Recorlev prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Recorlev patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Laboratory Testing Prior to RECORLEV Initiation
- Obtain baseline liver tests [alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), total bilirubin]. Carefully consider the risks and potential benefits of initiating RECORLEV in patients with AST or ALT above normal but less than or equal to 3 times the upper limit of normal [see Contraindications (4 ), Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )].
- Obtain baseline electrocardiogram (ECG) [see Contraindications (4 ), Warnings and Precautions (5.2 )].
- Correct hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia prior to starting RECORLEV [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 )].
Recommended Dosage, Titration, and Monitoring for Efficacy
- Initiate dosage at 150 mg orally twice daily, with or without food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )].
- Titrate the dosage by 150 mg daily, no more frequently than every 2-3 weeks based on 24-hour urine free cortisol levels and patient tolerability [see Dosage and Administration (2.4 )] . Monitor cortisol levels from at least two 24-hour urine free cortisol collections every 2-3 weeks until an adequate clinical response is achieved.
- The maximum recommended dosage is 1200 mg per day, administered as 600 mg twice daily.
- The dosage may be reduced to 150 mg once daily if needed for reasons of tolerability [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 , 2.4 )].
- Once the maintenance dosage is achieved, monitor cortisol levels from at least two 24-hour urine free cortisol collections at least every 1-2 months or as indicated.
- If 24-hour urine free cortisol levels remain above the upper normal limit after treatment with the maximum recommended dosage of 1200 mg per day, or the patient cannot tolerate treatment with RECORLEV, consider discontinuing RECORLEV and switching patient to another therapy.
Monitoring for Safety
Perform the following monitoring during RECORLEV treatment. Refer to Dosage Interruptions and Modifications below for recommendations pertaining to management of liver, cortisol, or ECG abnormalities [see Dosage and Administration (2.4 )].
Hepatotoxicity
- Serious hepatotoxicity has been reported in patients receiving RECORLEV, and therefore frequent monitoring of liver tests is recommended.
- Monitor liver enzymes and bilirubin weekly for at least 6 weeks after starting RECORLEV, every 2 weeks for the next 6 weeks, monthly for the next 3 months, and then as clinically indicated.
- After any dose interruption or dose increase, monitor on a weekly basis until a stable dosage is achieved [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )].
QT Prolongation
- Conduct an ECG before each dose increase. After a stable dosage is established, monitor routinely for an effect on the QT interval.
- Monitor blood potassium and magnesium levels periodically during treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 )].
Hypocortisolism
- Monitor 24-hour urine free cortisol, morning serum or plasma cortisol, and patient’s signs and symptoms for hypocortisolism periodically during RECORLEV treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 )].
Dosage Interruptions and Modifications
Hepatotoxicity
Refer to Table 1 for management of hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 ) ] .
| ALT or AST | Total Bilirubin | Recommendation |
≥ 5 x ULN | Any value | Permanently discontinue RECORLEV. |
≥ 3 x ULN | > 2 x ULN | Permanently discontinue RECORLEV. |
≥ 3 to < 5 x ULN | ≤ 2 x ULN |
|
> ULN to <3 x ULN | Any value |
|
QT Prolongation
- Temporarily discontinue RECORLEV if the QTcF interval is longer than 500 msec.
- After correction of other possible contributing factors (e.g., hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, use of concomitant drugs), RECORLEV may be resumed at a lower dosage when the QTcF interval returns to 500 msec or less.
- If QT interval prolongation recurs after restarting RECORLEV, permanently discontinue RECORLEV [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 )] .
Hypocortisolism
- Decrease the dosage or temporarily discontinue RECORLEV if urine free cortisol or morning serum or plasma cortisol levels fall below the target range, there is a rapid decrease in cortisol levels, or if signs and/or symptoms consistent with hypocortisolism are reported.
- Stop RECORLEV and administer exogenous glucocorticoid replacement therapy if morning serum or plasma cortisol levels are below target range and signs and/or symptoms of adrenal insufficiency or hypocortisolism are present.
- Re-initiate RECORLEV at a lower dosage when cortisol levels are within target ranges and signs and/or symptoms of hypocortisolism have resolved [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 )] . The dosage may be titrated to the previous dose associated with hypocortisolism if the reduced dosage has been well tolerated and the reduced dosage does not achieve an adequate clinical response.
Missed Dose
If a dose of RECORLEV is missed, the patient should take the next dose at the regularly scheduled time.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Recorlev prescribing information
WARNING: HEPATOTOXICITY AND QT PROLONGATION
Hepatotoxicity
• Cases of hepatotoxicity with a fatal outcome or requiring liver transplantation have been reported with use of oral ketoconazole. Some patients had no obvious risk factors for liver disease. Serious hepatotoxicity has been reported in patients receiving RECORLEV [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )].
• RECORLEV is contraindicated in patients with cirrhosis, acute liver disease or poorly controlled chronic liver disease, recurrent symptomatic cholelithiasis, a prior history of drug induced liver injury due to ketoconazole or any azole antifungal therapy that required discontinuation of treatment, or extensive metastatic liver disease [see Contraindications (4 ), Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )].
• Evaluate liver enzymes prior to and during treatment. Interrupt RECORLEV treatment immediately if signs of hepatotoxicity occur [see Dosage and Administration (2.1 , 2.3 , 2.4 ), Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )].
QT Prolongation • RECORLEV is associated with dose-related QT interval prolongation. QT interval prolongation may lead to life-threatening ventricular dysrhythmias such as torsades de pointes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 )].
• Coadministration of RECORLEV with other drugs that prolong the QT interval associated with ventricular arrhythmias, including torsades de pointes, and use in patients with a prolonged QTcF interval of greater than 470 msec at baseline, history of torsades de pointes, ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, or long QT syndrome (including first-degree family history) are contraindicated [see Contraindications (4 ), Drug Interactions (7.1 , 7.2 )].
• Perform an ECG and correct hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia prior to and during treatment. Temporarily discontinue RECORLEV if QTcF interval exceeds 500 msec [Dosage and Administration (2.1 , 2.3 , 2.4 )].
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
RECORLEV is indicated for the treatment of endogenous hypercortisolemia in adult patients with Cushing’s syndrome for whom surgery is not an option or has not been curative.
Limitations of Use
RECORLEV is not approved for the treatment of fungal infections. The safety and effectiveness of RECORLEV for the treatment of fungal infections have not been established.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Laboratory Testing Prior to RECORLEV Initiation
- Obtain baseline liver tests [alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), total bilirubin]. Carefully consider the risks and potential benefits of initiating RECORLEV in patients with AST or ALT above normal but less than or equal to 3 times the upper limit of normal [see Contraindications (4 ), Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )].
- Obtain baseline electrocardiogram (ECG) [see Contraindications (4 ), Warnings and Precautions (5.2 )].
- Correct hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia prior to starting RECORLEV [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 )].
Recommended Dosage, Titration, and Monitoring for Efficacy
- Initiate dosage at 150 mg orally twice daily, with or without food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )].
- Titrate the dosage by 150 mg daily, no more frequently than every 2-3 weeks based on 24-hour urine free cortisol levels and patient tolerability [see Dosage and Administration (2.4 )] . Monitor cortisol levels from at least two 24-hour urine free cortisol collections every 2-3 weeks until an adequate clinical response is achieved.
