Get your patient on Revatio (Sildenafil Citrate)
Revatio prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Revatio patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Adults: 20 mg three times a day Dose may be increased based on symptoms and tolerability. (2.1 )
- Pediatric patients (2.2 )
- ≤20 kg: 10 mg three times a day
- 20 kg to 45 kg: 20 mg three times a day
- >45 kg: 20 mg three times a day. Dose may be increased based on symptoms and tolerability.
- Injection (Adults): 10 mg three times a day administered as an intravenous bolus injection. (2.1 )
Recommended Dosage in Adults
Oral Dosage
The recommended dosage of REVATIO is 20 mg three times a day. Dose may be titrated to a maximum of 80 mg three times a day, if required, based on symptoms and tolerability [see Clinical Studies (14) ] .
Although dose-response improvement in exercise ability was not observed in short-term studies in adults with PAH, the delay in clinical worsening with long-term use of sildenafil in Study A1481324 supports dosing up to a maximum of 80 mg three times a day [see Clinical Studies (14) ] .
Intravenous Dosage
The recommended dose is 10 mg administered as an intravenous bolus injection three times a day. The dose of REVATIO injection does not need to be adjusted for body weight .
A 10-mg dose of REVATIO injection is predicted to provide pharmacological effect of sildenafil and its N-desmethyl metabolite equivalent to that of a 20-mg oral dose .
Recommended Dosage in Pediatric Patients
Oral Dosage
The recommended dosage in patients ≤20 kg is 10 mg three times a day.
For pediatric patients 20 kg to 45 kg, the recommended dosage is 20 mg three times a day.
For pediatric patients 45 kg and greater, the recommended dosage is 20 mg three times a day. A maximum dose in pediatric patients has not been identified. Based on the experience in adults, dose may be titrated to a maximum of 40 mg three times a day for pediatric patients >45 kg, if required, based on symptoms and tolerability [see Clinical Studies (14) ] .
Reconstitution of the Powder for Oral Suspension
Note: Reconstitute the contents of the bottle with a total volume of 90 mL (60 mL followed by 30 mL) . Refer to the detailed instructions below.
- Tap the bottle to loosen the powder.
- Add 60 mL of water to the bottle.
- Replace the cap and shake the bottle vigorously for a minimum of 30 seconds.
- Add another 30 mL of water to the bottle.
- Replace the cap and shake the bottle vigorously for a minimum of 30 seconds.
- Remove cap and press the bottle adaptor into the neck of the bottle. Replace the cap on the bottle.
- Write the expiration date of the reconstituted oral suspension on the bottle label (the expiration date of the reconstituted oral suspension is 60 days from the date of reconstitution) .
Incompatibilities
Do not mix with any other medication or additional flavoring agent.

Revatio prescribing information
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Adults
REVATIO is indicated for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) (World Health Organization [WHO] Group I) in adults to improve exercise ability and delay clinical worsening [see Clinical Studies (14) ] .
Pediatric Patients (1 to 17 Years old)
REVATIO is indicated in pediatric patients 1 to 17 years old for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) (WHO Group I) to improve exercise ability and, in pediatric patients too young to perform standardized exercise testing, pulmonary hemodynamics thought to underlie improvements in exercise [see Clinical Studies (14) ] .
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Adults: 20 mg three times a day Dose may be increased based on symptoms and tolerability. (2.1 )
- Pediatric patients (2.2 )
- ≤20 kg: 10 mg three times a day
- 20 kg to 45 kg: 20 mg three times a day
- >45 kg: 20 mg three times a day. Dose may be increased based on symptoms and tolerability.
- Injection (Adults): 10 mg three times a day administered as an intravenous bolus injection. (2.1 )
Recommended Dosage in Adults
Oral Dosage
The recommended dosage of REVATIO is 20 mg three times a day. Dose may be titrated to a maximum of 80 mg three times a day, if required, based on symptoms and tolerability [see Clinical Studies (14) ] .
Although dose-response improvement in exercise ability was not observed in short-term studies in adults with PAH, the delay in clinical worsening with long-term use of sildenafil in Study A1481324 supports dosing up to a maximum of 80 mg three times a day [see Clinical Studies (14) ] .
Intravenous Dosage
The recommended dose is 10 mg administered as an intravenous bolus injection three times a day. The dose of REVATIO injection does not need to be adjusted for body weight .
A 10-mg dose of REVATIO injection is predicted to provide pharmacological effect of sildenafil and its N-desmethyl metabolite equivalent to that of a 20-mg oral dose .
Recommended Dosage in Pediatric Patients
Oral Dosage
The recommended dosage in patients ≤20 kg is 10 mg three times a day.
For pediatric patients 20 kg to 45 kg, the recommended dosage is 20 mg three times a day.
For pediatric patients 45 kg and greater, the recommended dosage is 20 mg three times a day. A maximum dose in pediatric patients has not been identified. Based on the experience in adults, dose may be titrated to a maximum of 40 mg three times a day for pediatric patients >45 kg, if required, based on symptoms and tolerability [see Clinical Studies (14) ] .
Reconstitution of the Powder for Oral Suspension
Note: Reconstitute the contents of the bottle with a total volume of 90 mL (60 mL followed by 30 mL) . Refer to the detailed instructions below.
- Tap the bottle to loosen the powder.
- Add 60 mL of water to the bottle.
- Replace the cap and shake the bottle vigorously for a minimum of 30 seconds.
- Add another 30 mL of water to the bottle.
- Replace the cap and shake the bottle vigorously for a minimum of 30 seconds.
- Remove cap and press the bottle adaptor into the neck of the bottle. Replace the cap on the bottle.
- Write the expiration date of the reconstituted oral suspension on the bottle label (the expiration date of the reconstituted oral suspension is 60 days from the date of reconstitution) .
Incompatibilities
Do not mix with any other medication or additional flavoring agent.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
REVATIO Tablets
White, film-coated, round tablets engraved with “RVT20” containing sildenafil citrate equivalent to 20 mg of sildenafil.
REVATIO for Oral Suspension
White to off-white powders containing 1.57 g of sildenafil citrate (equivalent to 1.12 g of sildenafil) in a bottle for reconstitution to 10 mg/mL. Following reconstitution with 90 mL of water, the total volume of the oral suspension is 112 mL. A 2-mL oral dosing syringe (with 0.5 mL and 2 mL dose markings) and a press-in bottle adaptor are also provided.
REVATIO Injection
Single use vial containing 10 mg/12.5 mL of sildenafil.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Limited published data from randomized controlled trials, case-controlled trials, and case series do not report a clear association with sildenafil and major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes when sildenafil is used during pregnancy. There are risks to the mother and fetus from untreated pulmonary arterial hypertension (see Clinical Considerations ). Animal reproduction studies conducted with sildenafil showed no evidence of embryo-fetal toxicity or teratogenicity at doses up to 32- and 65-times the recommended human dose (RHD) of 20 mg three times a day in rats and rabbits, respectively (see Data ) .
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-Associated Maternal and/or Embryo/Fetal Risk
Pregnant women with untreated pulmonary arterial hypertension are at risk for heart failure, stroke, preterm delivery, and maternal and fetal death.
Data
Animal Data
No evidence of teratogenicity, embryotoxicity, or fetotoxicity was observed in pregnant rats or rabbits dosed with sildenafil 200 mg/kg/day during organogenesis, a level that is, on a mg/m 2 basis, 32- and 65-times, respectively, the recommended human dose (RHD) of 20 mg three times a day. In a rat pre- and postnatal development study, the no‑observed-adverse-effect dose was 30 mg/kg/day (equivalent to 5-times the RHD on a mg/m 2 basis).
Lactation
Risk Summary
Limited published data from a case report describe the presence of sildenafil and its active metabolite in human milk. There is insufficient information about the effects of sildenafil on the breastfed infant and no information on the effects of sildenafil on milk production. Limited clinical data during lactation preclude a clear determination of the risk of REVATIO to an infant during lactation.
Pediatric Use
The safety and efficacy of REVATIO have been established in pediatric patients 1 to 17 years old, for the treatment of PAH (WHO Group I) to improve exercise ability and, in patients too young to perform standard exercising testing, pulmonary hemodynamics thought to underlie improvements in exercise Use of REVATIO for this indication is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies in adults with additional PK and safety data in pediatric patients aged 1 year and older [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) , Clinical Studies (14) ] . The safety and effectiveness of REVATIO have not been established in pediatric patients younger than 1 year of age.
