravenous infusion or as a subcutaneous injection. ORENCIA may be used as monotherapy or concomitantly with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) other than JAK inhibitors or bDMARDs (e.g., TNF antagonists).
Intravenous Dosage
Reconstitute ORENCIA lyophilized powder and administer after dilution [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) ] as a 30-minute intravenous infusion utilizing the weight range-based dosing recommended in Table 1. Following the initial intravenous infusion, administer as an intravenous infusion at 2 and 4 weeks and every 4 weeks thereafter.
| Body Weight of Adult Patient | Dose | Number of Vials a |
|---|---|---|
| a Each vial provides 250 mg of abatacept for administration. | ||
Less than 60 kg | 500 mg | 2 |
60 to 100 kg | 750 mg | 3 |
More than 100 kg | 1,000 mg | 4 |
Subcutaneous Dosage
Prior to the first subcutaneous dose, an optional loading dose may be administered as a single intravenous infusion (as per body weight categories in Table 1). If an intravenous loading dose is used, administer the first subcutaneous injection within one day of the infusion. Administer ORENCIA 125 mg in prefilled syringes or in ORENCIA ClickJect™ autoinjector by subcutaneous injection once weekly [see Dosage and Administration (2.6) ] .
For patients switching from ORENCIA intravenous therapy to subcutaneous administration, administer the first subcutaneous dose instead of the next scheduled intravenous dose.
Dosage in Polyarticular Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
For pediatric patients with pJIA, either administer ORENCIA as an intravenous infusion (only patients 6 years of age and older) or as a subcutaneous injection (only patients 2 years of age and older) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4) ] . ORENCIA may be used as monotherapy or concomitantly with methotrexate.
Intravenous Dosage
Administer ORENCIA as a 30-minute intravenous infusion based on body weight [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) ] :
- For body weight less than 75 kg, administer a dose of 10 mg/kg.
- For body weight of 75 kg or greater, administer as per the recommendations in Table 1 (follow the adult intravenous dosing regimen), not to exceed a maximum dose of 1,000 mg.
Following the initial intravenous infusion, administer infusions at 2 and 4 weeks and every 4 weeks thereafter. Immediately discard any unused portion in the vials.
Subcutaneous Dosage
Administer ORENCIA for subcutaneous injection, without an intravenous loading dose, utilizing the weight range-based dosing as recommended in Table 2 [see Dosage and Administration (2.6) ] . Subsequently administer once weekly.
| Body Weight of Pediatric Patient | Dose (once weekly) |
|---|---|
10 to less than 25 kg | 50 mg |
25 to less than 50 kg | 87.5 mg |
50 kg or more | 125 mg |
Patients with pJIA may self-inject with ORENCIA or the patient’s caregiver may administer ORENCIA if both the healthcare practitioner and the parent/legal guardian determine it is appropriate. The ability of pediatric patients to self-inject with the autoinjector has not been tested.
Dosage in Psoriatic Arthritis
Adult Patients
For adult patients with psoriatic arthritis, administer as an intravenous infusion or a subcutaneous injection.
ORENCIA may be used with or without non-biologic DMARDs.
Intravenous Dosage
Administer ORENCIA as a 30-minute intravenous infusion utilizing the weight range-based dosing specified in Table 1. Following the initial intravenous administration, administer an intravenous infusion at 2 and 4 weeks and every 4 weeks thereafter.
Subcutaneous Dosage
Administer 125 mg of ORENCIA subcutaneously once weekly (no intravenous loading dose is needed) [see Dosage and Administration (2.6) ] .
For patients switching from ORENCIA intravenous infusions to subcutaneous administration, administer the first subcutaneous dose instead of the next scheduled intravenous dose.
Pediatric Patients
Administer ORENCIA as a subcutaneous injection in pediatric patients 2 years of age and older with psoriatic arthritis [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4) ] . ORENCIA may be used as monotherapy or concomitantly with methotrexate. Intravenous administration is not approved for pediatric patients with psoriatic arthritis.
Subcutaneous Dosage
Administer ORENCIA for subcutaneous injection weekly, utilizing the weight range-based dosage as recommended in Table 3 [see Dosage and Administration (2.6) ] .
Body Weight of Pediatric Patient | Dose (once weekly) |
10 to less than 25 kg | 50 mg |
25 to less than 50 kg | 87.5 mg |
50 kg or more | 125 mg |
Pediatric patients with psoriatic arthritis may self-inject with ORENCIA or the patient’s caregiver may administer ORENCIA if both the healthcare practitioner and the parent/legal guardian determine it is appropriate. The ability of pediatric patients to self-inject with the autoinjector has not been tested.
Dosage in Prophylaxis of Acute Graft versus Host Disease in Adults and Pediatric Patients Aged 2 Years and Older
Antiviral Prophylactic Treatment
Before administering ORENCIA, administer recommended antiviral prophylactic treatment for Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) reactivation, and continue for six months following HSCT. In addition, consider prophylactic antivirals for Cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection/reactivation during treatment and for six months following HSCT [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ].
Intravenous Dosing Regimen
For patients 6 years and older, administer ORENCIA 10 mg/kg (maximum dose of 1,000 mg) as an intravenous infusion over 60 minutes on the day before transplantation (Day -1), followed by administration on Days 5, 14, and 28 after transplantation.
For patients 2 to less than 6 years old, administer ORENCIA 15 mg/kg as an intravenous infusion over 60 minutes on the day before transplantation (Day -1), followed by 12 mg/kg as an intravenous infusion over 60 minutes on Days 5, 14, and 28 after transplantation.
Preparation and Administration Instructions for Intravenous Infusion
Calculate the ORENCIA dose, the total volume of reconstituted solution required, and the number of ORENCIA vials needed. For a full dose, less than the full contents of one vial or more than one vial may be needed. Using aseptic technique, reconstitute, dilute, and then administer ORENCIA as follows:
Reconstitution
- Use the vial only if the vacuum is present.
- Reconstitute each vial of supplied ORENCIA lyophilized powder (each vial supplies 250 mg of abatacept) with 10 mL of Sterile Water for Injection, USP (direct the stream toward the inside wall of the vial) to obtain a concentration of 25 mg/mL. Use only the provided silicone-free syringe with an 18- to 21-gauge needle:
- If the ORENCIA lyophilized powder is accidently reconstituted using a siliconized syringe, the solution may develop a few translucent particles (discard any solutions prepared using siliconized syringes).
- If the silicone-free disposable syringe is dropped or becomes contaminated, use a new silicone-free disposable syringe. To obtain new silicone-free syringes, contact Bristol-Myers Squibb at 1-800-ORENCIA.
- Gently swirl the vial to minimize foam formation, until the contents are completely dissolved. Do not shake. Avoid prolonged or vigorous agitation.
- Upon complete dissolution of the lyophilized powder, vent the vial with a needle to dissipate any foam that may be present.
- Visually inspect the reconstituted solution (the solution should be clear and colorless to pale yellow). Do not use if opaque particles, discoloration, or other foreign particles are present.
- Repeat steps 2) through 5) if two, three, or four vials are needed for a dose (see Table 1).
Dilution
- Must further dilute the reconstituted ORENCIA solution to 100 mL as follows:
- From a 100 mL infusion bag or bottle of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, withdraw a volume equal to the volume of the reconstituted ORENCIA solution required for the patient’s dose.
- Slowly add the reconstituted ORENCIA solution(s) into the infusion bag or bottle using the silicone-free disposable syringe provided with each vial .
- Gently mix. Do not shake the bag or bottle . The final concentration of abatacept in the bag or bottle will depend upon the amount of abatacept added, but will be no more than 10 mg/mL. Immediately discard any unused portion in the ORENCIA vial.
Administration
- Prior to administration, visually inspect the ORENCIA diluted solution for particulate matter and discoloration. Discard the diluted solution if any particulate matter or discoloration is observed.
- Using an infusion set and a sterile, non-pyrogenic, low-protein-binding filter (pore size of 0.2 μm to 1.2 μm), administer the entire diluted ORENCIA solution over:
- 30 minutes for RA, pJIA, and adults with PsA
- 60 minutes for aGVHD prophylaxis
- Must complete the infusion of the diluted ORENCIA solution within 24 hours of reconstitution of the ORENCIA vials.
Do not infuse ORENCIA concomitantly in the same intravenous line with other agents. No physical or biochemical compatibility studies have been conducted to evaluate the coadministration of ORENCIA with other drugs.
Storage of Diluted ORENCIA Solution
May store the diluted ORENCIA solution at room temperature or refrigerate at 2ºC to 8ºC (36ºF to 46ºF) up to 24 hours before use. Discard the diluted solution if not administered within 24 hours.
Recommendations for Subcutaneous Administration
ORENCIA prefilled syringes and ORENCIA ClickJect autoinjectors are intended for:
- Subcutaneous use only and are not intended for intravenous infusion.
- Use under the guidance of a healthcare practitioner.
After proper training in subcutaneous injection technique, a patient or the patient’s caregiver may administer a subcutaneous injection of ORENCIA (ClickJect autoinjector or prefilled syringe) if a healthcare practitioner determines that it is appropriate. Instruct patients and/or caregivers to follow the directions provided in the Instructions for Use for additional details on administration. Specifically instruct them to inject the full amount (which provides the proper dose of ORENCIA), rotate injection sites, and to avoid injections into areas where the skin is tender, bruised, red, or hard.
Visually inspect for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. Do not use ORENCIA prefilled syringes or ORENCIA ClickJect autoinjectors exhibiting particulate matter or discoloration. ORENCIA should be clear to slightly opalescent and colorless to pale yellow.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Intravenous Infusion
- For injection: 250 mg lyophilized powder in a single-dose vial. (3)
Subcutaneous Use
- Intravenous Infusion
- For injection: 250 mg white lyophilized powder in a single-dose vial [see Dosage and Administration (2.1 , 2.2 , 2.3 , 2.5 )] .
- Subcutaneous Use
- Injection: 50 mg/0.4 mL, 87.5 mg/0.7 mL, and 125 mg/mL of a clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to pale-yellow solution in a single-dose prefilled glass syringe.
- Injection: 125 mg/mL of a clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to pale-yellow solution in a single-dose prefilled ClickJect autoinjector.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
The data with ORENCIA use in pregnant women are insufficient to inform on drug-associated risk. However, there are clinical considerations for administering live vaccines to infants who were exposed to ORENCIA while in utero (see Clinical Considerations) . In reproductive toxicology studies in rats and rabbits, no fetal malformations were observed with intravenous administration of ORENCIA during organogenesis at doses that produced exposures approximately 29 times the exposure at the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 10 mg/kg/month on an AUC basis. However, in a pre- and postnatal development study in rats, ORENCIA altered immune function in female rats at 11 times the MRHD on an AUC basis.
Clinical Considerations
Infants and Administration of Live Vaccines
It is unknown if abatacept can cross the placenta into the fetus when a woman is treated with ORENCIA during pregnancy. Abatacept is an immunomodulatory agent. It is unknown if the immune response of an infant who was exposed in utero to abatacept and subsequently administered a live vaccine is impacted. Risks and benefits should be considered prior to vaccinating such infants [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ] .
Data
Human Data
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of ORENCIA use in pregnant women. The data with ORENCIA use in pregnant women are insufficient to inform on drug-associated risk.
Animal Data
Intravenous administration of abatacept during organogenesis to mice (10, 55, or 300 mg/kg/day), rats (10, 45, or 200 mg/kg/day), and rabbits (10, 45, or 200 mg/kg every 3 days) produced exposures in rats and rabbits that were approximately 29 times the MRHD on an AUC basis (at maternal doses of 200 mg/kg/day in rats and rabbits), and no embryotoxicity or fetal malformations were observed in any species.
In a study of pre- and postnatal development in rats (10, 45, or 200 mg/kg every 3 days from gestation day 6 through lactation day 21), alterations in immune function in female offspring, consisting of a 9-fold increase in T-cell-dependent antibody response relative to controls on postnatal day (PND) 56 and thyroiditis in a single female pup on PND 112, occurred at approximately 11 times the MRHD on an AUC basis (at a maternal dose of 200 mg/kg). No adverse effects were observed at approximately 3 times the MRHD (a maternal dose of 45 mg/kg). It is not known if immunologic perturbations in rats are relevant indicators of a risk for development of autoimmune diseases in humans exposed in utero to abatacept. Exposure to abatacept in the juvenile rat, which may be more representative of the fetal immune system state in the human, resulted in immune system abnormalities including inflammation of the thyroid and pancreas [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.2) ] .
Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information regarding the presence of abatacept in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. However, abatacept was present in the milk of lactating rats dosed with abatacept.
Pediatric Use
Polyarticular Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
The safety and effectiveness of ORENCIA for reducing signs and symptoms in patients 2 years of age and older with moderately to severely active polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis (pJIA) have been established (ORENCIA may be used as monotherapy or concomitantly with methotrexate). Use of ORENCIA for this indication is supported by evidence from the following studies:
- Intravenous Use : A randomized withdrawal efficacy, safety, and pharmacokinetic study of intravenous ORENCIA in 190 pediatric patients 6 to 17 years of age with pJIA [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) and Clinical Studies (14.2) ] . Given that population pharmacokinetic (PK) analyses (after intravenous ORENCIA administration) showed that clearance of abatacept increased with baseline body weight, intravenous ORENCIA is administered either weight-based or weight ranged based [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) ] . Intravenous ORENCIA administration has not been studied in patients younger than 6 years of age.
- Subcutaneous Use : An open-label PK and safety study of subcutaneous ORENCIA in 205 pediatric patients aged 2 to 17 years old with pJIA, extrapolation of effectiveness of intravenous ORENCIA in patients with pJIA and subcutaneous ORENCIA in patients with RA [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) and Clinical Studies (14.2)] . Given that population PK analyses (after subcutaneous ORENCIA injection) in pJIA patients showed that there was a trend toward higher clearance of abatacept with increasing body weight, subcutaneous ORENCIA dosage is weight range-based [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) ] .
