Rebif prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Rebif patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- For subcutaneous injection only (2.1 )
- The recommended dose is either 22 mcg or 44 mcg injected subcutaneously three times per week (2.1 )
- Titration: Generally, the starting dose should be 20% of the prescribed dose three times per week, and increased over a 4 week period to the targeted recommended dose of either 22 mcg or 44 mcg injected subcutaneously three times per week (2.1 )
- Analgesics and/or antipyretics on treatment days may help ameliorate flu-like symptoms (2.3 )
Dosing Information
The recommended dose of REBIF is either 22 mcg or 44 mcg injected subcutaneously three times per week. REBIF should be administered, if possible, at the same time (preferably in the late afternoon or evening) on the same three days (e.g., Monday, Wednesday, and Friday) at least 48 hours apart each week.
Generally, patients should be started at 20% of the prescribed dose three times per week and increased over a 4-week period to the targeted dose, either 22 mcg three times per week (see Table 1 ) or 44 mcg three times per week (see Table 2 ). Patients prescribed a targeted dose of 22 mcg three times per week should use the prefilled syringes for titration.
A Titration Pack containing 6 doses of 8.8 mcg (0.2 mL) and 6 doses of 22 mcg (0.5 mL) is available for use during the titration period in both REBIF prefilled syringes and REBIF Rebidose autoinjectors.
| Week of Use | Dose | Syringe to Use | Amount of syringe |
|---|---|---|---|
| Week 1 Titration | 4.4 mcg | 8.8 mcg syringe | Use half of syringe |
| Week 2 Titration | 4.4 mcg | 8.8 mcg syringe | Use half of syringe |
| Week 3 Titration | 11 mcg | 22 mcg syringe | Use half of syringe |
| Week 4 Titration | 11 mcg | 22 mcg syringe | Use half of syringe |
| Week 5 and after | 22 mcg | 22 mcg syringe or autoinjector | Use full syringe or autoinjector |
| Week of Use | Dose | Syringe or Autoinjector to Use | Amount of syringe or autoinjector |
|---|---|---|---|
| Week 1 Titration | 8.8 mcg | 8.8 mcg syringe or autoinjector | Use full syringe or autoinjector |
| Week 2 Titration | 8.8 mcg | 8.8 mcg syringe or autoinjector | Use full syringe or autoinjector |
| Week 3 Titration | 22 mcg | 22 mcg syringe or autoinjector | Use full syringe or autoinjector |
| Week 4 Titration | 22 mcg | 22 mcg syringe or autoinjector | Use full syringe or autoinjector |
| Week 5 and after | 44 mcg | 44 mcg syringe or autoinjector | Use full syringe or autoinjector |
Decreased peripheral blood counts or elevated liver function tests may necessitate dose reduction or discontinuation of REBIF administration until toxicity is resolved [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 , 5.5) and Adverse Reactions (6) ].
Important Administration Instructions
REBIF is intended for use under the guidance and supervision of a physician. It is recommended that physicians or qualified medical personnel train patients in the proper technique for self-administering subcutaneous injections using the prefilled syringe or injection device approved for use with REBIF. Injection depth of the REBIF Rebidose autoinjector is fixed at 8 mm; the healthcare provider should determine the injection technique.
The initial injection should be performed under the supervision of an appropriately qualified healthcare provider.
Appropriate instruction for self-injection or injection by another person should be provided to the patient or their caregiver, including careful review of the REBIF Medication Guide and the REBIF Rebidose autoinjector Instructions for Use that accompanies the product. Users should demonstrate competency in all aspects of the injection prior to independent use. If a patient is to self-administer REBIF, the physical and cognitive ability of that patient to self-administer and properly dispose of prefilled syringes or the REBIF Rebidose autoinjectors should be assessed. Patients with severe neurological deficits should not self-administer injections without assistance from a trained caregiver.
Advise patients and caregivers to:
- visually inspect REBIF for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration
- use aseptic technique when administering REBIF
- rotate site of injection with each dose to minimize the likelihood of severe injection site reactions, including necrosis or localized infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ]
- use a puncture-resistant container for safe disposal of used needles, prefilled syringes and REBIF Rebidose autoinjectors
- do not re-use needles, syringes or REBIF Rebidose autoinjectors
Premedication for Flu-like Symptoms
Concurrent use of analgesics and/or antipyretics may help ameliorate flu-like symptoms associated with REBIF use on treatment days.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Rebif prescribing information
| Warnings and Precautions (5.7 ) | 7/2023 |
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
REBIF is indicated for the treatment of relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (MS), to include clinically isolated syndrome, relapsing-remitting disease, and active secondary progressive disease, in adults.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- For subcutaneous injection only (2.1 )
- The recommended dose is either 22 mcg or 44 mcg injected subcutaneously three times per week (2.1 )
- Titration: Generally, the starting dose should be 20% of the prescribed dose three times per week, and increased over a 4 week period to the targeted recommended dose of either 22 mcg or 44 mcg injected subcutaneously three times per week (2.1 )
- Analgesics and/or antipyretics on treatment days may help ameliorate flu-like symptoms (2.3 )
Dosing Information
The recommended dose of REBIF is either 22 mcg or 44 mcg injected subcutaneously three times per week. REBIF should be administered, if possible, at the same time (preferably in the late afternoon or evening) on the same three days (e.g., Monday, Wednesday, and Friday) at least 48 hours apart each week.
Generally, patients should be started at 20% of the prescribed dose three times per week and increased over a 4-week period to the targeted dose, either 22 mcg three times per week (see Table 1 ) or 44 mcg three times per week (see Table 2 ). Patients prescribed a targeted dose of 22 mcg three times per week should use the prefilled syringes for titration.
