Get your patient on Prevymis (Letermovir)
Prevymis prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Prevymis patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Adult and Pediatric Patients 12 Years of Age and Older and Weighing at least 30 kg Who Are HSCT Recipients or Adult and Pediatric Patients 12 Years of Age and Older and Weighing at least 40 kg Who Are Kidney Transplant Recipients:
- HSCT : 480 mg administered once daily orally or as an intravenous (IV) infusion over 1 hour through 100 days post-HSCT. In patients at risk for late CMV infection and disease, PREVYMIS may be continued through 200 days post-HSCT. (2.1 , 2.3 )
- Kidney Transplant : 480 mg administered once daily orally or as an IV infusion over 1 hour through 200 days post-transplant. (2.1 , 2.3 )
- Pediatric Patients 6 Months to Less than 12 Years of Age or 12 Years of Age and Older and Weighing Less than 30 kg Who Are HSCT Recipients:
- PREVYMIS injection must be diluted prior to administration. (2.1 )
- PREVYMIS injection must be administered through a sterile 0.2 micron or 0.22 micron polyethersulfone (PES) in-line filter. (2.1 , 2.10 )
- Following the completion of PREVYMIS prophylaxis, monitoring for CMV reactivation in HSCT recipients is recommended. (2.2 )
- Dosage Adjustment: If PREVYMIS is co-administered with cyclosporine, the dosage of PREVYMIS should be decreased to 240 mg once daily in adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older. (2.4 ) If PREVYMIS is co-administered with cyclosporine in pediatric patients less than 12 years of age, dose adjustment may be required. (2.6 )
- Instructions for Use should be followed for preparation and administration of PREVYMIS oral pellets. (2.9 )
- Do not use PREVYMIS injection with IV bags and infusion set materials containing the plasticizer diethylhexyl phthalate (DEHP). (2.10 , 2.13 )
Important Dosing and Administration Information
- PREVYMIS is available in 3 dosage forms:
- PREVYMIS Tablets
- Administer orally with or without food.
- Swallow tablets whole.
- PREVYMIS Oral Pellets
- Administer orally mixed with soft food or via nasogastric tube (NG tube) or gastric tube (G tube) [see Dosage and Administration (2.9) ] .
- Do not crush or chew.
- PREVYMIS Injection
- PREVYMIS injection must be diluted prior to administration.
- Administer PREVYMIS through a sterile 0.2 micron or 0.22 micron polyethersulfone (PES) in-line filter.
- Administer by intravenous infusion via a peripheral catheter or central venous line at a constant rate over 1 hour.
- Do not administer as an intravenous bolus injection.
- PREVYMIS injection, which contains hydroxypropyl betadex, should be used only in patients unable to take oral therapy. Patients should be switched to oral PREVYMIS as soon as they are able to take oral medications. If possible, intravenous administration should not exceed 4 weeks [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] .
- PREVYMIS Tablets
- No dosage adjustment is necessary when switching formulations in adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] .
- Dosage adjustment may be necessary for pediatric patients less than 12 years of age when switching between oral and intravenous formulations (see Table 1 and Table 2 ) [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) ] .
Patient Monitoring
Following the completion of PREVYMIS prophylaxis, monitoring for CMV reactivation in HSCT recipients is recommended [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ] .
Recommended Dosage for Adult and Pediatric Patients 12 Years of Age and Older Who Are HSCT or Kidney Transplant Recipients
HSCT: Adult and Pediatric Patients 12 Years of Age and Older and Weighing at least 30 kg
The recommended dosage of PREVYMIS is 480 mg administered orally or intravenously once daily. When PREVYMIS is administered orally, the recommended dosage is one 480 mg tablet once daily or two 240 mg tablets once daily. Four 120 mg packets of oral pellets once daily can be used for patients who cannot swallow tablets [see Dosage and Administration (2.9) ] . For preparation and administration instructions of intravenous dosing refer to instructions in subsection 2.10 [see Dosage and Administration (2.10) ]. For pediatric patients less than 12 years of age or weighing less than 30 kg, refer to weight-based dosing in Table 1 and Table 2 [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) ] .
Initiate PREVYMIS between Day 0 and Day 28 post-HSCT (before or after engraftment) and continue through Day 100 post-HSCT. In patients at risk for late CMV infection and disease, PREVYMIS may be continued through Day 200 post-HSCT [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ] .
Dosage of PREVYMIS should be adjusted when co-administered with cyclosporine [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) ] .
Kidney Transplant: Adult and Pediatric Patients 12 Years of Age and Older and Weighing at least 40 kg
The recommended dosage of PREVYMIS is 480 mg administered orally or intravenously once daily. When PREVYMIS is administered orally, the recommended dosage is one 480 mg tablet once daily or two 240 mg tablets once daily. Four 120 mg packets of oral pellets once daily can be used for patients who cannot swallow tablets [see Dosage and Administration (2.9) ] . For preparation and administration instructions of intravenous dosing refer to instructions in subsection 2.10 [see Dosage and Administration (2.10) ].
Initiate PREVYMIS between Day 0 and Day 7 post-transplant and continue through Day 200 post-transplant.
Dosage of PREVYMIS should be adjusted when co-administered with cyclosporine [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) ] .
Dosage Adjustment When Co-administered with Cyclosporine for Adult and Pediatric Patients 12 Years of Age and Older Who Are HSCT or Kidney Transplant Recipients
- If oral or intravenous PREVYMIS is co-administered with cyclosporine, the dosage of PREVYMIS should be decreased to 240 mg once daily in the following populations [see Drug Interactions (7.1 , 7.2 , 7.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] :
- HSCT: adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older and weighing at least 30 kg
or - Kidney transplant: adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older and weighing at least 40 kg.
- HSCT: adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older and weighing at least 30 kg
- If cyclosporine is initiated after starting PREVYMIS, the next dose of PREVYMIS should be decreased to 240 mg once daily.
- If cyclosporine is discontinued after starting PREVYMIS, the next dose of PREVYMIS should be increased to 480 mg once daily.
- If cyclosporine dosing is interrupted due to high cyclosporine levels, no dose adjustment of PREVYMIS is needed.
Recommended Dosage for Pediatric Patients 6 Months to Less than 12 Years of Age or 12 Years of Age and Older and Weighing Less than 30 kg Who Are HSCT Recipients
The recommended dosages of PREVYMIS for pediatric HSCT recipients 6 months to less than 12 years of age are based on weight and shown in Table 1 (tablets or oral pellets) and Table 2 (injection) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . PREVYMIS can be administered orally (tablet or pellet) or intravenously once daily. Dosage adjustment may be necessary for pediatric patients less than 12 years of age when switching between oral and intravenous formulations (see Table 1 and Table 2 ) .
Initiate PREVYMIS between Day 0 and Day 28 post-HSCT (before or after engraftment) and continue through Day 100 post-HSCT. In patients at risk for late CMV infection and disease, PREVYMIS may be continued through Day 200 post-HSCT [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ] .
| Body Weight | Daily Oral Dose | Tablets | Oral Pellets |
|---|---|---|---|
| 30 kg and above | 480 mg | One 480 mg tablet or Two 240 mg tablets | Four 120 mg packets of oral pellets |
| 15 kg to less than 30 kg | 240 mg | One 240 mg tablet | Two 120 mg packets of oral pellets |
| 7.5 kg to less than 15 kg | 120 mg | Not recommended | One 120 mg packet of oral pellets |
| 6 kg to less than 7.5 kg | 80 mg | Not recommended | Four 20 mg packets of oral pellets |
| Body Weight | Daily IV Refer to Subsection 2.10 for intravenous preparation and administration dosing instructions Dose |
|---|---|
| 30 kg and above | 480 mg |
| 15 kg to less than 30 kg | 120 mg |
| 7.5 kg to less than 15 kg | 60 mg |
| 6 kg to less than 7.5 kg | 40 mg |
Dosage Adjustment When Co-administered with Cyclosporine for Pediatric Patients 6 Months to Less than 12 Years of Age or 12 Years of Age and Older and Weighing Less than 30 kg Who Are HSCT Recipients
If oral or intravenous PREVYMIS is co-administered with cyclosporine in pediatric HSCT recipients 6 months to less than 12 years of age, the dosage of PREVYMIS may require adjustment as shown in Table 3 [see Drug Interactions (7.1 , 7.2 , 7.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
- If cyclosporine is initiated after starting PREVYMIS, the next dose of PREVYMIS should be the daily oral or intravenous dose co-administered with cyclosporine (Table 3)
- If cyclosporine is discontinued after starting PREVYMIS, the next dose of PREVYMIS should be the daily oral or intravenous dose administered without cyclosporine (Table 1 or Table 2)
- If cyclosporine dosing is interrupted due to high cyclosporine levels, no dose adjustment of PREVYMIS is needed.
| Body Weight | Daily Oral Dose | Tablets | Oral Pellets | Daily IV Refer to Subsection 2.10 for intravenous preparation and administration dosing instructions Dose |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 kg and above | 240 mg | One 240 mg tablet | Two 120 mg packets of oral pellets | 240 mg |
| 15 kg to less than 30 kg | 120 mg | Not recommended | One 120 mg packet of oral pellets | 120 mg |
| 7.5 kg to less than 15 kg | 60 mg | Not recommended | Three 20 mg packets of oral pellets | 60 mg |
| 6 kg to less than 7.5 kg | 40 mg | Not recommended | Two 20 mg packets of oral pellets | 40 mg |
Use in Patients with Renal Impairment
- For adult patients with creatinine clearance (CLcr) greater than 10 mL/min and pediatric patients with a similar degree of renal impairment (based on age-appropriate assessment of renal function), no dosage adjustment of PREVYMIS is required based on renal impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) , and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
- There are insufficient data in adult patients with CLcr 10 mL/min or less or in patients on dialysis or in pediatric patients with a similar degree of renal impairment (based on age-appropriate assessment of renal function) to make PREVYMIS dosing recommendations.
- In adult patients with CLcr less than 50 mL/min and in pediatric patients with a similar degree of renal impairment (based on age-appropriate assessment of renal function) receiving PREVYMIS injection, accumulation of the intravenous vehicle, hydroxypropyl betadex, may occur. Closely monitor serum creatinine levels in these patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] .
Use in Patients with Hepatic Impairment
No dosage adjustment of PREVYMIS is required for patients with mild (Child-Pugh Class A) or moderate (Child-Pugh Class B) hepatic impairment. PREVYMIS is not recommended for patients with severe (Child-Pugh Class C) hepatic impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7) ] .
Preparation and Administration of Oral Pellets
PREVYMIS oral pellets can be administered:
- orally after mixing with soft food or
- via NG tube or G tube.
Preparation and Administration Mixed with Soft Food
- See Instructions for Use for details on the preparation and administration of PREVYMIS oral pellets mixed with soft food.
- Do not crush or chew PREVYMIS oral pellets.
- Mix PREVYMIS oral pellets with 1 to 3 teaspoons of soft food (such as applesauce, yogurt, or pudding) that is at or below room temperature. Do not use hot food.
- Administer entire mixture within 10 minutes of mixing PREVYMIS oral pellets with the soft food.
Preparation and Administration via NG Tube or G Tube
See Instructions for Use , Table 4 (NG tube) and Table 5 (G tube) for details on the preparation and administration of PREVYMIS oral pellets via NG tube or G tube.
- Pour PREVYMIS oral pellets into a medicine cup containing room temperature water (see Initial Volume in Table 4 and Table 5). Do not mix PREVYMIS oral pellets with hot or cold (refrigerated) water.
- Wait 10 minutes. Do not shake or swirl the medicine cup. PREVYMIS oral pellets will not dissolve but will become loose or broken up. The entire mixture should be administered (see steps 3 and 4) within 2 hours.
- Stir the mixture with the syringe and administer entire mixture right away using the syringe and NG tube or G tube.
- Add room temperature water (see Rinse Volume in Table 4 and Table 5) to the medicine cup for rinsing, stir with a syringe and administer the entire rinse mixture using the syringe and NG tube or G tube.
- Flush the NG tube or G tube with the volume of water recommended by the NG or G tube manufacturer.
| Dosage | NG Tube Fr = French; PUR = polyurethane | Syringe Type With ENFit syringe, a medicine straw (large bore) is needed to aid withdrawal of the mixture from the medicine cup. | Mixing Container | Initial Volume (mL) | Rinse Volume (mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 120 mg to 480 mg | Any ≥ 8 Fr NG tube | Appropriately sized ENFit or catheter-tipped syringe | Medicine Cup | 15 | 15 |
| 40 mg to 80 mg | 5 Fr PUR NG tube or Any ≥ 6 Fr NG tube | 3 | 2 |
| Dosage | G Tube Fr = French; PUR = polyurethane | Syringe Type With ENFit syringe, a medicine straw (large bore) is needed to aid withdrawal of the mixture from the medicine cup. | Mixing Container | Initial Volume (mL) | Rinse Volume (mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 120 mg to 480 mg | Any G tube | Appropriately sized ENFit or catheter-tipped syringe | Medicine Cup | 15 | 15 |
| 40 mg to 80 mg | Any 12 Fr G tube | 3 | 2 |
Preparation and Administration of Intravenous Solution
PREVYMIS injection is supplied in 30 mL single-dose vials containing either 240 mg/12 mL per vial (20 mg/mL) or 480 mg/24 mL per vial (20 mg/mL).
PREVYMIS vials are for single use only. Discard any unused portion.
Preparation Instructions
- PREVYMIS must be diluted prior to intravenous (IV) use. Only 0.9% Sodium Chloride and 5% Dextrose are chemically and physically compatible with PREVYMIS injection.
- Do not shake PREVYMIS vial.
- Inspect vial contents for discoloration and particulate matter prior to dilution. PREVYMIS injection is a clear colorless solution and may contain a few product-related small translucent or white particles.
- Do not use the vial if the solution is cloudy, discolored, or contains matter other than a few small translucent or white particles.
- Once diluted, the solution of PREVYMIS is clear, and ranges from colorless to yellow. Variations of color within this range do not affect the quality of the product.
- Do not use PREVYMIS injection with IV bags and infusion set materials containing the plasticizer diethylhexyl phthalate (DEHP). Use only with IV bags and infusion set materials that are DEHP-free. Materials that are phthalate-free are also DEHP-free.
- Use compatible IV bags and infusion set materials. PREVYMIS injection is compatible with the following IV bags and infusion set materials. PREVYMIS injection is not recommended with any IV bags or infusion set materials not listed below (note that PREVYMIS injection is not recommended for use with polyurethane-containing IV administration set tubing).
- IV Bags Materials:
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC), ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) and polyolefin (polypropylene and polyethylene) - Infusion Sets Materials:
PVC, polyethylene (PE), polybutadiene (PBD), silicone rubber (SR), styrene–butadiene copolymer (SBC), styrene-butadiene-styrene copolymer (SBS), polystyrene (PS) - Plasticizers:
Tris (2-ethylhexyl) trimellitate (TOTM), benzyl butyl phthalate (BBP) - Catheters:
Radiopaque polyurethane
- IV Bags Materials:
- For the 480 mg or 240 mg dose , add PREVYMIS injection (see Table 6 ) into a 250 mL pre-filled IV bag containing either 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP or 5% Dextrose Injection, USP and mix bag gently. Do not shake.