During the conduct of the pediatric studies (STARTS-1 and STARTS-2) [see Clinical Studies (14) ] , an imbalance in the number of deaths was noted: 5/55 (9.1%), 10/74 (13.5%), and 22/100 (22%) in the sildenafil low, medium, and high dose groups, respectively. The causes of death were related to the progression of PAH. This safety observation in pediatrics was not confirmed in a study conducted in adults designed to evaluate this risk (Study A1481324).Given the beneficial effects on clinical worsening and death observed in adults with increasing doses (Study A1481324) and the expected similarity of disease in pediatrics and adults, a causal association for the observed dose-related effect on mortality in pediatric patients is unlikely, and therefore, the available data support dosing in pediatric patients >45 kg up to a maximum of 40 mg three times a day.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of REVATIO did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment for mild to moderate impairment is required. Severe impairment has not been studied [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Patients with Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment is required (including severe impairment CLcr <30 mL/min) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
CONTRAINDICATIONS
REVATIO is contraindicated in patients with:
- Concomitant use of organic nitrates in any form, either regularly or intermittently, because of the greater risk of hypotension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
- Concomitant use of riociguat, a guanylate cyclase stimulator. Phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE-5) inhibitors, including sildenafil, may potentiate the hypotensive effects of riociguat.
- Known hypersensitivity to sildenafil or any component of the tablet, injection, or oral suspension. Hypersensitivity, including anaphylactic reaction, anaphylactic shock and anaphylactoid reaction, has been reported in association with the use of sildenafil.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Vasodilation effects may be more common in patients with hypotension or on antihypertensive therapy. (5.1 )
- Use in pulmonary veno-occlusive disease (PVOD) may cause pulmonary edema and is not recommended. (5.2 )
- Hearing or visual impairment: Seek medical attention if sudden decrease or loss of vision or hearing occurs. (5.4 , 5.5 )
- Pulmonary hypertension (PH) secondary to sickle cell disease: REVATIO may cause serious vaso-occlusive crises. (5.8 )
Hypotension
REVATIO has vasodilatory properties, resulting in mild and transient decreases in blood pressure. Before prescribing REVATIO, carefully consider whether patients with certain underlying conditions could be adversely affected by such vasodilatory effects (e.g., patients on antihypertensive therapy or with resting hypotension [blood pressure less than 90/50], fluid depletion, severe left ventricular outflow obstruction, or autonomic dysfunction). Monitor blood pressure when co‑administering blood pressure lowering drugs with REVATIO.
Worsening Pulmonary Vascular Occlusive Disease
Pulmonary vasodilators may significantly worsen the cardiovascular status of patients with pulmonary veno‑occlusive disease (PVOD). Since there are no clinical data on administration of REVATIO to patients with veno‑occlusive disease, administration of REVATIO to such patients is not recommended. Should signs of pulmonary edema occur when REVATIO is administered, consider the possibility of associated PVOD.
Epistaxis
The incidence of epistaxis was 13% in patients taking REVATIO with PAH secondary to CTD. This effect was not seen in idiopathic PAH (REVATIO 3%, placebo 2%) patients. The incidence of epistaxis was also higher in REVATIO-treated patients with a concomitant oral vitamin K antagonist (9% versus 2% in those not treated with concomitant vitamin K antagonist).
The safety of REVATIO is unknown in patients with bleeding disorders or active peptic ulceration.
Visual Loss
When used to treat erectile dysfunction, non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION), a cause of decreased vision including permanent loss of vision, has been reported post marketing in temporal association with the use of PDE-5 inhibitors, including sildenafil. Most patients had underlying anatomic or vascular risk factors for developing NAION, including low cup to disc ratio (“crowded disc”).
Advise patients to seek immediate medical attention in the event of a sudden loss of vision in one or both eyes while taking REVATIO.
There are no controlled clinical data on the safety or efficacy of REVATIO in patients with retinitis pigmentosa, a minority of whom have genetic disorders of retinal phosphodiesterases. Therefore, use of REVATIO in patients with retinitis pigmentosa is not recommended.
Hearing Loss
Cases of sudden decrease or loss of hearing, which may be accompanied by tinnitus and dizziness, have been reported in temporal association with the use of PDE-5 inhibitors, including REVATIO. In some of the cases, medical conditions and other factors were reported that may have played a role. In many cases, medical follow-up information was limited. It is not possible to determine whether these reported events are related directly to the use of REVATIO, to the patient’s underlying risk factors for hearing loss, a combination of these factors, or to other factors.
Advise patients to seek prompt medical attention in the event of sudden decrease or loss of hearing while taking PDE-5 inhibitors, including REVATIO.
Combination with Other PDE-5 inhibitors
Sildenafil is also marketed as VIAGRA ® . The safety and efficacy of combinations of REVATIO with VIAGRA or other PDE‑5 inhibitors have not been studied. Inform patients taking REVATIO not to take VIAGRA or other PDE‑5 inhibitors.
Priapism
Use REVATIO with caution in patients with anatomical deformation of the penis (e.g., angulation, cavernosal fibrosis, or Peyronie’s disease) or in patients who have conditions, which may predispose them to priapism (e.g., sickle cell anemia, multiple myeloma, or leukemia). In the event of an erection that persists longer than 4 hours, the patient should seek immediate medical assistance. If priapism (painful erection greater than 6 hours in duration) is not treated immediately, penile tissue damage and permanent loss of potency could result.
Vaso-occlusive Crisis in Patients with Pulmonary Hypertension Secondary to Sickle Cell Disease
In a small, prematurely terminated study of patients with pulmonary hypertension (PH) secondary to sickle cell disease, vaso‑occlusive crises requiring hospitalization were more commonly reported by patients who received REVATIO than by those randomized to placebo. The effectiveness and safety of REVATIO in the treatment of PH secondary to sickle cell disease has not been established.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse events are discussed elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hypotension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- Vision Loss [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ]
- Hearing Loss [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ]
- Priapism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ]
- Vaso-occlusive Crisis in Patients with Pulmonary Hypertension Secondary to Sickle Cell Disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) ]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
In a 12-week, placebo-controlled clinical study and an open-label extension study (SUPER-1) in 277 REVATIO-treated adults with PAH (WHO Group I) [see Clinical Studies (14) ] the adverse reactions that were reported by at least 10% of REVATIO-treated patients in any dosing group, and were more frequent in REVATIO-treated patients than in placebo-treated patients are shown in Table 1. Adverse reactions were generally transient and mild to moderate in nature. The overall frequency of discontinuation in REVATIO-treated patients was 3% (20 mg and 40 mg three times a day) and 8% (80 mg three times a day). The overall frequency of discontinuation for placebo was 3%.
REVATIO 20 mg (n = 69) | REVATIO 40 mg (n = 67) | REVATIO 80 mg (n = 71) | Placebo (n = 70) | |
Headache | 46% | 42% | 49% | 39% |
Flushing | 10% | 9% | 16% | 4% |
Pain in Limb | 7% | 15% | 9% | 6% |
Myalgia | 7% | 6% | 14% | 4% |
Back Pain | 13% | 13% | 9% | 11% |
Dyspepsia | 13% | 8% | 13% | 7% |
Diarrhea | 9% | 12% | 10% | 6% |
In a placebo-controlled fixed dose titration study (PACES-1) of REVATIO (starting with recommended dose of 20 mg and increased to 40 mg and then 80 mg all three times a day) as an adjunct to intravenous epoprostenol in patients with PAH, no new safety issues were identified except for edema, which occurred in 25% of subjects in the combined REVATIO + epoprostenol group compared with 13% of subjects in the epoprostenol group [see Clinical Studies (14) ] .
In a study to assess the effects of multiple doses of REVATIO on mortality in adults with PAH (StudyA1481324), the lower dose 5 mg TID group showed a higher observed number of deaths (all related to underlying disease/disease under study), serious adverse events, and severe adverse events than the 20 mg and 80 mg TID groups [see Clinical Studies (14) ] . Overall, the safety data for sildenafil 80 mg TID dose in Study A1481324 was consistent with the established safety profile of sildenafil in previous adult PAH studies.
Pediatric Patients
REVATIO was studied in a total of 234 PAH pediatric patients 1 to 17 years of age in a 16‑week, double-blind placebo‑controlled study (STARTS-1); 220 patients continued in a long-term extension study (STARTS-2). Erection increased was observed in 9% of patients treated with sildenafil in STARTS-1. No other new adverse reactions were identified in pediatric patients [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4) ] .