A Titration Pack containing 6 doses of 8.8 mcg (0.2 mL) and 6 doses of 22 mcg (0.5 mL) is available for use during the titration period in both REBIF prefilled syringes and REBIF Rebidose autoinjectors.
| Week of Use | Dose | Syringe to Use | Amount of syringe |
|---|---|---|---|
| Week 1 Titration | 4.4 mcg | 8.8 mcg syringe | Use half of syringe |
| Week 2 Titration | 4.4 mcg | 8.8 mcg syringe | Use half of syringe |
| Week 3 Titration | 11 mcg | 22 mcg syringe | Use half of syringe |
| Week 4 Titration | 11 mcg | 22 mcg syringe | Use half of syringe |
| Week 5 and after | 22 mcg | 22 mcg syringe or autoinjector | Use full syringe or autoinjector |
| Week of Use | Dose | Syringe or Autoinjector to Use | Amount of syringe or autoinjector |
|---|---|---|---|
| Week 1 Titration | 8.8 mcg | 8.8 mcg syringe or autoinjector | Use full syringe or autoinjector |
| Week 2 Titration | 8.8 mcg | 8.8 mcg syringe or autoinjector | Use full syringe or autoinjector |
| Week 3 Titration | 22 mcg | 22 mcg syringe or autoinjector | Use full syringe or autoinjector |
| Week 4 Titration | 22 mcg | 22 mcg syringe or autoinjector | Use full syringe or autoinjector |
| Week 5 and after | 44 mcg | 44 mcg syringe or autoinjector | Use full syringe or autoinjector |
Decreased peripheral blood counts or elevated liver function tests may necessitate dose reduction or discontinuation of REBIF administration until toxicity is resolved [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 , 5.5) and Adverse Reactions (6) ].
Important Administration Instructions
REBIF is intended for use under the guidance and supervision of a physician. It is recommended that physicians or qualified medical personnel train patients in the proper technique for self-administering subcutaneous injections using the prefilled syringe or injection device approved for use with REBIF. Injection depth of the REBIF Rebidose autoinjector is fixed at 8 mm; the healthcare provider should determine the injection technique.
The initial injection should be performed under the supervision of an appropriately qualified healthcare provider.
Appropriate instruction for self-injection or injection by another person should be provided to the patient or their caregiver, including careful review of the REBIF Medication Guide and the REBIF Rebidose autoinjector Instructions for Use that accompanies the product. Users should demonstrate competency in all aspects of the injection prior to independent use. If a patient is to self-administer REBIF, the physical and cognitive ability of that patient to self-administer and properly dispose of prefilled syringes or the REBIF Rebidose autoinjectors should be assessed. Patients with severe neurological deficits should not self-administer injections without assistance from a trained caregiver.
Advise patients and caregivers to:
- visually inspect REBIF for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration
- use aseptic technique when administering REBIF
- rotate site of injection with each dose to minimize the likelihood of severe injection site reactions, including necrosis or localized infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ]
- use a puncture-resistant container for safe disposal of used needles, prefilled syringes and REBIF Rebidose autoinjectors
- do not re-use needles, syringes or REBIF Rebidose autoinjectors
Premedication for Flu-like Symptoms
Concurrent use of analgesics and/or antipyretics may help ameliorate flu-like symptoms associated with REBIF use on treatment days.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- Injection: 8.8 mcg per 0.2 mL in a graduated, single-dose REBIF prefilled syringe
- Injection: 22 mcg per 0.5 mL in a graduated, single-dose REBIF prefilled syringe
- Injection: 44 mcg per 0.5 mL in a graduated, single-dose REBIF prefilled syringe
- Injection: 8.8 mcg per 0.2 mL in a single-dose prefilled REBIF Rebidose autoinjector
- Injection: 22 mcg per 0.5 mL in a single-dose prefilled REBIF Rebidose autoinjector
- Injection: 44 mcg per 0.5 mL in a single-dose prefilled REBIF Rebidose autoinjector
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Pregnancy: Epidemiological data do not suggest a clear relationship between interferon beta use and major congenital malformations, but interferon beta may cause fetal harm based on animal data (8.1 ).
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Data from a large population-based cohort study, as well as other published studies over several decades, have not identified a drug-associated risk of major birth defects with the use of interferon beta during early pregnancy. Findings regarding a potential risk for low birth weight or miscarriage with the use of interferon beta in pregnancy have been inconsistent (see Data ) . It is unclear whether, as a class of products, administration of interferon beta therapies to pregnant animals at doses greater than those used clinically results in an increased rate of abortion. The potential for REBIF to have adverse effects on embryofetal development has not been fully assessed in animals [ see Data ].
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively. The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown.
Data
Human data
The majority of observational studies reporting on pregnancies exposed to interferon beta products did not identify an association between the use of interferon beta products during early pregnancy and an increased risk of major birth defects.
In a population-based cohort study conducted in Finland and Sweden, data were collected from 1996—2014 in Finland and from 2005—2014 in Sweden on 2,831 pregnancy outcomes from women with MS. 797 pregnancies were in women exposed to interferon beta only. No evidence was found of an increased risk of major birth defects among women with MS exposed to interferon beta products compared to women with MS that were unexposed to any non-steroid therapy for MS (n=1,647) within the study. No increased risks were observed for miscarriages and ectopic pregnancies, though there were limitations in obtaining complete data capture for these outcomes, making the interpretation of the findings more difficult.
