Get your patient on Procysbi (Cysteamine Bitartrate)
Procysbi prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Procysbi patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Recommended Dosage in Cysteamine-Naïve Patients
- See full prescribing information for weight-based dosing tables for the starting and maintenance dosage. (2.2 )
- For initial intolerance, temporarily discontinue and then re-start PROCYSBI at a lower dosage and gradually increase to the maintenance dosage. (2.2 )
Switching from Immediate-release Cysteamine to PROCYSBI
- Start with a total daily dose of PROCYSBI equal to the previous total daily dose of immediate-release cysteamine bitartrate. (2.3 )
Dose Titration
- Adjust dose to achieve a therapeutic target white blood cell (WBC) cystine concentration. (2.4 , 2.5 )
- If a dose adjustment is required, increase the dosage by 10%. The maximum dosage is 1.95 grams/m 2 per day. (2.4 )
- If adverse reactions occur, decrease the dosage. Some patients may be unable to achieve their therapeutic target. (2.4 )
Preparation and Administration (2.6 )
- Capsules : Swallow whole; do not crush or chew capsules or capsule contents. Take the capsules with fruit juice (except grapefruit juice) or water.
- Oral Granules: Do not crush or chew the granules. Sprinkle and mix the granules in applesauce, berry jelly or fruit juice (except grapefruit juice).
- For patients who cannot swallow the capsules or with gastrostomy tubes, see the full prescribing information on how to prepare and administer the capsules and oral granules.
- Administer PROCYSBI at least 1 hour before or 1 hour after medications containing bicarbonate or carbonate.
- Do not eat for at least 2 hours before and for at least 30 minutes after taking PROCYSBI. If unable to take PROCYSBI without eating, take with food but limit the amount of food to approximately 4 ounces (½ cup) 1 hour before through 1 hour after administration. Avoid high fat food close to dosing.
- Avoid drinking alcohol while taking PROCYSBI.
Important Dosing Instructions
- Initiate cysteamine treatment immediately after diagnosis of nephropathic cystinosis.
- Cysteamine-naïve Patients: Start PROCYSBI at a fraction of the maintenance dosage.
- Patients 1 year to less than 6 years : Gradually increase the dosage, allowing a minimum of 2 weeks between adjustments [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) ] .
- Patients 6 years of age and older : Gradually increase the dosage over 4 to 6 weeks until the maintenance dosage is achieved.
- Patients switching from immediate-release cysteamine: Start the total daily dosage of PROCYSBI at a dosage equal to the previous total daily dosage of immediate-release cysteamine [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] .
- If adverse reactions occur, decrease the PROCYSBI dosage.
- After the maintenance dosage of PROCYSBI is achieved: The dosage may need to be further increased to achieve a therapeutic target WBC cystine concentration. The maximum dosage of PROCYSBI is 1.95 grams/m 2 of body surface area per day [see Dosage and Administration (2.4 , 2.5) ] .
- Round dose calculations to the nearest incremental dosage that can be administered using the available strengths of PROCYSBI delayed-release capsules or packets of oral granules. Only use whole capsules or entire contents of the packets.
Starting and Maintenance Dosing in Cysteamine-Naïve Patients
- Start treatment with a dosage equal to ⅙ to ¼ of the maintenance dosage.
- The maintenance dosage after initial dose escalation is 1.3 g/m 2 of body surface area per day divided into two doses given every 12 hours. Table 1 shows the recommended starting and maintenance dosages of PROCYSBI, converted from body-surface area to body weight.
- Patients 1 year to less than 6 years : Increase the dosage in 10% increments to the maintenance dosage, while monitoring WBC cystine concentrations. Allow a minimum of 2 weeks between dosage adjustments [see Dosage and Administration (2.4 , 2.5) ] . If a patient achieves the therapeutic target WBC cystine concentration at a dosage below the recommended weight-based maintenance dosage, then stop dosage escalation and use the dosage as the patient's maintenance dosage.
- Patients 6 years of age and older : Gradually increase the dosage over 4 to 6 weeks until the maintenance dosage is achieved.
- If a patient experiences initial intolerance, temporarily discontinue PROCYSBI and then re-start at a lower dosage and gradually increase dosage.
| Weight in kilograms | Starting PROCYSBI Dosage in mg every 12 hours, as a Fraction of the Maintenance Dosage | Maintenance PROCYSBI Dosage in mg every 12 hours Higher dosages may be required to achieve target therapeutic WBC cystine concentration [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) ] . | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ⅙ of dosage | ¼ of dosage | ||
| 5 or less | 25 | 50 | 200 |
| 6 to 10 | 50 | 75 | 300 |
| 11 to 15 | 75 | 100 | 400 |
| 16 to 20 | 100 | 125 | 500 |
| 21 to 25 | 100 | 150 | 600 |
| 26 to 30 | 125 | 175 | 700 |
| 31 to 40 | 125 | 200 | 800 |
| 41 to 50 | 150 | 225 | 900 |
| 51 kg and greater | 175 | 250 | 1000 |
Switching Patients from Immediate-Release Cysteamine Bitartrate
- When switching patients from immediate-release cysteamine bitartrate to PROCYSBI, the starting total daily dose of PROCYSBI is equal to the previous total daily dose of immediate-release cysteamine bitartrate. Divide the total daily dose by two and administer every 12 hours.
- For patients who may experience temporary intolerance upon starting PROCYSBI, decrease the dosage and then gradually increase to the maintenance dosage.
- Measure the WBC cystine concentration two weeks after initiation of PROCYSBI [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) ] . Adjust the PROCYSBI dosage as needed to achieve the therapeutic target WBC cystine concentration [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) ] . The maximum dosage of PROCYSBI is 1.95 grams/m 2 per day.
Dosage Titration to Therapeutic Target WBC Cystine Concentration
- Measure WBC cystine concentration and titrate the PROCYSBI dosage as needed to achieve the therapeutic target WBC cysteine concentration [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) ] .
- If the measured WBC cystine concentration is above the target level for cystine depletion, consider the following before dose adjustment: adherence to medication and dosing interval, the timing between the last dose and the blood draw for the laboratory measurement, and the timing of PROCYSBI administration in relation to food or other administration instructions.
- If a dose adjustment is required, increase the dosage by 10%, rounded to nearest dosage that can be administered using the available strengths of capsules or packets of oral granules. For patients 1 year to less than 6 years of age, allow a minimum of two weeks between dose increments. The maximum dosage of PROCYSBI is 1.95 grams/m 2 per day.
- If adverse reactions occur, decrease the PROCYSBI dosage. Some patients may be unable to achieve their therapeutic target due to poor tolerability of PROCYSBI [see Warnings and Precautions (5) , Adverse Reactions (6.1) ].
Laboratory Monitoring
- WBC cystine concentration may be measured using the mixed leukocyte assay or by using assays for specific WBC subsets (e.g., granulocyte method). The methods used for measuring cystine and total protein content may also vary among individual laboratories [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2) ] .
- Normal WBC cystine ranges and therapeutic target levels for cystine depletion depend upon the assay method used by the individual laboratory. WBC cystine values obtained from using different assay methods may not be comparable. Refer to the assay-specific therapeutic target for cystine depletion. When using the mixed leukocyte assay, the recommended target WBC cystine concentration is less than 1 nmol ½ cystine/mg protein .
- The recommended frequency of monitoring WBC cystine concentration is as follows:
- Cysteamine-naïve patients 1 year to less than 6 years : Obtain measurement two weeks after initiation of PROCYSBI treatment and continue monitoring during dosage titration period until the therapeutic target WBC cystine concentration is achieved. Once the therapeutic target is achieved, continue monitoring monthly for 3 months, then quarterly for 1 year, and then twice-yearly, at a minimum.
- Cysteamine-naïve patients greater than 6 years : Obtain measurement after reaching the maintenance PROCYSBI dosage, then monthly for 3 months, quarterly for 1 year, and then twice-yearly, at a minimum.
- Patients switching from immediate-release cysteamine to PROCYSBI : Obtain measurement two weeks after initiation of PROCYSBI treatment and continue monitoring if further dosage titration is required to achieve therapeutic target WBC cystine concentration. Once the therapeutic target is achieved, continue monitoring quarterly for 6 months, then twice yearly, at a minimum.
- Obtain blood samples for WBC cystine concentration measurement 12 hours after the patient's last PROCYSBI dose, prior to administration of the next dose (i.e., trough concentration). In addition, it is important to accurately record the time of the last dose, the actual dose, and the time the blood sample was taken.
Preparation and Administration
- PROCYSBI delayed-release capsules:
- Swallow capsules whole. Do not crush or chew capsules or capsule contents.
- Take capsules with fruit juice (except grapefruit juice) or water.
- For patients who cannot swallow the capsules, the capsules can be opened and the capsule contents sprinkled on and mixed in applesauce, berry jelly or fruit juice (except grapefruit juice) and administered orally, as described below.
