Perjeta prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Perjeta patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- For intravenous infusion only. Do not administer as an intravenous push or bolus. (2.5 )
- HER2 testing: Perform using FDA-approved tests by laboratories with demonstrated proficiency. (2.1 )
- The initial PERJETA dose is 840 mg administered as a 60-minute intravenous infusion, followed every 3 weeks thereafter by 420 mg administered as a 30 to 60 minute intravenous infusion. (2.3 )
- MBC: Administer PERJETA, trastuzumab or trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk, and docetaxel every 3 weeks. (2.3 )
- Neoadjuvant: Administer PERJETA, trastuzumab or trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk, and chemotherapy preoperatively every 3 weeks for 3 to 6 cycles. (2.3 )
- Adjuvant: Administer PERJETA, trastuzumab or trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk, and chemotherapy postoperatively every 3 weeks for a total of 1 year (up to 18 cycles). (2.3 )
Evaluation and Testing Before Initiating Perjeta
Assess left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) prior to initiation of PERJETA and at regular intervals during treatment [see Boxed Warning , Dosage and Administration (2.4) , Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ].
Verify the pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to the initiation of PERJETA [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) , Use in Specific Populations (8.1 , 8.3) ].
Patient Selection
Select patients based on HER2 protein overexpression or HER2 gene amplification in tumor specimens [see Indications and Usage (1) and Clinical Studies (14) ] . Assessment of HER2 protein overexpression and HER2 gene amplification should be performed using FDA-approved tests specific for breast cancer by laboratories with demonstrated proficiency.
Information on the FDA-approved tests for the detection of HER2 protein overexpression and HER2 gene amplification is available at: http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics.
Improper assay performance, including use of suboptimally fixed tissue, failure to utilize specified reagents, deviation from specific assay instructions, and failure to include appropriate controls for assay validation, can lead to unreliable results.
Recommended Dosage and Administration
The initial dose of PERJETA is 840 mg administered as a 60-minute intravenous infusion, followed every 3 weeks by a dose of 420 mg administered as an intravenous infusion over 30 to 60 minutes.
When administered with PERJETA, the recommended initial dose of trastuzumab is 8 mg/kg administered as a 90-minute intravenous infusion, followed every 3 weeks by a dose of 6 mg/kg administered as an intravenous infusion over 30 to 90 minutes.
When administered with PERJETA, the recommended initial dose of trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk is 600 mg/10,000 units (600 mg trastuzumab and 10,000 units hyaluronidase) administered subcutaneously over approximately 2 to 5 minutes once every three weeks irrespective of the patient's body weight.
Administer PERJETA, trastuzumab or trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk, and taxane sequentially. PERJETA and trastuzumab or trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk can be given in any order. Administer taxane after PERJETA and trastuzumab or trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk. An observation period of 30 to 60 minutes is recommended after each PERJETA infusion and before commencement of any subsequent administration of trastuzumab or trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk, or taxane [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ].
In patients receiving an anthracycline-based regimen, administer PERJETA and trastuzumab or trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk after completion of the anthracycline.
Metastatic Breast Cancer (MBC)
When administered with PERJETA, the recommended initial dose of docetaxel is 75 mg/m 2 administered as an intravenous infusion. The dose may be escalated to 100 mg/m 2 administered every 3 weeks if the initial dose is well tolerated.
Neoadjuvant Treatment of Breast Cancer
Administer PERJETA every 3 weeks for 3 to 6 cycles as part of one of the following treatment regimens [see Clinical Studies (14.2 , 14.3) ] :
- Four preoperative cycles of PERJETA in combination with trastuzumab or trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk and docetaxel followed by 3 postoperative cycles of fluorouracil, epirubicin, and cyclophosphamide (FEC)
- Three or four preoperative cycles of FEC alone followed by 3 or 4 preoperative cycles of PERJETA in combination with docetaxel and trastuzumab or trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk
- Six preoperative cycles of PERJETA in combination with docetaxel, carboplatin, and trastuzumab (TCH) or trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk (escalation of docetaxel above 75 mg/m 2 is not recommended)
- Four preoperative cycles of dose-dense doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide (ddAC) alone followed by 4 preoperative cycles of PERJETA in combination with paclitaxel and trastuzumab or trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk
Following surgery, administer PERJETA and trastuzumab or trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk to complete 1 year of treatment (up to 18 cycles) or until disease recurrence or unmanageable toxicity, whichever occurs first.
Adjuvant Treatment of Breast Cancer
As part of a regimen including standard anthracycline- and/or taxane-based chemotherapy, administer PERJETA in combination with trastuzumab or trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk every 3 weeks for a total of 1 year (up to 18 cycles) or until disease recurrence or unmanageable toxicity, whichever occurs first. Administer PERJETA on Day 1 of the first taxane-containing cycle [see Clinical Studies (14.3) ] .
Important Dosing Considerations
Missed Dose
The recommended dosage modifications for delayed or missed doses are listed in Table 1 .
| Time between two sequential doses | PERJETA | Trastuzumab (intravenous) | Trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk |
|---|---|---|---|
| < 6 weeks | Administer PERJETA 420 mg intravenously as soon as possible. Do not wait until the next planned dose. | Administer trastuzumab 6 mg/kg intravenously as soon as possible. Do not wait until the next planned dose. | Administer trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk 600 mg/10,000 units subcutaneously as soon as possible. Do not wait until the next planned dose. |
| ≥ 6 weeks | Readminister PERJETA loading dose of 840 mg intravenously as a 60 minute infusion, followed by a maintenance dose of 420 mg administered intravenously over a period of 30 to 60 minutes every 3 weeks thereafter. | Readminister trastuzumab loading dose of 8 mg/kg intravenously over approximately 90 minutes, followed by a maintenance dose of 6 mg/kg administered intravenously over a period of 30 or 90 minutes every 3 weeks thereafter. |
Permanently discontinue PERJETA if trastuzumab or trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk treatment is discontinued.
Dose reductions are not recommended for PERJETA.
For chemotherapy dose modifications, see relevant prescribing information.
Dosage Modification for Adverse Reactions
Left Ventricular Dysfunction
Assess left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) prior to initiation of PERJETA and at regular intervals during treatment. The recommended dosage modifications for LVEF decrease are listed in Table 2 [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ].
| Pre-treatment LVEF: | Monitor LVEF every: | Withhold PERJETA and trastuzumab or trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk for at least 3 weeks for an LVEF decrease to: | Resume PERJETA and trastuzumab or trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk after 3 weeks if LVEF has recovered to: | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metastatic Breast Cancer | ≥ 50% | ~12 weeks | Either | Either | ||
| <40% | 40%-45% with a fall of ≥10%-points below pre-treatment value | >45% | 40%-45% with a fall of <10%-points below pre-treatment value | |||
| Early Breast Cancer | ≥ 55% For patients receiving anthracycline-based chemotherapy, a LVEF of ≥ 50% is required after completion of anthracyclines, before starting PERJETA and trastuzumab or trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk. | ~12 weeks (once during neoadjuvant therapy) | <50% with a fall of ≥10%-points below pre-treatment value | Either | ||
| ≥50% | <10% points below pre-treatment value | |||||
Infusion-Related Reactions
The infusion rate of PERJETA may be slowed or interrupted if the patient develops an infusion-related reaction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ] .
Hypersensitivity Reactions/Anaphylaxis
The infusion should be discontinued immediately if the patient experiences a serious hypersensitivity reaction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ] .
Preparation for Administration
Administer as an intravenous infusion only. Do not administer as an intravenous push or bolus. Do not mix PERJETA with other drugs.
Preparation
Prepare the solution for infusion, using aseptic technique, as follows:
- Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulates and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
- Withdraw the appropriate volume of PERJETA solution from the vial(s) using a sterile needle and syringe.
- Dilute into a 250 mL 0.45% Sodium Chloride Injection or 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection infusion bag.
- Mix diluted solution by gentle inversion. Do not shake.
- Administer immediately once prepared.
- If the diluted infusion solution is not used immediately, it can be stored refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36 °F to 46 °F) for up to 24 hours.
- Dilute with 0.45% Sodium Chloride Injection or 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection only. Do not use 5% Dextrose Injection.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Perjeta prescribing information
WARNING: LEFT VENTRICULAR DYSFUNCTION and EMBRYO-FETAL TOXICITY
- Left Ventricular Dysfunction: PERJETA can cause subclinical and clinical cardiac failure manifesting as decreased LVEF and CHF. Evaluate cardiac function prior to and during treatment. Discontinue PERJETA treatment for a confirmed clinically significant decrease in left ventricular function [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) , Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Adverse Reactions (6.1) ].
- Embryo-fetal Toxicity: Exposure to PERJETA can cause embryo-fetal death and birth defects. Advise patients of these risks and the need for effective contraception [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1) (8.3) ].
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
PERJETA is a HER2/neu receptor antagonist indicated for:
- Use in combination with trastuzumab and docetaxel for treatment of adults with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer (MBC) who have not received prior anti-HER2 therapy or chemotherapy for metastatic disease. (1.1 )
- Use in combination with trastuzumab and chemotherapy as
- neoadjuvant treatment of adults with HER2-positive, locally advanced, inflammatory, or early stage breast cancer (either greater than 2 cm in diameter or node positive) as part of a complete treatment regimen for early breast cancer. (1.2 , 2.2 , 14.2 )
- adjuvant treatment of adults with HER2-positive early breast cancer at high risk of recurrence (1.2 , 2.2 , 14.3 )
Metastatic Breast Cancer (MBC)
PERJETA is indicated for use in combination with trastuzumab and docetaxel for the treatment of adults with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer who have not received prior anti-HER2 therapy or chemotherapy for metastatic disease [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Clinical Studies (14.1) ] .
Early Breast Cancer (EBC)
PERJETA is indicated for use in combination with trastuzumab and chemotherapy for
- the neoadjuvant treatment of adults with HER2-positive, locally advanced, inflammatory, or early stage breast cancer (either greater than 2 cm in diameter or node positive) as part of a complete treatment regimen for early breast cancer [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Clinical Studies (14.2) ] .
- the adjuvant treatment of adults with HER2-positive early breast cancer at high risk of recurrence [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Clinical Studies (14.3) ] .
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- For intravenous infusion only. Do not administer as an intravenous push or bolus. (2.5 )
- HER2 testing: Perform using FDA-approved tests by laboratories with demonstrated proficiency. (2.1 )
- The initial PERJETA dose is 840 mg administered as a 60-minute intravenous infusion, followed every 3 weeks thereafter by 420 mg administered as a 30 to 60 minute intravenous infusion. (2.3 )
- MBC: Administer PERJETA, trastuzumab or trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk, and docetaxel every 3 weeks. (2.3 )
- Neoadjuvant: Administer PERJETA, trastuzumab or trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk, and chemotherapy preoperatively every 3 weeks for 3 to 6 cycles. (2.3 )
- Adjuvant: Administer PERJETA, trastuzumab or trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk, and chemotherapy postoperatively every 3 weeks for a total of 1 year (up to 18 cycles). (2.3 )
Evaluation and Testing Before Initiating Perjeta
Assess left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) prior to initiation of PERJETA and at regular intervals during treatment [see Boxed Warning , Dosage and Administration (2.4) , Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ].
