Dosage & Administration
By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Pombiliti + Opfolda Prescribing Information
Life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, have been reported in POMBILITI-treated patients. In clinical trials, 43 (27%) POMBILITI-treated patients experienced hypersensitivity reactions, including 4 (3%) patients who reported severe hypersensitivity reactions and 4 (3%) additional patients who experienced anaphylaxis (fulfilling at least one of the Sampson criteria). Three of the 4 (2%) patients experiencing anaphylaxis discontinued from the trial
Prior to POMBILITI administration, consider pretreating with antihistamines, antipyretics, and/or corticosteroids. Appropriate medical support measures, including cardiopulmonary resuscitation equipment, should be readily available during POMBILITI administration.
- If aseverehypersensitivity reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) occurs, POMBILITI should be discontinued immediately, and appropriate medical treatment should be initiated. The risks and benefits of readministering POMBILITI following severe hypersensitivity reaction (including anaphylaxis) should be considered. Patients may be rechallenged using slower infusion rates. In patients with severe hypersensitivity reaction, desensitization measures to POMBILITI may be considered. If the decision is made to readminister POMBILITI, ensure the patient tolerates the infusion. If the patient tolerates the infusion, the dosage (dose and/or the rate) may be increased to reach the approved recommended dosage.
- If amild or moderatehypersensitivity reaction occurs, the infusion rate may be slowed or temporarily stopped[see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
In clinical trials, IARs were reported to occur at any time during and/or within a few hours after the POMBILITI infusion and were more likely to occur with higher infusion rates. IARs were reported in 48 (32%) POMBILITI-treated patients in clinical trials. In these trials, 4 (3%) POMBILITI-treated patients reported 11 severe IARs including symptoms of pharyngeal edema, anaphylactic reaction, urticaria, pruritus, chills, dyspnea, and flushing. The majority of IARs were assessed as mild to moderate. IARs that led to treatment discontinuation were urticaria, anaphylactic reaction, chills, and hypotension.
Antihistamines, antipyretics, and/or corticosteroids can be given prior to POMBILITI administration to reduce the risk of infusion-associated reactions (IARs). However, IARs may still occur in patients after receiving pretreatment.
- IfsevereIARs occur, immediately discontinue the POMBILITI infusion, initiate appropriate medical treatment, and assess the benefits and risks of readministering POMBILITI following severe IARs. Patients may be rechallenged using slower infusion rates. Once a patient tolerates the infusion, the infusion rate may be increased to reach the recommended infusion rate.
- Ifmild or moderateIARs occur regardless of pretreatment, decreasing the infusion rate or temporarily stopping the infusion may ameliorate the symptoms[see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Patients with an acute underlying illness at the time of POMBILITI infusion may be at greater risk for IARs. Patients with advanced Pompe disease may have compromised cardiac and respiratory function, which may predispose them to a higher risk of severe complications from IARs.
Patients susceptible to fluid volume overload, or those with acute underlying respiratory illness or compromised cardiac or respiratory function for whom fluid restriction is indicated may be at risk of serious exacerbation of their cardiac or respiratory status during the POMBILITI infusion. More frequent monitoring of vitals should be performed during POMBILITI infusion in these patients. Some patients may require prolonged observation times.
POMBILITI is indicated, in combination with Opfolda, for the treatment of adult patients with late-onset Pompe disease (lysosomal acid alpha-glucosidase [GAA] deficiency) weighing ≥40 kg and who are not improving on their current enzyme replacement therapy (ERT).
- Verify pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential prior to initiating treatment. ()
2.1 Pregnancy Evaluation Prior to Initiating TreatmentVerify the pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to initiating POMBILITI in combination with Opfolda
[see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)]. - Administer POMBILITI in combination with Opfolda. ()
2.2 Recommended Dosage and AdministrationPOMBILITI must be administered in combination with Opfolda (see Figure 1for the dosing timeline). If the Opfolda dose is missed, POMBILITI should not be administered. Refer to the Opfolda Prescribing Information for Opfolda dosage and administration recommendations.
Prior to POMBILITI administration, consider pretreating with antihistamines, antipyretics, and/or corticosteroids
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2)]. If premedication was used with previous enzyme replacement therapy (ERT), prior to POMBILITI administration, pretreat with antihistamines, antipyretics, and/or corticosteroids.The recommended dosage of POMBILITI is 20 mg/kg (of actual body weight) administered every other week as an intravenous infusion over approximately 4 hours (see Table 1for the recommended total infusion volume based on the patient’s weight).
Start POMBILITI in combination with Opfolda 2 weeks after the last ERT dose.
