Revlimid prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Revlimid patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- MM combination therapy: 25 mg once daily orally on Days 1-21 of repeated 28-day cycles. (2.1 ).
- MM maintenance therapy following auto-HSCT: 10 mg once daily continuously on Days 1-28 of repeated 28-day cycles (2.1 ).
- MDS: 10 mg once daily (2.2 ).
- MCL: 25 mg once daily orally on Days 1-21 of repeated 28-day cycles (2.3 ).
- FL or MZL: 20 mg once daily orally on Days 1-21 of repeated 28-day cycles for up to 12 cycles (2.4 ).
- Renal impairment: Adjust starting dose based on the creatinine clearance value (2.6 ).
- For concomitant therapy doses, see Full Prescribing Information (2.1 , 2.4 , 14.1 , 14.4 ).
Recommended Dosage for Multiple Myeloma
REVLIMID Combination Therapy
The recommended starting dose of REVLIMID is 25 mg orally once daily on Days 1-21 of repeated 28-day cycles in combination with dexamethasone. Refer to Section 14.1 for specific dexamethasone dosing. For patients greater than 75 years old, the starting dose of dexamethasone may be reduced [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ] . Treatment should be continued until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
In patients who are not eligible for auto-HSCT, treatment should continue until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. For patients who are auto-HSCT-eligible, hematopoietic stem cell mobilization should occur within 4 cycles of a REVLIMID-containing therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12) ].
Dose Adjustments for Hematologic Toxicities During MM Treatment
Dose modification guidelines, as summarized in Table 1 below, are recommended to manage Grade 3 or 4 neutropenia or thrombocytopenia or other Grade 3 or 4 toxicity judged to be related to REVLIMID.
Platelet counts | ||
Thrombocytopenia in MM | ||
When Platelets | Recommended Course | |
Fall below 30,000/mcL | Interrupt REVLIMID treatment, follow CBC weekly | |
Return to at least 30,000/mcL | Resume REVLIMID at next lower dose. Do not dose below 2.5 mg daily | |
For each subsequent drop below 30,000/mcL | Interrupt REVLIMID treatment | |
Return to at least 30,000/mcL | Resume REVLIMID at next lower dose. Do not dose below 2.5 mg daily | |
Absolute Neutrophil counts (ANC) | ||
Neutropenia in MM | ||
When Neutrophils | Recommended Course | |
Fall below 1,000/mcL | Interrupt REVLIMID treatment, follow CBC weekly | |
Return to at least 1,000/mcL and neutropenia is the only toxicity | Resume REVLIMID at 25 mg daily or initial starting dose | |
Return to at least 1,000/mcL and if other toxicity | Resume REVLIMID at next lower dose. Do not dose below 2.5 mg daily | |
For each subsequent drop below 1,000/mcL | Interrupt REVLIMID treatment | |
Return to at least 1,000/mcL | Resume REVLIMID at next lower dose. Do not dose below 2.5 mg daily | |
REVLIMID Maintenance Therapy Following Auto-HSCT
Following auto-HSCT, initiate REVLIMID maintenance therapy after adequate hematologic recovery (ANC at least 1,000/mcL and/or platelet counts at least 75,000/mcL). The recommended starting dose of REVLIMID is 10 mg once daily continuously (Days 1-28 of repeated 28-day cycles) until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. After 3 cycles of maintenance therapy, the dose can be increased to 15 mg once daily if tolerated.
Dose Adjustments for Hematologic Toxicities During MM Treatment
Dose modification guidelines, as summarized in Table 2 below, are recommended to manage Grade 3 or 4 neutropenia or thrombocytopenia or other Grade 3 or 4 toxicity judged to be related to REVLIMID.
Platelet counts | ||
Thrombocytopenia in MM | ||
When Platelets | Recommended Course | |
Fall below 30,000/mcL | Interrupt REVLIMID treatment, follow CBC weekly | |
Return to at least 30,000/mcL | Resume REVLIMID at next lower dose, continuously for Days 1-28 of repeated 28-day cycle | |
If at the 5 mg daily dose, | Interrupt REVLIMID treatment. Do not dose below 5 mg daily for Day 1 to 21 of 28 day cycle | |
Return to at least 30,000/mcL | Resume REVLIMID at 5 mg daily for Days 1 to 21 of 28-day cycle. Do not dose below 5 mg daily for Day 1 to 21 of 28 day cycle | |
Absolute Neutrophil counts (ANC) | ||
Neutropenia in MM | ||
When Neutrophils | Recommended Course | |
Fall below 500/mcL | Interrupt REVLIMID treatment, follow CBC weekly | |
Return to at least 500/mcL | Resume REVLIMID at next lower dose, continuously for Days 1-28 of repeated 28-day cycle | |
If at 5 mg daily dose, | Interrupt REVLIMID treatment. Do not dose below 5 mg daily for Days 1 to 21 of 28-day cycle | |
Return to at least 500/mcL | Resume REVLIMID at 5 mg daily for Days 1 to 21 of 28-day cycle. Do not dose below 5 mg daily for Days 1 to 21 of 28-day cycle | |
Recommended Dosage for Myelodysplastic Syndromes
The recommended starting dose of REVLIMID is 10 mg daily. Treatment is continued or modified based upon clinical and laboratory findings. Continue treatment until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Dose Adjustments for Hematologic Toxicities During MDS Treatment
Patients who are dosed initially at 10 mg and who experience thrombocytopenia should have their dosage adjusted as follows:
Platelet counts
If thrombocytopenia develops WITHIN 4 weeks of starting treatment at 10 mg daily in MDS
If baseline is at least 100,000/mcL | |
When Platelets | Recommended Course |
Fall below 50,000/mcL | Interrupt REVLIMID treatment |
Return to at least 50,000/mcL | Resume REVLIMID at 5 mg daily |
If baseline is below 100,000/mcL | |
When Platelets | Recommended Course |
Fall to 50% of the baseline value | Interrupt REVLIMID treatment |
If baseline is at least 60,000/mcL and returns to at least 50,000/mcL | Resume REVLIMID at 5 mg daily |
If baseline is below 60,000/mcL and returns to at least 30,000/mcL | Resume REVLIMID at 5 mg daily |
If thrombocytopenia develops AFTER 4 weeks of starting treatment at 10 mg daily in MDS
| When Platelets | Recommended Course |
|---|---|
Fall below 30,000/mcL or below 50,000/mcL with platelet transfusions | Interrupt REVLIMID treatment |
Return to at least 30,000/mcL (without hemostatic failure) | Resume REVLIMID at 5 mg daily |
Patients who experience thrombocytopenia at 5 mg daily should have their dosage adjusted as follows:
If thrombocytopenia develops during treatment at 5 mg daily in MDS
| When Platelets | Recommended Course |
|---|---|
Fall below 30,000/mcL or below 50,000/mcL with platelet transfusions | Interrupt REVLIMID treatment |
Return to at least 30,000/mcL (without hemostatic failure) | Resume REVLIMID at 2.5 mg daily |
Patients who are dosed initially at 10 mg and experience neutropenia should have their dosage adjusted as follows:
Absolute Neutrophil counts (ANC)
If neutropenia develops WITHIN 4 weeks of starting treatment at 10 mg daily in MDS
If baseline ANC is at least 1,000/mcL | |
When Neutrophils | Recommended Course |
Fall below 750/mcL | Interrupt REVLIMID treatment |
Return to at least 1,000/mcL | Resume REVLIMID at 5 mg daily |
If baseline ANC is below 1,000/mcL | |
When Neutrophils | Recommended Course |
Fall below 500/mcL | Interrupt REVLIMID treatment |
Return to at least 500/mcL | Resume REVLIMID at 5 mg daily |
If neutropenia develops AFTER 4 weeks of starting treatment at 10 mg daily in MDS
| When Neutrophils | Recommended Course |
|---|---|
Fall below 500/mcL for at least 7 days or below 500/mcL associated with fever (at least 38.5°C) | Interrupt REVLIMID treatment |
Return to at least 500/mcL | Resume REVLIMID at 5 mg daily |
Patients who experience neutropenia at 5 mg daily should have their dosage adjusted as follows:
If neutropenia develops during treatment at 5 mg daily in MDS
| When Neutrophils | Recommended Course |
|---|---|
Fall below 500/mcL for at least 7 days or below 500/mcL associated with fever (at least 38.5°C) | Interrupt REVLIMID treatment |
Return to at least 500/mcL | Resume REVLIMID at 2.5 mg daily |
Recommended Dosage for Mantle Cell Lymphoma
The recommended starting dose of REVLIMID is 25 mg/day orally on Days 1-21 of repeated 28-day cycles for relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma. Treatment should be continued until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Treatment is continued, modified or discontinued based upon clinical and laboratory findings.
Dose Adjustments for Hematologic Toxicities During MCL Treatment
Dose modification guidelines as summarized below are recommended to manage Grade 3 or 4 neutropenia or thrombocytopenia or other Grade 3 or 4 toxicities considered to be related to REVLIMID.
Platelet counts
Thrombocytopenia during treatment in MCL
| When Platelets | Recommended Course |
|---|---|
Fall below 50,000/mcL | Interrupt REVLIMID treatment and follow CBC weekly |
Return to at least 50,000/mcL | Resume REVLIMID at 5 mg less than the previous dose. Do not dose below 5 mg daily |
Absolute Neutrophil counts (ANC)
Neutropenia during treatment in MCL
| When Neutrophils | Recommended Course |
|---|---|
Fall below 1,000/mcL for at least 7 days | Interrupt REVLIMID treatment and follow CBC weekly |
Return to at least 1,000/mcL | Resume REVLIMID at 5 mg less than the previous dose. Do not dose below 5 mg daily |
Recommended Dosage for Follicular Lymphoma or Marginal Zone Lymphoma
The recommended starting dose of REVLIMID is 20 mg orally once daily on Days 1-21 of repeated 28-day cycles for up to 12 cycles of treatment in combination with a rituximab-product. Refer to Section 14.4 for specific rituximab dosing from the AUGMENT trial. For dose adjustments due to toxicity with rituximab, refer to the product prescribing information.
Dose Adjustments for Hematologic Toxicities during FL or MZL Treatment
Dose modification guidelines, as summarized below, are recommended to manage Grade 3 or 4 neutropenia or thrombocytopenia or other Grade 3 or 4 toxicity judged to be related to REVLIMID.
Platelet counts
Thrombocytopenia during treatment in FL or MZL
| When Platelets | Recommended Course |
|---|---|
Fall below 50,000/mcL | Interrupt REVLIMID treatment and follow CBC weekly. |
Return to at least 50,000/mcL | If patient starting dose was 20 mg daily, resume REVLIMID at 5 mg less than the previous dose. Do not dose below 5 mg daily. |
Absolute Neutrophil counts (ANC)
Neutropenia during treatment in FL or MZL
| When Neutrophils | Recommended Course |
|---|---|
Fall below 1,000/mcL for at least 7 days | Interrupt REVLIMID treatment and follow CBC weekly. |
Return to at least 1,000/mcL | If patient starting dose was 20 mg daily, resume REVLIMID at 5 mg less than the previous dose. Do not dose below 5 mg daily. |
Dosage Modifications for Non-Hematologic Adverse Reactions
For non-hematologic Grade 3/4 toxicities judged to be related to REVLIMID, hold treatment and restart at the physician's discretion at next lower dose level when toxicity has resolved to Grade 2 or below.
Permanently discontinue REVLIMID for angioedema, anaphylaxis, Grade 4 rash, skin exfoliation, bullae, or any other severe dermatologic reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9 , 5.15) ] .
Recommended Dosage for Patients with Renal Impairment
The recommendations for dosing patients with renal impairment are shown in the following table [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Renal Function | Dose in REVLIMID Combination Therapy for MM and MCL | Dose in REVLIMID Combination Therapy for FL and MZL | Dose in REVLIMID Maintenance Therapy Following Auto-HSCT for MM and for MDS |
CLcr 30 to 60 mL/min | 10 mg once daily | 10 mg once daily | 5 mg once daily |
CLcr below 30 mL/min (not requiring dialysis) | 15 mg every other day | 5 mg once daily | 2.5 mg once daily |
CLcr below 30 mL/min (requiring dialysis) | 5 mg once daily. On dialysis days, administer the dose following dialysis. | 5 mg once daily. On dialysis days, administer the dose following dialysis. | 2.5 mg once daily. On dialysis days, administer the dose following dialysis. |
REVLIMID Combination Therapy for MM: For CLcr of 30 to 60 mL/min, consider escalating the dose to 15 mg after 2 cycles if the patient tolerates the 10 mg dose of lenalidomide without dose-limiting toxicity.
REVLIMID Maintenance Therapy Following Auto-HSCT for MM and for MCL and MDS: Base subsequent REVLIMID dose increase or decrease on individual patient treatment tolerance [see Dosage and Administration (2.1 - 2.3) ] .
REVLIMID Combination Therapy for FL or for MZL: For patients with CLcr of 30 to 60 mL/min, after 2 cycles, the REVLIMID dose may be increased to 15 mg orally if the patient has tolerated therapy.
Administration
Advise patients to take REVLIMID orally at about the same time each day, either with or without food. Advise patients to swallow REVLIMID capsules whole with water and not to open, break, or chew them.

Revlimid prescribing information
WARNING: EMBRYO-FETAL TOXICITY, HEMATOLOGIC TOXICITY, and VENOUS and ARTERIAL THROMBOEMBOLISM
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Do not use REVLIMID during pregnancy. Lenalidomide, a thalidomide analogue, caused limb abnormalities in a developmental monkey study. Thalidomide is a known human teratogen that causes severe life-threatening human birth defects. If lenalidomide is used during pregnancy, it may cause birth defects or embryo-fetal death. In females of reproductive potential, obtain 2 negative pregnancy tests before starting REVLIMID ® treatment. Females of reproductive potential must use 2 forms of contraception or continuously abstain from heterosexual sex during and for 4 weeks after REVLIMID treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 ), and Medication Guide (17 )]. To avoid embryo-fetal exposure to lenalidomide, REVLIMID is only available through a restricted distribution program, the Lenalidomide REMS program (5.2 ).
Information about the Lenalidomide REMS program is available at www.lenalidomiderems.com or by calling the REMS Call Center at 1-888-423-5436.
Hematologic Toxicity (Neutropenia and Thrombocytopenia)
REVLIMID can cause significant neutropenia and thrombocytopenia. Eighty percent of patients with del 5q myelodysplastic syndromes had to have a dose delay/reduction during the major study. Thirty-four percent of patients had to have a second dose delay/reduction. Grade 3 or 4 hematologic toxicity was seen in 80% of patients enrolled in the study. Patients on therapy for del 5q myelodysplastic syndromes should have their complete blood counts monitored weekly for the first 8 weeks of therapy and at least monthly thereafter. Patients may require dose interruption and/or reduction. Patients may require use of blood product support and/or growth factors [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 )] .
Venous and Arterial Thromboembolism
REVLIMID has demonstrated a significantly increased risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE), as well as risk of myocardial infarction and stroke in patients with multiple myeloma who were treated with REVLIMID and dexamethasone therapy. Monitor for and advise patients about signs and symptoms of thromboembolism. Advise patients to seek immediate medical care if they develop symptoms such as shortness of breath, chest pain, or arm or leg swelling. Thromboprophylaxis is recommended and the choice of regimen should be based on an assessment of the patient’s underlying risks [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4 )].
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
REVLIMID is a thalidomide analogue indicated for the treatment of adult patients with:
- Multiple myeloma (MM), in combination with dexamethasone (1.1 ).
- MM, as maintenance following autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (auto-HSCT) (1.1 ).
- Transfusion-dependent anemia due to low- or intermediate-1-risk myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) associated with a deletion 5q abnormality with or without additional cytogenetic abnormalities (1.2 ).
- Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) whose disease has relapsed or progressed after two prior therapies, one of which included bortezomib (1.3 ).
- Previously treated follicular lymphoma (FL), in combination with a rituximab product (1.4 ).
- Previously treated marginal zone lymphoma (MZL), in combination with a rituximab product (1.5 ).
Limitations of Use:
- REVLIMID is not indicated and is not recommended for the treatment of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) outside of controlled clinical trials (1.4 ).
Multiple Myeloma
REVLIMID in combination with dexamethasone is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with multiple myeloma (MM).
REVLIMID is indicated as maintenance therapy in adult patients with MM following autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (auto-HSCT).
Myelodysplastic Syndromes
REVLIMID is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with transfusion-dependent anemia due to low- or intermediate-1-risk myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) associated with a deletion 5q cytogenetic abnormality with or without additional cytogenetic abnormalities.
Mantle Cell Lymphoma
REVLIMID is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) whose disease has relapsed or progressed after two prior therapies, one of which included bortezomib.
Follicular Lymphoma
REVLIMID in combination with a rituximab product, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with previously treated follicular lymphoma (FL).
Marginal Zone Lymphoma
REVLIMID in combination with a rituximab product, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with previously treated marginal zone lymphoma (MZL).
Limitations of Use
REVLIMID is not indicated and is not recommended for the treatment of patients with CLL outside of controlled clinical trials [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ] .
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- MM combination therapy: 25 mg once daily orally on Days 1-21 of repeated 28-day cycles. (2.1 ).
- MM maintenance therapy following auto-HSCT: 10 mg once daily continuously on Days 1-28 of repeated 28-day cycles (2.1 ).
- MDS: 10 mg once daily (2.2 ).
- MCL: 25 mg once daily orally on Days 1-21 of repeated 28-day cycles (2.3 ).
- FL or MZL: 20 mg once daily orally on Days 1-21 of repeated 28-day cycles for up to 12 cycles (2.4 ).
- Renal impairment: Adjust starting dose based on the creatinine clearance value (2.6 ).
- For concomitant therapy doses, see Full Prescribing Information (2.1 , 2.4 , 14.1 , 14.4 ).
Recommended Dosage for Multiple Myeloma
REVLIMID Combination Therapy
The recommended starting dose of REVLIMID is 25 mg orally once daily on Days 1-21 of repeated 28-day cycles in combination with dexamethasone. Refer to Section 14.1 for specific dexamethasone dosing. For patients greater than 75 years old, the starting dose of dexamethasone may be reduced [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ] . Treatment should be continued until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
In patients who are not eligible for auto-HSCT, treatment should continue until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. For patients who are auto-HSCT-eligible, hematopoietic stem cell mobilization should occur within 4 cycles of a REVLIMID-containing therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12) ].
Dose Adjustments for Hematologic Toxicities During MM Treatment
Dose modification guidelines, as summarized in Table 1 below, are recommended to manage Grade 3 or 4 neutropenia or thrombocytopenia or other Grade 3 or 4 toxicity judged to be related to REVLIMID.
Platelet counts | ||
Thrombocytopenia in MM | ||
When Platelets | Recommended Course Days 1-21 of repeated 28-day cycle | |
Fall below 30,000/mcL | Interrupt REVLIMID treatment, follow CBC weekly | |
Return to at least 30,000/mcL | Resume REVLIMID at next lower dose. Do not dose below 2.5 mg daily | |
For each subsequent drop below 30,000/mcL | Interrupt REVLIMID treatment | |
Return to at least 30,000/mcL | Resume REVLIMID at next lower dose. Do not dose below 2.5 mg daily | |
Absolute Neutrophil counts (ANC) | ||
Neutropenia in MM | ||
When Neutrophils | Recommended Course Days 1-21 of repeated 28-day cycle | |
Fall below 1,000/mcL | Interrupt REVLIMID treatment, follow CBC weekly | |
Return to at least 1,000/mcL and neutropenia is the only toxicity | Resume REVLIMID at 25 mg daily or initial starting dose | |
Return to at least 1,000/mcL and if other toxicity | Resume REVLIMID at next lower dose. Do not dose below 2.5 mg daily | |
For each subsequent drop below 1,000/mcL | Interrupt REVLIMID treatment | |
Return to at least 1,000/mcL | Resume REVLIMID at next lower dose. Do not dose below 2.5 mg daily | |
REVLIMID Maintenance Therapy Following Auto-HSCT
Following auto-HSCT, initiate REVLIMID maintenance therapy after adequate hematologic recovery (ANC at least 1,000/mcL and/or platelet counts at least 75,000/mcL). The recommended starting dose of REVLIMID is 10 mg once daily continuously (Days 1-28 of repeated 28-day cycles) until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. After 3 cycles of maintenance therapy, the dose can be increased to 15 mg once daily if tolerated.