Verify the pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to the initiation of PERJETA [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) , Use in Specific Populations (8.1 , 8.3) ].
Patient Selection
Select patients based on HER2 protein overexpression or HER2 gene amplification in tumor specimens [see Indications and Usage (1) and Clinical Studies (14) ] . Assessment of HER2 protein overexpression and HER2 gene amplification should be performed using FDA-approved tests specific for breast cancer by laboratories with demonstrated proficiency.
Information on the FDA-approved tests for the detection of HER2 protein overexpression and HER2 gene amplification is available at: http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics.
Improper assay performance, including use of suboptimally fixed tissue, failure to utilize specified reagents, deviation from specific assay instructions, and failure to include appropriate controls for assay validation, can lead to unreliable results.
Recommended Dosage and Administration
The initial dose of PERJETA is 840 mg administered as a 60-minute intravenous infusion, followed every 3 weeks by a dose of 420 mg administered as an intravenous infusion over 30 to 60 minutes.
When administered with PERJETA, the recommended initial dose of trastuzumab is 8 mg/kg administered as a 90-minute intravenous infusion, followed every 3 weeks by a dose of 6 mg/kg administered as an intravenous infusion over 30 to 90 minutes.
When administered with PERJETA, the recommended initial dose of trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk is 600 mg/10,000 units (600 mg trastuzumab and 10,000 units hyaluronidase) administered subcutaneously over approximately 2 to 5 minutes once every three weeks irrespective of the patient's body weight.
Administer PERJETA, trastuzumab or trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk, and taxane sequentially. PERJETA and trastuzumab or trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk can be given in any order. Administer taxane after PERJETA and trastuzumab or trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk. An observation period of 30 to 60 minutes is recommended after each PERJETA infusion and before commencement of any subsequent administration of trastuzumab or trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk, or taxane [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ].
In patients receiving an anthracycline-based regimen, administer PERJETA and trastuzumab or trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk after completion of the anthracycline.
Metastatic Breast Cancer (MBC)
When administered with PERJETA, the recommended initial dose of docetaxel is 75 mg/m 2 administered as an intravenous infusion. The dose may be escalated to 100 mg/m 2 administered every 3 weeks if the initial dose is well tolerated.
Neoadjuvant Treatment of Breast Cancer
Administer PERJETA every 3 weeks for 3 to 6 cycles as part of one of the following treatment regimens [see Clinical Studies (14.2 , 14.3) ] :
- Four preoperative cycles of PERJETA in combination with trastuzumab or trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk and docetaxel followed by 3 postoperative cycles of fluorouracil, epirubicin, and cyclophosphamide (FEC)
- Three or four preoperative cycles of FEC alone followed by 3 or 4 preoperative cycles of PERJETA in combination with docetaxel and trastuzumab or trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk
- Six preoperative cycles of PERJETA in combination with docetaxel, carboplatin, and trastuzumab (TCH) or trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk (escalation of docetaxel above 75 mg/m 2 is not recommended)
- Four preoperative cycles of dose-dense doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide (ddAC) alone followed by 4 preoperative cycles of PERJETA in combination with paclitaxel and trastuzumab or trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk
Following surgery, administer PERJETA and trastuzumab or trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk to complete 1 year of treatment (up to 18 cycles) or until disease recurrence or unmanageable toxicity, whichever occurs first.
Adjuvant Treatment of Breast Cancer
As part of a regimen including standard anthracycline- and/or taxane-based chemotherapy, administer PERJETA in combination with trastuzumab or trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk every 3 weeks for a total of 1 year (up to 18 cycles) or until disease recurrence or unmanageable toxicity, whichever occurs first. Administer PERJETA on Day 1 of the first taxane-containing cycle [see Clinical Studies (14.3) ] .
Important Dosing Considerations
Missed Dose
The recommended dosage modifications for delayed or missed doses are listed in Table 1 .
| Time between two sequential doses | PERJETA | Trastuzumab (intravenous) | Trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk |
|---|---|---|---|
| < 6 weeks | Administer PERJETA 420 mg intravenously as soon as possible. Do not wait until the next planned dose. | Administer trastuzumab 6 mg/kg intravenously as soon as possible. Do not wait until the next planned dose. | Administer trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk 600 mg/10,000 units subcutaneously as soon as possible. Do not wait until the next planned dose. |
| ≥ 6 weeks | Readminister PERJETA loading dose of 840 mg intravenously as a 60 minute infusion, followed by a maintenance dose of 420 mg administered intravenously over a period of 30 to 60 minutes every 3 weeks thereafter. | Readminister trastuzumab loading dose of 8 mg/kg intravenously over approximately 90 minutes, followed by a maintenance dose of 6 mg/kg administered intravenously over a period of 30 or 90 minutes every 3 weeks thereafter. |
Permanently discontinue PERJETA if trastuzumab or trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk treatment is discontinued.
Dose reductions are not recommended for PERJETA.
For chemotherapy dose modifications, see relevant prescribing information.
Dosage Modification for Adverse Reactions
Left Ventricular Dysfunction
Assess left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) prior to initiation of PERJETA and at regular intervals during treatment. The recommended dosage modifications for LVEF decrease are listed in Table 2 [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ].
| Pre-treatment LVEF: | Monitor LVEF every: | Withhold PERJETA and trastuzumab or trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk for at least 3 weeks for an LVEF decrease to: | Resume PERJETA and trastuzumab or trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk after 3 weeks if LVEF has recovered to: | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metastatic Breast Cancer | ≥ 50% | ~12 weeks | Either | Either | ||
| <40% | 40%-45% with a fall of ≥10%-points below pre-treatment value | >45% | 40%-45% with a fall of <10%-points below pre-treatment value | |||
| Early Breast Cancer | ≥ 55% For patients receiving anthracycline-based chemotherapy, a LVEF of ≥ 50% is required after completion of anthracyclines, before starting PERJETA and trastuzumab or trastuzumab hyaluronidase-oysk. | ~12 weeks (once during neoadjuvant therapy) | <50% with a fall of ≥10%-points below pre-treatment value | Either | ||
| ≥50% | <10% points below pre-treatment value | |||||
Infusion-Related Reactions
The infusion rate of PERJETA may be slowed or interrupted if the patient develops an infusion-related reaction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ] .
Hypersensitivity Reactions/Anaphylaxis
The infusion should be discontinued immediately if the patient experiences a serious hypersensitivity reaction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ] .
Preparation for Administration
Administer as an intravenous infusion only. Do not administer as an intravenous push or bolus. Do not mix PERJETA with other drugs.
Preparation
Prepare the solution for infusion, using aseptic technique, as follows:
- Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulates and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
- Withdraw the appropriate volume of PERJETA solution from the vial(s) using a sterile needle and syringe.
- Dilute into a 250 mL 0.45% Sodium Chloride Injection or 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection infusion bag.
- Mix diluted solution by gentle inversion. Do not shake.
- Administer immediately once prepared.
- If the diluted infusion solution is not used immediately, it can be stored refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36 °F to 46 °F) for up to 24 hours.
- Dilute with 0.45% Sodium Chloride Injection or 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection only. Do not use 5% Dextrose Injection.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Injection: 420 mg/14 mL (30 mg/mL) clear to slightly opalescent and colorless to pale brown solution in a single-dose vial
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential: Verify the pregnancy status of females prior to initiation of PERJETA. (8.3 )
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Pharmacovigilance Program
There is a pregnancy pharmacovigilance program for PERJETA. If PERJETA is administered during pregnancy, or if a patient becomes pregnant while receiving PERJETA or within 7 months following the last dose of PERJETA in combination with trastuzumab, health care providers and patients should immediately report PERJETA exposure to Genentech at 1-888-835-2555.
Risk Summary
Based on its mechanism of action and findings in animal studies, PERJETA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. There are no available data on the use of PERJETA in pregnant women. However, in post-marketing reports, use of another HER2/neu receptor antagonist (trastuzumab) during pregnancy resulted in cases of oligohydramnios and oligohydramnios sequence manifesting as pulmonary hypoplasia, skeletal abnormalities, and neonatal death. In an animal reproduction study, administration of pertuzumab to pregnant cynomolgus monkeys during the period of organogenesis resulted in oligohydramnios, delayed fetal kidney development, and embryo-fetal deaths at clinically relevant exposures that were 2.5 to 20-fold greater than exposures in humans receiving the recommended dose, based on C max [see Data ]. Apprise the patient of the potential risks to a fetus. There are clinical considerations if PERJETA in combination with trastuzumab is used during pregnancy or within 7 months prior to conception [see Clinical Considerations ] .
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Fetal/Neonatal Adverse Reactions
Monitor women who received PERJETA in combination with trastuzumab during pregnancy or within 7 months prior to conception for oligohydramnios. If oligohydramnios occurs, perform fetal testing that is appropriate for gestational age and consistent with community standards of care.
Data
Animal Data
Pregnant cynomolgus monkeys were treated on Gestational Day (GD)19 with loading doses of 30 to 150 mg/kg pertuzumab, followed by bi-weekly doses of 10 to 100 mg/kg. These dose levels resulted in clinically relevant exposures of 2.5 to 20-fold greater than exposures in humans receiving the recommended dose, based on C max . Intravenous administration of pertuzumab from GD19 through GD50 (period of organogenesis) was embryotoxic, with dose-dependent increases in embryo-fetal death between GD25 to GD70. The incidences of embryo-fetal loss were 33, 50, and 85% for dams treated with bi-weekly pertuzumab doses of 10, 30, and 100 mg/kg, respectively (2.5 to 20-fold greater than the recommended human dose, based on C max ). At Caesarean section on GD100, oligohydramnios, decreased relative lung and kidney weights, and microscopic evidence of renal hypoplasia consistent with delayed renal development were identified in all pertuzumab dose groups. Pertuzumab exposure was reported in offspring from all treated groups, at levels of 29% to 40% of maternal serum levels at GD100.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information regarding the presence of pertuzumab in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant or the effects on milk production. Published data suggest that human IgG is present in human milk but does not enter the neonatal and infant circulation in substantial amounts. Consider the developmental and health benefits of breast feeding along with the mother's clinical need for PERJETA treatment and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from PERJETA or from the underlying maternal condition. This consideration should also take into account the elimination half-life of pertuzumab and the trastuzumab wash out period of 7 months .