- The maximum recommended dosage is 1200 mg per day, administered as 600 mg twice daily.
- The dosage may be reduced to 150 mg once daily if needed for reasons of tolerability [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 , 2.4 )].
- Once the maintenance dosage is achieved, monitor cortisol levels from at least two 24-hour urine free cortisol collections at least every 1-2 months or as indicated.
- If 24-hour urine free cortisol levels remain above the upper normal limit after treatment with the maximum recommended dosage of 1200 mg per day, or the patient cannot tolerate treatment with RECORLEV, consider discontinuing RECORLEV and switching patient to another therapy.
Monitoring for Safety
Perform the following monitoring during RECORLEV treatment. Refer to Dosage Interruptions and Modifications below for recommendations pertaining to management of liver, cortisol, or ECG abnormalities [see Dosage and Administration (2.4 )].
Hepatotoxicity
- Serious hepatotoxicity has been reported in patients receiving RECORLEV, and therefore frequent monitoring of liver tests is recommended.
- Monitor liver enzymes and bilirubin weekly for at least 6 weeks after starting RECORLEV, every 2 weeks for the next 6 weeks, monthly for the next 3 months, and then as clinically indicated.
- After any dose interruption or dose increase, monitor on a weekly basis until a stable dosage is achieved [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )].
QT Prolongation
- Conduct an ECG before each dose increase. After a stable dosage is established, monitor routinely for an effect on the QT interval.
- Monitor blood potassium and magnesium levels periodically during treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 )].
Hypocortisolism
- Monitor 24-hour urine free cortisol, morning serum or plasma cortisol, and patient’s signs and symptoms for hypocortisolism periodically during RECORLEV treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 )].
Dosage Interruptions and Modifications
Hepatotoxicity
Refer to Table 1 for management of hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 ) ] .
| ALT or AST | Total Bilirubin | Recommendation |
≥ 5 x ULN | Any value | Permanently discontinue RECORLEV. |
≥ 3 x ULN | > 2 x ULN | Permanently discontinue RECORLEV. |
≥ 3 to < 5 x ULN | ≤ 2 x ULN |
|
> ULN to <3 x ULN | Any value |
|
QT Prolongation
- Temporarily discontinue RECORLEV if the QTcF interval is longer than 500 msec.
- After correction of other possible contributing factors (e.g., hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, use of concomitant drugs), RECORLEV may be resumed at a lower dosage when the QTcF interval returns to 500 msec or less.
- If QT interval prolongation recurs after restarting RECORLEV, permanently discontinue RECORLEV [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 )] .
Hypocortisolism
- Decrease the dosage or temporarily discontinue RECORLEV if urine free cortisol or morning serum or plasma cortisol levels fall below the target range, there is a rapid decrease in cortisol levels, or if signs and/or symptoms consistent with hypocortisolism are reported.
- Stop RECORLEV and administer exogenous glucocorticoid replacement therapy if morning serum or plasma cortisol levels are below target range and signs and/or symptoms of adrenal insufficiency or hypocortisolism are present.
- Re-initiate RECORLEV at a lower dosage when cortisol levels are within target ranges and signs and/or symptoms of hypocortisolism have resolved [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 )] . The dosage may be titrated to the previous dose associated with hypocortisolism if the reduced dosage has been well tolerated and the reduced dosage does not achieve an adequate clinical response.
Missed Dose
If a dose of RECORLEV is missed, the patient should take the next dose at the regularly scheduled time.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets: 150 mg, round, pink, film-coated, and imprinted in black ink with “LEV” above “150” on one side; the other side is plain.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Levoketoconazole is the 2S, 4R enantiomer of ketoconazole. The available published data from case series and case-control studies on the use of the racemic ketoconazole during pregnancy are insufficient to determine a drug-associated risk of major birth defects. There are no available data on ketoconazole use during pregnancy to inform the risk of miscarriage. There are risks to the mother and fetus from untreated Cushing’s syndrome (see Clinical Considerations) . No animal reproduction studies have been performed with levoketoconazole. However, levoketoconazole constituted about 70% of the exposure in humans and animals after racemic ketoconazole administration. In animal reproduction studies, embryotoxic effects were observed in pregnant mice, rats and rabbits, and fetal malformations were observed in rats, following oral dosing of racemic ketoconazole during the period of organogenesis at doses equal and less than the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD), respectively (see Data) . Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus and consider whether the benefits of treatment with RECORLEV outweigh the risks.
The estimated background risk for major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15−20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-Associated Maternal and/or Embryo/Fetal Risk
Active Cushing’s syndrome during pregnancy has been associated with an increased risk of maternal and fetal morbidity and mortality (including gestational diabetes, gestational hypertension, pre-eclampsia, maternal death, miscarriage, intrauterine fetal demise, preterm birth and neonatal death).
Labor or Delivery
Dystocia (difficult labor) was noted in mice and rats administered oral ketoconazole during the period of organogenesis at exposures below the MRHD of levoketoconazole (by body surface area (BSA)). The clinical relevance of these findings for human is unknown.
Data
Animal Data
Racemic ketoconazole containing levoketoconazole was administered orally to rats, mice, and rabbits during the period of organogenesis. Levoketoconazole constituted about 70% of the exposure in animals after racemic ketoconazole administration.
Mice were administered 10, 20, and 40 mg/kg/day ketoconazole during the period of organogenesis (gestation days 6 to 18). Embryolethality (resorptions and still births) was observed at ≥ 20 mg/kg/day (below the MRHD of levoketoconazole based on BSA comparison). There was no maternal toxicity in mice up to the highest dose of 40 mg/kg/day (below the MRHD of levoketoconazole by BSA), however, females failed to deliver naturally and Cesarean examination 3 days after the due date showed increased resorptions and dead fetuses.
Rats were administered 10, 20, 40, and 80 mg/kg/day during the period of organogenesis (gestation days 6 to 18). Increased incidences of resorbed fetuses and still births were noted at ≥40 mg/kg/day (below the MRHD of levoketoconazole by BSA). Fetal malformations (oligodactyly, syndactyly, absence of metacarpal and/or metatarsal bones, and cleft palate) were noted at ≥80 mg/kg/day of ketoconazole (at the MRHD of levoketoconazole by BSA). Dystocia and prolonged gestation were observed in rats at ≥10 mg/kg/day (below the MRHD of levoketoconazole by BSA).
In rabbits, oral gavage doses of 0, 10 and 40 mg/kg/day ketoconazole were administered during the period of organogenesis (gestation days 6 through 18). Increased incidences of resorbed fetuses and still births were observed at ≥10 mg/kg/day (below MRHD of levoketoconazole by BSA).