The safety and effectiveness of ORENCIA use in pJIA in pediatric patients less than two years of age have not been established.
Acute Graft Versus Host Disease Prophylaxis
The safety and effectiveness of ORENCIA for the prophylaxis of Acute Graft Versus Host Disease (aGVHD), in combination with a calcineurin inhibitor and methotrexate, in pediatric patients aged 2 years of age and older undergoing HSCT from a matched or 1 allele-mismatched unrelated donor have been established. Use of ORENCIA for this indication is supported by evidence from:
- adequate and well-controlled studies in adults and pediatric patients aged 6 years and older administered a dose of 10 mg/kg intravenously on the day before transplantation followed by a dose of 10 mg/kg intravenously on Days 5, 14, and 28 after transplantation and
- pharmacokinetic modeling and simulations of abatacept exposure in pediatric patients aged 2 to less than 6 years administered a dose of 15 mg/kg intravenously on the day before transplantation followed by a dose of 12 mg/kg intravenously on Days 5, 14, and 28 after transplantation.
Furthermore, the course of disease is sufficiently similar in pediatric patients aged 2 years to less than 6 years to that of patients aged 6 years and older to allow extrapolation of data to younger pediatric patients [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) and Clinical Studies (14.4) ] . No new safety signals were observed in pediatric patients aged 6 years and older in Study GVHD-1.
The safety and effectiveness of ORENCIA for this indication have not been established in pediatric patients less than 2 years of age.
Psoriatic Arthritis
Subcutaneous Administration
The safety and effectiveness of subcutaneous ORENCIA have been established for treatment of psoriatic arthritis in pediatric patients 2 to 17 years old.
Use of ORENCIA in this age group is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies of ORENCIA in adults with PsA, pharmacokinetic data from adult patients with RA, adult patients with PsA, and pediatric patients with pJIA, and safety data from clinical studies in pediatric patients 2 to 17 years old with pJIA using the subcutaneous formulation.
The observed pre-dose (trough) concentrations are generally comparable between adults with RA and PsA and pediatric patients with JIA with active polyarthritis, and the PK exposure is expected to be comparable between adult PsA and pediatric patients with PsA. [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) , and Clinical Studies (14.1 , 14.2 , 14.3 )].
The safety and effectiveness of subcutaneous ORENCIA have not been established in pediatric patients less than 2 years old with psoriatic arthritis.
Intravenous Administration
The safety and effectiveness of intravenous ORENCIA in pediatric patients with psoriatic arthritis have not been established.
Juvenile Animal Toxicity Data
A juvenile animal study conducted in rats dosed with abatacept from 4 to 94 days of age (prior to immune system maturity) showed an increase in the incidence of infections leading to death at all doses compared with controls. Altered T-cell subsets including increased T-helper cells and reduced T-regulatory cells were observed. In addition, inhibition of T-cell-dependent antibody responses (TDAR) was observed. Upon following these animals into adulthood, lymphocytic inflammation of the thyroid and pancreatic islets was observed. In contrast, studies in adult mice and monkeys have not demonstrated similar findings. As the immune system of the rat is undeveloped in the first few weeks after birth, the relevance of these results to humans is unknown.
Geriatric Use
Rheumatoid Arthritis
A total of 323 patients 65 years of age and older, including 53 patients 75 years and older, received ORENCIA in clinical studies. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between geriatric patients (patients aged 65 years of age and older) and younger adults, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between geriatric patients and younger adults, but greater sensitivity of some geriatric patients cannot be ruled out. The frequency of serious infection and malignancy among ORENCIA-treated patients over age 65 was higher than for those under age 65. Because there is a higher incidence of infections and malignancies in the geriatric population in general, caution should be used when treating geriatric patients.
Acute Graft Versus Host Disease Prophylaxis
Of the 116 patients in Study GVHD-1 who received ORENCIA at a dose of 10 mg/kg for the prophylaxis of aGVHD, 12 (10%) were 65 years of age and older, and 2 (2%) patients were 75 years of age and older [see Clinical Studies (14.4) ]. Clinical studies of ORENCIA for aGVHD did not include sufficient numbers of patients 65 years of age and older to determine whether they respond differently from younger adult patients.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Concomitant use with a TNF antagonist can increase the risk of infections and serious infections. (5.1)
- Hypersensitivity and anaphylaxis have occurred. (5.2)
- Serious infections reported. Patients with a history of recurrent infections or underlying conditions predisposing to infections may experience more infections. Discontinue if a serious infection develops. (5.3)
- Screen for latent TB infection prior to initiating therapy. Patients testing positive should be treated prior to initiating ORENCIA. (5.3)
- Screen for viral hepatitis prior to initiating ORENCIA. (5.3)
- Update vaccinations prior to initiating ORENCIA. Live vaccines should not be given concurrently or within 3 months of discontinuation. ORENCIA may blunt the effectiveness of some immunizations. (5.4)
- COPD patients may develop more frequent respiratory adverse reactions. (5.5)
- Cytomegalovirus (CMV) and Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) reactivation in patients treated for aGVHD prophylaxis. (5.7)
Increased Risk of Infection with Concomitant Use of TNF Antagonists, Other Biologic RA/PsA Therapy, or JAK Inhibitors
In controlled clinical trials in patients with adult RA, patients receiving concomitant intravenous ORENCIA and TNF antagonist therapy experienced more infections (63% vs. 43%) and serious infections (4.4% vs. 0.8%) compared to patients treated with only TNF antagonists [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] . These trials failed to demonstrate an important enhancement of efficacy with concomitant administration of ORENCIA with TNF antagonists; therefore, concurrent therapy with ORENCIA and a TNF antagonist is not recommended. While transitioning from TNF antagonist therapy to ORENCIA therapy, patients should be monitored for signs of infection. Additionally, concomitant use of ORENCIA with other biologic RA/PsA therapy or JAK inhibitors is not recommended.
Hypersensitivity Reactions
In clinical trials of 2688 adult RA patients treated with intravenous ORENCIA, there were two cases (<0.1%) of anaphylaxis reactions. Other reactions potentially associated with drug hypersensitivity, such as hypotension, urticaria, and dyspnea, each occurred in less than 0.9% of ORENCIA-treated patients. Of the 190 ORENCIA-treated patients in pJIA clinical trials, there was one case of a hypersensitivity reaction (0.5%) [see Adverse Reactions (6.1 )] .
In postmarketing experience, fatal anaphylaxis following the first infusion of ORENCIA and life-threatening cases of angioedema have been reported. Angioedema has occurred as early as after the first dose of ORENCIA, but also has occurred with subsequent doses. Angioedema reactions have occurred within hours of administration and in some instances had a delayed onset (i.e., days).
Appropriate medical support measures for the treatment of hypersensitivity reactions should be available for immediate use in the event of a reaction. If an anaphylactic or other serious allergic reaction occurs, administration of intravenous or subcutaneous ORENCIA should be stopped immediately with appropriate therapy instituted, and the use of ORENCIA should be permanently discontinued.
Infections
Serious infections, including sepsis and pneumonia, have been reported in patients receiving ORENCIA (serious infections were reported in 3% and 1.9% of RA patients treated with intravenous ORENCIA and placebo, respectively) [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] . Some of these infections have been fatal. Many of the serious infections have occurred in patients on concomitant immunosuppressive therapy which in addition to their underlying disease, could further predispose them to infection. A higher rate of serious infections has been observed in adult RA patients treated with concurrent TNF antagonists and ORENCIA compared to those treated with ORENCIA alone [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
Healthcare providers should exercise caution when considering the use of ORENCIA in patients with a history of recurrent infections, underlying conditions which may predispose them to infections, or chronic, latent, or localized infections. Patients who develop a new infection while undergoing treatment with ORENCIA should be monitored closely. Administration of ORENCIA should be discontinued if a patient develops a serious infection.
Prior to initiating ORENCIA, patients should be screened for latent tuberculosis (TB) infection according to current TB guidelines. ORENCIA has not been studied in patients with a positive TB screen, and the safety of ORENCIA in individuals with latent TB infection is unknown. Patients testing positive in TB screening should be treated by standard medical practice prior to therapy with ORENCIA.
Antirheumatic therapies have been associated with hepatitis B reactivation. Therefore, screening for viral hepatitis should be performed in accordance with published guidelines before starting therapy with ORENCIA. In clinical studies with ORENCIA, patients who screened positive for hepatitis were excluded from study.
Immunizations
Prior to initiating ORENCIA in pediatric and adult patients, update vaccinations in accordance with current vaccination guidelines. ORENCIA-treated patients may receive current non-live vaccines. Live vaccines should not be given concurrently with ORENCIA or within 3 months after discontinuation. No data are available on the secondary transmission of infection from persons receiving live vaccines to patients receiving ORENCIA. In addition, there are clinical considerations for administering live vaccines to infants who were exposed to ORENCIA while in utero [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ] . Based on its mechanism of action, ORENCIA may blunt the effectiveness of some immunizations.
Increased Risk of Adverse Reactions When Used in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
In Study V, adult COPD patients treated with ORENCIA for RA developed adverse reactions more frequently than those treated with placebo, including COPD exacerbations, cough, rhonchi, and dyspnea. A greater percentage of patients treated with ORENCIA developed a serious adverse event compared to patients treated with placebo (27% vs 6%) [see Clinical Studies (14.1) and Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] . Use of ORENCIA in patients with COPD should be undertaken with caution and such patients should be monitored for worsening of their respiratory status.
Immunosuppression
The possibility exists for drugs inhibiting T-cell activation, including ORENCIA, to affect host defenses against infections and malignancies since T cells mediate cellular immune responses. In clinical trials in patients with adult RA, a higher rate of infections was seen in ORENCIA-treated patients compared to placebo-treated patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) and Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] . The impact of treatment with ORENCIA on the development and course of malignancies is not fully understood [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] . There have been reports of malignancies, including skin cancer in patients receiving ORENCIA [see Adverse Reactions (6.3) ] . Periodic skin examinations are recommended for all ORENCIA-treated patients, particularly those with risk factors for skin cancer.
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) and Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) Reactivation in aGVHD Prophylaxis after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant (HSCT)
Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder (PTLD) occurred in patients who received ORENCIA for aGVHD prophylaxis during unrelated HSCT. Of 116 patients who received ORENCIA, 4 patients (3.4%) experienced PTLD. All the PTLD events were associated with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection. Three of the four patients were EBV serology positive at baseline; one patient had negative baseline EBV serology with donor EBV serology unknown. Three of the 4 patients discontinued acyclovir prophylaxis at day 30 post-transplant. The range of time to onset of the events was 49 to 89 days post-transplant. Monitor patients for EBV reactivation in accordance with institutional practices. Provide prophylaxis for EBV infection for 6 months post-transplantation to prevent EBV-associated PTLD [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) ] .
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) invasive disease occurred in patients who received ORENCIA for aGVHD prophylaxis during unrelated HSCT. Of 116 patients who received ORENCIA, 7% experienced CMV invasive diseases up to day 225 post-transplant. All the patients who experienced CMV invasive disease were CMV serology positive at baseline. The median time to onset of the event was 91 days post-transplant. CMV invasive diseases predominantly involved the gastrointestinal tract [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
Monitor patients for CMV infection/reactivation for 6 months post-transplant regardless of the results of donor and recipient pre-transplant CMV serology. Consider prophylaxis for CMV infection/reactivation [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) ] .
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Increased Risk of Infection with Concomitant Use with TNF Antagonists, Other Biologic RA/PsA Therapy, or JAK Inhibitors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
- Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
- Increased Risk of Adverse Reactions When Used in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ]
- Immunosuppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ]
- Cytomegalovirus (CMV) and Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) Reactivation in aGVHD Prophylaxis after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant (HSCT) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying and controlled conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not predict the rates observed in a broader patient population in clinical practice.
Adverse Reactions in Adult Patients with RA
Adverse Reactions in Adult Patients with RA Treated with Intravenous ORENCIA
The data from placebo-controlled studies described herein reflect exposure to ORENCIA administered intravenously in patients with active RA (1955 patients with ORENCIA, 989 with placebo) (Studies I through VI) [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ] . The studies had either a double-blind, placebo-controlled period of 6 months (258 patients with ORENCIA, 133 with placebo) or 1 year (1697 patients with ORENCIA, 856 with placebo). A subset of these patients received concomitant biologic DMARD therapy, such as a TNF antagonist (204 patients with ORENCIA, 134 with placebo). The concomitant use of ORENCIA with a TNF antagonist is not recommended [see Indications and Usage (1.5) ] . The majority of patients in RA clinical studies received one or more of the following concomitant medications with ORENCIA: methotrexate, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, TNF antagonist, azathioprine, chloroquine, gold, hydroxychloroquine, leflunomide, sulfasalazine, and anakinra.
The most serious adverse reactions were serious infections and malignancies. The most commonly reported adverse events (occurring in ≥10% of patients treated with ORENCIA) were headache, upper respiratory tract infection, nasopharyngitis, and nausea.
The adverse reactions most frequently resulting in clinical intervention (interruption or discontinuation of ORENCIA) were due to infection. The most frequently reported infections resulting in dose interruption were upper respiratory tract infection (1%), bronchitis (0.7%), and herpes zoster (0.7%). The most frequent infections resulting in discontinuation were pneumonia (0.2%), localized infection (0.2%), and bronchitis (0.1%).