Two small cohort studies that examined pregnancies exposed to interferon beta products (without differentiating between subtypes of interferon beta products) suggested that a decrease in mean birth weight may be associated with interferon beta exposure during pregnancy, but this finding was not confirmed in larger observational studies. Two small studies observed an increased prevalence of miscarriage, although the finding was only statistically significant in one study. Most studies enrolled patients later in pregnancy, which made it difficult to ascertain the true percentage of miscarriages. In one small cohort study, a significantly increased risk of preterm birth following interferon beta exposure during pregnancy was observed.
Animal data
In a study in pregnant cynomolgus monkeys, interferon beta was administered daily (intramuscular doses approximately 1, 2, and 7 times the maximum recommended cumulative weekly human dose, based on body surface area) either throughout the period of organogenesis or later in pregnancy (gestation day 90 to term). No adverse effects on embryofetal development were observed; however, the possibility of adverse effects cannot be ruled out because of the small number of animals tested (six per dose group at each developmental period).
Lactation
Risk Summary
Limited published literature has described the presence of interferon beta-1a products in human milk at low levels. There are no data on the effects of interferon beta-1a on milk production. Therefore, the developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for REBIF and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from REBIF or from the underlying maternal condition.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of REBIF did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently than younger subjects. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
REBIF is contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to natural or recombinant interferon beta, human albumin, or any other component of the formulation.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Depression and Suicide: Advise patients to immediately report any symptoms of depression and/or suicidal ideation; consider discontinuation of REBIF if depression occurs (5.1 )
- Hepatic Injury: Monitor liver function tests; monitor patients for signs and symptoms of hepatic injury; consider discontinuing REBIF if hepatic injury occurs (5.2 )
- Anaphylaxis and Other Allergic Reactions: Discontinue REBIF if anaphylaxis occurs (5.3 )
- Injection Site Reactions Including Necrosis: Do not administer REBIF into affected area until fully healed; if multiple lesions occur, change injections sites or discontinue REBIF until healing of skin lesions (5.4 )
- Decreased Peripheral Blood Counts: Monitor complete blood counts (5.5 )
- Thrombotic Microangiopathy: Cases of thrombotic microangiopathy have been reported. Discontinue REBIF if clinical symptoms and laboratory findings consistent with TMA occur (5.6 ).
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Cases of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) have been reported in patients treated with interferon beta products, including REBIF. Discontinue REBIF if PAH is diagnosed (5.7 )
- Seizures: Monitor for seizures when administering REBIF to patients, particularly those with pre-existing seizure disorders (5.8 )
Depression and Suicide
REBIF (interferon beta-1a) should be used with caution in patients with depression, a condition that is common in people with multiple sclerosis. Depression, suicidal ideation, and suicide attempts have been reported to occur with increased frequency in patients receiving interferon compounds, including REBIF. In addition, there have been postmarketing reports of suicide in patients treated with REBIF. Patients should be advised to report immediately any symptoms of depression and/or suicidal ideation to the prescribing physician. If a patient develops depression, cessation of treatment with REBIF should be considered.
Hepatic Injury
Severe liver injury, including some cases of hepatic failure requiring liver transplantation, has been reported rarely in patients taking REBIF. Symptoms of liver dysfunction began from one to six months following the initiation of REBIF. If jaundice or other symptoms of liver dysfunction appear, treatment with REBIF should be discontinued immediately due to the potential for rapid progression to liver failure.
Asymptomatic elevation of hepatic transaminases (particularly SGPT) is common with interferon therapy [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] . REBIF should be initiated with caution in patients with active liver disease, alcohol abuse, increased serum SGPT (> 2.5 times ULN), or a history of significant liver disease. Also, the potential risk of REBIF used in combination with known hepatotoxic products should be considered prior to REBIF administration, or when adding new agents to the regimen of patients already on REBIF. Reduction of REBIF dose should be considered if SGPT rises above 5 times the upper limit of normal. The dose may be gradually re-escalated when enzyme levels have normalized [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9) and Dosage and Administration (2.1) ].
Anaphylaxis and Other Allergic Reactions
Anaphylaxis has been reported as a rare complication of REBIF use. Other allergic reactions have included skin rash and urticaria, and have ranged from mild to severe without a clear relationship to dose or duration of exposure. Several allergic reactions, some severe, have occurred after prolonged use. Discontinue REBIF if anaphylaxis occurs.
Injection Site Reactions Including Necrosis
Injection site reactions, including injection site necrosis, can occur with the use of interferon beta products, including REBIF. In controlled clinical trials, injection site reactions occurred more frequently in REBIF-treated patients (92% in the 44 mcg group and 89% in the 22 mcg group) than in placebo-treated patients (39%) and at a higher frequency in REBIF treated patients (83%) than in AVONEX-treated patients (28%). Injection site necrosis also occurred more frequently in REBIF-treated patients (3% in the 44 mcg group and 1% in the 22 mcg group) than in placebo- treated patients (0) during the two years of therapy.
Injection site reactions including injection site pain, erythema, edema, cellulitis, abscess, and necrosis have been reported in the postmarketing setting. Some occurred more than 2 years after initiation of REBIF. Necrosis occurred at single and at multiple injection sites. Some cases of injection site necrosis required treatment with intravenous antibiotics and surgical intervention (debridement and skin grafting). Some cases of injection site abscesses and cellulitis required treatment with hospitalization for surgical drainage and intravenous antibiotics.
Patient understanding and use of aseptic self-injection techniques and procedures should be periodically evaluated, particularly if injection site necrosis has occurred. Patients should be advised of the importance of rotating sites of injection with each dose and not reusing syringes. Patients should be advised against injecting an area which is inflamed, edematous, erythematous, ecchymotic, or has any other signs of infection. These signs should be reported to a healthcare professional immediately. If multiple lesions occur, change injection site or discontinue therapy until healing occurs.