- For the 120 mg or 60 mg dose , add PREVYMIS injection into a pre-filled IV bag containing either 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP or 5% Dextrose Injection, USP (see Table 6 ) and mix bag gently. Do not shake.
| PREVYMIS Dose | Volume of PREVYMIS 20 mg/mL to be Withdrawn from Vial | Volume of Diluent |
|---|---|---|
| 480 mg | 24 mL | 250 mL |
| 240 mg | 12 mL | 250 mL |
| 120 mg | 6 mL | 100 mL |
| 60 mg | 3 mL | 50 mL |
- For the 40 mg dose , prepare a dilution of PREVYMIS injection according to Table 7 in either 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP or 5% Dextrose Injection, USP and mix bag gently. Transfer 20 mL from the prepared dilution into an appropriately sized IV bag or syringe. Do not shake.
| PREVYMIS Dose | Preparation of 2 mg/mL PREVYMIS Dilution | Final Infusion Volume of the Prepared 2 mg/mL PREVYMIS Dilution |
|---|---|---|
| 40 mg | Add 5 mL of 20 mg/mL PREVYMIS to 45 mL of diluent (0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection or 5% Dextrose Injection) and mix gently | 20 mL |
Administration Instructions
- Administer the entire contents of the intravenous bag or syringe by intravenous infusion via a peripheral catheter or central venous line at a constant rate over 1 hour [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) ] .
- The diluted solution must be administered through a sterile 0.2 micron or 0.22 micron polyethersulfone (PES) in-line filter. Do not administer through a filter other than a sterile 0.2 micron or 0.22 micron PES in-line filter.
- Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration.
- Discard if the diluted solution is cloudy, discolored, or contains matter other than a few small translucent or white particles.
Storage of the Diluted Solution
The diluted solutions (as prepared in Table 6 or Table 7) are stable for up to 24 hours at room temperature or up to 48 hours under refrigeration at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) (this time includes storage of the diluted solution in the intravenous bag through the duration of infusion).
Compatible Drug Products Used for Intravenous Administration
Compatible Drug Products
The physical compatibility of PREVYMIS injection with selected injectable drug products was evaluated in two commonly available diluents. PREVYMIS should not be co-administered through the same intravenous line (or cannula) with other drug products and diluent combinations except those listed below. Refer to the respective prescribing information of the co-administered drug(s) to confirm compatibility of simultaneous co-administration.
List of Compatible Drug Products when PREVYMIS and Drug Products are Prepared in 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP:
- Ampicillin sodium, ampicillin sodium/sulbactam sodium, anti-thymocyte globulin, caspofungin, daptomycin, fentanyl citrate, fluconazole, furosemide, human insulin, magnesium sulfate, methotrexate, micafungin.
List of Compatible Drug Products when PREVYMIS and Drug Products are Prepared in 5% Dextrose Injection, USP:
- Amphotericin B (lipid complex) Amphotericin B (lipid complex) is compatible with PREVYMIS. However, Amphotericin B (liposomal) is incompatible [see Dosage and Administration (2.13) ] . , anidulafungin, cefazolin sodium, ceftaroline, ceftriaxone sodium, doripenem, famotidine, folic acid, ganciclovir sodium, hydrocortisone sodium succinate, morphine sulfate, norepinephrine bitartrate, pantoprazole sodium, potassium chloride, potassium phosphate, tacrolimus, telavancin, tigecycline.
Incompatible Drug Products and Other Materials Used for Intravenous Administration
Incompatible Drug Products
PREVYMIS injection is physically incompatible with amiodarone hydrochloride, amphotericin B (liposomal), aztreonam, cefepime hydrochloride, ciprofloxacin, cyclosporine, diltiazem hydrochloride, filgrastim, gentamicin sulfate, levofloxacin, linezolid, lorazepam, midazolam HCl, mycophenolate mofetil hydrochloride, ondansetron, palonosetron.
Incompatible IV Bags and Infusion Set Materials
PREVYMIS injection is incompatible with diethylhexyl phthalate (DEHP) plasticizers and polyurethane-containing IV administration set tubing.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Prevymis prescribing information
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
CMV Prophylaxis in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant (HSCT) Recipients
PREVYMIS ® is indicated for prophylaxis of cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection and disease in adult and pediatric patients 6 months of age and older and weighing at least 6 kg who are CMV-seropositive recipients [R+] of an allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT).
CMV Prophylaxis in Kidney Transplant Recipients
PREVYMIS is indicated for prophylaxis of CMV disease in adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older and weighing at least 40 kg who are kidney transplant recipients at high risk (Donor CMV seropositive/Recipient CMV seronegative [D+/R-]).
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Adult and Pediatric Patients 12 Years of Age and Older and Weighing at least 30 kg Who Are HSCT Recipients or Adult and Pediatric Patients 12 Years of Age and Older and Weighing at least 40 kg Who Are Kidney Transplant Recipients:
- HSCT : 480 mg administered once daily orally or as an intravenous (IV) infusion over 1 hour through 100 days post-HSCT. In patients at risk for late CMV infection and disease, PREVYMIS may be continued through 200 days post-HSCT. (2.1 , 2.3 )
- Kidney Transplant : 480 mg administered once daily orally or as an IV infusion over 1 hour through 200 days post-transplant. (2.1 , 2.3 )
- Pediatric Patients 6 Months to Less than 12 Years of Age or 12 Years of Age and Older and Weighing Less than 30 kg Who Are HSCT Recipients:
- PREVYMIS injection must be diluted prior to administration. (2.1 )
- PREVYMIS injection must be administered through a sterile 0.2 micron or 0.22 micron polyethersulfone (PES) in-line filter. (2.1 , 2.10 )
- Following the completion of PREVYMIS prophylaxis, monitoring for CMV reactivation in HSCT recipients is recommended. (2.2 )
- Dosage Adjustment: If PREVYMIS is co-administered with cyclosporine, the dosage of PREVYMIS should be decreased to 240 mg once daily in adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older. (2.4 ) If PREVYMIS is co-administered with cyclosporine in pediatric patients less than 12 years of age, dose adjustment may be required. (2.6 )
- Instructions for Use should be followed for preparation and administration of PREVYMIS oral pellets. (2.9 )
- Do not use PREVYMIS injection with IV bags and infusion set materials containing the plasticizer diethylhexyl phthalate (DEHP). (2.10 , 2.13 )
Important Dosing and Administration Information
- PREVYMIS is available in 3 dosage forms:
- PREVYMIS Tablets
- Administer orally with or without food.
- Swallow tablets whole.
- PREVYMIS Oral Pellets
- Administer orally mixed with soft food or via nasogastric tube (NG tube) or gastric tube (G tube) [see Dosage and Administration (2.9) ] .
- Do not crush or chew.
- PREVYMIS Injection
- PREVYMIS injection must be diluted prior to administration.
- Administer PREVYMIS through a sterile 0.2 micron or 0.22 micron polyethersulfone (PES) in-line filter.
- Administer by intravenous infusion via a peripheral catheter or central venous line at a constant rate over 1 hour.
- Do not administer as an intravenous bolus injection.
- PREVYMIS injection, which contains hydroxypropyl betadex, should be used only in patients unable to take oral therapy. Patients should be switched to oral PREVYMIS as soon as they are able to take oral medications. If possible, intravenous administration should not exceed 4 weeks [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] .
- PREVYMIS Tablets
- No dosage adjustment is necessary when switching formulations in adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] .
- Dosage adjustment may be necessary for pediatric patients less than 12 years of age when switching between oral and intravenous formulations (see Table 1 and Table 2 ) [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) ] .
Patient Monitoring
Following the completion of PREVYMIS prophylaxis, monitoring for CMV reactivation in HSCT recipients is recommended [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ] .
Recommended Dosage for Adult and Pediatric Patients 12 Years of Age and Older Who Are HSCT or Kidney Transplant Recipients
HSCT: Adult and Pediatric Patients 12 Years of Age and Older and Weighing at least 30 kg
The recommended dosage of PREVYMIS is 480 mg administered orally or intravenously once daily. When PREVYMIS is administered orally, the recommended dosage is one 480 mg tablet once daily or two 240 mg tablets once daily. Four 120 mg packets of oral pellets once daily can be used for patients who cannot swallow tablets [see Dosage and Administration (2.9) ] . For preparation and administration instructions of intravenous dosing refer to instructions in subsection 2.10 [see Dosage and Administration (2.10) ]. For pediatric patients less than 12 years of age or weighing less than 30 kg, refer to weight-based dosing in Table 1 and Table 2 [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) ] .
Initiate PREVYMIS between Day 0 and Day 28 post-HSCT (before or after engraftment) and continue through Day 100 post-HSCT. In patients at risk for late CMV infection and disease, PREVYMIS may be continued through Day 200 post-HSCT [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ] .
Dosage of PREVYMIS should be adjusted when co-administered with cyclosporine [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) ] .
Kidney Transplant: Adult and Pediatric Patients 12 Years of Age and Older and Weighing at least 40 kg
The recommended dosage of PREVYMIS is 480 mg administered orally or intravenously once daily. When PREVYMIS is administered orally, the recommended dosage is one 480 mg tablet once daily or two 240 mg tablets once daily. Four 120 mg packets of oral pellets once daily can be used for patients who cannot swallow tablets [see Dosage and Administration (2.9) ] . For preparation and administration instructions of intravenous dosing refer to instructions in subsection 2.10 [see Dosage and Administration (2.10) ].
Initiate PREVYMIS between Day 0 and Day 7 post-transplant and continue through Day 200 post-transplant.
Dosage of PREVYMIS should be adjusted when co-administered with cyclosporine [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) ] .
Dosage Adjustment When Co-administered with Cyclosporine for Adult and Pediatric Patients 12 Years of Age and Older Who Are HSCT or Kidney Transplant Recipients
- If oral or intravenous PREVYMIS is co-administered with cyclosporine, the dosage of PREVYMIS should be decreased to 240 mg once daily in the following populations [see Drug Interactions (7.1 , 7.2 , 7.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] :
- HSCT: adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older and weighing at least 30 kg or
- Kidney transplant: adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older and weighing at least 40 kg.
- If cyclosporine is initiated after starting PREVYMIS, the next dose of PREVYMIS should be decreased to 240 mg once daily.
- If cyclosporine is discontinued after starting PREVYMIS, the next dose of PREVYMIS should be increased to 480 mg once daily.
- If cyclosporine dosing is interrupted due to high cyclosporine levels, no dose adjustment of PREVYMIS is needed.
Recommended Dosage for Pediatric Patients 6 Months to Less than 12 Years of Age or 12 Years of Age and Older and Weighing Less than 30 kg Who Are HSCT Recipients
The recommended dosages of PREVYMIS for pediatric HSCT recipients 6 months to less than 12 years of age are based on weight and shown in Table 1 (tablets or oral pellets) and Table 2 (injection) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . PREVYMIS can be administered orally (tablet or pellet) or intravenously once daily. Dosage adjustment may be necessary for pediatric patients less than 12 years of age when switching between oral and intravenous formulations (see Table 1 and Table 2 ) .
Initiate PREVYMIS between Day 0 and Day 28 post-HSCT (before or after engraftment) and continue through Day 100 post-HSCT. In patients at risk for late CMV infection and disease, PREVYMIS may be continued through Day 200 post-HSCT [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ] .
| Body Weight | Daily Oral Dose | Tablets | Oral Pellets |
|---|---|---|---|
| 30 kg and above | 480 mg | One 480 mg tablet or Two 240 mg tablets | Four 120 mg packets of oral pellets |
| 15 kg to less than 30 kg | 240 mg | One 240 mg tablet | Two 120 mg packets of oral pellets |
| 7.5 kg to less than 15 kg | 120 mg | Not recommended | One 120 mg packet of oral pellets |
| 6 kg to less than 7.5 kg | 80 mg | Not recommended | Four 20 mg packets of oral pellets |
| Body Weight | Daily IV Refer to Subsection 2.10 for intravenous preparation and administration dosing instructions Dose |
|---|---|
| 30 kg and above | 480 mg |
| 15 kg to less than 30 kg | 120 mg |
| 7.5 kg to less than 15 kg | 60 mg |
| 6 kg to less than 7.5 kg | 40 mg |
Dosage Adjustment When Co-administered with Cyclosporine for Pediatric Patients 6 Months to Less than 12 Years of Age or 12 Years of Age and Older and Weighing Less than 30 kg Who Are HSCT Recipients
If oral or intravenous PREVYMIS is co-administered with cyclosporine in pediatric HSCT recipients 6 months to less than 12 years of age, the dosage of PREVYMIS may require adjustment as shown in Table 3 [see Drug Interactions (7.1 , 7.2 , 7.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
- If cyclosporine is initiated after starting PREVYMIS, the next dose of PREVYMIS should be the daily oral or intravenous dose co-administered with cyclosporine (Table 3)
- If cyclosporine is discontinued after starting PREVYMIS, the next dose of PREVYMIS should be the daily oral or intravenous dose administered without cyclosporine (Table 1 or Table 2)
- If cyclosporine dosing is interrupted due to high cyclosporine levels, no dose adjustment of PREVYMIS is needed.
| Body Weight | Daily Oral Dose | Tablets | Oral Pellets | Daily IV Refer to Subsection 2.10 for intravenous preparation and administration dosing instructions Dose |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 kg and above | 240 mg | One 240 mg tablet | Two 120 mg packets of oral pellets | 240 mg |
| 15 kg to less than 30 kg | 120 mg | Not recommended | One 120 mg packet of oral pellets | 120 mg |
| 7.5 kg to less than 15 kg | 60 mg | Not recommended | Three 20 mg packets of oral pellets | 60 mg |
| 6 kg to less than 7.5 kg | 40 mg | Not recommended | Two 20 mg packets of oral pellets | 40 mg |
Use in Patients with Renal Impairment
- For adult patients with creatinine clearance (CLcr) greater than 10 mL/min and pediatric patients with a similar degree of renal impairment (based on age-appropriate assessment of renal function), no dosage adjustment of PREVYMIS is required based on renal impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) , and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
- There are insufficient data in adult patients with CLcr 10 mL/min or less or in patients on dialysis or in pediatric patients with a similar degree of renal impairment (based on age-appropriate assessment of renal function) to make PREVYMIS dosing recommendations.
- In adult patients with CLcr less than 50 mL/min and in pediatric patients with a similar degree of renal impairment (based on age-appropriate assessment of renal function) receiving PREVYMIS injection, accumulation of the intravenous vehicle, hydroxypropyl betadex, may occur. Closely monitor serum creatinine levels in these patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] .
Use in Patients with Hepatic Impairment
No dosage adjustment of PREVYMIS is required for patients with mild (Child-Pugh Class A) or moderate (Child-Pugh Class B) hepatic impairment. PREVYMIS is not recommended for patients with severe (Child-Pugh Class C) hepatic impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7) ] .
Preparation and Administration of Oral Pellets
PREVYMIS oral pellets can be administered:
- orally after mixing with soft food or
- via NG tube or G tube.
Preparation and Administration Mixed with Soft Food
- See Instructions for Use for details on the preparation and administration of PREVYMIS oral pellets mixed with soft food.