Lactation
Risk Summary
Published data from one lactating woman show that ketoconazole is present in human milk in low amounts, with no reported adverse effects on the breastfed infant. However, these limited data are not sufficient to inform the risk to a breastfed infant with exposure to ketoconazole through breast milk. There are no data available on the effects of ketoconazole on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in the breastfed infant, including liver toxicity, advise patients not to breastfeed during treatment with RECORLEV and for one day (5 times the half-life) after the final dose.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Infertility
RECORLEV may lower testosterone levels [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5 )] and impair male and female fertility. Ketoconazole tablets (containing equal parts levoketoconazole and dextroketoconazole in a racemic mixture) have been demonstrated to lower serum testosterone in humans. Once therapy with ketoconazole tablets was discontinued, serum testosterone levels returned to baseline values. Testosterone levels are impaired with ketoconazole doses of 800 mg per day and abolished by 1600 mg per day. Clinical manifestations of decreased testosterone concentrations may include gynecomastia, impotence and oligospermia. In rat fertility studies, oral ketoconazole administered at doses equivalent to the MRHD of levoketoconazole by BSA during premating to implantation caused impaired fertility in male and female rats. In dog fertility studies, levoketoconazole targeted the reproductive tissues of male dogs in a dose-dependent manner with associated effects on spermatogenesis and maturation of spermatozoa. The effect was reversible upon discontinuation of treatment [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1 )] .
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of RECORLEV in pediatric patients below the age of 18 have not been established.
Geriatric Use
Of the 166 patients in clinical trials with RECORLEV, 12 (7%) were 65 years and older, with one patient 75 years of age. Clinical studies of RECORLEV did not include sufficient number of patients 65 years of age and older to determine whether they respond differently from younger adult patients.
Renal Impairment
There is no experience with RECORLEV in patients with renal impairment. The overall pharmacokinetics of racemic ketoconazole in patients with renal impairment were not significantly different when compared with healthy subjects.
Hepatic Impairment
The use of RECORLEV is contraindicated in patients with cirrhosis, acute liver disease or poorly controlled chronic liver disease, recurrent symptomatic cholelithiasis, a prior history of drug induced liver injury due to ketoconazole or any azole antifungal therapy that required discontinuation of treatment, or extensive metastatic liver disease [see Contraindications (4 ), Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )] .
CONTRAINDICATIONS
RECORLEV is contraindicated in patients:
- With cirrhosis, acute liver disease or poorly controlled chronic liver disease, baseline AST or ALT greater than 3 times the upper limit of normal, recurrent symptomatic cholelithiasis, a prior history of drug induced liver injury due to ketoconazole or any azole antifungal therapy that required discontinuation of treatment, or extensive metastatic liver disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )] .
- Taking drugs that cause QT prolongation associated with ventricular arrhythmias, including torsades de pointes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 )] .
- With a prolonged QTcF interval of greater than 470 msec at baseline, history of torsades de pointes, ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, or long QT syndrome (including first-degree family history) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 )] .
- With known hypersensitivity to levoketoconazole, ketoconazole or any excipient in RECORLEV [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4 ), Adverse Reactions (6.2 )] .
- Taking certain drugs that are sensitive substrates of CYP3A4 or CYP3A4 and P-gP [see Drug Interactions (7.1 )] .
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Hepatotoxicity
Cases of hepatotoxicity with a fatal outcome or requiring liver transplantation have been reported with the use of oral ketoconazole, the racemic mixture from which levoketoconazole is derived. Some patients had no obvious risk factors for liver disease. Serious hepatotoxicity has been reported in patients receiving RECORLEV, irrespective of the dosages used or the treatment duration. Drug-induced liver injury (peak ALT or AST greater than 3 times upper limit of normal) occurred in 13% of patients using RECORLEV.
RECORLEV is contraindicated in patients with cirrhosis, acute liver disease or poorly controlled chronic liver disease, baseline AST or ALT greater than 3 times the upper limit of normal, recurrent symptomatic cholelithiasis, a prior history of drug induced liver injury due to ketoconazole or any azole antifungal therapy that required discontinuation of treatment, or extensive metastatic liver disease [see Contraindications (4 )] .
Avoid concomitant use of RECORLEV with hepatotoxic drugs. Advise patient to avoid excessive alcohol consumption while on treatment with RECORLEV [see Drug Interactions (7.3 )] .
Prompt recognition of liver injury is essential. At baseline, obtain liver tests [see Dosage and Administration (2.1 )] . During RECORLEV treatment, regularly monitor liver enzymes, with more frequent monitoring during dosage titration [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 )] .
Permanently discontinue RECORLEV treatment immediately if AST or ALT exceeds or is equal to 5 times the upper limit of normal, or AST or ALT exceeds or is equal to 3 times the upper limit of normal and total bilirubin concentration increases to more than 2 times the upper limit of normal.
Repeat liver tests within approximately 3 days following the initial abnormal liver test, until the levels are stable. Monitor at regular intervals thereafter, no less than every 7 to 10 days, until resolution of the abnormality (or return to baseline levels) or until an alternative cause has been identified [see Dosage and Administration (2.4 )].
For AST or ALT elevations less than 3 times the upper limit of normal, or AST or ALT elevations equal to or greater than 3 to less than 5 times the upper limit of normal and total bilirubin concentration less than 2 times the upper limit of normal, monitor liver tests and manage hepatotoxicity with RECORLEV dosage interruption or modifications [see Dosage and Administration (2.4 )] . If a liver abnormality significantly above the patient’s baseline recurs after restarting RECORLEV, permanently discontinue RECORLEV.
QT Prolongation
RECORLEV is associated with dose-related QT interval prolongation. QT interval prolongation may lead to life-threatening ventricular dysrhythmias such as torsades de pointes. During Studies 1 and 2, which excluded patients with baseline QTcF interval greater than 470 msec, 4 (2.4%) patients experienced QTcF>500 msec, and 23 (14.7%) patients experienced change-from-baseline QTcF >60 msec. Resolution typically occurred following a dosage interruption and in some cases correction of electrolyte abnormalities.
RECORLEV may also elevate plasma concentrations of certain drugs known to prolong QT intervals. Prolongation of the QT interval from certain drugs can result in life-threatening ventricular dysrhythmias such as torsades de pointes [see Drug Interactions (7.1 , 7.2 )] .
RECORLEV is contraindicated in patients taking other drugs known to cause QT interval prolongation associated with ventricular arrhythmias, including torsades de pointes, and is contraindicated in patients with a prolonged QTcF interval of greater than 470 msec at baseline, history of torsades de pointes, ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, or long QT syndrome (including first-degree family history) [see Contraindications (4 ), Drug Interactions (7.1 , 7.2 )].
Use RECORLEV with caution in patients with other risk factors for QT prolongation, such as congestive heart failure, bradyarrhythmias, and uncorrected electrolyte abnormalities, with more frequent ECG monitoring considered.
Obtain a baseline QT interval measurement and regularly monitor ECG for an effect on the QT interval during RECORLEV treatment. Correct hypokalemia and/or hypomagnesemia prior to RECORLEV initiation and monitor periodically during treatment [see Dosage and Administration (2.1 , 2.3 )] . Temporarily discontinue RECORLEV if the QTcF interval exceeds 500 msec. After the QTcF interval returns to less than 500 msec and contributing factors are corrected, re-institution of RECORLEV at a lower dose may be considered. If QT interval prolongation recurs after restarting RECORLEV, permanently discontinue RECORLEV [see Dosage and Administration (2.4 )] .
Hypocortisolism
RECORLEV lowers cortisol levels and may lead to hypocortisolism with a potential for life-threatening adrenal insufficiency. Adrenal insufficiency was observed in 7% of patients during the clinical program of RECORLEV [see Adverse Reactions (6.1 )] . Lowering of cortisol levels can cause nausea, vomiting, fatigue, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, and dizziness. Significant lowering of serum cortisol levels may result in adrenal insufficiency that can be manifested by hypotension, abnormal electrolyte levels, and hypoglycemia.