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Pregnancy Testing
Verify the pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to the initiation of PERJETA.
Contraception
Females
Based on the mechanism of action and animal data, PERJETA can cause embryo-fetal harm when administered during pregnancy. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for 7 months following the last dose of PERJETA in combination with trastuzumab [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ].
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of PERJETA have not been established in pediatric patients.
Geriatric Use
In CLEOPATRA, NeoSphere, TRYPHAENA, BERENICE, and APHINITY, 464 patients who received PERJETA were ≥ 65 years of age and 47 were ≥ 75 years of age.
The incidence of adverse reactions was increased in patients aged ≥ 65 years of age compared to patients aged < 65 years of age for decreased appetite, anemia, decreased weight, asthenia, dysgeusia, peripheral neuropathy, and hypomagnesemia.
No overall differences in efficacy of PERJETA were observed in patients aged ≥ 65 and <65 years of age. Clinical studies did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged ≥ 75 years to determine if these patients respond differently than younger patients.
Based on a population pharmacokinetic analysis, no significant difference was observed in the pharmacokinetics of pertuzumab between patients < 65 years (n=306) and patients ≥ 65 years (n=175).
Renal Impairment
Dose adjustments of PERJETA are not needed in patients with mild (creatinine clearance [CLcr] 60 to 90 mL/min) or moderate (CLcr 30 to 60 mL/min) renal impairment. No dose adjustment can be recommended for patients with severe renal impairment (CLcr less than 30 mL/min) because of the limited pharmacokinetic data available [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
CONTRAINDICATIONS
PERJETA is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to pertuzumab or to any of its excipients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Infusion-Related Reactions: PERJETA can cause serious infusion reactions, including fatal events: Monitor for signs and symptoms. If a significant infusion-associated reaction occurs, slow or interrupt the infusion and administer appropriate medical therapies. (5.3 )
- Hypersensitivity Reactions/Anaphylaxis: PERJETA can cause hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis: Monitor for signs and symptoms, including angioedema. If a severe hypersensitivity reaction/anaphylaxis occurs, discontinue the infusion immediately and administer appropriate medical therapies. (5.4 )
Left Ventricular Dysfunction
PERJETA can cause left ventricular dysfunction, including symptomatic heart failure. Decreases in LVEF have been reported with drugs that block HER2 activity, including PERJETA.
Assess LVEF prior to initiation of PERJETA and at regular intervals during treatment to ensure that LVEF is within normal limits. If the LVEF declines and has not improved, or has declined further at the subsequent assessment, consider permanent discontinuation of PERJETA and trastuzumab [see Dosage Modification for Adverse Reactions (2.5) ] .
In the PERJETA-treated patients with MBC in CLEOPATRA, left ventricular dysfunction occurred in 4% of patients and symptomatic left ventricular systolic dysfunction (LVSD) (congestive heart failure) occurred in 1% of patients. Patients who received prior anthracyclines or prior radiotherapy to the chest area may be at higher risk of decreased LVEF or left ventricular dysfunction.
In patients receiving PERJETA as a neoadjuvant treatment in combination with trastuzumab and docetaxel in NeoSphere, LVEF decline > 10% and a drop to < 50% occurred in 8% of patients and left ventricular dysfunction occurred in 3% of patients. LVEF recovered to ≥ 50% in all these patients.
In patients receiving neoadjuvant PERJETA in TRYPHAENA, LVEF decline > 10% and a drop to < 50% occurred in 7% of patients treated with PERJETA plus trastuzumab and FEC followed by PERJETA plus trastuzumab and docetaxel, 16% of patients treated with PERJETA plus trastuzumab and docetaxel following FEC, and 11% of patients treated with PERJETA in combination with TCH. Left ventricular dysfunction occurred in 6% of patients treated with PERJETA plus trastuzumab and FEC followed by PERJETA plus trastuzumab and docetaxel, 4% of patients treated with PERJETA plus trastuzumab and docetaxel following FEC, and 3% of patients treated with PERJETA in combination with TCH. Symptomatic LVSD occurred in 4% of patients treated with PERJETA plus trastuzumab and docetaxel following FEC, 1% of patients treated with PERJETA in combination with TCH, and none of the patients treated with PERJETA plus trastuzumab and FEC followed by PERJETA plus trastuzumab and docetaxel. LVEF recovered to ≥ 50% in all but one patient.
In patients receiving neoadjuvant PERJETA in BERENICE, in the neoadjuvant period, LVEF decline ≥ 10% and a drop to < 50% as measured by ECHO/MUGA assessment occurred in 7% of patients treated with PERJETA plus trastuzumab and paclitaxel following ddAC, and 2% of patients treated with PERJETA plus trastuzumab and docetaxel following FEC. Ejection fraction decreased (asymptomatic LVD) occurred in 7% of patients treated with PERJETA plus trastuzumab and paclitaxel following ddAC and 4% of the patients treated with PERJETA plus trastuzumab and docetaxel following FEC in the neoadjuvant period. Symptomatic LVSD (NYHA Class III/IV Congestive Heart Failure) occurred in 2% of patients treated with PERJETA plus trastuzumab and paclitaxel following ddAC and none of the patients treated with PERJETA plus trastuzumab and docetaxel following FEC in the neoadjuvant period.
In patients receiving adjuvant PERJETA in APHINITY, the incidence of symptomatic heart failure (NYHA Class III/IV) with a LVEF decline ≥ 10% and a drop to < 50% was 0.6%. Of the patients who experienced symptomatic heart failure, 47% of PERJETA-treated patients had recovered (defined as 2 consecutive LVEF measurements above 50%) at the data cutoff. The majority of the events (86%) were reported in anthracycline-treated patients. Asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic (NYHA Class II) declines in LVEF ≥ 10% and a drop to < 50% were reported in 3% of PERJETA-treated patients, of whom 80% recovered at the data cutoff.
PERJETA has not been studied in patients with a pretreatment LVEF value of < 50%, a prior history of CHF, decreases in LVEF to < 50% during prior trastuzumab therapy, or conditions that could impair left ventricular function such as uncontrolled hypertension, recent myocardial infarction, serious cardiac arrhythmia requiring treatment or a cumulative prior anthracycline exposure to > 360 mg/m 2 of doxorubicin or its equivalent.
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on its mechanism of action and findings in animal studies, PERJETA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. PERJETA is a HER2/neu receptor antagonist. Cases of oligohydramnios and oligohydramnios sequence manifesting as pulmonary hypoplasia, skeletal abnormalities, and neonatal death have been reported with use of another HER2/neu receptor antagonist (trastuzumab) during pregnancy. In an animal reproduction study, administration of pertuzumab to pregnant cynomolgus monkeys during the period of organogenesis resulted in oligohydramnios, delayed fetal kidney development, and embryo-fetal death at exposures 2.5 to 20 times the exposure in humans at the recommended dose, based on C max .
Verify the pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to the initiation of PERJETA. Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential that exposure to PERJETA in combination with trastuzumab during pregnancy or within 7 months prior to conception can result in fetal harm, including embryo-fetal death or birth defects. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for 7 months following the last dose of PERJETA in combination with trastuzumab [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1 , 8.3) ] .
Infusion-Related Reactions
PERJETA can cause serious infusion reactions, including fatal events [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ].
In CLEOPATRA, on the first day, when only PERJETA was administered, infusion-related reactions occurred in 13% of patients and < 1% were Grade 3 or 4. The most common infusion reactions (≥ 1%) were pyrexia, chills, fatigue, headache, asthenia, hypersensitivity, and vomiting. During the second cycle when all drugs were administered on the same day, the most common infusion reactions in the PERJETA-treated group (≥ 1%) were fatigue, dysgeusia, hypersensitivity, myalgia, and vomiting.
In APHINITY, when PERJETA was administered in combination with trastuzumab and chemotherapy on the same day, infusion-related reactions occurred in 21% of patients with <1% of patients experiencing Grade 3-4 events.
Observe patients closely for 60 minutes after the first infusion and for 30 minutes after subsequent infusions of PERJETA. If a significant infusion-related reaction occurs, slow or interrupt the infusion, and administer appropriate medical therapies. Monitor patients carefully until complete resolution of signs and symptoms. Consider permanent discontinuation in patients with severe infusion reactions [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) ].
Hypersensitivity Reactions/Anaphylaxis
PERJETA can cause hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis.
In CLEOPATRA, the overall frequency of hypersensitivity/anaphylaxis reactions was 11% in PERJETA-treated patients, with Grade 3 – 4 hypersensitivity reactions and anaphylaxis occurring in 2% of patients.
In NeoSphere, TRYPHAENA, BERENICE, and APHINITY, hypersensitivity/anaphylaxis events were consistent with those observed in CLEOPATRA. In APHINITY, the overall frequency of hypersensitivity/anaphylaxis was 5% in the PERJETA treated group. The incidence was highest in the PERJETA plus TCH treated group (8%) with 1% Grade 3 – 4 events.
Observe patients closely for hypersensitivity reactions. Severe hypersensitivity, including anaphylaxis and fatal events, have been observed in patients treated with PERJETA [see Clinical Trials Experience (6.1) ] . Angioedema has been described in post-marketing reports. Medications to treat such reactions, as well as emergency equipment, should be available for immediate use prior to administration of PERJETA. PERJETA is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to pertuzumab or to any of its excipients [see Contraindications (4) ].
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the label:
- Left Ventricular Dysfunction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
- Infusion-Related Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
- Hypersensitivity Reactions/Anaphylaxis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
Metastatic Breast Cancer (MBC)
CLEOPATRA
The safety of PERJETA in combination with trastuzumab and docetaxel was evaluated in a randomized trial (CLEOPATRA) in patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ] . Patients received either PERJETA administered at an initial dose of 840 mg followed by 420 mg every 3 weeks thereafter or placebo in combination with trastuzumab (initial dose of 8 mg/kg, followed by 6 mg/kg every 3 weeks thereafter) and docetaxel (75 mg/m2 by intravenous infusion every 3 weeks for 6 cycles). The median duration of study treatment was 18.1 months for patients in the PERJETA-treated group.
Permanent discontinuation of PERJETA, trastuzumab, and docetaxel due to adverse reactions occurred in 6% of patients. Adverse reactions that led to permanent discontinuation of PERJETA, trastuzumab, and docetaxel in >1% of patients were left ventricular dysfunction.
The safety profile of PERJETA remained unchanged with an additional 2.75 years of follow-up (median total follow-up of 50 months) in CLEOPATRA.
The most common adverse reactions (> 30%) with PERJETA in combination with trastuzumab and docetaxel were diarrhea, alopecia, neutropenia, nausea, fatigue, rash, and peripheral neuropathy. The most common Grade 3 – 4 adverse reactions (> 2%) were neutropenia, febrile neutropenia, leukopenia, diarrhea, peripheral neuropathy, anemia, asthenia, and fatigue. An increased incidence of febrile neutropenia was observed for Asian patients in both treatment arms compared with patients of other races and from other geographic regions. Among Asian patients, the incidence of febrile neutropenia was higher in the pertuzumab-treated group (26%) compared with the placebo-treated group (12%).