- For patients with a gastrostomy tube, the capsules can be opened and the capsule contents mixed in applesauce and administered via the gastrostomy tube, as described below.
- PROCYSBI delayed-release oral granules:
- Do not crush or chew oral granules.
- Sprinkle and mix the intact granules in applesauce, berry jelly or fruit juice (except grapefruit juice) and administered orally, as described below.
- For patients with a gastrostomy tube, the oral granules can be mixed in applesauce and administered via a gastrostomy tube, as described below.
- Administer PROCYSBI at least 1 hour before or 1 hour after medications containing bicarbonate or carbonate [see Drug Interactions (7.1) ].
- Do not eat for at least 2 hours before taking PROCYSBI and for at least 30 minutes after to maximize absorption. If patients are unable to take PROCYSBI without eating, take with food and limit the amount of food to approximately 4 ounces (½ cup) within 1 hour before taking PROCYSBI through 1 hour after taking PROCYSBI. Take PROCYSBI in a consistent manner in regard to food. Avoid high fat food close to dosing of PROCYSBI.
- Avoid drinking alcohol while taking PROCYSBI [see Drug Interactions (7.2) ].
Oral Administration in Food or Liquid
Administration of PROCYSBI capsules or oral granules with foods and liquids not included below has not been studied clinically and is not recommended.
Administration in Applesauce or Berry Jelly:
- Place approximately 4 ounces (½ cup) or a smaller amount that can be consumed in one feeding of either applesauce or berry jelly into a clean container.
- Open the capsule(s) or packet(s).
- Sprinkle all the intact granules that are inside the capsule(s) or packet(s) on applesauce or berry jelly.
- Mix the granules with the applesauce or berry jelly. Do not crush the granules.
- Consume the entire contents within 30 minutes of mixing. Do not chew the granules. Do not save the applesauce or berry jelly and granules for later use.
Administration in Fruit Juice (except grapefruit juice):
- Pour approximately 4 ounces (½ cup) of fruit juice into a clean cup.
- Open the capsule(s) or packet(s).
- Sprinkle all the intact granules into the juice.
- Gently stir until mixed. Do not crush the granules.
- Drink the entire contents within 30 minutes of mixing. Do not chew the granules. Do not save the fruit juice and granules mixture for later use.
Administration in Applesauce via a Gastrostomy (G) Tube (14 French or larger)
A bolus (straight) feeding tube is recommended.
- Flush the gastrostomy tube button first with 5 mL of water to clear the button.
- Open the capsule(s) or packet(s) and empty the granules into a clean container with approximately 4 ounces (½ cup) of applesauce. Use only strained applesauce with no chunks. A minimum of 1 ounce (⅛cup) of applesauce may be used for children 25 kg or less starting PROCYSBI at a dose of 1 or 2 capsules or packets.
- Mix the intact granules into the applesauce. Do not crush the granules.
- Draw up the mixture into a syringe. Keep the feeding tube horizontal during administration and apply rapid and steady pressure (10 mL/10 seconds) to dispense the syringe contents into the tube within 30 minutes of preparation.
- Repeat step 3 until all of the mixture is administered. Do not save the applesauce and granule mixture for later use.
- Draw up a minimum of 10 mL of fruit juice or water into another syringe, swirl gently, and flush the tube.
Missed Doses
- If a dose is missed, take the dose as soon as possible up to 8 hours after the scheduled time. However, if a dose is missed and the next scheduled dose is due in less than 4 hours, do not take the missed dose and take the next dose at the usual scheduled time. Do not take 2 doses at one time to make up for a missed dose.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Procysbi prescribing information
| Warnings and Precautions, Fibrosing Colonopathy (5.4 ) | 02/2022 |
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
PROCYSBI is indicated for the treatment of nephropathic cystinosis in adults and pediatric patients 1 year of age and older.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Recommended Dosage in Cysteamine-Naïve Patients
- See full prescribing information for weight-based dosing tables for the starting and maintenance dosage. (2.2 )
- For initial intolerance, temporarily discontinue and then re-start PROCYSBI at a lower dosage and gradually increase to the maintenance dosage. (2.2 )
Switching from Immediate-release Cysteamine to PROCYSBI
- Start with a total daily dose of PROCYSBI equal to the previous total daily dose of immediate-release cysteamine bitartrate. (2.3 )
Dose Titration
- Adjust dose to achieve a therapeutic target white blood cell (WBC) cystine concentration. (2.4 , 2.5 )
- If a dose adjustment is required, increase the dosage by 10%. The maximum dosage is 1.95 grams/m 2 per day. (2.4 )
- If adverse reactions occur, decrease the dosage. Some patients may be unable to achieve their therapeutic target. (2.4 )
Preparation and Administration (2.6 )
- Capsules : Swallow whole; do not crush or chew capsules or capsule contents. Take the capsules with fruit juice (except grapefruit juice) or water.
- Oral Granules: Do not crush or chew the granules. Sprinkle and mix the granules in applesauce, berry jelly or fruit juice (except grapefruit juice).
- For patients who cannot swallow the capsules or with gastrostomy tubes, see the full prescribing information on how to prepare and administer the capsules and oral granules.
- Administer PROCYSBI at least 1 hour before or 1 hour after medications containing bicarbonate or carbonate.
- Do not eat for at least 2 hours before and for at least 30 minutes after taking PROCYSBI. If unable to take PROCYSBI without eating, take with food but limit the amount of food to approximately 4 ounces (½ cup) 1 hour before through 1 hour after administration. Avoid high fat food close to dosing.
- Avoid drinking alcohol while taking PROCYSBI.
Important Dosing Instructions
- Initiate cysteamine treatment immediately after diagnosis of nephropathic cystinosis.
- Cysteamine-naïve Patients: Start PROCYSBI at a fraction of the maintenance dosage.
- Patients 1 year to less than 6 years : Gradually increase the dosage, allowing a minimum of 2 weeks between adjustments [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) ] .
- Patients 6 years of age and older : Gradually increase the dosage over 4 to 6 weeks until the maintenance dosage is achieved.
- Patients switching from immediate-release cysteamine: Start the total daily dosage of PROCYSBI at a dosage equal to the previous total daily dosage of immediate-release cysteamine [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] .
- If adverse reactions occur, decrease the PROCYSBI dosage.
- After the maintenance dosage of PROCYSBI is achieved: The dosage may need to be further increased to achieve a therapeutic target WBC cystine concentration. The maximum dosage of PROCYSBI is 1.95 grams/m 2 of body surface area per day [see Dosage and Administration (2.4 , 2.5) ] .
- Round dose calculations to the nearest incremental dosage that can be administered using the available strengths of PROCYSBI delayed-release capsules or packets of oral granules. Only use whole capsules or entire contents of the packets.
Starting and Maintenance Dosing in Cysteamine-Naïve Patients
- Start treatment with a dosage equal to ⅙ to ¼ of the maintenance dosage.
- The maintenance dosage after initial dose escalation is 1.3 g/m 2 of body surface area per day divided into two doses given every 12 hours. Table 1 shows the recommended starting and maintenance dosages of PROCYSBI, converted from body-surface area to body weight.
- Patients 1 year to less than 6 years : Increase the dosage in 10% increments to the maintenance dosage, while monitoring WBC cystine concentrations. Allow a minimum of 2 weeks between dosage adjustments [see Dosage and Administration (2.4 , 2.5) ] . If a patient achieves the therapeutic target WBC cystine concentration at a dosage below the recommended weight-based maintenance dosage, then stop dosage escalation and use the dosage as the patient's maintenance dosage.
- Patients 6 years of age and older : Gradually increase the dosage over 4 to 6 weeks until the maintenance dosage is achieved.
- If a patient experiences initial intolerance, temporarily discontinue PROCYSBI and then re-start at a lower dosage and gradually increase dosage.
| Weight in kilograms | Starting PROCYSBI Dosage in mg every 12 hours, as a Fraction of the Maintenance Dosage | Maintenance PROCYSBI Dosage in mg every 12 hours Higher dosages may be required to achieve target therapeutic WBC cystine concentration [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) ] . | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ⅙ of dosage | ¼ of dosage | ||
| 5 or less | 25 | 50 | 200 |
| 6 to 10 | 50 | 75 | 300 |
| 11 to 15 | 75 | 100 | 400 |
| 16 to 20 | 100 | 125 | 500 |
| 21 to 25 | 100 | 150 | 600 |
| 26 to 30 | 125 | 175 | 700 |
| 31 to 40 | 125 | 200 | 800 |
| 41 to 50 | 150 | 225 | 900 |
| 51 kg and greater | 175 | 250 | 1000 |
Switching Patients from Immediate-Release Cysteamine Bitartrate
- When switching patients from immediate-release cysteamine bitartrate to PROCYSBI, the starting total daily dose of PROCYSBI is equal to the previous total daily dose of immediate-release cysteamine bitartrate. Divide the total daily dose by two and administer every 12 hours.