Dose Adjustments for Hematologic Toxicities During MM Treatment
Dose modification guidelines, as summarized in Table 2 below, are recommended to manage Grade 3 or 4 neutropenia or thrombocytopenia or other Grade 3 or 4 toxicity judged to be related to REVLIMID.
Platelet counts | ||
Thrombocytopenia in MM | ||
When Platelets | Recommended Course | |
Fall below 30,000/mcL | Interrupt REVLIMID treatment, follow CBC weekly | |
Return to at least 30,000/mcL | Resume REVLIMID at next lower dose, continuously for Days 1-28 of repeated 28-day cycle | |
If at the 5 mg daily dose, For a subsequent drop below 30,000/mcL | Interrupt REVLIMID treatment. Do not dose below 5 mg daily for Day 1 to 21 of 28 day cycle | |
Return to at least 30,000/mcL | Resume REVLIMID at 5 mg daily for Days 1 to 21 of 28-day cycle. Do not dose below 5 mg daily for Day 1 to 21 of 28 day cycle | |
Absolute Neutrophil counts (ANC) | ||
Neutropenia in MM | ||
When Neutrophils | Recommended Course | |
Fall below 500/mcL | Interrupt REVLIMID treatment, follow CBC weekly | |
Return to at least 500/mcL | Resume REVLIMID at next lower dose, continuously for Days 1-28 of repeated 28-day cycle | |
If at 5 mg daily dose, For a subsequent drop below 500/mcL | Interrupt REVLIMID treatment. Do not dose below 5 mg daily for Days 1 to 21 of 28-day cycle | |
Return to at least 500/mcL | Resume REVLIMID at 5 mg daily for Days 1 to 21 of 28-day cycle. Do not dose below 5 mg daily for Days 1 to 21 of 28-day cycle | |
Recommended Dosage for Myelodysplastic Syndromes
The recommended starting dose of REVLIMID is 10 mg daily. Treatment is continued or modified based upon clinical and laboratory findings. Continue treatment until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Dose Adjustments for Hematologic Toxicities During MDS Treatment
Patients who are dosed initially at 10 mg and who experience thrombocytopenia should have their dosage adjusted as follows:
Platelet counts
If thrombocytopenia develops WITHIN 4 weeks of starting treatment at 10 mg daily in MDS
If baseline is at least 100,000/mcL | |
When Platelets | Recommended Course |
Fall below 50,000/mcL | Interrupt REVLIMID treatment |
Return to at least 50,000/mcL | Resume REVLIMID at 5 mg daily |
If baseline is below 100,000/mcL | |
When Platelets | Recommended Course |
Fall to 50% of the baseline value | Interrupt REVLIMID treatment |
If baseline is at least 60,000/mcL and returns to at least 50,000/mcL | Resume REVLIMID at 5 mg daily |
If baseline is below 60,000/mcL and returns to at least 30,000/mcL | Resume REVLIMID at 5 mg daily |
If thrombocytopenia develops AFTER 4 weeks of starting treatment at 10 mg daily in MDS
| When Platelets | Recommended Course |
|---|---|
Fall below 30,000/mcL or below 50,000/mcL with platelet transfusions | Interrupt REVLIMID treatment |
Return to at least 30,000/mcL (without hemostatic failure) | Resume REVLIMID at 5 mg daily |
Patients who experience thrombocytopenia at 5 mg daily should have their dosage adjusted as follows:
If thrombocytopenia develops during treatment at 5 mg daily in MDS
| When Platelets | Recommended Course |
|---|---|
Fall below 30,000/mcL or below 50,000/mcL with platelet transfusions | Interrupt REVLIMID treatment |
Return to at least 30,000/mcL (without hemostatic failure) | Resume REVLIMID at 2.5 mg daily |
Patients who are dosed initially at 10 mg and experience neutropenia should have their dosage adjusted as follows:
Absolute Neutrophil counts (ANC)
If neutropenia develops WITHIN 4 weeks of starting treatment at 10 mg daily in MDS
If baseline ANC is at least 1,000/mcL | |
When Neutrophils | Recommended Course |
Fall below 750/mcL | Interrupt REVLIMID treatment |
Return to at least 1,000/mcL | Resume REVLIMID at 5 mg daily |
If baseline ANC is below 1,000/mcL | |
When Neutrophils | Recommended Course |
Fall below 500/mcL | Interrupt REVLIMID treatment |
Return to at least 500/mcL | Resume REVLIMID at 5 mg daily |
If neutropenia develops AFTER 4 weeks of starting treatment at 10 mg daily in MDS
| When Neutrophils | Recommended Course |
|---|---|
Fall below 500/mcL for at least 7 days or below 500/mcL associated with fever (at least 38.5°C) | Interrupt REVLIMID treatment |
Return to at least 500/mcL | Resume REVLIMID at 5 mg daily |
Patients who experience neutropenia at 5 mg daily should have their dosage adjusted as follows:
If neutropenia develops during treatment at 5 mg daily in MDS
| When Neutrophils | Recommended Course |
|---|---|
Fall below 500/mcL for at least 7 days or below 500/mcL associated with fever (at least 38.5°C) | Interrupt REVLIMID treatment |
Return to at least 500/mcL | Resume REVLIMID at 2.5 mg daily |
Recommended Dosage for Mantle Cell Lymphoma
The recommended starting dose of REVLIMID is 25 mg/day orally on Days 1-21 of repeated 28-day cycles for relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma. Treatment should be continued until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Treatment is continued, modified or discontinued based upon clinical and laboratory findings.
Dose Adjustments for Hematologic Toxicities During MCL Treatment
Dose modification guidelines as summarized below are recommended to manage Grade 3 or 4 neutropenia or thrombocytopenia or other Grade 3 or 4 toxicities considered to be related to REVLIMID.
Platelet counts
Thrombocytopenia during treatment in MCL
| When Platelets | Recommended Course |
|---|---|
Fall below 50,000/mcL | Interrupt REVLIMID treatment and follow CBC weekly |
Return to at least 50,000/mcL | Resume REVLIMID at 5 mg less than the previous dose. Do not dose below 5 mg daily |
Absolute Neutrophil counts (ANC)
Neutropenia during treatment in MCL
| When Neutrophils | Recommended Course |
|---|---|
Fall below 1,000/mcL for at least 7 days OR Falls below 1,000/mcL with an associated temperature at least 38.5°C OR Falls below 500/mcL | Interrupt REVLIMID treatment and follow CBC weekly |
Return to at least 1,000/mcL | Resume REVLIMID at 5 mg less than the previous dose. Do not dose below 5 mg daily |
Recommended Dosage for Follicular Lymphoma or Marginal Zone Lymphoma
The recommended starting dose of REVLIMID is 20 mg orally once daily on Days 1-21 of repeated 28-day cycles for up to 12 cycles of treatment in combination with a rituximab-product. Refer to Section 14.4 for specific rituximab dosing from the AUGMENT trial. For dose adjustments due to toxicity with rituximab, refer to the product prescribing information.
Dose Adjustments for Hematologic Toxicities during FL or MZL Treatment
Dose modification guidelines, as summarized below, are recommended to manage Grade 3 or 4 neutropenia or thrombocytopenia or other Grade 3 or 4 toxicity judged to be related to REVLIMID.
Platelet counts
Thrombocytopenia during treatment in FL or MZL
| When Platelets | Recommended Course |
|---|---|
Fall below 50,000/mcL | Interrupt REVLIMID treatment and follow CBC weekly. |
Return to at least 50,000/mcL | If patient starting dose was 20 mg daily, resume REVLIMID at 5 mg less than the previous dose. Do not dose below 5 mg daily. If patient starting dose was 10 mg daily, resume at 5 mg less than previous dose. Do not dose below 2.5 mg daily. |
Absolute Neutrophil counts (ANC)
Neutropenia during treatment in FL or MZL
| When Neutrophils | Recommended Course |
|---|---|
Fall below 1,000/mcL for at least 7 days OR Falls below 1,000/mcL with an associated temperature at least 38.5°C OR Falls below 500/mcL | Interrupt REVLIMID treatment and follow CBC weekly. |
Return to at least 1,000/mcL | If patient starting dose was 20 mg daily, resume REVLIMID at 5 mg less than the previous dose. Do not dose below 5 mg daily. If patient starting dose was 10 mg daily, resume at 5 mg less than previous dose. Do not dose below 2.5 mg daily. |
Dosage Modifications for Non-Hematologic Adverse Reactions
For non-hematologic Grade 3/4 toxicities judged to be related to REVLIMID, hold treatment and restart at the physician's discretion at next lower dose level when toxicity has resolved to Grade 2 or below.
Permanently discontinue REVLIMID for angioedema, anaphylaxis, Grade 4 rash, skin exfoliation, bullae, or any other severe dermatologic reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9 , 5.15) ] .
Recommended Dosage for Patients with Renal Impairment
The recommendations for dosing patients with renal impairment are shown in the following table [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Renal Function (Cockcroft-Gault) | Dose in REVLIMID Combination Therapy for MM and MCL | Dose in REVLIMID Combination Therapy for FL and MZL | Dose in REVLIMID Maintenance Therapy Following Auto-HSCT for MM and for MDS |
CLcr 30 to 60 mL/min | 10 mg once daily | 10 mg once daily | 5 mg once daily |
CLcr below 30 mL/min (not requiring dialysis) | 15 mg every other day | 5 mg once daily | 2.5 mg once daily |
CLcr below 30 mL/min (requiring dialysis) | 5 mg once daily. On dialysis days, administer the dose following dialysis. | 5 mg once daily. On dialysis days, administer the dose following dialysis. | 2.5 mg once daily. On dialysis days, administer the dose following dialysis. |
REVLIMID Combination Therapy for MM: For CLcr of 30 to 60 mL/min, consider escalating the dose to 15 mg after 2 cycles if the patient tolerates the 10 mg dose of lenalidomide without dose-limiting toxicity.
REVLIMID Maintenance Therapy Following Auto-HSCT for MM and for MCL and MDS: Base subsequent REVLIMID dose increase or decrease on individual patient treatment tolerance [see Dosage and Administration (2.1 - 2.3) ] .
REVLIMID Combination Therapy for FL or for MZL: For patients with CLcr of 30 to 60 mL/min, after 2 cycles, the REVLIMID dose may be increased to 15 mg orally if the patient has tolerated therapy.
Administration
Advise patients to take REVLIMID orally at about the same time each day, either with or without food. Advise patients to swallow REVLIMID capsules whole with water and not to open, break, or chew them.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Capsules:
- 2.5 mg, white and blue-green opaque hard capsules imprinted "REV" on one half and "2.5 mg" on the other half in black ink
- 5 mg, white opaque capsules imprinted "REV" on one half and "5 mg" on the other half in black ink
- 10 mg, blue/green and pale yellow opaque capsules imprinted "REV" on one half and "10 mg" on the other half in black ink
- 15 mg, powder blue and white opaque capsules imprinted "REV" on one half and "15 mg" on the other half in black ink
- 20 mg, powder blue and blue-green opaque hard capsules imprinted "REV" on one half and "20 mg" on the other half in black ink
- 25 mg, white opaque capsules imprinted "REV" on one half and "25 mg" on the other half in black ink
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed (8.2 ).
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in females exposed to REVLIMID during pregnancy as well as female partners of male patients who are exposed to REVLIMID. This registry is also used to understand the root cause for the pregnancy. Report any suspected fetal exposure to REVLIMID to the FDA via the MedWatch program at 1-800-FDA-1088 and also to the REMS Call Center at 1-888-423-5436.
Risk Summary
Based on the mechanism of action [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1) ] and findings from animal studies [see Data] , REVLIMID can cause embryo-fetal harm when administered to a pregnant female and is contraindicated during pregnancy [see Boxed Warning , Contraindications (4.1) , and Use in Specific Populations (5.1) ] .
REVLIMID is a thalidomide analogue. Thalidomide is a human teratogen, inducing a high frequency of severe and life-threatening birth defects such as amelia (absence of limbs), phocomelia (short limbs), hypoplasticity of the bones, absence of bones, external ear abnormalities (including anotia, micropinna, small or absent external auditory canals), facial palsy, eye abnormalities (anophthalmos, microphthalmos), and congenital heart defects. Alimentary tract, urinary tract, and genital malformations have also been documented and mortality at or shortly after birth has been reported in about 40% of infants.
Lenalidomide caused thalidomide-type limb defects in monkey offspring. Lenalidomide crossed the placenta after administration to pregnant rabbits and pregnant rats [see Data ] . If this drug is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential risk to a fetus.
If pregnancy does occur during treatment, immediately discontinue the drug. Under these conditions, refer patient to an obstetrician/gynecologist experienced in reproductive toxicity for further evaluation and counseling. Report any suspected fetal exposure to REVLIMID to the FDA via the MedWatch program at 1-800-FDA-1088 and also to the REMS Call Center at 1-888-423-5436.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. The estimated background risk in the U.S. general population of major birth defects is 2%-4% and of miscarriage is 15%-20% of clinically recognized pregnancies.
Data
Animal data
In an embryo-fetal developmental toxicity study in monkeys, teratogenicity, including thalidomide-like limb defects, occurred in offspring when pregnant monkeys received oral lenalidomide during organogenesis. Exposure (AUC) in monkeys at the lowest dose was 0.17 times the human exposure at the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 25 mg. Similar studies in pregnant rabbits and rats at 20 times and 200 times the MRHD respectively, produced embryo lethality in rabbits and no adverse reproductive effects in rats.
In a pre- and post-natal development study in rats, animals received lenalidomide from organogenesis through lactation. The study revealed a few adverse effects on the offspring of female rats treated with lenalidomide at doses up to 500 mg/kg (approximately 200 times the human dose of 25 mg based on body surface area). The male offspring exhibited slightly delayed sexual maturation and the female offspring had slightly lower body weight gains during gestation when bred to male offspring. As with thalidomide, the rat model may not adequately address the full spectrum of potential human embryo-fetal developmental effects for lenalidomide.
Following daily oral administration of lenalidomide from Gestation Day 7 through Gestation Day 20 in pregnant rabbits, fetal plasma lenalidomide concentrations were approximately 20-40% of the maternal C max. Following a single oral dose to pregnant rats, lenalidomide was detected in fetal plasma and tissues; concentrations of radioactivity in fetal tissues were generally lower than those in maternal tissues. These data indicated that lenalidomide crossed the placenta.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information regarding the presence of lenalidomide in human milk, the effects of REVLIMID on the breastfed child, or the effects of REVLIMID on milk production. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for adverse reactions in breastfed children from REVLIMID, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with REVLIMID.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Pregnancy Testing
REVLIMID can cause fetal harm when administered during pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ] . Verify the pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to initiating REVLIMID therapy and during therapy. Advise females of reproductive potential that they must avoid pregnancy 4 weeks before therapy, while taking REVLIMID, during dose interruptions and for at least 4 weeks after completing therapy.
Females of reproductive potential must have 2 negative pregnancy tests before initiating REVLIMID. The first test should be performed within 10-14 days, and the second test within 24 hours prior to prescribing REVLIMID. Once treatment has started and during dose interruptions, pregnancy testing for females of reproductive potential should occur weekly during the first 4 weeks of use, then pregnancy testing should be repeated every 4 weeks in females with regular menstrual cycles. If menstrual cycles are irregular, the pregnancy testing should occur every 2 weeks. Pregnancy testing and counseling should be performed if a patient misses her period or if there is any abnormality in her menstrual bleeding. REVLIMID treatment must be discontinued during this evaluation.
Contraception
Females
Females of reproductive potential must commit either to abstain continuously from heterosexual sexual intercourse or to use 2 methods of reliable birth control simultaneously: one highly effective form of contraception – tubal ligation, IUD, hormonal (birth control pills, injections, hormonal patches, vaginal rings, or implants), or partner's vasectomy, and 1 additional effective contraceptive method – male latex or synthetic condom, diaphragm, or cervical cap. Contraception must begin 4 weeks prior to initiating treatment with REVLIMID, during therapy, during dose interruptions, and continuing for 4 weeks following discontinuation of REVLIMID therapy. Reliable contraception is indicated even where there has been a history of infertility, unless due to hysterectomy. Females of reproductive potential should be referred to a qualified provider of contraceptive methods, if needed.
Males
Lenalidomide is present in the semen of males who take REVLIMID. Therefore, males must always use a latex or synthetic condom during any sexual contact with females of reproductive potential while taking REVLIMID and for up to 4 weeks after discontinuing REVLIMID, even if they have undergone a successful vasectomy. Male patients taking REVLIMID must not donate sperm and for up to 4 weeks after discontinuing REVLIMID.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness have not been established in pediatric patients.
Geriatric Use
MM In Combination : Overall, of the 1613 patients in the NDMM study who received study treatment, 94% (1521 /1613) were 65 years of age or older, while 35% (561/1613) were over 75 years of age. The percentage of patients over age 75 was similar between study arms (Rd Continuous: 33%; Rd18: 34%; MPT: 33%). Overall, across all treatment arms, the frequency in most of the adverse reaction categories (eg, all adverse reactions, grade 3/4 adverse reactions, serious adverse reactions) was higher in older (> 75 years of age) than in younger (≤ 75 years of age) subjects. Grade 3 or 4 adverse reactions in the General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions body system were consistently reported at a higher frequency (with a difference of at least 5%) in older subjects than in younger subjects across all treatment arms. Grade 3 or 4 adverse reactions in the Infections and Infestations, Cardiac Disorders (including cardiac failure and congestive cardiac failure), Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders, and Renal and Urinary Disorders (including renal failure) body systems were also reported slightly, but consistently, more frequently (<5% difference), in older subjects than in younger subjects across all treatment arms. For other body systems (e.g., Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders, Infections and Infestations, Cardiac Disorders, Vascular Disorders), there was a less consistent trend for increased frequency of grade 3/4 adverse reactions in older vs younger subjects across all treatment arms Serious adverse reactions were generally reported at a higher frequency in the older subjects than in the younger subjects across all treatment arms.
MM Maintenance Therapy : Overall, 10% (106/1018) of patients were 65 years of age or older, while no patients were over 75 years of age. Grade 3 or 4 adverse reactions were higher in the REVLIMID arm (more than 5% higher) in the patients 65 years of age or older versus younger patients. The frequency of Grade 3 or 4 adverse reactions in the Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders were higher in the REVLIMID arm (more than 5% higher) in the patients 65 years of age or older versus younger patients. There were not a sufficient number of patients 65 years of age or older in REVLIMID maintenance studies who experienced either a serious adverse reaction, or discontinued therapy due to an adverse reaction to determine whether elderly patients respond relative to safety differently from younger patients.
MM After At Least One Prior Therapy : Of the 703 MM patients who received study treatment in Studies 1 and 2, 45% were age 65 or over while 12% of patients were age 75 and over. The percentage of patients age 65 or over was not significantly different between the REVLIMID/dexamethasone and placebo/dexamethasone groups. Of the 353 patients who received REVLIMID/dexamethasone, 46% were age 65 and over. In both studies, patients > 65 years of age were more likely than patients ≤ 65 years of age to experience DVT, pulmonary embolism, atrial fibrillation, and renal failure following use of REVLIMID. No differences in efficacy were observed between patients over 65 years of age and younger patients.