Table 3 summarizes the adverse reactions in CLEOPATRA that occurred ≥ 10% of patients in the PERJETA-treated group.
| Adverse Reactions | PERJETA + trastuzumab + docetaxel n=407 % | Placebo + trastuzumab + docetaxel n=397 % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades % | Grades 3 – 4 % | All Grades % | Grades 3 – 4 % | |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||||
| Diarrhea | 67 | 8 | 46 | 5 |
| Nausea | 42 | 1 | 42 | 0.5 |
| Vomiting | 24 | 1 | 24 | 2 |
| Stomatitis | 19 | 0.5 | 15 | 0.3 |
| Constipation | 15 | 0 | 25 | 1 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||||
| Alopecia | 61 | 0 | 60 | 0.3 |
| Rash | 34 | 0.7 | 24 | 0.8 |
| Nail disorder | 23 | 1 | 23 | 0.3 |
| Pruritus | 14 | 0 | 10 | 0 |
| Dry skin | 11 | 0 | 4 | 0 |
| Blood and lymphatic system disorders | ||||
| Neutropenia | 53 | 49 | 50 | 46 |
| Anemia | 23 | 2 | 19 | 4 |
| Leukopenia | 18 | 12 | 20 | 15 |
| Febrile neutropenia In this table this denotes an adverse reaction that has been reported in association with a fatal outcome | 14 | 13 | 8 | 7 |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | ||||
| Fatigue | 37 | 2 | 37 | 3 |
| Mucosal inflammation | 28 | 1 | 20 | 1 |
| Asthenia | 26 | 2 | 30 | 2 |
| Peripheral edema | 23 | 0.5 | 30 | 0.8 |
| Pyrexia | 19 | 1 | 18 | 0.5 |
| Nervous system disorders | ||||
| Neuropathy peripheral | 32 | 3 | 34 | 2 |
| Headache | 21 | 1 | 17 | 0.5 |
| Dysgeusia | 18 | 0 | 16 | 0 |
| Dizziness | 13 | 0.5 | 12 | 0 |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders | ||||
| Decreased appetite | 29 | 2 | 26 | 2 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||||
| Myalgia | 23 | 1 | 24 | 0.8 |
| Arthralgia | 15 | 0.2 | 16 | 0.8 |
| Infections and infestations | ||||
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 17 | 0.7 | 13 | 0 |
| Nasopharyngitis | 12 | 0 | 13 | 0.3 |
| Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders | ||||
| Dyspnea | 14 | 1 | 16 | 2 |
| Eye disorders | ||||
| Lacrimation increased | 14 | 0 | 14 | 0 |
| Psychiatric disorders | ||||
| Insomnia | 13 | 0 | 13 | 0 |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions in < 10% of patients in the PERJETA-treated group in CLEOPATRA included paronychia (7%).
Adverse Reactions Reported in Patients Receiving PERJETA and Trastuzumab After Discontinuation of Docetaxel
In CLEOPATRA, adverse reactions that occurred after discontinuation of docetaxel included diarrhea (19%), upper respiratory tract infection (13%), rash (12%), headache (11%), and fatigue (11%).
Neoadjuvant Treatment of Breast Cancer
NeoSphere
The safety of PERJETA was evaluated in a randomized trial (NeoSphere) in patients with operable, locally advanced, or inflammatory HER2-positive breast cancer (T2-4d) who were scheduled for neoadjuvant therapy [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ] .
In combination with trastuzumab and docetaxel, PERJETA was given intravenously at an initial dose of 840 mg, followed by 420 mg every 3 weeks for 4 cycles. After surgery, patients in the PERJETA plus trastuzumab arm received docetaxel every 3 weeks for 4 cycles prior to FEC.
Permanent discontinuation of neoadjuvant PERJETA due to an adverse reaction occurred in 0.9% of patients.
The most common adverse reactions (> 30%) were alopecia, neutropenia, diarrhea, and nausea. The most common Grade 3 – 4 adverse reactions (> 2%) were neutropenia, febrile neutropenia, leukopenia, and diarrhea.
Table 4 summarizes the adverse reactions in NeoSphere that occurred ≥ 10% of patients who received neoadjuvant PERJETA with trastuzumab and docetaxel followed by FEC.
| Adverse Reactions | Trastuzumab + docetaxel n=107 % | PERJETA + trastuzumab + docetaxel n=107 % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades % | Grades 3 – 4 % | All Grades % | Grades 3 – 4 % | |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||||
| Alopecia | 66 | 0 | 65 | 0 |
| Rash | 21 | 2 | 26 | 0.9 |
| Blood and lymphatic system disorders | ||||
| Neutropenia | 64 | 59 | 50 | 45 |
| Leukopenia | 21 | 11 | 9 | 5 |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||||
| Nausea | 36 | 0 | 39 | 0 |
| Diarrhea | 34 | 4 | 46 | 6 |
| Vomiting | 12 | 0 | 13 | 0 |
| Stomatitis | 7 | 0 | 18 | 0 |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | ||||
| Fatigue | 27 | 0 | 26 | 0.9 |
| Mucosal inflammation | 21 | 0 | 26 | 2 |
| Asthenia | 18 | 0 | 21 | 2 |
| Pyrexia | 10 | 0 | 17 | 0 |
| Peripheral edema | 10 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||||
| Myalgia | 22 | 0 | 22 | 0 |
| Arthralgia | 8 | 0 | 10 | 0 |
| Nervous system disorders | ||||
| Peripheral Sensory Neuropathy | 12 | 0.9 | 8 | 0.9 |
| Headache | 11 | 0 | 11 | 0 |
| Dysgeusia | 10 | 0 | 15 | 0 |
| Psychiatric disorders | ||||
| Insomnia | 11 | 0 | 8 | 0 |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders | ||||
| Decreased appetite | 7 | 0 | 14 | 0 |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions in < 10% of patients receiving neoadjuvant PERJETA with trastuzumab and docetaxel followed by FEC included anemia, febrile neutropenia, dizziness, upper respiratory tract infection, and increased lacrimation.
Neoadjuvant Treatment of Breast Cancer
TRYPHAENA
The safety of PERJETA was evaluated in patients with HER2-positive locally advanced, operable, or inflammatory (T2-4d) breast cancer in TRYPHAENA [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ].
Adverse reactions resulting in permanent discontinuation of any component of neoadjuvant treatment occurred in 7% of patients receiving PERJETA in combination with trastuzumab and docetaxel following FEC and 8% for patients receiving PERJETA in combination with TCH.
The most common adverse reactions (>2%) resulting in permanent discontinuation of PERJETA were left ventricular dysfunction, drug hypersensitivity, and neutropenia.
For PERJETA administered in combination with trastuzumab and docetaxel for 3 cycles following 3 cycles of FEC, the most common adverse reactions (> 30%) were diarrhea, nausea, alopecia, neutropenia, vomiting, and fatigue. The most common Grade 3 – 4 adverse reactions (> 2%) were neutropenia, leukopenia, febrile neutropenia, diarrhea, left ventricular dysfunction, anemia, dyspnea, nausea, and vomiting.
For PERJETA administered in combination with docetaxel, carboplatin, and trastuzumab (TCH) for 6 cycles, the most common adverse reactions (> 30%) were diarrhea, alopecia, neutropenia, nausea, fatigue, vomiting, anemia, and thrombocytopenia. The most common Grade 3 – 4 adverse reactions (> 2%) were neutropenia, febrile neutropenia, anemia, leukopenia, diarrhea, thrombocytopenia, vomiting, fatigue, ALT increased, hypokalemia, and hypersensitivity.
Table 5 summarizes the adverse reactions in TRYPHAENA that occurred in > 10% of patients who received neoadjuvant PERJETA with trastuzumab and docetaxel following FEC or who received neoadjuvant PERJETA in combination with TCH.
| Adverse Reactions | PERJETA + trastuzumab + docetaxel following FEC | PERJETA + TCH | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n=75 % | n=76 % | |||
| All Grades % | Grades 3 – 4 % | All Grades % | Grades 3 – 4 % | |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||||
| Diarrhea | 61 | 5 | 72 | 12 |
| Nausea | 53 | 3 | 45 | 0 |
| Vomiting | 36 | 3 | 39 | 5 |
| Dyspepsia | 8 | 0 | 22 | 0 |
| Constipation | 23 | 0 | 16 | 0 |
| Stomatitis | 17 | 0 | 12 | 0 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||||
| Alopecia | 52 | 0 | 55 | 0 |
| Rash | 11 | 0 | 21 | 1 |
| Palmar-Plantar Erythrodysaesthesia Syndrome | 11 | 0 | 8 | 0 |
| Dry skin | 9 | 0 | 11 | 0 |
| Blood and lymphatic system disorders | ||||
| Neutropenia | 47 | 43 | 49 | 46 |
| Leukopenia | 16 | 12 | 17 | 12 |
| Anemia | 9 | 4 | 38 | 17 |
| Febrile neutropenia | 9 | 9 | 17 | 17 |
| Thrombocytopenia | 1 | 0 | 30 | 12 |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | ||||
| Fatigue | 36 | 0 | 42 | 4 |
| Mucosal inflammation | 20 | 0 | 17 | 1 |
| Pyrexia | 9 | 0 | 16 | 0 |
| Asthenia | 15 | 1 | 13 | 1 |
| Edema peripheral | 4 | 0 | 9 | 0 |
| Psychiatric disorders | ||||
| Insomnia | 13 | 0 | 21 | 0 |
| Nervous system disorders | ||||
| Headache | 15 | 0 | 17 | 0 |
| Dysgeusia | 13 | 0 | 21 | 0 |
| Dizziness | 8 | 1 | 16 | 0 |
| Neuropathy peripheral | 1 | 0 | 11 | 0 |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders | ||||
| Decreased appetite | 11 | 0 | 21 | 0 |
| Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders | ||||
| Epistaxis | 11 | 0 | 16 | 1 |
| Dyspnea | 8 | 3 | 11 | 1 |
| Oropharyngeal pain | 7 | 0 | 12 | 0 |
| Cough | 5 | 0 | 12 | 0 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||||
| Myalgia | 11 | 1 | 11 | 0 |
| Arthralgia | 12 | 0 | 7 | 0 |
| Eye disorders | ||||
| Lacrimation increased | 5 | 0 | 8 | 0 |
| Investigations | ||||
| ALT increased | 3 | 0 | 11 | 4 |
| Immune system disorders | ||||
| Hypersensitivity | 1 | 0 | 12 | 3 |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions in < 10% of patients who received neoadjuvant PERJETA with trastuzumab and docetaxel following FEC or who received neoadjuvant PERJETA in combination with TCH included nail disorder, paronychia, pruritus, upper respiratory tract infection, and nasopharyngitis.