- For patients who may experience temporary intolerance upon starting PROCYSBI, decrease the dosage and then gradually increase to the maintenance dosage.
- Measure the WBC cystine concentration two weeks after initiation of PROCYSBI [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) ] . Adjust the PROCYSBI dosage as needed to achieve the therapeutic target WBC cystine concentration [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) ] . The maximum dosage of PROCYSBI is 1.95 grams/m 2 per day.
Dosage Titration to Therapeutic Target WBC Cystine Concentration
- Measure WBC cystine concentration and titrate the PROCYSBI dosage as needed to achieve the therapeutic target WBC cysteine concentration [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) ] .
- If the measured WBC cystine concentration is above the target level for cystine depletion, consider the following before dose adjustment: adherence to medication and dosing interval, the timing between the last dose and the blood draw for the laboratory measurement, and the timing of PROCYSBI administration in relation to food or other administration instructions.
- If a dose adjustment is required, increase the dosage by 10%, rounded to nearest dosage that can be administered using the available strengths of capsules or packets of oral granules. For patients 1 year to less than 6 years of age, allow a minimum of two weeks between dose increments. The maximum dosage of PROCYSBI is 1.95 grams/m 2 per day.
- If adverse reactions occur, decrease the PROCYSBI dosage. Some patients may be unable to achieve their therapeutic target due to poor tolerability of PROCYSBI [see Warnings and Precautions (5) , Adverse Reactions (6.1) ].
Laboratory Monitoring
- WBC cystine concentration may be measured using the mixed leukocyte assay or by using assays for specific WBC subsets (e.g., granulocyte method). The methods used for measuring cystine and total protein content may also vary among individual laboratories [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2) ] .
- Normal WBC cystine ranges and therapeutic target levels for cystine depletion depend upon the assay method used by the individual laboratory. WBC cystine values obtained from using different assay methods may not be comparable. Refer to the assay-specific therapeutic target for cystine depletion. When using the mixed leukocyte assay, the recommended target WBC cystine concentration is less than 1 nmol ½ cystine/mg protein .
- The recommended frequency of monitoring WBC cystine concentration is as follows:
- Cysteamine-naïve patients 1 year to less than 6 years : Obtain measurement two weeks after initiation of PROCYSBI treatment and continue monitoring during dosage titration period until the therapeutic target WBC cystine concentration is achieved. Once the therapeutic target is achieved, continue monitoring monthly for 3 months, then quarterly for 1 year, and then twice-yearly, at a minimum.
- Cysteamine-naïve patients greater than 6 years : Obtain measurement after reaching the maintenance PROCYSBI dosage, then monthly for 3 months, quarterly for 1 year, and then twice-yearly, at a minimum.
- Patients switching from immediate-release cysteamine to PROCYSBI : Obtain measurement two weeks after initiation of PROCYSBI treatment and continue monitoring if further dosage titration is required to achieve therapeutic target WBC cystine concentration. Once the therapeutic target is achieved, continue monitoring quarterly for 6 months, then twice yearly, at a minimum.
- Obtain blood samples for WBC cystine concentration measurement 12 hours after the patient's last PROCYSBI dose, prior to administration of the next dose (i.e., trough concentration). In addition, it is important to accurately record the time of the last dose, the actual dose, and the time the blood sample was taken.
Preparation and Administration
- PROCYSBI delayed-release capsules:
- Swallow capsules whole. Do not crush or chew capsules or capsule contents.
- Take capsules with fruit juice (except grapefruit juice) or water.
- For patients who cannot swallow the capsules, the capsules can be opened and the capsule contents sprinkled on and mixed in applesauce, berry jelly or fruit juice (except grapefruit juice) and administered orally, as described below.
- For patients with a gastrostomy tube, the capsules can be opened and the capsule contents mixed in applesauce and administered via the gastrostomy tube, as described below.
- PROCYSBI delayed-release oral granules:
- Do not crush or chew oral granules.
- Sprinkle and mix the intact granules in applesauce, berry jelly or fruit juice (except grapefruit juice) and administered orally, as described below.
- For patients with a gastrostomy tube, the oral granules can be mixed in applesauce and administered via a gastrostomy tube, as described below.
- Administer PROCYSBI at least 1 hour before or 1 hour after medications containing bicarbonate or carbonate [see Drug Interactions (7.1) ].
- Do not eat for at least 2 hours before taking PROCYSBI and for at least 30 minutes after to maximize absorption. If patients are unable to take PROCYSBI without eating, take with food and limit the amount of food to approximately 4 ounces (½ cup) within 1 hour before taking PROCYSBI through 1 hour after taking PROCYSBI. Take PROCYSBI in a consistent manner in regard to food. Avoid high fat food close to dosing of PROCYSBI.
- Avoid drinking alcohol while taking PROCYSBI [see Drug Interactions (7.2) ].
Oral Administration in Food or Liquid
Administration of PROCYSBI capsules or oral granules with foods and liquids not included below has not been studied clinically and is not recommended.
Administration in Applesauce or Berry Jelly:
- Place approximately 4 ounces (½ cup) or a smaller amount that can be consumed in one feeding of either applesauce or berry jelly into a clean container.
- Open the capsule(s) or packet(s).
- Sprinkle all the intact granules that are inside the capsule(s) or packet(s) on applesauce or berry jelly.
- Mix the granules with the applesauce or berry jelly. Do not crush the granules.
- Consume the entire contents within 30 minutes of mixing. Do not chew the granules. Do not save the applesauce or berry jelly and granules for later use.
Administration in Fruit Juice (except grapefruit juice):
- Pour approximately 4 ounces (½ cup) of fruit juice into a clean cup.
- Open the capsule(s) or packet(s).
- Sprinkle all the intact granules into the juice.
- Gently stir until mixed. Do not crush the granules.
- Drink the entire contents within 30 minutes of mixing. Do not chew the granules. Do not save the fruit juice and granules mixture for later use.
Administration in Applesauce via a Gastrostomy (G) Tube (14 French or larger)
A bolus (straight) feeding tube is recommended.
- Flush the gastrostomy tube button first with 5 mL of water to clear the button.
- Open the capsule(s) or packet(s) and empty the granules into a clean container with approximately 4 ounces (½ cup) of applesauce. Use only strained applesauce with no chunks. A minimum of 1 ounce (⅛cup) of applesauce may be used for children 25 kg or less starting PROCYSBI at a dose of 1 or 2 capsules or packets.
- Mix the intact granules into the applesauce. Do not crush the granules.
- Draw up the mixture into a syringe. Keep the feeding tube horizontal during administration and apply rapid and steady pressure (10 mL/10 seconds) to dispense the syringe contents into the tube within 30 minutes of preparation.
- Repeat step 3 until all of the mixture is administered. Do not save the applesauce and granule mixture for later use.
- Draw up a minimum of 10 mL of fruit juice or water into another syringe, swirl gently, and flush the tube.
Missed Doses
- If a dose is missed, take the dose as soon as possible up to 8 hours after the scheduled time. However, if a dose is missed and the next scheduled dose is due in less than 4 hours, do not take the missed dose and take the next dose at the usual scheduled time. Do not take 2 doses at one time to make up for a missed dose.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
PROCYSBI delayed-release capsules:
- 25 mg cysteamine: the capsules have a light blue opaque cap imprinted with "PRO" in white ink and a light blue opaque body imprinted with "25 mg" in white ink.
- 75 mg cysteamine: the capsules have a dark blue opaque cap imprinted with "PRO" in white ink and a light blue opaque body imprinted with "75 mg" in white ink.
PROCYSBI delayed-release oral granules:
- 75 mg cysteamine: white to off-white granules in single-use packets
- 300 mg cysteamine: white to off-white granules in single-use packets
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Lactation: Breastfeeding is not recommended. (8.2 )
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no available data on PROCYSBI use in pregnant women to inform any drug-associated risks for birth defects or miscarriage [see Data ] . Cysteamine (administered as cysteamine bitartrate) was teratogenic and fetotoxic in rats at doses less than the recommended human maintenance dose.
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
Data
Animal Data
Embryo-fetal development studies were conducted in rats using oral administration of cysteamine bitartrate, with a dose range of 37.5 to 150 mg/kg per day of cysteamine equivalent (about 0.2 to 0.7 times the recommended human maintenance dose based on body surface area). Cysteamine bitartrate was fetotoxic and produced adverse developmental effects. Observed teratogenic findings were cleft palate, kyphosis, heart ventricular septal defects, microcephaly and exencephaly.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information on the presence of cysteamine in human milk, the effects on the breast-fed infant, or the effects on milk production. Cysteamine is present in the milk of lactating rats [see Data ]. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed infants from cysteamine, breastfeeding is not recommended.
Data
A decrease in survival occurred in neonatal rats nursed by mothers receiving cysteamine [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13) ] .