Most Common Adverse Reactions in Adult Patients with RA Treated with Intravenous ORENCIA
Adverse reactions occurring in 3% or more of patients and at least 1% more frequently in ORENCIA-treated patients (intravenous) during placebo-controlled RA studies are summarized in Table 4.
| Intravenous ORENCIA (n=1955) a | Placebo (n=989) b | |
|---|---|---|
| • Occurred in ≥3% patients and >1% more frequently in ORENCIA-treated patients. a Includes 204 patients on concomitant biologic DMARDs (adalimumab, anakinra, etanercept, or infliximab). b Includes 134 patients on concomitant biologic DMARDs (adalimumab, anakinra, etanercept, or infliximab). | ||
Headache | 18% | 13% |
Nasopharyngitis | 12% | 9% |
Dizziness | 9% | 7% |
Cough | 8% | 7% |
Back pain | 7% | 6% |
Hypertension | 7% | 4% |
Dyspepsia | 6% | 4% |
Urinary tract infection | 6% | 5% |
Rash | 4% | 3% |
Pain in extremity | 3% | 2% |
Infections in Adult Patients with RA Treated with Intravenous ORENCIA
In the placebo-controlled trials in patients with RA, infections were reported in 54% of intravenous ORENCIA-treated patients and 48% of placebo-treated patients. The most commonly reported infections (reported in 5%-13% of patients) were upper respiratory tract infection, nasopharyngitis, sinusitis, urinary tract infection, influenza, and bronchitis. Other infections reported in fewer than 5% of patients at a higher frequency (>0.5%) with ORENCIA compared to placebo, were rhinitis, herpes simplex, and pneumonia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ] .
Serious infections were reported in 3% of patients treated with ORENCIA and 1.9% of patients treated with placebo. The most common (0.2%-0.5%) serious infections reported with ORENCIA were pneumonia, cellulitis, urinary tract infection, bronchitis, diverticulitis, and acute pyelonephritis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ] .
Malignancies in Adult Patients with RA Treated with Intravenous ORENCIA
In the placebo-controlled portions of the clinical trials (1955 patients treated for RA with ORENCIA for a median of 12 months), the overall frequencies of malignancies were similar in the ORENCIA- and placebo-treated patients (1.3% and 1.1%, respectively). However, more cases of lung cancer were observed in ORENCIA-treated patients (4 cases, 0.2%) than placebo-treated patients (0 cases, 0%). In the cumulative intravenous ORENCIA clinical trials in patients with RA (placebo-controlled and uncontrolled, open-label) a total of 8 cases of lung cancer (0.21 cases per 100 patient-years) and 4 lymphomas (0.10 cases per 100 patient-years) were observed in 2688 patients (3827 patient-years). The rate observed for lymphoma is approximately 3.5-fold higher than expected in an age- and gender-matched general population based on the National Cancer Institute's Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Database. Patients with RA, particularly those with highly active disease, are at a higher risk for the development of lymphoma. Other malignancies included skin, breast, bile duct, bladder, cervical, endometrial, lymphoma, melanoma, myelodysplastic syndrome, ovarian, prostate, renal, thyroid, and uterine cancers [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ] . The potential role of ORENCIA in the development of malignancies in humans is unknown.
Infusion-Related Reactions and Hypersensitivity Reactions in Adult Patients with RA Treated with Intravenous ORENCIA
Acute infusion-related events (adverse reactions occurring within 1 hour of the start of the infusion) in Studies III, IV, and V [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ] were more common in the ORENCIA-treated patients than the placebo patients (9% for ORENCIA, 6% for placebo). The most frequently reported events (1%-2%) were dizziness, headache, and hypertension.
Acute infusion-related events that were reported in >0.1% and ≤1% of patients treated with ORENCIA included cardiopulmonary symptoms, such as hypotension, increased blood pressure, and dyspnea; other symptoms included nausea, flushing, urticaria, cough, hypersensitivity, pruritus, rash, and wheezing. Most of these reactions were mild (68%) to moderate (28%). Fewer than 1% of ORENCIA-treated patients discontinued due to an acute infusion-related event. In controlled trials, 6 ORENCIA-treated patients compared to 2 placebo-treated patients discontinued study treatment due to acute infusion-related events.
In clinical trials of 2688 adult RA patients treated with intravenous ORENCIA, there were two cases (<0.1%) of anaphylaxis. Other reactions potentially associated with drug hypersensitivity, such as hypotension, urticaria, and dyspnea, each occurred in less than 0.9% of ORENCIA-treated patients and generally occurred within 24 hours of ORENCIA infusion. Appropriate medical support measures for the treatment of hypersensitivity reactions should be available for immediate use in the event of a reaction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] .
Adverse Reactions in Patients with COPD Treated for RA with Intravenous ORENCIA
In Study V [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ] , there were 37 and 17 patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) who were treated for RA with ORENCIA and placebo, respectively. The COPD patients treated with ORENCIA for RA developed adverse events more frequently than those treated with placebo (97% vs 88%, respectively). Respiratory disorders occurred more frequently in ORENCIA-treated patients compared to placebo-treated patients (43% vs 24%, respectively) including COPD exacerbation, cough, rhonchi, and dyspnea. A greater percentage of ORENCIA-treated patients developed a serious adverse event compared to placebo-treated patients (27% vs 6%), including COPD exacerbation [3 of 37 patients (8%)] and pneumonia [1 of 37 patients (3%)] [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ] .
Adverse Reactions in Methotrexate-Naive Patients with RA Treated with Intravenous ORENCIA
Study VI was an active-controlled clinical trial in methotrexate-naive patients [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ] . The safety experience in these patients was consistent with the patients in Studies I-V.
Adverse Reactions in Adult Patients with RA Treated with Subcutaneous or Intravenous ORENCIA
The data described below are derived from Study SC-1. Study SC-1 was a randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, non-inferiority study that compared the safety of ORENCIA administered subcutaneously or intravenously in 1457 patients with RA, who received background methotrexate, and experienced an inadequate response to methotrexate (MTX-IR) [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ] . The adverse reaction profile in patients treated with subcutaneous ORENCIA was similar to the adverse reaction profile in patients treated with intravenous ORENCIA and consistent with intravenous ORENCIA administered in Studies I-VI.
Injection Site Reactions in Adult RA Patients Treated with Subcutaneous ORENCIA
The overall frequency of injection site reactions in Study SC-1 was 2.6% (19/736) and 2.5% (18/721) for the subcutaneous ORENCIA group and the subcutaneous placebo group (given intravenous ORENCIA), respectively [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ] . All these injection site reactions (including hematoma, pruritus, and erythema) were mild (83%) to moderate (17%) in severity, and none necessitated drug discontinuation.
Adverse Reactions in Adult Patients with PsA
Adverse Reactions in Adult Patients with PsA Treated with Intravenous or Subcutaneous ORENCIA
The safety of ORENCIA was evaluated in 594 patients with PsA (341 patients on ORENCIA and 253 patients on placebo), in two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials [see Clinical Studies (14.3) ]. Of the 341 patients who received ORENCIA, 128 patients received intravenous ORENCIA (PsA-I) and 213 patients received subcutaneous ORENCIA (PsA-II). The safety profile was comparable between ORENCIA given intravenously in Study PsA-I and ORENCIA given subcutaneously in Study PsA-II and also consistent with the safety profile of ORENCIA in patients with RA [see Warnings and Precautions (5) , Adverse Reactions (6.1 )].
Adverse Reactions in Patients with pJIA
Adverse Reactions in Patients with pJIA Treated with Intravenous ORENCIA
In general, the adverse events in pediatric patients with polyarticular JIA (pJIA) treated with intravenous ORENCIA were similar in frequency and type to those seen in adult patients with RA treated with intravenous ORENCIA [see Warnings and Precautions (5 ) and Adverse Reactions (6) ] .
Study JIA-1 was a three-part study including an open-label extension that assessed the safety of intravenous ORENCIA in 190 pediatric patients, 6 to 17 years of age, with pJIA. Overall frequency of adverse events in the 4‑month, lead-in, open-label period of the study was 70%; infections occurred at a frequency of 36% [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ] . The most common infections were upper respiratory tract infection and nasopharyngitis. The infections resolved without sequelae, and the types of infections were consistent with those commonly seen in outpatient pediatric populations. Other events that occurred at a prevalence of at least 5% were headache, nausea, diarrhea, cough, pyrexia, and abdominal pain.
A total of 6 serious adverse events [acute lymphocytic leukemia, ovarian cyst, varicella infection, disease flare (2), and joint wear] were reported during the initial 4 months of treatment with intravenous ORENCIA.
Of the 190 pediatric patients with pJIA treated with intravenous ORENCIA in clinical trials, there was one case of a hypersensitivity reaction (0.5%). During Periods A, B, and C, acute infusion-related reactions occurred at a frequency of 4%, 2%, and 3%, respectively, and were consistent with the types of events reported in adults.
Upon continued treatment in the open-label extension period, the types of adverse events were similar in frequency and type to those seen in adult patients, except for a single patient diagnosed with multiple sclerosis while on open-label treatment.
Adverse Reactions in Patients with pJIA Treated with Subcutaneous ORENCIA
Study JIA-2 was an open-label study with a 4-month short-term period and a long-term extension period that assessed the safety of subcutaneous ORENCIA in 205 pediatric patients, 2 to 17 years of age with pJIA. The adverse reaction profile in patients with pJIA treated with ORENCIA administered subcutaneously in Study JIA-2 were consistent with the adverse reaction profile in patients with pJIA treated with intravenous Study JIA-1.
There were no reported cases of hypersensitivity reactions. Local injection‑site reactions occurred at a frequency of 4.4%.
Adverse Reactions in Patients Undergoing Unrelated-Donor Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (HSCT) with Intravenous ORENCIA
The data described herein were from one clinical study of ORENCIA (GVHD-1) for aGVHD prophylaxis in patients 6 years and older with hematologic malignancies who were undergoing unrelated HSCT wherein all patients were receiving calcineurin inhibitor and methotrexate as the standard of care for aGVHD prophylaxis [see Clinical Studies (14.4) ] . Two cohorts were studied at 10 mg/kg (maximum dose of 1,000 mg) as an intravenous infusion over 60 minutes on the day before transplantation (Day-1), followed by administration on Days 5, 14, and 28 after transplantation:
1) A single-arm cohort of ORENCIA-treated patients (n=43) who underwent 7 of 8 Human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-matched HSCT from unrelated donors (7 of 8 cohort) and
2) A randomized cohort comprised of ORENCIA-treated patients (n=73) and placebo-treated patients (n=69) who underwent 8 of 8 HLA-matched HSCT from unrelated donors (8 of 8 cohort).
Of the 116 patients who received ORENCIA, 27 (23%) were 6 to less than 17 years of age [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4) ] .
The safety information from the date of first dose of ORENCIA up to Day 225 post-transplantation from this study is presented below. The incidence of adverse reactions was determined based on pooled data of ORENCIA-treated patients from the 2 study cohorts (n=116).
Serious adverse reactions reported in > 5% of patients who received ORENCIA in combination with a calcineurin inhibitor and methotrexate included pyrexia (20%), pneumonia (8%), acute kidney injury (7%), diarrhea (6%), hypoxia (5%), and nausea (5%).
Permanent discontinuation of ORENCIA due to an adverse reaction occurred in two patients (1.7%) due to one case each of pneumonia and allergic reaction.
The most common (≥10%) adverse reactions in the ORENCIA treated patients were anemia, hypertension, CMV reactivation/CMV infection, pyrexia, pneumonia, epistaxis, CD4 lymphocytes decreased, hypermagnesemia, and acute kidney injury.
Table 5 summarizes the frequency of adverse reactions reported in the study of ORENCIA in GVHD-1.
| 7 of 8 Cohort | 8 of 8 Cohort | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adverse Reaction | ORENCIA (+CNI and MTX) (N=43) | ORENCIA (+CNI and MTX) (N=73) | Placebo (+CNI and MTX) (N=69) | |||
All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) | |
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders | ||||||
Anemia | 56 | 56 | 69 | 69 | 57 | 57 |
CD4 lymphocytes decreased | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 9 | 9 |
Vascular Disorders | ||||||
Hypertension | 49 | 49 | 43 | 43 | 38 | 38 |
General Disorders and Administrative Site Conditions | ||||||
Pyrexia | 28 | 9 | 19 | 10 | 20 | 4 |
Infections and Infestations | ||||||
CMV Reactivation/CMV Infection | 26 | 26 | 32 | 32 | 22 | 22 |
Pneumonia | 19 | 19 | 12 | 12 | 10 | 9 |
Respiratory and Mediastinal Disorders | ||||||
Epistaxis | 12 | 12 | 16 | 16 | 10 | 10 |
Renal and Urinary Disorders | ||||||
Acute kidney injury | 9 | 7 | 15 | 15 | 10 | 10 |
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders | ||||||
Hypermagnesemia | 5 | 5 | 18 | 18 | 10 | 10 |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions in <10% of patients who received ORENCIA in combination with calcineurin inhibitor and methotrexate in Study GVHD-1 included EBV reactivation.
Immunogenicity
As with all therapeutic proteins, there is potential for immunogenicity. The detection of antibody formation is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Additionally, the observed incidence of antibody (including neutralizing antibody) positivity in an assay may be influenced by several factors, including assay methodology, sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant medications, and underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of the incidence of antibodies in the studies described below with the incidence of antibodies in other studies or to other abatacept products may be misleading.
Immunogenicity in Adult Patients with RA Treated with Intravenous ORENCIA
Antibodies directed against the entire abatacept molecule or to the CTLA-4 portion of abatacept were assessed by ELISA assays in RA patients for up to 2 years following repeated treatment with intravenous ORENCIA. Thirty-four of 1993 (2%) patients developed binding antibodies to the entire abatacept molecule or to the CTLA-4 portion of abatacept. Because trough levels of abatacept can interfere with assay results, a subset analysis was performed. In the subset analysis, 9 of 154 (6%) patients that had discontinued intravenous ORENCIA treatment for over 56 days developed antibodies. Samples with confirmed binding activity to CTLA-4 were assessed for the presence of neutralizing antibodies in a cell-based luciferase reporter assay. Six of 9 (67%) evaluable patients were shown to possess neutralizing antibodies. However, the development of neutralizing antibodies may be underreported due to lack of assay sensitivity.
No correlation of anti-abatacept antibody development to clinical response or adverse events was observed.