- Do not crush or chew PREVYMIS oral pellets.
- Mix PREVYMIS oral pellets with 1 to 3 teaspoons of soft food (such as applesauce, yogurt, or pudding) that is at or below room temperature. Do not use hot food.
- Administer entire mixture within 10 minutes of mixing PREVYMIS oral pellets with the soft food.
Preparation and Administration via NG Tube or G Tube
See Instructions for Use , Table 4 (NG tube) and Table 5 (G tube) for details on the preparation and administration of PREVYMIS oral pellets via NG tube or G tube.
- Pour PREVYMIS oral pellets into a medicine cup containing room temperature water (see Initial Volume in Table 4 and Table 5). Do not mix PREVYMIS oral pellets with hot or cold (refrigerated) water.
- Wait 10 minutes. Do not shake or swirl the medicine cup. PREVYMIS oral pellets will not dissolve but will become loose or broken up. The entire mixture should be administered (see steps 3 and 4) within 2 hours.
- Stir the mixture with the syringe and administer entire mixture right away using the syringe and NG tube or G tube.
- Add room temperature water (see Rinse Volume in Table 4 and Table 5) to the medicine cup for rinsing, stir with a syringe and administer the entire rinse mixture using the syringe and NG tube or G tube.
- Flush the NG tube or G tube with the volume of water recommended by the NG or G tube manufacturer.
| Dosage | NG Tube Fr = French; PUR = polyurethane | Syringe Type With ENFit syringe, a medicine straw (large bore) is needed to aid withdrawal of the mixture from the medicine cup. | Mixing Container | Initial Volume (mL) | Rinse Volume (mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 120 mg to 480 mg | Any ≥ 8 Fr NG tube | Appropriately sized ENFit or catheter-tipped syringe | Medicine Cup | 15 | 15 |
| 40 mg to 80 mg | 5 Fr PUR NG tube or Any ≥ 6 Fr NG tube | 3 | 2 |
| Dosage | G Tube Fr = French; PUR = polyurethane | Syringe Type With ENFit syringe, a medicine straw (large bore) is needed to aid withdrawal of the mixture from the medicine cup. | Mixing Container | Initial Volume (mL) | Rinse Volume (mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 120 mg to 480 mg | Any G tube | Appropriately sized ENFit or catheter-tipped syringe | Medicine Cup | 15 | 15 |
| 40 mg to 80 mg | Any 12 Fr G tube | 3 | 2 |
Preparation and Administration of Intravenous Solution
PREVYMIS injection is supplied in 30 mL single-dose vials containing either 240 mg/12 mL per vial (20 mg/mL) or 480 mg/24 mL per vial (20 mg/mL).
PREVYMIS vials are for single use only. Discard any unused portion.
Preparation Instructions
- PREVYMIS must be diluted prior to intravenous (IV) use. Only 0.9% Sodium Chloride and 5% Dextrose are chemically and physically compatible with PREVYMIS injection.
- Do not shake PREVYMIS vial.
- Inspect vial contents for discoloration and particulate matter prior to dilution. PREVYMIS injection is a clear colorless solution and may contain a few product-related small translucent or white particles.
- Do not use the vial if the solution is cloudy, discolored, or contains matter other than a few small translucent or white particles.
- Once diluted, the solution of PREVYMIS is clear, and ranges from colorless to yellow. Variations of color within this range do not affect the quality of the product.
- Do not use PREVYMIS injection with IV bags and infusion set materials containing the plasticizer diethylhexyl phthalate (DEHP). Use only with IV bags and infusion set materials that are DEHP-free. Materials that are phthalate-free are also DEHP-free.
- Use compatible IV bags and infusion set materials. PREVYMIS injection is compatible with the following IV bags and infusion set materials. PREVYMIS injection is not recommended with any IV bags or infusion set materials not listed below (note that PREVYMIS injection is not recommended for use with polyurethane-containing IV administration set tubing).
- IV Bags Materials: Polyvinyl chloride (PVC), ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) and polyolefin (polypropylene and polyethylene)
- Infusion Sets Materials: PVC, polyethylene (PE), polybutadiene (PBD), silicone rubber (SR), styrene–butadiene copolymer (SBC), styrene-butadiene-styrene copolymer (SBS), polystyrene (PS)
- Plasticizers: Tris (2-ethylhexyl) trimellitate (TOTM), benzyl butyl phthalate (BBP)
- Catheters: Radiopaque polyurethane
- For the 480 mg or 240 mg dose , add PREVYMIS injection (see Table 6 ) into a 250 mL pre-filled IV bag containing either 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP or 5% Dextrose Injection, USP and mix bag gently. Do not shake.
- For the 120 mg or 60 mg dose , add PREVYMIS injection into a pre-filled IV bag containing either 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP or 5% Dextrose Injection, USP (see Table 6 ) and mix bag gently. Do not shake.
| PREVYMIS Dose | Volume of PREVYMIS 20 mg/mL to be Withdrawn from Vial | Volume of Diluent |
|---|---|---|
| 480 mg | 24 mL | 250 mL |
| 240 mg | 12 mL | 250 mL |
| 120 mg | 6 mL | 100 mL |
| 60 mg | 3 mL | 50 mL |
- For the 40 mg dose , prepare a dilution of PREVYMIS injection according to Table 7 in either 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP or 5% Dextrose Injection, USP and mix bag gently. Transfer 20 mL from the prepared dilution into an appropriately sized IV bag or syringe. Do not shake.
| PREVYMIS Dose | Preparation of 2 mg/mL PREVYMIS Dilution | Final Infusion Volume of the Prepared 2 mg/mL PREVYMIS Dilution |
|---|---|---|
| 40 mg | Add 5 mL of 20 mg/mL PREVYMIS to 45 mL of diluent (0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection or 5% Dextrose Injection) and mix gently | 20 mL |
Administration Instructions
- Administer the entire contents of the intravenous bag or syringe by intravenous infusion via a peripheral catheter or central venous line at a constant rate over 1 hour [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) ] .
- The diluted solution must be administered through a sterile 0.2 micron or 0.22 micron polyethersulfone (PES) in-line filter. Do not administer through a filter other than a sterile 0.2 micron or 0.22 micron PES in-line filter.
- Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration.
- Discard if the diluted solution is cloudy, discolored, or contains matter other than a few small translucent or white particles.
Storage of the Diluted Solution
The diluted solutions (as prepared in Table 6 or Table 7) are stable for up to 24 hours at room temperature or up to 48 hours under refrigeration at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) (this time includes storage of the diluted solution in the intravenous bag through the duration of infusion).
Compatible Drug Products Used for Intravenous Administration
Compatible Drug Products
The physical compatibility of PREVYMIS injection with selected injectable drug products was evaluated in two commonly available diluents. PREVYMIS should not be co-administered through the same intravenous line (or cannula) with other drug products and diluent combinations except those listed below. Refer to the respective prescribing information of the co-administered drug(s) to confirm compatibility of simultaneous co-administration.
List of Compatible Drug Products when PREVYMIS and Drug Products are Prepared in 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP:
- Ampicillin sodium, ampicillin sodium/sulbactam sodium, anti-thymocyte globulin, caspofungin, daptomycin, fentanyl citrate, fluconazole, furosemide, human insulin, magnesium sulfate, methotrexate, micafungin.
List of Compatible Drug Products when PREVYMIS and Drug Products are Prepared in 5% Dextrose Injection, USP:
- Amphotericin B (lipid complex) Amphotericin B (lipid complex) is compatible with PREVYMIS. However, Amphotericin B (liposomal) is incompatible [see Dosage and Administration (2.13) ] . , anidulafungin, cefazolin sodium, ceftaroline, ceftriaxone sodium, doripenem, famotidine, folic acid, ganciclovir sodium, hydrocortisone sodium succinate, morphine sulfate, norepinephrine bitartrate, pantoprazole sodium, potassium chloride, potassium phosphate, tacrolimus, telavancin, tigecycline.
Incompatible Drug Products and Other Materials Used for Intravenous Administration
Incompatible Drug Products
PREVYMIS injection is physically incompatible with amiodarone hydrochloride, amphotericin B (liposomal), aztreonam, cefepime hydrochloride, ciprofloxacin, cyclosporine, diltiazem hydrochloride, filgrastim, gentamicin sulfate, levofloxacin, linezolid, lorazepam, midazolam HCl, mycophenolate mofetil hydrochloride, ondansetron, palonosetron.
Incompatible IV Bags and Infusion Set Materials
PREVYMIS injection is incompatible with diethylhexyl phthalate (DEHP) plasticizers and polyurethane-containing IV administration set tubing.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets
- PREVYMIS 240 mg tablet: yellow oval tablet with "591" on one side and corporate logo on the other side.
- PREVYMIS 480 mg tablet: pink oval, bi-convex tablet with "595" on one side and corporate logo on the other side.
Oral Pellets
- PREVYMIS oral pellets: beige round pellets in packets. Each packet contains 20 mg letermovir.
- PREVYMIS oral pellets: beige round pellets in packets. Each packet contains 120 mg letermovir.
Injection
- PREVYMIS 240 mg/12 mL (20 mg/mL) injection: clear and colorless solution in a single-dose vial.
- PREVYMIS 480 mg/24 mL (20 mg/mL) injection: clear and colorless solution in a single-dose vial.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
No adequate human data are available to establish whether PREVYMIS poses a risk to pregnancy outcomes. In animal reproduction studies, embryo-fetal developmental toxicity (including fetal malformations) was observed in rats during the period of organogenesis at letermovir exposures (AUC) 11 times higher than human exposure at the recommended human dose (RHD). In rabbits, no embryo-fetal developmental toxicity was noted at exposures that were not maternally toxic (up to letermovir exposures 2 times higher than human exposure at the RHD). In a rat pre/post-natal development study, total litter loss was observed at maternal letermovir exposures approximately 2 times higher than human exposure at the RHD (see Data ) .
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
Letermovir was administered orally to pregnant rats at 0, 10, 50 or 250 mg/kg/day from gestation days 6 to 17. Developmental toxicities, including skeletal malformations and umbilical cord shortening, were observed at 250 mg/kg/day (approximately 11 times higher than human exposure at the RHD). In addition, decreased fetal body weight and skeletal variations (due to maternal toxicity) were observed at this dose. No embryo-fetal toxicities were observed at 50 mg/kg/day (approximately 3 times higher than human exposure at the RHD).
Letermovir was administered orally to pregnant rabbits at 0, 25, 75 or 225 mg/kg/day from gestation days 6 to 20. Developmental toxicities, including spontaneous abortion, increased post-implantation loss, and skeletal variations, were observed at a maternally toxic dose (225 mg/kg/day; approximately 2 times higher than human exposure at the RHD). No embryo-fetal toxicities were observed at 75 mg/kg/day (less than human exposure at the RHD).
In the pre/post-natal development study, letermovir was administered orally to pregnant rats at 0, 10, 45 or 180 mg/kg/day from gestation day 6 to lactation day 22. At 180 mg/kg/day (approximately 2 times higher than human exposure at the RHD), total litter loss due to stillbirth or possible maternal neglect was observed in 5 of 23 pregnant females by post-partum/lactation day 4. In surviving offspring, slight developmental delays in vaginal opening and pinna unfolding were accompanied by reduced body weight gain at this dose. No toxicities were observed at 45 mg/kg/day (similar to human exposure at the RHD).
Lactation
Risk Summary
It is not known whether letermovir is present in human breast milk, affects human milk production, or has effects on the breastfed child.
When administered to lactating rats, letermovir was present in the milk of lactating rats as well as the blood of nursing pups (see Data ) .
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for PREVYMIS and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from PREVYMIS or from the underlying maternal condition.
Data
In a lactation study, letermovir was excreted in milk when administered intravenously (at 10 mg/kg) to lactating rats on post-partum/lactation day 10. Letermovir was also detected in the blood of nursing pups on post-partum/lactation day 21 in the pre/post-natal developmental study.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Infertility
There are no data on the effect of letermovir on human fertility. Decreased fertility due to testicular toxicity was observed in male rats [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1 , 13.2) ] .
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of PREVYMIS have been established for:
- Prophylaxis of CMV infection and disease in pediatric CMV-seropositive recipients of an allogeneic HSCT 6 months of age and older and weighing at least 6 kg, and
- Prophylaxis of CMV disease in pediatric kidney transplant recipients 12 years of age and older and weighing at least 40 kg who are at high risk [D+/R-].
HSCT Recipients: The use of PREVYMIS for prophylaxis of CMV infection and disease in pediatric recipients of an allogeneic HSCT is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies in adults with additional pharmacokinetic and safety data from pediatric patients in Trial P030. The safety and pharmacokinetic results were similar to those in adults [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) , Adverse Reactions (6.1) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) , Clinical studies (14.2 , 14.4) ].
Kidney Transplant Recipients: The use of PREVYMIS for prophylaxis of CMV disease in high-risk [D+/R-] kidney transplant recipients 12 years of age and older and weighing at least 40 kg is supported by evidence from an adequate and well-controlled study in adults and safety data from pediatric HSCT recipients (Trial P030). Letermovir exposures are expected to be similar between adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older and weighing at least 40 kg [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) , Adverse Reactions (6.1) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) , Clinical studies (14.3 , 14.4) ].
The safety and effectiveness of PREVYMIS have not been established for:
- HSCT recipients less than 6 months of age or weighing less than 6 kg, or
- Kidney transplant recipients less than 12 years of age or weighing less than 40 kg.
Geriatric Use
Of the 373 subjects treated with PREVYMIS in Trial P001, 56 (15%) subjects were 65 years of age or older. Of the 144 subjects treated with PREVYMIS in Trial P040, 32 (22%) subjects were 65 years of age or older. Of the 292 subjects treated with PREVYMIS in Trial P002, 48 (16%) subjects were 65 years of age or older. Safety and efficacy were similar across older and younger subjects in each trial. No dosage adjustment of PREVYMIS is required based on age [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Renal Impairment
For adult patients with CLcr greater than 10 mL/min (by Cockcroft-Gault equation), and pediatric patients with a similar degree of renal impairment (based on age-appropriate assessment of renal function), no dosage adjustment of PREVYMIS is required based on renal impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . The safety of PREVYMIS in adult patients with end-stage renal disease (CLcr less than 10 mL/min) or in pediatric patients with a similar degree of renal impairment (based on age-appropriate assessment of renal function), including patients on dialysis, is unknown.
In adult patients with CLcr less than 50 mL/min and in pediatric patients with a similar degree of renal impairment (based on age-appropriate assessment of renal function) receiving PREVYMIS injection, accumulation of the intravenous vehicle, hydroxypropyl betadex, could occur . Closely monitor serum creatinine levels in these patients [see Dosage and Administration (2.7) and Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] .
Hepatic Impairment
No dosage adjustment of PREVYMIS is required for patients with mild (Child-Pugh Class A) or moderate (Child-Pugh Class B) hepatic impairment. PREVYMIS is not recommended for patients with severe (Child-Pugh Class C) hepatic impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- PREVYMIS is contraindicated in patients receiving pimozide or ergot alkaloids:
- Pimozide: Concomitant administration of PREVYMIS in patients receiving pimozide may result in increased concentrations of pimozide due to inhibition of cytochrome P450 3A (CYP3A) by letermovir, which may lead to QT prolongation and torsades de pointes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Drug Interactions (7.2 , 7.3) ] .