Of the 148 patients with del 5q MDS enrolled in the major study, 38% were age 65 and over, while 33% were age 75 and over. Although the overall frequency of adverse reactions (100%) was the same in patients over 65 years of age as in younger patients, the frequency of serious adverse reactions was higher in patients over 65 years of age than in younger patients (54% vs. 33%). A greater proportion of patients over 65 years of age discontinued from the clinical studies because of adverse reactions than the proportion of younger patients (27% vs. 16%). No differences in efficacy were observed between patients over 65 years of age and younger patients.
Of the 134 patients with MCL enrolled in the MCL trial, 63% were age 65 and over, while 22% of patients were age 75 and over. The overall frequency of adverse reactions was similar in patients over 65 years of age and in younger patients (98% vs. 100%). The overall incidence of grade 3 and 4 adverse reactions was also similar in these 2 patient groups (79% vs. 78%, respectively). The frequency of serious adverse reactions was higher in patients over 65 years of age than in younger patients (55% vs. 41%). No differences in efficacy were observed between patients over 65 years of age and younger patients.
FL or MZL in Combination: Overall, 48% (282/590) of patients were 65 years of age or older, while 14% (82/590) of patients were over 75 years of age. The overall frequency of adverse reactions was similar in patients 65 years of age or older and younger patients for both studies pooled (98%). Grade 3 or 4 adverse reactions were higher in the REVLIMID arm (more than 5% higher) in the patients 65 years of age or older versus younger patients (71% versus 59%). The frequency of Grade 3 or 4 adverse reactions were higher in the REVLIMID arm (more than 5% higher) in the patients 65 years of age or older versus younger patients in the Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders (47% versus 40%) and Infections and Infestations (16% versus 11%). Serious adverse reactions were higher in the REVLIMID arm (more than 5% higher) in the patients 65 years of age or older versus younger patients (37% versus 18%). The frequency of serious adverse reactions were higher in the REVLIMID arm (more than 5% higher) in the patients 65 years of age or older versus younger patients in Infections and Infestations (15% versus 6%).
Since elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection. Monitor renal function.
Renal Impairment
Adjust the starting dose of REVLIMID based on the creatinine clearance value and for patients on dialysis [see Dosage and Administration (2.6) ].
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Pregnancy
REVLIMID can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant female. Limb abnormalities were seen in the offspring of monkeys that were dosed with lenalidomide during organogenesis. This effect was seen at all doses tested. Due to the results of this developmental monkey study, and lenalidomide's structural similarities to thalidomide, a known human teratogen, lenalidomide is contraindicated in females who are pregnant [see Boxed Warning ]. If this drug is used during pregnancy or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential risk to a fetus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 , 5.2) , Use in Special Populations (8.1 , 8.3) ] .
Severe Hypersensitivity Reactions
REVLIMID is contraindicated in patients who have demonstrated severe hypersensitivity (e.g., angioedema, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis) to lenalidomide [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9 , 5.15 )].
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Increased Mortality: serious and fatal cardiac adverse reactions occurred in patients with CLL treated with REVLIMID (5.5 ).
- Second Primary Malignancies (SPM): Higher incidences of SPM were observed in controlled trials of patients with MM receiving REVLIMID (5.6 ).
- Increased Mortality: Observed in patients with MM when pembrolizumab was added to dexamethasone and a thalidomide analogue (5.7 ).
- Hepatotoxicity: Hepatic failure including fatalities; monitor liver function. Stop REVLIMID and evaluate if hepatotoxicity is suspected (5.8 ).
- Severe Cutaneous Reactions: Discontinue REVLIMID for severe reactions (5.9 ).
- Tumor lysis syndrome (TLS) including fatalities: Monitor patients at risk of TLS (i.e., those with high tumor burden) and take appropriate precautions (5.10 ).
- Tumor flare reaction: Serious tumor flare reactions, including fatal reactions, have occurred during investigational use of REVLIMID for chronic lymphocytic leukemia and lymphoma (5.11 ).
- Impaired Stem Cell mobilization: A decrease in the number of CD34+ cells collected after treatment (> 4 cycles) with REVLIMID has been reported. Consider early referral to transplant center (5.12 ).
- Early mortality in MCL: Higher rate of early deaths have occurred in patients with MCL (5.14 ).
- Hypersensitivity: Monitor patients for potential hypersensitivity. Discontinue REVLIMID for angioedema and anaphylaxis (5.15 ).
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
REVLIMID is a thalidomide analogue and is contraindicated for use during pregnancy. Thalidomide is a known human teratogen that causes life-threatening human birth defects or embryo-fetal death [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ]. An embryo-fetal development study in monkeys indicates that lenalidomide produced malformations in the offspring of female monkeys who received the drug during pregnancy, similar to birth defects observed in humans following exposure to thalidomide during pregnancy.
REVLIMID is only available through the Lenalidomide REMS program [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] .
Females of Reproductive Potential
Females of reproductive potential must avoid pregnancy for at least 4 weeks before beginning REVLIMID therapy, during therapy, during dose interruptions and for at least 4 weeks after completing therapy.
Females must commit either to abstain continuously from heterosexual sexual intercourse or to use two methods of reliable birth control, beginning 4 weeks prior to initiating treatment with REVLIMID, during therapy, during dose interruptions and continuing for 4 weeks following discontinuation of REVLIMID therapy.
Two negative pregnancy tests must be obtained prior to initiating therapy. The first test should be performed within 10-14 days and the second test within 24 hours prior to prescribing REVLIMID therapy and then weekly during the first month, then monthly thereafter in females with regular menstrual cycles or every 2 weeks in females with irregular menstrual cycles [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3) ] .
Males
Lenalidomide is present in the semen of patients receiving the drug. Therefore, males must always use a latex or synthetic condom during any sexual contact with females of reproductive potential while taking REVLIMID and for up to 4 weeks after discontinuing REVLIMID, even if they have undergone a successful vasectomy. Male patients taking REVLIMID must not donate sperm and for up to 4 weeks after discontinuing REVLIMID [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3) ].
Blood Donation
Patients must not donate blood during treatment with REVLIMID and for 4 weeks following discontinuation of the drug because the blood might be given to a pregnant female patient whose fetus must not be exposed to REVLIMID.
Lenalidomide REMS Program
Because of the embryo-fetal risk [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] , REVLIMID is available only through a restricted program under a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS), the Lenalidomide REMS program.
Required components of the Lenalidomide REMS program include the following:
- Prescribers must be certified with the Lenalidomide REMS program by enrolling and complying with the REMS requirements.
- Patients must sign a Patient-Physician agreement form and comply with the REMS requirements. In particular, female patients of reproductive potential who are not pregnant must comply with the pregnancy testing and contraception requirements [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3) ] and males must comply with contraception requirements [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3) ] .
- Pharmacies must be certified with the Lenalidomide REMS program, must only dispense to patients who are authorized to receive REVLIMID and comply with REMS requirements.
Further information about the Lenalidomide REMS program is available at www.lenalidomiderems.com or by telephone at 1-888-423-5436.
Hematologic Toxicity
REVLIMID can cause significant neutropenia and thrombocytopenia. Monitor patients with neutropenia for signs of infection. Advise patients to observe for bleeding or bruising, especially with use of concomitant medication that may increase risk of bleeding. Patients taking REVLIMID should have their complete blood counts assessed periodically as described below [see Dosage and Administration (2.1 , 2.2 , 2.3) ] .
Monitor complete blood counts (CBC) in patients taking REVLIMID in combination with dexamethasone or as REVLIMID maintenance therapy for MM every 7 days (weekly) for the first 2 cycles, on Days 1 and 15 of Cycle 3, and every 28 days (4 weeks) thereafter. A dose interruption and/or dose reduction may be required [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) ] . In the MM maintenance therapy trials, Grade 3 or 4 neutropenia was reported in up to 59% of REVLIMID-treated patients and Grade 3 or 4 thrombocytopenia in up to 38% of REVLIMID-treated patients [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
Monitor complete blood counts (CBC) in patients taking REVLIMID for MDS weekly for the first 8 weeks and at least monthly thereafter. Grade 3 or 4 hematologic toxicity was seen in 80% of patients enrolled in the MDS study. In the 48% of patients who developed Grade 3 or 4 neutropenia, the median time to onset was 42 days (range, 14-411 days), and the median time to documented recovery was 17 days (range, 2-170 days). In the 54% of patients who developed Grade 3 or 4 thrombocytopenia, the median time to onset was 28 days (range, 8-290 days), and the median time to documented recovery was 22 days (range, 5-224 days) [see Boxed Warning and Dosage and Administration (2.2) ] .
Monitor complete blood counts (CBC) in patients taking REVLIMID for MCL weekly for the first cycle (28 days), every 2 weeks during cycles 2-4, and then monthly thereafter. Patients may require dose interruption and/or dose reduction. In the MCL trial, Grade 3 or 4 neutropenia was reported in 43% of the patients. Grade 3 or 4 thrombocytopenia was reported in 28% of the patients.
Monitor complete blood counts (CBC) in patients taking REVLIMID for FL or MZL weekly for the first 3 weeks of Cycle 1 (28 days), every 2 weeks during Cycles 2-4, and then monthly thereafter. Patients may require dose interruption and/or dose reduction. In the AUGMENT and MAGNIFY trials, Grade 3 or 4 neutropenia was reported in 50% and 33%, respectively, of patients in the REVLIMID/rituximab arm. Grade 3 or 4 thrombocytopenia was reported in 2% and 8%, respectively, of patients in the REVLIMID/rituximab arm [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
Venous and Arterial Thromboembolism
Venous thromboembolic events (VTE [DVT and PE]) and arterial thromboembolic events (ATE, myocardial infarction and stroke) are increased in patients treated with REVLIMID.
A significantly increased risk of DVT (7.4%) and of PE (3.7%) occurred in patients with MM after at least one prior therapy who were treated with REVLIMID and dexamethasone therapy compared to patients treated in the placebo and dexamethasone group (3.1% and 0.9%) in clinical trials with varying use of anticoagulant therapies. In the newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (NDMM) study in which nearly all patients received antithrombotic prophylaxis, DVT was reported as a serious adverse reaction (3.6%, 2.0%, and 1.7%) in the Rd Continuous, Rd18, and MPT Arms, respectively. The frequency of serious adverse reactions of PE was similar between the Rd Continuous, Rd18, and MPT Arms (3.8%, 2.8%, and 3.7%, respectively) [see Boxed Warning and Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
Myocardial infarction (1.7%) and stroke (CVA) (2.3%) are increased in patients with MM after at least one prior therapy who were treated with REVLIMID and dexamethasone therapy compared to patients treated with placebo and dexamethasone (0.6%, and 0.9%) in clinical trials. In the NDMM study, myocardial infarction (including acute) was reported as a serious adverse reaction (2.3%, 0.6%, and 1.1%) in the Rd Continuous, Rd18, and MPT Arms, respectively. The frequency of serious adverse reactions of CVA was similar between the Rd Continuous, Rd18, and MPT Arms (0.8%, 0.6 %, and 0.6%, respectively) [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ].
Patients with known risk factors, including prior thrombosis, may be at greater risk and actions should be taken to try to minimize all modifiable factors (e.g. hyperlipidemia, hypertension, smoking).
In controlled clinical trials that did not use concomitant thromboprophylaxis, 21.5% overall thrombotic events (Standardized MedDRA Query Embolic and Thrombotic events) occurred in patients with refractory and relapsed MM who were treated with REVLIMID and dexamethasone compared to 8.3% thrombosis in patients treated with placebo and dexamethasone. The median time to first thrombosis event was 2.8 months. In the NDMM study in which nearly all patients received antithrombotic prophylaxis, the overall frequency of thrombotic events was 17.4% in patients in the combined Rd Continuous and Rd18 Arms, and was 11.6% in the MPT Arm. The median time to first thrombosis event was 4.3 months in the combined Rd Continuous and Rd18 Arms.
In the AUGMENT trial, the incidence of VTE (including DVT and PE) in FL or MZL patients was 3.4% in the REVLIMID/rituximab arm [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] . In the AUGMENT trial, the incidence of ATE (including MI) in FL or MZL patients was 0.6% in the REVLIMID/rituximab arm [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
Thromboprophylaxis is recommended. The regimen of thromboprophylaxis should be based on an assessment of the patient's underlying risks. Instruct patients to report immediately any signs and symptoms suggestive of thrombotic events. ESAs and estrogens may further increase the risk of thrombosis and their use should be based on a benefit-risk decision in patients receiving REVLIMID [see Drug Interactions (7.2) ].
Increased Mortality in Patients with CLL
In a prospective randomized (1:1) clinical trial in the first line treatment of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia, single agent REVLIMID therapy increased the risk of death as compared to single agent chlorambucil. In an interim analysis, there were 34 deaths among 210 patients on the REVLIMID treatment arm compared to 18 deaths among 211 patients in the chlorambucil treatment arm, and hazard ratio for overall survival was 1.92 [95% CI: 1.08 – 3.41], consistent with a 92% increase in the risk of death. The trial was halted for safety in July 2013.
Serious adverse cardiovascular reactions, including atrial fibrillation, myocardial infarction, and cardiac failure occurred more frequently in the REVLIMID treatment arm. REVLIMID is not indicated and not recommended for use in CLL outside of controlled clinical trials.
Second Primary Malignancies
In clinical trials in patients with MM receiving REVLIMID, an increase of hematologic plus solid tumor second primary malignancies (SPM) notably AML and MDS have been observed. An increase in hematologic SPM including AML and MDS occurred in 5.3% of patients with NDMM receiving REVLIMID in combination with oral melphalan compared with 1.3% of patients receiving melphalan without REVLIMID. The frequency of AML and MDS cases in patients with NDMM treated with REVLIMID in combination with dexamethasone without melphalan was 0.4%.
In patients receiving REVLIMID maintenance therapy following high dose intravenous melphalan and auto-HSCT, hematologic SPM occurred in 7.5% of patients compared to 3.3% in patients receiving placebo. The incidence of hematologic plus solid tumor (excluding squamous cell carcinoma and basal cell carcinoma) SPM was 14.9%, compared to 8.8% in patients receiving placebo with a median follow-up of 91.5 months. Non-melanoma skin cancer SPM, including squamous cell carcinoma and basal cell carcinoma, occurred in 3.9% of patients receiving REVLIMID maintenance, compared to 2.6% in the placebo arm.
In patients with relapsed or refractory MM treated with REVLIMID/dexamethasone, the incidence of hematologic plus solid tumor (excluding squamous cell carcinoma and basal cell carcinoma) SPM was 2.3% versus 0.6% in the dexamethasone alone arm. Non-melanoma skin cancer SPM, including squamous cell carcinoma and basal cell carcinoma, occurred in 3.1% of patients receiving REVLIMID/dexamethasone, compared to 0.6% in the dexamethasone alone arm.
Patients who received REVLIMID-containing therapy until disease progression did not show a higher incidence of invasive SPM than patients treated in the fixed duration REVLIMID-containing arms. Monitor patients for the development of second primary malignancies. Take into account both the potential benefit of REVLIMID and the risk of second primary malignancies when considering treatment with REVLIMID.
In the AUGMENT trial with FL or MZL patients receiving REVLIMID/rituximab therapy, hematologic plus solid tumor SPMs, notably AML, have been observed. In the AUGMENT trial, hematologic SPM of AML occurred in 0.6% of patients with FL or MZL receiving REVLIMID/rituximab therapy. The incidence of hematologic plus solid tumor SPMs (excluding nonmelanoma skin cancers) was 1.7% in the REVLIMID/rituximab arm with a median follow-up of 29.8 months (range 0.5 to 51.3 months) [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] . Monitor patients for the development of second primary malignancies. Take into account both the potential benefit of REVLIMID and the risk of second primary malignancies when considering treatment with REVLIMID.
Increased Mortality in Patients with MM When Pembrolizumab Is Added to a Thalidomide Analogue and Dexamethasone
In two randomized clinical trials in patients with MM, the addition of pembrolizumab to a thalidomide analogue plus dexamethasone, a use for which no PD-1 or PD-L1 blocking antibody is indicated, resulted in increased mortality. Treatment of patients with MM with a PD-1 or PD-L1 blocking antibody in combination with a thalidomide analogue plus dexamethasone is not recommended outside of controlled clinical trials.
Hepatotoxicity
Hepatic failure, including fatal cases, has occurred in patients treated with REVLIMID in combination with dexamethasone. In clinical trials, 15% of patients experienced hepatotoxicity (with hepatocellular, cholestatic and mixed characteristics); 2% of patients with MM and 1% of patients with myelodysplasia had serious hepatotoxicity events. The mechanism of drug-induced hepatotoxicity is unknown. Pre-existing viral liver disease, elevated baseline liver enzymes, and concomitant medications may be risk factors. Monitor liver enzymes periodically. Stop REVLIMID upon elevation of liver enzymes. After return to baseline values, treatment at a lower dose may be considered.
Severe Cutaneous Reactions
Severe cutaneous reactions including Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) have been reported. DRESS may present with a cutaneous reaction (such as rash or exfoliative dermatitis), eosinophilia, fever, and/or lymphadenopathy with systemic complications such as hepatitis, nephritis, pneumonitis, myocarditis, and/or pericarditis. These events can be fatal. Patients with a prior history of Grade 4 rash associated with thalidomide treatment should not receive REVLIMID. Consider REVLIMID interruption or discontinuation for Grade 2-3 skin rash. Permanently discontinue REVLIMID for Grade 4 rash, exfoliative or bullous rash, or for other severe cutaneous reactions such as SJS, TEN or DRESS [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) ] .
Tumor Lysis Syndrome
Fatal instances of tumor lysis syndrome (TLS) have been reported during treatment with REVLIMID. The patients at risk of TLS are those with high tumor burden prior to treatment. Monitor patients at risk closely and take appropriate preventive approaches. In the AUGMENT trial in FL or MZL patients, TLS occurred in 2 patients (1.1%) in the REVLIMID/rituximab arm. TLS occurred in 1 patient (0.5%) in the MAGNIFY trial during the REVLIMID/rituximab induction period; the event was a serious, Grade 3 adverse reaction.
Tumor Flare Reaction
Tumor flare reaction (TFR), including fatal reactions, have occurred during investigational use of REVLIMID for CLL and lymphoma, and is characterized by tender lymph node swelling, low grade fever, pain and rash. REVLIMID is not indicated and not recommended for use in CLL outside of controlled clinical trials.
Monitoring and evaluation for TFR is recommended in patients with MCL, FL, or MZL. Tumor flare reaction may mimic progression of disease (PD).
In the MCL trial, 13/134 (10%) of subjects experienced TFR; all reports were Grade 1 or 2 in severity. All of the events occurred in Cycle 1 and one patient developed TFR again in Cycle 11. In the AUGMENT trial in FL or MZL patients, TFR was reported in 19/176 (10.8%) of patients in REVLIMID with rituximab arm; one patient in the REVLIMID/rituximab arm experienced a Grade 3 TFR. In the MAGNIFY trial, 9/222 (4.1%) of patients experienced TFR; all reports were Grade 1 or 2 in severity and 1 event was considered as serious. In a separate MCL phase 2 trial, one case of TFR resulted in a fatal outcome.
REVLIMID may be continued in patients with Grade 1 and 2 TFR without interruption or modification, at the physician's discretion. Patients with Grade 1 and 2 TFR may also be treated with corticosteroids, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and/or narcotic analgesics for management of TFR symptoms. In patients with Grade 3 or 4 TFR, it is recommended to withhold treatment with REVLIMID until TFR resolves to ≤ Grade 1. Patients with Grade 3 or 4 TFR may be treated for management of symptoms per the guidance for treatment of Grade 1 and 2 TFR.
Impaired Stem Cell Mobilization
A decrease in the number of CD34+ cells collected after treatment (> 4 cycles) with REVLIMID has been reported. In patients who are auto-HSCT candidates, referral to a transplant center should occur early in treatment to optimize the timing of the stem cell collection. In patients who received more than 4 cycles of a REVLIMID-containing treatment or for whom inadequate numbers of CD 34+ cells have been collected with G-CSF alone, G-CSF with cyclophosphamide or the combination of G-CSF with a CXCR4 inhibitor may be considered.