Immunogenicity in Adult RA Patients Treated with Subcutaneous or Intravenous ORENCIA
Study SC-1 compared the immunogenicity to abatacept following subcutaneous or intravenous ORENCIA administration. The overall immunogenicity frequency to abatacept was 1% (8/725) and 2% (16/710) for the subcutaneous and intravenous groups, respectively. The rate is consistent with previous experience, and there was no correlation of immunogenicity with effects on pharmacokinetics, safety, or efficacy.
Immunogenicity in Adult RA Patients Treated with Subcutaneous ORENCIA Monotherapy
Study SC-2 was conducted to determine the effect of subcutaneous monotherapy use of ORENCIA on immunogenicity (without an intravenous loading dose) in 100 RA patients, who had not previously received ORENCIA or other CTLA4Ig. Patients in this study received either subcutaneous ORENCIA plus methotrexate (n=51) or subcutaneous ORENCIA monotherapy (n=49). No patients in either group developed anti-abatacept antibodies after 4 months of treatment. The safety observed in this study was consistent with that observed in the other subcutaneous studies.
Immunogenicity in Adult RA Patients After Treatment, Withdrawal, and then Restart of Subcutaneous ORENCIA
Study SC-3 was conducted to investigate the immunogenicity in adult RA patients after treatment, withdrawal (three months), and restart of ORENCIA subcutaneous treatment (patients were treated concomitantly with methotrexate). One hundred sixty-seven patients were enrolled in the first 3‑month treatment period and responders (n=120) were randomized to either subcutaneous ORENCIA or placebo for the second 3-month period (withdrawal period). Patients from this period then received open-label ORENCIA treatment in the final 3-month period of the study (period 3). At the end of the withdrawal period, 0/38 (0%) patients who continued to receive subcutaneous ORENCIA developed anti-abatacept antibodies compared to 7/73 (10%) of patients who had subcutaneous ORENCIA withdrawn during this period. Half of the patients who received subcutaneous placebo during the withdrawal period received a single intravenous infusion of ORENCIA at the start of period 3 and half received intravenous placebo. At the end of period 3, when all patients again received subcutaneous ORENCIA, the immunogenicity rates were 1/38 (3%) in the group who received subcutaneous ORENCIA throughout, and 2/73 (3%) in the group that had received placebo during the withdrawal period. Upon reinitiating therapy, there were no injection reactions and no differences in response to therapy in patients who were withdrawn from subcutaneous therapy for up to 3 months compared to those who remained on subcutaneous therapy (these results occurred in those who received or did not receive an intravenous loading dose). The safety observed in this study was consistent with that observed in the other studies.
Immunogenicity in Patients with pJIA Treated with Intravenous ORENCIA
Antibodies directed against the entire abatacept molecule or to the CTLA-4 portion of abatacept were assessed by ELISA assays in patients with pJIA following repeated treatment with intravenous ORENCIA throughout the open-label period. For patients who were withdrawn from therapy for up to 6 months during the double-blind period, the rate of antibody formation to the CTLA-4 portion of the molecule was 41% (22/54), while for those who remained on therapy the rate was 13% (7/54). Twenty of these patients had samples that could be tested for antibodies with neutralizing activity; of these, 8 (40%) patients were shown to possess neutralizing antibodies.
The presence of antibodies was generally transient, and titers were low. The presence of antibodies was not associated with adverse events, changes in efficacy, or an effect on serum concentrations of abatacept. For patients who were withdrawn from ORENCIA during the double-blind period for up to 6 months, no serious acute infusion-related events were observed upon re-initiation of ORENCIA therapy.
Immunogenicity in Patients Treated for Prophylaxis of aGVHD with Intravenous ORENCIA
Immunogenicity was assessed in patients undergoing HSCT. Overall, immunogenicity incidence and associated antibody titers were low from the 4-dose intravenous ORENCIA regimen used in this study. Of the 114 immunogenicity evaluable subjects in the ORENCIA groups, none were positive during the ORENCIA treatment period (Day -1 to Day 28 following transplant). During the off-treatment period (Day 29 and up to Day 180 following transplant); 6 of 91 immunogenicity evaluable subjects (6.6%) were positive for CTLA4 and possibly Ig; 4 of the 6 positive subjects were found to have at least one positive sample with neutralization activity. In this study, immunogenicity positive subjects only had ADA positive samples on Day 180 (off-treatment period) and thus due to the timing of the response, the impact on PK, safety, or efficacy could not be determined.
Postmarketing Experience
Adverse reactions have been reported during the postapproval use of ORENCIA. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to ORENCIA. Based on the postmarketing experience with ORENCIA, the following adverse reactions have been identified:
- Vasculitis (including cutaneous vasculitis and leukocytoclastic vasculitis)
- New or worsening psoriasis
- Non-melanoma skin cancers (basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma)
- Angioedema reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
During postmarketing experience with intravenous ORENCIA, systemic infusion reactions were similar to that seen in the clinical trial experience with intravenous ORENCIA with the exception of one case of fatal anaphylaxis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] . Postmarketing reports of systemic injection reactions (e.g., pruritus, throat tightness, dyspnea) have occurred following the use of subcutaneous ORENCIA.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Immunosuppressants
Concomitant administration of a TNF antagonist with ORENCIA has been associated with an increased risk of serious infections and no significant additional efficacy over use of the TNF antagonists alone. Concurrent therapy with ORENCIA and TNF antagonists is not recommended [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ].
There is insufficient experience to assess the safety and efficacy of ORENCIA administered concurrently with other biologic RA therapy, such as anakinra, or other biologic PsA therapy, and JAK inhibitors and therefore such use is not recommended. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
Blood Glucose Testing
Parenteral drug products containing maltose can interfere with the readings of blood glucose monitors that use test strips with glucose dehydrogenase pyrroloquinoline quinone (GDH-PQQ). The GDH-PQQ based glucose monitoring systems may react with the maltose present in ORENCIA for intravenous administration, resulting in falsely elevated blood glucose readings on the day of infusion. When receiving intravenous ORENCIA, patients that require blood glucose monitoring should be advised to consider methods that do not react with maltose, such as those based on glucose dehydrogenase nicotine adenine dinucleotide (GDH-NAD), glucose oxidase, or glucose hexokinase test methods.
ORENCIA for subcutaneous administration does not contain maltose; therefore, patients do not need to alter their glucose monitoring.
DESCRIPTION
Abatacept is a selective T-cell costimulation modulator. Abatacept is a soluble fusion protein that consists of the extracellular domain of human cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4) linked to the modified Fc (hinge, CH2, and CH3 domains) portion of human immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1). Abatacept is produced by recombinant DNA technology in a mammalian cell expression system. The apparent molecular weight of abatacept is 92 kilodaltons.
ORENCIA (abatacept) for injection is a sterile, white, preservative-free lyophilized powder for reconstitution and dilution prior to intravenous infusion. Following reconstitution of the lyophilized powder with 10 mL of Sterile Water for Injection, USP, the reconstituted solution of ORENCIA is clear, colorless to pale yellow, with a concentration of 25 mg/mL and with a pH range of 7.2 to 7.8. Each single-dose vial of ORENCIA provides 250 mg abatacept, maltose (500 mg), monobasic sodium phosphate (17.2 mg), and sodium chloride (14.6 mg).
ORENCIA (abatacept) injection is a sterile, preservative-free, clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to pale-yellow solution with a pH range of 6.8 to 7.4 for subcutaneous administration. ORENCIA injection is supplied as a single-dose prefilled syringe or as a single-dose ClickJect autoinjector (see Table 6).
| Presentation | Active Ingredient Quantity and Volume | Inactive Ingredient Content |
|---|---|---|
ORENCIA injection 50 mg/0.4 mL prefilled syringe | 50 mg of abatacept in 0.4 mL of solution | dibasic sodium phosphate anhydrous (0.335 mg) monobasic sodium phosphate monohydrate (0.114 mg) poloxamer 188 (3.2 mg) sucrose (68 mg) qs to 0.4 mL Water for Injection, USP |
ORENCIA injection 87.5 mg/0.7 mL prefilled syringe | 87.5 mg of abatacept in 0.7 mL of solution | dibasic sodium phosphate anhydrous (0.587 mg) monobasic sodium phosphate monohydrate (0.200 mg) poloxamer 188 (5.6 mg) sucrose (119 mg) qs to 0.7 mL Water for Injection, USP |
ORENCIA injection 125 mg/mL prefilled syringe and ClickJect autoinjector | 125 mg of abatacept in 1 mL of solution | dibasic sodium phosphate anhydrous (0.838 mg) monobasic sodium phosphate monohydrate (0.286 mg) poloxamer 188 (8 mg) sucrose (170 mg) qs to 1 mL Water for Injection, USP |
Unlike the lyophilized formulation for intravenous use, the ORENCIA solutions for subcutaneous administration contain no maltose.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Abatacept, a selective costimulation modulator, inhibits T-cell (T lymphocyte) activation by binding to CD80 and CD86, thereby blocking interaction with CD28. This interaction provides a costimulatory signal necessary for full activation of T lymphocytes. Activated T lymphocytes are implicated in the pathogenesis of RA, pJIA and PsA and are found in the synovium of patients with RA, pJIA and PsA.
In vitro , abatacept decreases T-cell proliferation and inhibits the production of the cytokines TNF alpha (TNFα), interferon-γ, and interleukin-2. In a rat collagen-induced arthritis model, abatacept suppresses inflammation, decreases anti-collagen antibody production, and reduces antigen specific production of interferon-γ. The relationship of these biological response markers to the mechanisms by which ORENCIA exerts its clinical effects is unknown.
Pharmacodynamics
In clinical trials with ORENCIA at doses approximating 10 mg/kg, decreases were observed in serum levels of soluble interleukin-2 receptor (sIL-2R), interleukin-6 (IL-6), rheumatoid factor (RF), C-reactive protein (CRP), matrix metalloproteinase-3 (MMP3), and TNFα. The relationship of these biological response markers to the mechanisms by which ORENCIA exerts its clinical effects is unknown.
No formal pharmacodynamic analyses of biologic response markers have been performed in patients exposed to ORENCIA as prophylaxis for aGVHD.
Pharmacokinetics
Healthy Adults and Adult RA - Intravenous Administration
The pharmacokinetics of abatacept were studied in healthy adult subjects after a single 10 mg/kg intravenous infusion and in RA patients after multiple 10 mg/kg intravenous infusions of ORENCIA (see Table 7).
| PK Parameter | Healthy Subjects (After 10 mg/kg Single Dose) n=13 | RA Patients (After 10 mg/kg Multiple Doses a ) n=14 |
|---|---|---|
| a Multiple intravenous infusions of ORENCIA were administered at days 1, 15, 30, and monthly thereafter. | ||
Peak Concentration (C max ) [mcg/mL] | 292 (175-427) | 295 (171-398) |
Terminal half-life (t 1/2 ) [days] | 16.7 (12-23) | 13.1 (8-25) |
Systemic clearance (CL) [mL/h/kg] | 0.23 (0.16-0.30) | 0.22 (0.13-0.47) |
Volume of distribution (Vss) [L/kg] | 0.09 (0.06-0.13) | 0.07 (0.02-0.13) |
The pharmacokinetics of abatacept in RA patients and healthy subjects appeared to be comparable. In RA patients, after multiple intravenous infusions, the pharmacokinetics of abatacept showed proportional increases of C max and AUC over the dose range of 2 mg/kg to 10 mg/kg. At 10 mg/kg, serum concentration appeared to reach a steady state by day 60 with a mean (range) trough concentration of 24 mcg/mL (1 to 66 mcg/mL). No systemic accumulation of abatacept occurred upon continued repeated treatment with 10 mg/kg at monthly intervals in RA patients.
Population pharmacokinetic analyses in RA patients revealed that there was a trend toward higher clearance of abatacept with increasing body weight. Age and gender (when corrected for body weight) did not affect clearance. Concomitant methotrexate, NSAIDs, corticosteroids, and TNF antagonists did not influence abatacept clearance.
No formal studies were conducted to examine the effects of either renal or hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of abatacept.
Adult RA - Subcutaneous Administration
Abatacept exhibited linear pharmacokinetics following subcutaneous administration. The mean (range) for C min and C max at steady state observed after 85 days of treatment was 32.5 mcg/mL (6.6 to 113.8 mcg/mL) and 48.1 mcg/mL (9.8 to 132.4 mcg/mL), respectively. The bioavailability of abatacept following subcutaneous administration relative to intravenous administration was 79%. Mean estimates for systemic clearance (0.28 mL/h/kg), volume of distribution (0.11 L/kg), and terminal half-life (14.3 days) were comparable between subcutaneous and intravenous administration.
Study SC-2 was conducted to determine the effect of subcutaneous monotherapy use of ORENCIA on immunogenicity (without an intravenous loading dose) in 100 RA patients [see Adverse Reactions (6.3) ] . In this study, a mean trough concentration of 12.6 mcg/mL was achieved after 2 weeks of dosing.
Consistent with the intravenous data, population pharmacokinetic analyses for subcutaneous ORENCIA in RA patients revealed that there was a trend toward higher clearance of abatacept with increasing body weight [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) ] . Age and gender (when corrected for body weight) did not affect apparent clearance. Concomitant medication, such as methotrexate, corticosteroids, and NSAIDs, did not influence abatacept apparent clearance.
Polyarticular Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis - Intravenous Administration
In Study JIA-1 among patients 6 to 17 years of age, the mean (range) steady state serum peak and trough concentrations of abatacept were 217 mcg/mL (57 to 700 mcg/mL) and 11.9 mcg/mL (0.15 to 44.6 mcg/mL) [see Clinical Studies (14.2)] . Population pharmacokinetic analyses of the serum concentration data showed that clearance of abatacept increased with baseline body weight [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) ] . The estimated mean (range) clearance of abatacept in the juvenile idiopathic arthritis patients was 0.4 mL/h/kg (0.20 to 1.12 mL/h/kg). After accounting for the effect of body weight, the clearance of abatacept was not related to age and gender. Concomitant methotrexate, corticosteroids, and NSAIDs were also shown not to influence abatacept clearance.