- Ergot alkaloids: Concomitant administration of PREVYMIS in patients receiving ergot alkaloids may result in increased concentrations of ergot alkaloids (ergotamine and dihydroergotamine) due to inhibition of CYP3A by letermovir, which may lead to ergotism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Drug Interactions (7.2 , 7.3) ] .
- PREVYMIS is contraindicated with pitavastatin and simvastatin when co-administered with cyclosporine. Concomitant administration of PREVYMIS in combination with cyclosporine may result in significantly increased pitavastatin or simvastatin concentrations, which may lead to myopathy or rhabdomyolysis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Drug Interactions (7.2 , 7.3) ] .
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Risk of Adverse Reactions or Reduced Therapeutic Effect Due to Drug Interactions: The concomitant use of PREVYMIS with certain drugs may result in potentially significant drug interactions, some of which may lead to adverse reactions (PREVYMIS or concomitant drugs) or reduced therapeutic effect of PREVYMIS or the concomitant drug. Consult the full prescribing information for contraindications and dosage recommendations for concomitant drugs. (4 , 5.1 , 7.1 , 7.2 , 7.3 )
- Risks Associated with Hydroxypropyl Betadex Excipient in Intravenous Formulation: Intravenous formulation of PREVYMIS contains the excipient hydroxypropyl betadex. PREVYMIS injection should be used only in patients unable to take oral therapy. If possible, intravenous administration should not exceed 4 weeks. In patients with renal impairment, accumulation of hydroxypropyl betadex may occur. Animal studies have shown the potential for hydroxypropyl betadex to cause ototoxicity. (5.2 , 8.6 , 13.2 )
Risk of Adverse Reactions or Reduced Therapeutic Effect Due to Drug Interactions
The concomitant use of PREVYMIS and certain drugs may result in potentially significant drug interactions, some of which may lead to adverse reactions (PREVYMIS or concomitant drugs) or reduced therapeutic effect of PREVYMIS or the concomitant drug [see Contraindications (4) and Drug Interactions (7.1 , 7.2 , 7.3) ] .
See Table 11 for steps to prevent or manage these possible or known significant drug interactions, including dosing recommendations. Consider the potential for drug interactions prior to and during PREVYMIS therapy; review concomitant medications during PREVYMIS therapy; and monitor for adverse reactions associated with PREVYMIS and concomitant medications.
Risks Associated with Hydroxypropyl Betadex Excipient in Intravenous Formulation
Intravenous formulation of PREVYMIS contains the excipient hydroxypropyl betadex. PREVYMIS injection should be used only in patients unable to take oral therapy and patients should be switched to oral PREVYMIS as soon as they are able to take oral medications. If possible, intravenous administration should not exceed 4 weeks [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) ].
In patients with renal impairment, accumulation of hydroxypropyl betadex may occur. In adult patients with CLcr less than 50 mL/min and in pediatric patients with a similar degree of renal impairment (based on age-appropriate assessment of renal function) receiving PREVYMIS injection, closely monitor serum creatinine levels [see Dosage and Administration (2.7) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6) ] .
Animal studies have shown the potential for hydroxypropyl betadex to cause ototoxicity [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.2) ]. The active ingredient, letermovir, is not known to be associated with ototoxicity.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
- Adult HSCT Patients: Most common adverse events (occurring in at least 10% of subjects in the PREVYMIS group and at a frequency at least 2% greater than placebo) are nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, peripheral edema, cough, headache, fatigue, and abdominal pain. (6.1 )
- Adult Kidney Transplant Patients: Most common adverse event (occurring in at least 10% of subjects in the PREVYMIS group and at a frequency greater than valganciclovir) is diarrhea. (6.1 )
- Pediatric Patients: Adverse events in pediatric patients are similar to adults. (6.1 )
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC at 1-877-888-4231 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch .
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adult CMV-seropositive Recipients [R+] of an Allogeneic HSCT
Prophylaxis Through Week 14 (~100 days) Post-HSCT
The safety of PREVYMIS was evaluated in a Phase 3 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (P001) in which 565 subjects were randomized and treated with PREVYMIS (N=373) or placebo (N=192) through Week 14 post-HSCT. Adverse events were those reported while subjects were on study medication or within two weeks of study medication completion/discontinuation. The mean time for reporting adverse events and laboratory abnormalities was approximately 22% longer in the PREVYMIS arm compared to the placebo arm.
Cardiac Adverse Events
The cardiac adverse event rate was higher in subjects receiving PREVYMIS (13%) compared to subjects receiving placebo (6%). The most common cardiac adverse events were tachycardia (reported in 4% of PREVYMIS subjects and in 2% of placebo subjects) and atrial fibrillation (reported in 3% of PREVYMIS subjects and in 1% of placebo subjects). Among those subjects who experienced one or more cardiac adverse events, 85% of PREVYMIS and 92% of placebo subjects had events reported as mild or moderate in severity.
Common Adverse Events
The rate of adverse events occurring in at least 10% of subjects in the PREVYMIS group and at a frequency at least 2% greater than placebo are outlined in Table 8.
| Adverse Events | PREVYMIS (N=373) | Placebo (N=192) |
|---|---|---|
| nausea | 27% | 23% |
| diarrhea | 26% | 24% |
| vomiting | 19% | 14% |
| peripheral edema | 14% | 9% |
| cough | 14% | 10% |
| headache | 14% | 9% |
| fatigue | 13% | 11% |
| abdominal pain | 12% | 9% |
Overall, similar proportions of subjects in each group discontinued study medication due to an adverse event (13% of PREVYMIS subjects vs. 12% of placebo subjects). The most frequently reported adverse event that led to study drug discontinuation was nausea, occurring in 2% of PREVYMIS subjects and 1% of placebo subjects. Hypersensitivity reaction, with associated moderate dyspnea, occurred in one subject following the first infusion of IV PREVYMIS after switching from oral PREVYMIS, leading to treatment discontinuation.
Laboratory Abnormalities
Selected laboratory abnormalities reported during treatment or within 2 weeks of stopping treatment are presented in Table 9.
| PREVYMIS N=373 | Placebo N=192 | |
|---|---|---|
| Absolute neutrophil count (cells/μL) | ||
| < 500 | 19% | 19% |
| 500 – < 750 | 4% | 7% |
| 750 – < 1000 | 8% | 9% |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | ||
| < 6.5 | 2% | 1% |
| 6.5 – < 8.0 | 14% | 15% |
| 8.0 – < 9.5 | 41% | 43% |
| Platelets (cells/μL) | ||
| < 25000 | 27% | 21% |
| 25000 – < 50000 | 17% | 18% |
| 50000 – < 100000 | 20% | 30% |
| Serum creatinine (mg/dL) | ||
| > 2.5 | 2% | 3% |
| > 1.5 – 2.5 | 17% | 20% |
The median time to engraftment (defined as absolute neutrophil count ≥ 500/mm 3 on 3 consecutive days after transplantation) was 19 days in the PREVYMIS group and 18 days in the placebo group.
Prophylaxis From Week 14 (~100 days) Through Week 28 (~200 days) Post-HSCT
The safety of PREVYMIS was evaluated in a Phase 3 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (P040) in which 218 subjects who completed PREVYMIS prophylaxis through ~100 days post-HSCT were randomized to treatment with PREVYMIS (N=144) or placebo (N=74) through Week 28 (~200 days) post-HSCT. Adverse events were those reported while subjects were on study drug or within two weeks of study drug completion/discontinuation.
The most commonly reported adverse events in P040 were similar to those reported in P001. Study drug was discontinued due to an adverse event in 5% of PREVYMIS subjects and 1% of placebo subjects. The cardiac adverse event rate was 4% in the PREVYMIS and placebo groups.
The rates of hematologic laboratory abnormalities were comparable in the PREVYMIS and placebo groups. Serum creatinine abnormalities > 1.5 mg/dL occurred in 15% of PREVYMIS and 8% of placebo subjects.
Adult Kidney Transplant Recipients [D+/R-]
The safety of PREVYMIS was evaluated in a Phase 3 randomized, double-blind, active comparator-controlled trial (P002) in which 589 subjects were treated with PREVYMIS (N=292) or valganciclovir (N=297) through Week 28 post-transplant. Adverse events were those reported while subjects were on study medication or within two weeks of study medication completion/discontinuation. In these subjects, diarrhea was reported in at least 10% of subjects in the PREVYMIS group and at a frequency greater than valganciclovir (PREVYMIS, 32%; valganciclovir, 29%). Study drug was discontinued due to an adverse event in 4% of PREVYMIS subjects and 14% of valganciclovir subjects. The most frequently reported adverse events that led to study drug discontinuation were neutropenia (PREVYMIS, 1%; valganciclovir, 2%) and leukopenia (PREVYMIS, 1%; valganciclovir, 5%).
Laboratory Abnormalities
Selected laboratory abnormalities reported through Week 28 post-transplant are presented in Table 10.
| PREVYMIS N=292 | Valganciclovir N=297 | |
|---|---|---|
| Absolute neutrophil count (cells/μL) | ||
| < 500 | 2% | 7% |
| 500 – < 750 | 1% | 4% |
| 750 – < 1000 | 1% | 8% |
| Total < 1000 | 5% | 18% |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | ||
| < 6.5 | 2% | 0% |
| 6.5 – < 8.0 | 4% | 5% |
| 8.0 – < 9.5 | 29% | 32% |
| Total < 9.5 | 34% | 37% |
| Platelets (cells/μL) | ||
| < 50000 | 0% | 0% |
| 50000 – < 100000 | 1% | 3% |
| Total < 100000 | 1% | 3% |
| Leukocytes (cells/μL) | ||
| < 1000 | 1% | 2% |
| 1000 – < 2000 | 5% | 19% |
| 2000 – < 2500 | 4% | 14% |
| Total < 2500 | 10% | 35% |
| Serum creatinine (mg/dL) | ||
| > 2.5 | 24% | 22% |
| > 1.5 – 2.5 | 49% | 52% |
| Total > 1.5 | 73% | 73% |
Pediatric Recipients of an Allogeneic HSCT
The safety of PREVYMIS was evaluated in 63 pediatric subjects aged 2 months to less than 18 years of age who received an allogeneic HSCT (P030). PREVYMIS was administered orally (tablet or pellet) or intravenously. The duration of PREVYMIS exposure ranged from 3 days to 102 days (median duration 84 days). The safety profile was consistent with the safety profile observed in clinical trials of PREVYMIS in adults [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4) and Clinical Studies (14.4) ].
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Dosage Adjustment: If PREVYMIS is co-administered with cyclosporine, the dosage of PREVYMIS should be decreased to 240 mg once daily in adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older. (2.4 ) If PREVYMIS is co-administered with cyclosporine in pediatric patients less than 12 years of age, dose adjustment may be required. (2.6 )
- Co-administration of PREVYMIS may alter the plasma concentrations of other drugs and other drugs may alter the plasma concentrations of PREVYMIS. Consult the full prescribing information prior to and during treatment for potential drug interactions. (2.4 , 2.6 , 4 , 5.1 , 7.1 , 7.2 , 7.3 , 7.4 , 12.3 )
Potential for Other Drugs to Affect PREVYMIS
Letermovir is a substrate of organic anion-transporting polypeptide 1B1/3 (OATP1B1/3) and P-glycoprotein (P-gp) transporters and UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1/3 (UGT1A1/3) enzymes. Co-administration of PREVYMIS with drugs that are inhibitors of OATP1B1/3 transporters may result in increases in letermovir plasma concentrations (Table 11).
Co-administration of PREVYMIS with inducers of transporters (e.g., P-gp) and/or enzymes (e.g., UGTs) is not recommended due to the potential for a decrease in letermovir plasma concentrations (see Table 11 ) .
Potential for PREVYMIS to Affect Other Drugs
Co-administration of PREVYMIS with midazolam results in increased midazolam plasma concentrations, indicating that letermovir is a moderate inhibitor of CYP3A [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . Co-administration of PREVYMIS with drugs that are CYP3A substrates may result in clinically relevant increases in the plasma concentrations of co-administered CYP3A substrates (Table 11) [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
Letermovir is an inhibitor of OATP1B1/3 transporters. Co-administration of PREVYMIS with drugs that are substrates of OATP1B1/3 transporters may result in a clinically relevant increase in plasma concentrations of co-administered OATP1B1/3 substrates (Table 11).
The magnitude of CYP3A- and OATP1B1/3-mediated drug interactions on co-administered drugs may be different when PREVYMIS is co-administered with cyclosporine. See the prescribing information for cyclosporine for information on drug interactions with cyclosporine.
Established and Other Potentially Significant Drug Interactions
If dose adjustments of concomitant medications are made due to treatment with PREVYMIS, doses should be readjusted after treatment with PREVYMIS is completed.