REVATIO Injection
Adverse events with REVATIO injection were similar to those seen with oral tablets.
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of sildenafil (marketed for both PAH and erectile dysfunction). Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Cardiovascular Events
In postmarketing experience with sildenafil at doses indicated for erectile dysfunction, serious cardiovascular, cerebrovascular, and vascular events, including myocardial infarction, sudden cardiac death, ventricular arrhythmia, cerebrovascular hemorrhage, transient ischemic attack, hypertension, pulmonary hemorrhage, and subarachnoid and intracerebral hemorrhages have been reported in temporal association with the use of the drug. Most, but not all, of these patients had preexisting cardiovascular risk factors. Many of these events were reported to occur during or shortly after sexual activity, and a few were reported to occur shortly after the use of sildenafil without sexual activity. Others were reported to have occurred hours to days after use concurrent with sexual activity. It is not possible to determine whether these events are related directly to sildenafil, to sexual activity, to the patient’s underlying cardiovascular disease, or to a combination of these or other factors.
Nervous System
Seizure, seizure recurrence
Ophthalmologic
NAION [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) , Patient Counseling Information (17) ] .
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Nitrates
Concomitant use of REVATIO with nitrates in any form is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4) ] .
Strong CYP3A Inhibitors
Concomitant use of REVATIO with strong CYP3A inhibitors is not recommended [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Moderate-to-Strong CYP3A Inducers
Concomitant use of REVATIO with moderate-to-strong CYP3A inducers (such as bosentan) decreases the sildenafil exposure. Dose up-titration of REVATIO may be needed when initiating treatment with moderate-to-strong CYP3A inducers. Reduce the dose of REVATIO to 20 mg three times a day when discontinuing treatment with moderate-to-strong CYP3A inducers [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) and Clinical Studies (14) ] .
DESCRIPTION
REVATIO, phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE-5) inhibitor, is the citrate salt of sildenafil, a selective inhibitor of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP)-specific phosphodiesterase type-5 (PDE-5). Sildenafil is also marketed as VIAGRA ® for erectile dysfunction.
Sildenafil citrate is designated chemically as 1-[[3-(6,7-dihydro-1-methyl-7-oxo-3-propyl-1 H -pyrazolo [4,3- d ] pyrimidin-5-yl)-4-ethoxyphenyl] sulfonyl]-4-methylpiperazine citrate and has the following structural formula:
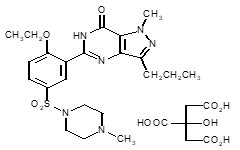
Sildenafil citrate is a white to off-white crystalline powder with a solubility of 3.5 mg/mL in water and a molecular weight of 666.7.
REVATIO (sildenafil) Tablets: REVATIO is formulated as white, film-coated round tablets for oral administration. Each tablet contains sildenafil citrate equivalent to 20 mg of sildenafil. In addition to the active ingredient, sildenafil citrate, each tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: anhydrous dibasic calcium phosphate, croscarmellose sodium, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, titanium dioxide, and triacetin.
REVATIO (sildenafil) Injection: REVATIO is supplied as a clear, colorless, sterile, ready to use solution in a single‑use vial containing 10 mg/12.5 mL of sildenafil. Each mL of solution contains 1.124 mg sildenafil citrate (equivalent to 0.8 mg sildenafil), 50.5 mg dextrose, and water for injection.
REVATIO (sildenafil) for Oral Suspension: REVATIO is supplied as white to off-white powders containing 1.57 g of sildenafil citrate (equivalent to1.12 g sildenafil) in an amber glass bottle intended for reconstitution. Following reconstitution with 90 mL water, the total volume of the oral suspension is 112 mL and the oral suspension contains 10 mg/mL sildenafil. The inactive ingredients include citric acid anhydrous, colloidal silicon dioxide anhydrous, grape flavor, sodium benzoate, sodium citrate dihydrate, sorbitol, sucralose, titanium dioxide, and xanthan gum. In addition to the bottle, a press-in bottle adapter and an oral dosing syringe (with 0.5 mL and 2 mL dose markings) are provided.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Sildenafil is an inhibitor of cGMP specific PDE-5 in the smooth muscle of the pulmonary vasculature, where PDE-5 is responsible for degradation of cGMP. Sildenafil, therefore, increases cGMP within pulmonary vascular smooth muscle cells resulting in relaxation. In patients with PAH, this can lead to vasodilation of the pulmonary vascular bed and, to a lesser degree, vasodilatation in the systemic circulation.
Studies in vitro have shown that sildenafil is selective for PDE5. Its effect is more potent on PDE5 than on other known phosphodiesterases (10-fold for PDE6, greater than 80-fold for PDE1, greater than 700-fold for PDE2, PDE3, PDE4, PDE7, PDE8, PDE9, PDE10, and PDE11). The approximately 4,000-fold selectivity for PDE-5 versus PDE3 is important because PDE3 is involved in control of cardiac contractility. Sildenafil is only about 10 times as potent for PDE5 compared to PDE6, an enzyme found in the retina and involved in the phototransduction pathway of the retina. This lower selectivity is thought to be the basis for abnormalities related to color vision observed with higher doses or plasma levels [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2) ] .
In addition to pulmonary vascular smooth muscle and the corpus cavernosum, PDE5 is also found in other tissues including vascular and visceral smooth muscle and in platelets. The inhibition of PDE5 in these tissues by sildenafil may be the basis for the enhanced platelet anti-aggregatory activity of nitric oxide observed in vitro , and the mild peripheral arterial-venous dilatation in vivo .
Pharmacodynamics
Effects of REVATIO on Hemodynamic Measures
Adults
Patients on all REVATIO doses achieved a statistically significant reduction in mean pulmonary arterial pressure (mPAP) compared to those on placebo in a study with no background vasodilators [see SUPER-1 in Clinical Studies (14) ] . Data on other hemodynamic measures for the REVATIO 20 mg three times a day and placebo dosing regimens is displayed in Table 2. The relationship between these effects and improvements in 6-minute walk distance is unknown.
| mPAP = mean pulmonary arterial pressure; PVR = pulmonary vascular resistance; SVR = systemic vascular resistance; RAP = right atrial pressure; CO = cardiac output; HR = heart rate. | ||
Placebo (n = 65) The number of patients per treatment group varied slightly for each parameter due to missing assessments. | REVATIO 20 mg (n = 65) | |
mPAP (mmHg) | 0.6 (-0.8, 2.0) | -2.1 (-4.3, 0.0) |
PVR (dyn×s/cm 5 ) | 49 (-54, 153) | -122 (-217, -27) |
SVR (dyn×s/cm 5 ) | -78 (-197, 41) | -167 (-307, -26) |
RAP (mmHg) | 0.3 (-0.9, 1.5) | -0.8 (-1.9, 0.3) |
CO (L/min) | -0.1 (-0.4, 0.2) | 0.4 (0.1, 0.7) |
HR (beats/min) | -1.3 (-4.1, 1.4) | -3.7 (-5.9, -1.4) |
Pediatric Patients
Patients on REVATIO medium and high dose groups achieved a dose related improvements in pulmonary vascular resistance index (PVRI) and mean pulmonary arterial pressure (mPAP) compared to those on placebo [see STARTS-1 in Clinical Studies (14) ] . Improvements were observed with cardiac index in all three REVATIO dose groups over placebo. Data on other hemodynamic measures for the REVATIO low, medium and high dose groups compared to placebo is displayed in Table 3.