Thyroid Disorders
Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism have been reported [see Adverse Reactions (6.2) ] . Measure thyroid function before start of REVLIMID treatment and during therapy.
Early Mortality in Patients with MCL
In another MCL study, there was an increase in early deaths (within 20 weeks), 12.9% in the REVLIMID arm versus 7.1% in the control arm. On exploratory multivariate analysis, risk factors for early deaths include high tumor burden, MIPI score at diagnosis, and high WBC at baseline (≥ 10 x 10 9 /L).
Hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity, including angioedema, anaphylaxis, and anaphylactic reactions to REVLIMID has been reported. Permanently discontinue REVLIMID for angioedema and anaphylaxis [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) ] .
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described in detail in other sections of the prescribing information:
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity [see Boxed Warning , Warnings and Precautions (5.1 , 5.2) ]
- Hematologic Toxicity [see Boxed Warning , Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
- Venous and Arterial Thromboembolism [see Boxed Warning , Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ]
- Increased Mortality in Patients with CLL [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ]
- Second Primary Malignancies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ]
- Increased Mortality in Patients with MM When Pembrolizumab Is Added to a Thalidomide Analogue and Dexamethasone [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) ]
- Severe Cutaneous Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9) ]
- Tumor Lysis Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10) ]
- Tumor Flare Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11) ]
- Impaired Stem Cell Mobilization [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12) ]
- Thyroid Disorders [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13) ]
- Early Mortality in Patients with MCL [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14) ]
- Hypersensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.15) ]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Newly Diagnosed MM – REVLIMID Combination Therapy:
Data were evaluated from 1613 patients in a large phase 3 study who received at least one dose of REVLIMID with low dose dexamethasone (Rd) given for 2 different durations of time (i.e., until progressive disease [Arm Rd Continuous; N=532] or for up to eighteen 28-day cycles [72 weeks, Arm Rd18; N=540] or who received melphalan, prednisone and thalidomide (Arm MPT; N=541) for a maximum of twelve 42-day cycles (72 weeks). The median treatment duration in the Rd Continuous arm was 80.2 weeks (range 0.7 to 246.7) or 18.4 months (range 0.16 to 56.7).
In general, the most frequently reported adverse reactions were comparable in Arm Rd Continuous and Arm Rd18, and included diarrhea, anemia, constipation, peripheral edema, neutropenia, fatigue, back pain, nausea, asthenia, and insomnia. The most frequently reported Grade 3 or 4 reactions included neutropenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, pneumonia, asthenia, fatigue, back pain, hypokalemia, rash, cataract, lymphopenia, dyspnea, DVT, hyperglycemia, and leukopenia. The highest frequency of infections occurred in Arm Rd Continuous (75%) compared to Arm MPT (56%). There were more grade 3 and 4 and serious adverse reactions of infection in Arm Rd Continuous than either Arm MPT or Rd18.
In the Rd Continuous arm, the most common adverse reactions leading to dose interruption of REVLIMID were infection events (28.8%); overall, the median time to the first dose interruption of REVLIMID was 7 weeks. The most common adverse reactions leading to dose reduction of REVLIMID in the Rd Continuous arm were hematologic events (10.7%); overall, the median time to the first dose reduction of REVLIMID was 16 weeks. In the Rd Continuous arm, the most common adverse reactions leading to discontinuation of REVLIMID were infection events (3.4%).
In both Rd arms, the frequencies of onset of adverse reactions were generally highest in the first 6 months of treatment and then the frequencies decreased over time or remained stable throughout treatment, except for cataracts. The frequency of onset of cataracts increased over time with 0.7% during the first 6 months and up to 9.6% by the 2nd year of treatment with Rd Continuous.
Table 4 summarizes the adverse reactions reported for the Rd Continuous, Rd18, and MPT treatment arms.
| Note: A subject with multiple occurrences of an adverse reaction is counted only once under the applicable Body System/Adverse Reaction. a All treatment-emergent adverse events in at least 5% of subjects in the Rd Continuous or Rd18 Arms and at least a 2% higher frequency (%) in either the Rd Continuous or Rd18 Arms compared to the MPT Arm. b All grade 3 or 4 treatment-emergent adverse events in at least 1% of subjects in the Rd Continuous or Rd18 Arms and at least a 1% higher frequency (%) in either the Rd Continuous or Rd18 Arms compared to the MPT Arm. c Serious treatment-emergent adverse events in at least 1% of subjects in the Rd Continuous or Rd18 Arms and at least a 1% higher frequency (%) in either the Rd Continuous or Rd18 Arms compared to the MPT Arm. d Preferred terms for the blood and lymphatic system disorders body system were included by medical judgment as known adverse reactions for Rd Continuous/Rd18, and have also been reported as serious. e Footnote “a” not applicable. f Footnote “b” not applicable. @ - adverse reactions in which at least one resulted in a fatal outcome. % - adverse reactions in which at least one was considered to be life threatening (if the outcome of the reaction was death, it is included with death cases). •Adverse reactions included in combined adverse reaction terms : Abdominal Pain : Abdominal pain, abdominal pain upper, abdominal pain lower, gastrointestinal pain Pneumonias : Pneumonia, lobar pneumonia, pneumonia pneumococcal, bronchopneumonia, pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia, pneumonia legionella, pneumonia staphylococcal, pneumonia klebsiella, atypical pneumonia, pneumonia bacterial, pneumonia escherichia, pneumonia streptococcal, pneumonia viral Sepsis : Sepsis, septic shock, urosepsis, escherichia sepsis, neutropenic sepsis, pneumococcal sepsis, staphylococcal sepsis, bacterial sepsis, meningococcal sepsis, enterococcal sepsis, klebsiella sepsis, pseudomonal sepsis Rash : Rash, rash pruritic, rash erythematous, rash maculo-papular, rash generalized, rash papular, exfoliative rash, rash follicular, rash macular, drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms, erythema multiforme, rash pustular Deep Vein Thrombosis : Deep vein thrombosis, venous thrombosis limb, venous thrombosis | ||||||
Body System Adverse Reaction | All Adverse Reactions a | Grade 3/4 Adverse Reactions b | ||||
Rd Continuous (N = 532) | Rd18 (N = 540) | MPT (N = 541) | Rd Continuous (N = 532) | Rd18 (N = 540) | MPT (N = 541) | |
General disorders and administration site conditions | ||||||
Fatigue % | 173 (33) | 177 (33) | 154 (28) | 39 ( 7) | 46 ( 9) | 31 ( 6) |
Asthenia | 150 (28) | 123 (23) | 124 (23) | 41 ( 8) | 33 ( 6) | 32 ( 6) |
Pyrexia c | 114 (21) | 102 (19) | 76 (14) | 13 ( 2) | 7 ( 1) | 7 ( 1) |
Non-cardiac chest pain f | 29 ( 5) | 31 ( 6) | 18 ( 3) | <1% | < 1% | < 1% |
Gastrointestinal disorders | ||||||
Diarrhea | 242 (45) | 208 (39) | 89 (16) | 21 ( 4) | 18 ( 3) | 8 ( 1) |
Abdominal pain % f | 109 (20) | 78 (14) | 60 (11) | 7 ( 1) | 9 ( 2) | < 1% |
Dyspepsia f | 57 (11) | 28 ( 5) | 36 ( 7) | <1% | < 1% | 0 ( 0) |
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||||||
Back pain c | 170 (32) | 145 (27) | 116 (21) | 37 ( 7) | 34 ( 6) | 28 ( 5) |
Muscle spasms f | 109 (20) | 102 (19) | 61 (11) | < 1% | < 1% | < 1% |
Arthralgia f | 101 (19) | 71 (13) | 66 (12) | 9 ( 2) | 8 ( 1) | 8 ( 1) |
Bone pain f | 87 (16) | 77 (14) | 62 (11) | 16 ( 3) | 15 ( 3) | 14 ( 3) |
Pain in extremity f | 79 (15) | 66 (12) | 61 (11) | 8 ( 2) | 8 ( 1) | 7 ( 1) |
Musculoskeletal pain f | 67 (13) | 59 (11) | 36 ( 7) | < 1% | < 1% | < 1% |
Musculoskeletal chest pain f | 60 (11) | 51 ( 9) | 39 ( 7) | 6 ( 1) | < 1% | < 1% |
Muscular weakness f | 43 ( 8) | 35 ( 6) | 29 ( 5) | < 1% | 8 ( 1) | < 1% |
Neck pain f | 40 ( 8) | 19 ( 4) | 10 ( 2) | < 1% | < 1% | < 1% |
Infections and infestations | ||||||
Bronchitis c | 90 (17) | 59 (11) | 43 ( 8) | 9 ( 2) | 6 ( 1) | < 1% |
Nasopharyngitis f | 80 (15) | 54 (10) | 33 ( 6) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) |
Urinary tract infection f | 76 (14) | 63 (12) | 41 ( 8) | 8 ( 2) | 8 ( 1) | < 1% |
Upper respiratory tract infection c% f | 69 (13) | 53 ( 10) | 31 ( 6) | < 1% | 8 ( 1) | < 1% |
Pneumonia c@ | 93 (17) | 87 (16) | 56 (10) | 60 (11) | 57 (11) | 41 ( 8) |
Respiratory tract infection % | 35 ( 7) | 25 ( 5) | 21 ( 4) | 7 ( 1) | < 1% | < 1% |
Influenza f | 33 ( 6) | 23 ( 4) | 15 ( 3) | < 1% | < 1% | 0 ( 0) |
Gastroenteritis f | 32 ( 6) | 17 ( 3) | 13 ( 2) | 0 ( 0) | < 1% | < 1% |
Lower respiratory tract infection | 29 ( 5) | 14 ( 3) | 16 ( 3) | 10 ( 2) | < 1% | < 1% |
Rhinitis f | 29 ( 5) | 24 ( 4) | 14 ( 3) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) |
Cellulitis c | < 5% | < 5% | < 5% | 8 ( 2) | < 1% | < 1% |
Sepsis c@ | 33 ( 6) | 26 ( 5) | 18 ( 3) | 26 ( 5) | 20 ( 4) | 13 ( 2) |
Nervous system disorders | ||||||
Headache f | 75 (14) | 52 ( 10) | 56 (10) | < 1% | < 1% | < 1% |
Dysgeusia f | 39 ( 7) | 45 ( 8) | 22 ( 4) | < 1% | 0 ( 0.0) | < 1% |
Blood and lymphatic system disorders d | ||||||
Anemia | 233 (44) | 193 (36) | 229 (42) | 97 (18) | 85 (16) | 102 (19) |
Neutropenia | 186 (35) | 178 (33) | 328 (61) | 148 (28) | 143 (26) | 243 (45) |
Thrombocytopenia | 104 (20) | 100 (19) | 135 (25) | 44 ( 8) | 43 ( 8) | 60 (11) |
Febrile neutropenia | 7 ( 1) | 17 ( 3) | 15 ( 3) | 6 ( 1) | 16 ( 3) | 14 ( 3) |
Pancytopenia | < 1% | 6 ( 1) | 7 ( 1) | < 1% | < 1% | < 1% |
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | ||||||
Cough f | 121 (23) | 94 (17) | 68 (13) | < 1% | < 1% | < 1% |
Dyspnea c,e | 117 (22) | 89 (16) | 113 (21) | 30 ( 6) | 22 ( 4) | 18 ( 3) |
Epistaxis f | 32 ( 6) | 31 ( 6) | 17 ( 3) | < 1% | < 1% | 0 ( 0) |
Oropharyngeal pain f | 30 ( 6) | 22 ( 4) | 14 ( 3) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) |
Dyspnea exertional e | 27 ( 5) | 29 ( 5) | < 5% | 6 ( 1) | < 1% | 0 ( 0) |
Metabolism and nutrition disorders | ||||||
Decreased appetite | 123 (23) | 115 (21) | 72 (13) | 14 ( 3) | 7 ( 1) | < 1% |
Hypokalemia % | 91 (17) | 62 (11) | 38 ( 7) | 35 ( 7) | 20 ( 4) | 11 ( 2) |
Hyperglycemia | 62 (12) | 52 (10) | 19 ( 4) | 28 ( 5) | 23 ( 4) | 9 ( 2) |
Hypocalcemia | 57 (11) | 56 (10) | 31 ( 6) | 23 ( 4) | 19 ( 4) | 8 ( 1) |
Dehydration % | 25 ( 5) | 29 ( 5) | 17 ( 3) | 8 ( 2) | 13 ( 2) | 9 ( 2) |
Gout e | < 5% | < 5% | < 5% | 8 ( 2) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) |
Diabetes mellitus % e | < 5% | < 5% | < 5% | 8 ( 2) | < 1% | < 1% |
Hypophosphatemia e | < 5% | < 5% | < 5% | 7 ( 1) | < 1% | < 1% |
Hyponatremia % e | < 5% | < 5% | < 5% | 7 ( 1) | 13 ( 2) | 6 ( 1) |
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||||||
Rash | 139 (26) | 151 (28) | 105 (19) | 39 ( 7) | 38 ( 7) | 33 ( 6) |
Pruritus f | 47 ( 9) | 49 ( 9) | 24 ( 4) | < 1% | < 1% | < 1% |
Psychiatric disorders | ||||||
Insomnia | 147 (28) | 127 (24) | 53 ( 10) | < 1% | 6 ( 1) | 0 ( 0) |
Depression | 58 (11) | 46 ( 9) | 30 ( 6) | 10 ( 2) | < 1% | < 1% |
Vascular disorders | ||||||
Deep vein thrombosis c% | 55 (10) | 39 ( 7) | 22 ( 4) | 30 ( 6) | 20 ( 4) | 15 ( 3) |
Hypotension c% | 51 (10) | 35 ( 6) | 36 ( 7) | 11 ( 2) | 8 ( 1) | 6 ( 1) |
Injury, Poisoning, and Procedural Complications | ||||||
Fall f | 43 ( 8) | 25 ( 5) | 25 ( 5) | < 1% | 6 ( 1) | 6 ( 1) |
Contusion f | 33 ( 6) | 24 ( 4) | 15 ( 3) | < 1% | < 1% | 0 ( 0) |
Eye disorders | ||||||
Cataract | 73 (14) | 31 ( 6) | < 1% | 31 ( 6) | 14 ( 3) | < 1% |
Cataract subcapsular e | < 5% | < 5% | < 5% | 7 ( 1) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) |
Investigations | ||||||
Weight decreased | 72 (14) | 78 (14) | 48 ( 9) | 11 ( 2) | < 1% | < 1% |
Cardiac disorders | ||||||
Atrial fibrillation c | 37 ( 7) | 25 ( 5) | 25 ( 5) | 13 ( 2) | 9 ( 2) | 6 ( 1) |
Myocardial infarction (including acute) c ,e | < 5% | < 5% | < 5% | 10 ( 2) | < 1% | < 1% |
Renal and Urinary disorders | ||||||
Renal failure (including acute) c@,f | 49 ( 9) | 54 (10) | 37 ( 7) | 28 ( 5) | 33 ( 6) | 29 ( 5) |
Neoplasms benign, malignant and unspecified (Including cysts and polyps) | ||||||
Squamous cell carcinoma c e | < 5% | < 5% | < 5% | 8 ( 2) | < 1% | 0 ( 0) |
Basal cell carcinoma c e,f | < 5% | < 5% | < 5% | < 1% | < 1% | 0 ( 0) |
Newly Diagnosed MM - REVLIMID Maintenance Therapy Following Auto-HSCT:
Data were evaluated from 1018 patients in two randomized trials who received at least one dose of REVLIMID 10 mg daily as maintenance therapy after auto-HSCT until progressive disease or unacceptable toxicity. The mean treatment duration for REVLIMID treatment was 30.3 months for Maintenance Study 1 and 24.0 months for Maintenance Study 2 (overall range across both studies from 0.1 to 108 months). As of the cut-off date of 1 Mar 2015, 48 patients (21%) in the Maintenance Study 1 REVLIMID arm were still on treatment and none of the patients in the Maintenance Study 2 REVLIMID arm were still on treatment at the same cut-off date
The adverse reactions listed from Maintenance Study 1 included events reported post-transplant (completion of high-dose melphalan /auto-HSCT), and the maintenance treatment period. In Maintenance Study 2, the adverse reactions were from the maintenance treatment period only. In general, the most frequently reported adverse reactions (more than 20% in the REVLIMID arm) across both studies were neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, anemia, upper respiratory tract infection, bronchitis, nasopharyngitis, cough, gastroenteritis, diarrhea, rash, fatigue, asthenia, muscle spasm and pyrexia. The most frequently reported Grade 3 or 4 reactions (more than 20% in the REVLIMID arm) included neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and leukopenia. The serious adverse reactions lung infection and neutropenia (more than 4.5%) occurred in the REVLIMID arm.
For REVLIMID, the most common adverse reactions leading to dose interruption were hematologic events (29.7%, data available in Maintenance Study 2 only). The most common adverse reaction leading to dose reduction of REVLIMID were hematologic events (17.7%, data available in Maintenance Study 2 only). The most common adverse reactions leading to discontinuation of REVLIMID were thrombocytopenia (2.7%) in Maintenance Study 1 and neutropenia (2.4%) in Maintenance Study 2.
The frequencies of onset of adverse reactions were generally highest in the first 6 months of treatment and then the frequencies decreased over time or remained stable throughout treatment.