Decreased Peripheral Blood Counts
Decreased peripheral blood counts in all cell lines, including pancytopenia, have been reported in REBIF-treated patients. In controlled clinical trials, leukopenia occurred at a higher frequency in REBIF-treated patients (36% in 44 mcg group and 28% in 22 mcg group) than in placebo-treated patients (14%) and at a higher frequency in REBIF-treated patients (6%) compared to the AVONEX-treated patients (<1%). Thrombocytopenia and anemia occurred more frequently in 44 mcg REBIF-treated patients (8% and 5%, respectively) than in placebo-treated patients (2% and 3%, respectively). In a pooled analysis of 7 placebo controlled trials with REBIF doses of 22 mcg or 44 mcg, the rate of pancytopenia (in subjects with normal baseline values who developed laboratory values less than the lower limit of normal for all 3 hematology parameters simultaneously) was higher in the total REBIF group (5.5 per 1000 subject-year) than in the placebo group (1.2 per 1000 subject-year). Patients should be monitored for symptoms or signs of decreased blood counts. Monitoring of complete blood and differential white blood cell counts is also recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) and Warnings and Precautions (5.9) ].
Thrombotic Microangiopathy
Cases of thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA), including thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and hemolytic uremic syndrome, some fatal, have been reported with interferon beta products, including REBIF. Cases have been reported several weeks to years after starting interferon beta products. Discontinue REBIF if clinical symptoms and laboratory findings consistent with TMA occur, and manage as clinically indicated.
Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Cases of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) have been reported with interferon beta products, including REBIF. PAH has occurred in patients treated with interferon beta products in the absence of other contributory factors. Many of the reported cases required hospitalization, including one case with interferon beta in which the patient underwent a lung transplant. PAH has developed at various time points after initiating therapy with interferon beta products and may occur several years after starting treatment.
Patients who develop unexplained symptoms (e.g., dyspnea, new or increasing fatigue) should be assessed for PAH. If alternative etiologies have been ruled out and a diagnosis of PAH is confirmed, discontinue treatment and manage as clinically indicated.
Seizures
Caution should be exercised when administering REBIF to patients with pre-existing seizure disorders. Seizures have been temporally associated with the use of beta interferons, including REBIF, in clinical trials and in postmarketing reports.
Laboratory Tests
In addition to those laboratory tests normally required for monitoring patients with multiple sclerosis, blood cell counts and liver function tests are recommended at regular intervals (1, 3, and 6 months) following introduction of REBIF therapy and then periodically thereafter in the absence of clinical symptoms. Patients with myelosuppression may require more intensive monitoring of complete blood cell counts, with differential and platelet counts [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) and Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ] . New or worsening thyroid abnormalities have developed in some patients treated with REBIF. Thyroid function tests are recommended every 6 months in patients with a history of thyroid dysfunction or as clinically indicated.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in more detail in the Warnings and Precautions section of the label:
- Depression and Suicide [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- Hepatic Injury [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
- Anaphylaxis and Other Allergic Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
- Injection Site Reactions including Necrosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ]
- Decreased Peripheral Blood Counts [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ]
- Thrombotic Microangiopathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ]
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ]
- Seizures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) ]
- Laboratory Tests [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9) ]
Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of REBIF cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of other drugs and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
A total of 712 patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS) in two controlled clinical trials took REBIF (22 mcg or 44 mcg given three times per week) [see Clinical Studies (14) ]. Ages ranged from 18 to 55 years. Nearly three-fourths of the patients were female, and more than 90% were Caucasian, largely reflecting the general demographics of the population of patients with multiple sclerosis.
The most commonly reported adverse reactions were injection site disorders, influenza-like symptoms (headache, fatigue, fever, rigors, chest pain, back pain, myalgia), abdominal pain, depression, elevation of liver enzymes and hematologic abnormalities. The most frequently reported adverse reactions resulting in clinical intervention (e.g., discontinuation of REBIF, adjustment in dosage, or the need for concomitant medication to treat an adverse reaction were injection site disorders, influenza-like symptoms, depression, and elevation of liver enzymes [see Warnings and Precautions (5) ] .
Study 1 was a 2-year placebo-controlled study in RRMS patients treated with REBIF 22 mcg (n=189), 44 mcg (n=184), or placebo (n=187). Table 3 enumerates adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities that occurred at an incidence that was at least 2% more in either REBIF-treated group than was observed in the placebo group.
| Body System | Placebo tiw (n=187) | REBIF 22 mcg tiw (n=189) | REBIF 44 mcg tiw (n=184) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred Term | % | % | % |
| BODY AS A WHOLE | |||
| Influenza-like symptoms | 51 | 56 | 59 |
| Headache | 63 | 65 | 70 |
| Fatigue | 36 | 33 | 41 |
| Fever | 16 | 25 | 28 |
| Rigors | 5 | 6 | 13 |
| Chest pain | 5 | 6 | 8 |
| Malaise | 1 | 4 | 5 |
| INJECTION SITE DISORDERS | |||
| Injection Site Reaction | 39 | 89 | 92 |
| Injection Site Necrosis | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| NERVOUS SYSTEM DISORDERS | |||
| Hypertonia | 5 | 7 | 6 |
| Coordination Abnormal | 2 | 5 | 4 |
| Convulsions | 2 | 5 | 4 |
| Somnolence | 1 | 4 | 5 |
| ENDOCRINE DISORDERS | |||
| Thyroid Disorder | 3 | 4 | 6 |
| GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM DISORDERS | |||
| Abdominal Pain | 17 | 22 | 20 |
| Dry Mouth | 1 | 1 | 5 |
| LIVER AND BILIARY SYSTEM DISORDERS | |||
| SGPT Increased | 4 | 20 | 27 |
| SGOT Increased | 4 | 10 | 17 |
| Bilirubinemia | 1 | 3 | 2 |
| MUSCULO-SKELETAL SYSTEM DISORDERS | |||
| Myalgia | 20 | 25 | 25 |
| Back Pain | 20 | 23 | 25 |
| Skeletal Pain | 10 | 15 | 10 |
| HEMATOLOGIC DISORDERS | |||
| Leukopenia | 14 | 28 | 36 |
| Lymphadenopathy | 8 | 11 | 12 |
| Thrombocytopenia | 2 | 2 | 8 |
| Anemia | 3 | 3 | 5 |
| SKIN DISORDERS | |||
| Rash Erythematous | 3 | 7 | 5 |
| Rash Maculo-Papular | 2 | 5 | 4 |
| Hyperhidrosis | 2 | 4 | 4 |
| URINARY SYSTEM DISORDERS | |||
| Micturition Frequency | 4 | 2 | 7 |
| Urinary Incontinence | 2 | 4 | 2 |
| VISION DISORDERS | |||
| Vision Abnormal | 7 | 7 | 13 |
| Xerophthalmia | 0 | 3 | 1 |
Adverse reactions in Study 2, a 1-year active-controlled (vs. interferon beta-1a, 30 mcg once weekly intramuscular injection, n=338) study including 339 patients with MS treated with REBIF were generally similar to those in Study 1, taking into account the disparity in study durations.