Parameter [Estimate (95% CI)] | Low Dose | Medium Dose | High Dose |
PVRI (%) | -2% (-20%, 20%) n = 37 | -18% (-32%, -2%) n = 51 | -27% (-39%, -14%) n = 68 |
mPAP (mmHg) | 1.6 (-4.5, 7.6) n = 39 | -3.5 (-8.9, 1.9) n = 55 | -7.3 (-12.4, -2.1) n = 71 |
CI (%) | 10% (-4%, 26%) n = 37 | 4% (-7%, 18%) n = 51 | 15% (3%, 29%) n = 69 |
SVRI (%) | -9% (-22%, 7%) n = 37 | -5% (-17%, 10%) n = 50 | -16% (-26%, -4%) n = 68 |
RAP (mmHg) | -0.17 (-1.91, 1.57) n = 39 | -0.19 (-1.73, 1.36) n = 55 | -1.14 (-2.61, 0.33) n = 71 |
HR (%) | 3% (-5%, 12%) n = 39 | 2% (-5%, 9%) n = 55 | -2% (-9%, 5%) n = 71 |
Abbreviations: CI = cardiac index; HR = heart rate; mPAP = mean pulmonary arterial pressure; PVRI = pulmonary vascular resistance index; RAP = right atrial pressure; SVRI = systemic vascular resistance index. Note: n = 52, 56, 55, 54, 56, and 56 placebo patients for PVRI, mPAP, CI, SVRI, RAP and HR, respectively. | |||
Effects of REVATIO on Blood Pressure
Single oral doses of sildenafil 100 mg administered to healthy volunteers produced decreases in supine blood pressure (mean maximum decrease in systolic/diastolic blood pressure of 8/5 mmHg). The decrease in blood pressure was most notable approximately 1-2 hours after dosing and was not different from placebo at 8 hours. Similar effects on blood pressure were noted with 25 mg, 50 mg, and 100 mg doses of sildenafil, therefore the effects are not related to dose or plasma levels within this dosage range. Larger effects were recorded among patients receiving concomitant nitrates [see Contraindications (4) ] .
Single oral doses of sildenafil up to 100 mg in healthy volunteers produced no clinically relevant effects on electrocardiogram (ECG). After chronic dosing of 80 mg three times a day to patients with PAH, no clinically relevant effects on ECG were reported.
After chronic dosing of 80 mg three times a day sildenafil to healthy volunteers, the largest mean change from baseline in supine systolic and supine diastolic blood pressures was a decrease of 9.0 mmHg and 8.4 mmHg, respectively.
After chronic dosing of 80 mg three times a day sildenafil to patients with systemic hypertension, the mean change from baseline in systolic and diastolic blood pressures was a decrease of 9.4 and 9.1 mmHg, respectively.
After chronic dosing of 80 mg three times a day sildenafil to patients with PAH, lesser reductions than above in systolic and diastolic blood pressures were observed (a decrease in both of 2 mmHg).
Effects of REVATIO on Vision
At single oral doses of 100 mg and 200 mg, transient dose-related impairment of color discrimination (blue/green) was detected using the Farnsworth-Munsell 100-hue test, with peak effects near the time of peak plasma levels. This finding is consistent with the inhibition of PDE6, which is involved in phototransduction in the retina. An evaluation of visual function at doses up to 200 mg revealed no effects of REVATIO on visual acuity, intraocular pressure, or pupillometry.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption and Distribution
REVATIO is rapidly absorbed after oral administration, with a mean absolute bioavailability of 41% (25 to 63%). Maximum observed plasma concentrations are reached within 30 to 120 minutes (median 60 minutes) of oral dosing in the fasted state. When REVATIO is taken with a high-fat meal, the rate of absorption is reduced, with a mean delay in T max of 60 minutes and a mean reduction in C max of 29%. The mean steady state volume of distribution (Vss) for sildenafil is 105 L, indicating distribution into the tissues. Sildenafil and its major circulating N-desmethyl metabolite are both approximately 96% bound to plasma proteins. Protein binding is independent of total drug concentrations.
Bioequivalence was established between the 20 mg tablet and the 10 mg/mL oral suspension when administered as a 20 mg single oral dose of sildenafil (as citrate).
Metabolism and Excretion
Sildenafil is cleared predominantly by the CYP3A (major route) and cytochrome P450 2C9 (CYP2C9, minor route) hepatic microsomal isoenzymes. The major circulating metabolite results from N-desmethylation of sildenafil, and is, itself, further metabolized. This metabolite has a phosphodiesterase selectivity profile similar to sildenafil and an in vitro potency for PDE-5 approximately 50% of the parent drug. In healthy volunteers, plasma concentrations of this metabolite are approximately 40% of those seen for sildenafil, so that the metabolite accounts for about 20% of sildenafil’s pharmacologic effects. In patients with PAH, however, the ratio of the metabolite to sildenafil is higher. Both sildenafil and the active metabolite have terminal half-lives of about 4 hours.
After either oral or intravenous administration, sildenafil is excreted as metabolites predominantly in the feces (approximately 80% of the administered oral dose) and to a lesser extent in the urine (approximately 13% of the administered oral dose).
REVATIO Injection: The pharmacokinetic profile of REVATIO has been characterized following intravenous administration. A 10 mg dose of REVATIO Injection is predicted to provide a pharmacological effect of sildenafil and its N-desmethyl metabolite equivalent to that of a 20 mg oral dose.
Population Pharmacokinetics
Age, gender, race, and renal and hepatic function were included as factors assessed in the population pharmacokinetic model to evaluate sildenafil pharmacokinetics in patients with PAH. The dataset available for the population pharmacokinetic evaluation contained a wide range of demographic data and laboratory parameters associated with hepatic and renal function. None of these factors had a significant impact on sildenafil pharmacokinetics in patients with PAH.
In patients with PAH, the average steady-state concentrations were 20 to 50% higher when compared to those of healthy volunteers. There was also a doubling of C min levels compared to healthy volunteers. Both findings suggest a lower clearance and/or a higher oral bioavailability of sildenafil in patients with PAH compared to healthy volunteers.
Pediatric Patients
Body weight was shown to be a good predictor of drug exposure in children. Sildenafil plasma concentration half-life values were estimated to range from 2.9 to 4.4 hours for a range of 10 to 70 kg of body weight. T max was estimated at approximately 1 hour.
Geriatric Patients
Healthy elderly volunteers (65 years or over) had a reduced clearance of sildenafil, resulting in approximately 84% and 107% higher plasma concentrations of sildenafil and its active N-desmethyl metabolite, respectively, compared to those seen in healthy younger volunteers (18 to 45 years). Due to age-differences in plasma protein binding, the corresponding increase in the AUC of free (unbound) sildenafil and its active N-desmethyl metabolite were 45% and 57%, respectively.
Renal Impairment
In volunteers with mild (CLcr = 50-80 mL/min) and moderate (CLcr = 30-49 mL/min) renal impairment, the pharmacokinetics of a single oral dose of sildenafil (50 mg) was not altered. In volunteers with severe (CLcr less than 30 mL/min) renal impairment, sildenafil clearance was reduced, resulting in approximately doubling of AUC and C max compared to age-matched volunteers with no renal impairment. In addition, N-desmethyl metabolite AUC and C max values were significantly increased 200% and 79%, respectively, in patients with severe renal impairment compared to patients with normal renal function.
Hepatic Impairment
In volunteers with mild to moderate hepatic cirrhosis (Child-Pugh class A and B), sildenafil clearance was reduced, resulting in increases in AUC (84%) and C max (47%) compared to age-matched volunteers with no hepatic impairment. Patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class C) have not been studied.
Drug Interaction Studies
In vitro studies
Sildenafil metabolism is principally mediated by the CYP3A (major route) and CYP2C9 (minor route) cytochrome P450 isoforms. Therefore, inhibitors of these isoenzymes may reduce sildenafil clearance and inducers of these isoenzymes may increase sildenafil clearance.
Sildenafil is a weak inhibitor of the cytochrome P450 isoforms 1A2, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, 2E1 and 3A (IC50 greater than150 µM).
Sildenafil is not expected to affect the pharmacokinetics of compounds which are substrates of these CYP enzymes at clinically relevant concentrations.
In vivo studies
The effects of other drugs on sildenafil pharmacokinetics and the effects of sildenafil on the exposure to other drugs are shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2, respectively.