Table 5 summarizes the adverse reactions reported for the REVLIMID and placebo maintenance treatment arms.
| Note : Adverse Events (AEs) are coded to Body System /Adverse Reaction using MedDRA v15.1. A subject with multiple occurrences of an adverse reaction is counted only once under the applicable Body System/Adverse Reaction. a All treatment-emergent AEs in at least 5% of patients in the REVLIMID Maintenance group and at least 2% higher frequency (%) than the Placebo Maintenance group. b All grade 3 or 4 treatment-emergent AEs in at least 1% of patients in the REVLIMID Maintenance group and at least 1% higher frequency (%) than the Placebo Maintenance group. c All serious treatment-emergent AEs in at least 1% of patients in the REVLIMID Maintenance group and at least 1% higher frequency (%) than the Placebo Maintenance group. d Footnote “a” not applicable for either study e Footnote “b” not applicable for either study @ - ADRs where at least one resulted in a fatal outcome % - ADRs where at least one was considered to be Life Threatening (if the outcome of the event was death, it is included with death cases) # - All adverse reactions under Body System of Infections and Infestation except for rare infections of Public Health interest will be considered listed •Adverse Reactions for combined ADR terms (based on relevant TEAE PTs included in Maintenance Studies 1 and 2 [per MedDRA v 15.1]): Pneumonias Bronchopneumonia, Lobar pneumonia, Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia, Pneumonia, Pneumonia klebsiella, Pneumonia legionella, Pneumonia mycoplasmal, Pneumonia pneumococcal, Pneumonia streptococcal, Pneumonia viral, Lung disorder, Pneumonitis Sepsis : Bacterial sepsis, Pneumococcal sepsis, Sepsis, Septic shock, Staphylococcal sepsis Peripheral neuropathy : Neuropathy peripheral, Peripheral motor neuropathy, Peripheral sensory neuropathy, Polyneuropathy Deep vein thrombosis : Deep vein thrombosis, Thrombosis, Venous thrombosis | ||||||||
Body System Adverse Reaction | Maintenance Study 1 | Maintenance Study 2 | ||||||
All Adverse Reactions a | Grade 3/4 Adverse Reactions b | All Adverse Reactions a | Grade 3/4 Adverse Reactions b | |||||
REVLIMID (N=224) n (%) | Placebo (N=221) n (%) | REVLIMID (N=224) n (%) | Placebo (N=221) n (%) | REVLIMID (N=293) n (%) | Placebo (N=280) n (%) | REVLIMID (N=293) n (%) | Placebo (N=280) n (%) | |
Blood and lymphatic system disorders | ||||||||
Neutropenia c % | 177 ( 79) | 94 ( 43) | 133 ( 59) | 73 ( 33) | 178 ( 61) | 33 ( 12) | 158 ( 54) | 21 ( 8) |
Thrombocytopenia c % | 162 ( 72) | 101 ( 46) | 84 ( 38) | 67 ( 30) | 69 ( 24) | 29 ( 10) | 38 ( 13) | 8 ( 3) |
Leukopenia c | 51 ( 23) | 25 ( 11) | 45 ( 20) | 22 ( 10) | 93 ( 32) | 21 ( 8) | 71 ( 24) | 5 ( 2) |
Anemia | 47 ( 21) | 27 ( 12) | 23 ( 10) | 18 ( 8) | 26 ( 9) | 15 ( 5) | 11 ( 4) | 3 ( 1) |
Lymphopenia | 40 ( 18) | 29 ( 13) | 37 ( 17) | 26 ( 12) | 13 ( 4) | 3 ( 1) | 11 ( 4) | < 1% |
Pancytopenia c d % | < 1% | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) | 12 ( 4) | < 1% | 7 ( 2) | < 1% |
Febrile neutropenia c | 39 ( 17) | 34 ( 15) | 39 ( 17) | 34 ( 15) | 7 ( 2) | < 1% | 5 ( 2) | < 1% |
Infections and infestations # | ||||||||
Upper respiratory tract infection e | 60 ( 27) | 35 ( 16) | 7 ( 3) | 9 ( 4) | 32 ( 11) | 18 ( 6) | < 1% | 0 ( 0) |
Neutropenic infection | 40 ( 18) | 19 ( 9) | 27 ( 12) | 14 ( 6) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) |
Pneumonias • c % | 31 ( 14) | 15 ( 7) | 23 ( 10) | 7 ( 3) | 50 ( 17) | 13 ( 5) | 27 ( 9) | 5 ( 2) |
Bronchitis c | 10 ( 4) | 9 ( 4) | < 1% | 5 ( 2) | 139 ( 47) | 104 ( 37) | 4 ( 1) | < 1% |
Nasopharyngitis e | 5 ( 2) | < 1% | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) | 102 ( 35) | 84 ( 30) | < 1% | 0 ( 0) |
Gastroenteritis c | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) | 66 ( 23) | 55 ( 20) | 6 ( 2) | 0 ( 0) |
Rhinitis e | < 1% | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) | 44 ( 15) | 19 ( 7) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) |
Sinusitis e | 8 ( 4) | 3 ( 1) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) | 41 ( 14) | 26 ( 9) | 0 ( 0) | < 1% |
Influenza c | 8 ( 4) | 5 ( 2) | < 1% | < 1% | 39 ( 13) | 19 ( 7) | 3 ( 1) | 0 ( 0) |
Lung infection c | 21 ( 9) | < 1% | 19 ( 8) | < 1% | 9 ( 3) | 4 ( 1) | < 1% | 0 ( 0) |
Lower respiratory tract infection e | 13 ( 6) | 5 ( 2) | 6 ( 3) | 4 ( 2) | 4 ( 1) | 4 ( 1) | 0 ( 0) | < 1% |
Infection c | 12 ( 5) | 6 ( 3) | 9 ( 4) | 5 ( 2) | 17 ( 6) | 5 ( 2) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) |
Urinary tract infection c d e | 9 ( 4) | 5 ( 2) | 4 ( 2) | 4 ( 2) | 22 ( 8) | 17 ( 6) | < 1% | 0 ( 0) |
Lower respiratory tract infection bacterial d | 6 ( 3) | < 1% | 4 ( 2) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) |
Bacteremia d | 5 ( 2) | 0 ( 0) | 4 ( 2) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) |
Herpes zoster c d | 11 ( 5) | 10 ( 5) | 3 ( 1) | < 1% | 29 ( 10) | 25 ( 9) | 6 ( 2) | < 1% |
Sepsis • c d @ | < 1% | < 1% | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) | 6 ( 2) | < 1% | 4 ( 1) | < 1% |
Gastrointestinal disorders | ||||||||
Diarrhea | 122 ( 54) | 83 ( 38) | 22 ( 10) | 17 ( 8) | 114 ( 39) | 34 ( 12) | 7 ( 2) | 0 ( 0) |
Nausea e | 33 ( 15) | 22 ( 10) | 16 ( 7) | 10 ( 5) | 31 ( 11) | 28 ( 10) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) |
Vomiting | 17 ( 8) | 12 ( 5) | 8 ( 4) | 5 ( 2) | 16 ( 5) | 15 ( 5) | < 1% | 0 ( 0) |
Constipation e | 12 ( 5) | 8 ( 4) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) | 37 ( 13) | 25 ( 9) | < 1% | 0 ( 0) |
Abdominal pain e | 8 ( 4) | 7 ( 3) | < 1% | 4 ( 2) | 31 ( 11) | 15 ( 5) | < 1% | < 1% |
Abdominal pain upper e | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) | 20 ( 7) | 12 ( 4) | < 1% | 0 ( 0) |
General disorders and administration site conditions | ||||||||
Asthenia | 0 ( 0) | < 1% | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) | 87 ( 30) | 53 ( 19) | 10 ( 3) | < 1% |
Fatigue | 51 ( 23) | 30 ( 14) | 21 ( 9) | 9 ( 4) | 31 ( 11) | 15 ( 5) | 3 ( 1) | 0 ( 0) |
Pyrexia e | 17 ( 8) | 10 ( 5) | < 1% | < 1% | 60 ( 20) | 26 ( 9) | < 1% | 0 ( 0) |
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||||||||
Dry skin e | 9 ( 4) | 4 ( 2) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) | 31 ( 11) | 21 ( 8) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) |
Rash | 71 ( 32) | 48 ( 22) | 11 ( 5) | 5 ( 2) | 22 ( 8) | 17 ( 6) | 3 ( 1) | 0 ( 0) |
Pruritus | 9 ( 4) | 4 ( 2) | 3 ( 1) | 0 ( 0) | 21 ( 7) | 25 ( 9) | < 1% | 0 ( 0) |
Nervous system disorders | ||||||||
Paresthesia e | < 1% | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) | 39 ( 13) | 30 ( 11) | < 1% | 0 ( 0) |
Peripheral neuropathy • e | 34 ( 15) | 30 ( 14) | 8 ( 4) | 8 ( 4) | 29 ( 10) | 15 ( 5) | 4 ( 1) | < 1% |
Headache d | 11 ( 5) | 8 ( 4) | 5 ( 2) | < 1% | 25 ( 9) | 21 ( 8) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) |
Investigations | ||||||||
Alanine aminotransferase increased | 16 ( 7) | 3 ( 1) | 8 ( 4) | 0 ( 0) | 5 ( 2) | 5 ( 2) | 0 ( 0) | < 1% |
Aspartate aminotransferase increased d | 13 ( 6) | 5 ( 2) | 6 ( 3) | 0 ( 0) | < 1% | 5 ( 2) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) |
Metabolism and nutrition disorders | ||||||||
Hypokalemia | 24 ( 11) | 13 ( 6) | 16 ( 7) | 12 ( 5) | 12 ( 4) | < 1% | < 1% | 0 ( 0) |
Dehydration | 9 ( 4 ) | 5 ( 2) | 7 ( 3) | 3 ( 1) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) |
Hypophosphatemia d | 16 ( 7) | 15 ( 7) | 13 ( 6) | 14 ( 6) | 0 ( 0) | < 1% | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) |
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||||||||
Muscle spasms e | 0 ( 0) | < 1% | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) | 98 ( 33) | 43 ( 15) | < 1% | 0 ( 0) |
Myalgia e | 7 ( 3) | 8 ( 4) | 3 ( 1) | 5 ( 2) | 19 ( 6) | 12 ( 4) | < 1% | < 1% |
Musculoskeletal pain e | < 1% | < 1% | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) | 19 ( 6) | 11 ( 44) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) |
Hepatobiliary disorders | ||||||||
Hyperbilirubinemia e | 34 ( 15) | 19 ( 9) | 4 ( 2) | < 1% | 4 ( 1) | < 1% | < 1% | 0 ( 0) |
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | ||||||||
Cough e | 23 ( 10) | 12 ( 5) | 3 ( 1) | < 1% | 80 ( 27) | 56 ( 20) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) |
Dyspnea c e | 15 ( 7) | 9 ( 4) | 8 ( 4) | 4 ( 2) | 17 ( 6) | 9 ( 3) | < 1% | 0 ( 0) |
Rhinorrhea e | 0 ( 0) | 3 ( 1) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) | 15 ( 5) | 6 ( 2) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) |
Pulmonary embolism c d e | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) | 0 ( 0) | 3 ( 1) | 0 ( 0) | < 1% | 0 ( 0) |
Vascular disorders | ||||||||
Deep vein thrombosis •c d % | 8 ( 4) | < 1% | 5 ( 2) | < 1% | 7 ( 2) | < 1% | 4 ( 1) | < 1% |
Neoplasms benign, malignant and unspecified (including cysts and polyps) | ||||||||
Myelodysplastic syndrome c d e | 5 ( 2) | 0 ( 0) | < 1% | 0 ( 0) | 3 ( 1) | 0 ( 0) | < 1% | 0 ( 0) |
After At Least One Prior Therapy for MM:
Data were evaluated from 703 patients in two studies who received at least one dose of REVLIMID/dexamethasone (353 patients) or placebo/dexamethasone (350 patients).
In the REVLIMID/dexamethasone treatment group, 269 patients (76%) had at least one dose interruption with or without a dose reduction of REVLIMID compared to 199 patients (57%) in the placebo/dexamethasone treatment group. Of these patients who had one dose interruption with or without a dose reduction, 50% in the REVLIMID/dexamethasone treatment group had at least one additional dose interruption with or without a dose reduction compared to 21% in the placebo/dexamethasone treatment group. Most adverse reactions and Grade 3/4 adverse reactions were more frequent in patients who received the combination of REVLIMID/dexamethasone compared to placebo/dexamethasone.
Tables 6, 7, and 8 summarize the adverse reactions reported for REVLIMID/dexamethasone and placebo/dexamethasone groups.
Body System Adverse Reaction | REVLIMID/Dex (N=353) n (%) | Placebo/Dex (N=350) n (%) |
Blood and lymphatic system disorders | ||
Neutropenia % | 149 (42) | 22 ( 6) |
Anemia @ | 111 (31) | 83 (24) |
Thrombocytopenia @ | 76 (22) | 37 (11) |
Leukopenia | 28 ( 8) | 4 ( 1) |
Lymphopenia | 19 ( 5) | 5 ( 1) |
General disorders and administration site conditions | ||
Fatigue | 155 (44) | 146 (42) |
Pyrexia | 97 (27) | 82 (23) |
Peripheral edema | 93 (26) | 74 (21) |
Chest pain | 29 ( 8) | 20 ( 6) |
Lethargy | 24 ( 7) | 8 ( 2) |
Gastrointestinal disorders | ||
Constipation | 143 (41) | 74 (21) |
Diarrhea @ | 136 (39) | 96 (27) |
Nausea @ | 92 (26) | 75 (21) |
Vomiting @ | 43 (12) | 33 ( 9) |
Abdominal pain @ | 35 ( 10) | 22 ( 6) |
Dry mouth | 25 ( 7) | 13 ( 4) |
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||
Muscle cramp | 118 (33) | 74 (21) |
Back pain | 91 (26) | 65 (19) |
Bone pain | 48 (14) | 39 (11) |
Pain in limb | 42 (12) | 32 ( 9) |
Nervous system disorders | ||
Dizziness | 82 (23) | 59 (17) |
Tremor | 75 (21) | 26 ( 7) |
Dysgeusia | 54 (15) | 34 ( 10) |
Hypoesthesia | 36 (10) | 25 ( 7) |
Neuropathy a | 23 ( 7) | 13 ( 4) |
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | ||
Dyspnea | 83 (24) | 60 (17) |
Nasopharyngitis | 62 (18) | 31 ( 9) |
Pharyngitis | 48 (14) | 33 ( 9) |
Bronchitis | 40 (11) | 30 ( 9) |
Infections b and infestations | ||
Upper respiratory tract infection | 87 (25) | 55 (16) |
Pneumonia @ | 48 (14) | 29 ( 8) |
Urinary tract infection | 30 ( 8) | 19 ( 5) |
Sinusitis | 26 ( 7) | 16 ( 5) |
Skin and subcutaneous system disorders | ||
Rash c | 75 (21) | 33 ( 9) |
Sweating increased | 35 ( 10) | 25 ( 7) |
Dry skin | 33 ( 9) | 14 ( 4) |
Pruritus | 27 ( 8) | 18 ( 5) |
Metabolism and nutrition disorders | ||
Anorexia | 55 (16) | 34 ( 10) |
Hypokalemia | 48 (14) | 21 ( 6) |
Hypocalcemia | 31 ( 9) | 10 ( 3) |
Appetite decreased | 24 ( 7) | 14 ( 4) |
Dehydration | 23 ( 7) | 15 ( 4) |
Hypomagnesemia | 24 ( 7) | 10 ( 3) |
Investigations | ||
Weight decreased | 69 (20) | 52 (15) |
Eye disorders | ||
Blurred vision | 61 (17) | 40 (11) |
Vascular disorders | ||
Deep vein thrombosis % | 33 ( 9) | 15 ( 4) |
Hypertension | 28 ( 8) | 20 ( 6) |
Hypotension | 25 ( 7) | 15 ( 4) |
Body System Adverse Reaction | REVLIMID/Dex (N=353) n (%) | Placebo/Dex (N=350) n (%) |
Blood and lymphatic system disorders | ||
Neutropenia % | 118 (33) | 12 ( 3) |
Thrombocytopenia @ | 43 (12) | 22 ( 6) |
Anemia @ | 35 ( 10) | 20 ( 6) |
Leukopenia | 14 ( 4) | < 1% |
Lymphopenia | 10 ( 3) | 4 ( 1) |
Febrile neutropenia % | 8 ( 2) | 0 ( 0) |
General disorders and administration site conditions | ||
Fatigue | 23 ( 7) | 17 ( 5) |
Vascular disorders | ||
Deep vein thrombosis % | 29 ( 8) | 12 ( 3) |
Infections and infestations | ||
Pneumonia @ | 30 ( 8) | 19 ( 5) |
Urinary tract infection | 5 ( 1) | < 1% |
Metabolism and nutrition disorders | ||
Hypokalemia | 17 ( 5) | 5 ( 1) |
Hypocalcemia | 13 ( 4) | 6 ( 2) |
Hypophosphatemia | 9 ( 3) | 0 ( 0) |
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | ||
Pulmonary embolism @ | 14 ( 4) | < 1% |
Respiratory distress @ | 4 ( 1) | 0 ( 0) |
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||
Muscle weakness | 20 ( 6) | 10 ( 3) |
Gastrointestinal disorders | ||
Diarrhea @ | 11 ( 3) | 4 ( 1) |
Constipation | 7 ( 2) | < 1% |
Nausea @ | 6 ( 2) | < 1% |
Cardiac disorders | ||
Atrial fibrillation @ | 13 ( 4) | 4 ( 1) |
Tachycardia | 6 ( 2) | < 1% |
Cardiac failure congestive @ | 5 ( 1) | < 1% |
Nervous system disorders | ||
Syncope | 10 ( 3) | < 1% |
Dizziness | 7 ( 2) | < 1% |
Eye disorders | ||
Cataract | 6 ( 2) | < 1% |
Cataract unilateral | 5 ( 1) | 0 ( 0) |
Psychiatric disorder | ||
Depression | 10 ( 3) | 6 ( 2) |
| Body System Adverse Reaction | REVLIMID/Dex (N=353) n (%) | Placebo/Dex (N=350) n (%) |
|---|---|---|
| For Tables 6, 7 and 8 above: @ - adverse reactions in which at least one resulted in a fatal outcome. % - adverse reactions in which at least one was considered to be life threatening (if the outcome of the reaction was death, it is included with death cases). | ||
Blood and lymphatic system disorders | ||
Febrile neutropenia % | 6 ( 2) | 0 ( 0) |
Vascular disorders | ||
Deep vein thrombosis % | 26 ( 7) | 11 ( 3) |
Infections and infestations | ||
Pneumonia @ | 33 ( 9) | 21 ( 6) |
Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders | ||
Pulmonary embolism @ | 13 ( 4) | < 1% |
Cardiac disorders | ||
Atrial fibrillation @ | 11 ( 3) | < 1% |
Cardiac failure congestive @ | 5 ( 1) | 0 ( 0) |
Nervous system disorders | ||
Cerebrovascular accident @ | 7 ( 2) | < 1% |
Gastrointestinal disorders | ||
Diarrhea @ | 6 ( 2) | < 1% |
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||
Bone pain | 4 ( 1) | 0 ( 0) |
Median duration of exposure among patients treated with REVLIMID/dexamethasone was 44 weeks while median duration of exposure among patients treated with placebo/dexamethasone was 23 weeks. This should be taken into consideration when comparing frequency of adverse reactions between two treatment groups REVLIMID/dexamethasone vs. placebo/dexamethasone.
Venous and Arterial Thromboembolism [see Boxed Warning , Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ]
VTE and ATE are increased in patients treated with REVLIMID.
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) was reported as a serious (7.4%) or severe (8.2%) adverse drug reaction at a higher rate in the REVLIMID/dexamethasone group compared to 3.1 % and 3.4% in the placebo/dexamethasone group, respectively in the 2 studies in patients with at least 1 prior therapy with discontinuations due to DVT adverse reactions reported at comparable rates between groups. In the NDMM study, DVT was reported as an adverse reaction (all grades: 10.3%, 7.2%, 4.1%), as a serious adverse reaction (3.6%, 2.0%, 1.7%), and as a Grade 3/4 adverse reaction (5.6%, 3.7%, 2.8%) in the Rd Continuous, Rd18, and MPT Arms, respectively. Discontinuations and dose reductions due to DVT adverse reactions were reported at comparable rates between the Rd Continuous and Rd18 Arms (both <1%). Interruption of REVLIMID treatment due to DVT adverse reactions was reported at comparable rates between the Rd Continuous (2.3%) and Rd18 (1.5%) arms. Pulmonary embolism (PE) was reported as a serious adverse drug reaction (3.7%) or Grade 3/4 (4.0%) at a higher rate in the REVLIMID/dexamethasone group compared to 0.9% (serious or grade 3/4) in the placebo/dexamethasone group in the 2 studies in patients with, at least 1 prior therapy, with discontinuations due to PE adverse reactions reported at comparable rates between groups. In the NDMM study, the frequency of adverse reactions of PE was similar between the Rd Continuous, Rd18, and MPT Arms for adverse reactions (all grades: 3.9%, 3.3%, and 4.3%, respectively), serious adverse reactions (3.8%, 2.8%, and 3.7%, respectively), and grade 3/4 adverse reactions (3.8%, 3.0%, and 3.7%, respectively).
Myocardial infarction was reported as a serious (1.7%) or severe (1.7%) adverse drug reaction at a higher rate in the REVLIMID/dexamethasone group compared to 0.6 % and 0.6% respectively in the placebo/dexamethasone group. Discontinuation due to MI (including acute) adverse reactions was 0.8% in REVLIMID/dexamethasone group and none in the placebo/dexamethasone group. In the NDMM study, myocardial infarction (including acute) was reported as an adverse reaction (all grades: 2.4%, 0.6%, and 1.1%), as a serious adverse reaction, (2.3%, 0.6%, and 1.1%), or as a severe adverse reaction (1.9%, 0.6%, and 0.9%) in the Rd Continuous, Rd18, and MPT Arms, respectively.