Initiate the POMBILITI infusion approximately 1 hour after oral administration of Opfolda. If the POMBILITI infusion cannot be started within 3 hours of oral administration of Opfolda, reschedule POMBILITI in combination with Opfolda at least 24 hours after Opfolda was last taken. If POMBILITI in combination with Opfolda are both missed, re-start treatment as soon as possible.
Figure 1. Dosing Timeline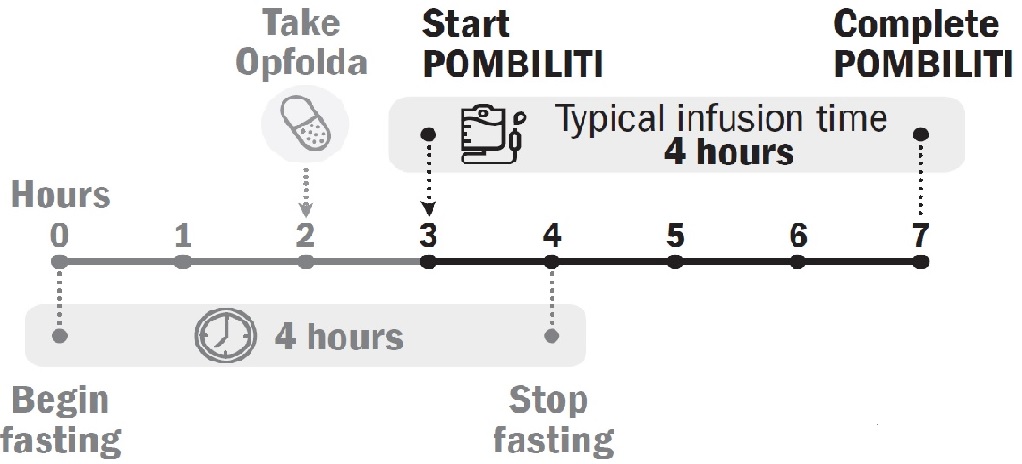

Figure 1 - Consider administering antihistamines, antipyretics, and/or corticosteroids prior to POMBILITI administration. ()
2.2 Recommended Dosage and AdministrationPOMBILITI must be administered in combination with Opfolda (see Figure 1for the dosing timeline). If the Opfolda dose is missed, POMBILITI should not be administered. Refer to the Opfolda Prescribing Information for Opfolda dosage and administration recommendations.
Prior to POMBILITI administration, consider pretreating with antihistamines, antipyretics, and/or corticosteroids
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2)]. If premedication was used with previous enzyme replacement therapy (ERT), prior to POMBILITI administration, pretreat with antihistamines, antipyretics, and/or corticosteroids.The recommended dosage of POMBILITI is 20 mg/kg (of actual body weight) administered every other week as an intravenous infusion over approximately 4 hours (see Table 1for the recommended total infusion volume based on the patient’s weight).
Start POMBILITI in combination with Opfolda 2 weeks after the last ERT dose.
Initiate the POMBILITI infusion approximately 1 hour after oral administration of Opfolda. If the POMBILITI infusion cannot be started within 3 hours of oral administration of Opfolda, reschedule POMBILITI in combination with Opfolda at least 24 hours after Opfolda was last taken. If POMBILITI in combination with Opfolda are both missed, re-start treatment as soon as possible.
Figure 1. Dosing Timeline

Figure 1 - Recommended POMBILITI dosage is 20 mg/kg (of actual body weight) administered every other week as an intravenous infusion over approximately 4 hours. ()
2.2 Recommended Dosage and AdministrationPOMBILITI must be administered in combination with Opfolda (see Figure 1for the dosing timeline). If the Opfolda dose is missed, POMBILITI should not be administered. Refer to the Opfolda Prescribing Information for Opfolda dosage and administration recommendations.
Prior to POMBILITI administration, consider pretreating with antihistamines, antipyretics, and/or corticosteroids
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2)]. If premedication was used with previous enzyme replacement therapy (ERT), prior to POMBILITI administration, pretreat with antihistamines, antipyretics, and/or corticosteroids.The recommended dosage of POMBILITI is 20 mg/kg (of actual body weight) administered every other week as an intravenous infusion over approximately 4 hours (see Table 1for the recommended total infusion volume based on the patient’s weight).
Start POMBILITI in combination with Opfolda 2 weeks after the last ERT dose.
Initiate the POMBILITI infusion approximately 1 hour after oral administration of Opfolda. If the POMBILITI infusion cannot be started within 3 hours of oral administration of Opfolda, reschedule POMBILITI in combination with Opfolda at least 24 hours after Opfolda was last taken. If POMBILITI in combination with Opfolda are both missed, re-start treatment as soon as possible.