Immunogenicity
Anaphylaxis and other allergic reactions have been observed with the use of REBIF [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ] . As with all therapeutic proteins, there is a potential for immunogenicity. In Study 1, the presence of neutralizing antibodies (NAb) to REBIF was determined by collecting and analyzing serum pre-study and at 6 month time intervals during the 2 years of the clinical trial. Serum NAb were detected in 59/189 (31%) and 45/184 (24%) of REBIF-treated patients at the 22 mcg and 44 mcg three times per week doses, respectively, at one or more times during the study. The data reflect the percentage of patients whose test results were considered positive for antibodies to REBIF using an antiviral cytopathic effect assay, and are highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Additionally, the observed incidence of NAb positivity in an assay may be influenced by several factors including sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant medications and underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of the incidence of antibodies to REBIF with the incidence of antibodies to other products may be misleading.
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of REBIF. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Autoimmune Disorders: Drug-induced lupus erythematosus , autoimmune hepatitis
Eye Disorders: Retinal vascular disorders (i.e. retinopathy, cotton wool spots or obstruction of retinal artery or vein)
Respiratory, Thoracic and mediastinal disorders: Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders: Hemolytic anemia
DESCRIPTION
REBIF (interferon beta-1a) is a purified 166 amino acid glycoprotein with a molecular weight of approximately 22,500 daltons. It is produced by recombinant DNA technology using genetically engineered Chinese Hamster Ovary cells into which the human interferon beta gene has been introduced. The amino acid sequence of REBIF is identical to that of natural fibroblast derived human interferon beta. Natural interferon beta and interferon beta-1a (REBIF) are glycosylated with each containing a single N-linked complex carbohydrate moiety.
Using a reference standard calibrated against the World Health Organization natural interferon beta standard (Second International Standard for Interferon, Human Fibroblast GB 23 902 531), REBIF has a specific activity of approximately 270 million international units (MIU) of antiviral activity per mg of interferon beta-1a determined specifically by an in vitro cytopathic effect bioassay using WISH cells and Vesicular Stomatitis virus. REBIF 8.8 mcg, 22 mcg and 44 mcg contains approximately 2.4 million international units, 6 million international units or 12 million international units, respectively, of antiviral activity using this method.
REBIF (interferon beta-1a) is formulated as a sterile solution in a prefilled syringe or REBIF Rebidose autoinjector intended for subcutaneous (sc) injection. Each 0.5 mL (0.5 cc) of REBIF contains either 22 mcg or 44 mcg of interferon beta-1a, 2 mg or 4 mg albumin (human), 27.3 mg mannitol, 0.4 mg sodium acetate, and water for injection. Each 0.2 mL (0.2 cc) of REBIF contains 8.8 mcg of interferon beta-1a, 0.8 mg albumin (human), 10.9 mg mannitol, 0.16 mg sodium acetate, and water for injection.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
The mechanism(s) by which REBIF (interferon beta-1a) exerts its therapeutic effects in patients with multiple sclerosis is unknown.
Pharmacodynamics
The relationships between serum interferon beta-1a levels and measurable pharmacodynamic activities to the mechanism(s) by which REBIF exerts its effects in multiple sclerosis are unknown. No gender-related effects on pharmacodynamic parameters have been observed.
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of REBIF (interferon beta-1a) in people with multiple sclerosis have not been evaluated. In healthy subjects, a single subcutaneous (sc) injection of 60 mcg of REBIF (liquid formulation) resulted in a peak serum concentration (C max ) of 5.1 ± 1.7 IU/mL (mean ± SD), with a median time of peak serum concentration (T max ) of 16 hours. The serum elimination half-life (t1/2) was 69 ± 37 hours, and the area under the serum concentration versus time curve (AUC) from zero to 96 hours was 294 ± 81 IU h/mL. Following every other day sc injections in healthy subjects, an increase in AUC of approximately 240% was observed, suggesting that accumulation of interferon beta-1a occurs after repeat administration. Total clearance is approximately 33-55 L/hour. There have been no observed gender-related effects on pharmacokinetic parameters. Pharmacokinetics of REBIF in pediatric and geriatric patients or patients with renal or hepatic insufficiency have not been established.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis: REBIF has not been tested for carcinogenic potential in animals.
Mutagenesis: Interferon beta was negative in an in vitro bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assay and an in vitro cytogenetic assay in human lymphocytes in the presence and absence of metabolic activation.
