Get your patient on Panretin - Alitretinoin gel (Alitretinoin)
Panretin - Alitretinoin gel prescribing information
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Kaposi’s Sarcoma
PANRETIN GEL is indicated for topical treatment of cutaneous lesions in adults with AIDS related Kaposi’s sarcoma (KS).
Limitations of Use: PANRETIN GEL is not indicated when systemic anti-KS therapy is required (including more than 10 new KS lesions in the prior month, symptomatic lymphedema, symptomatic pulmonary KS, or symptomatic visceral involvement) [see Clinical Studies (14.1 )] .
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
PANRETIN GEL is for topical use only. Do not use occlusive dressings with PANRETIN GEL.
- Apply PANRETIN GEL twice daily to coat the entire cutaneous Kaposi sarcoma lesions.
- Gradually increase the application frequency up to four (4) times a day as tolerated.
- Continue PANRETIN GEL as long as patient is deriving benefit.
- Reduce application frequency for application site toxicity. Interrupt treatment for severe irritation; may resume at a reduced application frequency once symptoms improve.
- Avoid application of gel to normal skin and do not apply on or near mucosal surfaces.
- Wash hands after application unless gel is applied to Kaposi sarcoma lesions on the hands.
- Allow gel to dry for three to five minutes before covering with clothing.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Topical Gel: 0.1% alitretinoin (clear yellow gel) in a 60-gram tube.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Risk Summary Based on findings in animal studies and its mechanism of action, PANRETIN GEL can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Oral administration of alitretinoin to pregnant animals during the period of organogenesis was teratogenic and embryo lethal at exposures at least 5 times the estimated daily human topical dose ( see Data ). There are no data on the use of PANRETIN GEL in pregnant women. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to the fetus. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively. Data Animal Data Oral administration of alitretinoin to pregnant rabbits during the period of organogenesis resulted in early resorptions, post-implantation loss, and fetal defects (limb, craniofacial, fused sternebrae) at doses ≥ 0.5 mg/kg/day (approximately 5 times the estimated daily human topical dose based on body surface area, assuming complete systemic absorption of alitretinoin, when PANRETIN GEL is administered as a 60 g tube over 1 month in a 60 kg human). Early resorptions and post-implantation loss also occurred in rats administered oral alitretinoin at doses ≥5 mg/kg/day (approximately 25 times the estimated daily human topical dose based on body surface area). Limb and craniofacial defects also occurred in mice administered oral alitretinoin on day 11 of gestation at single doses ≥50 mg/kg (approximately 127 times the estimated daily human topical dose based on body surface area).
Lactation
Risk Summary
It is not known whether alitretinoin or its metabolites are excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for adverse reactions from PANRETIN GEL in the nursing child, advise patients that breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with PANRETIN GEL and for 1 week after the last dose.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Pregnancy Testing
Verify pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to initiating PANRETIN GEL.
Contraception
Females
PANRETIN GEL can cause embryo-fetal harm when administered to pregnant women [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1 )] . Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with PANRETIN GEL and for 1 week after the last dose.
Males
Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with PANRETIN GEL and for 1 week after the last dose.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of PANRETIN GEL have not been established in pediatric patients.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of PANRETIN GEL did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger adult patients.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
PANRETIN GEL is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to retinoids or to any of the ingredients of the product.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
• Embryo-Fetal Toxicity : Can cause fetal harm. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use an effective method of contraception. (5.1 . 8.1 , 8.3 ) • Photosensitivity : Minimize exposure to sunlight and sunlamps. (5.2 ) • DEET toxicity : Do not use DEET-containing products (5.3 )
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on data from animal studies and its mechanism of action, PANRETIN GEL can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Oral administration of alitretinoin to pregnant animals during the period of organogenesis was teratogenic and embryo-lethal at exposures 5 times the estimated daily human topical dose. Advise women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise women of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with PANRETIN GEL and for 1 week after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1 , 8.3 )] .
Photosensitivity
Retinoids as a class have been associated with photosensitivity. Advise patients to minimize exposure of treated areas to sunlight and sunlamps during the use of PANRETIN GEL.
Toxicity with DEET-Containing Products
Animal toxicology studies showed increased DEET toxicity when DEET was included as part of the formulation. Advise patients to not use PANRETIN GEL concurrently with products that contain DEET (N,N-diethyl-m-toluamide), a common component of insect repellent products.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling: • Photosensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 )]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of PANRETIN GEL was assessed in two multicenter, prospective, randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled trials (Trial 1 and Trial 2) in patients with cutaneous lesions of AIDS-related KS [see Clinical Studies (14.1 )] . In a pooled analysis of both trials, the most common adverse reactions in ≥ 5% of patients were rash, pain, paresthesia, pruritis, exfoliative dermatitis, edema, and skin disorder.