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of PROCYSBI have been established in pediatric patients 1 year of age and older for the treatment of nephropathic cystinosis. Use of PROCYSBI is supported by evidence from patients switched to PROCYSBI from immediate-release cysteamine bitartrate in two trials: an open-label, randomized, cross-over trial in adults and pediatric patients aged 6 years and older (n=43) and an open-label extension trial in pediatric patients aged 2 years and older (n=59). Another open-label trial was conducted in cysteamine naïve pediatric patients 1 year to less than 6 years of age (n=15) [see Clinical Trials (14.2) ] . The safety profile in pediatric patients was similar to adults. In patients less than 6 years of age, vomiting occurred in 12/15 cysteamine treatment naïve patients compared to 11/13 patients switched from immediate-release cysteamine to PROCYSBI.
The safety and effectiveness of PROCYSBI have not been established in patients less than 1 year of age.
Geriatric Use
No studies with PROCYSBI have been conducted in geriatric patients.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
The use of PROCYSBI is contraindicated in patients with a serious hypersensitivity reaction, including anaphylaxis, to penicillamine or cysteamine.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Ehlers-Danlos-like Syndrome: Reduce dosage if skin and bone lesions occur. (5.1 )
- Skin Rash: Discontinue if severe skin rash such as erythema multiforme bullosa or toxic epidermal necrolysis occurs. (5.2 )
- Gastrointestinal (GI) Ulcers and Bleeding: Monitor for GI symptoms and consider decreasing the dose if severe symptoms occur. (5.3 )
- Fibrosing Colonopathy: Evaluate patients with severe, persistent, and/or worsening abdominal symptoms for fibrosing colonopathy. If the diagnosis is confirmed, permanently discontinue PROCYSBI and switch to immediate-release cysteamine bitartrate capsules (5.4 )
- Central Nervous System (CNS) Symptoms: Monitor for CNS symptoms; interrupt or reduce the dose for severe symptoms or those that persist or progress (5.5 ).
- Leukopenia and/or Elevated Alkaline Phosphatase Levels: Monitor white blood cell count and alkaline phosphatase levels; decrease or discontinue the dose until values revert to normal. (5.6 )
- Benign Intracranial Hypertension: Monitor for signs and symptoms; interrupt or reduce the dose for signs/symptoms that persist, or discontinue if diagnosis is confirmed. (5.7 )
Ehlers-Danlos-like Syndrome
Skin and bone lesions that resemble clinical findings for Ehlers-Danlos-like syndrome have been reported in patients treated with high doses of immediate-release cysteamine bitartrate or other cysteamine salts. These include molluscoid pseudotumors (purplish hemorrhagic lesions), skin striae, bone lesions (including osteopenia, compression fractures, scoliosis and genu valgum), leg pain, and joint hyperextension. One patient on immediate-release cysteamine bitartrate with serious skin lesions subsequently died of acute cerebral ischemia with marked vasculopathy. Monitor patients for development of skin or bone lesions and interrupt PROCYSBI dosing if patients develop these lesions. PROCYSBI may be restarted at a lower dose under close supervision, then slowly increase to the appropriate therapeutic dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.1 , 2.4) ] .
Skin Rash
Severe skin rashes such as erythema multiforme bullosa or toxic epidermal necrolysis have been reported in patients receiving immediate-release cysteamine bitartrate. If severe skin rashes develop, permanently discontinue use of PROCYSBI [see Contraindications (4) ] .
Gastrointestinal Ulcers and Bleeding
Gastrointestinal (GI) ulceration and bleeding have been reported in patients receiving immediate-release cysteamine bitartrate. GI tract symptoms including nausea, vomiting, anorexia and abdominal pain, sometimes severe, have been associated with cysteamine. If severe GI tract symptoms develop, consider decreasing the dose of PROCYSBI [see Dosage and Administration (2.1 , 2.4) ] .
Fibrosing Colonopathy
Fibrosing colonopathy, including colonic stricture formation, has been reported with postmarketing use of PROCYSBI in pediatric and young adult patients with nephropathic cystinosis. Some of these patients had been treated with PROCYSBI for prolonged periods of time. Reported symptoms include: abdominal pain, vomiting, bloody or persistent diarrhea, and fecal incontinence. Evaluate patients with severe, persistent, and/or worsening abdominal symptoms for fibrosing colonopathy. If the diagnosis is confirmed, permanently discontinue PROCYSBI and switch to immediate-release cysteamine bitartrate capsules. An association between methacrylic acid-ethyl acrylate copolymer (an inactive ingredient in PROCYSBI) and fibrosing colonopathy cannot be ruled out.
Central Nervous System Symptoms
Central Nervous System (CNS) symptoms such as seizures, lethargy, somnolence, depression, and encephalopathy have been associated with immediate-release cysteamine. Neurological complications have also been described in some patients with cystinosis who have not been treated with cysteamine. Carefully evaluate and monitor patients who develop CNS symptoms. Interrupt medication or adjust the dose as necessary for patients with severe symptoms or with symptoms that persist or progress. Inform patients that PROCYSBI may impair their ability to perform tasks such as driving or operating machinery.
Leukopenia and/or Elevated Alkaline Phosphatase Levels
Cysteamine has been associated with reversible leukopenia and elevated alkaline phosphatase levels. Monitor white blood cell counts and alkaline phosphatase levels. If tests values remain elevated, consider decreasing the dose or discontinuing the drug until values revert to normal.
Benign Intracranial Hypertension
Benign intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri; PTC) and/or papilledema have been reported in patients receiving immediate-release cysteamine bitartrate treatment. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of PTC, including headache, tinnitus, dizziness, nausea, diplopia, blurry vision, loss of vision, pain behind the eye or pain with eye movement. If signs/symptoms persist, interrupt dosing or decrease the dose and refer the patient to an ophthalmologist. If the diagnosis is confirmed, permanently discontinue use of PROCYSBI.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are also discussed in other sections of the labeling:
- Ehlers-Danlos-like Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- Skin Rash [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
- Gastrointestinal (GI) Ulcers and Bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
- Fibrosing Colonopathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ]
- Central Nervous System Symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ]
- Leukopenia and/or Elevated Phosphatase Levels [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ]
- Benign Intracranial Hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared with rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
The data described below reflect exposure to cysteamine in 345 patients with nephropathic cystinosis (246 patients receiving immediate-release cysteamine as cysteamine hydrochloride or phosphocysteamine, and 80 patients receiving PROCYSBI) in open-label clinical trials.
Clinical Trials Experience with PROCYSBI in Patients Switched from Immediate-Release Cysteamine Bitartrate
Sixty-two patients with nephropathic cystinosis (38 males and 24 females) received PROCYSBI in two clinical trials at doses ranging from 0.29 grams/m 2 per day to 2.19 grams/m 2 per day [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ]. All patients were switched from immediate-release cysteamine to PROCYSBI. Forty-three patients, ages 6 to 26 years old, received PROCYSBI in an 8-week, open-label, randomized, cross-over trial comparing PROCYSBI to immediate-release cysteamine bitartrate. Forty of 43 patients continued PROCYSBI treatment in an open-label extension trial (36 patients were treated with PROCYSBI for longer than 2 years, and 20 patients were treated for longer than 5 years). An additional 19 patients (6 renal transplanted patients and 13 patients aged 2 to 6 years) were enrolled directly into this trial (12 patients were treated with PROCYSBI for longer than 2 years, and 9 patients were treated for longer than 5 years).
In the open-label, randomized, cross-over trial, a higher incidence of adverse reactions was reported in patients during the PROCYSBI treatment period compared with the immediate-release cysteamine bitartrate treatment period (see Table 2 ). Other significant adverse reactions reported during clinical trials included hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis.
| Adverse Reaction | Immediate-Release Cysteamine | PROCYSBI |
|---|---|---|
| (n = 41) % | (n = 43) % | |
| Vomiting/emesis | 12 | 19 |
| Nausea | 7 | 16 |
| Abdominal pain/discomfort | 0 | 14 |
| Headache | 0 | 9 |
| Dizziness | 0 | 5 |
| Anorexia/loss of appetite | 5 | 2 |
In the open-label extension trial (N=59), the most commonly reported adverse reactions (>15%) were vomiting, headache, diarrhea, nausea, conjunctivitis, influenza, gastroenteritis, nasopharyngitis, abdominal pain, dehydration, ear infection, upper respiratory tract infection, fatigue, arthralgia, cough, and pain in extremity.