Polyarticular Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis - Subcutaneous Administration
In Study JIA-2 among patients 2 to 17 years of age, steady state of abatacept was achieved by Day 85 following the weekly body-weight–tiered subcutaneous ORENCIA dosing [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ] . Comparable trough concentrations across weight tiers and age groups were achieved by the body-weight–tiered subcutaneous dosing regimen. The mean (range) trough concentration of abatacept at Day 113 was 44.4 mcg/mL (13.4 to 88.1 mcg/mL), 46.6 mcg/mL (22.4 to 97.0 mcg/mL), and 38.5 mcg/mL (9.3 to 73.2 mcg/mL) in pediatric JIA patients weighing 10 to <25 kg, 25 to <50 kg, and ≥50 kg, respectively.
Consistent with the intravenous data, population pharmacokinetic analyses for subcutaneous ORENCIA in JIA patients revealed that there was a trend toward higher clearance of abatacept with increasing body weight [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) ] . Age and gender (when corrected for body weight) did not affect apparent clearance. Concomitant medication, such as methotrexate, corticosteroids, and NSAIDs, did not influence abatacept apparent clearance.
Adult Psoriatic Arthritis - Intravenous and Subcutaneous Administration
In Study PsA-I, a dose ranging study, intravenous ORENCIA was administered at 3 mg/kg, weight range-based dosing: 500 mg for patients weighing less than 60 kg, 750 mg for patients weighing 60 to 100 kg, and 1,000 mg for patients weighing greater than 100 kg, or doses of 30 mg/kg on Days 1 and 15 followed by weight-range-based dosing [see Clinical Studies (14.3) ] . Following monthly intravenous ORENCIA administration, abatacept showed linear PK over the dose range in this study. At the weight-range-based dosing (see above), the steady state of abatacept was reached by Day 57 and the geometric mean (CV%) trough concentration (C min ) was 24.3 mcg/mL (40.8%) at Day 169. In Study PsA-II following weekly subcutaneous administration of ORENCIA at 125 mg, the steady state of abatacept was reached at Day 57 and the geometric mean (CV%) C min was 25.6 mcg/mL (47.7%) at Day 169.
Consistent with the RA results, population pharmacokinetic analyses for abatacept in PsA patients revealed that there was a trend toward higher clearance (L/h) of abatacept with increasing body weight [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] . In addition, relative to the RA patients with the same body weight, abatacept clearance in PsA patients was approximately 8% lower, resulting in higher abatacept exposures in patients with PsA. This slight difference in exposures, however, is not considered to be clinically meaningful.
Prophylaxis of Acute Graft versus Host Disease – Intravenous Administration
| a C min observed on Day 5 of the treatment period; n = 18 for the 7/8 Cohort; n = 32 for the 8/8 Cohort. C max , t 1/2 , CL, and Vss are model predicted after first 10 mg/kg ORENCIA intravenous infusion. | ||
PK Parameter | 7 of 8 Cohort n=42 | 8 of 8 Cohort n=73 |
Minimum Concentration (C min ) a [mcg/mL] | 59 (26-112) | 43 (25-73) |
Peak Concentration (C max ) [mcg/mL] | 221 (163-292) | 172 (107-254) |
Terminal half-life (t 1/2 ) [days] | 20.6 (6-43) | 20.8 (12-38) |
Systemic clearance (CL) [mL/h/kg] | 0.26 (0.15-0.65) | 0.32 (0.18-0.56) |
Volume of distribution (Vss) [L/kg] | 0.13 (0.08-0.27) | 0.17 (0.11-0.26) |
In a study of patients who received ORENCIA for prophylaxis of acute Graft Versus Host Disease (aGVHD) aged 6 years and older, the geometric mean (%CV) trough concentrations (C min ) of abatacept on Day 63 after transplant after 4 doses utilizing weight-based dosing of 10 mg/kg (maximum dose of 1,000 mg) administered on the day before transplantation (Day -1), followed by a dose on Day 5, 14, and 28 after transplant, were 22.5 mcg/mL (243.9 %CV) for recipients of 8 of 8 Human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-matched HSCTs from unrelated donors (URD), and 31.1 mcg/mL (114.4 %CV) for recipients of 7 of 8 HLA-matched HSCTs from unrelated donors (URD), respectively.
Population pharmacokinetic analyses in patients with aGVHD demonstrated that 7 of 8 HLA-matched HSCT recipients had 29% lower clearance compared to 8 of 8 HLA-matched HSCT recipients. Consistent with previous data, increasing body weight was associated with higher clearance of abatacept, while age (when corrected for body weight) did not affect apparent clearance. Concomitant medication, such as methotrexate and calcineurin inhibitors (e.g., cyclosporine and tacrolimus), did not influence abatacept clearance.
Based on population PK modeling and simulation with data from patients aged 6 and older, simulated exposures of abatacept following the first and last dose in pediatric subjects 2 to less than 6 years of age who received 15 mg/kg of ORENCIA via 60-minute intravenous infusion on Day -1, followed by 12 mg/kg via 60-minute intravenous infusion on Day 5, 14, and 28 are comparable to those in pediatric patients 6 to less than 17 years of age and adults patients who received 10 mg/kg via 60-minute intravenous infusion on Day -1, 5, 14, and 28.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In a mouse carcinogenicity study, weekly subcutaneous injections of 20, 65, or 200 mg/kg of abatacept administered for up to 84 weeks in males and 88 weeks in females were associated with increases in the incidence of malignant lymphomas (all doses) and mammary gland tumors (intermediate- and high-dose in females). The mice from this study were infected with murine leukemia virus and mouse mammary tumor virus. These viruses are associated with an increased incidence of lymphomas and mammary gland tumors, respectively, in immunosuppressed mice. The doses used in these studies produced exposures 0.8, 2.0, and 3.0 times higher, respectively, than the exposure associated with the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 10 mg/kg based on AUC (area under the time-concentration curve). The relevance of these findings to the clinical use of ORENCIA is unknown.
In a one-year toxicity study in cynomolgus monkeys, abatacept was administered intravenously once weekly at doses up to 50 mg/kg (producing 9 times the MRHD exposure based on AUC). Abatacept was not associated with any significant drug-related toxicity. Reversible pharmacological effects consisted of minimal transient decreases in serum IgG and minimal to severe lymphoid depletion of germinal centers in the spleen and/or lymph nodes. No evidence of lymphomas or preneoplastic morphologic changes was observed, despite the presence of a virus (lymphocryptovirus) known to cause these lesions in immunosuppressed monkeys within the time frame of this study. The relevance of these findings to the clinical use of ORENCIA is unknown.
No mutagenic potential of abatacept was observed in the in vitro bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) or Chinese hamster ovary/hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyl-transferase (CHO/HGPRT) forward point mutation assays with or without metabolic activation, and no chromosomal aberrations were observed in human lymphocytes treated with abatacept with or without metabolic activation.
Abatacept had no adverse effects on male or female fertility in rats at doses up to 200 mg/kg every three days (11 times the MRHD exposure based on AUC).
Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
In studies of adult mice and monkeys, inhibition of TDAR was apparent. However, infection and mortality, altered T-helper cells, and inflammation of thyroid and pancreas were not observed.
CLINICAL STUDIES
Adult Rheumatoid Arthritis
Description of Clinical Studies of Intravenous ORENCIA for the Treatment of Patients with RA
The efficacy and safety of ORENCIA for intravenous administration were assessed in six randomized, double-blind, controlled studies (five placebo-controlled and one active-controlled) in patients ≥18 years of age with active RA diagnosed according to American College of Rheumatology (ACR) criteria. Studies I, II, III, IV, and VI required patients to have at least 12 tender and 10 swollen joints at randomization, and Study V did not require any specific number of tender or swollen joints. ORENCIA or placebo treatment was given intravenously at weeks 0, 2, and 4 and then every 4 weeks thereafter in Studies I, II, III, IV, and VI.
- Study I (NCT00279760) evaluated ORENCIA as monotherapy in 122 patients with active RA who had failed at least one non-biologic DMARD or etanercept.
- In Study II (NCT00162266) and Study III (NCT00048568), the efficacy of ORENCIA were assessed in patients with an inadequate response to MTX and who were continued on their stable dose of MTX.
- In Study IV (NCT00048581), the efficacy of ORENCIA was assessed in patients with an inadequate response to a TNF antagonist, with the TNF antagonist discontinued prior to randomization; other DMARDs were permitted.
- Study V (NCT00048932) primarily assessed safety in patients with active RA requiring additional intervention in spite of current therapy with DMARDs; all DMARDs used at enrollment were continued. Patients in Study V were not excluded for comorbid medical conditions.
- In Study VI (NCT00122382), the efficacy and safety of ORENCIA were assessed in methotrexate-naive patients with RA of less than 2 years disease duration. In Study VI, patients previously naive to methotrexate were randomized to receive ORENCIA plus methotrexate or methotrexate plus placebo.
Study I patients were randomized to receive one of three doses of ORENCIA (0.5, 2, or 10 mg/kg) or placebo ending at week 8. Study II patients were randomized to receive ORENCIA 2 or 10 mg/kg or placebo for 12 months. Study III, IV, V, and VI patients were randomized to receive a dose of ORENCIA based on weight range or placebo for 12 months (Studies III, V, and VI) or 6 months (Study IV). The dose of ORENCIA was 500 mg for patients weighing less than 60 kg, 750 mg for patients weighing 60 to 100 kg, and 1,000 mg for patients weighing greater than 100 kg.
Description of Clinical Studies of Subcutaneous or Intravenous ORENCIA for the Treatment of Patients with Adult RA
The efficacy of ORENCIA for subcutaneous administration were assessed in Study SC-1 (NCT00559585), which was a randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, non-inferiority study that compared ORENCIA administered subcutaneously to ORENCIA administered intravenously in 1457 patients with moderate to severely active RA, receiving background methotrexate (MTX), and experiencing an inadequate response to methotrexate (MTX-IR). In Study SC-1, patients were randomized with stratification by body weight (<60 kg, 60 to 100 kg, >100 kg) to receive (1) ORENCIA 125 mg subcutaneous injections weekly, after a single intravenous loading dose of ORENCIA based on body weight or (2) ORENCIA intravenously on Days 1, 15, 29, and every four weeks thereafter. Subjects continued taking their current dose of MTX from the day of randomization.
Clinical Response in Adult RA Patients
The percent of ORENCIA-treated patients achieving ACR 20, 50, and 70 responses and major clinical response in Studies I, III, IV, and VI are shown in Table 9. ORENCIA-treated patients had higher ACR 20, 50, and 70 response rates at 6 months compared to placebo-treated patients. Month 6 ACR response rates in Study II for the 10 mg/kg group were similar to the ORENCIA group in Study III.
In Studies III and IV, improvement in the ACR 20 response rate versus placebo was observed within 15 days in some patients and within 29 days versus MTX in Study VI. In Studies II, III, and VI, ACR response rates were maintained to 12 months in ORENCIA-treated patients. ACR responses were maintained up to three years in the open-label extension of Study II. In Study III, ORENCIA-treated patients experienced greater improvement than placebo-treated patients in morning stiffness.
In Study VI, a greater proportion of patients treated with ORENCIA plus MTX achieved a low level of disease activity as measured by a DAS28-CRP less than 2.6 at 12 months compared to those treated with MTX plus placebo (Table 9). Of patients treated with ORENCIA plus MTX who achieved DAS28-CRP less than 2.6, 54% had no active joints, 17% had one active joint, 7% had two active joints, and 22% had three or more active joints, where an active joint was a joint that was rated as tender or swollen or both.
In Study SC-1, the main outcome measure was ACR 20 at 6 months. The pre-specified non-inferiority margin was a treatment difference of −7.5%. As shown in Table 10, the study demonstrated non-inferiority of ORENCIA administered subcutaneously to intravenous infusions of ORENCIA with respect to ACR 20 responses up to 6 months of treatment. ACR 50 and 70 responses are also shown in Table 9. No major differences in ACR responses were observed between intravenous and subcutaneous treatment groups in subgroups based on weight categories (less than 60 kg, 60 to 100 kg, and more than 100 kg; data not shown).
| Percent of Patients | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intravenous Administration | Subcutaneous or Intravenous Administration | |||||||||
| Inadequate Response to DMARDs | Inadequate Response to Methotrexate (MTX) | Inadequate Response to TNF Antagonists | MTX-Naive | Inadequate Response to MTX | ||||||
| Study I | Study III | Study IV | Study VI | Study SC-1 | ||||||
| • p<0.05, ORENCIA (ORN) vs placebo (PBO) or MTX. † p<0.01, ORENCIA vs placebo or MTX. ‡ p<0.001, ORENCIA vs placebo or MTX. § 95% CI: −4.2, 4.8 (based on prespecified margin for non-inferiority of −7.5%). a 10 mg/kg. b Dosing based on weight range [ see Dosage and Administration (2.1) ] . c Major clinical response is defined as achieving an ACR 70 response for a continuous 6-month period. d Refer to text for additional description of remaining joint activity. e Per protocol data is presented in table. For ITT; n=736, 721 for SC and IV ORENCIA, respectively. | ||||||||||
Response Rate | ORN a n=32 | PBO n=32 | ORN b +MTX n=424 | PBO +MTX n=214 | ORN b + DMARDs n=256 | PBO + DMARDs n=133 | ORN b +MTX n=256 | PBO +MTX n=253 | ORN e SC +MTX n=693 | ORN e IV +MTX n=678 |
ACR 20 | ||||||||||
Month 3 | 53% | 31% | 62% ‡ | 37% | 46% ‡ | 18% | 64%• | 53% | 68% | 69% |
Month 6 | NA | NA | 68% ‡ | 40% | 50% ‡ | 20% | 75% † | 62% | 76% § | 76% |
Month 12 | NA | NA | 73% ‡ | 40% | NA | NA | 76% ‡ | 62% | NA | NA |
ACR 50 | ||||||||||
Month 3 | 16% | 6% | 32% ‡ | 8% | 18% † | 6% | 40% ‡ | 23% | 33% | 39% |
Month 6 | NA | NA | 40% ‡ | 17% | 20% ‡ | 4% | 53% ‡ | 38% | 52% | 50% |
Month 12 | NA | NA | 48% ‡ | 18% | NA | NA | 57% ‡ | 42% | NA | NA |
ACR 70 | ||||||||||
Month 3 | 6% | 0 | 13% ‡ | 3% | 6%• | 1% | 19% † | 10% | 13% | 16% |
Month 6 | NA | NA | 20% ‡ | 7% | 10% † | 2% | 32% † | 20% | 26% | 25% |
Month 12 | NA | NA | 29% ‡ | 6% | NA | NA | 43% ‡ | 27% | NA | NA |
Major Clinical Response c | NA | NA | 14% ‡ | 2% | NA | NA | 27% ‡ | 12% | NA | NA |
DAS28-CRP <2.6 d | ||||||||||
Month 12 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 41% ‡ | 23% | NA | NA |
The results of the components of the ACR response criteria for Studies III, IV, and SC-1 are shown in Table 10 (results at Baseline [BL] and 6 months [6 M]). In ORENCIA-treated patients, greater improvement was seen in all ACR response criteria components through 6 and 12 months than in placebo-treated patients.