Neoadjuvant Treatment of Breast Cancer
BERENICE
The safety of PERJETA was evaluated in a two-arm non-randomized study (BERENICE) in patient with HER2-positive locally advanced, inflammatory, or early-stage HER2-positive breast cancer [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ].
Adverse reactions resulting in permanent discontinuation of any component of neoadjuvant treatment were 14% for patients receiving PERJETA in combination with trastuzumab and paclitaxel following ddAC and 8% for patients receiving PERJETA in combination with trastuzumab and docetaxel following FEC. The most common adverse reactions (>1%) resulting in permanent discontinuation of any component of neoadjuvant treatment were peripheral neuropathy, decreased ejection fraction, diarrhea, neutropenia and infusion-related reaction.
For PERJETA administered in combination with trastuzumab and paclitaxel for 4 cycles following 4 cycles of ddAC, the most common adverse reactions (> 30%) were nausea, diarrhea, alopecia, fatigue, constipation, peripheral neuropathy and headache. The most common Grade 3 – 4 adverse reactions (> 2%) were neutropenia, febrile neutropenia, decreased neutrophil count, decreased white blood cell count, anemia, diarrhea, peripheral neuropathy, increased ALT, and nausea.
For PERJETA administered in combination with trastuzumab and docetaxel for 4 cycles following 4 cycles of FEC, the most common adverse reactions (> 30%) were diarrhea, nausea, alopecia, asthenia, constipation, fatigue, mucosal inflammation, vomiting, myalgia, and anemia. The most common Grade 3 – 4 adverse reactions (> 2%) were febrile neutropenia, diarrhea, neutropenia, decreased neutrophil count stomatitis, fatigue, vomiting, mucosal inflammation, neutropenic sepsis and anemia.
Table 6 summarizes the adverse reactions in BERENICE that occurred in ≥ 10% of patients who received neoadjuvant PERJETA with trastuzumab and paclitaxel following ddAC or who received neoadjuvant PERJETA with trastuzumab and docetaxel following FEC.
| Adverse Reactions | PERJETA + trastuzumab + paclitaxel following ddAC n=199 % | PERJETA + trastuzumab + docetaxel following FEC n=198 % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades % | Grades 3 – 4 % | All Grades % | Grades 3 – 4 % | |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||||
| Nausea | 71 | 3 | 69 | 2 |
| Diarrhea | 67 | 3 | 69 | 10 |
| Constipation | 35 | 0.5 | 38 | 0.5 |
| Vomiting | 23 | 1 | 35 | 4 |
| Stomatitis | 25 | 0 | 27 | 5 |
| Dyspepsia | 19 | 0 | 16 | 0 |
| Upper abdominal pain | 6 | 0 | 13 | 0 |
| Abdominal pain | 5 | 0 | 10 | 0 |
| Gastroesophageal reflux disease | 12 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||||
| Alopecia | 62 | 0 | 59 | 0 |
| Rash | 14 | 0 | 11 | 0 |
| Dry skin | 14 | 0 | 10 | 0 |
| Nail discoloration | 15 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| Palmar-Plantar Erythrodysaesthesia Syndrome | 6 | 0 | 10 | 0.5 |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | ||||
| Fatigue | 58 | 1 | 38 | 5 |
| Asthenia | 19 | 2 | 41 | 0 |
| Mucosal inflammation | 22 | 1 | 37 | 4 |
| Pyrexia | 15 | 0 | 18 | 0 |
| Peripheral edema | 9 | 0 | 12 | 1 |
| Nervous system disorders | ||||
| Peripheral neuropathy | 42 | 3 | 26 | 0.5 |
| Headache | 30 | 0.5 | 14 | 0.5 |
| Dysgeusia | 20 | 0 | 19 | 0.5 |
| Paresthesia | 15 | 0 | 9 | 0 |
| Dizziness | 12 | 0 | 8 | 0 |
| Blood and lymphatic system disorders | ||||
| Anemia | 27 | 3 | 30 | 3 |
| Neutropenia | 22 | 12 | 16 | 9 |
| Febrile neutropenia | 7 | 7 | 17 | 17 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||||
| Myalgia | 20 | 0 | 33 | 1 |
| Arthralgia | 20 | 0 | 21 | 1 |
| Back pain | 10 | 0 | 9 | 0 |
| Pain in extremity | 10 | 0 | 8 | 0 |
| Bone pain | 12 | 0.5 | 5 | 0 |
| Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders | ||||
| Epistaxis | 25 | 0 | 19 | 0 |
| Dyspnea | 15 | 0.5 | 15 | 0.5 |
| Cough | 20 | 0.5 | 9 | 0 |
| Oropharyngeal pain | 10 | 0 | 8 | 0.5 |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders | ||||
| Decreased appetite | 20 | 0 | 23 | 0 |
| Psychiatric disorders | ||||
| Insomnia | 19 | 0 | 13 | 0 |
| Vascular disorders | ||||
| Hot flush | 19 | 0 | 13 | 0 |
| Injury, poisoning and procedural complications | ||||
| Infusion-related reaction | 16 | 1 | 13 | 1 |
| Eye disorders | ||||
| Increased lacrimation | 9 | 0 | 18 | 0 |
| Investigations | ||||
| Decreased white blood cell count | 11 | 4 | 3 | 2 |
| Infections and infestations | ||||
| Urinary tract infection | 11 | 1 | 2 | 0 |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions in < 10% of patients who received PERJETA in combination with trastuzumab and paclitaxel following ddAC or patients receiving PERJETA in combination with trastuzumab and docetaxel following FEC included pruritus, nail disorder, paronychia, upper respiratory tract infection, and nasopharyngitis.
Adjuvant Treatment of Breast Cancer
APHINITY
The safety of PERJETA was evaluated in a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study (APHINITY) conducted in patients with HER2-positive early breast cancer who had their primary tumor excised prior to randomization [see Clinical Studies (14.3) ].
Patients were randomized to receive either PERJETA in combination with trastuzumab and chemotherapy or placebo in combination with trastuzumab and chemotherapy. Investigators selected one of three anthracycline-based or non-anthracycline-based chemotherapy regimens for patients. PERJETA and trastuzumab were administered intravenously every 3 weeks starting on Day 1 of the first taxane-containing cycle, for a total of 52 weeks (up to 18 cycles) or until recurrence, withdrawal of consent, or unmanageable toxicity.
Serious adverse reactions (hospitalization) due to diarrhea in the PERJETA-treated group was 2.4%. The incidence of diarrhea was higher when chemotherapy was administered with PERJETA (61%) and was higher when administered with non-anthracycline based therapy (85%) than with anthracycline based therapy (67%). The median duration of diarrhea was 8 days. The median duration of Grade ≥3 diarrhea was 20 days. The incidence of diarrhea during the period PERJETA and trastuzumab were administered without chemotherapy was 18% in the PERJETA-treated group.
Adverse reactions resulting in permanent discontinuation of any study therapy were 13% for patients in the PERJETA-treated group. Adverse reactions resulting in permanent discontinuation of PERJETA was 7%. The most common adverse reactions (>0.5%) resulting in permanent discontinuation of any study treatment were ejection fraction decreased, neuropathy peripheral, diarrhea, and cardiac failure.
When PERJETA was administered in combination with trastuzumab and chemotherapy, the most common adverse reactions (> 30%) were diarrhea, nausea, alopecia, fatigue, peripheral neuropathy, and vomiting. The most common Grade 3 – 4 adverse reactions (> 2%) were neutropenia, febrile neutropenia, diarrhea, neutrophil count decreased, anemia, white blood cell count decreased, leukopenia, fatigue, nausea, and stomatitis.
Table 7 summarizes the adverse reactions that occurred in ≥ 10% of patients who received adjuvant PERJETA in combination with trastuzumab and chemotherapy followed by PERJETA and trastuzumab for a total of 52 weeks (up to 18 cycles) or until recurrence, withdrawal of consent, or unmanageable toxicity.
| Adverse Reactions | PERJETA + trastuzumab + chemotherapy n=2364 % | Placebo + trastuzumab + chemotherapy n=2405 % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades % | Grades 3 – 4 % | All Grades % | Grades 3 – 4 % | |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||||
| Diarrhea | 71 | 10 | 45 | 4 |
| Nausea | 69 | 2 | 65 | 2 |
| Vomiting | 32 | 2 | 30 | 2 |
| Constipation | 29 | 0.5 | 32 | 0.3 |
| Stomatitis | 28 | 2 | 24 | 1 |
| Dyspepsia | 14 | 0 | 14 | 0 |
| Abdominal pain | 12 | 0.5 | 11 | 0.6 |
| Abdominal pain upper | 10 | 0.3 | 9 | 0.2 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||||
| Alopecia | 67 | <0.1 | 67 | <0.1 |
| Rash | 26 | 0.4 | 20 | 0.2 |
| Pruritus | 14 | 0.1 | 9 | <0.1 |
| Dry skin | 13 | 0.1 | 11 | <0.1 |
| Nail disorder | 12 | 0.2 | 12 | 0.1 |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | ||||
| Fatigue | 49 | 4 | 44 | 3 |
| Mucosal inflammation | 23 | 2 | 19 | 0.7 |
| Asthenia | 21 | 1 | 21 | 2 |
| Pyrexia | 20 | 0.6 | 20 | 0.7 |
| Edema peripheral | 17 | 0 | 20 | 0.2 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||||
| Arthralgia | 29 | 0.9 | 33 | 1 |
| Myalgia | 26 | 0.9 | 30 | 1 |
| Pain in extremity | 10 | 0.2 | 10 | 0.2 |
| Blood and lymphatic system disorders | ||||
| Anemia | 28 | 7 | 23 | 5 |
| Neutropenia | 25 | 16 | 23 | 16 |
| Febrile neutropenia In this table this denotes an adverse reaction that has been reported in association with a fatal outcome | 12 | 12 | 11 | 11 |
| Nervous system disorders | ||||
| Dysgeusia | 26 | 0.1 | 22 | <0.1 |
| Neuropathy peripheral | 33 | 1 | 32 | 1 |
| Headache | 22 | 0.3 | 23 | 0.4 |
| Paresthesia | 12 | 0.5 | 10 | 0.2 |
| Dizziness | 11 | 0 | 11 | 0.2 |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders | ||||
| Decreased appetite | 24 | 0.8 | 20 | 0.4 |
| Vascular disorders | ||||
| Hot flush | 20 | 0.2 | 21 | 0.4 |
| Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders | ||||
| Epistaxis | 18 | <0.1 | 14 | 0 |
| Cough | 16 | <0.1 | 15 | <0.1 |
| Dyspnea | 12 | 0.4 | 12 | 0.5 |
| Psychiatric disorders | ||||
| Insomnia | 17 | 0.3 | 17 | <0.1 |
| Investigations | ||||
| Neutrophil count decreased | 14 | 10 | 14 | 10 |
| Eye disorders | ||||
| Lacrimation increased | 13 | 0 | 13 | <0.1 |
| Infections and infestations | ||||
| Nasopharyngitis | 13 | <0.1 | 12 | 0.1 |
| Injury, poisoning and procedural complications | ||||
| Radiation skin injury | 13 | 0.3 | 11 | 0.3 |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions in < 10% of patients who received PERJETA in combination with trastuzumab and anthracycline-based or non-anthracycline-based chemotherapy regimens included l eukopenia, upper respiratory tract infection, and paronychia
Adverse Reactions in Patients Receiving PERJETA and Trastuzumab After Discontinuation of Chemotherapy
In APHINITY, adverse reactions that occurred after discontinuation of chemotherapy in >10% included diarrhea (18%), arthralgia (15%), radiation skin injury (12%), and hot flush (12%).