Figure 1. Dosing Timeline

Figure 1 - Start POMBILITI in combination with Opfolda 2 weeks after the last ERT dose. ()
2.2 Recommended Dosage and AdministrationPOMBILITI must be administered in combination with Opfolda (see Figure 1for the dosing timeline). If the Opfolda dose is missed, POMBILITI should not be administered. Refer to the Opfolda Prescribing Information for Opfolda dosage and administration recommendations.
Prior to POMBILITI administration, consider pretreating with antihistamines, antipyretics, and/or corticosteroids
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2)]. If premedication was used with previous enzyme replacement therapy (ERT), prior to POMBILITI administration, pretreat with antihistamines, antipyretics, and/or corticosteroids.The recommended dosage of POMBILITI is 20 mg/kg (of actual body weight) administered every other week as an intravenous infusion over approximately 4 hours (see Table 1for the recommended total infusion volume based on the patient’s weight).
Start POMBILITI in combination with Opfolda 2 weeks after the last ERT dose.
Initiate the POMBILITI infusion approximately 1 hour after oral administration of Opfolda. If the POMBILITI infusion cannot be started within 3 hours of oral administration of Opfolda, reschedule POMBILITI in combination with Opfolda at least 24 hours after Opfolda was last taken. If POMBILITI in combination with Opfolda are both missed, re-start treatment as soon as possible.
Figure 1. Dosing Timeline

Figure 1 - Initiate the POMBILITI infusion approximately 1 hour after oral administration of Opfolda. If the POMBILITI infusion cannot be started within 3 hours of oral administration of Opfolda, reschedule POMBILITI in combination with Opfolda at least 24 hours after Opfolda was last taken. If POMBILITI in combination with Opfolda are both missed, re-start treatment as soon as possible. ()
2.2 Recommended Dosage and AdministrationPOMBILITI must be administered in combination with Opfolda (see Figure 1for the dosing timeline). If the Opfolda dose is missed, POMBILITI should not be administered. Refer to the Opfolda Prescribing Information for Opfolda dosage and administration recommendations.
Prior to POMBILITI administration, consider pretreating with antihistamines, antipyretics, and/or corticosteroids
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2)]. If premedication was used with previous enzyme replacement therapy (ERT), prior to POMBILITI administration, pretreat with antihistamines, antipyretics, and/or corticosteroids.The recommended dosage of POMBILITI is 20 mg/kg (of actual body weight) administered every other week as an intravenous infusion over approximately 4 hours (see Table 1for the recommended total infusion volume based on the patient’s weight).
Start POMBILITI in combination with Opfolda 2 weeks after the last ERT dose.
Initiate the POMBILITI infusion approximately 1 hour after oral administration of Opfolda. If the POMBILITI infusion cannot be started within 3 hours of oral administration of Opfolda, reschedule POMBILITI in combination with Opfolda at least 24 hours after Opfolda was last taken. If POMBILITI in combination with Opfolda are both missed, re-start treatment as soon as possible.
Figure 1. Dosing Timeline

Figure 1 - See the full prescribing information for dosage modifications due to hypersensitivity reactions or IARs. ()
2.3 Dosage and Administration Modifications Due to Hypersensitivity Reactions and/or Infusion-Associated ReactionsIn the event of a
severehypersensitivity reaction (including anaphylaxis) or asevereinfusion-associated reaction (IAR), immediately discontinue the POMBILITI infusion, and initiate appropriate medical treatment. For additional recommendations in the event of a severe hypersensitivity reaction[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2)].In the event of a
mild to moderatehypersensitivity reaction ormoderateIAR, consider temporarily holding or slowing the infusion rate and initiating appropriate medical treatment[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2)]. If symptoms:- Persist despite temporarily holding or slowing the infusion, stop the infusion for 30 to 60 minutes, monitor the patient, and consider resuming the infusion at a reduced rate if symptoms have improved. If symptoms continue to persist, discontinue the infusion, and consider re-initiating the infusion within 7 to 14 days with appropriate premedication.
- Subside following holding or slowing the infusion, increase the infusion rate to the rate at which the reaction occurred and consider continuing to increase the rate (every 30 minutes) in a stepwise manner up to the target infusion rate. Closely monitor the patient.
- Must be reconstituted and diluted prior to use. ()
2.4 Reconstitution and Dilution InstructionsUse aseptic technique during preparation. Reconstitute and dilute POMBILITI in the following manner:
Reconstitute the Lyophilized Powder- Determine the number of POMBILITI vials to be reconstituted based on the calculated dose (based on patient’s actual body weight in kg)[see ].