Clinical Trials Experience with PROCYSBI in Cysteamine-Naïve Patients
Seventeen cysteamine-naïve patients (fifteen patients between the ages of 1 and 5 years, one 9-year old and one 22-year old) received PROCYSBI in an open-label clinical trial [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ] . Serious adverse reactions occurring in at least 2 patients (>10%) were: gastroenteritis/viral gastroenteritis (n=6), vomiting (n=4), and electrolyte imbalance (n=2). Three patients with serious adverse reactions of gastroenteritis also had dehydration. Common adverse reactions reported at a frequency of >10% (occurring in at least 2 patients) are shown in Table 3.
| Adverse Reaction | PROCYSBI N = 17 n (%) |
|---|---|
| Vomiting | 13 (77) |
| Gastroenteritis/viral gastroenteritis | 9 (53) |
| Diarrhea | 6 (35) |
| Breath odor | 4 (24) |
| Nausea | 3 (18) |
| Electrolyte imbalance | 2 (12) |
| Headache | 2 (12) |
Clinical Trials Experience with Immediate-Release Cysteamine
The most frequent adverse reactions involved the gastrointestinal and central nervous systems and were especially prominent at the initiation of cysteamine therapy. Most patients were able to resume therapy at lower doses. The most common reactions (>5%) were vomiting, anorexia, fever, diarrhea, lethargy, and rash. Other adverse reactions included nausea, bad breath, abdominal pain, headache, dizziness, and urticaria.
Withdrawals due to intolerance, vomiting, anorexia, lethargy, and fever occurred more frequently in those patients receiving 1.95 grams/m 2 per day as compared with 1.3 grams/m 2 per day of immediate-release cysteamine bitartrate.
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of cysteamine bitartrate. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Musculoskeletal: Joint hyperextension, leg pain, osteopenia, compression fracture, scoliosis, genu valgum [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
- Skin : Erythema multiforme bullosa, toxic epidermal necrolysis, Ehlers-Danlos-like syndrome, molluscoid pseudotumors, skin striae, skin fragility [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 , 5.2) ].
- Gastrointestinal: Fibrosing colonopathy reported with PROCYSBI [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ].
- Central Nervous System : seizures, lethargy, somnolence, depression and encephalopathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ] , benign intracranial hypertension (or PTC) and/or papilledema [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ].
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Drugs that Increase Gastric pH
Drugs that increase the gastric pH (e.g., medications containing bicarbonate or carbonate) may alter the pharmacokinetics of cysteamine due to the premature release of cysteamine from PROCYSBI and increase WBC cystine concentration. Concomitant administration of 20 mg omeprazole did not affect the pharmacokinetics of cysteamine when PROCYSBI was administered with 240 mL of orange juice or with 240 mL of water [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ]. Monitor WBC cystine concentration when drugs that increase the gastric pH are concomitantly used [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) ].
Use with Alcohol
Consumption of alcohol with PROCYSBI may increase the rate of cysteamine release and/or adversely alter the pharmacokinetic properties, as well as the effectiveness and safety of PROCYSBI. Therefore, do not consume alcoholic beverages during treatment with PROCYSBI [see Dosage and Administration (2.6) ].
Other Medications Used for the Management of Fanconi Syndrome
PROCYSBI can be administered with other electrolyte and mineral replacements necessary for management of Fanconi syndrome, as well as vitamin D and thyroid hormone.
DESCRIPTION
PROCYSBI, for oral administration, is a cystine-depleting agent that lowers the cystine content of cells in patients with nephropathic cystinosis, an inherited defect of lysosomal transport.
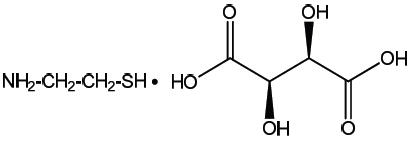
PROCYSBI contains the bitartrate salt of cysteamine. The chemical name for cysteamine bitartrate is ethanethiol, 2-amino, (2 R ,3 R )-2,3-dihydroxybutanedioate (1:1) (salt). Cysteamine bitartrate is a highly water soluble white powder with a molecular weight of 227.24 and the molecular formula C 2 H 7 NS ∙ C 4 H 6 O 6 . It has the following chemical structure:
Each PROCYSBI delayed-release capsule contains either 25 mg cysteamine (equivalent to 74 mg cysteamine bitartrate) or 75 mg cysteamine (equivalent to 221 mg cysteamine bitartrate).
Each packet of PROCYSBI delayed-release oral granules contains either 75 mg cysteamine (equivalent to 221 mg cysteamine bitartrate) or 300 mg cysteamine (equivalent to 884 mg cysteamine bitartrate).
PROCYSBI delayed release granules contain the following inactive ingredients: Eudragit ® L 30 D-55 (methacrylic acid-ethyl acrylate copolymer), hypromellose, microcrystalline cellulose, purified water, sodium lauryl sulfate, talc, and triethyl citrate. Additionally the capsule shell contains the following inactive ingredients: gelatin, ink (blue and white), and titanium dioxide.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Cysteamine is an aminothiol that participates within lysosomes in a thiol-disulfide interchange reaction converting cystine into cysteine and cysteine-cysteamine mixed disulfide, both of which can exit the lysosome in patients with cystinosis.
Pharmacodynamics
Normal individuals and persons heterozygous for cystinosis have WBC cystine concentrations of less than 0.2 and usually below 1 nmol ½ cystine/mg protein, respectively, when measured using the mixed leukocyte assay. Untreated patients with nephropathic cystinosis have elevations of WBC cystine concentration above 2 nmol ½ cystine/mg protein.
After the administration of a single dose of PROCYSBI, peak concentrations of cysteamine were observed at 3 hours post-dose. The nadir of WBC cystine closely followed the peak concentrations at 3.5 hours post-dose, and returned to baseline WBC concentrations at 12 hours-post dose. The cystine concentration in WBC lysate was measured with LC/MS/MS and total protein content in human WBC lysate was measured using the bicinchoninic acid (BCA) assay. A correction factor was applied to the total protein content for the difference in results from the Lowry method. The cystine concentration in nmol ½ cystine/mg protein was calculated by multiplying nmol cystine/mg protein by 2 [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) ].
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of cysteamine with administration of PROCYSBI were evaluated in 43 patients age ranged from 6 to 26 years (mean age 12 years) with cystinosis and with an estimated glomerular filtration rate of greater than 30 mL/minutes/1.73 m2. Table 4 shows the mean pharmacokinetic parameters for PROCYSBI and immediate-release cysteamine bitartrate at steady state. The mean (± SD) dose for PROCYSBI was 656 ± 144 mg/m2 (given every 12 hours) and for immediate-release cysteamine bitartrate was 404 ± 88 mg/m2 (given every 6 hours).
| Immediate-release cysteamine bitartrate given every 6 hours | PROCYSBI given every 12 hours | |
|---|---|---|
| C max (mg/L) | 2.7 ± 1.4 | 3.6 ± 1.8 |
| AUC 0-6h (min•mg/L) | 351 ± 153 | NA |
| AUC 0-12h (min•mg/L) | NA | 726 ± 339 |
| AUC inf (min•mg/L) | 380 ± 157 | 785 ± 358 |
| T max (min) | 73 ± 31 | 188 ± 88 |
| t½ (min) | 90 ± 24 | 253 ± 403 |
| CL/F (L/min) | 1.4 ± 0.8 | 1.2 ± 0.8 |
| Vd/F (L) | 198 ± 159 | 382 ± 404 |
Absorption
The pharmacokinetics of cysteamine with administration of PROCYSBI are consistent with a delayed-release formulation; the mean T max for cysteamine was 188 minutes with PROCYSBI compared with 73 minutes for immediate-release cysteamine bitartrate.
The mean plasma cysteamine peak and AUC were similar when a single PROCYSBI dose of 600 mg was administered with 240 mL orange juice or with 240 mL water. The systemic exposure to cysteamine was similar when PROCYSBI was administered with orange juice as a whole capsule and sprinkled in applesauce in the fasted state. In a food effect study conducted in healthy subjects (n=20), administration of a meal 30 minutes following PROCYSBI administration (intact capsules) decreased C max by 34% and AUC 0-t by 32% compared to administration of a meal 2 hours post-dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.6) ] .
Distribution
Cysteamine was moderately bound to human plasma proteins, predominantly to albumin, with mean protein binding of about 52%. Plasma protein binding was independent of concentration over the concentration range achieved clinically with the recommended doses. The volume of distribution (Vd/F) was 382 L for PROCYSBI compared with 198 L for immediate-release cysteamine bitartrate.
Elimination
After each dose of PROCYSBI the cysteamine concentration in the blood continues to decline for approximately 30 minutes and the WBC cystine concentration increases accordingly .
The apparent clearance (Cl/F) of cysteamine was similar between PROCYSBI (1.2 ± 0.8 L/min) and immediate-release cysteamine bitartrate (1.4 ± 0.8 L/min).
The half-life was 253 minutes for PROCYSBI and 90 minutes for immediate-release cysteamine bitartrate.