Table 11 provides a listing of established or potentially clinically significant drug interactions. The drug interactions described are based on adult studies conducted with PREVYMIS or are predicted drug interactions that may occur with PREVYMIS [see Contraindications (4) , Warnings and Precautions (5.1) , and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
| Concomitant Drug Class and/or Clearance Pathway: Drug Name | Effect on Concentration ↓ =decrease, ↑ =increase | Clinical Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-arrhythmic Agents | ||
| amiodarone | ↑ amiodarone | Close clinical monitoring for adverse events related to amiodarone is recommended during co-administration. Frequently monitor amiodarone concentrations when amiodarone is co-administered with PREVYMIS. |
| Antibiotics | ||
| nafcillin | ↓ letermovir | Co-administration of PREVYMIS and nafcillin is not recommended due to potential for loss of efficacy of PREVYMIS. |
| Anticoagulants | ||
| warfarin | ↓ warfarin | When PREVYMIS is co-administered with warfarin, frequently monitor International Normalized Ratio (INR) Refer to the respective prescribing information. . |
| Anticonvulsants | ||
| carbamazepine | ↓ letermovir | Co-administration of PREVYMIS and carbamazepine is not recommended due to potential for loss of efficacy of PREVYMIS. |
| phenobarbital | ↓ letermovir | Co-administration of PREVYMIS and phenobarbital is not recommended due to potential for loss of efficacy of PREVYMIS. |
| phenytoin | ↓ letermovir ↓ phenytoin | Co-administration of PREVYMIS and phenytoin is not recommended due to potential for loss of efficacy of PREVYMIS. |
| Antidiabetic Agents | ||
| Examples: glyburide, repaglinide, rosiglitazone | ↑ glyburide ↑ repaglinide ↑ rosiglitazone | When PREVYMIS is co-administered with glyburide, repaglinide, or rosiglitazone, frequently monitor glucose concentrations. When PREVYMIS is co-administered with cyclosporine, use of repaglinide is not recommended. |
| Antifungals | ||
| voriconazole These interactions have been studied [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . | ↓ voriconazole | If concomitant administration of voriconazole is necessary, closely monitor for reduced effectiveness of voriconazole. |
| Antimycobacterials | ||
| rifabutin | ↓ letermovir | Co-administration of PREVYMIS and rifabutin is not recommended due to potential for loss of efficacy of PREVYMIS. |
| rifampin | ↓ letermovir | Co-administration of PREVYMIS and rifampin is not recommended due to potential for loss of efficacy of PREVYMIS. |
| Antipsychotics | ||
| pimozide | ↑ pimozide | Co-administration is contraindicated due to risk of QT prolongation and torsades de pointes [see Contraindications (4) ] . |
| thioridazine | ↓ letermovir | Co-administration of PREVYMIS and thioridazine is not recommended due to potential for loss of efficacy of PREVYMIS. |
| Endothelin Antagonists | ||
| bosentan | ↓ letermovir | Co-administration of PREVYMIS and bosentan is not recommended due to potential for loss of efficacy of PREVYMIS. |
| Ergot Alkaloids | ||
| ergotamine, dihydroergotamine | ↑ ergotamine, dihydroergotamine | Co-administration is contraindicated due to risk of ergotism [see Contraindications (4) ] . |
| Herbal Products | ||
| St. John's wort ( Hypericum perforatum ) | ↓ letermovir | Co-administration of PREVYMIS and St. John's wort is not recommended due to potential for loss of efficacy of PREVYMIS. |
| HIV Medications | ||
| efavirenz | ↓ letermovir | Co-administration of PREVYMIS and efavirenz is not recommended due to potential for loss of efficacy of PREVYMIS. |
| etravirine | ↓ letermovir | Co-administration of PREVYMIS and etravirine is not recommended due to potential for loss of efficacy of PREVYMIS. |
| nevirapine | ↓ letermovir | Co-administration of PREVYMIS and nevirapine is not recommended due to potential for loss of efficacy of PREVYMIS. |
| HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors | ||
| atorvastatin | ↑ atorvastatin | When PREVYMIS is co-administered with atorvastatin, do not exceed an atorvastatin dosage of 20 mg daily. Closely monitor patients for myopathy and rhabdomyolysis. When PREVYMIS is co-administered with cyclosporine, use of atorvastatin is not recommended. |
| pitavastatin, simvastatin | ↑ HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors | Co-administration of PREVYMIS and pitavastatin or simvastatin is not recommended. When PREVYMIS is co-administered with cyclosporine, use of either pitavastatin or simvastatin is contraindicated due to significantly increased pitavastatin or simvastatin concentrations and risk of myopathy or rhabdomyolysis [see Contraindications (4) ] . |
| fluvastatin, lovastatin, pravastatin, rosuvastatin | ↑ HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors | When PREVYMIS is co-administered with these statins, a statin dosage reduction may be necessary. Closely monitor patients for myopathy and rhabdomyolysis. When PREVYMIS is co-administered with cyclosporine, use of lovastatin is not recommended. When PREVYMIS is co-administered with cyclosporine, refer to the statin prescribing information for specific statin dosing recommendations. |
| Immunosuppressants | ||
| cyclosporine | ↑ cyclosporine ↑ letermovir | Decrease the dosage of PREVYMIS to 240 mg once daily in adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . Dose adjustment may be required in pediatric patients less than 12 years of age [see Dosage and Administration (2.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . Frequently monitor cyclosporine whole blood concentrations during treatment and after discontinuation of PREVYMIS and adjust the dose of cyclosporine accordingly. |
| sirolimus | ↑ sirolimus | When PREVYMIS is co-administered with sirolimus, frequently monitor sirolimus whole blood concentrations during treatment and after discontinuation of PREVYMIS and adjust the dose of sirolimus accordingly. When PREVYMIS is co-administered with cyclosporine and sirolimus, refer to the sirolimus prescribing information for specific sirolimus dosing recommendations. |
| tacrolimus | ↑ tacrolimus | Frequently monitor tacrolimus whole blood concentrations during treatment and after discontinuation of PREVYMIS and adjust the dose of tacrolimus accordingly. |
| Proton Pump Inhibitors | ||
| omeprazole | ↓ omeprazole | Clinical monitoring and dose adjustment may be needed. |
| pantoprazole | ↓ pantoprazole | Clinical monitoring and dose adjustment may be needed. |
| Wakefulness-Promoting Agents | ||
| modafinil | ↓ letermovir | Co-administration of PREVYMIS and modafinil is not recommended due to potential for loss of efficacy of PREVYMIS. |
| CYP3A Substrates | ||
| Examples: alfentanil, fentanyl, midazolam, and quinidine | ↑ CYP3A substrate | When PREVYMIS is co-administered with a CYP3A substrate, refer to the prescribing information for dosing of the CYP3A substrate with a moderate CYP3A inhibitor. When PREVYMIS is co-administered with cyclosporine, the combined effect on CYP3A substrates may be similar to a strong CYP3A inhibitor. Refer to the prescribing information for dosing of the CYP3A substrate with a strong CYP3A inhibitor. CYP3A substrates pimozide and ergot alkaloids are contraindicated [see Contraindications (4) ] . |
Drugs without Clinically Significant Interactions with PREVYMIS
No clinically significant interactions were observed in adult clinical drug-drug interaction studies of letermovir and acyclovir, digoxin, mycophenolate mofetil, fluconazole, itraconazole, posaconazole, ethinyl estradiol, and levonorgestrel.
DESCRIPTION
PREVYMIS contains letermovir, an inhibitor of the CMV DNA terminase complex, and is administered orally or by intravenous infusion.
Letermovir has a molecular formula of C 29 H 28 F 4 N 4 O 4 and a molecular weight of 572.55. The chemical name for letermovir is (4 S )-2-{8-Fluoro-2-[4-(3- methoxyphenyl)piperazin-1-yl]-3-[2-methoxy-5- (trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-3,4-dihydroquinazolin-4-yl}acetic acid. Letermovir is very slightly soluble in water.
The chemical structure of letermovir is:
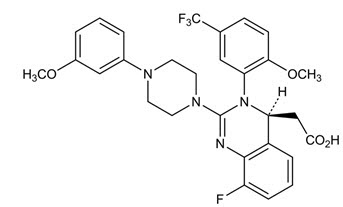
PREVYMIS is available as 240 mg and 480 mg tablets. PREVYMIS tablets contain either 240 mg or 480 mg of letermovir and the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone 25, and film-coated with a coating material containing the following inactive ingredients: hypromellose 2910, iron oxide red (only for 480 mg tablets), iron oxide yellow, lactose monohydrate, titanium dioxide, and triacetin. Carnauba wax is added as a polishing agent.
PREVYMIS is available as 20 mg and 120 mg packets of oral pellets. PREVYMIS packets of oral pellets contain either 20 mg or 120 mg of letermovir. PREVYMIS oral pellets contain the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone K-29/32, and are film-coated with a coating material containing the following inactive ingredients: hypromellose 2910, iron oxide red, iron oxide yellow, lactose monohydrate, titanium dioxide, and triacetin.
PREVYMIS is also available as 240 mg/12 mL (20 mg/mL) and 480 mg/24 mL (20 mg/mL) injection for intravenous infusion. PREVYMIS injection is a clear, preservative-free sterile solution and may contain a few small translucent or white particles in single-dose vials of either 240 mg or 480 mg per vial. Each 1 mL of solution contains 20 mg letermovir, hydroxypropyl betadex (150 mg), sodium chloride (3.1 mg), sodium hydroxide (1.2 mg), and Water for Injection. The amount of sodium hydroxide may be adjusted to achieve a pH of approximately 7.5.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
PREVYMIS is an antiviral drug against CMV [see Microbiology (12.4) ] .
Pharmacodynamics
Cardiac Electrophysiology
In a thorough QT trial in healthy adult subjects, letermovir at the therapeutic IV dose or at a dose of 2 times the approved IV dose did not prolong QTc to any clinically relevant extent.
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetic properties of letermovir are displayed in Table 12.
| Pharmacokinetics in Adult HSCT Recipients | |
| Treatment Regimen | Steady-state median (90% prediction interval) AUC (ng∙hr/mL) of PREVYMIS |
| 480 mg oral once daily, no cyclosporine | 34,400 (16,900, 73,700) |
| 480 mg IV once daily, no cyclosporine | 100,000 (65,300, 148,000) |
| 240 mg oral once daily, with cyclosporine | 60,800 (28,700, 122,000) |
| 240 mg IV once daily, with cyclosporine | 70,300 (46,200, 106,000) |
| Pharmacokinetics in Adult Kidney Transplant Recipients | |
| Treatment Regimen | Steady-state median (90% prediction interval) AUC (ng∙hr/mL) of PREVYMIS |
| 480 mg oral once daily, no cyclosporine | 62,700 (17,500, 139,000) |
| 240 mg oral once daily, with cyclosporine | 71,900 (42,400, 125,000) |
| Pharmacokinetics in Adult Healthy Subjects | |
| Treatment Regimen | Steady-state geometric mean AUC and Cmax of PREVYMIS |
| 480 mg oral once daily | Cmax: 13,000 ng/mL |
| AUC: 71,500 ng•hr/mL | |
| Dose proportionality | Greater than proportional following single and multiple oral or IV doses of PREVYMIS 240 mg and 480 mg |
| Accumulation ratio Based on geometric mean data. | Cmax: 1.03 AUC: 1.22 |
| Time to steady-state | 9-10 days |
| Absorption | |
| Bioavailability | Healthy adult subjects administered PREVYMIS without cyclosporine: 94% at an oral dose range of 240 mg to 480 mg Adult HSCT recipients administered PREVYMIS without cyclosporine: 35% with 480 mg oral once daily Adult HSCT recipients administered PREVYMIS with cyclosporine: 85% with 240 mg oral once daily Adult kidney transplant recipients administered PREVYMIS without cyclosporine: 56% 95% CI (46%, 65%) with 480 mg oral once daily |
| Median Tmax (hr) | 1.5 to 3.0 hr |
| Effect of food (relative to fasting) Values refer to geometric mean ratio [fed/fasted] percentage and 90% confidence interval back transformed from linear mixed-effects model performed on natural log-transformed values. The meal administered was a standard high fat and high calorie meal (33 grams protein, 65 grams carbohydrates, 58 grams fat; 920 total calories). | AUC: 99.63% [84.27% - 117.80%] Cmax: 129.82% [104.35% -161.50%] |
| Oral pellets versus tablet (fasting) | AUC and Cmax values were comparable when comparing PREVYMIS tablet (240 mg) and PREVYMIS oral pellets (2 X 120 mg) |
| Distribution | |
| Mean steady-state volume of distribution | 45.5 L following IV administration in adult HSCT recipients |
| % In vitro bound to human plasma proteins | 99% across the concentration range of 0.2 to 50 mg/L |
| In vitro blood-to plasma ratio | 0.56 across the concentration range of 0.1 to 10 mg/L |
| Metabolism | |
| In vitro metabolism | UGT1A1/1A3 (minor) |
| Drug-related component in plasma | 97% unchanged parent No major metabolites detected in plasma |
| Elimination | |
| Route of elimination | Hepatic uptake (OATP1B1/3) |
| Mean terminal t 1/2 (hr) | 12 hrs after dosing of PREVYMIS 480 mg IV once daily |
| % of dose excreted in feces Single oral administration of radiolabeled letermovir in mass balance study. | 93% |
| % of dose excreted in urine | <2% |
| % of unchanged drug excreted in feces | 70% |
Specific Populations
Pediatric Patients
Letermovir AUC in pediatric HSCT recipients was estimated using population pharmacokinetic analysis using Trial P030 data (see Table 13 and Table 14 ). Exposures for pediatric HSCT recipients for body weight bands 6 kg and above are within the range of exposures observed at the recommended doses of PREVYMIS in adults (see Table 12 ).
| Body Weight | Oral Dose, No Cyclosporine | Steady-state Median (90% Prediction Interval) Medians and 90% prediction intervals are based on simulations using the pediatric HSCT population PK model with inter-individual variability. | Oral Dose, With Cyclosporine | Steady-state Median (90% Prediction Interval) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 kg and above Includes pediatric patients 12 years of age and older or weighing ≥ 30 kg. | 480 mg | 38,500 (18,100, 78,100) | 240 mg | 50,200 (24,100, 102,000) |
| 15 kg to less than 30 kg | 240 mg | 39,600 (21,300, 71,800) | 120 mg | 53,200 (27,800, 102,000) |
| 7.5 kg to less than 15 kg | 120 mg | 32,900 (16,800, 61,200) | 60 mg | 42,300 (22,300, 81,500) |
| 6 kg to less than 7.5 kg Includes pediatric patients 6 months of age and older and weighing 6 kg to < 7.5 kg. | 80 mg | 29,400 (16,600, 54,100) | 40 mg | 39,200 (20,900, 71,800) |
| Body Weight | IV Dose, No Cyclosporine | Steady-state Median (90% Prediction Interval) Medians and 90% prediction intervals are based on simulations using the pediatric HSCT population PK model with inter-individual variability. | IV Dose, With Cyclosporine | Steady-state Median (90% Prediction Interval) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 kg and above Includes pediatric patients 12 years of age and older or weighing ≥ 30 kg. | 480 mg | 114,000 (53,900, 230,000) | 240 mg | 61,400 (29,300, 128,000) |
| 15 kg to less than 30 kg | 120 mg | 56,400 (29,100, 110,000) | 120 mg | 62,300 (32,100, 114,000) |
| 7.5 kg to less than 15 kg | 60 mg | 45,900 (24,500, 86,400) | 60 mg | 49,900 (26,300, 96,300) |
| 6 kg to less than 7.5 kg Includes pediatric patients 6 months of age and older and weighing 6 kg to < 7.5 kg. | 40 mg | 42,800 (23,800, 79,200) | 40 mg | 46,400 (26,300, 86,500) |
Age, Gender, Race, and Weight
Age (18 to 82 years), gender, race, and body weight (up to 100 kg) did not have a clinically significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of letermovir in adult subjects.
Renal Impairment
Clinical Study in a Renally Impaired Population
Letermovir AUC was approximately 1.9- and 1.4-fold higher in adult subjects with moderate (eGFR greater than or equal to 30 to 59 mL/min/1.73m 2 ) and severe (eGFR less than 30 mL/min/1.73m 2 ) renal impairment, respectively, compared to healthy adult subjects.
Post-kidney Transplant
Based on population pharmacokinetic analysis, letermovir AUC was approximately 1.1-, 1.3- and 1.4-fold higher in adult subjects with mild (CLcr greater than or equal to 60 to less than 90 mL/min), moderate (CLcr greater than or equal to 30 to less than 60 mL/min) and severe (CLcr greater than or equal to 15 to less than 30 mL/min) renal impairment, respectively, compared to adult subjects with CLcr greater than or equal to 90 mL/min.
Intravenous Formulation
Hydroxypropyl betadex present in the intravenous letermovir formulation is mainly eliminated by glomerular filtration. Decreased elimination of hydroxypropyl betadex has been reported in the literature in patients with severe renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
Letermovir AUC was approximately 1.6- and 3.8-fold higher in adult subjects with moderate (Child-Pugh Class B [CP-B], score of 7-9) and severe (Child-Pugh Class C [CP-C], score of 10-15) hepatic impairment, respectively, compared to healthy adult subjects.
Drug Interaction Studies
Drug interaction studies were performed in healthy adult subjects with PREVYMIS and drugs likely to be co-administered or drugs commonly used as probes for pharmacokinetic interactions (see Table 15 and Table 16 ) .