Impairment of Fertility: In studies in normally cycling female cynomolgus monkeys given daily subcutaneous injections of interferon beta for six months at doses of up to 9 times the recommended weekly human dose (based on body surface area), no effects were observed on either menstrual cycling or serum estradiol levels. In male monkeys, the same doses of interferon beta had no demonstrable adverse effects on sperm count, motility, morphology, or function.
CLINICAL STUDIES
Two multicenter studies evaluated the safety and efficacy of REBIF in patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis.
Study 1 was a randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled study in patients with multiple sclerosis for at least one year, Kurtzke Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) scores ranging from 0 to 5, and at least 2 acute exacerbations in the previous 2 years. Patients with chronic progressive forms of multiple sclerosis were excluded from the study. Patients received subcutaneous injections of either placebo (n = 187), REBIF 22 mcg (n = 189), or REBIF 44 mcg (n = 184) administered three times per week for two years. Doses of study agents were progressively increased to their target doses during the first 4 to 8 weeks for each patient in the study [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) ].
The primary efficacy endpoint was the number of clinical exacerbations. Numerous secondary efficacy endpoints were also evaluated and included exacerbation-related parameters, effects of treatment on progression of disability and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-related parameters. Progression of disability was defined as an increase in the EDSS score of at least one point sustained for at least 3 months. Neurological examinations were completed every 3 months, during suspected exacerbations, and coincident with MRI scans. All patients underwent proton density T2-weighted (PD/T2) MRI scans at baseline and every 6 months. A subset of 198 patients underwent PD/T2 and T1-weighted gadolinium-enhanced (Gd)-MRI scans monthly for the first 9 months. Of the 560 patients enrolled, 533 (95%) provided 2 years of data and 502 (90%) received 2 years of study agent.
Study results are shown in Table 4 and Figure 1. REBIF at doses of 22 mcg and 44 mcg administered three times per week significantly reduced the number of exacerbations per patient as compared to placebo. Differences between the 22 mcg and 44 mcg groups were not significant (p >0.05).
| Placebo | REBIF 22 mcg | REBIF 44 mcg | |
|---|---|---|---|
| n = 187 | n = 189 | n = 184 | |
| Exacerbation-related | |||
| Mean number of exacerbations per patient over 2 years Intent-to-treat analysis , Poisson regression model adjusted for center and time on study | 2.56 | 1.82 p<0.001 compared to placebo | 1.73 p<0.0001 compared to placebo |
| (Percent reduction) | (29%) | (32%) | |
| Percent (%) of patients exacerbation-free at 2 years Logistic regression adjusted for center. Patients lost to follow-up prior to an exacerbation were excluded from this analysis. (Analysis included 185, 183, and 184 patients for three times per week placebo, 22 mcg REBIF, and 44 mcg REBIF, respectively). | 15% | 25% p<0.05 compared to placebo | 32% |
| Median time to first exacerbation (months) , Cox proportional hazard model adjusted for center | 4.5 | 7.6 | 9.6 |
| MRI | n = 172 | n = 171 | n = 171 |
| Median percent (%) change of MRI PD-T2 lesion area at 2 years ANOVA on ranks adjusted for center. Patients with missing scans were excluded from this analysis. | 11.0% | -1.2% | -3.8% |
| Median number of active lesions per patient per scan (PD/T2; 6 monthly) | 2.25 | 0.75 | 0.5 |
The time to onset of progression in disability sustained for three months was significantly longer in patients treated with REBIF than in placebo-treated patients. The Kaplan-Meier estimates of the proportions of patients with sustained disability are depicted in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Proportions of Patients with Sustained Disability Progression

Study 2 was a randomized, open-label, evaluator-blinded, active comparator study. Patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis with EDSS scores ranging from 0 to 5.5, and at least 2 exacerbations in the previous 2 years were eligible for inclusion. Patients with chronic progressive forms of multiple sclerosis were excluded from the study. Patients were randomized to treatment with three times per week subcutaneous injections of REBIF 44 mcg (n=339) or once weekly intramuscular injections of 30 mcg AVONEX (n=338). Study duration was 48 weeks.
The primary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of patients who remained exacerbation-free at 24 weeks. The principal secondary endpoint was the mean number per patient per scan of combined unique active MRI lesions through 24 weeks, defined as any lesion that was T1 active or T2 active. Neurological examinations were performed every three months by a neurologist blinded to treatment assignment. Patient visits were conducted monthly, and mid-month telephone contacts were made to inquire about potential exacerbations. If an exacerbation was suspected, the patient was evaluated with a neurological examination. MRI scans were performed monthly and analyzed in a treatment-blinded manner.
Patients treated with REBIF 44 mcg three times per week were more likely to remain relapse-free at 24 and 48 weeks than were patients treated with AVONEX 30 mcg once per week (Table 5). This study does not support any conclusion regarding effects on the accumulation of physical disability.