Hypocortisolism may occur at any time during RECORLEV treatment. Evaluate patients for precipitating causes of hypocortisolism (infection, physical stress, etc.). Monitor 24-hour urine free cortisol, morning serum or plasma cortisol, and patient’s signs and symptoms periodically during RECORLEV treatment [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 )] .
Decrease the dosage or temporarily discontinue RECORLEV if urine free cortisol or morning blood cortisol levels fall below the target range, there is a rapid decrease in cortisol levels, or if signs and/or symptoms consistent with hypocortisolism are reported [see Dosage and Administration (2.4 )] .
Stop RECORLEV and administer exogenous glucocorticoid replacement therapy if morning serum or plasma cortisol levels are below target range and signs and/or symptoms of adrenal insufficiency, or hypocortisolism, are present. After RECORLEV discontinuation, cortisol suppression may persist beyond the 4- to 6- hour half-life of RECORLEV.
If treatment is interrupted due to hypocortisolism, re-initiate RECORLEV at a lower dosage when cortisol levels are within target ranges and patient’s signs and/or symptoms have resolved [see Dosage and Administration (2.4 )] . The dosage may be titrated to the previous dose associated with hypocortisolism if the reduced dosage has been well tolerated and the reduced dosage does not achieve an adequate clinical response.
Educate patients on the symptoms associated with hypocortisolism and advise them to contact a healthcare provider if they occur.
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions have been reported in 1% of patients treated with RECORLEV in the clinical trials [see Adverse Reactions (6.1 )] .
Anaphylaxis has been reported after a single dose of oral ketoconazole. Hypersensitivity reactions including urticaria have also been reported for ketoconazole [see Adverse Reactions (6.2 )].
RECORLEV is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to levoketoconazole, ketoconazole or any excipient in RECORLEV.
Risks Related to Decreased Testosterone
RECORLEV may lower serum testosterone in men and women. Potential clinical manifestations of decreased testosterone concentrations in men may include gynecomastia, impotence and oligospermia. Potential clinical manifestations of decreased testosterone concentrations in women include decreased libido and mood changes. Inform patients of the symptoms associated with low testosterone levels and advise patients to contact a healthcare provider if they occur.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )]
- QT Prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 )]
- Hypocortisolism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 )]
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4 )]
- Risks related to Decreased Testosterone [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5 )]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of RECORLEV was evaluated in a multicenter, randomized-withdrawal study (Study 1) and in a multicenter, single-arm, open-label study (Study 2). During the two studies, 166 patients were exposed to RECORLEV, of which 104 patients were exposed for more than 6 months and 51 patients were exposed for at least 1 year. In both studies, most patients took RECORLEV twice daily in total daily dosages ranging from 300 mg to 1200 mg [see Clinical Studies (14 )] .
Adverse reactions, excluding hepatic injury, reported in ≥10% of patients treated with RECORLEV in Study 1 are presented in Table 2 listed in order of overall decreasing frequency of events.
| N = total number of patients, n = number of patients experiencing the event, (%) = proportion of patients experiencing the event. a Hemorrhage/contusion includes blood urine present, epistaxis, eye hemorrhage, gingival bleeding, hematoma, hematuria, hemorrhoidal hemorrhage, melena, and scleral hemorrhage. b Arrhythmia includes electrocardiogram QT prolonged, electrocardiogram T wave abnormal, palpitations, sinus tachycardia, tachycardia paroxysmal, and ventricular extrasystoles. c Abdominal pain/dyspepsia includes abdominal pain, abdominal distension, dyspepsia, gastric disorder, and related terms | |
| Adverse Reaction Types | N= 84 n (%) |
| Nausea/Vomiting | 25 (30%) |
| Hypokalemia | 24 (29%) |
| Systemic hypertension | 20 (24%) |
Hemorrhage/Contusion a | 19 (23%) |
| Headache | 18 (21%) |
| Abnormal uterine bleeding | 17 (20%) |
| Arrhythmia b | 16 (19%) |
| Fatigue | 15 (18%) |
| Upper respiratory infection | 15 (18%) |
| Abdominal pain/Dyspepsia c | 13 (15%) |
Dizziness | 13 (15%) |
| Diarrhea | 13 (15%) |
| Decreased appetite | 11 (13%) |
| Dry mouth | 9 (11%) |
| Dry skin | 9 (11%) |
| Adrenal insufficiency | 8 (10%) |
Other notable adverse reactions which occurred with a frequency less than 10% during Study 1 were: alopecia (6%), gastrointestinal infection (6%), urinary tract infection (6%), hypogonadism (2%), and hypersensitivity (1%).
Adverse reactions, excluding hepatic injury, reported in ≥10% of patients treated with RECORLEV in Study 2 are presented in Table 3 listed in order of overall decreasing frequency of events.
N = total number of patients, n = number of patients experiencing the event, (%) = proportion of patients experiencing the event. a Erythema includes flushing. b Hemorrhage/Contusion includes blood urine present, conjunctival hemorrhage, ecchymosis, epistaxis, hematoma, hyphemia, and red blood cells urine. c Abdominal pain/dyspepsia includes abdominal discomfort, abdominal distension, dyspepsia, gastritis, and other related terms. d Arrhythmia includes bradycardia, carotid pulse increased, defect conduction intraventricular, electrocardiogram QT prolonged, electrocardiogram T wave abnormal, heart rate increased, palpitations and sinus bradycardia. | |
Adverse Reaction Type | N = 94 n (%) |
| Erythema a | 40 (43%) |
Hemorrhage/Contusion b | 38 (40%) |
Fatigue | 37 (39%) |
Headache | 36 (38%) |
Nausea/Vomiting | 35 (37%) |
Abdominal pain/dyspepsia c | 31 (33%) |
Arthritis | 26 (28%) |
Upper respiratory infection | 26 (28%) |
Myalgia | 24 (26%) |
Abnormal uterine bleeding | 23 (24%) |
Arrhythmia d | 23 (24%) |
| Back pain | 21 (22%) |
Insomnia/Sleep disturbances | 21 (22%) |
Peripheral edema | 19 (20%) |
Systemic hypertension | 19 (20%) |
Diarrhea | 18 (19%) |
Pre-Syncope/Syncope | 17 (18%) |
Rash | 16 (17%) |
Urinary tract infection | 15 (16%) |
Hypokalemia | 14 (15%) |
Pruritus | 14 (15%) |
Disturbance in attention | 13 (14%) |
Irritability | 13 (14%) |
Depression | 11 (12%) |
Dry skin | 11 (12%) |
Alopecia | 10 (11%) |
Other notable adverse reactions which occurred with a frequency less than 10% during Study 2 were: gastrointestinal infections (5%), decreased libido (5%), hypogonadism (4%), adrenal insufficiency (3%), and gynecomastia (3%).
Description of Selected Adverse Reactions
Hepatic Injury and Elevated Liver Function Tests
Liver-related adverse reactions reported in patients treated with RECORLEV in Studies 1 and 2 are presented in Table 4 . Table 5 summarizes patients who had at least one ALT or AST measurement greater than the upper limit of reference range (ULN) in post baseline visits in Studies 1 and 2 combined who had tests in the normal range at baseline. There were 11 out of 166 patients who had an AST or ALT above the ULN to ˂3 x ULN at baseline. Of these patients, 3 had increases above 3 x ULN, and none had increases above 5 x ULN. Liver test abnormalities improved with cessation of medication.