In vitro results indicate that letermovir is a substrate of drug metabolizing enzymes CYP3A, CYP2D6, UGT1A1, and UGT1A3, and transporters OATP1B1/3 and P-gp. Oxidative metabolism is considered to be a minor elimination pathway based on in vivo human data. Inhibitors of OATP1B1/3 may result in increases in letermovir plasma concentrations. Changes in letermovir plasma concentrations due to inhibition of P-gp/BCRP by itraconazole were not clinically relevant. Changes in letermovir plasma concentrations due to inhibition of UGTs are not anticipated to be clinically relevant.
Based on in vitro studies, the metabolism of letermovir is not mediated by CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C18, CYP2C19, CYP2E1, CYP4A11, UGT1A4, UGT1A6, UGT1A7, UGT1A8, UGT1A9, UGT1A10, UGT2B4, UGT2B7, UGT2B15, or UGT2B17. The transport of letermovir is not mediated by OATP2B1, OCT1, OAT1, BCRP, or MRP2 in vitro .
Letermovir is a time-dependent inhibitor and inducer of CYP3A in vitro . Co-administration of PREVYMIS with midazolam resulted in increased exposure of midazolam, indicating that the net effect of letermovir on CYP3A is moderate inhibition (see Table 16 ) . Based on these results, co-administration of PREVYMIS with CYP3A substrates may increase the plasma concentrations of the CYP3A substrates [see Contraindications (4) , Warnings and Precautions (5.1) , Drug Interactions (7.2 , 7.3) , and Table 11 ] . Letermovir is a reversible inhibitor of CYP2C8 in vitro . When co-administered with PREVYMIS, plasma concentrations of CYP2C8 substrates are predicted to be increased [see Table 11 in Drug Interactions (7.3) ]. Co-administration of PREVYMIS reduced the exposure of voriconazole, most likely due to the induction of voriconazole elimination pathways, CYP2C9 and CYP2C19. Co-administration of PREVYMIS with CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 substrates may decrease the plasma concentrations of the CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 substrates [see Table 11 in Drug Interactions (7.3) ] . Letermovir is an inducer of CYP2B6 in vitro ; the clinical relevance is unknown.
Letermovir inhibited efflux transporters P-gp, breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP), bile salt export pump (BSEP), multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 (MRP2), OAT3, and hepatic uptake transporter OATP1B1/3 in vitro . Co-administration of PREVYMIS with substrates of OATP1B1/3 transporters (e.g., atorvastatin, a known substrate of CYP3A, OATP1B1/3, and potentially BCRP) may result in a clinically relevant increase in plasma concentrations of OATP1B1/3 substrates [see Table 11 in Drug Interactions (7.3) ] . There were no clinically relevant changes in plasma concentrations of digoxin, a P-gp substrate, or acyclovir, an OAT3 substrate, following co-administration with PREVYMIS in clinical studies (see Table 16 ) . The effect of letermovir on BCRP, BSEP, and MRP2 substrates was not evaluated in clinical studies; the clinical relevance is unknown.
Based on in vitro results letermovir is not an inhibitor of CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1, UGT1A4, UGT1A6, UGT1A9, or UGT2B7 and is not an inducer of CYP1A2. Letermovir is not an inhibitor of OATP2B1, OCT1, OCT2, or OAT1 in vitro .
| Co-administered Drug | Regimen of Co-administered Drug | Letermovir Regimen | Geometric Mean Ratio [90% CI] of Letermovir PK with/without Co-administered Drug (No Effect=1.00) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC | Cmax | C24hr C12hr for tacrolimus | |||
| Abbreviations: PO= oral | |||||
| Antifungals | |||||
| fluconazole | 400 mg single dose PO | 480 mg single dose PO | 1.11 (1.01, 1.23) | 1.06 (0.93, 1.21) | 1.28 (1.15, 1.43) |
| itraconazole | 200 mg once daily PO | 480 mg once daily PO | 1.33 (1.17, 1.51) | 1.21 (1.05, 1.39) | 1.90 (1.58, 2.28) |
| Antimycobacterials | |||||
| rifampin | 600 mg single dose PO | 480 mg single dose PO | 2.03 (1.84, 2.26) | 1.59 (1.46, 1.74) | 2.01 (1.59, 2.54) |
| 600 mg single dose IV | 480 mg single dose PO | 1.58 (1.38, 1.81) | 1.37 (1.16, 1.61) | 0.78 (0.65, 0.93) | |
| 600 mg once daily PO | 480 mg once daily PO | 0.81 (0.67, 0.98) | 1.01 (0.79, 1.28) | 0.14 (0.11, 0.19) | |
| 600 mg once daily PO (24 hours after rifampin) These data are the effect of rifampin on letermovir 24 hours after final rifampin dose. | 480 mg once daily PO | 0.15 (0.13, 0.17) | 0.27 (0.22, 0.31) | 0.09 (0.06, 0.12) | |
| Immunosuppressants | |||||
| cyclosporine | 200 mg single dose PO | 240 mg once daily PO | 2.11 (1.97, 2.26) | 1.48 (1.33, 1.65) | 2.06 (1.81, 2.35) |
| mycophenolate mofetil | 1 g single dose PO | 480 mg once daily PO | 1.18 (1.04, 1.32) | 1.11 (0.92, 1.34) | 1.39 (1.12, 1.74) |
| tacrolimus | 5 mg single dose PO | 80 mg twice daily PO | 1.02 (0.97, 1.07) | 0.92 (0.84, 1.00) | 1.02 (0.93, 1.12) |
| Co-administered Drug | Regimen of Co-administered Drug | Letermovir Regimen | Geometric Mean Ratio [90% CI] of Co-administered Drug PK with/without Letermovir (No Effect=1.00) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC | Cmax | C24hr C12hr reported for voriconazole. | |||
| Abbreviations: PO=oral | |||||
| CYP3A Substrates | |||||
| midazolam | 1 mg single dose IV | 240 mg once daily PO | 1.47 (1.37, 1.58) | 1.05 (0.94, 1.17) | 2.74 (2.16, 3.49) |
| 2 mg single dose PO | 240 mg once daily PO | 2.25 (2.04, 2.48) | 1.72 (1.55, 1.92) | Not available | |
| P-gp Substrates | |||||
| digoxin | 0.5 mg single dose PO | 240 mg twice daily PO | 0.88 (0.80, 0.96) | 0.75 (0.63, 0.89) | 0.90 (0.84, 0.96) |
| Immunosuppressants | |||||
| cyclosporine | 50 mg single dose PO | 240 mg once daily PO | 1.66 (1.51, 1.82) | 1.08 (0.97, 1.19) | 2.19 (1.80, 2.66) |
| mycophenolate mofetil | 1 g single dose PO | 480 mg once daily PO | 1.08 (0.97, 1.20) | 0.96 (0.82, 1.12) | 1.04 (0.86, 1.27) |
| tacrolimus | 5 mg single dose PO | 480 mg once daily PO | 2.42 (2.04, 2.88) | 1.57 (1.32, 1.86) | 2.53 (2.12, 3.03) |
| sirolimus | 2 mg single dose PO | 480 mg once daily PO | 3.40 (3.01, 3.85) | 2.76 (2.48, 3.06) | 3.15 (2.80, 3.55) |
| Antifungals and Antivirals | |||||
| acyclovir | 400 mg single dose PO | 480 mg once daily PO | 1.02 (0.87, 1.2) | 0.82 (0.71, 0.93) | 1.13 (0.94, 1.36) |
| fluconazole | 400 mg single dose PO | 480 mg single dose PO | 1.03 (0.99, 1.08) | 0.95 (0.92, 0.99) | 1.04 (1.00, 1.08) |
| itraconazole | 200 mg once daily PO | 480 mg once daily PO | 0.76 (0.71, 0.81) | 0.84 (0.76, 0.92) | 0.67 (0.61, 0.73) |
| posaconazole | 300 mg single dose PO | 480 mg once daily PO | 0.98 (0.82, 1.17) | 1.11 (0.95, 1.29) | 1.10 (0.94, 1.30) |
| voriconazole | 200 mg twice daily PO | 480 mg once daily PO | 0.56 (0.51, 0.62) | 0.61 (0.53, 0.71) | 0.49 (0.42, 0.57) |
| HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors | |||||
| atorvastatin | 20 mg single dose PO | 480 mg once daily PO | 3.29 (2.84, 3.82) | 2.17 (1.76, 2.67) | 3.62 (2.87, 4.55) |
| Oral Contraceptives | |||||
| ethinyl estradiol (EE) /levonorgestrel (LNG) | 0.03 mg EE single dose PO | 480 mg once daily PO | 1.42 (1.32, 1.52) | 0.89 (0.83, 0.96) | 1.57 (1.45, 1.70) |
| 0.15 mg LNG single dose PO | 1.36 (1.30, 1.43) | 0.95 (0.86, 1.04) | 1.38 (1.32, 1.46) | ||
Microbiology
Mechanism of Action
Letermovir inhibits the CMV DNA terminase complex (pUL51, pUL56, and pUL89) which is required for viral DNA processing and packaging. Biochemical characterization and electron microscopy demonstrated that letermovir affects the production of proper unit length genomes and interferes with virion maturation. Genotypic characterization of virus resistant to letermovir confirmed that letermovir targets the terminase complex.
Antiviral Activity
The median EC 50 value of letermovir against a collection of clinical CMV isolates in a cell-culture model of infection was 2.1 nM (range = 0.7 nM to 6.1 nM, n = 74). There was no significant difference in EC 50 value by CMV gB genotype (gB1=29; gB2=27; gB3=11; and gB4=3).
Combination Antiviral Activity
No antagonism of the antiviral activity was seen when letermovir was combined with CMV DNA polymerase inhibitors (cidofovir, foscarnet, or ganciclovir).
Viral Resistance
In Cell Culture
CMV mutants with reduced susceptibility to letermovir have been selected in cell culture and the resistance mutations map to UL51, UL56, and UL89. Resistance-associated substitutions were found in pUL51 (P91S, A95V), pUL56 (C25F, S229F, V231A/L, N232Y, V236A/L/M, E237D, L241P, T244K/R, L254F, L257F/I, K258E, F261C/L/S, Y321C, C325F/R/W/Y, L328V, M329T, A365S, N368D, R369G/M/S), and pUL89 (N320H, D344E). EC 50 values for recombinant CMV mutants expressing these substitutions are 1.6- to 9,300-fold higher than those for the wild-type reference virus.
In Clinical Studies
In a Phase 2b trial evaluating letermovir or placebo in 131 adult HSCT recipients, DNA sequence analysis of a select region of UL56 (amino acids 231 to 369) was performed on samples obtained from 12 letermovir-treated subjects who experienced prophylaxis failure and for whom on-treatment samples were available for analysis. One subject had a letermovir resistance substitution, pUL56 V236M (19-50-fold reduction in susceptibility).
In a Phase 3 trial (P001), DNA sequence analysis of the entire coding regions of UL56 and UL89 was performed on samples obtained from 50 letermovir-treated adult subjects who had received at least one dose of study drug and experienced prophylaxis failure and for whom samples were available for analysis. The pUL56 substitutions V236M (19-50-fold reduction), E237G (13-fold reduction), C325W (9300-fold reduction), and R369T (52-fold reduction) were detected in 3 subjects; however, no 2 subjects had substitutions at the same positions.
In a Phase 3 trial (P040), DNA sequence analysis of the entire coding regions of UL51, UL56 and UL89 was performed on samples obtained from 32 adult subjects (regardless of treatment group) who experienced prophylaxis failure or who discontinued early with CMV viremia. No letermovir resistance-associated substitutions were detected above the validated assay limit.
In a Phase 3 trial (P002), DNA sequence analysis of the entire coding regions of UL51, UL56 and UL89 was performed on samples obtained from 52 letermovir-treated adult subjects who experienced CMV disease or who discontinued early with CMV viremia. No previously characterized resistance-associated substitutions were identified. Novel substitutions were detected in letermovir-treated subjects at resistance-associated positions (pUL56 S229Y [2-fold reduction; n=1] and pUL56 M329I [0.77-fold reduction; n=9]) at low frequencies, ranging between 0.05 to 0.07.
In a Phase 2b trial (P030), DNA sequence analysis of the entire coding regions of UL51, UL56 and UL89 was performed on samples obtained from 10 letermovir-treated pediatric subjects at a visit for evaluation of CMV infection. A total of 2 letermovir resistance-associated substitutions both mapping to pUL56 were detected in 2 subjects. One subject had the substitution C325W (9300-fold reduction), and the other had R369S (38-fold reduction).
Cross Resistance
Cross resistance is not likely with drugs outside of this class. Letermovir is fully active against viral populations with substitutions conferring resistance to CMV DNA polymerase inhibitors (cidofovir, foscarnet, and ganciclovir). These DNA polymerase inhibitors are expected to be fully active against viral populations with substitutions conferring resistance to letermovir.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis and Mutagenesis
Letermovir was not genotoxic in in vitro or in vivo assays, including microbial mutagenesis assays, chromosomal aberration in Chinese hamster ovary cells, and in an in vivo mouse micronucleus study.
Letermovir was not carcinogenic in a 6-month RasH2 transgenic mouse study up to the highest doses tested (150 mg/kg/day in males and 300 mg/kg/day in females). Based on a comprehensive assessment of the available toxicology data and the CMV-specific target, letermovir is not expected to be carcinogenic in humans.
Impairment of Fertility
In a fertility and early embryonic development study in rats, no effects of letermovir on female fertility were observed at letermovir exposures (AUC) approximately 5 times higher than human exposure at the RHD.
In male rat fertility studies, decreased fertility associated with irreversible testicular toxicity was observed at ≥180 mg/kg/day (greater than or equal to 3 times the human exposure at the RHD). No fertility or testicular effects were observed at dose levels resulting in letermovir exposures (AUC) similar to human exposure at the RHD [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.2) ] .
Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Testicular toxicity in rats observed at ≥180 mg/kg/day (greater than or equal to 3 times the human exposure at the RHD) was characterized by decreased testis weight, bilateral seminiferous tubular degeneration, decreased sperm count and motility, and resultant decreased male fertility. Male reproductive system toxicities were not observed in either a monkey testicular toxicity study up to 240 mg/kg/day (approximately 2 times higher than human exposure at the RHD), or a general toxicology study in mice up to 250 mg/kg/day (approximately 3 times higher than human exposure at the RHD).
The excipient, hydroxypropyl betadex, present in the IV letermovir formulation, has been associated with hearing loss resulting from damage to the inner ear in multiple animal species. In published studies in rats, a single subcutaneous dose of 2000 mg/kg hydroxypropyl betadex resulted in changes in hearing parameters and associated decreases in outer hair cells in the inner ear. These findings were observed at hydroxypropyl betadex levels approximately 3 times higher than those present in the letermovir IV drug product at the MRHD, based on body surface area (BSA) comparisons. No adverse changes in hearing parameters or hair cell populations in the inner ear were observed in rats following a single subcutaneous dose of 1000 mg/kg hydroxypropyl betadex, which corresponds to levels approximately 1.5 times higher than those present in the letermovir IV drug product at the MRHD, based on BSA comparisons [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] .