In Trial 1, severe local skin adverse reactions (erythema and edema with or without vesiculation) occurred in 10% of patients during the first 12 weeks of treatment (versus 0% in the vehicle control). Adverse reactions led to withdrawal from the study in 7% of patients.
In Trial 2, severe local skin adverse reactions (erythema and edema with or without vesiculation) occurred in 6% of patients during the first 12 weeks of treatment (versus 0% in the vehicle control) and 1 patient withdrew due to severe skin irritation.
Table 1 lists the most common application site adverse reactions that occurred in a least 5% of patients during the double-blind phase who received PANRETIN GEL in either of the two controlled studies.
TABLE 1: Adverse Reactions at Application Site in Trial 1 and 2 in ≥ 5% of Patients Treated with PANRETIN GEL
| A dverse Event Term | Trial 1 | Trial 2 | ||
| PANRETIN GEL N=134 % | Vehicle Gel N=134 % | PANRETIN GEL N=36 % | Vehicle Gel N=46 % | |
| Rash 1 | 77 | 11 | 25 | 4 |
| Pain 2 | 34 | 7 | 0 | 4 |
| Pruritus 3 | 11 | 4 | 8 | 4 |
| Exfoliative dermatitis 4 | 9 | 2 | 3 | 0 |
| Skin disorder 5 | 8 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Edema 6 | 8 | 3 | 3 | 0 |
| Parethesia 7 | 3 | 0 | 22 | 7 |
| Includes Investigator terms: 1 Erythema, scaling, irritation, redness, rash, dermatitis 2 Burning, pain 3 Itching, pruritus 4 Flaking, peeling, desquamation, exfoliation 5 Excoriation, cracking, scab, crusting, drainage, eschar, fissure or oozing 6 Edema, swelling, inflammation 7 Stinging, tingling | ||||
DESCRIPTION
PANRETIN GEL is a retinoid. PANRETIN GEL 0.1% contains alitretinoin and is intended for topical application only. The chemical name is (2E,4E,6Z,8E)-3,7-Dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic acid, also known as 9-cis-retinoic acid. Chemically, alitretinoin is related to vitamin A. It is a yellow powder with a molecular weight of 300.44 and a molecular formula of C 20 H 28 O 2 . It is slightly soluble in ethanol (7.01 mg/g at 25℃) and insoluble in water. The structural formula of alitretinoin is as follows: 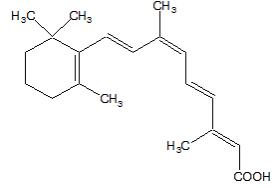
PANRETIN GEL is a clear, yellow gel containing 0.1% (w/w) alitretinoin. Each gram of PANRETIN GEL contains 1 mg alitretinoin. PANRETIN GEL contains the following inactive ingredients: butylated hydroxytoluene NF, dehydrated alcohol USP 92%, hydroxypropyl cellulose NF, and polyethylene glycol 400 NF.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Alitretinoin (9-cis-retinoic acid) is a naturally occurring endogenous retinoid that binds to and activates all known intracellular retinoid receptor subtypes (RARα, RARβ, RARγ, RXRα, RXRβ and RXRγ). Once activated these receptors function as transcription factors that regulate the expression of genes that control the process of cellular differentiation and proliferation in both normal and neoplastic cells. Alitretinoin inhibits the growth of Kaposi’s sarcoma (KS) cells in vitro.
Pharmacodynamics
Alitretinoin exposure-response relationships and the time course of pharmacodynamic response are unknown.
Pharmacokinetics
The range of 9-cis-retinoic acid plasma concentrations in patients with cutaneous lesions of AIDS-related KS after multiple daily applications of PANRETIN GEL for up to 60 weeks was similar to the range of circulating, naturally occurring 9-cis-retinoic acid plasma concentrations in untreated healthy participants.