DESCRIPTION
Pertuzumab is a recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody and HER2/neu receptor antagonist that targets the extracellular dimerization domain (Subdomain II) of the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 protein (HER2). Pertuzumab is produced by recombinant DNA technology in a mammalian cell (Chinese Hamster Ovary) culture. Pertuzumab has an approximate molecular weight of 148 kDa.
PERJETA (pertuzumab) injection is a sterile, preservative-free, clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to pale brown solution for intravenous infusion. Each single-dose vial contains 420 mg of pertuzumab,glacial acetic acid (9.2 mg), histidine (43.5 mg), polysorbate 20 (2.8 mg), and sucrose (575.1 mg) with a pH of 6.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Pertuzumab targets the extracellular dimerization domain (Subdomain II) of the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 protein (HER2) and, thereby, blocks ligand-dependent heterodimerization of HER2 with other HER family members, including EGFR, HER3, and HER4. As a result, pertuzumab inhibits ligand-initiated intracellular signaling through two major signal pathways, mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K). Inhibition of these signaling pathways can result in cell growth arrest and apoptosis, respectively. In addition, pertuzumab mediates antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC).
While pertuzumab alone inhibited the proliferation of human tumor cells, the combination of pertuzumab and trastuzumab augmented anti-tumor activity in HER2-overexpressing xenograft models.
Pharmacodynamics
The exposure-response relationship and time course of pharmacodynamic response for the safety and effectiveness of PERJETA have not been fully characterized.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
The effect of pertuzumab with an initial dose of 840 mg followed by a maintenance dose of 420 mg every three weeks on QTc interval was evaluated in a subgroup of 20 patients with HER2-positive breast cancer in CLEOPATRA. At the recommended dose of PERJETA, a mean increase in the QTc interval >20 ms was not observed. A small increase in the mean QTc interval (i.e., less than 10 ms) cannot be excluded because of the limitations of the trial design.
Pharmacokinetics
Based on a population PK analysis that included 481 patients, pertuzumab demonstrated linear pharmacokinetics at a dose range of 2 – 25 mg/kg.
With an initial dose of 840 mg followed by a maintenance dose of 420 mg every three weeks thereafter, the steady-state concentration of pertuzumab was reached after the first maintenance dose.
Elimination
The median clearance (CL) of pertuzumab was 0.24 L/day and the median half-life was 18 days.
Specific Populations
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of pertuzumab were observed based on age, sex, ethnicity (Japanese vs. non-Japanese), or disease status (neoadjuvant or adjuvant vs. metastatic setting). No dose adjustments based on body weight or baseline albumin level are needed, as the exposure changes are not considered clinically relevant.
Pertuzumab exposure in patients with mild (CLcr 60 to 90 mL/min, n=200) and moderate renal impairment (CLcr 30 to 60 mL/min, n=71) were similar to those in patients with normal renal function (CLcr greater than 90 mL/min, n=200). The pharmacokinetics of pertuzumab in patients with moderate to severe hepatic impairment or severe renal impairment is unknown.
Immunogenicity
The observed incidence of anti-drug antibodies (ADA) is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Differences in assay methods preclude meaningful comparisons of the incidence of ADA in the studies described below with the incidence of ADA in other studies, including those of PERJETA or of other pertuzumab products.
Patients in CLEOPATRA were tested at multiple time-points for anti-pertuzumab antibodies. 3% (13/389) of patients in the PERJETA-treated group and 7% (25/372) of patients in the placebo-treated group tested positive for anti-pertuzumab antibodies. Of these 38 patients, none experienced anaphylactic/hypersensitivity reactions that were clearly related to anti-pertuzumab antibodies. The presence of pertuzumab in patient serum at the levels expected at the time of ADA sampling can interfere with the ability of this assay to detect anti-pertuzumab antibodies. In addition, the assay may be detecting antibodies to trastuzumab. As a result, data may not accurately reflect the true incidence of anti-pertuzumab antibody development.
In the neoadjuvant period of BERENICE, 0.3% (1/383) of patients treated with PERJETA tested positive for anti-pertuzumab antibodies. This patient did not experience any anaphylactic/hypersensitivity reactions.
Because of limited immunogenicity data, the clinical impact of anti-pertuzumab antibodies is unknown. There was no identified clinically significant effect of anti-pertuzumab antibodies on the safety of PERJETA.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term studies in animals have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of pertuzumab.
Studies have not been performed to evaluate the mutagenic potential of pertuzumab.
No specific fertility studies in animals have been performed to evaluate the effect of pertuzumab. No adverse effects on male and female reproductive organs were observed in repeat-dose toxicity studies of up to six months duration in cynomolgus monkeys.
CLINICAL STUDIES
Metastatic Breast Cancer
CLEOPATRA (NCT00567190) was a multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of 808 patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer. HER2 overexpression was defined as a score of 3+ IHC or FISH amplification ratio of 2.0 or greater as determined by a central laboratory. Patients were randomly allocated 1:1 to receive placebo plus trastuzumab and docetaxel or PERJETA plus trastuzumab and docetaxel. Randomization was stratified by prior treatment (prior or no prior adjuvant/neoadjuvant anti-HER2 therapy or chemotherapy) and geographic region (Europe, North America, South America, and Asia). Patients with prior adjuvant or neoadjuvant therapy were required to have a disease-free interval of greater than 12 months before trial enrollment.
PERJETA was given intravenously at an initial dose of 840 mg, followed by 420 mg every 3 weeks thereafter. Trastuzumab was given intravenously at an initial dose of 8 mg/kg, followed by 6 mg/kg every 3 weeks thereafter. Patients were treated with PERJETA and trastuzumab until progression of disease, withdrawal of consent, or unacceptable toxicity. Docetaxel was given as an initial dose of 75 mg/m 2 by intravenous infusion every 3 weeks for at least 6 cycles. The docetaxel dose could be escalated to 100 mg/m 2 at the investigator's discretion if the initial dose was well tolerated. At the time of the primary analysis, the mean number of cycles of study treatment administered was 16.2 in the placebo-treated group and 19.9 in the PERJETA-treated group.
The major efficacy outcome measure of CLEOPATRA was progression-free survival (PFS) as assessed by an independent review facility (IRF). PFS was defined as the time from the date of randomization to the date of disease progression or death (from any cause) if the death occurred within 18 weeks of the last tumor assessment. Additional endpoints included overall survival (OS), PFS (investigator-assessed), objective response rate (ORR), and duration of response.
Patient demographic and baseline characteristics were balanced between the treatment arms. The median age was 54 (range 22 to 89 years), 59% were White, 32% were Asian, and 4% were Black. All were female with the exception of 2 patients (0.2%). Seventeen percent (17%) of patients were enrolled in North America, 14% in South America, 38% in Europe, and 31% in Asia. Tumor prognostic characteristics, including hormone receptor status (positive 48%, negative 50%), presence of visceral disease (78%) and non-visceral disease only (22%) were similar in the study arms. Approximately half of the patients received prior adjuvant or neoadjuvant anti-HER2 therapy or chemotherapy (PERJETA 46%, placebo 47%). Among patients with hormone receptor positive tumors, 45% received prior adjuvant hormonal therapy and 11% received hormonal therapy for metastatic disease. Eleven percent of patients received prior adjuvant or neoadjuvant trastuzumab.
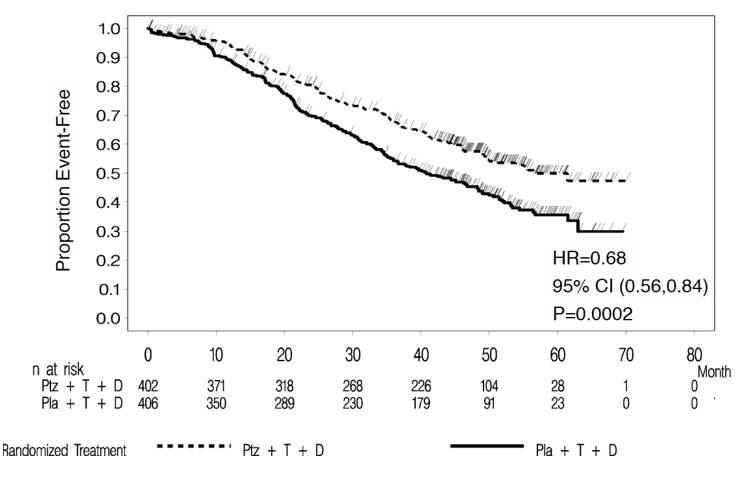
CLEOPATRA demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in IRF-assessed PFS in the PERJETA-treated group compared with the placebo-treated group. The results for investigator-assessed PFS were comparable to those observed for IRF-assessed PFS. A statistically significant OS improvement was demonstrated for the PERJETA-treated group compared with the placebo-treated group) with the final OS analysis. OS results in patient subgroups were consistent with those observed for IRF-assessed PFS with the exception of the subgroup of patients with disease limited to non-visceral metastasis [HR=1.11 (95% CI: 0.66, 1.85)].
| Endpoint | PERJETA + trastuzumab + docetaxel n=402 | Placebo + trastuzumab + docetaxel n=406 |
|---|---|---|
| CI=Confidence Interval | ||
| Progression-Free Survival (independent review) | ||
| Number of events (%) | 191 (47.5%) | 242 (59.6%) |
| Median (months) | 18.5 | 12.4 |
| Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.62 (0.51, 0.75) | |
| p-value | < 0.0001 | |
| Overall Survival Final analysis of overall survival performed when 389 patients had died. (final) | ||
| Deaths (%) | 168 (41.8%) | 221 (54.4%) |
| Median (months) | 56.5 | 40.8 |
| Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.68 (0.56, 0.84) | |
| p-value | 0.0002 | |
| Objective Response Rate (independent review) | n = 343 | n = 336 |
| Objective response (CR + PR) | 275 (80.2%) | 233 (69.3%) |
| Complete response (CR) (%) | 19 (5.5%) | 14 (4.2%) |
| Partial Response (PR) (%) | 256 (74.6%) | 219 (65.2%) |
| Difference in ORR (95% CI) | 10.8% (4.2%, 17.5%) | |
| p-value | 0.0011 | |
| Duration of Response Median (months) | 20.2 | 12.5 |
Consistent results were observed across several patient subgroups including age (< 65 or ≥ 65 years), race, geographic region, prior adjuvant/neoadjuvant anti-HER2 therapy or chemotherapy (yes or no), and prior adjuvant/neoadjuvant trastuzumab (yes or no). In the subgroup of patients with hormone receptor-negative disease (n=408), the hazard ratio was 0.55 (95% CI: 0.42, 0.72). In the subgroup of patients with hormone receptor-positive disease (n=388), the hazard ratio was 0.72 (95% CI: 0.55, 0.95). In the subgroup of patients with disease limited to non-visceral metastasis (n=178), the hazard ratio was 0.96 (95% CI: 0.61, 1.52).