N = total number of patients, n = number of patients experiencing the event, (%) = proportion of patients experiencing the event. a Liver enzyme elevation refers to elevation in aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase, or gamma-glutamyl transferase. | |
N = 166 n (%) | |
At least one liver related adverse reaction | 45 (27%) |
| Liver enzyme elevation a | 33 (20%) |
| Drug-induced liver injury | 3 (2%) |
Hepatic pain | 7 (4%) |
Hepatic steatosis | 1 (1%) |
Liver disorders | 4 (2%) |
N = total number of patients, n = number of patients experiencing the event, (%) = proportion of patients experiencing the event. a Not all elevations in liver enzymes were reported as adverse reactions during the studies. | ||
N = 155 n (%) a | Time to Event in Days Median (Range) | |
| AST or ALT > ULN | 70 (45%) | 73 (1-334) |
AST or ALT >3 x ULN | 17 (11%) | 83 (26-232) |
AST or ALT >5 x ULN | 7 (5%) | 104 (29-232) |
AST or ALT >10 x ULN | 4 (3%) | 166 (36-252) |
QTc Interval Prolongation
In Study 1 and 2, there were 4 (2.4%) patients who experienced QTcF>500 msec, and 23 (14.7%) patients who experienced change-from-baseline QTcF >60 msec, respectively [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 )] . Adverse reactions reported around the same time that may have been associated with QT prolongation included fatigue, hypertension, nausea/vomiting, and ventricular extrasystoles (see Tables 2 and 3 ).
Hypocortisolism
Hypocortisolism was reported in 11 (7%) of 166 patients across Studies 1 and 2, with events starting on median study day 96 (range 26-166). The majority of cases were managed by reducing the dosage or temporarily interrupting treatment with RECORLEV.
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified from published reports or postmarketing experience with ketoconazole. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to ketoconazole exposure.
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders : thrombocytopenia
Endocrine Disorders: adrenocortical insufficiency
Hepatobiliary Disorders: serious hepatotoxicity including hepatitis cholestatic, biopsy-confirmed hepatic necrosis, cirrhosis, hepatic failure including cases resulting in transplantation or death
Immune System Disorders: allergic conditions including anaphylactic shock, anaphylactic reaction, angioneurotic edema
Nervous System Disorders: reversible intracranial pressure increased (e.g., papilledema, fontanelle bulging in infants)
Reproductive System and Breast Disorders: erectile dysfunction; with dosages higher than 200 or 400mg daily, azoospermia.
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis, photosensitivity
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Consult approved product labeling for drugs that are substrates of CYP3A4, P-gp, OCT2, and MATE prior to initiating RECORLEV (7.1 )
- Sensitive CYP3A4 or CYP3A4 and P-gp Substrates : Concomitant use of RECORLEV with these substrates is contraindicated or not recommended (7.1 )
- Atorvastatin : Use lowest atorvastatin dose possible and monitor for adverse reactions for dosages exceeding 20 mg daily (7.1 )
- Metformin : Monitor glycemia, kidney function, and vitamin B12 and adjust metformin dosage as needed (7.1 )
- Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors or Inducers : Avoid use of these drugs 2 weeks before and during RECORLEV treatment (7.2 )
- Gastric Acid Modulators : See Full Prescribing Information for recommendations regarding concomitant use with RECORLEV (7.2 )
Effect of RECORLEV on Other Drugs
Levoketoconazole is a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor, as well as an inhibitor of the drug transporters P-gp, OCT2, and MATE1 in vivo. In vitro, levoketoconazole inhibits CYP2B6 and CYP2C8. Concomitant use of RECORLEV with drugs that are substrates of these CYP enzymes and transporters may increase the risk of adverse reactions of these drugs.
Consult the approved product labeling for drugs that are substrates of CYP3A4, P-gp, OCT2, and MATE1 prior to initiating therapy with RECORLEV.
Table 6 presents drugs affected by RECORLEV that are contraindicated or not recommended for use during RECORLEV use. It also includes the clinical impact and management recommendations for concomitant use of RECORLEV with atorvastatin and metformin.
a The drugs listed are substrates for CYP3A4 and/or P-gp. Other metabolism and/or transporter pathways may also contribute to elimination of the substrate drug. Consult the approved product labeling for the substrate drug for more information. b Strong CYP3A4 inhibitor [see Drug Interactions (7.2 )] . c Based on clinical drug interaction study with levoketoconazole. | |
CYP3A4 or CYP3A4 and P-gp Substrates a That May Prolong QT | |
Clinical Impact | Increases risk of QT prolongation and torsades de pointes. |
Prevention or Management | Concomitant use of RECORLEV with other drugs that cause QT prolongation associated with ventricular arrhythmias, including torsades de pointes, is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4 ), Warnings and Precautions (5.2 )]. |
Examples | Bosutinib, cisapride, clarithromycin b, cobimetinib, crizotinib, disopyramide, dofetilide, dronedarone, eliglustat (in patients that are poor or intermediate metabolizers of CYP2D6 and in patients taking strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitors), ivabradine, methadone, midostaurin, nicardipine, pimozide, quinidine, and ranolazine. |
Sensitive CYP3A4 or CYP3A4 and P-gp Substrates a | |
Clinical Impact | Increases plasma concentrations of the substrate and may increase the risk of the substrate’s adverse reactions. |
Prevention or Management | Concomitant use of RECORLEV with sensitive CYP3A4 or CYP3A4 and P-gp substrate drugs is contraindicated or not recommended [see Contraindications (4 )] . Refer to the prescribing information of the substrate drug. |
Examples | Alfentanil, avanafil, buspirone, conivaptan b , dabigatran etexilate, darifenacin, darunavir, digoxin, ebastine, everolimus, fexofenadine, ibrutinib, lomitapide, lovastatin, lurasidone, midazolam, naloxegol, nisoldipine, saquinavir, simvastatin, sirolimus, tacrolimus, tipranavir b , triazolam, and vardenafil. |
CYP3A4 Substrate Atorvastatin c | |
Clinical Impact | Increases plasma concentration of atorvastatin c and may increase the risk of atorvastatin-associated myopathy and rhabdomyolysis [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] . |
Prevention or Management | Concomitant use of RECORLEV with atorvastatin may require a dose reduction of atorvastatin. Use the lowest atorvastatin dose possible and monitor for adverse reactions when atorvastatin dosage exceeds 20 mg daily . |
OCT2 and MATE Substrate Metformin c | |
Clinical Impact | Increases plasma concentration of metformin c and may increase the risk of metformin’s adverse reactions [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] . May increase plasma concentrations of other OCT2 and MATE substrates and increase the risk of their adverse reactions . |
Prevention or Management | During RECORLEV dosage titration, monitor glycemia, kidney function, and Vitamin B12 in blood as per metformin prescribing information and adjust the dosage of metformin as needed. |
Effect of Other Drugs on RECORLEV
Table 7 presents clinically significant drug interactions that affect RECORLEV.
Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors | |
Clinical Impact | May increase plasma concentrations of levoketoconazole and increase the risk of adverse reactions from RECORLEV [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] . |
Prevention or Management | Administration of strong enzyme inhibitors of CYP3A4 with RECORLEV is not recommended. Avoid use of these drugs from 2 weeks before and during treatment with RECORLEV. |
Examples |
|
Strong CYP3A4 Inducers | |
Clinical Impact | May decrease plasma concentrations of levoketoconazole and reduce the efficacy of RECORLEV |
Prevention or Management | Administration of strong enzyme inducers of CYP3A4 with RECORLEV is not recommended. Avoid use of these drugs from 2 weeks before and during treatment with RECORLEV. |
Examples |
|
Gastric Acid Neutralizers | |
Clinical Impact | Impairs absorption of levoketoconazole from RECORLEV. |
Prevention or Management | Take gastric acid neutralizers a minimum of 2 hours after dosing with RECORLEV. |
Examples | Aluminum hydroxide |
Gastric Acid Suppressors | |
Clinical Impact | Impairs absorption of levoketoconazole from RECORLEV. |
Prevention or Management | Avoid use of gastric acid suppressors with RECORLEV. |
Examples | H2-receptor antagonists and proton pump inhibitors |
Sucralfate | |
Clinical Impact | Impairs absorption of levoketoconazole from RECORLEV. |
Prevention or Management | Avoid use of sucralfate with RECORLEV. |
Alcohol
Patients should be advised against excessive alcohol consumption while using RECORLEV [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )] . When used with alcohol cases of a disulfiram-like reaction have been reported with ketoconazole characterized by flushing, rash, peripheral edema, nausea, and headache. All symptoms completely resolved within a few hours.
DESCRIPTION
RECORLEV (levoketoconazole) tablets contain levoketoconazole as the active ingredient. Levoketoconazole is the 2S,4R- enantiomer derived from racemic ketoconazole and is a cortisol synthesis inhibitor.
The chemical name of levoketoconazole is 2S,4R cis-1-acetyl-4-[4-[[2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1H-imidazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl] methoxyl]phenyl] piperazine.
The molecular formula of levoketoconazole is C 26 H 28 Cl 2 N 4 O 4 with a molecular mass of 531.43 g/mol.
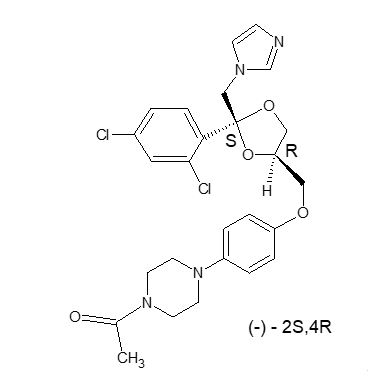
Levoketoconazole is a white or almost white crystalline powder. It is very slightly soluble in water but soluble in aqueous solutions below pH 2.
RECORLEV tablets for oral administration contain 150 mg of levoketoconazole and the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, modified corn starch, and silicified microcrystalline cellulose. The non-functional pink film-coating contains iron oxide red, macrogol/polyethylene glycol 3350, polyvinyl alcohol partially hydrolyzed, talc, and titanium dioxide. The tablets are printed with a black imprinting ink that contains ammonium hydroxide 28%, ferrosoferric oxide, isopropyl alcohol, propylene glycol, and shellac glaze 45% (20% esterified) in ethanol.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
In vitro, levoketoconazole inhibits key steps in the synthesis of cortisol and testosterone, principally those mediated by CYP11B1 (11β hydroxylase), CYP11A1 (the cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme, the first step in the conversion of cholesterol to pregnenolone), and CYP17A1 (17α-hydroxylase).
Pharmacodynamics
Cardiac Electrophysiology
The largest mean increase in QTc was 24 msec (UCI: 31 msec) following administration of levoketoconazole 150 mg to 600 mg twice daily (the approved recommended dosage) in patients with endogenous Cushing’s syndrome. The increase in QTc was dose-related.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Peak plasma concentrations of levoketoconazole occur approximately 1.5 to 2 hours following oral administration of a single dose of RECORLEV under fasted conditions regardless of dose. In healthy volunteers, C max increases approximately proportionally with dose, while AUC increases greater than dose proportionally from 150 mg to 600 mg. Levoketoconazole accumulates in plasma during multiple dosing of RECORLEV.
Levoketoconazole is a substrate of the intestinal (and liver) efflux transporter, P-gp.
Effect of Food
In a healthy volunteer study (N = 24), subjects administered a single, 600 mg oral dose of RECORLEV tablets with a high-fat meal (total caloric content of 875 calories; 160 protein calories, 170 carbohydrate calories, and 545 fat calories) resulted in an increase of AUC by 30% and no change in C max . The median T max was delayed from 2 to 4 hours. These changes are not considered to be clinically significant.
Distribution
Levoketoconazole has an apparent volume of distribution of 31 to 41 L, approximating total body water. Protein binding of levoketoconazole in human plasma is high (99.3%).
Elimination
Metabolism
No in vitro or in vivo studies of levoketoconazole metabolism have been performed. Racemic ketoconazole is metabolized extensively in the liver to several inactive metabolites (with respect to antifungal activity). CYP3A4 is the major enzyme involved in the metabolism of ketoconazole. The major identified metabolic pathways are oxidation and degradation of the imidazole and piperazine rings. In addition, oxidative O-dealkylation and aromatic hydroxylation occurs.
Excretion
Levoketoconazole is eliminated from plasma with a half-life of 3 to 4.5 hours after a single dose and 4 to 6 hours after multiple doses.
A mass-balance study has not been performed with levoketoconazole. Approximately 13% of a racemic ketoconazole dose is excreted in the urine, of which 2 to 4% is unchanged drug. The major route of excretion is through the bile into the intestinal tract with about 57% being excreted in the feces.
Specific Populations
Population pharmacokinetic modeling data from patients with Cushing’s syndrome suggest there is no impact of age or sex on the pharmacokinetics of levoketoconazole. The pharmacokinetics of levoketoconazole have not been formally studied in geriatric patients. Levoketoconazole has not been studied in patients younger than 18 years of age. Differences in pharmacokinetics among race/ethnicity groups are unknown.
Patients with Renal or Hepatic Impairment
Levoketoconazole has not been studied in patients with renal or hepatic impairment. The overall pharmacokinetics of racemic ketoconazole was not significantly altered in patients with renal failure when compared with healthy volunteers. [see Contraindications (4 )] . Given the extensive hepatic metabolism of ketoconazole, it is expected that clearance would be reduced in patients with impaired liver function.
Drug Interaction Studies
Levoketoconazole is a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor, as well as an inhibitor of the drug transporters P-gp, OCT2, and MATE1 in vivo. Concomitant administration of medications that are substrates of these enzymes or transporters may have their plasma concentrations affected by RECORLEV [see Drug Interactions (7.1 )] .