| REBIF 44 mcg | AVONEX 30 mcg | Absolute Difference | Risk of relapse on REBIF relative to AVONEX | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relapses | N=339 | N=338 | ||
| Proportion of patients relapse-free at 24 weeks Logistic regression model adjusted for treatment and center, intent to treat analysis | 75% p <0.001 (REBIF compared to AVONEX) | 63% | 12% (95% CI: 5%, 19%) | 0.68 (95% CI: 0.54, 0.86) |
| Proportion of patients relapse-free at 48 weeks | 62% p = 0.009 (REBIF compared to AVONEX) | 52% | 10% (95% CI: 2%, 17%) | 0.81 (95% CI: 0.68, 0.96) |
| MRI (through 24 weeks) | N=325 | N=325 | ||
| Median of the mean number of combined unique MRI lesions per patient per scan Nonparametric ANCOVA model adjusted for treatment and center, with baseline combined unique lesions as the single covariate (25 th , 75 th percentiles) | 0.17 (0.00, 0.67) | 0.33 (0.00, 1.25) |
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
REBIF is supplied as a sterile solution containing no preservative available in the following package presentations:
Prefilled Syringes :
- REBIF (interferon beta -1a) Titration Pack, NDC 44087-8822-1 - Six REBIF 8.8 mcg prefilled syringes and Six REBIF 22 mcg prefilled syringes
- REBIF (interferon beta -1a) 22 mcg Prefilled syringe - Twelve REBIF 22 mcg prefilled syringes, NDC 44087-0022 - 3
- REBIF (interferon beta -1a) 44 mcg Prefilled syringe - Twelve REBIF 44 mcg prefilled syringes, NDC 44087-0044-3
REBIF Rebidose Autoinjectors :
- REBIF Rebidose (interferon beta-1a) Titration Pack, NDC 44087-0188-1
- Six REBIF Rebidose 8.8 mcg autoinjectors with lime-green injector buttons and Six REBIF Rebidose 22 mcg with yellow injector buttons.
- REBIF Rebidose (interferon beta-1a) 22 mcg Autoinjector
- Twelve REBIF Rebidose 22 mcg autoinjectors with yellow injector buttons, NDC 44087-3322-1
- REBIF Rebidose (interferon beta-1a) 44 mcg Autoinjector
- Twelve REBIF Rebidose 44 mcg autoinjectors with teal-green injector buttons, NDC 44087-3344-1
REBIF should be stored refrigerated between 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C). DO NOT FREEZE. If needed, REBIF may be stored between 36°F to 77°F (2°C to 25°C) for up to 30 days and away from heat and light, but refrigeration is preferred.
Do not use beyond the expiration date printed on packages. REBIF contains no preservatives. Each prefilled syringe and REBIF Rebidose autoinjector is intended for a single dose. Unused portions should be discarded.
Instructions for Use REBIF (Re-bif) (interferon beta-1a) (in-ter-feer-on beta-one-â) Injection for subcutaneous use Prefilled Syringe
Read and follow the Instructions for Use that come with your REBIF prefilled syringe before you start using it and each time you get a refill. Before you use a REBIF prefilled syringe for the first time, make sure your healthcare provider shows you the right way to use it.
Important: For the REBIF Rebidose autoinjector, read the Instructions for Use that come with the REBIF Rebidose autoinjector.
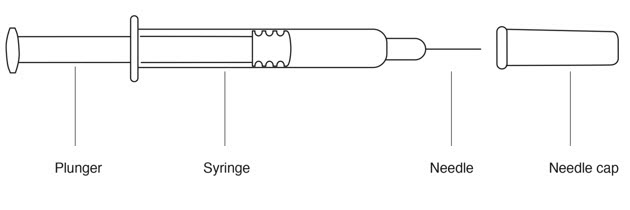
Parts of your REBIF Prefilled Syringe (See Figure A ).
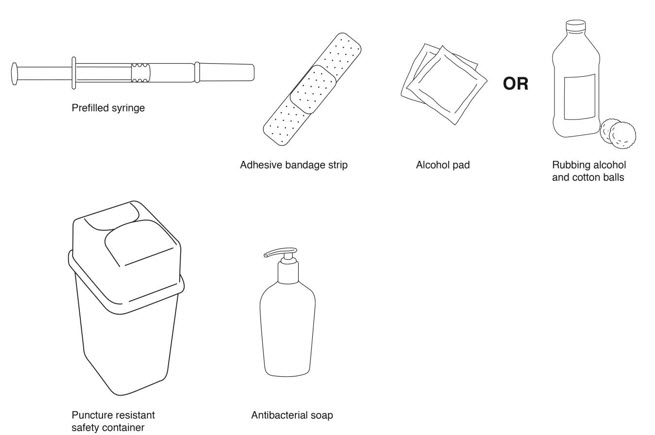
Supplies needed for a REBIF Injection (See Figure B ):
- REBIF prefilled syringe
- alcohol pad or cotton balls and rubbing alcohol
- small adhesive bandage strip if desired
- puncture resistant safety container for disposal of used syringes. See " Disposing of your Needles and Syringes Section " in Step 4 of the IFU.
- antibacterial soap
- an over-the-counter pain or fever reducing medicine, if your healthcare provider has recommended that you take this before, at the same time, or after you give yourself REBIF to help decrease the fever, chills, sweating and muscle aches (flu-like symptoms) that may happen.
Titration (Dosing) Schedule
- When first starting treatment with REBIF, your healthcare provider may prescribe either the 22 mcg or 44 mcg dose of REBIF. You should gradually increase the dose over 4 weeks, starting at 20% of the prescribed dose for the first 2 weeks, half-dose for the second 2 weeks (weeks 3 and 4), and then the full dose prescribed by your healthcare provider.