Stroke (CVA) was reported as a serious (2.3%) or severe (2.0%) adverse drug reaction in the REVLIMID/dexamethasone group compared to 0.9% and 0.9% respectively in the placebo/dexamethasone group. Discontinuation due to stroke (CVA) was 1.4% in REVLIMID/ dexamethasone group and 0.3% in the placebo/dexamethasone group. In the NDMM study, CVA was reported as an adverse reaction (all grades: 0.8%, 0.6%, and 0.6%), as a serious adverse reaction (0.8%, 0.6 %, and 0.6%), or as a severe adverse reaction (0.6%, 0.6%, 0.2%) in the Rd Continuous, Rd18, and MPT arms respectively.
Other Adverse Reactions: After At Least One Prior Therapy for MM
In these 2 studies, the following adverse drug reactions (ADRs) not described above that occurred at ≥1% rate and of at least twice of the placebo percentage rate were reported:
Blood and lymphatic system disorders: pancytopenia, autoimmune hemolytic anemia
Cardiac disorders: bradycardia, myocardial infarction, angina pectoris
Endocrine disorders: hirsutism
Eye disorders: blindness, ocular hypertension
Gastrointestinal disorders: gastrointestinal hemorrhage, glossodynia
General disorders and administration site conditions: malaise
Investigations: liver function tests abnormal, alanine aminotransferase increased
Nervous system disorders: cerebral ischemia
Psychiatric disorders: mood swings, hallucination, loss of libido
Reproductive system and breast disorders: erectile dysfunction
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: cough, hoarseness
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: exanthem, skin hyperpigmentation
Myelodysplastic Syndromes:
A total of 148 patients received at least 1 dose of 10 mg REVLIMID in the del 5q MDS clinical study. At least one adverse reaction was reported in all of the 148 patients who were treated with the 10 mg starting dose of REVLIMID. The most frequently reported adverse reactions were related to blood and lymphatic system disorders, skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders, gastrointestinal disorders, and general disorders and administrative site conditions .
Thrombocytopenia (61.5%; 91/148) and neutropenia (58.8%; 87/148) were the most frequently reported adverse reactions. The next most common adverse reactions observed were diarrhea (48.6%; 72/148), pruritus (41.9%; 62/148), rash (35.8%; 53/148) and fatigue (31.1%; 46/148). Table 9 summarizes the adverse reactions that were reported in ≥ 5% of the REVLIMID treated patients in the del 5q MDS clinical study. Table 10 summarizes the most frequently observed Grade 3 and Grade 4 adverse reactions regardless of relationship to treatment with REVLIMID. In the single-arm studies conducted, it is often not possible to distinguish adverse reactions that are drug-related and those that reflect the patient's underlying disease.
| a Body System and adverse reactions are coded using the MedDRA dictionary. Body System and adverse reactions are listed in descending order of frequency for the Overall column. A patient with multiple occurrences of an adverse reaction is counted only once under the applicable Body System/Adverse Reaction. | |
Body System Adverse Reaction a | 10 mg Overall (N=148) |
Patients with at least one adverse reaction | 148 (100) |
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders | |
Thrombocytopenia | 91 (61) |
Neutropenia | 87 (59) |
Anemia | 17 (11) |
Leukopenia | 12 (8) |
Febrile Neutropenia | 8 (5) |
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders | |
Pruritus | 62 (42) |
Rash | 53 (36) |
Dry Skin | 21 (14) |
Contusion | 12 (8) |
Night Sweats | 12 (8) |
Sweating Increased | 10 (7) |
Ecchymosis | 8 (5) |
Erythema | 8 (5) |
Gastrointestinal Disorders | |
Diarrhea | 72 (49) |
Constipation | 35 (24) |
Nausea | 35 (24) |
Abdominal Pain | 18 (12) |
Vomiting | 15 (10) |
Abdominal Pain Upper | 12 (8) |
Dry Mouth | 10 (7) |
Loose Stools | 9 (6) |
Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders | |
Nasopharyngitis | 34 (23) |
Cough | 29 (20) |
Dyspnea | 25 (17) |
Pharyngitis | 23 (16) |
Epistaxis | 22 (15) |
Dyspnea Exertional | 10 (7) |
Rhinitis | 10 (7) |
Bronchitis | 9 (6) |
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions | |
Fatigue | 46 (31) |
Pyrexia | 31 (21) |
Edema Peripheral | 30 (20) |
Asthenia | 22 (15) |
Edema | 15 (10) |
Pain | 10 (7) |
Rigors | 9 (6) |
Chest Pain | 8 (5) |
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders | |
Arthralgia | 32 (22) |
Back Pain | 31 (21) |
Muscle Cramp | 27 (18) |
Pain in Limb | 16 (11) |
Myalgia | 13 (9) |
Peripheral Swelling | 12 (8) |
Nervous System Disorders | |
Dizziness | 29 (20) |
Headache | 29 (20) |
Hypoesthesia | 10 (7) |
Dysgeusia | 9 (6) |
Peripheral Neuropathy | 8 (5) |
Infections and Infestations | |
Upper Respiratory Tract Infection | 22 (15) |
Pneumonia | 17 (11) |
Urinary Tract Infection | 16 (11) |
Sinusitis | 12 (8) |
Cellulitis | 8 (5) |
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders | |
Hypokalemia | 16 (11) |
Anorexia | 15 (10) |
Hypomagnesemia | 9 (6) |
Investigations | |
Alanine Aminotransferase Increased | 12 (8) |
Psychiatric Disorders | |
Insomnia | 15 (10) |
Depression | 8 (5) |
Renal and Urinary Disorders | |
Dysuria | 10 (7) |
Vascular Disorders | |
Hypertension | 9 (6) |
Endocrine Disorders | |
Acquired Hypothyroidism | 10 (7) |
Cardiac Disorders | |
Palpitations | 8 (5) |
| 1 Adverse reactions with frequency ≥1% in the 10 mg Overall group. Grade 3 and 4 are based on National Cancer Institute Common Toxicity Criteria version 2. 2 Adverse reactions are coded using the MedDRA dictionary. A patient with multiple occurrences of an adverse reaction is counted only once in the adverse reaction category. | |
Adverse Reactions 2 | 10 mg (N=148) |
Patients with at least one Grade 3/4 AE | 131 (89) |
Neutropenia | 79 (53) |
Thrombocytopenia | 74 (50) |
Pneumonia | 11 (7) |
Rash | 10 (7) |
Anemia | 9 (6) |
Leukopenia | 8 (5) |
Fatigue | 7 (5) |
Dyspnea | 7 (5) |
Back Pain | 7 (5) |
Febrile Neutropenia | 6 (4) |
Nausea | 6 (4) |
Diarrhea | 5 (3) |
Pyrexia | 5 (3) |
Sepsis | 4 (3) |
Dizziness | 4 (3) |
Granulocytopenia | 3 (2) |
Chest Pain | 3 (2) |
Pulmonary Embolism | 3 (2) |
Respiratory Distress | 3 (2) |
Pruritus | 3 (2) |
Pancytopenia | 3 (2) |
Muscle Cramp | 3 (2) |
Respiratory Tract Infection | 2 (1) |
Upper Respiratory Tract Infection | 2 (1) |
Asthenia | 2 (1) |
Multi-organ Failure | 2 (1) |
Epistaxis | 2 (1) |
Hypoxia | 2 (1) |
Pleural Effusion | 2 (1) |
Pneumonitis | 2 (1) |
Pulmonary Hypertension | 2 (1) |
Vomiting | 2 (1) |
Sweating Increased | 2 (1) |
Arthralgia | 2 (1) |
Pain in Limb | 2 (1) |
Headache | 2 (1) |
Syncope | 2 (1) |
In other clinical studies of REVLIMID in MDS patients, the following serious adverse reactions (regardless of relationship to study drug treatment) not described in Table 9 or 10 were reported:
Blood and lymphatic system disorders: warm type hemolytic anemia, splenic infarction, bone marrow depression, coagulopathy, hemolysis, hemolytic anemia, refractory anemia
Cardiac disorders: cardiac failure congestive, atrial fibrillation, angina pectoris, cardiac arrest, cardiac failure, cardio-respiratory arrest, cardiomyopathy, myocardial infarction, myocardial ischemia, atrial fibrillation aggravated, bradycardia, cardiogenic shock, pulmonary edema, supraventricular arrhythmia, tachyarrhythmia, ventricular dysfunction
Ear and labyrinth disorders: vertigo
Endocrine disorders: Basedow's disease
Gastrointestinal disorders: gastrointestinal hemorrhage, colitis ischemic, intestinal perforation, rectal hemorrhage, colonic polyp, diverticulitis, dysphagia, gastritis, gastroenteritis, gastroesophageal reflux disease, obstructive inguinal hernia, irritable bowel syndrome, melena, pancreatitis due to biliary obstruction, pancreatitis, perirectal abscess, small intestinal obstruction, upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage
General disorders and administration site conditions: disease progression, fall, gait abnormal, intermittent pyrexia, nodule, rigors, sudden death
Hepatobiliary disorders: hyperbilirubinemia, cholecystitis, acute cholecystitis, hepatic failure
Immune system disorders: hypersensitivity
Infections and infestations: infection bacteremia, central line infection, clostridial infection, ear infection, Enterobacter sepsis, fungal infection, herpes viral infection NOS, influenza, kidney infection, Klebsiella sepsis, lobar pneumonia, localized infection, oral infection, Pseudomonas infection, septic shock, sinusitis acute, sinusitis, Staphylococcal infection, urosepsis
Injury, poisoning and procedural complications: femur fracture, transfusion reaction, cervical vertebral fracture, femoral neck fracture, fractured pelvis, hip fracture, overdose, post procedural hemorrhage, rib fracture, road traffic accident, spinal compression fracture
Investigations: blood creatinine increased, hemoglobin decreased, liver function tests abnormal, troponin I increased
Metabolism and nutrition disorders: dehydration, gout, hypernatremia, hypoglycemia
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: arthritis, arthritis aggravated, gouty arthritis, neck pain, chondrocalcinosis pyrophosphate
Neoplasms benign, malignant and unspecified: acute leukemia, acute myeloid leukemia, bronchoalveolar carcinoma, lung cancer metastatic, lymphoma, prostate cancer metastatic
Nervous system disorders: cerebrovascular accident, aphasia, cerebellar infarction, cerebral infarction, depressed level of consciousness, dysarthria, migraine, spinal cord compression, subarachnoid hemorrhage, transient ischemic attack
Psychiatric disorders: confusional state
Renal and urinary disorders: renal failure, hematuria, renal failure acute, azotemia, calculus ureteric, renal mass
Reproductive system and breast disorders: pelvic pain
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: bronchitis, chronic obstructive airways disease exacerbated, respiratory failure, dyspnea exacerbated, interstitial lung disease, lung infiltration, wheezing
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis
Vascular system disorders: deep vein thrombosis, hypotension, aortic disorder, ischemia, thrombophlebitis superficial, thrombosis
Mantle Cell Lymphoma:
In the MCL trial, a total of 134 patients received at least 1 dose of REVLIMID. Their median age was 67 (range 43-83) years, 128/134 (96%) were Caucasian, 108/134 (81%) were males and 82/134 (61%) had duration of MCL for at least 3 years.
Table 11 summarizes the most frequently observed adverse reactions regardless of relationship to treatment with REVLIMID. Across the 134 patients treated in this study, median duration of treatment was 95 days (1-1002 days). Seventy-eight patients (58%) received 3 or more cycles of therapy, 53 patients (40%) received 6 or more cycles, and 26 patients (19%) received 12 or more cycles. Seventy-six patients (57%) underwent at least one dose interruption due to adverse reactions, and 51 patients (38%) underwent at least one dose reduction due to adverse reactions. Twenty-six patients (19%) discontinued treatment due to adverse reactions.
| 1 -MCL trial AEs – All treatment emergent AEs with ≥10% of subjects. 2 -MCL trial Grade 3/4 AEs – All treatment-emergent Grade 3/4 AEs in 2 or more subjects. $ -MCL trial Serious AEs – All treatment-emergent SAEs in 2 or more subjects. @ - Adverse reactions where at least one resulted in a fatal outcome. % - Adverse reactions where at least one was considered to be Life Threatening (if the outcome of the event was death, it is included with death cases). # - All adverse reactions under Body System of Infections except for rare infections of Public Health interest will be considered listed. + - All adverse reactions under HLT of Rash will be considered listed. | ||
Body System Adverse Reaction | All Adverse Reactions 1 (N=134) n (%) | Grade 3/4 Adverse Reactions 2 (N=134) n (%) |
General disorders and administration site conditions | ||
Fatigue | 45 (34) | 9 (7) |
Pyrexia $ | 31 (23) | 3 (2) |
Edema peripheral | 21 (16) | 0 |
Asthenia $ | 19 (14) | 4 (3) |
General physical health deterioration | 3 (2) | 2 (1) |
Gastrointestinal disorders | ||
Diarrhea $ | 42 (31) | 8 (6) |
Nausea $ | 40 (30) | 1 (<1) |
Constipation | 21 (16) | 1 (<1) |
Vomiting $ | 16 (12) | 1 (<1) |
Abdominal pain $ | 13 (10) | 5 ( 4) |
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||
Back pain | 18 (13) | 2 (1) |
Muscle spasms | 17 (13) | 1 (<1) |
Arthralgia | 11 (8) | 2 (1) |
Muscular weakness $ | 8 (6) | 2 ( 1) |
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | ||
Cough | 38 (28) | 1 (<1) |
Dyspnea $ | 24 (18) | 8 (6) |
Pleural Effusion | 10 (7) | 2 (1) |
Hypoxia | 3 (2) | 2 (1) |
Pulmonary embolism | 3 (2) | 2 ( 1) |
Respiratory distress $ | 2 (1) | 2 (1) |
Oropharyngeal pain | 13 (10) | 0 |
Infections and infestations | ||
Pneumonia @ $ | 19 (14) | 12 (9) |
Upper respiratory tract infection | 17 (13) | 0 |
Cellulitis $ | 3 (2) | 2 (1) |
Bacteremia $ | 2 (1) | 2 (1) |
Staphylococcal sepsis $ | 2 (1) | 2 (1) |
Urinary tract infection $ | 5 (4) | 2 (1) |
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||
Rash + | 30 (22) | 2 (1) |
Pruritus | 23 (17) | 1 (<1) |
Blood and lymphatic system disorders | ||
Neutropenia | 65 (49) | 58 (43) |
Thrombocytopenia % $ | 48 (36) | 37 (28) |
Anemia $ | 41 (31) | 15 (11) |
Leukopenia $ | 20 (15) | 9 (7) |
Lymphopenia | 10 ( 7) | 5 (4) |
Febrile neutropenia $ | 8 (6) | 8 (6) |
Metabolism and nutrition disorders | ||
Decreased appetite | 19 (14) | 1 (<1) |
Hypokalemia | 17 (13) | 3 (2) |
Dehydration $ | 10 (7) | 4 (3) |
Hypocalcemia | 4 (3) | 2 (1) |
Hyponatremia | 3 (2) | 3 (2) |
Renal and urinary disorders | ||
Renal failure $ | 5 (4) | 2 (1) |
Vascular disorders | ||
Hypotension @ $ | 9 (7) | 4 (3) |
Deep vein thrombosis $ | 5 (4) | 5 (4) |
Neoplasms benign, malignant and unspecified (including cysts and polyps) | ||
Tumor flare | 13 (10) | 0 |
Squamous cell carcinoma of skin $ | 4 (3) | 4 (3) |
Investigations | ||
Weight decreased | 17 (13) | 0 |
The following adverse reactions which have occurred in other indications including another MCL study and not described above have been reported (1%-10%) in patients treated with REVLIMID monotherapy for mantle cell lymphoma.
Cardiac disorder: Cardiac failure
Ear and labyrinth disorders: Vertigo
General disorders and administration site conditions: Chills
Infections and infestations: Respiratory tract infection, sinusitis, nasopharyngitis, oral herpes
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: Pain in extremity
Nervous system disorders: Dysgeusia, headache, neuropathy peripheral, lethargy
Psychiatric disorders: Insomnia
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Dry skin, night sweats
The following serious adverse reactions not described above and reported in 2 or more patients treated with REVLIMID monotherapy for mantle cell lymphoma.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders: Neutropenia
Cardiac disorder: Myocardial infarction (including acute MI), supraventricular tachycardia
Infections and infestations: Clostridium difficile colitis, sepsis
Neoplasms benign, malignant and unspecified (including cysts and polyps): Basal cell carcinoma
Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, pulmonary embolism
Follicular Lymphoma or Marginal Zone Lymphoma
The safety of REVLIMID/ rituximab was evaluated in 398 patients with either previously treated follicular lymphoma or marginal zone lymphoma in two clinical trials; AUGMENT (N=176) and MAGNIFY (N=222) [see Clinical Studies (14.4) ] . Subjects were 18 years or older in age, had an ECOG PS ≤2, ANC ≥1,000 cells/mm 3 and platelets≥ 75,000/mm 3 (unless secondary to bone marrow involvement by lymphoma), hemoglobin ≥8g/dL, AST and ALT ≤ 3 x ULN (unless documented liver involvement with lymphoma, and creatinine clearance of ≥ 30mL/min. Subjects with active HIV, hepatitis B or C were not eligible.
In the AUGMENT trial, patients received REVLIMID 20 mg daily by mouth on days 1 – 21 of each 28 day cycle with rituximab 375 mg/m 2 weekly (days 1, 8, 15 and 22 in cycle 1) then on day 1 of cycles 2-5 (n=176) or placebo with rituximab 375 mg/m 2 weekly (days 1, 8, 15 and 22 in cycle 1) then on day 1 of cycles 2-5 (n=180) for up to 12 cycles. In the MAGNIFY trial, patients received REVLIMID 20 mg by mouth daily, days 1-21 of each 28 day cycle with rituximab 375 mg/m 2 weekly (days 1, 8, 15 and 22 in cycle 1) then on day 1 of cycles 3, 5, 7, 9 and 11 in the induction phase of the trial (n=222). In the AUGMENT trial, 88.1% of patients completed at least 6 cycles of REVLIMID/rituximab, and 71% of patients completed 12 cycles. In the ongoing MAGNIFY trial as of May 1, 2017, 62.2% of patients completed at least 6 cycles of REVLIMID/rituximab, and 30.6% of patients completed 12 cycles.
Across both clinical trials (AUGMENT and MAGNIFY), patients had a median age of 64.5 years (26 to 91); 49% were male; and 81% were White.
Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 6 patients (1.5%) receiving REVLIMID/rituximab. Fatal adverse reactions (1 each) included cardio-respiratory arrest, arrhythmia, cardiopulmonary failure, multiple organ dysfunction syndrome, sepsis, and acute kidney injury. Serious adverse reactions occurred in 26% of patients receiving REVLIMID/rituximab in AUGMENT and 29% in MAGNIFY. The most frequent serious adverse reaction that occurred in ≥ 2.5% of patients in the REVLIMID/rituximab arm was febrile neutropenia (3%). Permanent discontinuation of REVLIMID or rituximab due to an adverse reaction occurred in 14.6% of patients in the REVLIMID/rituximab arm. The most common adverse reaction (in at least 1%) requiring permanent discontinuation of REVLIMID or rituximab was neutropenia (4.8%).