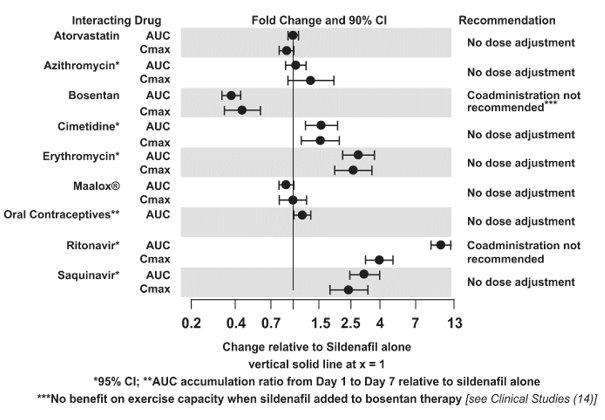
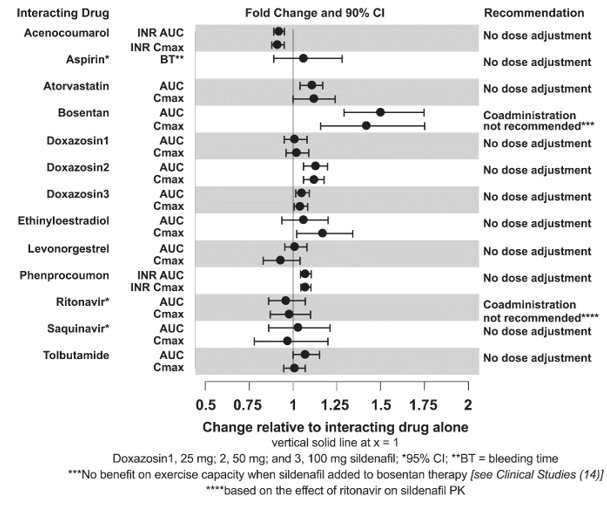
CYP3A Inhibitors and Beta Blockers
Population pharmacokinetic analysis of data from patients in clinical trials indicated an approximately 30% reduction in sildenafil clearance when it was co-administered with mild/moderate CYP3A inhibitors and an approximately 34% reductions in sildenafil clearance when co-administered with beta-blockers. Sildenafil exposure at a dose of 80 mg three times a day without concomitant medication is shown to be 5-fold the exposure at a dose of 20 mg three times a day. This concentration range covers the same increased sildenafil exposure observed in specifically‑designed drug interaction studies with CYP3A inhibitors (except for potent inhibitors such as ketoconazole, itraconazole, and ritonavir).
REVATIO Injection: Predictions based on a pharmacokinetic model suggest that drug-drug interactions with CYP3A inhibitors will be less than those observed after oral sildenafil administration.
CYP3A4 Inducers Including Bosentan
Concomitant administration of strong CYP3A inducers is expected to cause substantial decreases in plasma levels of sildenafil.
Population pharmacokinetic analysis of data from patients in clinical trials indicated approximately 3-fold the sildenafil clearance when it was co-administered with mild CYP3A inducers.
Epoprostenol
The mean reduction of sildenafil (80 mg three times a day) bioavailability when co-administered with epoprostenol was 28%, resulting in about 22% lower mean average steady state concentrations. Therefore, the slight decrease of sildenafil exposure in the presence of epoprostenol is not considered clinically relevant. The effect of sildenafil on epoprostenol pharmacokinetics is not known.
No significant interactions were shown with tolbutamide (250 mg) or warfarin (40 mg), both of which are metabolized by CYP2C9.
Alcohol
Sildenafil (50 mg) did not potentiate the hypotensive effect of alcohol in healthy volunteers with mean maximum blood alcohol levels of 0.08%.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Sildenafil was not carcinogenic when administered to rats for up to 24 months at 60 mg/kg/day, a dose resulting in total systemic exposure (AUC) to unbound sildenafil and its major metabolite 33- and 37-times, for male and female rats, respectively, the human exposure at the RHD of 20 mg three times a day. Sildenafil was not carcinogenic when administered to male and female mice for up to 21 and 18 months, respectively, at doses up to a maximally tolerated level of 10 mg/kg/day, a dose equivalent to the RHD on a mg/m 2 basis.
Sildenafil was negative in in vitro bacterial and Chinese hamster ovary cell assays to detect mutagenicity, and in vitro human lymphocytes and in vivo mouse micronucleus assays to detect clastogenicity.
There was no impairment of fertility in male or female rats given up to 60 mg sildenafil/kg/day, a dose producing a total systemic exposure (AUC) to unbound sildenafil and its major metabolite of 19- and 38-times for males and females, respectively, the human exposure at the RHD of 20 mg three times a day.
CLINICAL STUDIES
SUPER-1 ( NCT00644605) - REVATIO monotherapy [20 mg, 40 mg, and 80 mg three times a day]
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of REVATIO (SUPER-1) was conducted in 277 patients with PAH (defined as a mean pulmonary artery pressure ≥25 mmHg at rest with a pulmonary capillary wedge pressure <15 mmHg). Patients were predominantly WHO Functional Classes II-III. Allowed background therapy included a combination of anticoagulants, digoxin, calcium channel blockers, diuretics, and oxygen. The use of prostacyclin analogues, endothelin receptor antagonists, and arginine supplementation were not permitted. Patients who had failed to respond to bosentan were also excluded. Patients with left ventricular ejection fraction less than 45% or left ventricular shortening fraction less than 0.2 also were not studied.
Patients were randomized to receive placebo (n = 70) or REVATIO 20 mg (n = 69), 40 mg (n = 67) or 80 mg (n = 71) three times a day for a period of 12 weeks. They had either primary pulmonary hypertension (PPH) (63%), PAH associated with CTD (30%), or PAH following surgical repair of left-to-right congenital heart lesions (7%). The study population consisted of 25% men and 75% women with a mean age of 49 years (range: 18 to 81 years) and baseline 6-minute walk distance between 100 and 450 meters (mean 343).
The primary efficacy endpoint was the change from baseline at Week 12 (at least 4 hours after the last dose) in the 6‑minute walk distance. Placebo-corrected mean increases in walk distance of 45-50 meters were observed with all doses of REVATIO. These increases were significantly different from placebo, but the REVATIO dose groups were not different from each other (see Figure 3), indicating no additional clinical benefit from doses higher than 20 mg three times a day. The improvement in walk distance was apparent after 4 weeks of treatment and was maintained at Week 8 and Week 12.
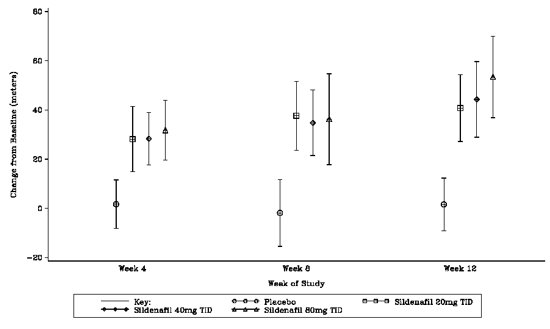
Figure 4 displays subgroup efficacy analyses in SUPER-1 for the change from baseline in 6-Minute Walk Distance at Week 12 including baseline walk distance, disease etiology, functional class, gender, age, and hemodynamic parameters.
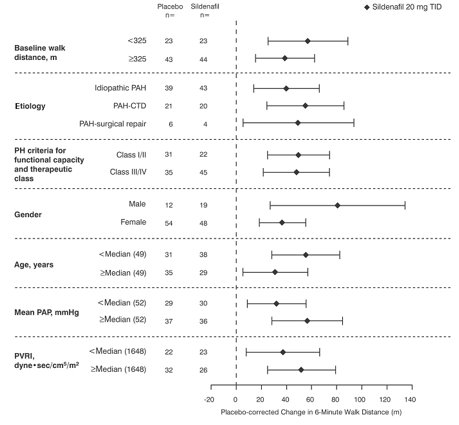
Key: PAH = pulmonary arterial hypertension; CTD = connective tissue disease; PH = pulmonary hypertension; PAP = pulmonary arterial pressure; PVRI = pulmonary vascular resistance index; TID = three times daily.
SUPER-2 (NCT00159887) Long-term Treatment of PAH
In a long-term follow-up of patients who were treated with sildenafil (n=277), K-M estimates of survival at 1, 2, and 3 years were 94%, 88% , and 79%, respectively. These uncontrolled observations do not allow comparison with a group not given sildenafil and cannot be used to determine the long term-effect of sildenafil on mortality.
PACES-1 (NCT00159861) - REVATIO Co-administered with Epoprostenol
A randomized, double-blind, placebo‑controlled study (PACES-1) was conducted in 267 patients with PAH who were taking stable doses of intravenous epoprostenol. Patients had to have a mean pulmonary artery pressure (mPAP) greater than or equal to 25 mmHg and a pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP) less than or equal to 15 mmHg at rest via right heart catheterization within 21 days before randomization, and a baseline 6-minute walk test distance greater than or equal to 100 meters and less than or equal to 450 meters (mean 349 meters). Patients were randomized to placebo or REVATIO (in a fixed titration starting from 20 mg to 40 mg and then 80 mg, three times a day) and all patients continued intravenous epoprostenol therapy.
At baseline patients had PPH (80%) or PAH secondary to CTD (20%); WHO Functional Class I (1%), II (26%), III (67%), or IV (6%); and the mean age was 48 years, 80% were female, and 79% were Caucasian.