CLINICAL STUDIES
Overview of Clinical Studies
An overview of the trials contributing to the assessment of efficacy and safety of PREVYMIS in HSCT and kidney transplant recipients is provided in Table 17.
| Trial (NCT Number) | Population | Trial Arms (N) N represents the number of subjects treated. | Duration of Prophylaxis Post-Transplant | Efficacy Endpoint |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P001 (NCT02137772) | Adult allogeneic HSCT recipients [R+] | PREVYMIS (373) Placebo (192) | Through Week 14 | Clinically significant CMV infection through Week 24 post-HSCT |
| P040 (NCT03930615) | Adult allogeneic HSCT recipients [R+] at risk for late CMV infection and disease | PREVYMIS (144) Placebo (74) | Extension of prophylaxis from Week 14 through Week 28 | Clinically significant CMV infection through Week 28 post-HSCT |
| P002 (NCT03443869) | Adult kidney transplant recipients [D+/R-] | PREVYMIS (292) Valganciclovir (297) | Through Week 28 | CMV disease through Week 52 post-kidney transplant |
| P030 (NCT03940586) | Pediatric allogeneic HSCT recipients | PREVYMIS (63) | Through Week 14 | Clinically significant CMV infection through Week 24 post-HSCT |
Adult CMV-seropositive Recipients [R+] of an Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant (Trial P001 and Trial P040)
Prophylaxis Through Week 14 (~100 days) Post-HSCT (Trial P001)
To evaluate PREVYMIS prophylaxis as a preventive strategy for CMV infection or disease in transplant recipients at high risk for CMV reactivation, the efficacy of PREVYMIS was assessed in a multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled Phase 3 Trial (P001, NCT02137772) in adult CMV-seropositive recipients [R+] of an allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT). Subjects were randomized (2:1) to receive either PREVYMIS at a dose of 480 mg once daily adjusted to 240 mg when co-administered with cyclosporine, or placebo. Randomization was stratified by investigational site and risk level for CMV reactivation at the time of study entry. Study drug was initiated after HSCT (at any time from Day 0 to Day 28 post-HSCT) and continued through Week 14 post-HSCT. Study drug was administered either orally or intravenously; the dose of PREVYMIS was the same regardless of the route of administration. Subjects received CMV DNA monitoring weekly until post-HSCT Week 14 and then bi-weekly until post-HSCT Week 24, with initiation of standard-of-care CMV pre-emptive therapy if CMV viremia was considered clinically significant. Subjects had continued follow-up through Week 48 post-HSCT.
Among the 565 treated subjects, 70 subjects were found to have CMV viremia prior to study drug initiation and were therefore excluded from the efficacy analyses. The efficacy population consisted of 325 subjects who received PREVYMIS (including 91 subjects who received at least one IV dose) and 170 who received placebo (including 41 subjects who received at least one IV dose). The IV formulation of PREVYMIS was used at investigators' discretion in subjects who were unable to take oral therapy (e.g., unable to tolerate oral intake). The median time to starting study drug was 8 days after transplantation. Thirty-four percent (34%) of subjects were engrafted at baseline. The median age was 55 years (range: 18 to 76 years). 57% were male; 84% were White; 9% were Asian; 2% were Black or African American; and 5% were other (American Indian or Alaska Native, multiple, and missing). 7% were Hispanic or Latino; 89% not Hispanic or Latino; and 4% other (not reported, unknown, and missing).
At baseline, 30% of all subjects had one or more of the following factors associated with increased risk for CMV reactivation (high risk stratum): Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA)-related donor with at least one mismatch at one of the following three HLA-gene loci: HLA-A, -B or –DR; haploidentical donor; unrelated donor with at least one mismatch at one of the following four HLA-gene loci: HLA-A, -B, -C and -DRB1; use of umbilical cord blood as stem cell source; use of ex vivo T-cell-depleted grafts; Grade 2 or greater Graft-Versus-Host Disease (GVHD) requiring systemic corticosteroids. The remaining 70% of subjects did not meet any of these high risk stratum criteria and were therefore included in the low risk stratum. Additionally, 48% of subjects received a myeloablative regimen, 51% were receiving cyclosporine, and 43% were receiving tacrolimus. The most common primary reasons for transplant were acute myeloid leukemia (38%), myelodysplastic syndrome (16%), and lymphoma (12%).
Clinically Significant CMV Infection
The primary efficacy endpoint of Trial P001 was the incidence of clinically significant CMV infection through Week 24 post-HSCT (prophylaxis failure). Clinically significant CMV infection was defined as the occurrence of either CMV end-organ disease, or initiation of anti-CMV pre-emptive therapy (PET) based on documented CMV viremia (using the Roche COBAS® AmpliPrep/COBAS TaqMan® assay, LLoQ is 137 IU/mL, which is approximately 150 copies/mL) and the clinical condition of the subject. The protocol-specified guidance for CMV DNA thresholds for the initiation of PET during the treatment period was ≥ 150 copies/mL or > 300 copies/mL for subjects in the high and low risk strata, respectively. From Week 14 through Week 24, the threshold was >300 copies/mL for both high and low risk strata subjects. The Non-Completer=Failure (NC=F) approach was used, where subjects who discontinued from the trial prior to Week 24 post-HSCT or had a missing outcome at Week 24 post-HSCT were counted as failures.
Efficacy results from Trial P001 are shown in Table 18.
| Parameter | PREVYMIS (N=325) | Placebo (N=170) |
|---|---|---|
| Note: FAS=Full analysis set; FAS includes randomized subjects who received at least one dose of study medication, and excludes subjects with detectable CMV DNA at baseline. Approach to handling missing values: Non-Completer=Failure (NC=F) approach. With NC=F approach, failure was defined as all subjects who developed clinically significant CMV infection or prematurely discontinued from the study or had a missing outcome through Week 24 post-HSCT visit window. | ||
| Proportion of subjects who failed prophylaxis | 38% | 61% |
| Reasons for failures The categories of failure are mutually exclusive and based on the hierarchy of categories in the order listed. | ||
| Clinically significant CMV infection by Week 24 Through Week 14, 8% of subjects in the PREVYMIS group and 39% of subjects in the placebo group experienced clinically significant CMV infection. | 18% | 42% |
| Initiation of PET based on documented CMV viremia | 16% | 40% |
| CMV end-organ disease | 2% | 2% |
| Discontinued from study before Week 24 Reasons for discontinuation included adverse event, death, lost to follow-up, physician decision, and withdrawal by subject. | 17% | 16% |
| Missing outcome in Week 24 visit window | 3% | 3% |
| Stratum-adjusted treatment difference (PREVYMIS-Placebo) 95% CI and p-value for the treatment differences in percent response were calculated using stratum-adjusted Mantel-Haenszel method with the difference weighted by the harmonic mean of sample size per arm for each stratum (high or low risk). | ||
| Difference (95% CI) | -23.5 (-32.5, -14.6) p-value <0.0001. | |
Efficacy results were consistent across high and low risk strata for CMV reactivation. The time to clinically significant CMV infection is shown in Figure 1. Among subjects in the PREVYMIS group, the cumulative rate of clinically significant CMV infection increased from 6.8% at the end of prophylaxis (Week 14) to 18.9% at Week 24. In the placebo group, the cumulative rate of clinically significant CMV infection increased from 41.3% at Week 14 to 44.3% at Week 24 [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) ].
| Figure 1: P001: Kaplan-Meier Plot of Time to Onset of Clinically Significant CMV Infection Through Week 24 Post-Transplant in HSCT Recipients (FAS Population) |
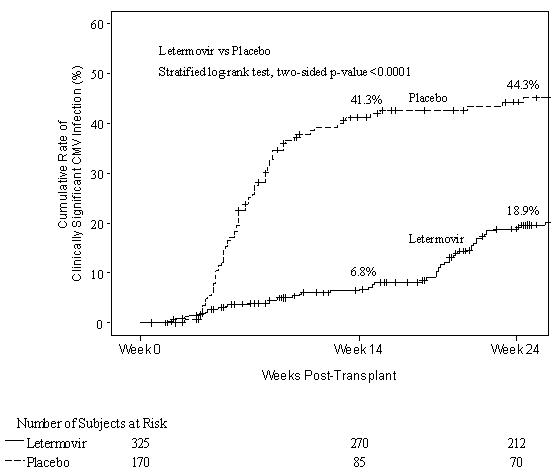 |
Post-hoc analysis demonstrated that among PREVYMIS-treated subjects, inclusion in the high risk stratum for CMV reactivation at baseline, occurrence of GVHD, and steroid use at any time after randomization may be associated with the development of clinically significant CMV infection between Week 14 and Week 24 post-HSCT.
Mortality
The Kaplan-Meier event rate for all-cause mortality in the PREVYMIS vs. placebo groups was 12% vs. 17% at Week 24 post-HSCT, and 24% vs. 28% at Week 48 post-HSCT.
Prophylaxis From Week 14 (~100 days) Through Week 28 (~200 days) Post-HSCT (Trial P040)
The efficacy of extending PREVYMIS prophylaxis from Week 14 (~100 days) through Week 28 (~200 days) post-HSCT in patients at risk for late CMV infection and disease was assessed in a multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled Phase 3 trial (P040, NCT03930615) in adult CMV-seropositive recipients [R+] of an allogeneic HSCT. Eligible subjects who completed PREVYMIS prophylaxis through ~100 days post-HSCT were randomized (2:1) to receive PREVYMIS or placebo from Week 14 through Week 28 post-HSCT. Subjects received PREVYMIS at a dose of 480 mg once daily (adjusted to 240 mg when co-administered with cyclosporine) or placebo. Study drug was administered either orally or IV; the dose of PREVYMIS was the same regardless of the route of administration. One subject received IV PREVYMIS for 2 days. Subjects were monitored through Week 28 post-HSCT for the primary efficacy endpoint with continued off-treatment follow-up through Week 48 post-HSCT.
Among the 218 treated subjects, 144 subjects received PREVYMIS and 74 received placebo. The median age was 55 years (range: 20 to 74 years); 62% were male; 79% were white; 11% were Asian; 2% were Black; 1% were multiple races; 6% had missing race; and 10% were Hispanic or Latino.
At study entry, all subjects had risk factors for late CMV infection and disease, with 64% having two or more risk factors. The risk factors included: HLA-related (sibling) donor with at least one mismatch at one of the following three HLA-gene loci: HLA-A, -B or –DR; haploidentical donor; unrelated donor with at least one mismatch at one of the following four HLA-gene loci: HLA-A, -B, -C and -DRB1; use of umbilical cord blood as stem cell source; use of ex vivo T-cell-depleted grafts; receipt of anti-thymocyte globulin; receipt of alemtuzumab; use of systemic prednisone (or equivalent) at a dose of ≥1 mg/kg of body weight per day. The most common reasons for transplant were acute myeloid leukemia (42%), acute lymphocytic leukemia (15%), and myelodysplastic syndrome (11%).
Clinically Significant CMV Infection
The primary efficacy endpoint of Trial P040 was the incidence of clinically significant CMV infection through Week 28 post-HSCT. Clinically significant CMV infection was defined as the occurrence of either CMV end-organ disease, or initiation of anti-CMV PET based on documented CMV viremia and the clinical condition of the subject. The Observed Failure (OF) approach was used, where subjects who discontinued prematurely from the study without viremia or were missing data at the timepoint were not counted as failures. The number of subjects who discontinued from the study before Week 28 without viremia was 14 (9.7%) in the PREVYMIS arm and 0 in the placebo arm. The number of subjects with a missing outcome in the Week 28 visit window was 3 (2.1%) in the PREVYMIS arm and 4 (5.4%) in the placebo arm, none had prior viremia.
Efficacy results from Trial P040 are shown in Table 19. Efficacy was consistent across subgroups based on participant characteristics (age, gender, race) and risk factors for late CMV infection and disease.
| Parameter | PREVYMIS (~200 days PREVYMIS) (N=144) | Placebo (~100 days PREVYMIS) (N=74) |
|---|---|---|
| Approach to handling missing values: Observed Failure (OF) approach. With the OF approach, failure was defined as all subjects who developed clinically significant CMV infection or discontinued prematurely from the study with CMV viremia from Week 14 (~100 days) through Week 28 (~200 days) post-HSCT. | ||
| N = Number of subjects in each treatment group. | ||
| Failures The categories of failure are mutually exclusive and based on the hierarchy of categories in the order listed. | 2.8% | 18.9% |
| Clinically significant CMV infection from Week 14 through Week 28 Clinically significant CMV infection was defined as CMV end-organ disease (proven or probable) or initiation of PET based on documented CMV viremia and the clinical condition of the subject. | 1.4% | 17.6% |
| Initiation of PET based on documented CMV viremia | 0.7% | 14.9% |
| CMV end-organ disease | 0.7% | 2.7% |
| Discontinued from study with CMV viremia before Week 28 | 1.4% | 1.4% |
| Stratum-adjusted treatment difference (PREVYMIS (~200 days PREVYMIS)-Placebo (~100 days PREVYMIS)) The 95% CIs and p-value for the treatment differences in percent response were calculated using stratum-adjusted Mantel-Haenszel method with the difference weighted by the harmonic mean of sample size per arm for each stratum (haploidentical donor yes or no). A one-sided p-value ≤0.0249 was used for declaring statistical significance. | ||
| Difference (95% CI) | -16.1 (-25.8, -6.5) p-value = 0.0005 | |
The time to clinically significant CMV infection is shown in Figure 2. Among subjects in the PREVYMIS group, the cumulative rate of clinically significant CMV infection increased from 1.6% at the end of prophylaxis (Week 28) to 15.6% at Week 38. In the placebo group, the cumulative rate of clinically significant CMV infection increased from 17.6% at Week 28 to 19.0% at Week 38. There were no additional cases of clinically significant CMV infection in either group between Weeks 38 and 48 [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) ].
| Figure 2: Trial P040 Kaplan-Meier Plot of Time to Onset of Clinically Significant CMV Infection From Week 14 Through Week 48 Post-transplant in HSCT Recipients at Risk for Late CMV Infection and Disease (FAS Population) |
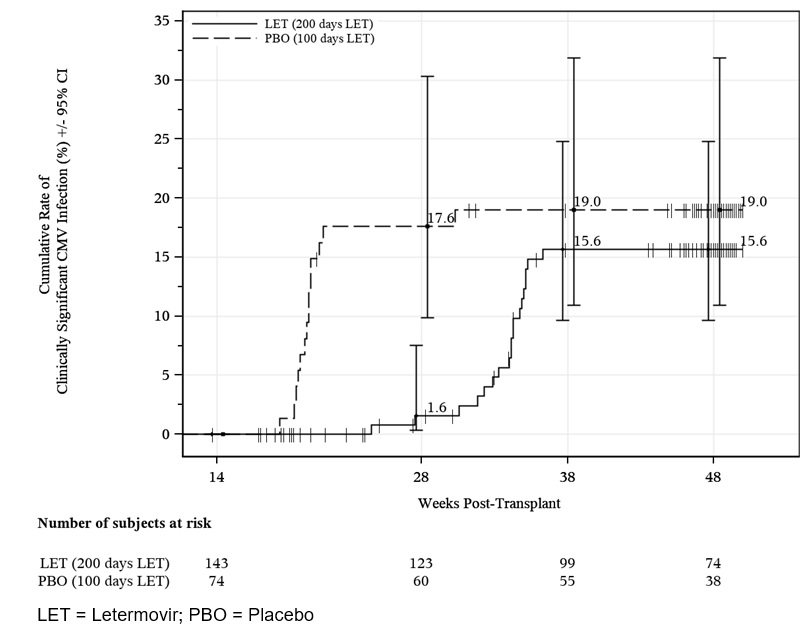 |
Adult CMV-seronegative Recipients of a Kidney Transplant from a CMV-seropositive Donor [D+/R-] (Trial P002)
To evaluate PREVYMIS prophylaxis as a preventive strategy for CMV disease in kidney transplant recipients, the efficacy of PREVYMIS was assessed in a multicenter, double-blind, active comparator-controlled non-inferiority Phase 3 trial (P002, NCT03443869) in adult kidney transplant recipients at high risk [D+/R-]. Subjects were randomized (1:1) to receive either PREVYMIS or valganciclovir. PREVYMIS was administered at a dose of 480 mg once daily (adjusted to 240 mg when co-administered with cyclosporine). PREVYMIS was given concomitantly with acyclovir. Valganciclovir was given concomitantly with a placebo to acyclovir. Randomization was stratified by the use or nonuse of highly cytolytic, anti-lymphocyte immunotherapy during induction. Study drug was initiated between Day 0 and Day 7 post-kidney transplant and continued through Week 28 (~200 days) post-transplant. Study drug was administered either orally or IV; the dose of PREVYMIS was the same regardless of the route of administration. Three subjects received IV PREVYMIS for a mean duration of 1.7 days. Subjects were monitored through Week 52 post-transplant.