Specific Populations
Pediatric patients 1 year to less than 6 years of age
The pharmacokinetics of cysteamine with administration of PROCYSBI at steady state were evaluated in 11 cysteamine treatment naïve patients between the ages of 1 and 5 years of age with nephropathic cystinosis. A mean (± SD) C max of 1.26 ± 0.86 mg/L was reached at an average T max of 199 ± 138 minutes and the mean (± SD) dose was 242 ± 93 mg/m 2 . The mean exposure was calculated to be 206 ± 113 minutes•mg/L (AUC last ) and 231 ± 123 minutes•mg/L (AUC inf ). The mean CL ss /F was estimated to be 0.69 ± 0.37 L/minutes with an average half-life (t ½ ) of 270 ± 56 minutes. Overall, the pharmacokinetics in patients between the ages of 1 and 5 years of age is comparable with those in older children and adults.
Patients with Renal Impairment
The pharmacokinetics of cysteamine with administration of a single oral dose of 600 mg PROCYSBI were evaluated in non-cystinosis subjects with renal impairment and healthy subjects with normal renal function (eGFR >90 mL/min/1.73m 2 ) matched for age, body mass index and sex.
The mean AUC inf and mean C max for cysteamine were 8%, and 3% lower, respectively, in subjects with mild renal impairment (eGFR 60 to 89 mL/min/1.73m 2 ) compared to healthy subjects. In subjects with moderate renal impairment (eGFR 30 to 59 mL/min/1.73m 2 ) and severe renal impairment (≤29 mL/min/1.73m 2 ), the mean AUC inf was 49% and 35% higher and the mean C max was 27% and 11% higher, respectively compared to healthy subjects. The mean t½ was 7 hours, 8.3 hours, and 8.8 hours in subjects with mild, moderate, and severe renal impairment, respectively and ranged from 6.6 to 7.5 hours in healthy subjects. The mean CL/F was 1.57, 1.08, and 1.09 L/min in mild, moderate, and severe renal impairment subjects compared to 1.40 to 1.60 L/min in healthy subjects.
In subjects with end-stage renal disease receiving 4 hours of hemodialysis, the geometric mean C max and AUC inf of cysteamine was 60% higher when PROCYSBI was administered 3 hours before hemodialysis, and 22% higher when administered 1 hour after completion of hemodialysis compared to healthy subjects. Approximately 4.3% (25.6 mg) of the 600 mg PROCYSBI dose was removed from the body with hemodialysis. The apparent clearance of cysteamine in subjects who received PROCYSBI before hemodialysis was approximately 65 mL/min.
The increased exposure to cysteamine in patients with renal impairment compared to healthy subjects is not considered to be clinically meaningful.
Drug Interaction Studies
An in vitro study indicates cysteamine bitartrate is not an inhibitor of CYP enzymes (CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1, and CYP3A4). The potential for cysteamine to affect the pharmacokinetics of other drugs via these enzymes is low.
Omeprazole
The effect of concomitant omeprazole on the pharmacokinetics of cysteamine was evaluated following co-administration of single PROCYSBI dose of 600 mg with 20 mg of omeprazole in comparison to administration of PROCYSBI alone in healthy subjects in two separate studies. In both studies omeprazole was dosed once daily for 5 days before co-administration with PROCYSBI and single dose PROCYSBI was given either with 240 mL orange juice in one study or with 240 mL water in another study. The pharmacokinetic parameters of cysteamine were not significantly different when PROCYSBI was administered with omeprazole compared to when PROCYSBI was administered alone, regardless whether PROCYSI was administered with orange juice or water [see Dosage and Administration (2.6) , Drug Interactions (7.1) ].
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Cysteamine has not been tested for its carcinogenic potential in long-term animal studies.
PROCYSBI was not mutagenic in the Ames test. It produced a negative response in an in-vitro sister chromatid exchange assay in human lymphocytes, but a positive response in a similar assay in hamster ovarian cells.
Repeat breeding reproduction studies were conducted in male and female rats. Cysteamine was found to have no effect on fertility and reproductive performance at an oral dose of 75 mg/kg per day (450 mg/m 2 per day, 0.4 times the recommended human dose based on body surface area). At an oral dose of 375 mg/kg per day (2250 mg/m 2 per day, 1.7 times the recommended human maintenance dose based on body surface area), it reduced the fertility of the adult rats and the survival of their offspring.
CLINICAL STUDIES
Clinical Trials with Immediate-Release Cysteamine
Efficacy of immediate-release cysteamine bitartrate was demonstrated in open-label clinical trials of cysteamine hydrochloride and phosphocysteamine.
An open-label clinical trial of cysteamine hydrochloride was conducted in 94 pediatric patients (mainly from the United States) with nephropathic cystinosis. Patients were treated with increasing doses of cysteamine hydrochloride (mean dose 54 mg/kg per day) to attain WBC cystine concentrations of less than 2 nmol ½ cystine/mg protein 5 to 6 hours post-dose. The clinical outcomes were compared with a historical control group of 17 pediatric patients who had been in the placebo group of a randomized placebo-controlled trial of ascorbic acid. Cysteamine-treated patients had been diagnosed at a mean age of 22 months and had a mean age of 46 months old at study entry; placebo patients had been diagnosed at about 29 months and had a mean age of about 52 months old at trial entry. The principal measures of effectiveness were serum creatinine and calculated creatinine clearance and growth (height).
The average median WBC cystine concentration during treatment was 1.7 ± 0.2 nmol ½ cystine/mg protein. There were 70 cysteamine-treated patients with a baseline serum creatinine of less than 2 mg/dL who were followed for at least 1 year, and 17 placebo patients. Twelve of the 94 cysteamine-treated patients required early dialysis or renal transplant. Median follow-up of cysteamine patients was over 32 months, and 20% were followed more than 5 years. Median follow-up of the placebo group was 20 months; only 1 patient was followed more than 24 months. Glomerular function among cysteamine-treated patients was maintained over time. Placebo-treated patients experienced a gradual rise in serum creatinine. Renal tubular function was not affected by treatment.
Calculated creatinine clearances were evaluated for two groups of pediatric patients, one with poor WBC cystine depletion (defined as median WBC cystine concentrations greater than 3 nmol ½ cystine/mg protein or WBC cystine concentrations not measured at least 2 times per year) and one with good WBC cystine depletion. The final mean creatinine clearance of the good depletion group was 20.8 mL/min/1.73 m 2 greater than the mean for the poor-depletion group.
Height-for-age measurements of treated patients were compared with height-for-age measurements of 143 patients initially screened for inclusion in the trial. Patients on treatment maintained growth (i.e., did not show increasing growth failure compared with normal scales) although growth velocity did not increase enough to allow patients to catch up to age norms for height.
In another open-label clinical trial, 46 patients who had completed the clinical trial of cysteamine hydrochloride (averaging 6.5 years of treatment) and 93 treatment naïve patients were treated with either cysteamine hydrochloride or phosphocysteamine (patient's choice). Patients had cystinosis diagnosed by elevated WBC cystine (mean 3.63 nmol ½ cystine/mg). Newly enrolled patients and the 46 continuing patients were required to have serum creatinine less than 3 mg/dL and 4 mg/dL, respectively. Patients were randomized to doses of 1.3 or 1.95 grams/m 2 per day and stratified according to whether the serum creatinine was above 1.2 mg/dL or not. Doses could be raised if WBC cystine concentrations were approximately 2 nmol ½ cystine/mg protein and lowered due to intolerance. The mean age of the newly enrolled patients was about 49 months for the cysteamine group and about 34 months for the phosphocysteamine group. The mean age of the patients in the long-term follow-up group was about 9 years.
Mean doses were 1.27 grams/m 2 per day and 1.87 grams/m 2 per day in the two groups and WBC cystine concentrations averaged 1.72 ± 1.65 nmol ½ cystine/mg protein and 1.86 ± 0.92 nmol ½ cystine/mg protein in the 1.3 grams/m 2 per day and 1.95 grams/m 2 per day in the two groups, respectively. In new patients, serum creatinine was essentially unchanged over the period of follow-up (about half of the patients were followed for 24 months) and phosphocysteamine and cysteamine hydrochloride had similar effects. The long-term follow-up group also had essentially no change in renal function (almost 80% were followed at least 2 years). In four studies of patients with untreated cystinosis, renal death (need for transplant or dialysis) occurred at median age of less than 10 years. Both new patients and patients in the long-term follow-up group maintained height (although they did not catch up from baseline). There was no apparent difference in height maintenance between the two doses.
Clinical Trials with PROCYSBI
Multi-Center, Open-Label, Randomized Clinical Trial in Patients Receiving Immediate-Release Cysteamine Bitartrate
A clinical trial comparing immediate-release cysteamine bitartrate and PROCYSBI was conducted in 43 (40 pediatric and 3 adult) patients with nephropathic cystinosis (Study RP103-03; NCT01000961). Patient age ranged from 6 to 26 years (mean age 12 years) and 56% were male. Patients with WBC cystine concentrations greater than 2 nmol ½ cystine/mg protein (measured using the mixed leukocyte assay) and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR corrected for body surface area) less than 30 mL/minute/1.73 m 2 at the time of screening were excluded from the trial. Prior to randomization, patients were to be on a stable dose of immediate-release cysteamine bitartrate administered every six hours. PROCYSBI dose adjustments of up to approximately 100% of the total daily dose of immediate-release cysteamine bitartrate were allowed by trial criteria. The average total daily dose of PROCYSBI for patients completing the clinical trial was approximately 91% of the average total daily dose of immediate-release cysteamine bitartrate for patients at trial entry.