- Remove vials from the refrigerator and set aside for approximately 30 minutes to allow vials to come to room temperature.
- Reconstitute each vial by slowly injecting 7.2 mL of Sterile Water for Injection, down the inside wall of each vial to avoid foaming. Avoid forceful impact of Sterile Water for Injection on the lyophilized powder and avoid foaming.
- Roll and tilt each vial to allow the lyophilized powder to dissolve completely which typically takes 2 minutes. Each vial will yield a concentration of 15 mg/mL. Do not invert, swirl, or shake.
- Visually inspect the reconstituted solution for particulate matter and discoloration. The reconstituted solution appears as a clear to opalescent, colorless to yellowish solution essentially particle free. Discard if foreign matter is observed or the solution is discolored.
Dilute the Reconstituted Solution- Remove airspace within a bag of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection. Remove an equal volume of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection from the bag that will be replaced by the total volume (mL) of reconstituted POMBILITI (see Table 1for the recommended total infusion volume based on the patient’s weight).
- Slowly withdraw 7 mL of reconstituted solution from each of the vials until the patient’s dose is obtained. Discard any remaining reconstituted solution in the last vial.
- Add the reconstituted solution slowly and directly into the infusion bag.
- To prevent foaming, gently invert infusion bag to mix the solution and avoid vigorous shaking or agitation. After dilution, the solution will have a final concentration of 0.5 to 4 mg/mL of cipaglucosidase alfa-atga. Do not use a pneumatic tube to transport the infusion bag.
- Administer the diluted solution at room temperature without delay[see ].
- Determine the number of POMBILITI vials to be reconstituted based on the calculated dose (based on patient’s actual body weight in kg)
- See the full prescribing information for administration instructions. ()
2.6 Administration InstructionsPrior to administration, inspect the infusion bag for foaming. If foaming is present, let foam dissipate before administering POMBILITI. If the diluted solution has been refrigerated, allow solution to equilibrate to room temperature for 30 minutes prior to infusion.
Use an administration set with an inline low protein binding 0.2‑micron filter to administer POMBILITI. Change filter if the filter becomes blocked.
Initiate the POMBILITI infusion approximately 1 hour after oral administration of Opfolda. In the event of POMBILITI infusion delay, the starting infusion time should not exceed 3 hours from the oral administration of Opfolda
[see ].The initial recommended infusion rate is 1 mg/kg/hour (see Table 1). Gradually increase the infusion rate by 2 mg/kg/hour every 30 minutes if there are no signs of hypersensitivity or infusion-associated reactions (IARs) until a maximum rate of 7 mg/kg/hour is reached; then, maintain the infusion rate at 7 mg/kg/hour until the infusion is complete. The approximate total infusion duration is 4 hours.
See Table 1for the rate of infusion at each step, expressed as mL/hour based on the recommended infusion volume by patient weight.
Do not infuse POMBILITI in the same intravenous line with other products.
Table 1. Recommended POMBILITI Infusion Volumes and Rates by Patient WeightPatient Weight Range Total Infusion Volume Step 1
1 mg/kg/hourStep 2
3 mg/kg/hourStep 3
5 mg/kg/hourStep 4
7 mg/kg/hourInfusion Rate in mL/hour 40–50 kg 250 mL 13 38 63 88 50.1–60 kg 300 mL 15 45 75 105 60.1-100 kg 500 mL 25 75 125 175 100.1–120 kg 600 mL 30 90 150 210 120.1–140 kg 700 mL 35 105 175 245
For injection: 105 mg of cipaglucosidase alfa-atga as a white to slightly yellowish lyophilized powder with a cake-like appearance in a single-dose vial for reconstitution
There are no data on the presence of cipaglucosidase alfa-atga, alone or in combination with miglustat, in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Cipaglucosidase alfa‑atga is present in animal milk
Evaluation of milk in rats from the pre- and post-natal development study of cipaglucosidase alfa atga in combination with miglustat (400 mg/kg and 60 mg/kg, respectively) showed excretion of cipaglucosidase alfa-atga and secretion of miglustat in rat milk. In this study, the ratio of cipaglucosidase alfa-atga exposure in rat milk to cipaglucosidase alfa-atga exposure in rat plasma was <4%, and the ratio of miglustat exposure in rat milk to the miglustat exposure in rat plasma was 1.7.
The concentration of drug in animal milk does not necessarily predict the concentration of drug in human milk.