There was a statistically significant greater increase from baseline in 6-minute walk distance at Week 16 (primary endpoint) for the REVATIO group compared with the placebo group. The mean change from baseline at Week 16 (last observation carried forward) was 30 meters for the REVATIO group compared with 4 meters for the placebo group giving an adjusted treatment difference of 26 meters (95% CI: 10.8, 41.2) (p = 0.0009).
Patients on REVATIO achieved a statistically significant reduction in mPAP compared to those on placebo. A mean placebo-corrected treatment effect of -3.9 mmHg was observed in favor of REVATIO (95% CI: -5.7, -2.1) (p = 0.00003).
Time to clinical worsening of PAH was defined as the time from randomization to the first occurrence of a clinical worsening event (death, lung transplantation, initiation of bosentan therapy, or clinical deterioration requiring a change in epoprostenol therapy). Table 4 displays the number of patients with clinical worsening events in PACES-1. Kaplan-Meier estimates and a stratified log-rank test demonstrated that placebo-treated patients were 3 times more likely to experience a clinical worsening event than REVATIO-treated patients and that REVATIO-treated patients experienced a significant delay in time to clinical worsening versus placebo-treated patients (p = 0.0074). Kaplan‑Meier plot of time to clinical worsening is presented in Figure 5.
Placebo (N = 131) | REVATIO (N = 134) | |||
Number of patients with clinical worsening first event | 23 | 8 | ||
First Event | All Events | First Event | All Events | |
Death, n | 3 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
Lung transplantation, n | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
Hospitalization due to PAH, n | 9 | 11 | 8 | 8 |
Clinical deterioration resulting in: Change of Epoprostenol Dose, n Initiation of Bosentan, n | 9 1 | 16 1 | 0 0 | 2 0 |
Proportion worsened 95% Confidence Interval | 0.187 (0.12 – 0.26) | 0.062 (0.02 – 0.10) | ||
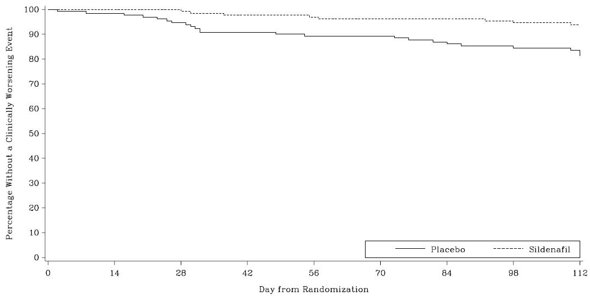
Improvements in WHO Functional Class for PAH were also demonstrated in patients on REVATIO compared to placebo. More than twice as many REVATIO-treated patients (36%) as placebo-treated patients (14%) showed an improvement in at least one functional New York Heart Association (NYHA) class for PAH.
Study A1481243 (NCT00323297) - REVATIO Added to Bosentan Therapy – Lack of Effect on Exercise Capacity
A randomized, double-blind, placebo‑controlled study was conducted in 103 patients with PAH who were on bosentan therapy for a minimum of 3 months. The PAH patients included those with primary PAH and PAH associated with CTD. Patients were randomized to placebo or sildenafil (20 mg three times a day) in combination with bosentan (62.5 to 125 mg twice a day). The primary efficacy endpoint was the change from baseline at Week 12 in 6-minute walk distance (6MWD). The results indicate that there is no significant difference in mean change from baseline on 6MWD observed between sildenafil 20 mg plus bosentan and bosentan alone.
STARTS-1 (NCT00159913) - Sildenafil in Treatment-Naive Children, Aged 1 to 17 Years, With Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
A total of 234 patients with PAH aged 1 to 17 years were treated in a randomized, double-blind, multi-center, placebo‑controlled parallel group, dose‑ranging study. Patients (38% male and 62% female) had body weight ≥8 kg and had idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (33%), or PAH associated with congenital heart disease (systemic‑to-pulmonary shunt 37%, surgical repair 30%). In this trial, 27% of patients were <7 years old. Patients were WHO Functional Class I (32%), II (51%), III (15%), or IV (0.4%).
Patients were naïve for specific PAH therapy and the use of prostacyclin, prostacyclin analogues and endothelin receptor antagonists were not permitted in the study, and neither were arginine supplementation, nitrates, alpha-blockers and potent CYP450 3A4 inhibitors.
The primary objective of the study was to assess the effect of REVATIO on percent change from baseline in PVO 2 , normalized to body weight, from baseline to week 16 as measured by the Cardiopulmonary Exercise Test (CPET) (patients who were developmentally able to perform the test, n = 115). Secondary endpoints included hemodynamic monitoring, symptom assessment, WHO Functional Class, change in background treatment, and quality of life measurements (n = 234).
Patients were allocated to one of three sildenafil treatment groups (low, medium, or high) or placebo. Actual doses administered were dependent on body weight (see Table 5).
Placebo | Low Dose | Medium Dose | High Dose | ||||
Body Weight (kg) | N | Dose | N | Dose | N | Dose | N |
≥8 - 20 | 18 | na | 10 mg | 15 | 20 mg | 35 | |
>20 ‑ 45 | 32 | 10 mg | 31 | 20 mg | 30 | 40 mg | 31 |
>45 | 10 | 10 mg | 11 | 40 mg | 10 | 80 mg | 11 |
The proportion of patients receiving supportive medicinal products at baseline (anticoagulants, digoxin, calcium channel blockers, diuretics and/or oxygen) was similar in the combined sildenafil treatment group (48%) and the placebo treatment group (42%).
The primary endpoint was a percentage change in VO 2peak from baseline to week 16 assessed by CPET. Mean baseline peak volume of oxygen consumed (VO 2 ) values were similar across the sildenafil treatment groups (17 to 18 ml/kg/min), and slightly higher for the placebo treatment group (20 ml/kg/min). See Figure 6.
A total of 45% of patients were evaluable for CPET, which comprised those children ≥7 years old and developmentally able to perform the test. Children <7 years were evaluable only for the secondary endpoints.
Mean increases in VO 2peak percentage change from baseline at Week 16, were observed with all 3 sildenafil doses (range of 6% to 13%, Figure 6), with little change with placebo (0.5%).
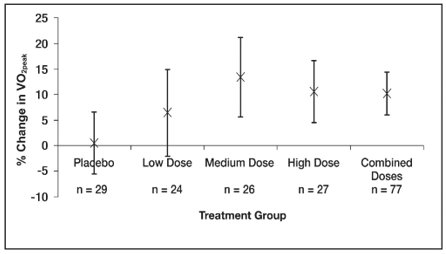
The estimated difference between the combined sildenafil doses and placebo was 8% (95% CI: -0.2 to 16). The results of the main analysis (combined dose groups versus placebo) were not statistically significant (p=0.056).
The estimated difference between the sildenafil medium dose group and placebo was 11±5% (95% CI: 2 to 21).
Impact on Hemodynamic Parameters
Dose related improvements were observed with PVRI and mPAP. Statistically significant PVRI reductions compared to placebo were seen with the sildenafil medium and high dose groups (18% [95% CI: -32% to -2%] and 27% [95% CI: -39% to -14%], respectively) but not the low dose group (2% (95% CI: -20%, 20%). The sildenafil medium and high dose groups displayed mPAP changes from baseline compared to placebo, of ‑3.5 mmHg (95% CI: ‑8.9, 1.9) and ‑7.3 mmHg (95% CI: ‑12.4, ‑2.1), respectively; while the low dose group showed little difference from placebo (difference of 1.6 mmHg [95% CI: -4.5, 7.6]). Improvements were observed with cardiac index with all three sildenafil groups over placebo, 10%, 4%, and 15% for the low, medium, and high dose groups, respectively [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2) ] .
STARTS-2 (NCT00159874) - Long-Term Survival with Oral Sildenafil Monotherapy in Treatment-Naïve Pediatric Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Of the 234 pediatric patients treated in the short-term, placebo-controlled study, 220 patients entered the long-term extension study. Patients who had been in the placebo group in the short-term study were randomly reassigned to sildenafil treatment; patients weighing ≤20 kg entered the medium or high dose groups (1:2), while patients weighing >20 kg entered the low, medium, or high dose groups (1:1:1). Of the total 229 patients who received sildenafil, there were 55, 74, and 100 patients in the low, medium, and high dose groups, respectively. Across the short-term and long-term studies, the overall duration of treatment from start of double-blind for individual patients ranged from 3 to 3,129 days. By sildenafil treatment group, median duration of sildenafil treatment was 1,696 days (excluding the 5 patients who received placebo in double-blind and were not treated in the long-term extension study).