Clinical drug interaction studies were conducted to evaluate the effects of levoketoconazole on the pharmacokinetics of atorvastatin, felodipine, and metformin in healthy volunteers. Results are displayed in Table 8 . For clinical recommendations regarding these interactions, [see Drug Interactions (7.1 )] .
a For coadministered drug + levoketoconazole vs coadministered drug alone. | ||||
Coadministered Drug | N | Levoketoconazole Dose | Ratio of Least Square Means (90% Confidence Interval) a | |
| AUC 0-∞ | C max | |||
Atorvastatin | 23 | 400 mg once daily | 317.6%(286.6-352.0%) | 96.7%(82.3 – 113.6%) |
Felodipine | 14 | 400 mg once daily | 1007.3%(868.8-1167.9%) | 937.1%(757.9-1158.8%) |
Metformin | 17 | 450 mg twicedaily | 220%(203 – 239%) | 182%(168 – 197%) |
In Vitro Studies Where Drug Interaction Potential was not Further Evaluated Clinically
In vitro, levoketoconazole inhibits CYP2B6 and CYP2C8, and induces CYP1A2.
Levoketoconazole does not inhibit CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, or CYP2D6, does not induce CYP2B6, and does not inhibit the OATP1B3, OAT1, OAT3, or MATE2-K transporters.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Levoketoconazole has not been evaluated for carcinogenic effects. Ketoconazole was not carcinogenic in an 18-month, oral study in Swiss albino mice or a 24-month oral carcinogenicity study in Wistar rats at dose levels of 5, 20 and 80 mg/kg/day of ketoconazole. The high dose in these studies was less than the MRHD of levoketoconazole in the mouse and equal to the MRHD of levoketoconazole in rats based on a BSA comparison.
Mutagenesis
Mutagenic potential of levoketoconazole has not been evaluated. Ketoconazole did not show any signs of mutagenic potential when evaluated using the dominant lethal mutation test or the Ames Salmonella microsomal activator assay.
Impairment of Fertility
In animal fertility studies, oral ketoconazole impaired both male and female fertility in rats in a dose and duration dependent manner. In female rats, oral doses up to 40 mg/kg of ketoconazole (lower than the MRHD for levoketoconazole by BSA) had no effect on fertility. Doses of ≥75 mg/kg of ketoconazole (at the MRHD for levoketoconazole by BSA) decreased the pregnancy rate and number of implantation sites, and in males decreased sperm content (motility, count, morphology), which correlated with lower plasma testosterone levels and testicular histological changes. When administered for longer durations (up to 3 months), decreased fertility in male rats was observed at doses as low as 24 mg/kg/day of ketoconazole (lower than the MRHD for levoketoconazole by BSA).
In male beagle dogs, an oral dose of 25 mg/kg/day ketoconazole for up to 4 weeks (at the MRHD for levoketoconazole by BSA) resulted in decreased sperm motility, decreased sperm count, increased abnormal sperm and atrophy of the testes. These effects were reversed after withdrawal of treatment.
CLINICAL STUDIES
The effectiveness of RECORLEV in patients with Cushing's syndrome was evaluated in two studies, Study 1 and Study 2.
Study 1
Study 1 consisted of an open-label dose titration and maintenance phase of up to 19 weeks duration, followed by an 8-week double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized withdrawal phase (NCT03277690 ).
Study 1 enrolled 84 Cushing’s syndrome patients with persistent or recurrent disease despite surgery, previously medically treated patients, and previously untreated patients. The etiology of Cushing's syndrome was Cushing's disease for 70 (83%) patients, adrenal Cushing’s syndrome in 8 (10%) patients, ectopic ACTH secretion for 2 (2%) patients, and unknown for 4 (5%) patients. Patients with pituitary or adrenal carcinoma were excluded. Twelve (14%) patients who had previously received RECORLEV in Study 2 were also enrolled in Study 1. The mean age at baseline was 45 years; 76% of patients were female. Overall, the mean time since diagnosis was 63 months before treatment with the first dose in this study. Persistence or recurrence of Cushing’s syndrome was evidenced by the mean of three 24-hour UFC levels greater than or equal to 1.5 × upper limit of normal (normal range: 11 to 138 nmol/day or 4 to 50 µg/day). For the 79 patients who underwent dose titration, the mean mUFC (SD) at study baseline was 785 nmol/day (932), which corresponds to approximately 6 × ULN. The median mUFC at baseline was 479 nmol/day, which corresponds to approximately 3.5 × ULN. Seventy-two (72) patients were naïve to treatment with RECORLEV, seven (7) patients were treated with RECORLEV in Study 2 but were not on therapeutic dose (dose at which mUFC level was ≤ ULN, or maximum allowed dose [600 mg twice daily] had been reached, or a clinically meaningful partial response based on clinical judgement, and the maximum tolerated dose had been reached) prior to the enrollment in Study 1. Five (5) of 84 patients continued treatment with therapeutic dose of RECORLEV prior to the enrollment in Study 1; these patients were enrolled directly in the randomized withdrawal phase.
Dose Titration and Maintenance Phase (14-19 weeks)
Seventy-nine (79) patients entered the dose titration and maintenance phase. Patients naïve to treatment with RECORLEV were started on 150 mg of RECORLEV orally twice daily. Patients who previously participated in Study 2 could start on a dose higher than 150 mg twice daily. The dose could be titrated in 150-mg increments at 2-week intervals to a maximum of 600 mg twice daily to achieve mUFC within the normal range. The dose was increased if mUFC was above ULN and was reduced based on individual tolerability. Patients who achieved a stable therapeutic dose for at least 4 weeks and achieved a normal mUFC at the end of the dose titration and maintenance phase were eligible for the randomized withdrawal phase.
Randomized Withdrawal Phase (approximately 8 weeks)
Forty-four (44) patients entered the randomized withdrawal phase: 39 patients from dose titration and maintenance phase and 5 patients directly from Study 2. Patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to either continue RECORLEV or receive matched placebo for approximately 2 months or until early rescue was necessary (i.e., for mUFC >1.5 × ULN).
Efficacy Assessment and Results
The key secondary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of patients with mUFC normalization, defined as a patient with mUFC at or below the ULN at the end of randomized withdrawal phase without meeting a requirement for early rescue during the randomized withdrawal phase.
Out of the 79 patients who entered the dose titration and maintenance phase, 37 (47%) patients who met the requirement to be on a stable therapeutic dose for at least 4 weeks and established normal mUFC at the end of the dose titration and maintenance phase, and 2 patients who did not meet the requirement due to abnormal mUFC, continued to the randomized-withdrawal phase. Out of 5 patients from Study 2 who were enrolled directly in the randomized withdrawal phase, 2 patients had normal mUFC.
Among the 39 patients who had normal mUFC at the randomized withdrawal phase baseline, 21 were randomized to the RECORLEV group and 18 to the placebo group. The number and percent of patients who had normal mUFC at the end of the randomized withdrawal phase was 11/21 (52.4%) in RECORLEV group and 1/18 (5.6%) in placebo group, and the treatment difference (CI) was 46.8% (16.5%, 70.2%). Out of 11 patients with normal mUFC at the end of the randomized-withdrawal phase, 7 patients in the RECORLEV group had normal mUFC throughout the randomized-withdrawal phase. Figure 1 depicts the mUFC during the randomized-withdrawal phase of Study 1. The line for the placebo group should be interpreted with caution as majority of placebo patients were rescued early due to high mUFC levels and were not included in the analysis.