| Intravenous Administration | Subcutaneous or Intravenous Administration | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inadequate Response to MTX | Inadequate Response to TNF Antagonists | Inadequate Response to MTX | ||||||||||
| Study III | Study IV | Study SC-1 c | ||||||||||
| † p<0.01, ORENCIA (ORN) vs placebo (PBO), based on mean percent change from baseline. ‡ p<0.001, ORENCIA vs placebo, based on mean percent change from baseline. a Visual analog scale: 0 = best, 100 = worst. b Health Assessment Questionnaire: 0 = best, 3 = worst; 20 questions; 8 categories: dressing and grooming, arising, eating, walking, hygiene, reach, grip, and activities. c SC-1 is a non-inferiority study. Per protocol data is presented in table. | ||||||||||||
ORN +MTX n=424 | PBO +MTX n=214 | ORN +DMARDs n=256 | PBO +DMARDs n=133 | ORN SC +MTX n=693 | ORN IV +MTX n=678 | |||||||
Component (median) | BL | 6 M | BL | 6 M | BL | 6 M | BL | 6 M | BL | 6 M | BL | 6 M |
Number of tender joints (0-68) | 28 | 7 ‡ | 31 | 14 | 30 | 13 ‡ | 31 | 24 | 27 | 5 | 27 | 6 |
Number of swollen joints (0-66) | 19 | 5 ‡ | 20 | 11 | 21 | 10 ‡ | 20 | 14 | 18 | 4 | 18 | 3 |
Pain a | 67 | 27 ‡ | 70 | 50 | 73 | 43 † | 74 | 64 | 71 | 25 | 70 | 28 |
Patient global assessment a | 66 | 29 ‡ | 64 | 48 | 71 | 44 ‡ | 73 | 63 | 70 | 26 | 68 | 27 |
Disability index b | 1.75 | 1.13 ‡ | 1.75 | 1.38 | 1.88 | 1.38 ‡ | 2.00 | 1.75 | 1.88 | 1.00 | 1.75 | 1.00 |
Physician global assessment a | 69 | 21 ‡ | 68 | 40 | 71 | 32 ‡ | 69 | 54 | 65 | 16 | 65 | 15 |
CRP (mg/dL) | 2.2 | 0.9 ‡ | 2.1 | 1.8 | 3.4 | 1.3 ‡ | 2.8 | 2.3 | 1.6 | 0.7 | 1.8 | 0.7 |
The percent of patients achieving the ACR 50 response for Study III by visit is shown in Figure 1. The time course for the ORENCIA group in Study VI was similar to that in Study III.
Figure 1: Percent of Patients Achieving ACR 50 Response by Visit• (Study III)
 •The same patients may not have responded at each time point.
•The same patients may not have responded at each time point.
The percent of patients achieving the ACR 50 response for Study SC-1 in the ORENCIA subcutaneous (SC) and intravenous (IV) treatment arms at each treatment visit was as follows: Day 15—SC 3%, IV 5%; Day 29—SC 11%, IV 14%; Day 57—SC 24%, IV 30%; Day 85—SC 33%, IV 38%; Day 113—SC 39%, IV 41%; Day 141—SC 46%, IV 47%; Day 169—SC 51%, IV 50%.
Radiographic Response in Adult RA Patients
In Study III and Study VI, structural joint damage was assessed radiographically and expressed as change from baseline in the Genant-modified Total Sharp Score (TSS) and its components, the Erosion Score (ES) and Joint Space Narrowing (JSN) score. ORENCIA/MTX slowed the progression of structural damage compared to placebo/MTX after 12 months of treatment as shown in Table 11.
| Parameter | ORENCIA/MTX | Placebo/MTX | Differences | P-value d |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Patients with an inadequate response to MTX. b MTX-naive patients. c Patients received 1 year of placebo/MTX followed by 1 year of ORENCIA/MTX. d Based on a nonparametric ANCOVA model. | ||||
Study III | ||||
First Year | ||||
TSS | 1.07 | 2.43 | 1.36 | <0.01 |
ES | 0.61 | 1.47 | 0.86 | <0.01 |
JSN score | 0.46 | 0.97 | 0.51 | <0.01 |
Second Year | ||||
TSS | 0.48 | 0.74 c | ||
ES | 0.23 | 0.22 c | ||
JSN score | 0.25 | 0.51 c | ||
Study VI | ||||
First Year | ||||
TSS | 0.6 | 1.1 | 0.5 | 0.04 |
In the open-label extension of Study III, 75% of patients initially randomized to ORENCIA/MTX and 65% of patients initially randomized to placebo/MTX were evaluated radiographically at Year 2. As shown in Table 11, progression of structural damage in ORENCIA/MTX-treated patients was further reduced in the second year of treatment.
Following 2 years of treatment with ORENCIA/MTX, 51% of patients had no progression of structural damage as defined by a change in the TSS of zero or less compared with baseline. Fifty-six percent (56%) of ORENCIA/MTX-treated patients had no progression during the first year compared to 45% of placebo/MTX-treated patients. In their second year of treatment with ORENCIA/MTX, more patients had no progression than in the first year (65% vs 56%).
Physical Function Response and Health-Related Outcomes in Adult RA Patients
Improvement in physical function was measured by the Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ-DI). In the HAQ-DI, ORENCIA demonstrated greater improvement from baseline versus placebo in Studies II-V and versus MTX in Study VI. In Study SC-1, improvement from baseline as measured by HAQ-DI at 6 months and over time was similar between subcutaneous and intravenous ORENCIA administration. The results from Studies II and III are shown in Table 12. Similar results were observed in Study V compared to placebo and in Study VI compared to MTX. During the open-label period of Study II, the improvement in physical function has been maintained for up to 3 years.
| Inadequate Response to Methotrexate | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study II | Study III | |||
| ••• p<0.001, ORENCIA vs placebo. a 10 mg/kg. b Dosing based on weight range [ see Dosage and Administration (2.1) ] . c Modified Health Assessment Questionnaire: 0 = best, 3 = worst; 8 questions; 8 categories: dressing and grooming, arising, eating, walking, hygiene, reach, grip, and activities. d Health Assessment Questionnaire: 0 = best, 3 = worst; 20 questions; 8 categories: dressing and grooming, arising, eating, walking, hygiene, reach, grip, and activities. | ||||
HAQ Disability Index | ORENCIA a +MTX (n=115) | Placebo +MTX (n=119) | ORENCIA b +MTX (n=422) | Placebo +MTX (n=212) |
Baseline (Mean) | 0.98 c | 0.97 c | 1.69 d | 1.69 d |
Mean Improvement Year 1 | 0.40 c, ••• | 0.15 c | 0.66 d, ••• | 0.37 d |
Health-related quality of life was assessed by the SF-36 questionnaire at 6 months in Studies II, III, and IV and at 12 months in Studies II and III. In these studies, improvement was observed in the ORENCIA group as compared with the placebo group in all 8 domains of the SF-36 as well as the Physical Component Summary (PCS) and the Mental Component Summary (MCS).
Polyarticular Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
Polyarticular Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis - Intravenous Administration
The safety and efficacy of ORENCIA with intravenous administration were assessed in Study JIA-1 (NCT00095173), a three-part study including an open-label extension in pediatric patients with polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis (pJIA). Patients 6 to 17 years of age (n=190) with moderately to severely active pJIA who had an inadequate response to one or more DMARDs, such as MTX or TNF antagonists, were treated. Patients had a disease duration of approximately 4 years with moderately to severely active disease at study entry, as determined by baseline counts of active joints (mean, 16) and joints with loss of motion (mean, 16); patients had elevated C-reactive protein (CRP) levels (mean, 3.2 mg/dL) and ESR (mean, 32 mm/h). The patients enrolled had JIA subtypes that at disease onset included oligoarticular (16%), polyarticular (64%; 20% were rheumatoid factor positive), and systemic JIA without systemic manifestations (20%). At study entry, 74% of patients were receiving MTX (mean dose, 13.2 mg/m 2 per week) and remained on a stable dose of MTX (those not receiving MTX did not initiate MTX treatment during the study).
In Period A (open-label, lead-in), patients received 10 mg/kg (maximum 1,000 mg per dose) intravenously on days 1, 15, 29, and monthly thereafter. Response was assessed utilizing the ACR Pediatric 30 definition of improvement, defined as ≥30% improvement in at least 3 of the 6 JIA core set variables and ≥30% worsening in not more than 1 of the 6 JIA core set variables. Patients demonstrating an ACR Pedi 30 response at the end of Period A were randomized into the double-blind phase (Period B) and received either ORENCIA or placebo for 6 months or until disease flare. Disease flare was defined as a ≥30% worsening in at least 3 of the 6 JIA core set variables with ≥30% improvement in not more than 1 of the 6 JIA core set variables; ≥2 cm of worsening of the Physician or Parent Global Assessment was necessary if used as 1 of the 3 JIA core set variables used to define flare, and worsening in ≥2 joints was necessary if the number of active joints or joints with limitation of motion was used as 1 of the 3 JIA core set variables used to define flare.
At the conclusion of Period A, pediatric ACR 30/50/70 responses were 65%, 50%, and 28%, respectively. Pediatric ACR 30 responses were similar in all subtypes of JIA studied.
During the double-blind randomized withdrawal phase (Period B), ORENCIA-treated patients (intravenous) experienced significantly fewer disease flares compared to placebo-treated patients (20% vs 53%); 95% CI of the difference (15%, 52%). The risk of disease flare among patients continuing on intravenous ORENCIA was less than one-third than that for patients withdrawn from intravenous ORENCIA treatment (hazard ratio=0.31, 95% CI [0.16, 0.59]). Among patients who received intravenous ORENCIA throughout the study (Period A, Period B, and the open-label extension Period C), the proportion of pediatric ACR 30/50/70 responders has remained consistent for 1 year.
Polyarticular Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis - Subcutaneous Administration
ORENCIA for subcutaneous administration without an intravenous loading dose was assessed in Study JIA-2 (NCT01844518), a 2-period, open-label study that included pediatric patients 2 to 17 years of age (n=205). Patients had active polyarticular disease at the time of the study and had inadequate response to at least one nonbiologic or biologic DMARD. The JIA patient subtypes at study entry included polyarticular (79%; 22% were rheumatoid factor positive), extended and persistent oligoarticular (14%), enthesitis-related arthritis (1%), and systemic JIA without systemic manifestations (2%). Patients had a mean disease duration of 2.5 years with active joints (mean, 11.9), joints with loss of motion (mean, 10.4), and elevated C-reactive protein (CRP) levels (mean, 1.2 mg/dL). At study entry, 80% of patients were receiving MTX and remained on a stable dose of MTX. Patients received weekly open-label ORENCIA subcutaneously by a weight-tiered dosing regimen. The primary objective of the study was evaluation of PK in order to support the extrapolation of efficacy based on exposure to ORENCIA supported by descriptive efficacy [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
JIA ACR 30/50/70 responses assessed at 4 months in the 2- to 17-year-old patients treated with subcutaneous ORENCIA were consistent with the results from intravenous ORENCIA in Study JIA-1.
Psoriatic Arthritis
The efficacy of ORENCIA was assessed in 594 adult patients (18 years and older) with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), in two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies (Studies PsA-I [NCT00534313] and PsA-II [NCT01860976]). Patients had active PsA (≥3 swollen joints and ≥3 tender joints) despite prior treatment with DMARD therapy and had one qualifying psoriatic skin lesion of at least 2 cm in diameter. In PsA-I and PsA-II, 37% and 61% of patients, respectively, were treated with TNF antagonists previously.
During the initial 24-week, double-blind period of Study PsA-I, 170 patients were randomized to receive one of four intravenous treatments on Days 1, 15, 29, and then every 28 days (there was no escape during the 24-week period):
- Placebo
- ORENCIA 3 mg/kg
- ORENCIA 500 mg for patients weighing less than 60 kg, ORENCIA 750 mg for patients weighing 60 to 100 kg, and ORENCIA 1,000 mg for patients weighing greater than 100 kg (weight-range-based dosing), or
- ORENCIA 30 mg/kg on Days 1 and 15 followed by weight range-based ORENCIA dosing (i.e., 500 mg for patients weighing less than 60 kg, 750 mg for patients weighing 60 to 100 kg, and 1,000 mg for patients weighing greater than 100 kg).
After the 24-week double blind period in Study PsA-I, patients received open-label intravenous ORENCIA every 28 days.