Figure 1 Kaplan-Meier Curve of Progression-Free Survival for CLEOPATRA (IRF-Assessed)
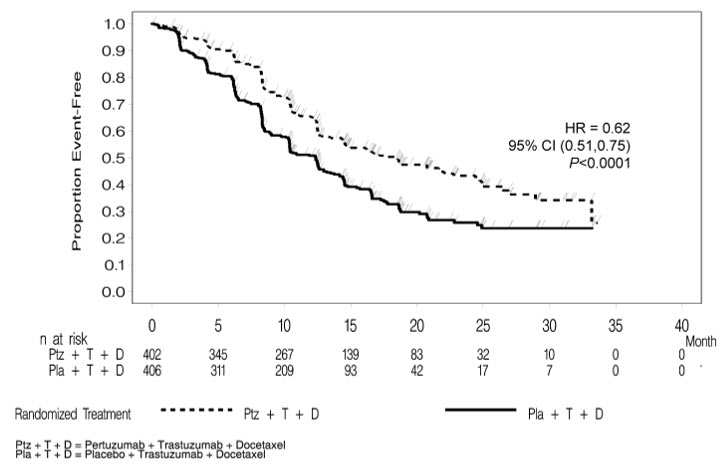
Figure 2 Kaplan-Meier Curve of Overall Survival for CLEOPATRA (Final Analysis)
Neoadjuvant Treatment of Breast Cancer
NeoSphere
NeoSphere (NCT00545688) was a multicenter, randomized trial conducted in 417 patients with operable, locally advanced, or inflammatory HER2-positive breast cancer (T2-4d) who were scheduled for neoadjuvant therapy. HER2 overexpression was defined as a score of 3+ IHC or FISH amplification ratio of 2.0 or greater as determined by a central laboratory. Patients were randomly allocated to receive 1 of 4 neoadjuvant regimens prior to surgery as follows: trastuzumab plus docetaxel, PERJETA plus trastuzumab and docetaxel, PERJETA plus trastuzumab, or PERJETA plus docetaxel. Randomization was stratified by breast cancer type (operable, locally advanced, or inflammatory) and estrogen receptor (ER) or progesterone receptor (PgR) positivity.
PERJETA was given intravenously at an initial dose of 840 mg, followed by 420 mg every 3 weeks for 4 cycles. Trastuzumab was given intravenously at an initial dose of 8 mg/kg, followed by 6 mg/kg every 3 weeks for 4 cycles. Docetaxel was given as an initial dose of 75 mg/m 2 by intravenous infusion every 3 weeks for 4 cycles. The docetaxel dose could be escalated to 100 mg/m 2 at the investigator's discretion if the initial dose was well tolerated. Following surgery all patients received 3 cycles of 5-fluorouracil (600 mg/m 2 ), epirubicin (90 mg/m 2 ), and cyclophosphamide (600 mg/m 2 ) (FEC) given intravenously every 3 weeks and trastuzumab administered intravenously every 3 weeks to complete 1 year of therapy. After surgery, patients in the PERJETA plus trastuzumab arm received docetaxel every 3 weeks for 4 cycles prior to FEC.
The major efficacy outcome measure was pathological complete response (pCR) rate in the breast (ypT0/is) defined as the absence of invasive cancer in the breast and lymph nodes (ypT0/is ypN0) for the efficacy analysis.
Demographics were balanced (median age was 49 – 50 years old, the majority were White (71%) and all were female. Overall, 7% of patients had inflammatory cancer, 32% had locally advanced cancer, and 61% had operable cancer. Approximately half the patients in each treatment group had hormone receptor-positive disease (defined as ER-positive and/or PgR-positive).
Statistically significant improvements in pCR rates were observed in patients receiving PERJETA plus trastuzumab and docetaxel compared to patients receiving trastuzumab plus docetaxel. The pCR rates and magnitude of improvement with PERJETA were lower in the subgroup of patients with hormone receptor-positive tumors compared to patients with hormone receptor-negative tumors. The efficacy results are summarized in Table 9 .
| Endpoint | H+T N=107 | Ptz+H+T N=107 | Ptz+H N=107 | Ptz+T N=96 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T=docetaxel, Ptz=PERJETA, H=trastuzumab CI=Confidence Interval | ||||
| pCR ypT0/is ypN0 (absence of invasive cancer in the breast and lymph nodes) based on intention-to-treat population , n (%) [95% CI] 95% CI for one sample binomial using Pearson-Clopper method. | 23 (21.5%) [14.1, 30.5] | 42 (39.3%) [30.0, 49.2] | 12 (11.2%) [5.9, 18.8] | 17 (17.7%) [10.7, 26.8] |
| p-value (with Simes correction for CMH test) p-value from Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel (CMH) test, with Simes multiplicity adjustment | 0.0063 (vs. H+T) | 0.0223 (vs. H+T) | 0.0018 (vs. Ptz+H+T) | |
| Hormone receptor-positive subgroup | N=50 | N=50 | N=51 One patient had unknown hormone receptor status. The patient did not achieve a pCR. | N=46 |
| pCR, n (%) [95% CI] | 6 (12.0%) [4.5, 24.3] | 11 (22.0%) [11.5, 36.0] | 1 (2.0%) [0.1, 10.5] | 4 (8.7%) [2.4, 20.8] |
| Hormone receptor-negative subgroup | N=57 | N=57 | N=55 | N=50 |
| pCR, n (%) [95% CI] | 17 (29.8%) [18.4, 43.4] | 31 (54.4%) [40.7, 67.6] | 11 (20.0%) [10.4, 33.0] | 13 (26.0%) [14.6, 40.3] |
TRYPHAENA
TRYPHAENA(NCT00976989) was a three-arm, randomized (1:1:1) study in the neoadjuvant setting conducted in 225 patients with HER2-positive locally advanced, operable, or inflammatory (T2-4d) breast cancer designed primarily to assess cardiac safety. HER2 overexpression was defined as a score of 3+ IHC or FISH amplification ratio of 2.0 or greater as determined by a central laboratory.
Patients were randomly allocated to receive 1 of 3 neoadjuvant regimens prior to surgery as follows: 3 cycles of FEC followed by 3 cycles of docetaxel all in combination with PERJETA and trastuzumab, 3 cycles of FEC alone followed by 3 cycles of docetaxel and trastuzumab in combination with PERJETA, or 6 cycles of docetaxel, carboplatin, and trastuzumab (TCH) in combination with PERJETA. Randomization was stratified by breast cancer type (operable, locally advanced, or inflammatory) and ER and/or PgR positivity.
PERJETA was given by intravenous infusion at an initial dose of 840 mg, followed by 420 mg every 3 weeks. Trastuzumab was given by intravenous infusion at an initial dose of 8 mg/kg, followed by 6 mg/kg every 3 weeks. 5-Fluorouracil (500 mg/m 2 ), epirubicin (100 mg/m 2 ), and cyclophosphamide (600 mg/m 2 ) [FEC] were given intravenously every 3 weeks for 3 cycles. In the PERJETA plus trastuzumab, docetaxel, and FEC arms, docetaxel was given as an initial dose of 75 mg/m 2 by intravenous infusion every 3 weeks for 3 cycles with the option to escalate to 100 mg/m 2 at the investigator's discretion if the initial dose was well tolerated. However, in the PERJETA plus TCH arm, docetaxel was given intravenously at 75 mg/m 2 (no escalation was permitted) and carboplatin (AUC 6) was given intravenously every 3 weeks for 6 cycles. Following surgery all patients received trastuzumab to complete 1 year of therapy, which was administered intravenously every 3 weeks.
Demographics were balanced (median age was 49-50 years old, the majority were White [76%]) and all were female. Overall 6% of patients had inflammatory cancer, 25% had locally advanced cancer and 69% had operable cancer, with approximately half the patients in each treatment group having ER-positive and/or PgR-positive disease.
The pCR (ypT0/is ypN0) rates were 56.2% (95% CI: 44.1%, 67.8%), 54.7% (95% CI: 42.7%, 66.2%), and 63.6% (95% CI: 51.9%, 74.3%) for patients treated with PERJETA plus trastuzumab and FEC followed by PERJETA plus trastuzumab and docetaxel, PERJETA plus trastuzumab and docetaxel following FEC, or PERJETA plus TCH, respectively . The pCR rates were lower in the subgroups of patients with hormone receptor-positive tumors: 41.0% (95% CI: 25.6%, 57.9%), 45.7% (95% CI: 28.8%, 63.4%), and 47.5% (95% CI: 31.5%, 63.9%) than with hormone receptor-negative tumors: 73.5% (95% CI: 55.6%, 87.1%), 62.5% (95% CI: 45.8%, 77.3%), and 81.1% (95% CI: 64.8%, 92.0%), respectively.
BERENICE
A two-arm non-randomized study (BERENICE, NCT02132949) was conducted in 401 patients with HER2-positive locally advanced, inflammatory, or early-stage HER2-positive breast cancer. HER2 overexpression was defined as a score of 3+ IHC or ISH amplification ratio of 2.0 or greater as determined by a central laboratory.
Patients received 1 of 2 neoadjuvant regimens prior to surgery as follows: 4 cycles of dose dense doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide (ddAC) followed by 4 cycles of PERJETA in combination with trastuzumab and weekly paclitaxel for 12 weeks or 4 cycles of 5-fluorouracil, epirubicin and cyclophosphamide (FEC) followed by 4 cycles of PERJETA in combination with trastuzumab and docetaxel. The choice of neoadjuvant treatment regimen was made by the Investigator on a site-specific basis. Dosing for the regimens was as follows:
- PERJETA was given by intravenous infusion at an initial dose of 840 mg, followed by 420 mg every 3 weeks. Trastuzumab was given by intravenous infusion at an initial dose of 8 mg/kg, followed by 6 mg/kg every 3 weeks.