The most common adverse reactions occurring in at least 20% of subjects were; neutropenia (48%), fatigue (37%), diarrhea (32%), constipation (27%), nausea (21%), and cough (20%).
| Note : Adverse reactions are coded to body system/adverse reaction using MedDRA 21. A patient with multiple occurrences of an adverse reaction is counted only once under the applicable Body System/Adverse reaction. 1 All treatment-emergent AEs in at least 5% of patients in the REVLIMID + rituximab group and at least 1% higher frequency (%) than the rituximab + placebo group (control arm). 2 All grade 3 or 4 treatment-emergent AEs in at least 1% of patients in the REVLIMID + rituximab group and at least 1% higher frequency (%) than the rituximab + placebo group (control arm). 3 All serious treatment-emergent AEs in at least 1% of patients in the REVLIMID + rituximab group and at least 1% higher frequency (%) than the rituximab + placebo group (control arm). $ Serious ADR reported. @ - adverse reactions in which at least one resulted in a fatal outcome. % - adverse reactions in which at least one was considered to be life threatening (if the outcome of the reaction was death, it is included with death cases). •Adverse Reactions for combined ADR terms (based on relevant TEAE PTs [per MedDRA version 21.0]): a "Thromboembolic events" combined term includes the following PTs: pulmonary embolism, deep vein thrombosis, cerebrovascular accident, embolism, and thrombosis. b "Cough" combined AE term includes the following PTs: cough and productive cough. | ||||
| c “Abdominal pain” combined AE term includes the following PTs: abdominal pain and abdominal pain upper. d "Rash" combined AE term includes the following PTs: rash maculo-papular, rash erythematous, rash macular, rash papular, rash pruritic, and rash generalized. e "Pruritus" combined AE term includes the following PTs: pruritus, pruritus generalized, rash pruritic, and pruritus allergic. | ||||
All Adverse Reactions 1 | Grade 3 / 4 Adverse Reactions 2 | |||
Body System Adverse Reaction • | REVLIMID + Rituximab Arm (N=176) n (%) | Rituximab + Placebo (Control Arm) (N=180) n (%) | REVLIMID + Rituximab Arm (N=176) n (%) | Rituximab + Placebo (Control Arm) (N=180) n (%) |
Infections and infestations | ||||
Upper respiratory tract infection | 32 (18) | 23 (13) | 2 (1.1) | 4 (2.2) |
Influenza % | 17 (10) | 8 (4.4) | 1 (< 1) | 0 (0) |
Pneumonia 3,$,% | 13 (7) | 6 (3.3) | 6 (3.4) | 4 (2.2) |
Sinusitis | 13 (7) | 5 (2.8) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
Urinary tract infection $ | 13 (7) | 7 (3.9) | 1 (< 1) | 1 (< 1) |
Bronchitis | 8 (4.5) | 6 (3.3) | 2 (1.1) | 0 (0) |
Gastroenteritis $ | 6 (3.4) | 4 (2.2) | 2 (1.1) | 0 (0) |
Neoplasms benign, malignant and unspecified (including cysts and polyps) | ||||
Tumor flare $ | 19 (11) | 1 (< 1) | 1 (< 1) | 0 (0) |
Blood and lymphatic disorders | ||||
Neutropenia 3,$, % | 102 (58) | 40 (22) | 88 (50) | 23 (13) |
Leukopenia $,% | 36 (20) | 17 (9) | 12 (7) | 3 (1.7) |
Anemia 3,$ | 28 (16) | 8 (4.4) | 8 (4.5) | 1 (< 1) |
Thrombocytopenia 3,$,% | 26 (15) | 8 (4.4) | 4 (2.3) | 2 (1.1) |
Lymphopenia | 8 (4.5) | 14 (8) | 5 (2.8) | 2 (1.1) |
Febrile Neutropenia 3,$,% | 5 (2.8) | 1 (< 1) | 5 (2.8) | 1 (< 1) |
Metabolism and nutrition disorders | ||||
Decreased Appetite | 23 (13) | 11 (6) | 2 (1.1) | 0 (0) |
Hypokalemia % | 14 (8) | 5 (2.8) | 4 (2.3) | 0 (0) |
Hyperuricemia | 10 (6) | 8 (4.4) | 1 (< 1) | 1 (< 1) |
Nervous system disorders | ||||
Headache | 26 (15) | 17 (9) | 1 (< 1) | 0 (0) |
Dizziness | 15 (9) | 9 (5) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
Vascular disorders | ||||
Hypotension % | 9 (5) | 1 (< 1) | 1 (< 1) | 0 (0) |
Thromboembolic events a,$ | 8 (4.5) | 2 (1.1) | 4 (2.3) | 2 (1.1) |
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | ||||
Cough b | 43 (24) | 35 (19) | 1 (< 1) | 0 (0) |
Dyspnea $ | 19 (11) | 8 (4.4) | 2 (1.1) | 1 (< 1) |
Oropharyngeal pain | 10 (6) | 8 (4.4) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
Pulmonary Embolism 3,$ | 4 (2.3) | 1 (< 1) | 4 (2.3) | 1 (< 1) |
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease $ | 3 (1.7) | 0 (0) | 2 (1.1) | 0 (0) |
Respiratory failure 3,$ | 2 (1.1) | 1 (< 1) | 2 (1.1) | 0 (0) |
Gastrointestinal disorders | ||||
Diarrhea $,% | 55 (31) | 41 (23) | 5 (2.8) | 0 (0) |
Constipation | 46 (26) | 25 (14) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
Abdominal pain c ,$ | 32 (18) | 20 (11) | 2 (1.1) | 0 (0) |
Vomiting $ | 17 (10) | 13 (7) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
Dyspepsia | 16 (9) | 5 (2.8) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
Stomatitis | 9 (5) | 7 (3.9) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||||
Rash $,d | 39 (22) | 14 (8) | 5 (2.8) | 2 (1.1) |
Pruritus $,e | 36 (20) | 9 (5) | 2 (1.1) | 0 (0) |
Dry skin | 9 (5) | 6 (3.3) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
Dermatitis acneiform | 8 (4.5) | 0 (0) | 2 (1.1) | 0 (0) |
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||||
Muscle Spasms | 23 (13) | 9 (5) | 1 (< 1) | 1 (< 1) |
Pain in Extremity $ | 8 (4.5) | 9 (5) | 2 (1) | 0 (0) |
Renal disorders | ||||
Acute Kidney Injury 3,$,@,% | 3 (1.7) | 0 (0) | 2 (1.1) | 0 (0) |
Cardiac disorders | ||||
Supraventricular tachycardia 3,$ | 2 (1.1) | 0 (0) | 2 (1.1) | 0 (0) |
General disorders and administration site conditions | ||||
Fatigue | 38 (22) | 33 (18) | 2 (1.1) | 1 (< 1) |
Pyrexia 3,$ | 37 (21) | 27 (15) | 1 (< 1) | 3 (1.7) |
Asthenia $,% | 24 (14) | 19 (11) | 2 (1.1) | 1 (< 1) |
Edema Peripheral $ | 23 (13) | 16 (9) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
Chills | 14 (8) | 8 (4.4) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
Malaise | 13 (7) | 10 (6) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
Influenza like illness | 9 (5) | 7 (3.9) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
Psychiatric disorders | ||||
Insomnia | 14 (8) | 11 (6) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
Investigations | ||||
Alanine Aminotransferase Increased | 18 (10) | 15 (8) | 3 (1.7) | 1 (< 1) |
WBC count decreased | 16 (9) | 13 (7) | 5 (2.8) | 2 (1.1) |
Lymphocyte count decreased | 12 (7) | 12 (7) | 6 (3.4) | 2 (1.1) |
Blood bilirubin increased | 10 (6) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
Weight Decreased | 12 (7) | 2 (1.1) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse drug reactions have been identified from the worldwide post-marketing experience with REVLIMID. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure [see Warnings and Precautions Section (5.8 to 5.11 , and 5.13) ]
Endocrine disorders: Hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism
Hepatobiliary disorders: Hepatic failure (including fatality), toxic hepatitis, cytolytic hepatitis, cholestatic hepatitis, mixed cytolytic/cholestatic hepatitis, transient abnormal liver laboratory tests
Immune system disorders: Angioedema, anaphylaxis, acute graft-versus-host disease (following allogeneic hematopoietic transplant), solid organ transplant rejection
Infections and infestations: Viral reactivation (such as hepatitis B virus and herpes zoster), progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML)
Neoplasms benign, malignant and unspecified (including cysts and polyps): Tumor lysis syndrome, tumor flare reaction
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: Pneumonitis
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS)
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Digoxin
When digoxin was co-administered with multiple doses of REVLIMID (10 mg/day) the digoxin C max and AUC inf were increased by 14%. Periodically monitor digoxin plasma levels, in accordance with clinical judgment and based on standard clinical practice in patients receiving this medication, during administration of REVLIMID.
Concomitant Therapies That May Increase the Risk of Thrombosis
Erythropoietic agents, or other agents that may increase the risk of thrombosis, such as estrogen containing therapies, should be used with caution after making a benefit-risk assessment in patients receiving REVLIMID [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ] .
Warfarin
Co-administration of multiple doses of REVLIMID (10 mg/day) with a single dose of warfarin (25 mg) had no effect on the pharmacokinetics of lenalidomide or R- and S-warfarin. Expected changes in laboratory assessments of PT and INR were observed after warfarin administration, but these changes were not affected by concomitant REVLIMID administration. It is not known whether there is an interaction between dexamethasone and warfarin. Close monitoring of PT and INR is recommended in patients with MM taking concomitant warfarin.
DESCRIPTION
REVLIMID, a thalidomide analogue, is an immunomodulatory agent with antiangiogenic and antineoplastic properties. The chemical name is 3-(4-amino-1-oxo 1,3-dihydro-2 H -isoindol-2-yl) piperidine-2,6-dione and it has the following chemical structure:
3-(4-amino-1-oxo 1,3-dihydro-2 H -isoindol-2-yl) piperidine-2,6-dione
The empirical formula for lenalidomide is C 13 H 13 N 3 O 3, and the gram molecular weight is 259.3.
Lenalidomide is an off-white to pale-yellow solid powder. It is soluble in organic solvent/water mixtures, and buffered aqueous solvents. Lenalidomide is more soluble in organic solvents and low pH solutions. Solubility was significantly lower in less acidic buffers, ranging from about 0.4 to 0.5 mg/ml. Lenalidomide has an asymmetric carbon atom and can exist as the optically active forms S(-) and R(+), and is produced as a racemic mixture with a net optical rotation of zero.
REVLIMID is available in 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg, 15 mg, 20 mg and 25 mg capsules for oral administration. Each capsule contains lenalidomide as the active ingredient and the following inactive ingredients: lactose anhydrous, microcrystalline cellulose, croscarmellose sodium, and magnesium stearate. The 5 mg and 25 mg capsule shell contains gelatin, titanium dioxide and black ink. The 2.5 mg and 10 mg capsule shell contains gelatin, FD&C blue #2, yellow iron oxide, titanium dioxide and black ink. The 15 mg capsule shell contains gelatin, FD&C blue #2, titanium dioxide and black ink. The 20 mg capsule shell contains gelatin, FD&C blue #2, yellow iron oxide, titanium dioxide and black ink.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Lenalidomide is an analogue of thalidomide with immunomodulatory, antiangiogenic, and antineoplastic properties. Cellular activities of lenalidomide are mediated through its target cereblon, a component of a cullin ring E3 ubiquitin ligase enzyme complex. In vitro, in the presence of drug, substrate proteins (including Aiolos, Ikaros, and CK1α) are targeted for ubiquitination and subsequent degradation leading to direct cytotoxic and immunomodulatory effects. Lenalidomide inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of certain hematopoietic tumor cells including MM, mantle cell lymphoma, and del (5q) myelodysplastic syndromes, follicular lymphoma and marginal zone lymphoma in vitro . Lenalidomide causes a delay in tumor growth in some in vivo nonclinical hematopoietic tumor models including MM. Immunomodulatory properties of lenalidomide include increased number and activation of T cells and natural killer (NK) cells leading to direct and enhanced antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) via increased secretion of interleukin-2 and interferon-gamma, increased numbers of NKT cells, and inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α and IL-6) by monocytes. In MM cells, the combination of lenalidomide and dexamethasone synergizes the inhibition of cell proliferation and the induction of apoptosis. The combination of lenalidomide and rituximab increases ADCC and direct tumor apoptosis in follicular lymphoma cells and increases ADCC in marginal zone lymphoma cells compared to rituximab alone in vitro .
Pharmacodynamics
Cardiac Electrophysiology
The effect of lenalidomide on the QTc interval was evaluated in 60 healthy male subjects in a thorough QT study. At a dose two times the maximum recommended dose, lenalidomide did not prolong the QTc interval. The largest upper bound of the two-sided 90% CI for the mean differences between lenalidomide and placebo was below 10 ms.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Following single and multiple doses of REVLIMID in patients with MM or MDS, the maximum plasma concentrations occurred between 0.5 and 6 hours post-dose. The single and multiple dose pharmacokinetic disposition of lenalidomide is linear with AUC and C max values increasing proportionally with dose. Multiple doses of REVLIMID at the recommended dosage does not result in drug accumulation.
Administration of a single 25 mg dose of REVLIMID with a high-fat meal in healthy subjects reduces the extent of absorption, with an approximate 20% decrease in AUC and 50% decrease in C max . In the trials where the efficacy and safety were established for REVLIMID, the drug was administered without regard to food intake. REVLIMID can be administered with or without food.
The oral absorption rate of lenalidomide in patients with MCL is similar to that observed in patients with MM or MDS.
Distribution
In vitro [ 14 C]-lenalidomide binding to plasma proteins is approximately 30%.
Lenalidomide is present in semen at 2 hours (1379 ng/ejaculate) and 24 hours (35 ng/ejaculate) after the administration of REVLIMID 25 mg daily.
Elimination
The mean half-life of lenalidomide is 3 hours in healthy subjects and 3 to 5 hours in patients with MM, MDS or MCL.
Metabolism
Lenalidomide undergoes limited metabolism. Unchanged lenalidomide is the predominant circulating component in humans. Two identified metabolites are 5-hydroxy-lenalidomide and N-acetyl-lenalidomide; each constitutes less than 5% of parent levels in circulation.
Excretion
Elimination is primarily renal. Following a single oral administration of [ 14 C]-lenalidomide 25 mg to healthy subjects, approximately 90% and 4% of the radioactive dose was eliminated within ten days in urine and feces, respectively. Approximately 82% of the radioactive dose was excreted as lenalidomide in the urine within 24 hours. Hydroxy-lenalidomide and N-acetyl-lenalidomide represented 4.6% and 1.8% of the excreted dose, respectively. The renal clearance of lenalidomide exceeds the glomerular filtration rate.
Specific Populations
Renal Impairment: Eight subjects with mild renal impairment (creatinine clearance (CLcr) 50 to 79 mL/min calculated using Cockcroft-Gault), 9 subjects with moderate renal impairment (CLcr 30 to 49 mL/min), 4 subjects with severe renal impairment (CLcr < 30 mL/min), and 6 patients with end stage renal disease (ESRD) requiring dialysis were administered a single 25 mg dose of REVLIMID. Three healthy subjects of similar age with normal renal function (CLcr > 80 mL/min) were also administered a single 25 mg dose of REVLIMID. As CLcr decreased, half-life increased and drug clearance decreased linearly. Patients with moderate and severe impairment had a 3-fold increase in half-life and a 66% to 75% decrease in drug clearance compared to healthy subjects. Patients on hemodialysis (n=6) had an approximate 4.5-fold increase in half-life and an 80% decrease in drug clearance compared to healthy subjects. Approximately 30% of the drug in body was removed during a 4-hour hemodialysis session.
Adjust the starting dose of REVLIMID in patients with renal impairment based on the CLcr value [see Dosage and Administration (2.6) ] .
Hepatic Impairment: Mild hepatic impairment (defined as total bilirubin > 1 to 1.5 times upper limit normal (ULN) or any aspartate transaminase greater than ULN) did not influence the disposition of lenalidomide. No pharmacokinetic data is available for patients with moderate to severe hepatic impairment.
Other Intrinsic Factors: Age (39 to 85 years), body weight (33 to 135 kg), sex, race, and type of hematological malignancies (MM, MDS or MCL) did not have a clinically relevant effect on lenalidomide clearance in adult patients.
Drug Interactions
Co-administration of a single dose or multiple doses of dexamethasone (40 mg) had no clinically relevant effect on the multiple dose pharmacokinetics of REVLIMID (25 mg).
Co-administration of REVLIMID (25 mg) after multiple doses of a P-gp inhibitor such as quinidine (600 mg twice daily) did not significantly increase the Cmax or AUC of lenalidomide.
Co-administration of the P-gp inhibitor and substrate temsirolimus (25 mg),with REVLIMID (25 mg) did not significantly alter the pharmacokinetics of lenalidomide, temsirolimus, or sirolimus (metabolite of temsirolimus).
In vitro studies demonstrated that REVLIMID is a substrate of P-glycoprotein (P-gp). REVLIMID is not a substrate of human breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP), multidrug resistance protein (MRP) transporters MRP1, MRP2, or MRP3, organic anion transporters (OAT) OAT1 and OAT3, organic anion transporting polypeptide 1B1 (OATP1B1), organic cation transporters (OCT) OCT1 and OCT2, multidrug and toxin extrusion protein (MATE) MATE1, and organic cation transporters novel (OCTN) OCTN1 and OCTN2. Lenalidomide is not an inhibitor of P-gp, bile salt export pump (BSEP), BCRP, MRP2, OAT1, OAT3, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, or OCT2. Lenalidomide does not inhibit or induce CYP450 isoenzymes. Also, lenalidomide does not inhibit bilirubin glucuronidation formation in human liver microsomes with UGT1A1 genotyped as UGT1A1•1/•1, UGT1A1•1/•28, and UGT1A1•28/•28.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies with lenalidomide have not been conducted.
Lenalidomide was not mutagenic in the bacterial reverse mutation assay (Ames test) and did not induce chromosome aberrations in cultured human peripheral blood lymphocytes, or mutations at the thymidine kinase (tk) locus of mouse lymphoma L5178Y cells. Lenalidomide did not increase morphological transformation in Syrian Hamster Embryo assay or induce micronuclei in the polychromatic erythrocytes of the bone marrow of male rats.
A fertility and early embryonic development study in rats, with administration of lenalidomide up to 500 mg/kg (approximately 200 times the human dose of 25 mg, based on body surface area) produced no parental toxicity and no adverse effects on fertility.
CLINICAL STUDIES
Multiple Myeloma
Randomized, Open-Label Clinical Trial in Patients with Newly Diagnosed MM:
A randomized multicenter, open-label, 3-arm trial of 1,623 patients, was conducted to compare the efficacy and safety of REVLIMID and low-dose dexamethasone (Rd) given for 2 different durations of time to that of melphalan, prednisone and thalidomide (MPT) in newly diagnosed MM patients who were not a candidate for stem cell transplant. In the first arm of the study, Rd was given continuously until progressive disease [Arm Rd Continuous]. In the second arm, Rd was given for up to eighteen 28-day cycles [72 weeks, Arm Rd18]). In the third arm, melphalan, prednisone and thalidomide (MPT) was given for a maximum of twelve 42-day cycles (72 weeks). For the purposes of this study, a patient who was < 65 years of age was not a candidate for SCT if the patient refused to undergo SCT therapy or the patient did not have access to SCT due to cost or other reasons. Patients were stratified at randomization by age (≤75 versus >75 years), stage (ISS Stages I and II versus Stage III), and country.
Patients in the Rd Continuous and Rd18 arms received REVLIMID 25 mg once daily on Days 1 to 21 of 28-day cycles. Dexamethasone was dosed 40 mg once daily on Days 1, 8, 15, and 22 of each 28-day cycle. For patients over > 75 years old, the starting dose of dexamethasone was 20 mg orally once daily on days 1,8,15, and 22 of repeated 28-day cycles. Initial dose and regimens for Rd Continuous and Rd18 were adjusted according to age and renal function. All patients received prophylactic anticoagulation with the most commonly used being aspirin.
The demographics and disease-related baseline characteristics of the patients were balanced among the 3 arms. In general, study subjects had advanced-stage disease. Of the total study population, the median age was 73 in the 3 arms with 35% of total patients > 75 years of age; 59% had ISS Stage I/II; 41% had ISS stage III; 9% had severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance [CLcr] < 30 mL/min); 23% had moderate renal impairment (CLcr > 30 to 50 mL/min; 44% had mild renal impairment (CLcr > 50 to 80 mL/min). For ECOG Performance Status, 29% were Grade 0, 49% Grade 1, 21% Grade 2, 0.4% ≥ Grade 3.