Patients were allowed to receive stable doses of concomitant MTX, low dose corticosteroids (equivalent to ≤10 mg of prednisone) and/or NSAIDs during the trial. At enrollment, approximately 60% of patients were receiving MTX. At baseline, the mean (SD) CRP for ORENCIA IV was 17 mg/L (33.0) and mean number (SD) of tender joints and swollen joints was 22.2 (14.3) and 10.9 (7.6), respectively.
In PsA-II, 424 patients were randomized 1:1 to receive weekly doses of subcutaneous placebo or ORENCIA 125 mg without a loading dose for 24 weeks-in a double-blind manner, followed by open-label subcutaneous ORENCIA 125 mg weekly. Patients were allowed to receive stable doses of concomitant MTX, sulfasalazine, leflunomide, hydroxychloroquine, low dose corticosteroids (equivalent to ≤10 mg of prednisone) and/or NSAIDs during the trial. At randomization, 60% of patients were receiving MTX. The baseline disease characteristics included presence of joint erosion on X-rays in 84% (341/407) with a mean (SD) PsA-modified Sharp van der Heijde erosion score (SHS) of 10.8 (24.2), elevated serum C reactive protein (CRP) in 66% [277/421]) with a mean (SD) of 14.1 mg/L (25.9), and polyarticular disease in 98% (416/424) of patients with a mean number (SD) of tender joints and swollen joints of 20.2 (13.3) and 11.6 (7.5), respectively. Patients who had not achieved at least a 20% improvement from baseline in their swollen and tender joint counts by Week 16 escaped to open-label subcutaneous ORENCIA 125 mg weekly.
The primary endpoint for both PsA-I and PsA-II was the proportion of patients achieving ACR 20 response at Week 24 (Day 169).
Clinical Response in Adults with PsA
A greater proportion of adult patients with PsA achieved an ACR 20 response after treatment with intravenous ORENCIA (weight-range-based dosing as described above) compared to placebo in Study PsA-I and a greater proportion of adult patients with PsA achieved an ACR 20 response after treatment with subcutaneous 125 mg compared to placebo in Study PsA-II at Week 24. Responses were seen regardless of prior TNF antagonist treatment and regardless of concomitant non-biologic DMARD treatment. The percent of patients achieving ACR 20, 50, or 70 responses in Studies PsA‑I and PsA-II are presented in Table 13 below.
| PsA-I | PsA-II | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| • p<0.05 versus placebo. a Patients who had less than 20% improvement in tender or swollen joint counts at Week 16 met escape criteria and were considered non-responders. b Weight range-based intravenous dosing: ORENCIA 500 mg for patients weighing less than 60 kg, ORENCIA 750 mg for patients weighing 60 to 100 kg, and ORENCIA 1,000 mg for patients weighing greater than 100 kg. | ||||
ORENCIA Weight-Range-Based Intravenous Dosing b N=40 | Placebo N=42 | ORENCIA 125 mg Subcutaneous N=213 | Placebo N=211 | |
ACR 20 | 47.5%• | 19.0% | 39.4%• | 22.3% |
ACR 50 | 25.0% | 2.4% | 19.2% | 12.3% |
ACR 70 | 12.5% | 0% | 10.3% | 6.6% |
The percentage of patients in PsA-II achieving ACR 20 response through Week 24 is shown below in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Percent of Patients Achieving ACR 20 Response a in PsA-II Study Through Week 24 (Day 169)

Results were generally consistent across the ACR components in Study PsA-I and PsA-II.
Improvements in enthesitis and dactylitis were seen with ORENCIA treatment at Week 24 in both PsA-I and PsA-II.
Physical Function Response in Adults with PsA
In study PsA-I, there was a higher proportion of patients with at least a 0.30 decrease from baseline in Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index (HAQ-DI) score at Week 24, with an estimated difference for ORENCIA weight range-based dosing as described above (45%) vs. placebo (19%) of 26.1 (95% confidence interval: 6.8, 45.5). In study PsA-II, the proportion of patients with at least a 0.35 decrease from baseline in HAQ-DI on ORENCIA was 31%, as compared to 24% on placebo (estimated difference: 7%; 95% confidence interval: -1%, 16%). There was a higher adjusted mean change from baseline in HAQ-DI on ORENCIA (-0.33) vs. placebo (-0.20) at Week 24, with an estimated difference of -0.13 (95% confidence interval: -0.25, -0.01).
Prophylaxis of Acute Graft versus Host Disease
Study GVHD-1
The efficacy of ORENCIA, in combination with a calcineurin inhibitor (CNI) and methotrexate (MTX), for the prophylaxis of Acute Graft Versus Host Disease (aGVHD), was evaluated in a multicenter, two cohort clinical study (GVHD-1, NCT01743131) in patients age 6 years and older who underwent hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) from a matched or 1 allele-mismatched unrelated donor (URD). The two cohorts in GVHD-1 included:
- an open-label, single-arm study of 43 patients who underwent a 7 of 8 Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA)-matched HSCT (7 of 8 cohort); and
- a randomized (1:1), double-blind, placebo-controlled study of patients who underwent an 8 of 8 HLA-matched HSCT who received ORENCIA or placebo in combination with a CNI and MTX (8 of 8 cohort).
In both the 7/8 and 8/8 cohorts, ORENCIA was administered at a dose of 10 mg/kg (1,000 mg maximum dose) as an intravenous infusion over 60 minutes, beginning on the day before transplantation (Day -1), followed by administration on Days 5, 14, and 28 after transplantation. Baseline demographic and clinical characteristics of both the 7 of 8 and 8 of 8 cohorts are outlined below in Table 14.
7 of 8 Cohort | 8 of 8 Cohort | ||
ORENCIA (+ CNI and MTX) N=43 | ORENCIA (+ CNI and MTX) N=73 | Placebo (+CNI and MTX) N=69 | |
Age - Median | 38 | 44 | 40 |
Age - Range | 6-76 | 6-71 | 7-74 |
Gender - Male | 27 (63) | 41 (56) | 37 (54) |
White | 31 (72) | 63 (86) | 61 (88) |
Black or African American | 7 (16) | 3 (4.1) | 2 (2.9) |
Asian | 2 (4.7) | 4 (6) | 2 (2.9) |
Hispanic | 7 (16) | 4 (6) | 2 (2.9) |
Malignancy type | |||
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) | 15 (35) | 30 (41) | 22 (32) |
Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS) | 11 (26) | 15 (21) | 12 (17) |
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) | 8 (19) | 20 (27) | 22 (32) |
Acute leukemia or ambiguous lineage | 1 (2.3) | 0 | 1 (1.4) |
Hodgkin and Non-Hodgkin lymphoma | 1 (2.3) | 1 (1.4) | 1 (1.4) |
Acute Lymphoblastic Lymphoma in 2nd or Greater Complete Remission | 1 (2.3) | 4 (6) | 1 (1.4) |
Chronic Myelomonocytic leukemia | 1 (2.3) | 1 (1.4) | 4 (6) |
Chronic Myelogenous leukemia | 4 (9) | 1 (1.4) | 5 (7) |
Not reported | 1 (2.3) | 1 (1.4) | 1 (1.4) |
GVHD Prophylaxis | |||
Cyclosporine | 16 (37) | 11 (15) | 11 (16) |
Tacrolimus | 27 (63) | 62 (85) | 58 (84) |
Type of Graft | |||
Bone Marrow | 21 (49) | 33 (45) | 26 (38) |
Cytokine Mobilized Peripheral Blood (PBSC) | 22 (51) | 40 (55) | 43 (62) |
Conditioning Regimen | |||
TBI and Chemotherapy | 11 (26) | 20 (27) | 26 (38) |
Busulfan and Cyclophosphamide | 13 (30) | 28 (38) | 21 (30) |
Busulfan and Fludarabine | 8 (19) | 7 (10) | 2 (2.9) |
Melphalan and Fludarabine | 11 (26) | 18 (25) | 20 (29) |
Efficacy was established based on overall survival (OS) and grade II-IV aGVHD free survival (GFS) results assessed at Day 180 post-transplantation. ORENCIA + CNI and MTX did not significantly improve grade III-IV GFS versus placebo + CNI and MTX at Day 180 post-transplantation. The efficacy results of the GVHD-1 8 of 8 cohort are shown in Table 15.
| a Gr III-IV aGVHD Free Survival was measured from the date of transplantation until the onset of documented Grade III-IV aGVHD, or death by any cause up to Day 180 post-transplantation. b Gr II-IV aGVHD Free Survival was measured from the date of transplantation until the onset of documented Grade II-IV aGVHD, or death by any cause up to Day 180 post-transplantation. | ||
Endpoint | ORENCIA (+CNI and MTX) n=73 | Placebo (+CNI and MTX) n=69 |
Gr III-IV aGVHD Free Survival a Rate (95% CI) | 87% (77%, 93%) | 75% (63%, 84%) |
Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.55 (0.26, 1.18) | |
Gr II-IV aGVHD Free Survival b Rate (95% CI) | 50% (38%, 61%) | 32% (21%, 43%) |
Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.54 (0.35, 0.83) | |
Overall Survival Rate (95% CI) | 97% (89%, 99%) | 84% (73%, 91%) |
Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.33 (0.12, 0.93) | |
In an exploratory analysis of the 7 of 8 cohort of ORENCIA-treated patients (n=43), the rates of Grade III-IV GVHD-free survival, Grade II-IV GVHD-free survival, and overall survival at day 180 post-transplantation were 95% (95% CI 83%, 99%), 53% (95% CI 38%, 67%), and 98% (95% CI 85%, 100%), respectively.
Study GVHD-2
GVHD-2 (NCT05421299) was a clinical study that used data from the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research (CIBMTR). The study analyzed outcomes of ORENCIA in combination with a CNI and MTX, versus a CNI and MTX alone, for the prophylaxis of aGVHD, in patients 6 years of age or older who underwent HSCT from a 1 allele-mismatched URD between 2011 and 2018. The ORENCIA + CNI and MTX-treated group (n=54) included 42 patients from GVHD-1, in addition to 12 patients treated with ORENCIA outside of GVHD-1. The comparator group (n=162) was randomly selected in a 3:1 ratio to the ORENCIA-treated group from the CIBMTR registry from patients who had not received ORENCIA during the study period. Analyses used propensity score matching and inverse probability of treatment weighting to help address the impact of selection bias.
Efficacy was based on Overall Survival (OS) at Day 180 post-HSCT. The OS rate at Day 180 in the ORENCIA in combination with CNI and MTX group was 98% (95% CI: 78, 100) and the OS rate at Day 180 in the CNI and MTX group was 75% (95% CI: 67, 82).
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
For Intravenous Infusion
ORENCIA ® (abatacept) for injection is a white lyophilized powder for intravenous infusion after reconstitution and dilution. It is supplied as an individually packaged, single-dose vial (one may use less than the full contents of the vial or use more than one vial) with a silicone-free disposable syringe, providing 250 mg of abatacept:
NDC 0003-2187-13: in a carton presentation
For Subcutaneous Use
ORENCIA ® (abatacept) injection and ORENCIA ® ClickJect (abatacept) injection are clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to pale yellow solutions for subcutaneous administration.
Prefilled Syringe
ORENCIA (abatacept) injection, 50 mg/0.4 mL, 87.5 mg/0.7 mL, and 125 mg/mL, is supplied as single-dose disposable prefilled glass syringes with BD UltraSafe Passive™ needle guard and flange extenders.
The Type I glass syringe has a coated stopper and fixed stainless steel needle (5 bevel, 29-gauge thin wall, ½-inch needle) covered with a rigid needle shield. The prefilled syringe provides ORENCIA in the following packages:
NDC 0003-2814-11 (50 mg/0.4 mL): pack of 4 syringes with a passive needle safety guard
NDC 0003-2818-11 (87.5 mg/0.7 mL): pack of 4 syringes with a passive needle safety guard
NDC 0003-2188-11 (125 mg/mL): pack of 4 syringes with a passive needle safety guard
ClickJect Autoinjector
ORENCIA (abatacept) ClickJect, 125 mg/mL, is supplied as a single-dose disposable prefilled autoinjector. The Type I glass syringe contained in the autoinjector has a coated stopper and fixed stainless steel needle (5 bevel, 27-gauge special thin wall, ½-inch needle) covered with a rigid needle shield. The autoinjector provides 125 mg of abatacept in 1 mL and is provided in the following package:
NDC 0003-2188-51: pack of 4 autoinjectors
Storage
Refrigerate ORENCIA lyophilized powder supplied in a vial at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Do not use beyond the expiration date on the vial. Protect the vials from light by storing in the original package until time of use.
Refrigerate ORENCIA solution supplied in a prefilled syringe or ClickJect autoinjector at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Do not use beyond the expiration date on the prefilled syringe or autoinjector. Protect from light by storing in the original package until time of use. Do not allow the prefilled syringe or autoinjector to freeze.