Elimination
Metabolism
9-cis-retinoic acid is metabolized to 4-hydroxy-9-cis-retinoic acid and 4-oxo-9-cis-retinoic acid by CYP2C9, 3A4, 1A1, and 1A2. 4-oxo-9-cis-retinoic acid is the major circulating metabolite following oral administration of 9-cis-retinoic acid.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment Of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies with alitretinoin have not been conducted. Alitretinoin was not mutagenic in vitro (bacterial assay, Chinese hamster ovary cell HGPRT mutation assay) and was not clastogenic in vitro (chromosome aberration test in human lymphocytes) or in vivo (mouse micronucleus test).
CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Kaposi’s Sarcoma
PANRETIN GEL was evaluated in two multicenter, randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled studies in adult patients with cutaneous lesions of AIDS-related KS. In both studies the primary efficacy objective was the patients’ cutaneous KS tumor response rate through 12 weeks of study drug treatment which was assessed by evaluating from 3 to 8 KS index lesions according to the modified AIDS Clinical Trials Group (ACTG) response criteria as applied to topical therapy (i.e., evaluation of height and area reductions of the index lesions only; progressive disease in non-index lesions and new lesions were not considered progressive disease; progressive disease was scored only in the treated index lesions). A global evaluation by physicians was also carried out. It considered all the patient’s treated lesions (index and other) compared to baseline. In this evaluation, patients with at least a 50% improvement in the KS lesions were considered responders. In addition, photographs of lesions in patients considered responders by the modified ACTG criteria were examined by the FDA for a cosmetically beneficial response, defined as at least a 50% improvement in appearance compared to baseline, considering both the KS lesions and dermal toxicity at the lesion site, in at least 50% of the index lesions and maintained for at least 3 weeks. Visceral disease was not monitored in these trials and the appearance of new KS lesions was not considered part of the response assessment.
In Trial 1, a total of 268 patients were entered from centers in the U.S. and Canada. Patients were treated topically three to four times a day with either PANRETIN GEL or a matching vehicle gel for a minimum of 12 weeks, followed by an open-label phase in patients who had not yet progressed on PANRETIN GEL. Median age of patients was 39 years, 99% were men, 75% were White, 16% Hispanic, and 7% Black. Fifty-seven percent of patients had a CD4+ lymphocyte count <200/mm3 and 36% had CD4+ lymphocyte count less than 100/mm3; 12% had visceral KS. Responses during the double-blind phase are shown in Table 2 . New lesions in untreated areas were seen in about 50% of patients.
Trial 2 was an international study with a planned enrollment of 270 patients. Patients were treated topically twice a day with PANRETIN GEL or a matching vehicle for 12 weeks. The study was stopped early because of positive-interim results in the initial 82 patients. Median age of patients was 36 years for PANRETIN-GEL and 39 years for matching vehicle; all patients were men; 89% White; 5% Hispanic, and 4% Black; 67% had a CD4+ lymphocyte count ≤200/mm3 and 39% had CD4+ lymphocyte count ≤100/mm3; and 16% had visceral KS.
Results of the study are shown in Table 2 . Responses to PANRETIN GEL were seen both in previously untreated patients and in patients with prior systemic and/or topical KS treatment.
Table 2: Response Rates
| Trial 1 | Trial 2 | |||
| PANRETIN GEL N=134 | Vehicle Gel N=134 | PANRETIN GEL N=36 | Vehicle Gel N=45 | |
| Modified ACTG Response | 35%• | 16% | 36% | 7% |
| P = 0.0012 | ||||
| Physician’s Global Subjective Assessment (all treated lesions) | 19% | 4% | 47% | 11% |
| P = 0.00014 | ||||
| Photograph Response | 15% | 4% | 19% | 2% |
| P = 0.0026 | ||||
•All responses were partial responses except 1% complete response for modified ACTG response in Trial 1.
In the clinical trials, the cumulative percentage of patients who experienced a response was less than 1% at 2 weeks, 10% at 4 weeks, and 28% at 8 weeks. Photographs of some patients revealed an erythematous and edematous response, leading to a cosmetically mixed outcome.
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
PANRETIN GEL is a clear yellow gel and is supplied in a 60-gram tubes containing 0.1% alitretinoin. Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. PANRETIN GEL is flammable; keep away from heat or flame.
Mechanism of Action
Alitretinoin (9-cis-retinoic acid) is a naturally occurring endogenous retinoid that binds to and activates all known intracellular retinoid receptor subtypes (RARα, RARβ, RARγ, RXRα, RXRβ and RXRγ). Once activated these receptors function as transcription factors that regulate the expression of genes that control the process of cellular differentiation and proliferation in both normal and neoplastic cells. Alitretinoin inhibits the growth of Kaposi’s sarcoma (KS) cells in vitro.