Among the 589 treated subjects, 292 subjects received PREVYMIS and 297 received valganciclovir. The median age was 51 years (range: 18 to 82 years); 72% were male; 84% were White; 9% were Black; 3% were multiple; 2% were Asian; 1% Alaskan native or American Indian; 17% were Hispanic or Latino; and 60% received a kidney from a deceased donor. The most common primary reasons for transplant were congenital cystic kidney disease (17%), hypertension (16%), and diabetes/diabetic nephropathy (14%).
CMV Disease
The primary efficacy endpoint of Trial P002 was the incidence of CMV disease (CMV end-organ disease or CMV syndrome, confirmed by an independent adjudication committee) through Week 52 post-transplant. The Observed Failure (OF) approach was used, where subjects who discontinued prematurely from the study for any reason or were missing data at the timepoint were not counted as failures. The number of subjects who discontinued from the study before Week 52 was 32 (11%) in the PREVYMIS arm and 28 (9%) in the valganciclovir arm. The number of subjects with a missing outcome in the Week 52 visit window was 24 (8%) in the PREVYMIS arm and 25 (8%) in the valganciclovir arm.
Efficacy results from Trial P002 are shown in Table 20.
| Parameter | PREVYMIS (N=289) | Valganciclovir (N=297) |
|---|---|---|
| Note: Approach to handling missing values: Observed failure (OF) approach. With OF approach, subjects who discontinued from the study before Week 52 or had a missing outcome in the Week 52 visit window were not counted as failures. | ||
| CMV Disease CMV disease cases confirmed by an independent adjudication committee. Through Week 52 | 10% | 12% |
| CMV Syndrome Defined as evidence of CMV in blood by viral isolation, rapid culture, antigenemia, or nucleic acid testing, and two or more of the following: 1) fever ≥38°C for at least 2 days, 2) new or increased malaise/fatigue, 3) leukopenia or neutropenia on two separate measurements at least 24 hours apart, 4) ≥5% atypical lymphocytes, 5) thrombocytopenia, 6) elevation of ALT or AST to 2x ULN. | 8% | 11% |
| CMV End-organ Disease | 2% | <1% |
| Stratum-adjusted Treatment Difference The 95% CIs for the treatment differences in percent response were calculated using stratum-adjusted Mantel- Haenszel method with the difference weighted by the harmonic mean of sample size per arm for each stratum (use/non-use of highly cytolytic, anti-lymphocyte immunotherapy during induction). (PREVYMIS – Valganciclovir) | -1.4 (-6.5, 3.8) Based on a non-inferiority margin of 10%, PREVYMIS is non-inferior to valganciclovir. | |
Efficacy was comparable across all subgroups, including the use/nonuse of highly cytolytic, anti-lymphocyte immunotherapy during induction.
In an exploratory analysis of the incidence of CMV disease through Week 28 post-transplant, the difference (PREVYMIS – Valganciclovir) was -1.7% with 95% CI of (-3.4, 0.1). No subjects in the PREVYMIS group experienced CMV disease through Week 28 post-transplant (end of treatment period) compared with 5 subjects in the valganciclovir group.
Pediatric Recipients of an Allogeneic HSCT (Trial P030)
Sixty-three children 2 months to less than 18 years of age who had an allogeneic HSCT were enrolled in a multicenter, open-label, single-arm pharmacokinetic, safety and effectiveness study of PREVYMIS (P030, NCT03940586). Subjects received PREVYMIS daily either orally or intravenously for CMV prophylaxis within 28 days post-HSCT through Week 14 post-HSCT. The intravenous formulation was used for up to four weeks in subjects who were unable to take oral therapy. The daily doses of PREVYMIS were based on body weight [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 , 2.5) ]. Among the 63 treated subjects, 8 were 2 months to less than 2 years of age, 27 were 2 to less than 12 years of age and 28 were 12 to less than 18 years of age. The median age was 11 years; 70% were male; 70% were White; 14% were Asian; 5% were Black; and 22% were Hispanic or Latino [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4) ].
The efficacy analyses population consisted of 56 subjects who received at least one dose of study drug and had no detectable CMV DNA at baseline. The proportion of subjects who failed CMV prophylaxis through Week 24 post-HSCT was 25% (14 of the 56 subjects). Six subjects had initiation of pre-emptive therapy based on CMV viremia and 8 subjects discontinued from the study before Week 24. None of the subjects had CMV end-organ disease.
PREVYMIS is indicated for pediatric recipients of an allogeneic HSCT aged 6 months and older and weighing at least 6 kg.
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Tablets:
Each PREVYMIS 240 mg tablet is a yellow oval tablet; each tablet is debossed with "591" on one side and corporate logo on the other side. Each PREVYMIS 480 mg tablet is a pink oval, bi-convex tablet debossed with "595" on one side and corporate logo on the other side.
The 240 mg tablets are packaged into a carton (NDC 0006-3075-02) containing four (4) Child Resistant (CR) Dosepaks®, each containing a 7-count blister card for a total of 28 tablets, or into a carton (NDC 0006-3075-04) containing two (2) unit-dose 7-count blister cards for a total of 14 tablets.
The 480 mg tablets are packaged into a carton (NDC 0006-3076-02) containing four (4) Child Resistant (CR) Dosepaks®, each containing a 7-count blister card for a total of 28 tablets, or into a carton (NDC 0006-3076-04) containing two (2) unit-dose 7-count blister cards for a total of 14 tablets.
Store PREVYMIS tablets in the original package until use to protect from moisture.
Store PREVYMIS tablets at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Oral Pellets:
PREVYMIS oral pellets are supplied as beige round pellets in packets. Each packet contains 20 mg of letermovir.
PREVYMIS oral pellets are supplied as beige round pellets in packets. Each packet contains 120 mg of letermovir.
The 20 mg packets of PREVYMIS oral pellets are packaged into a carton (NDC 0006-5086-01). Each carton contains 30 child resistant packets.
The 120 mg packets of PREVYMIS oral pellets are packaged into a carton (NDC 0006-5085-01). Each carton contains 30 child resistant packets.
Store PREVYMIS oral pellets in the original packet until use.
Store PREVYMIS oral pellets at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Injection:
PREVYMIS is supplied as a sterile, clear and colorless solution for intravenous use of 240 mg/12 mL (20 mg/mL) or 480 mg/24 mL (20 mg/mL) that may contain a few product-related small translucent or white particles.
The single-dose vials are supplied in cartons that contain a 240 mg single-dose vial (NDC 0006-5003-01) or a 480 mg single-dose vial (NDC 0006-5004-01).
Store PREVYMIS injection vials at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Store in the original carton to protect from exposure to light.
| Important: Read this booklet first INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE PREVYMIS ® [PREH-vih-miss] (letermovir) oral pellets This Instructions for Use contains information on how to take PREVYMIS oral pellets. |
| Table of Contents |
Important information you need to know before taking PREVYMIS oral pellets
|
Taking PREVYMIS oral pellets PREVYMIS oral pellets can be taken by mouth after mixing with soft food or given through a gastric tube (G tube) or nasogastric tube (NG tube). Talk to your healthcare provider about which way to take PREVYMIS oral pellets. Follow 1 of these ways to take PREVYMIS oral pellets:
|
Mixing PREVYMIS oral pellets with soft food Important information about mixing PREVYMIS oral pellets with soft food
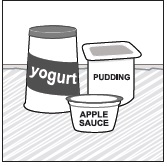 |
|
 |
|
 | Step 1: Wash your hands with soap and water. Dry your hands. |
 | Step 2: Check the expiration date located on the top of the carton.
|
 | Step 3: Check the pharmacy label for the number of PREVYMIS oral pellets packets needed for your dose. |
 | Step 4: Gather all of your supplies on a clean surface:
|
 | Step 6: Put 1 to 3 teaspoons (small spoons) of soft food into the small bowl. |
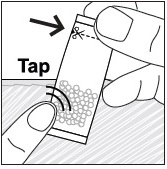 | Step 7: Tap the packets to loosen the pellets to the bottom of the packets.
|
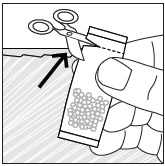 | Step 8: Cut open the packets with scissors at the dotted line. |
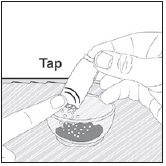 | Step 9: Lightly tap the packets to carefully sprinkle all of the PREVYMIS oral pellets onto the soft food in the same small bowl.
|
 | Step 10: Use the teaspoon to gently mix the food and PREVYMIS oral pellets together. |
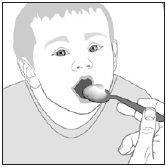 | Step 11: Take or give all of the PREVYMIS oral pellets mixture.
|
| Take or give all of the PREVYMIS oral pellets mixture within 10 minutes of mixing PREVYMIS oral pellets with the soft food. Throw away the PREVYMIS oral pellets mixed with soft food if you do not take it within 10 minutes, and prepare a new dose. |
 | Step 12: Cleaning up
|
 | Go to page 28 for Storing PREVYMIS oral pellets packets and page 32 to Learn more about PREVYMIS oral pellets . |
Giving PREVYMIS oral pellets through a gastric tube (G tube) or nasogastric tube (NG tube) These instructions are for giving PREVYMIS oral pellets through a G tube or NG tube.
 Gastric tube (G tube) Gastric tube (G tube) |  Nasogastric tube (NG tube) Nasogastric tube (NG tube) |
Ask your healthcare provider how to give PREVYMIS oral pellets through a G tube or NG tube and how to clean the G tube or NG tube. Ask your healthcare provider how to flush the G tube or NG tube before taking or giving a dose of PREVYMIS oral pellets.
Giving PREVYMIS oral pellets through a G tube or NG tube Important information you need to know before mixing PREVYMIS oral pellets with water |
 |
|
 | Step 1: Wash your hands with soap and water. Dry your hands. |
 | Step 2: Check the expiration date located on the top of the carton.
|
 | Step 3: Check the pharmacy label for the number of PREVYMIS oral pellets packets needed for your dose. |
 | Step 4: Gather all your supplies on a clean surface:
|
 | Step 5: Pour a small amount of room temperature water into the small glass.
|
 | Step 6: Place the tip of the syringe into the small glass of room temperature water. Pull up on the syringe plunger to measure the amount of water needed for your dose.
|
 | Step 7: Add the water to the medicine cup by holding the barrel of the syringe and pushing the syringe plunger all the way down. |
 | Step 8: Tap the packets to loosen the pellets to the bottom of the packets.
|
 | Step 9: Cut open the packets with scissors at the dotted line. |
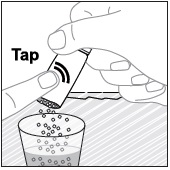 | Step 10: Lightly tap the packets to carefully pour the PREVYMIS oral pellets into the same medicine cup.
|
 | Step 11: Use a clock or timer and wait 10 minutes.
|
| Important: While waiting, keep the medicine cup in a safe place out of reach of children. |
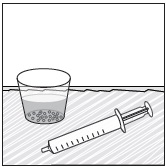 |
|
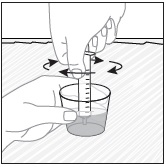 | Step 12: Gently stir the PREVYMIS oral pellets mixture with the syringe tip.
|
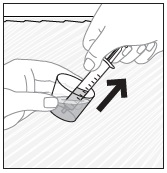 | Step 13: Tilt the medicine cup and pull up on the syringe plunger to draw up all of the PREVYMIS oral pellets mixture from the medicine cup. Give the PREVYMIS oral pellets mixture right away after it is drawn up into the syringe. |
 | Step 14: Give the PREVYMIS oral pellets mixture.
|
  | |
 | Step 15: Use the same syringe to withdraw more water from the small glass.
|
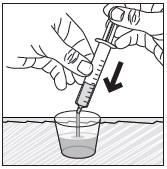 | Step 16: Slowly push the syringe plunger all the way down to add the water in the syringe into the same medicine cup. |
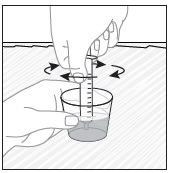 | Step 17: Gently stir the rinse mixture with the syringe tip.
|
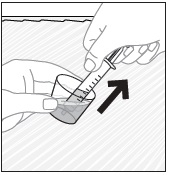 | Step 18: Tilt the medicine cup and pull up on the syringe plunger to draw up all of the rinse mixture from the medicine cup. |
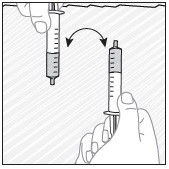 | Step 19: Give the rinse mixture.
|
  |
Step 20: Flush the G tube or NG tube right away using water.
|
 | Step 21: Cleaning up
|
 | Go to page 28 for Storing PREVYMIS oral pellets packets and page 32 to Learn more about PREVYMIS oral pellets . |
Storing PREVYMIS oral pellets packets
- Store PREVYMIS oral pellets at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Store PREVYMIS oral pellets in the original packet until you are ready to take them.
- Keep PREVYMIS oral pellets and all medicine out of the reach of children.
Learn more about PREVYMIS oral pellets
For more information on how to use PREVYMIS oral pellets, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist and read the PREVYMIS Patient Information.
For more information about PREVYMIS oral pellets, go to PREVYMIS.com or call 1-800-444-2080.
Distributed by: Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC Rahway, NJ 07065, USA
Copyright © 2024 Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA, and its affiliates. All rights reserved.
usifu-mk8228-op-2408r000
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Approved: 08/2024
Mechanism of Action
PREVYMIS is an antiviral drug against CMV [see Microbiology (12.4) ] .