Instructions for Use
ORENCIA ® (oh-REN-see-ah) (abatacept) Prefilled syringe with BD UltraSafe Passive ™ needle guard
ORENCIA ® prefilled syringe with BD UltraSafe Passive ™ needle guard (abatacept) Injection | 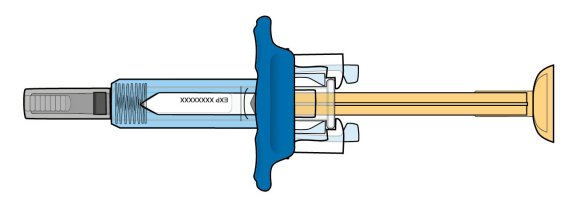 |
Read these instructions before you start using your ORENCIA prefilled syringe and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. Before you use the prefilled syringe for the first time, make sure your healthcare provider shows you the right way to use it and decides that you or a caregiver may be able to give your injections of ORENCIA at home. Important:
| |
Before you begin: get to know your prefilled syringe | |
There are 3 types of prefilled syringes: | |
 | |
The type of prefilled syringe you receive depends on the dose prescribed by your healthcare provider. The 125 mg/mL prefilled syringe is shown below. | |
Before use | 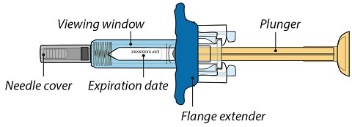 |
After use | 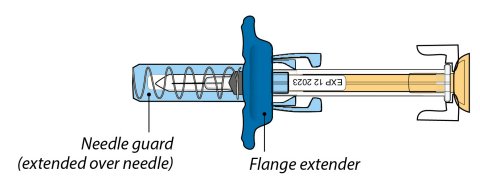 |
The prefilled syringe has a flange extender that makes it easier to hold and inject, and a needle guard that automatically covers the needle after a complete injection.
| |
Go to Step 1 | |
Step 1: Preparing for an ORENCIA injection
Gather and place supplies for your injection on a clean, flat surface. Only the prefilled syringe is included in the package: | |||
|  |
|  |
|  |
|  |
|  | ||
Let your prefilled syringe warm up. Remove 1 prefilled syringe from the refrigerator and wait 30 minutes to allow it to reach room temperature.
|  | ||
Wash your hands well with soap and water. |  | ||
Go to Step 2 | |||
Step 2: Examine the prefilled syringe
Hold the prefilled syringe by the body with the needle cover pointing down as shown.
| 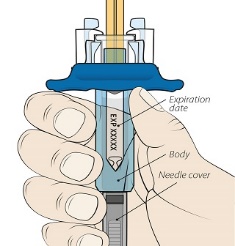 |
Check the Liquid.
| 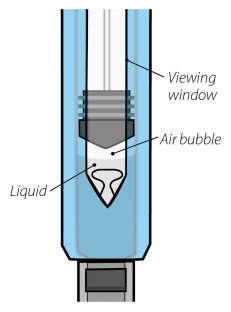 |
Note : the 50 mg prefilled syringe is shown. Note: It is normal to see an air bubble. Do not attempt to remove it. | |
Go to Step 3 | |
Step 3: Check the dose on the prefilled syringe
Hold the syringe at eye level. Look closely to make sure that the amount of liquid in the prefilled syringe is at or just above the fill line for your prescribed dose: |
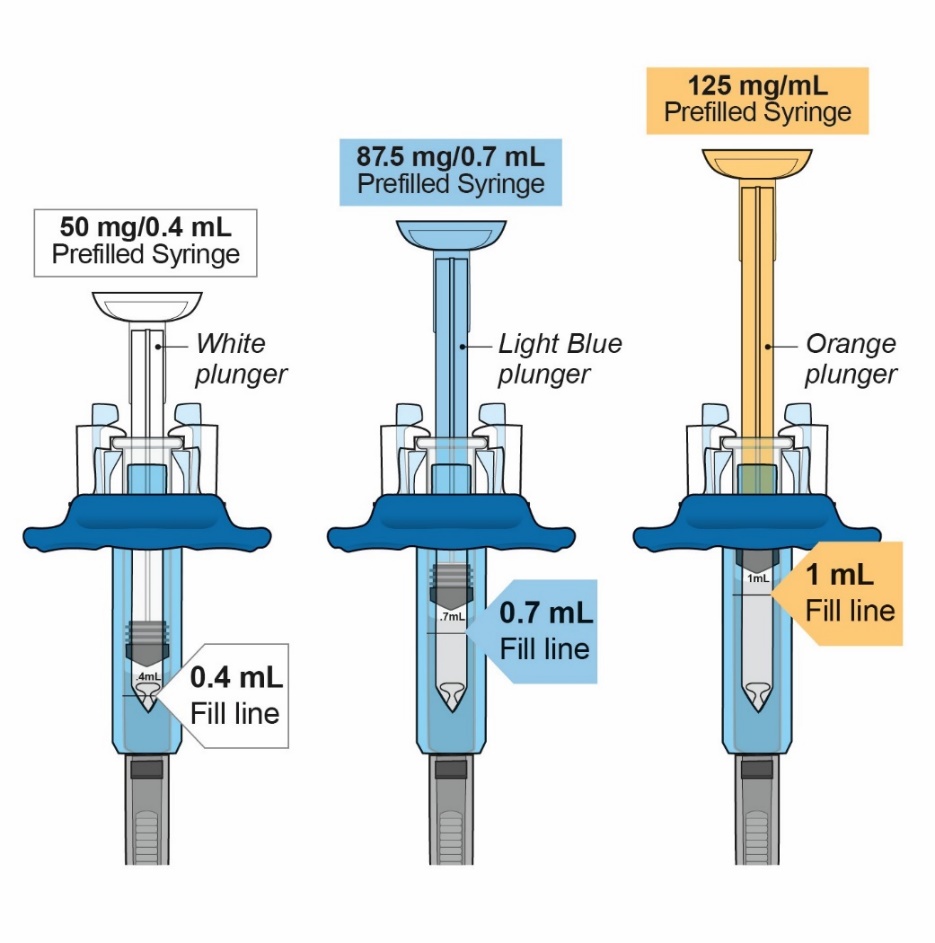 |
Do not use if your prefilled syringe does not have the correct amount of liquid. Call your pharmacist immediately. |
Go to Step 4 |
Step 4: Choose and prepare an injection site
Choose your injection site. Choose your injection site in either the stomach (abdomen) , front of the thighs, or outer area of upper arm (only if caregiver administered). Rotate injection site.
| 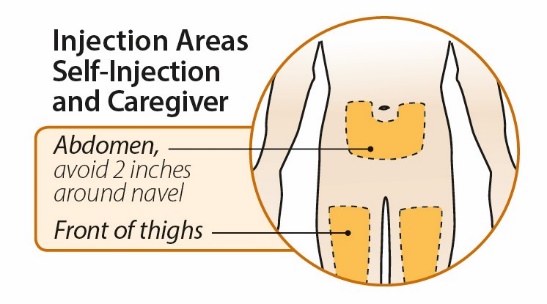 |
| 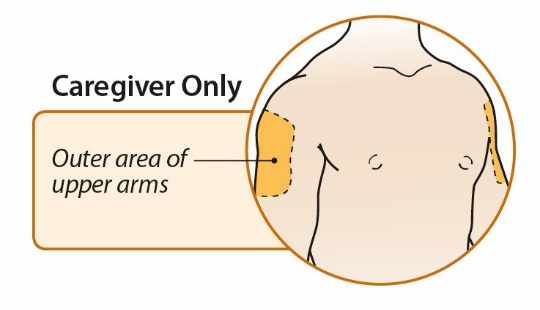 |
Gently clean injection site.
| |
Remove the needle cover by holding the body of the prefilled syringe with one hand and pulling the cover straight off with your other hand. Do not put the needle cover back on the needle after you remove it. Throw away the needle cover in your household trash.
Note : It is normal to see a drop of fluid leaving the needle. | 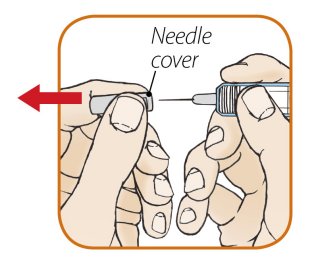 |
| |
Go to Step 5 | |
Step 5: Inject Your Dose of ORENCIA
Hold the body of the prefilled syringe in your hand using your thumb and index finger. With your other hand, pinch the area of skin you cleaned. | 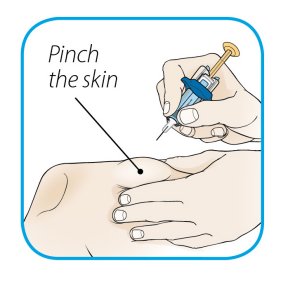 | ||
Insert the needle. Gently insert the needle into the pinched skin at a 45° angle. | 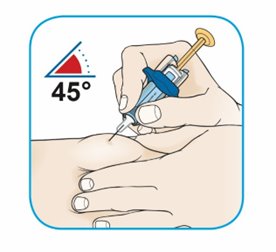 | ||
Complete all steps to deliver your full dose of the medicine. | |||
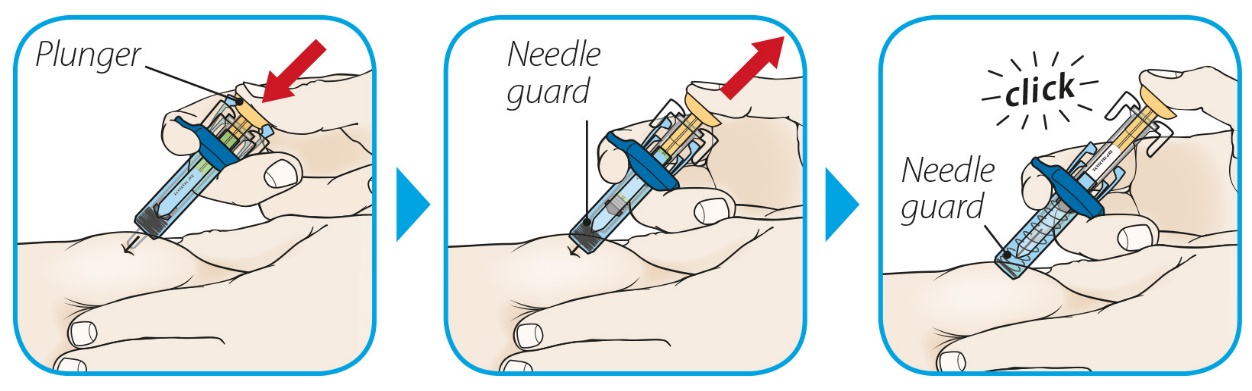 | |||
Inject: push the plunger with your thumb as far as it will go. | Release the needle guard: slowly lift your thumb from the plunger to activate the needle guard. | Confirm: after a complete injection, the needle guard will cover the needle and you may hear a click. | |
Remove the prefilled syringe and let go of the pinched skin. | |||
Go to Step 6 | |||
Step 6: After the injection
Care of injection site:
|  | ||
Throwing away (disposing of) used prefilled syringes:
| |||
| |||
| |||
See Frequently Asked Questions for additional throwing away (disposal) information. If your injection is administered by a caregiver, this person must also be careful handling the syringe to prevent accidental needle stick injury and possibly spreading infection. Keep the ORENCIA prefilled syringes and the sharps disposal container out of the reach of children. |  | ||
How to store ORENCIA prefilled syringe
| |||
Go to next page | |||
Frequently Asked Questions | |||
Q. | Why do I need to allow the prefilled syringe to warm up at room temperature for 30 minutes prior to injecting? | ||
A. | This step is primarily for your comfort. Never try to speed up the warming process in any way, like using the microwave or placing the syringe in warm water. | ||
Q. | Is it necessary to hold the skin pinch during the entire time I inject the dose? | ||
A. | You must pinch the skin during needle insertion however, for your comfort you may release the skin pinch as you deliver the injection. | ||
Q. | What if my prefilled syringe appears to be broken or damaged? | ||
A. | Do not use the prefilled syringe. Contact your healthcare provider or pharmacist for further instructions. | ||
Q. | What if I cannot clearly see the liquid inside the syringe? | ||
A. | Look at the syringe closely by holding at eye level and up to the light. You may tilt the syringe slowly to get a better view of the drug fluid. If you still have trouble, contact your healthcare provider or pharmacist for further instructions. | ||
Q. | Is it normal to feel a little bit of burning or pain during injection? | ||
A. | You may feel a prick from the needle. Sometimes, the medicine can cause slight irritation near the injection site. Discomfort should be mild to moderate. If you have any side effects, including pain, swelling, or discoloration near the injection site, contact your healthcare provider. | ||
Go to next page | |||
Frequently Asked Questions | |||
Q. | How should I dispose of a used prefilled syringe? | ||
A. | Place the used prefilled syringe into an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container. If you do not have one you may use a household container that is:
| ||
Q. | How should I keep my prefilled syringes cool while traveling? | ||
A. | Store them in a cool carrier between 36ºF to 46ºF (2ºC to 8ºC). Do not freeze them. Keep them in the original carton and protected from light. Your healthcare provider may know about special carrying cases. | ||
Q. | Can I take my prefilled syringes on an airplane? | ||
A. | Generally, you are allowed to carry your prefilled syringes with you on an airplane. Do not put them in your checked luggage. You should carry your prefilled syringes with you in your travel cooler at a temperature of 36ºF to 46ºF (2ºC to 8ºC). Keep your prefilled syringes in the original carton, and with its original preprinted labels and protected from light. | ||
Q. | What if my prefilled syringe does not stay cool for an extended period of time? Is it dangerous to use? | ||
A. | Contact 1-800-673-6242 for more information. | ||
Go to back cover | |||
If you have questions or concerns about your prefilled syringe, please contact your healthcare provider or call our toll-free help line at 1-800-673-6242. | |||
Bristol-Myers Squibb Company Princeton, NJ 08543 USA, U.S. License Number 1713
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
ORENCIA is a registered trademark of Bristol-Myers Squibb Company. BD UltraSafe Passive ™ is a trademark of Becton, Dickinson, and Company.
Revised 10/2023
Mechanism of Action
Abatacept, a selective costimulation modulator, inhibits T-cell (T lymphocyte) activation by binding to CD80 and CD86, thereby blocking interaction with CD28. This interaction provides a costimulatory signal necessary for full activation of T lymphocytes. Activated T lymphocytes are implicated in the pathogenesis of RA, pJIA and PsA and are found in the synovium of patients with RA, pJIA and PsA.
In vitro , abatacept decreases T-cell proliferation and inhibits the production of the cytokines TNF alpha (TNFα), interferon-γ, and interleukin-2. In a rat collagen-induced arthritis model, abatacept suppresses inflammation, decreases anti-collagen antibody production, and reduces antigen specific production of interferon-γ. The relationship of these biological response markers to the mechanisms by which ORENCIA exerts its clinical effects is unknown.