This trial demonstrated that at steady-state, PROCYSBI administered every 12 hours was non-inferior to immediate-release cysteamine bitartrate administered every 6 hours with respect to the depletion of WBC cystine concentrations (Table 5). Using a linear mixed effects statistical analysis model, the least-square-mean value of WBC cystine was 0.52 ± 0.06 nmol ½ cystine/mg protein after 12 hours under PROCYSBI and 0.44 ± 0.06 nmol ½ cystine/mg protein after 6 hours under immediate-release cysteamine; a difference of 0.08 ± 0.03 nmol ½ cystine/mg protein (95.8% Confidence Interval = 0.01 to 0.15).
| Immediate-release cysteamine bitartrate | PROCYSBI | |
|---|---|---|
| WBC cystine concentration in nmol ½ cystine/mg protein (LS Mean ± SE) | 0.44 ± 0.06 | 0.52 ± 0.06 |
| Difference in Treatment effect (LS mean ± SE) [95.8% CI; p-value] | 0.08 ± 0.03 [0.01 to 0.15; <0.0001] | |
Multi-Center, Single-Arm, Open-Label, Long-Term Extension Clinical Trial of PROCYSBI
Forty of the 41 patients completing the randomized trial continued treatment with PROCYSBI in an open-label extension trial, for a total treatment duration ranging from 1 month to 6.7 years in the study (Study RP103-03-04; NCT01197378). Thirty-six of the 40 patients continued treatment with PROCYSBI for at least 24 months and 20 patients continued treatment for longer than 60 months in the extension trial, and maintained their mean WBC cystine concentrations below 1 nmol ½ cystine/mg protein (measured using the mixed leukocyte assay) over this time period.
Thirteen pediatric patients, aged 2 to 6 years, were also enrolled in the extension trial and treated with PROCYSBI. All of them were on treatment with immediate-release cysteamine bitartrate at the time of enrollment. All 13 patients received at least 18 months of treatment with PROCYSBI, and their mean ± SD WBC cystine concentration (measured using the mixed leukocyte assay) decreased from 1.41 ± 1.03 nmol ½ cystine/mg protein at baseline to 1.22 ± 1.40 nmol ½ cystine/mg protein after 18 months of treatment. Seven of these pediatric patients were able to achieve a WBC cystine concentration (measured using the mixed leukocyte assay) of less than 1.0 nmol ½ cystine/mg protein after 18 months of treatment; their mean ± SD dose of PROCYSBI increased from 0.81 ± 0.25 grams/m 2 per day at baseline to 0.90 ± 0.25 grams/m 2 per day after 18 months of treatment.
During extended treatment with PROCYSBI, mean estimates of renal function, as measured by the eGFR, were maintained.
Multi-Center, Open-Label, Clinical Trial in Cysteamine Naïve Patients Less than 6 Years of Age
A clinical trial of PROCYSBI (Study RP103-08; NCT01744782) was conducted in 17 patients with a documented diagnosis of nephropathic cystinosis who were naïve to cysteamine treatment (15 patients between the ages of 1 and 5 years, one 9-year old and one 22-year old). The PROCYSBI starting dose was ¼ the maintenance dose of 1 gram/m 2 /day (actual dosing was based on weight bands using the available capsule strengths, as shown in (Table 1) and the dosage was gradually increased by 10% every 2 weeks. Dosage adjustment was allowed throughout the trial and was based on subject-specific factors (e.g., weight, tolerability) and WBC cystine concentrations. WBC cystine concentrations were obtained 30 minutes after the morning dose collected bi-monthly until the patient's WBC cystine concentration (using the mixed leukocyte assay) was < 1 nmol ½ cystine/mg protein. Treatment duration was at least 12 months.
Fourteen of the 15 patients between 1 year and less than 6 years of age completed 12 months of treatment, and 10 patients completed 18 months of treatment. Thirteen of the 14 patients achieved their highest total daily dosage of PROCYSBI following the 9-month visit (9-month visit for 8 subjects, 12-month visit for 4 subjects, and 18-month visit for 1 subject).
Some patients did not have WBC cystine samples collected at each visit or results were not reportable due to laboratory errors. Thus, the numbers of patients with available WBC cystine data varied across the time points analyzed. In patients with missing samples, dose escalation was continued if the patient's last reported WBC cystine concentration was > 1 nmol ½ cystine/mg protein.
In patients 1 year to less than 6 years, the mean (±SD) WBC cystine concentration on Day 1, 30 minutes following the first dose, was 3.17±2.95 nmol ½ cystine/mg protein (n=15 patients). At 12 months (13 patients with samples), the mean WBC cystine concentration was 0.80 ± 0.60 nmol ½ cystine/mg protein at 30 minutes post dose. At 18 months (9 patients with samples) the mean WBC cystine concentration was 0.74 ± 0.64 nmol ½ cystine/mg protein at 30 minutes post dose.
In patients 1 year to less than 6 years, the mean (±SD) weight percentiles at Day 1 (n=14), 12 months (n=13) and 18 months (n=10) were 3.5 ± 11.1, 11.9 ± 18.3, and 30.1 ± 28.2, respectively, and patient weight z-scores were -4.0 ± 2.1, -2.2 ± 1.7, and -1.3 ± 2.0, respectively. In the same patients, similar trends were observed for height.
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
PROCYSBI (cysteamine bitartrate) delayed-release capsules
- 25 mg cysteamine : A hard gelatin capsule with light blue opaque cap imprinted with "PRO" in white ink and light blue opaque body imprinted with "25 mg" in white ink, supplied as bottle of 60 capsules (NDC 75987-100-04). Each bottle contains one desiccant canister and one oxygen absorber canister.
- 75 mg cysteamine : A hard gelatin capsule with dark blue opaque cap imprinted with "PRO" in white ink and light blue opaque body imprinted with "75 mg" in white ink, supplied as bottle of 250 capsules (NDC 75987-101-08). Each bottle contains one desiccant canister and two oxygen absorber canisters.
PROCYSBI (cysteamine bitartrate) delayed-release oral granules
- 75 mg cysteamine: Single-use packets containing white to off-white granules, supplied as 60 packets in a carton (NDC 75987-140-13).
- 75 mg cysteamine: Single-use packets containing white to off-white granules, supplied as 120 packets in a carton (NDC 75987-140-14).
- 300 mg cysteamine: Single-use packets containing white to off-white granules, supplied as 60 packets in a carton (NDC 75987-145-13).
- 300 mg cysteamine: Single-use packets containing white to off-white granules, supplied as 120 packets in a carton (NDC 75987-145-14).
Storage and Handling
- Prior to dispensing, store PROCYSBI delayed-release capsules and PROCYSBI delayed-release oral granules in a refrigerator, 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F).
- Dispense PROCYSBI delayed-release capules and PROCYSBI delayed-release oral granules with a 4 month discard date.
- Dispense in original packaging. Do not subdivide or repackage.
- Do not remove desiccant or oxygen absorber(s) from the bottle of PROCYSBI delayed-release capsules. Keep bottles tightly closed in a dry place.
- Protect from light and moisture.
Instructions for the Patient
- Store PROCYSBI delayed-release capsules and PROCYSBI delayed-relase oral granules at room temperature, 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) in the original packaging. Do not subdivide or repackage.
- Protect from light and moisture.
- Do not store PROCYSBI delayed-release oral granules in opened packets.
Instructions for Use PROCYSBI ® (Pro-CIS-bee) (cysteamine bitartrate) delayed-release capsules and delayed-release oral granules
PROCYSBI is available as :
- Capsules in bottles (see " Taking PROCYSBI Capsules ")
- Oral granules in packets (see " Taking PROCYSBI Oral Granules ")
Your doctor will tell you the number of capsules or packets of oral granules you need to take for each dose. If you have any questions, talk to your doctor.
Taking PROCYSBI capsules
PROCYSBI capsules should be swallowed whole with fruit juice (except grapefruit juice) or water. If you cannot swallow the capsule whole, you can open each capsule and take the capsule contents with certain foods and juices, or the capsule contents can be given through a gastrostomy tube (G-tube).
Opening PROCYSBI capsules:
- Do not pinch the PROCYSBI capsule in the center.
- Do not crush or chew the PROCYSBI capsule.
- Use both hands to open the PROCYSBI capsule.
- Hold each end of the PROCYSBI capsule with your thumb and index (pointer) fingers and gently twist the two ends in opposite directions to open.