Peak VO 2 was assessed 1 year after the start of the placebo-controlled study. Of sildenafil-treated patients developmentally able to perform the CPET 59/114 patients (52%) had not shown any deterioration in PVO 2 from start of sildenafil. Similarly, 191 of 229 patients (83%) who had received sildenafil had either maintained or improved their WHO Functional Class at 1 year assessment.
Kaplan-Meier estimates of survival at 3 years in patients >20 kg in weight at baseline were 94%, 93%, and 85% in the low, medium, and high dose groups, respectively; for patients ≤20 kg in weight at baseline, the survival estimates were 94% and 93% for patients in the medium and high dose groups, respectively [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4) and Adverse Reactions (6.1) ].
Study A1481324 (NCT02060487) - Study to Assess the Effects of REVATIO on Mortality in Adults with PAH
A study to assess the effects of multiple doses of sildenafil on mortality in adults with PAH was conducted following the observation of a higher risk of mortality in pediatric patients taking a high dose of REVATIO TID, based on body weight, compared to those taking a lower dose of REVATIO in the long-term extension of the pediatric clinical trial.
The study was a randomized, double-blind, parallel-group study in 385 adults with PAH. Patients were randomly assigned 1:1:1 to one of three treatment groups (5, 20, and 80 mg TID). Most patients were PAH treatment naïve (83%). For most patients the etiology of PAH was idiopathic (72%). The most common WHO Functional Class was Class III (58% of patients). Treatment groups were well balanced with respect to baseline demographics of strata history of PAH treatment and etiology of PAH, as well as the WHO Functional Class categories.
The primary objective of the study was to compare sildenafil 80 mg TID versus 5 mg TID for mortality, with success defined by ruling out twice the mortality at 80 mg.
The key secondary efficacy endpoint was time to first event of clinical worsening, defined as a composite endpoint of all-cause mortality, hospitalization for worsening PAH or disease progression. An additional secondary endpoint was 6MWD at Months 6 and 12.
Overall Survival
At the time of a planned interim analysis (50% deaths) it was identified that the primary efficacy objective of this protocol was met and therefore the study was stopped. Based on the primary efficacy endpoint (mortality), the non-inferiority of sildenafil 80 mg TID arm versus 5 mg TID arm was met using a 2-sided significance level of 0.003 for the interim analysis. Primary comparison of the 80 mg TID group to the 5-mg TID group yielded the HR (99.7% CI) = 0.51 (0.22, 1.21); i.e., non-inferiority was established.
| Sildenafil 5 mg N = 129 | Sildenafil 20 mg N = 128 | Sildenafil 80 mg N = 128 | |
|---|---|---|---|
Patient‑years of follow‑up | 329.8 | 340.5 | 356.7 |
Number of deaths (%) | 34 (26) | 25 (20) | 19 (15) |
On treatment deaths On treatment deaths: Any death within 7 days of last dose was regarded as “On treatment”, thus might include deaths occurred after discontinuation from study treatment (%) | 22 (17) | 13 (10) | 15 (12) |
Off treatment deaths (%) | 12 (9) | 12 (9) | 4 (3) |
Hazard ratio relative to sildenafil 5 mg | |||
Hazard ratio estimate Hazard ratio estimates from the proportional Hazards model, stratified by actual previous PAH treatment and etiology of PAH. | 0.68 | 0.51 | |
99.7% CI | 0.31, 1.49 | 0.22, 1.21 | |
Hazard ratio relative to sildenafil 20 mg | |||
Hazard ratio estimate | 0.74 | ||
99.7% CI | 0.30 1.84 |
Kaplan-Meier estimates of survival at 3 years were 66%, 79%, and 85% in the 5-, 20-, and 80-mg TID dose groups, respectively
Clinical Worsening
Sildenafil 80 mg was also superior to 5 mg for time to first event of clinical worsening with HR (99.7% CI) = 0.44 (0.22, 0.89).
| Sildenafil 5 mg N = 129 | Sildenafil 20 mg N = 128 | Sildenafil 80 mg N = 128 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Note: Sildenafil 5 mg is not an approved dosage. Abbreviations: 6MWD = 6‑minute walk distance; CI = confidence interval; PAH = pulmonary arterial hypertension. | |||
Patient‑years of follow‑up | 249.6 | 276.4 | 306.5 |
Number of patients with clinical worsening | 52 | 36 | 28 |
First Event of clinical worsening Clinical worsening events were defined as reduction from baseline in the 6MWD test by at least 15% and worsening functional class from baseline, both confirmed by a second test/evaluation within 2 weeks. n (%) | |||
Disease progression Count of cases of disease progression as the first event of clinical worsening. | 8 (6) | 2 (2) | 6 (5) |
Hospitalization for PAH Count of non-elective hospital stays for worsening PAH as the first event of clinical worsening. | 28 (22) | 23 (18) | 11 (9) |
Death Count of deaths as the first event of clinical worsening. | 16 (12) | 11 (9) | 11 (9) |
Hazard ratio relative to sildenafil 5 mg | |||
Hazard ratio estimate | 0.63 | 0.44 | |
99.7% CI | 0.33, 1.21 | 0.22, 0.89 | |
p-value | 0.035 | <0.001 | |
Hazard ratio relative to sildenafil 20 mg | |||
Hazard ratio estimate Hazard ratio estimates from the proportional Hazards model, stratified by actual previous PAH treatment and etiology of PAH. P-value from the Wald test. | 0.72 | ||
99.7% CI | 0.34, 1.52 | ||
p‑value | 0.195 | ||
6MWD at Months 6 and 12
At baseline, the median of 6MWD for the intent‑to‑treat (ITT) population was 332 to 352 m. At Month 6, the median change from baseline was highest for sildenafil 80 mg TID with 28 m compared to 18 m and 19 m for sildenafil 5 mg TID and sildenafil 20 mg TID groups, respectively. The same was seen at Month 12, the median change from baseline for sildenafil 80 mg TID group was 33 m compared to 17 m for sildenafil 5 mg TID and 31 m in sildenafil 20 mg TID groups.
Overall, the safety data for sildenafil 20 mg TID and for the higher sildenafil 80 mg TID dose were consistent with the established safety profile of sildenafil in previous adult PAH studies [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
REVATIO tablets are supplied as white, film-coated, round tablets containing sildenafil citrate equivalent to the nominally indicated amount of sildenafil as follows:
REVATIO Tablets | |||
Package Configuration | Strength | NDC | Engraving on Tablet |
Bottle of 90 Tablets | 20 mg | 0069-4190-68 | RVT20 |
Recommended Storage for REVATIO Tablets: Store at controlled room temperature 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature] .
REVATIO injection is supplied as a clear, colorless, sterile, ready to use solution containing 10 mg sildenafil/12.5 mL presented in a single-use glass vial.
REVATIO Injection | ||
Package Configuration | Strength | NDC |
Vial individually packaged in a carton | 10 mg /12.5 mL | 0069-0338-01 |
Recommended Storage for REVATIO Injection: Store at controlled room temperature 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature] .
REVATIO powder for oral suspension is supplied in amber glass bottles. Each bottle contains white to off-white powders containing 1.57 g of sildenafil citrate (equivalent to 1.12 g sildenafil). Following reconstitution, the total volume of the oral suspension is 112 mL (10 mg sildenafil/mL). A 2 mL oral dosing syringe (with 0.5 mL and 2 mL dose markings) and a press‑in bottle adaptor are also provided.
REVATIO Powder for Oral Suspension | ||
Package Configuration | Strength | NDC |
Powder for oral suspension - bottle | 10 mg/mL (when reconstituted) | 0069-0336-21 |
Recommended storage for REVATIO for oral suspension: Store below 30°C (86°F) in the original package in order to protect from moisture.
Recommended storage for reconstituted oral suspension: Store below 30°C (86°F) or in refrigerator at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Do not freeze. The shelf-life of the reconstituted oral suspension is 60 days. Any remaining oral suspension should be discarded 60 days after reconstitution.
Instructions for Use
REVATIO ® (re-VAH-tee-oh) (sildenafil) oral suspension
Read this Instructions for Use before you start taking REVATIO oral suspension or giving REVATIO oral suspension to your child and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your or your child’s medical condition or treatment.
Important information:
- Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist to show you how to measure and take or give your child’s prescribed dose of REVATIO oral suspension.