- In the ddAC cohort, (doxorubicin 60 mg/m 2 and cyclophosphamide 600 mg/m 2 ) were given intravenously every 2 weeks (ddAC) for 4 cycles with G-CSF (granulocyte colony stimulating factor) support at investigator discretion, followed by paclitaxel 80 mg/m 2 given intravenously weekly for 12 weeks, with PERJETA and trastuzumab every 3 weeks from the start of paclitaxel for 4 cycles.
- In the FEC cohort, 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) (500 mg/m 2 ), epirubicin (100 mg/m 2 ), and cyclophosphamide (600 mg/m 2 ) were given intravenously every 3 weeks for 4 cycles, followed by docetaxel given as an initial dose of 75 mg/m 2 by intravenous infusion every 3 weeks for 4 cycles with PERJETA and trastuzumab, and with the option to escalate to 100 mg/m 2 at the investigator's discretion if the initial dose was well tolerated.
Following surgery, all patients received PERJETA and trastuzumab administered intravenously every 3 weeks to complete 1 year of therapy.
The median age was 49 years old (range 21-78), 12% of patients were 65 or older, 83% were White, and all but one patient was female (99.8%). Overall 3% of patients had inflammatory cancer, 23% had locally advanced cancer (Stage 3A or greater), 5% were not classified per TNM staging, with approximately two thirds of the patients in each treatment group having ER-positive and/or PgR-positive disease. All patients had an ECOG performance status of 0 or 1.
The pCR (ypT0/is ypN0) rates were 61.8% (95% CI: 54.7, 68.6) and 60.7% (95% CI: 53.6, 67.5) for patients treated with ddAC followed by PERJETA plus trastuzumab and paclitaxel, or FEC followed by PERJETA plus trastuzumab and docetaxel, respectively . The pCR rates were lower in the subgroups of patients with hormone receptor-positive tumors: 51.6% (95% CI: 42.6, 60.5%) and 57.3% (95% CI: 48.1, 66.1%) than with hormone receptor-negative tumors: 81.5% (95% CI: 70.0, 90.1%) and 68.0% (95% CI: 56.2, 78.3%), respectively.
Adjuvant Treatment of Breast Cancer
APHINITY (NCT01358877) was a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study conducted in 4804 patients with HER2-positive early breast cancer who had their primary tumor excised prior to randomization. Patients were then randomized to receive PERJETA or placebo, in combination with adjuvant trastuzumab and chemotherapy. Randomization was stratified by the following factors: region, nodal status, protocol version, central hormone receptor status, and adjuvant chemotherapy regimen.
Investigators selected one of the following anthracycline-based or non-anthracycline-based chemotherapy regimens for individual patients:
- 3 or 4 cycles of FEC (5-FU 500-600 mg/m 2 , epirubicin 90-120 mg/m 2 , cyclophosphamide 500-600 mg/m 2 ) or FAC (5-FU 500-600 mg/m 2 , doxorubicin 50 mg/m 2 , cyclophosphamide 500-600 mg/m 2 ), followed by 3 or 4 cycles of docetaxel (75 mg/m 2 which could be escalated to 100 mg/m 2 every 3 weeks) or 12 cycles of weekly paclitaxel (80 mg/m 2 ).
- 4 cycles of AC (doxorubicin 60 mg/m 2 and cyclophosphamide 500-600 mg/m 2 ) or EC (epirubicin 90-120 mg/m 2 and cyclophosphamide 500-600 mg/m 2 ) either every 3 weeks or every 2 weeks with GCSF support, followed by docetaxel (100 mg/m 2 for 3 cycles or 75 mg/m 2 for first cycle and 100 mg/m 2 for subsequent three cycles, or 75 mg/m 2 for four cycles) or 12 cycles of weekly paclitaxel (80 mg/m 2 ).
- 6 cycles of docetaxel (75 mg/m 2 ) in combination with carboplatin (AUC 6)
PERJETA and trastuzumab were administered intravenously every 3 weeks starting on Day 1 of the first taxane-containing cycle, for a total of 52 weeks (up to 18 cycles) or until recurrence, withdrawal of consent, or unmanageable toxicity.
After completion of chemotherapy, patients received radiotherapy and/or hormone therapy as per investigator's discretion.
The major efficacy outcome of the study was invasive disease-free survival (IDFS), defined as the time from randomization to first occurrence of ipsilateral local or regional invasive breast cancer recurrence, distant recurrence, contralateral invasive breast cancer, or death from any cause. Additional efficacy endpoints were IDFS including second primary non-breast cancer, disease-free survival (DFS), and overall survival (OS).
Demographics were balanced between the two treatment arms. The median age was 51 years (range 18-86), 13% of patients were 65 or older, and over 99% of patients were female. Sixty-three percent of patients had node-positive disease, 64% had hormone receptor-positive disease, and 71% were White. All patients had an ECOG performance status of 0 or 1. Seventy-eight percent received an anthracycline containing regimen.
PERJETA-treated patients and placebo-treated patients both received a median number of 18 cycles of anti-HER2 therapy. After a median follow-up of 45.4 months, a statistically significant improvement in IDFS was demonstrated in patients randomized to receive PERJETA compared with patients randomized to receive placebo. The efficacy results from APHINITY are summarized in Tables 10 and 11 and in Figure 3 .
| PERJETA + trastuzumab + chemotherapy N=2400 | Placebo + trastuzumab + chemotherapy N=2404 | |
|---|---|---|
| HR=Hazard Ratio, CI=Confidence Interval | ||
| Invasive Disease Free Survival (IDFS) | ||
| Number (%) of patients with event | 171 (7.1%) | 210 (8.7%) |
| HR [95% CI] All analyses stratified by nodal status, protocol version, central hormone receptor status, and adjuvant chemotherapy regimen. Stratification factors are defined according to the randomization data for IDFS. | 0.82 [0.67, 1.00] | |
| p-value (Log-Rank test, stratified) | 0.047 | |
| 3 year event-free rate 3-year event-free rate derived from Kaplan-Meier estimates , % [95% CI] | 94.1 [93.1, 95.0] | 93.2 [92.2, 94.3] |
| IDFS including second primary non-breast cancer | ||
| Number (%) of patients with event | 189 (7.9%) | 230 (9.6%) |
| HR [95% CI] | 0.83 [0.68, 1.00] | |
| 3 year event-free rate, % [95% CI] | 93.5 [92.5, 94.5] | 92.5 [91.4, 93.6] |
| Disease Free Survival (DFS) | ||
| Number (%) of patients with event | 192 (8.0%) | 236 (9.8%) |
| HR [95% CI] | 0.82 [0.68, 0.99] | |
| 3 year event-free rate, % [95% CI] | 93.4 [92.4, 94.4] | 92.3 [91.2, 93.4] |
| Overall Survival (OS) Data from first interim analysis | ||
| Number (%) of patients with event | 80 (3.3%) | 89 (3.7%) |
| HR [95% CI] | 0.89 [0.66, 1.21] | |
| 3 year event-free rate, % [95% CI] | 97.7 [97.0, 98.3] | 97.7 [97.1, 98.3] |
Figure 3 Kaplan-Meier Curve of Invasive Disease Free Survival from APHINITY (ITT Population)
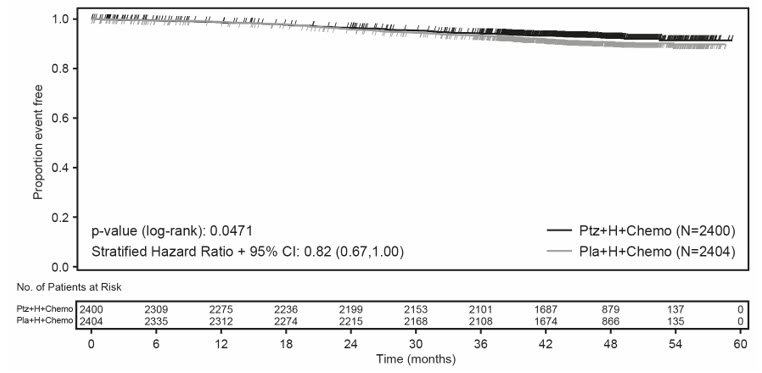
| Population | Number of events/Total N (%) | IDFS at 3 year (%, 95% CI) | Unstratified HR (95% CI) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PERJETA + trastuzumab + chemotherapy | Placebo + trastuzumab + chemotherapy | PERJETA + trastuzumab + chemotherapy | Placebo + trastuzumab + chemotherapy | ||
| Hormone Receptor Status | |||||
| Negative | 71/864 (8.2%) | 91/858 (10.6%) | 92.8 (90.8, 94.3) | 91.2 (89.0, 92.9) | 0.76 (0.56, 1.04) |
| Positive | 100/1536 (6.5%) | 119/1546 (7.7%) | 94.8 (93.5, 95.8) | 94.4 (93.1, 95.4) | 0.86 (0.66, 1.13) |
| Nodal Status | |||||
| Negative | 32/897 (3.6%) | 29/902 (3.2%) | 97.5 (96.3, 98.4) | 98.4 (97.3, 99.0) | 1.13 (0.68, 1.86) |
| Positive | 139/1503 (9.2%) | 181/1502 (12.1%) | 92.0 (90.5, 93.3) | 90.2 (88.5, 91.6) | 0.77 (0.62, 0.96) |
| Adjuvant Chemotherapy Regimen | |||||
| Anthracycline | 139/1865 (7.4%) | 171/1877 (9.1%) | 93.8 (92.6, 94.8) | 93.0 (91.8, 94.1) | 0.82 (0.66, 1.03) |
| Non-Anthracycline | 32/535 (6.0%) | 39/527 (7.4%) | 94.9 (92.6, 96.6) | 94.0 (91.5, 95.8) | 0.82 (0.51, 1.31) |
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
PERJETA (pertuzumab) injection is supplied as a 420 mg/14 mL (30 mg/mL) single-dose vial containing sterile, preservative-free, clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to pale brown solution. NDC 50242-145-01.
Storage and Handling
Store vials refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) in the original carton until time of use to protect from light.
Do not freeze. Do not shake.
DO NOT FREEZE. DO NOT SHAKE.
Mechanism of Action
Pertuzumab targets the extracellular dimerization domain (Subdomain II) of the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 protein (HER2) and, thereby, blocks ligand-dependent heterodimerization of HER2 with other HER family members, including EGFR, HER3, and HER4. As a result, pertuzumab inhibits ligand-initiated intracellular signaling through two major signal pathways, mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K). Inhibition of these signaling pathways can result in cell growth arrest and apoptosis, respectively. In addition, pertuzumab mediates antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC).
While pertuzumab alone inhibited the proliferation of human tumor cells, the combination of pertuzumab and trastuzumab augmented anti-tumor activity in HER2-overexpressing xenograft models.