Taking PROCYSBI with applesauce or berry jelly:
Do not take PROCYSBI with any food other than applesauce or berry jelly.
| Step 1 : | Place about ½ cup (4 ounces) of applesauce or berry jelly into a clean container. If needed, use a smaller amount you can finish in one feeding. Do not use any other food. |
| Step 2: | Open the PROCYSBI capsule. See " Opening PROCYSBI capsules " above. You may need to use more than 1 PROCYSBI capsule for the dose prescribed by your doctor. |
| Step 3: | Sprinkle the granules that are inside the capsule onto the applesauce or berry jelly. |
| Step 4: | Mix the granules with the applesauce or berry jelly. Do not crush the granules. |
| Step 5: | Swallow the applesauce or berry jelly and granules mixture within 30 minutes after preparing. Do not chew the granules. Do not save the applesauce or berry jelly and granules for later use. |
Taking PROCYSBI with fruit juice:
Do not take PROCYSBI with grapefruit juice.
| Step 1: | Pour about ½ cup (4 ounces) of fruit juice into a clean cup. |
| Step 2: | Open the PROCYSBI capsule. See " Opening PROCYSBI capsules " above. You may need to use more than 1 PROCYSBI capsule for the dose prescribed by your doctor. |
| Step 3: | Sprinkle all the granules that are inside the capsule into ½ cup (4 ounces) of fruit juice. |
| Step 4: | Stir gently until mixed. Do not crush the granules. |
| Step 5: | Drink all of the fruit juice and granules mixture within 30 minutes of mixing. Do not chew the granules. Do not save the fruit juice or water and granules mixture for later use. |
Giving PROCYSBI through a gastrostomy tube (G-tube):
It is best to use a straight (bolus) feeding tube.
For people who have a gastrostomy tube (G-tube) that is size 14 French or larger, PROCYSBI may be given as follows:
Use only strained applesauce with no chunks when giving PROCYSBI through a gastrostomy tube (G-tube).
| Step 1: | Flush the gastrostomy tube button with 5 mL of water to clear the button. |
| Step 2: | Place about ½ cup (4 ounces) of applesauce into a clean container. Children who weigh 55 pounds (25 kilograms) or less can take PROCYSBI with at least 1/8 cup (1 ounce) of applesauce. |
| Step 3: | Open the PROCYSBI capsule. See " Opening PROCYSBI capsules " above. You may need to use more than 1 PROCYSBI capsule for the dose prescribed by your doctor. |
| Step 4: | Sprinkle the granules that are inside the capsule on the applesauce. Gently mix the granules with the applesauce. Do not crush the granules. |
| Step 5: | Place the tip of a catheter tip syringe at the bottom of the container of applesauce and granules mixture. For an adult dose, draw up about 40 mL of the mixture. When giving to a child, draw up at least 10 mL of the mixture for doses of 1 or 2 capsules. |
| Step 6: | Place the tip of the catheter tip syringe into the feeding tube that will be connected to the gastrostomy tube. Fill the feeding tube with the applesauce and granules mixture. |
| Step 7: | Hold the feeding tube in a horizontal (straight across) position. Give the applesauce and granules mixture through the gastrostomy tube at a quick and steady rate of 10 mL over 10 seconds. |
| Step 8: | Repeat Step 5 through Step 7 until all of the applesauce and granules mixture is given. Give all of the applesauce and granules mixture through the gastrostomy tube within 30 minutes of mixing. Do not save the applesauce and granules mixture for later use. |
| Step 9: | Draw up at least 10 mL of fruit juice or water into another catheter tip syringe. Do not use grapefruit juice. Gently swirl the syringe. Flush the gastrostomy tube with the fruit juice or water. Use enough fruit juice or water to flush the gastrostomy tube so that there is no applesauce and granules mixture left in the gastrostomy tube. |
Taking PROCYSBI oral granules
You must mix the PROCYSBI oral granules in packets with certain foods and juices to take your PROCYSBI dose. PROCYSBI oral granules can also be given through a gastrostomy tube (G-tube).
Opening PROCYSBI oral granules in packets:
- Tear open the packet along the dotted (perforated) line.
- Do not store granules in opened packets for your next dose.
Taking PROCYSBI with applesauce or berry jelly:
Do not take PROCYSBI with any food other than applesauce or berry jelly.
| Step 1: | Place about ½ cup (4 ounces) of applesauce or berry jelly into a clean container. Do not use any other food. |
| Step 2: | Open the packet of PROCYSBI oral granules. See " Opening PROCYSBI oral granules in packets " above. You may need to use more than 1 packet of PROCYSBI oral granules for the dose prescribed by your doctor. |
| Step 3: | Sprinkle all the granules that are inside the packet onto the applesauce or berry jelly. |
| Step 4: | Mix the granules with the applesauce or berry jelly. Do not crush the granules. |
| Step 5: | Swallow the applesauce or berry jelly and granules mixture within 30 minutes after preparing. Do not chew the granules. Do not save the applesauce or berry jelly and granules for later use. |
Taking PROCYSBI with fruit juice:
Do not take PROCYSBI with grapefruit juice.
| Step 1: | Pour about ½ cup (4 ounces) of fruit juice into a clean cup. |
| Step 2: | Open the PROCYSBI packet. See " Opening PROCYSBI oral granules in packets " above. You may need to use more than 1 packet of PROCYSBI oral granules for the dose prescribed by your doctor. |
| Step 3: | Sprinkle all the granules that are inside the packet into ½ cup (4 ounces) of fruit juice. |
| Step 4: | Stir gently until mixed. Do not crush the granules. |
| Step 5: | Drink all of the fruit juice and granules mixture within 30 minutes of mixing. Do not chew the granules. Do not save the fruit juice and granules for later use. |
Giving PROCYSBI through a gastrostomy tube (G-tube):
It is best to use a straight (bolus) feeding tube.
For people who have a gastrostomy tube (G-tube) that is size 14 French or larger, PROCYSBI may be given as follows:
Use only strained applesauce with no chunks when giving PROCYSBI through a gastrostomy tube (G-tube).
| Step 1: | Flush the gastrostomy tube button with 5 mL of water to clear the button. |
| Step 2: | Place about ½ cup (4 ounces) of applesauce into a clean container. Children who weigh 55 pounds (25 kilograms) or less can take PROCYSBI with at least 1/8 cup (1 ounce) of applesauce. |
| Step 3: | Open the packet of PROCYSBI oral granules. See " Opening PROCYSBI oral granules in packets " above. You may need to use more than 1 packet of PROCYSBI oral granules for the dose prescribed by your doctor. |
| Step 4: | Sprinkle all the granules that are inside the packet on the applesauce. Gently mix the granules with the applesauce. Do not crush the granules. |
| Step 5: | Place the tip of a catheter tip syringe at the bottom of the container of applesauce and granules mixture. For an adult dose, draw up about 40 mL of the mixture. When giving to a child, draw up at least 10 mL of the mixture for doses of 1 or 2 packets. |
| Step 6: | Place the tip of the catheter tip syringe into the feeding tube that will be connected to the gastrostomy tube. Fill the feeding tube with the applesauce and granules mixture. |
| Step 7: | Hold the feeding tube in a horizontal (straight across) position. Give the applesauce and granules mixture through the gastrostomy tube at a quick and steady rate of 10 mL over 10 seconds. |
| Step 8: | Repeat Step 5 through Step 7 until all of the applesauce and granules mixture is given. Give all of the applesauce and granules mixture through the gastrostomy tube within 30 minutes of mixing. Do not save the applesauce and granules mixture for later use. |
| Step 9: | Draw up at least 10 mL of fruit juice into another catheter tip syringe. Do not use grapefruit juice. Gently swirl the syringe. Flush the gastrostomy tube with the fruit juice. Use enough fruit juice to flush the gastrostomy tube so that there is no applesauce and granules mixture left in the gastrostomy tube. |
How should I store PROCYSBI?
- Store PROCYSBI capsules and PROCYSBI oral granules at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Keep PROCYSBI in the original packaging. Do not put PROCYSBI in another container (repackage).
- Keep PROCYSBI in a dry place to protect from moisture.
- The PROCYSBI bottle contains a desiccant to help keep the medicine dry (protect it from moisture). Do not remove the desiccant from the bottle.
- Protect from light.
- Do not store opened packets of PROCYSBI oral granules for later use.
- Throw away (dispose of) any unused PROCYSBI by the "discard after" date on the bottle or carton.
Keep PROCYSBI and all medicines out of the reach of children.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Horizon Therapeutics USA, Inc., Deerfield, IL 60015
Revised: December 2024
Mechanism of Action
Cysteamine is an aminothiol that participates within lysosomes in a thiol-disulfide interchange reaction converting cystine into cysteine and cysteine-cysteamine mixed disulfide, both of which can exit the lysosome in patients with cystinosis.