Figure 1: Line Plot of the Mean Urinary Free Cortisol During the Randomized Withdrawal Phase of Study 1 - Observed Mean (± SE)
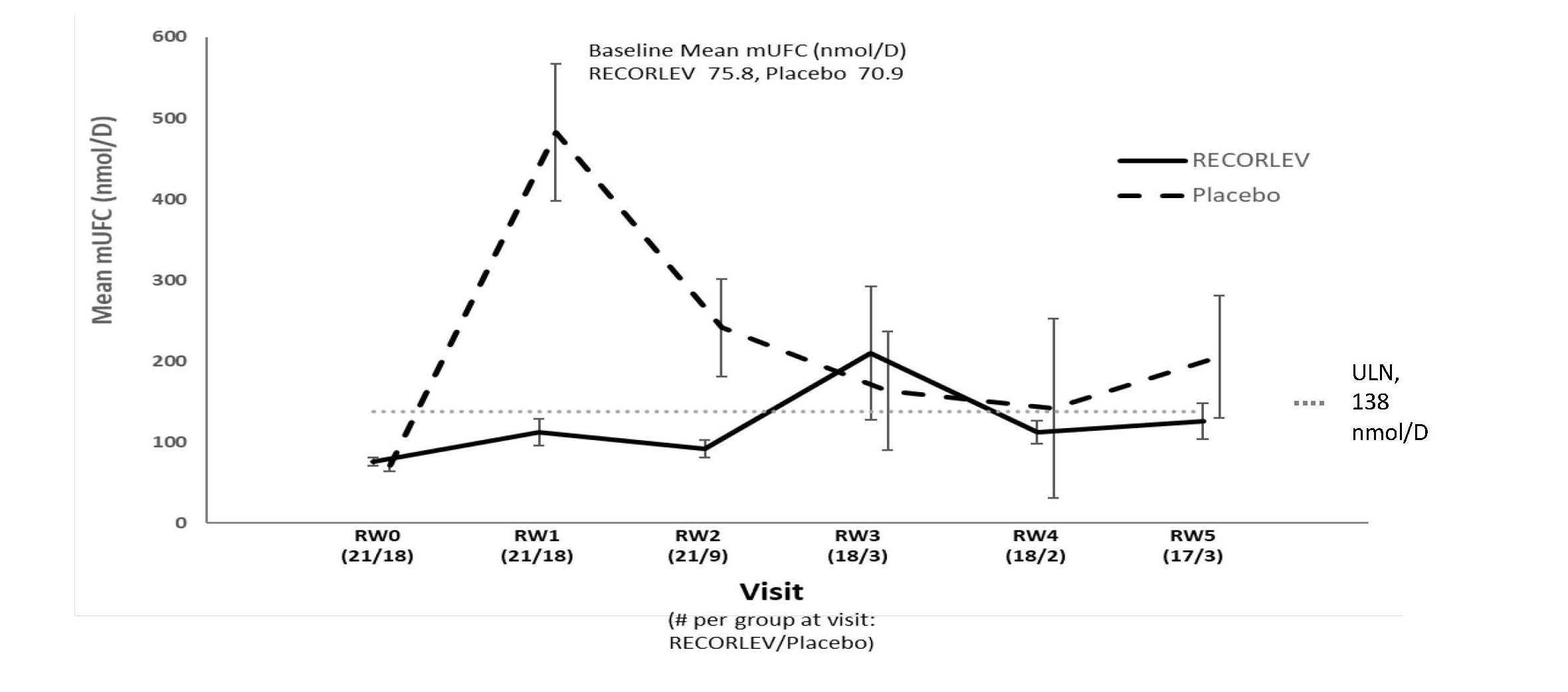
mUFC = Mean Urinary Free Cortisol; RW = Randomized Withdrawal; SE = Standard Error; ULN = Upper Limit of Normal
Only patients who remained in study with non-missing mUFC are included in the analysis
Study 2
Supportive evidence of efficacy was obtained from Study 2 which was a multicenter, single-arm, open-label study that consisted of three study phases (dose titration, maintenance, and extended evaluation) for a total estimated treatment duration of up to 73 weeks (NCT01838551 )
Study 2 enrolled 94 Cushing’s syndrome patients naïve to the treatment with RECORLEV with persistent or recurrent disease despite surgery, previously medically treated patients, and previously untreated patients. The etiology of Cushing's syndrome was benign pituitary adenoma for 80 (85%) patients, adrenal Cushing’s syndrome in 8 (9%) patients, ectopic ACTH secretion for 1 (1%) patient, and unknown source for 5 (5%) patients. Patients with pituitary or adrenal carcinoma were excluded. The mean age at enrollment was 44 years; 82% of patients were female. Overall, the mean time since diagnosis was 68 months before treatment with the first dose in this study. Persistence or recurrence of Cushing’s syndrome was evidenced by the mean of four 24-hour UFC (mUFC) levels greater than or equal to 1.5 times upper limit of normal (ULN); normal range: 11 to 138 nmol/day or 4 to 50 µg/day). The mean (SD) of the mean urinary free cortisol (mUFC) at baseline was 243 µg/day (269), which corresponds to approximately 5 x ULN. The median mUFC at baseline was 148 µg/day (range 59-1510), which corresponds to approximately 3 x ULN.
Dose Titration Phase (2 to 21 weeks)
Ninety-four (94) patients received a starting dosage of 150 mg RECORLEV orally twice daily that was titrated approximately every 2 to 3 weeks if mUFC was above the ULN to a maximum of 600 mg twice daily. Patients who achieved a therapeutic dose were continued to the maintenance phase. Therapeutic dose was defined as a dose at which mUFC level was ≤ ULN, or maximum allowed dose (600 mg twice daily) had been reached, or a clinically meaningful partial response based on clinical judgement, and the maximum tolerated dose had been reached.
Maintenance Phase (6 months)
Seventy-seven (77) patients who achieved a therapeutic dose in the dose titration phase entered the maintenance phase and continued treatment with therapeutic dose of RECORLEV for 6 months. The dose of RECORLEV was allowed to be decreased for safety or tolerability reasons or increased for loss of efficacy. The primary efficacy endpoint was evaluated at the end of maintenance phase.
Extended Evaluation Phase (6 months)
Sixty (60) patients entered the extended evaluation phase in which treatment with RECORLEV continued for an additional 6 months.
Efficacy Assessment and Results
The primary efficacy endpoint of the study was the proportion of patients with normalization of mUFC at the end of the 6-month maintenance phase. Normalization of mUFC was defined as mUFC at or below the ULN based on central laboratory result without requiring a dose increase during the maintenance phase. At the end of the maintenance phase, 29 of 94 patients (30.9%, 95% exact confidence interval 21.7%, 41.2%) met the primary endpoint.
Out of the 94 patients who enrolled in Study 2, 63 (67%) patients had normal mUFC at the end of the titration phase, 29 (30.9%) patients had normal mUFC at the end of the maintenance phase without any dose increase during the maintenance phase, and 16 (17%) patients had normal mUFC at the end of the extended evaluation phase without dose increase during maintenance or extended evaluation phase. However, because 51% of patients discontinued treatment prematurely due to adverse reaction, lack of efficacy, or other reasons, these results should be interpreted with caution.
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
RECORLEV (levoketoconazole) tablets, 150 mg are round, biconvex tablets, with a pink-colored film coating, containing 150 mg of levoketoconazole, and imprinted with an identification code in black ink with the “LEV” printed above the “150” on one side. The other side is plain.
Bottles of 50 with child-resistant closure: NDC 72065-003-01
Storage
Store RECORLEV at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) (see USP controlled room temperature).