- Your pharmacist will mix (reconstitute) REVATIO oral suspension before it is given to you. Do not take or give REVATIO oral suspension and contact your pharmacist if the medicine in the bottle is still a powder.
- Always use the oral dosing syringe that comes with REVATIO oral suspension. If your carton does not come with an oral dosing syringe, contact your pharmacist.
- Do not take or give REVATIO oral suspension if the bottle adaptor is not in the bottle. If the bottle adaptor is not in the bottle, contact your pharmacist.
- REVATIO oral suspension should not be mixed with any other medicine or flavoring.
Supplies you will need to take or give a dose of REVATIO oral suspension (See Figure A):
- 1 bottle of REVATIO oral suspension with pre-inserted bottle adaptor
- 1 oral dosing syringe (provided in the carton)
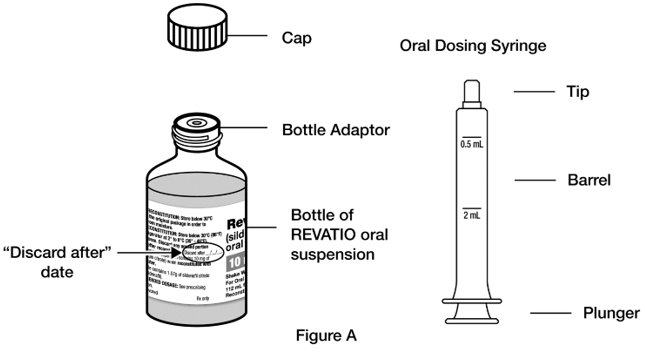
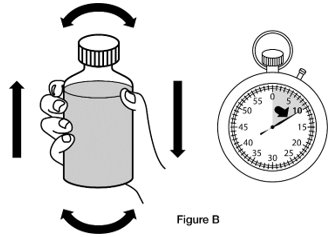
- Step 1. Shake the bottle of REVATIO oral suspension for 10 seconds before each use. (See Figure B)
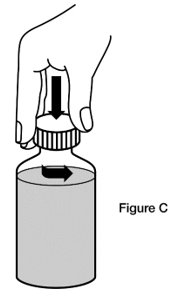
- Step 2. Remove the cap. Open the bottle by pushing down on the cap and twisting it in the direction of the arrow (counter-clockwise). (See Figure C)
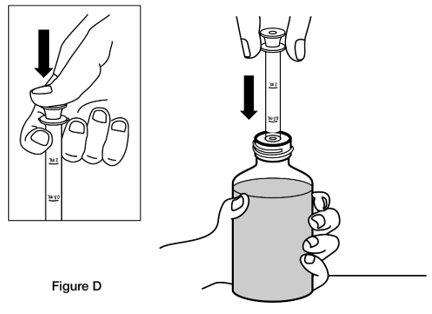
- Step 3. Fully push down (depress) the plunger of the oral dosing syringe. Then insert the tip of the oral dosing syringe into the bottle adaptor while holding the bottle upright, on a flat surface. (See Figure D)
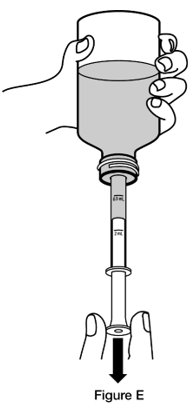
- Step 4. Turn the bottle upside down while holding the oral dosing syringe in place. Slowly pull back the plunger of the oral dosing syringe until the bottom of the plunger is even with the mL marking on the syringe for your or your child’s prescribed dose. (See Figure E)
If your child’s dose of REVATIO oral suspension is 1 mL (10 mg), measure 0.5 mL two times for a total of 1 mL of REVATIO oral suspension.
If your or your child’s dose of REVATIO oral suspension is more than 2 mL (20 mg), you will need to divide the dose. Follow the instructions given to you by your healthcare provider or pharmacist about how to prepare the divided dose.
If you see air bubbles in the oral dosing syringe, slowly push the plunger all the way up so that REVATIO oral suspension flows back into the bottle and repeat Step 4.
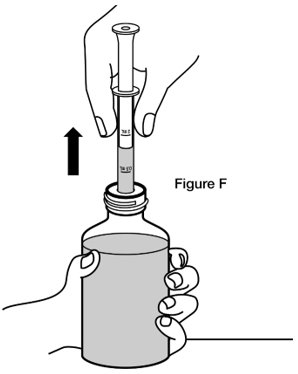
- Step 5. Turn the bottle back upright with the oral dosing syringe still in place. Place the bottle on a flat surface. Remove the oral dosing syringe from the bottle adaptor by pulling straight up on the barrel of the oral dosing syringe. (See Figure F) Do not press on the plunger of the oral dosing syringe at this time.
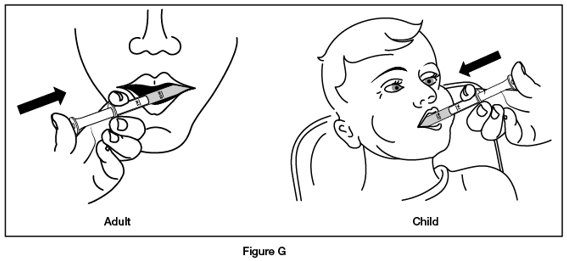
- Step 6. Put the tip of the oral dosing syringe into your or your child’s mouth and point it towards the inside of the cheek. Slowly push the plunger of the oral dosing syringe all the way down to give the entire dose. Do not squirt the medicine out quickly. (See Figure G)
If you are giving REVATIO oral suspension to a child, make sure they are in an upright position before giving the medicine.
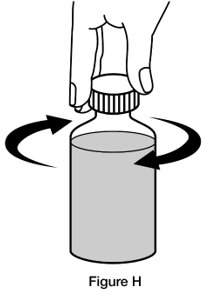
- Step 7. Replace the cap on the bottle, leaving the bottle adaptor in place. Turn the cap in the direction of the arrow (clockwise) to close the bottle. (See Figure H)
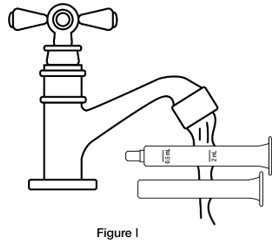
- Step 8. Wash the oral dosing syringe after each use. Pull the plunger out of the barrel and rinse both parts with water. (See Figure I)
- Step 9. Dry all parts with a clean paper towel. Push the plunger back into the barrel. Store the oral dosing syringe with the REVATIO oral suspension bottle.
How should I store REVATIO?
- Store mixed (reconstituted) REVATIO oral suspension below 86°F (30°C) or in a refrigerator between 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C).
- Do not freeze mixed REVATIO oral suspension.
- Throw away (discard) any remaining REVATIO oral suspension 60 days after mixed by the pharmacist. See the “Discard after” date written on the bottle label.
Keep REVATIO and all medicines out of the reach of children.
Distributed by: Viatris Specialty LLC, Morgantown, WV 26505 U.S.A.
UPJ:IFU:RVTTOSI:RX2 Revised: January 2023
This Instruction for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Mechanism of Action
Sildenafil is an inhibitor of cGMP specific PDE-5 in the smooth muscle of the pulmonary vasculature, where PDE-5 is responsible for degradation of cGMP. Sildenafil, therefore, increases cGMP within pulmonary vascular smooth muscle cells resulting in relaxation. In patients with PAH, this can lead to vasodilation of the pulmonary vascular bed and, to a lesser degree, vasodilatation in the systemic circulation.
Studies in vitro have shown that sildenafil is selective for PDE5. Its effect is more potent on PDE5 than on other known phosphodiesterases (10-fold for PDE6, greater than 80-fold for PDE1, greater than 700-fold for PDE2, PDE3, PDE4, PDE7, PDE8, PDE9, PDE10, and PDE11). The approximately 4,000-fold selectivity for PDE-5 versus PDE3 is important because PDE3 is involved in control of cardiac contractility. Sildenafil is only about 10 times as potent for PDE5 compared to PDE6, an enzyme found in the retina and involved in the phototransduction pathway of the retina. This lower selectivity is thought to be the basis for abnormalities related to color vision observed with higher doses or plasma levels [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2) ] .
In addition to pulmonary vascular smooth muscle and the corpus cavernosum, PDE5 is also found in other tissues including vascular and visceral smooth muscle and in platelets. The inhibition of PDE5 in these tissues by sildenafil may be the basis for the enhanced platelet anti-aggregatory activity of nitric oxide observed in vitro , and the mild peripheral arterial-venous dilatation in vivo .