POMBILITI in combination with Opfolda is contraindicated in pregnancy
Based on findings from animal reproduction studies, POMBILITI in combination with Opfolda may cause embryo-fetal harm when administered to a pregnant female and is contraindicated during pregnancy. In a rabbit embryo-fetal development study, great vessel and cardiac malformations were increased in offspring of pregnant rabbits treated with cipaglucosidase alfa‑atga in combination with oral miglustat at 16‑fold and 3‑fold, respectively, the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) based on plasma AUC exposure.
Verify the pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential prior to initiating treatment with POMBILITI in combination with Opfolda. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with POMBILITI in combination with Opfolda and for at least 60 days after the last dose
Based on findings from animal reproduction studies, POMBILITI in combination with Opfolda may cause embryo-fetal harm when administered to a pregnant female and is contraindicated during pregnancy. In a rabbit embryo-fetal development study, great vessel and cardiac malformations were increased in offspring of pregnant rabbits treated with cipaglucosidase alfa-atga in combination with miglustat at 16-fold and 3-fold, respectively, the MRHD of POMBILITI and Opfolda based on plasma AUC exposure. A No Observed Adverse Effect Level (NOAEL) was not identified for the combination. In a pre- and post-natal development study in rats, increases in pup mortality were seen following maternal treatment with cipaglucosidase alfa-atga (400 mg/kg) in combination with miglustat, or with cipaglucosidase alfa-atga (400 mg/kg) alone. The NOAEL for cipaglucosidase alfa-atga alone is 150 mg/kg (5-fold the POMBILITI MRHD margin). A NOAEL for the combination was not identified. Margins at the lowest observed adverse effect level (LOAEL), relative to exposures at the MRHD of POMBILITI and Opfolda were 20-fold and 4-fold, respectively, based on plasma AUC exposure
There are no available human data on POMBILITI in combination with Opfolda use in pregnant females to evaluate for a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes.
Reproductive toxicity studies of cipaglucosidase alfa-atga in rats and rabbits included pretreatment with diphenhydramine (DPH) to prevent or minimize hypersensitivity reactions.
In a rabbit embryo-fetal development study, cipaglucosidase alfa-atga (30, 70, or 175 mg/kg) was administered intravenously every other day to pregnant females during organogenesis (Gestation Day [GD] 7 through GD 19). Additional experimental groups received 25 mg/kg oral miglustat alone, or in combination with intravenous cipaglucosidase alfa-atga 175 mg/kg, with the same dosing frequency during organogenesis. Clusters of great vessel and cardiac malformations were increased in offspring of pregnant rabbits treated with the combination of cipaglucosidase alfa-atga and miglustat at 16-fold and 3-fold the MRHD of POMBILITI and Opfolda, respectively, based on plasma AUC exposure. A NOAEL for the combination was not identified. One fetus treated with cipaglucosidase alfa-atga alone (175 mg/kg) and one fetus treated with miglustat alone (25 mg/kg), each showed a similar cluster of these great vessel and cardiac malformations.
In a rat embryo-fetal development study, cipaglucosidase alfa-atga (75, 150, or 400 mg/kg) was administered intravenously every other day to pregnant rats during organogenesis (GD 6 through GD 18). Additional experimental groups received 60 mg/kg oral miglustat alone, or in combination with intravenous cipaglucosidase alfa-atga 400 mg/kg, with the same dosing frequency during organogenesis. No evidence of adverse effects was noted in pregnant rats or their offspring in any experimental group. The margin at the NOAEL for cipaglucosidase alfa‑atga (400 mg/kg) was 20-fold the POMBILITI MRHD based on plasma AUC exposure. The margin at the NOAEL for miglustat (60 mg/kg) was 4-fold the Opfolda MRHD based on plasma AUC exposure.
In a pre-and post-natal development study in rats, cipaglucosidase alfa-atga (75, 150, or 400 mg/kg) was administered intravenously every other day to pregnant females from GD 6 through GD 18, and from Lactation Day (LD) 1 through LD 19. Additional experimental groups received 60 mg/kg oral miglustat alone, or in combination with intravenous cipaglucosidase alfa‑atga 400 mg/kg, with the same dosing frequency during pregnancy and lactation. Maternal and pup mortality were increased with the combination, and pup mortality was also increased with cipaglucosidase alfa-atga 400 mg/kg alone. The NOAEL for cipaglucosidase alfa-atga alone is 150 mg/kg (5-fold the POMBILITI MRHD margin). A NOAEL was not identified for the combination, for which LOAEL margins at the MRHD of POMBILITI and Opfolda were 20-fold and 4-fold, respectively, based on plasma AUC exposure.