If your prescribed dose is 22 mcg of REBIF, a REBIF Titration Pack containing 6 prefilled syringes with 8.8 mcg and 6 prefilled syringes with 22 mcg should be prescribed to you for use during the 4-week starting period. Table 1 explains the amount to inject using the REBIF Titration Pack syringes to gradually increase to 22 mcg.
| Week of Use | Syringe to Use | Amount of syringe |
|---|---|---|
| Week 1 Titration | 8.8 mcg syringe | Use half of syringe |
| Week 2 Titration | 8.8 mcg syringe | Use half of syringe |
| Week 3 Titration | 22 mcg syringe | Use half of syringe |
| Week 4 Titration | 22 mcg syringe | Use half of syringe |
| Week 5 and on | 22 mcg syringe or autoinjector | Use full syringe or autoinjector |
If your prescribed dose is 44 mcg, you may be prescribed either a REBIF Titration Pack (described above) or REBIF Rebidose Titration Pack containing 6 autoinjectors with 8.8 mcg and 6 autoinjectors with 22 mcg for use during the 4 week titration period. Table 2 explains the amount to inject using the REBIF Titration Pack or REBIF Rebidose Titration Pack to gradually increase to 44 mcg.
| Week of Use | Syringe or Autoinjector to Use | Amount of syringe or autoinjector |
|---|---|---|
| Week 1 Titration | 8.8 mcg syringe or autoinjector | Use full syringe or autoinjector |
| Week 2 Titration | 8.8 mcg syringe or autoinjector | Use full syringe or autoinjector |
| Week 3 Titration | 22 mcg syringe or autoinjector | Use full syringe or autoinjector |
| Week 4 Titration | 22 mcg syringe or autoinjector | Use full syringe or autoinjector |
| Week 5 and on | 44 mcg syringe or autoinjector | Use full syringe or autoinjector |
Step 1. Preparing for your REBIF Injection
- Check the expiration date . Do not use if the medication is expired . The expiration date is printed on the syringe, plastic syringe packaging and carton.
- Remove your REBIF syringe from the refrigerator at least 30 minutes before you plan to use it so it can warm to room temperature. Do not heat or microwave the medication.
- Be sure that the dose, either, 8.8 mcg, 22 mcg or 44 mcg, described on the carton is the same as the dose prescribed by your healthcare provider.
- Remove the REBIF syringe from the plastic packaging. Keep the needle capped.
- Look at the contents of the syringe carefully. The liquid should be clear to slightly yellow. Do not use if the liquid is cloudy, discolored or contains particles . Use a different syringe.
Step 2. Choose and Prepare your Injection Site
- The best sites for giving yourself an injection are those areas with a layer of fat between the skin and muscle, like your thigh, the outer surface of your upper arm, your stomach or buttocks.
- Do not use the area near your waistline or within 2 inches of your navel. If you are very thin, use only the thigh or outer surface of the arm for injection.
- Use a different site each time you inject such as the thigh, hip, stomach or upper arm (See Figure C ) .
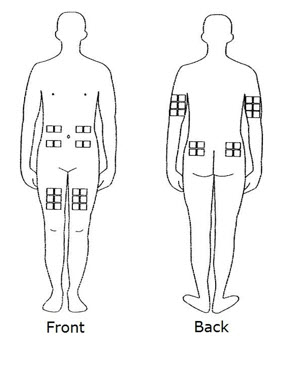
- Do not inject REBIF into an area of your body where the skin is irritated, reddened, bruised, infected or abnormal in any way.
- Wash your hands thoroughly with antibacterial soap before preparing to inject the medicine.
- Clean the injection site with an alcohol pad or cotton ball with rubbing alcohol using a circular motion. To avoid stinging, you should let your skin dry before you inject REBIF.
Step 3. Inject your REBIF
- Remove the needle cap from the syringe needle.
- If your healthcare provider has told you to use less than the full 0.5 mL dose, slowly push the plunger in until the amount of medicine left in the syringe is the amount healthcare provider told you to use.
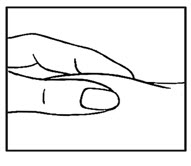
- Use your thumb and forefinger to pinch a pad of skin surrounding the cleaned injection site ( See Figure D ). Hold the syringe like a pencil with your other hand.
- While still pinching the skin, quickly insert the needle like a dart at about a 90 degree angle (just under the skin) into the pad of tissue as shown (See Figure E ).
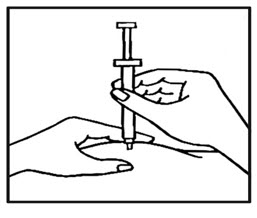
- After the needle is in, remove the hand that you used to pinch your skin and inject the medicine using a slow, steady push on the plunger until all the medicine is injected and the syringe is empty (See Figure F ) .
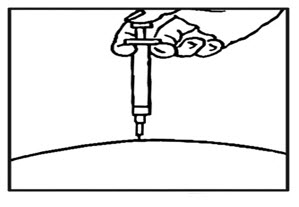
- Withdraw the needle and apply gentle pressure to the injection site with a dry cotton ball or sterile gauze. Applying a cold compress or ice pack to the injection site after injection may help reduce local skin reactions.
- Put a small adhesive bandage strip over the injection site, if desired.
- Keep a record of the date and location of each injection.
- After 2 hours, check the injection site for redness, swelling, or tenderness. If you have a skin reaction and it does not clear up in a few days, call your healthcare provider.
Step 4. Disposing of your Needles and Syringes
- Put your used needles, syringes, and autoinjectors, including REBIF, in an FDA-cleared sharps container right away after use. Do not throw away (dispose of) any syringes or autoinjectors in your household trash. If you do not have an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
- made of a heavy-duty plastic,
- closed with a tight-fitting, puncture-resistant lid,
- upright and stable during use,
- leak-resistant, and
- properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container.
- When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used autoinjectors and syringe needles. For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA's website at: http://www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal.
- Do not dispose of your used sharps disposal container in your household trash unless your community guidelines permit this. Do not recycle your used sharps disposal container.
Manufactured by: EMD Serono, Inc. Boston, MA 02210 U.S. License 1773
Marketed by: EMD Serono, Inc. Boston, MA 02210
Revised 02/2025
Mechanism of Action
The mechanism(s) by which REBIF (interferon beta-1a) exerts its therapeutic effects in patients with multiple sclerosis is unknown.