The primary efficacy endpoint, progression-free survival (PFS), was defined as the time from randomization to the first documentation of disease progression as determined by Independent Response Adjudication Committee (IRAC), based on International Myeloma Working Group [IMWG] criteria or death due to any cause, whichever occurred first during the study until the end of the PFS follow-up phase. For the efficacy analysis of all endpoints, the primary comparison was between Rd Continuous and MPT arms. The efficacy results are summarized in the table below. PFS was significantly longer with Rd Continuous than MPT: HR 0.72 (95% CI: 0.61-0.85 p <0.0001). A lower percentage of subjects in the Rd Continuous arm compared with the MPT arm had PFS events (52% versus 61%, respectively). The improvement in median PFS time in the Rd Continuous arm compared with the MPT arm was 4.3 months. The myeloma response rate was higher with Rd Continuous compared with MPT (75.1% versus 62.3%); with a complete response in 15.1% of Rd Continuous arm patients versus 9.3% in the MPT arm. The median time to first response was 1.8 months in the Rd Continuous arm versus 2.8 months in the MPT arm.
For the interim OS analysis with 03 March 2014 data cutoff, the median follow-up time for all surviving patients is 45.5 months, with 697 death events, representing 78% of prespecified events required for the planned final OS analysis (697/896 of the final OS events). The observed OS HR was 0.75 for Rd Continuous versus MPT (95% CI = 0.62, 0.90).
| CR = complete response; d = low-dose dexamethasone; HR = hazard ratio; IRAC = Independent Response Adjudication Committee; M = melphalan; NE = not estimable; OS = overall survival; P = prednisone; PFS = progression-free survival; PR = partial response; R = REVLIMID; Rd Continuous = Rd given until documentation of progressive disease; Rd18 = Rd given for ≤ 18 cycles; T = thalidomide; VGPR = very good partial response; vs = versus. a The median is based on the Kaplan-Meier estimate. b The 95% Confidence Interval (CI) about the median. c Based on Cox proportional hazards model comparing the hazard functions associated with the indicated treatment arms. d The p-value is based on the unstratified log-rank test of Kaplan-Meier curve differences between the indicated treatment arms. e Best assessment of response during the treatment phase of the study. f Including patients with no response assessment data or whose only assessment was "response not evaluable." g Data cutoff date = 24 May 2013. h Data cutoff date = 3 March 2014. | |||
Rd Continuous (N = 535) | Rd18 (N = 541) | MPT (N = 547) | |
PFS – IRAC (months) g | |||
Number of PFS events | 278 (52) | 348 (64.3) | 334 (61.1) |
Median a PFS time, months (95% CI) b | 25.5 (20.7, 29.4) | 20.7 (19.4, 22) | 21.2 (19.3, 23.2) |
HR [95% CI] c ; p-value d | |||
Rd Continuous vs MPT | 0.72 (0.61, 0.85); <0.0001 | ||
Rd Continuous vs Rd18 | 0.70 (0.60, 0.82) | ||
Rd18 vs MPT | 1.03 (0.89, 1.20) | ||
Overall Survival (months) h | |||
Number of Death events | 208 (38.9) | 228 (42.1) | 261 (47.7) |
Median a OS time, months (95% CI) b | 58.9 (56, NE) f | 56.7 (50.1, NE) | 48.5 (44.2, 52 ) |
HR [95% CI] c | |||
Rd Continuous vs MPT | 0.75 (0.62, 0.90) | ||
Rd Continuous vs Rd18 | 0.91 (0.75, 1.09) | ||
Rd18 vs MPT | 0.83 (0.69, 0.99) | ||
Response Rate e – IRAC, n (%) g | |||
CR | 81 (15.1) | 77 (14.2) | 51 (9.3) |
VGPR | 152 (28.4) | 154 (28.5) | 103 (18.8) |
PR | 169 (31.6) | 166 (30.7) | 187 (34.2) |
Overall response: CR, VGPR, or PR | 402 (75.1) | 397 (73.4) | 341 (62.3) |
Kaplan-Meier Curves of Progression-free Survival Based on IRAC Assessment (ITT MM Population) Between Arms Rd Continuous, Rd18 and MPT Cutoff date: 24 May 2013
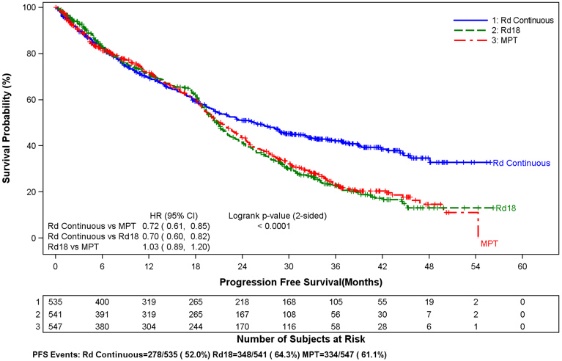
CI = confidence interval; d = low-dose dexamethasone; HR = hazard ratio; IRAC = Independent Response Adjudication Committee; M = melphalan; P = prednisone; R = REVLIMID; Rd Continuous = Rd given until documentation of progressive disease; Rd18 = Rd given for ≤ 18 cycles; T = thalidomide.
Kaplan-Meier Curves of Overall Survival (ITT MM Population) Between Arms Rd Continuous, Rd18 and MPT Cutoff date: 03 Mar 2014
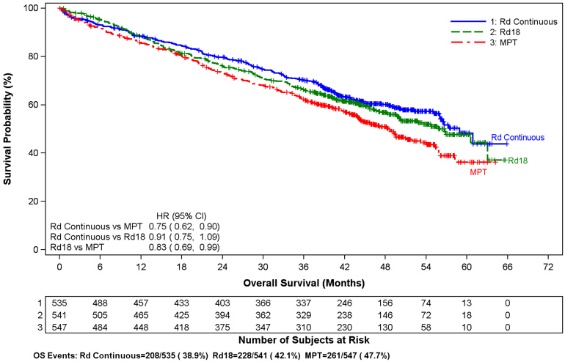
CI = confidence interval; d = low-dose dexamethasone; HR = hazard ratio; M = melphalan; P = prednisone; R = REVLIMID; Rd Continuous = Rd given until documentation of progressive disease; Rd18 = Rd given for ≤18 cycles; T = thalidomide.
Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials - Maintenance Following Auto-HSCT:
Two multicenter, randomized, double-blind, parallel group, placebo-controlled studies were conducted to evaluate the efficacy and safety of REVLIMID maintenance therapy in the treatment of MM patients after auto-HSCT. In Maintenance Study 1, patients between 18 and 70 years of age who had undergone induction therapy followed by auto-HSCT were eligible. Induction therapy must have occurred within 12 months. Within 90-100 days after auto-HSCT, patients with at least a stable disease response were randomized 1:1 to receive either REVLIMID or placebo maintenance. In Maintenance Study 2, patients aged < 65 years at diagnosis who had undergone induction therapy followed by auto-HSCT and had achieved at least a stable disease response at the time of hematologic recovery were eligible. Within 6 months after auto-HSCT, patients were randomized 1:1 to receive either REVLIMID or placebo maintenance. Patients eligible for both trials had to have CLcr ≥30 mL/minute.
In both studies, the REVLIMID maintenance dose was 10 mg once daily on days 1-28 of repeated 28-day cycles, could be increased to 15 mg once daily after 3 months in the absence of dose-limiting toxicity, and treatment was to be continued until disease progression or patient withdrawal for another reason. The dose was reduced, or treatment was temporarily interrupted or stopped, as needed to manage toxicity. A dose increase to 15 mg once daily occurred in 135 patients (58%) in Maintenance Study 1, and in 185 patients (60%) in Maintenance Study 2.
The demographics and disease-related baseline characteristics of the patients were similar across the two studies and reflected a typical MM population after auto-HSCT (see Table 14 ).
| Data cutoff date = 1 March 2015. | ||||
Maintenance Study 1 | Maintenance Study 2 | |||
REVLIMID N = 231 | Placebo N = 229 | REVLIMID N = 307 | Placebo N = 307 | |
Age (years) | ||||
Median | 58 | 58 | 57.5 | 58.1 |
(Min, max) | (29, 71) | (39, 71) | (22.7, 68.3) | (32.3, 67) |
Sex, n (%) | ||||
Male | 121 (52) | 129 (56) | 169 (55) | 181 (59) |
Female | 110 (48) | 100 (44) | 138 (45) | 126 (41) |
ISS Stage at Diagnosis, n (%) | ||||
Stage I or II | 120 (52) | 131 (57) | 232 (76) | 250 (81) |
Stage I | 62 (27) | 85 (37) | 128 (42) | 143 (47) |
Stage II | 58 (25) | 46 (20) | 104 (34) | 107 (35) |
Stage III | 39 (17) | 35 (15) | 66 (21) | 46 (15) |
Missing | 72 (31) | 63 (28) | 9 (3) | 11 (4) |
CrCl at Post-auto-HSCT, n (%) | ||||
< 50 mL/min | 23 (10) | 16 (7) | 10 (3) | 9 (3) |
≥ 50 mL/min | 201 (87) | 204 (89) | 178 (58) | 200 (65) |
Missing | 7 (3) | 9 (4) | 119 (39) | 98 (32) |
The major efficacy endpoint of both studies was PFS defined from randomization to the date of progression or death, whichever occurred first; the individual studies were not powered for an overall survival endpoint. Both studies were unblinded upon the recommendations of their respective data monitoring committees and after surpassing the respective thresholds for preplanned interim analyses of PFS. After unblinding, patients continued to be followed as before. Patients in the placebo arm of Maintenance Study 1 were allowed to cross over to receive REVLIMID before disease progression (76 patients [33%] crossed over to REVLIMID); patients in Maintenance Study 2 were not recommended to cross over. The efficacy results are summarized in the following table. In both studies, the primary analysis of PFS at unblinding was significantly longer with REVLIMID compared to placebo: Maintenance Study 1 HR 0.38 (95% CI: 0.27-0.54 p <0.001) and Maintenance Study 2 HR 0.50 (95% CI: 0.39-0.64 p <0.001). For both studies, PFS was updated with a cutoff date of 1 March 2015 as shown in the table and the following Kaplan Meier graphs. With longer follow-up (median 72.4 and 86.0 months, respectively), the updated PFS analyses for both studies continue to show a PFS advantage for REVLIMID compared to placebo: Maintenance Study 1 HR 0.38 (95% CI: 0.28-0.50) with median PFS of 68.6 months and Maintenance Study 2 HR 0.53 (95% CI: 0.44-0.64) with median PFS of 46.3 months.
Descriptive analysis of OS data with a cutoff date of 1 February 2016 are provided in Table 15. Median follow-up time was 81.6 and 96.7 months for Maintenance Study 1 and Maintenance Study 2, respectively. Median OS was 111.0 and 84.2 months for REVLIMID and placebo, respectively, for Maintenance Study 1, and 105.9 and 88.1 months, for REVLIMID and placebo, respectively, for Maintenance Study 2.
| Date of Unblinding in Maintenance Study 1 and 2 = 17 December 2009 and 7 July 2010, respectively. Auto-HSCT = autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; CI = confidence interval; ITT = intent to treat; NE = not estimable; PFS = progression-free survival. PFS at time of unblinding for Maintenance Study 2 was based on assessment by an Independent Review Committee. All other PFS analyses were based on assessment by investigator. Note: The median is based on Kaplan-Meier estimate, with 95% CIs about the median overall PFS time. Hazard ratio is based on a proportional hazards model stratified by stratification factors comparing the hazard functions associated with treatment arms (REVLIMID:placebo). | ||||
Maintenance Study 1 | Maintenance Study 2 | |||
REVLIMID N = 231 | Placebo N = 229 | REVLIMID N = 307 | Placebo N = 307 | |
PFS at Unblinding | ||||
PFS Events n (%) | 46 (20) | 98 (43) | 103 (34) | 160 (52) |
Median in months [95% CI] | 33.9 [NE, NE] | 19 [16.2, 25.6] | 41.2 [38.3, NE] | 23.0 [21.2, 28.0] |
Hazard Ratio [95% CI] | 0.38 [0.27, 0.54] | 0.50 [0.39, 0.64] | ||
Log-rank Test p-value | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
PFS at Updated Analysis 1 March 2015 (Studies 1 and 2) | ||||
PFS Events n (%) | 97 (42) | 116 (51) | 191 (62) | 248 (81) |
Median in months [95% CI] | 68.6 [52.8, NE] | 22.5 [18.8, 30.0] | 46.3 [40.1, 56.6] | 23.8 [21.0, 27.3] |
Hazard Ratio [95% CI] | 0.38 [0.28, 0.50] | 0.53 [0.44, 0.64] | ||
OS at Updated Analysis 1 Feb 2016 (Studies 1 and 2) | ||||
OS Events n (%) | 82 (35) | 114 (50) | 143 (47) | 160 (52) |
Median in months [95% CI] | 111 [101.8, NE] | 84.2 [71.0, 102.7] | 105.9 [88.8, NE] | 88.1 [80.7, 108.4] |
Hazard Ratio [95% CI] | 0.59 [0.44, 0.78] | 0.90 [0.72, 1.13] | ||
Kaplan-Meier Curves of Progression-free Survival from Randomization (ITT Post-Auto-HSCT Population) in MM Maintenance Study 1 between REVLIMID and Placebo Arms (Updated Cutoff Date 1 March 2015)
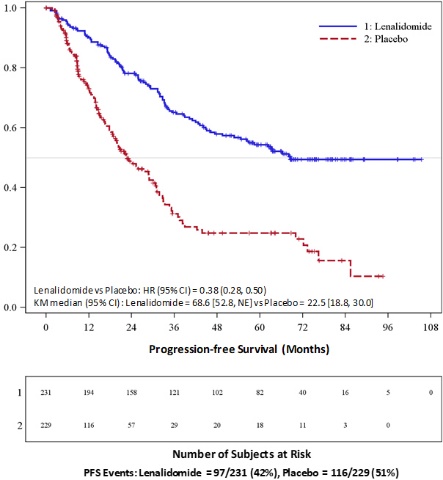
Auto-HSCT = autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; CI = confidence interval; HR = hazard ratio; ITT = intent to treat; KM = Kaplan-Meier; PFS = progression-free survival; vs = versus.
Kaplan-Meier Curves of Progression-free Survival from Randomization (ITT Post-Auto-HSCT Population) in MM Maintenance Study 2 between REVLIMID and Placebo Arms (Updated Cutoff Date 1 March 2015)
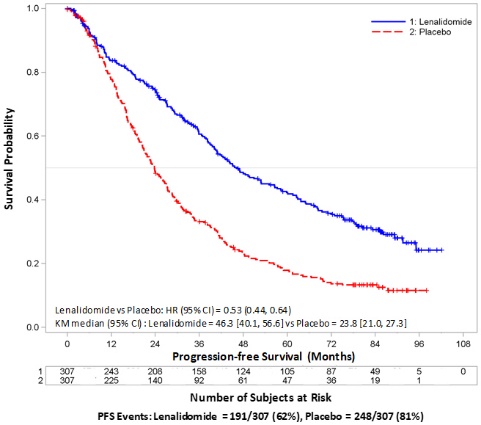
Auto-HSCT = autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; CI = confidence interval; HR = hazard ratio; ITT = intent to treat; KM = Kaplan-Meier; NE = not estimable; PFS = progression-free survival; vs = versus.
Randomized, Open-Label Clinical Studies in Patients with MM After At Least One Prior Therapy
Two randomized studies (Studies 1 and 2) were conducted to evaluate the efficacy and safety of REVLIMID. These multicenter, multinational, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies compared REVLIMID plus oral pulse high-dose dexamethasone therapy to dexamethasone therapy alone in patients with MM who had received at least one prior treatment. These studies enrolled patients with absolute neutrophil counts (ANC) ≥ 1000/mm 3 , platelet counts ≥ 75,000/mm 3 , serum creatinine ≤ 2.5 mg/dL, serum SGOT/AST or SGPT/ALT ≤ 3 x upper limit of normal (ULN), and serum direct bilirubin ≤ 2 mg/dL.
In both studies, patients in the REVLIMID/dexamethasone group took 25 mg of REVLIMID orally once daily on Days 1 to 21 and a matching placebo capsule once daily on Days 22 to 28 of each 28-day cycle. Patients in the placebo/dexamethasone group took 1 placebo capsule on Days 1 to 28 of each 28-day cycle. Patients in both treatment groups took 40 mg of dexamethasone orally once daily on Days 1 to 4, 9 to 12, and 17 to 20 of each 28-day cycle for the first 4 cycles of therapy.
The dose of dexamethasone was reduced to 40 mg orally once daily on Days 1 to 4 of each 28-day cycle after the first 4 cycles of therapy. In both studies, treatment was to continue until disease progression.
In both studies, dose adjustments were allowed based on clinical and laboratory findings. Sequential dose reductions to 15 mg daily, 10 mg daily and 5 mg daily were allowed for toxicity [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) ].
Table 16 summarizes the baseline patient and disease characteristics in the two studies. In both studies, baseline demographic and disease-related characteristics were comparable between the REVLIMID/dexamethasone and placebo/dexamethasone groups.
Study 1 | Study 2 | |||
REVLIMID/Dex N=177 | Placebo/Dex N=176 | REVLIMID/Dex N=176 | Placebo/Dex N=175 | |
Patient Characteristics | ||||
Age (years) | ||||
Median | 64 | 62 | 63 | 64 |
Min, Max | 36, 86 | 37, 85 | 33, 84 | 40, 82 |
Sex | ||||
Male | 106 (60%) | 104 (59%) | 104 (59%) | 103 (59%) |
Female | 71 (40%) | 72 (41%) | 72 (41%) | 72 (41%) |
Race/Ethnicity | ||||
White | 141(80%) | 148 (84%) | 172 (98%) | 175 (100%) |
Other | 36 (20%) | 28 (16%) | 4 (2%) | 0 (0%) |
ECOG Performance | ||||
Status 0-1 | 157 (89%) | 168 (95%) | 150 (85%) | 144 (82%) |
Disease Characteristics | ||||
Multiple Myeloma Stage (Durie-Salmon) | ||||
I | 3% | 3% | 6% | 5% |
II | 32% | 31% | 28% | 33% |
III | 64% | 66% | 65% | 63% |
β2-microglobulin (mg/L) | ||||
≤ 2.5 mg/L | 52 (29%) | 51 (29%) | 51 (29%) | 48 (27%) |
> 2.5 mg/L | 125 (71%) | 125 (71%) | 125 (71%) | 127 (73%) |
Number of Prior Therapies | ||||
1 | 38% | 38% | 32% | 33% |
≥ 2 | 62% | 62% | 68% | 67% |
Types of Prior Therapies | ||||
Stem Cell Transplantation | 62% | 61% | 55% | 54% |
Thalidomide | 42% | 46% | 30% | 38% |
Dexamethasone | 81% | 71% | 66% | 69% |
Bortezomib | 11% | 11% | 5% | 4% |
Melphalan | 33% | 31% | 56% | 52% |
Doxorubicin | 55% | 51% | 56% | 57% |
The primary efficacy endpoint in both studies was time to progression (TTP). TTP was defined as the time from randomization to the first occurrence of progressive disease.
Preplanned interim analyses of both studies showed that the combination of REVLIMID/dexamethasone was significantly superior to dexamethasone alone for TTP. The studies were unblinded to allow patients in the placebo/dexamethasone group to receive treatment with the REVLIMID/dexamethasone combination. For both studies, the extended follow-up survival data with crossovers were analyzed. In study 1, the median survival time was 39.4 months (95%CI: 32.9, 47.4) in REVLIMID/dexamethasone group and 31.6 months (95% CI: 24.1, 40.9) in placebo/dexamethasone group, with a hazard ratio of 0.79 (95% CI: 0.61-1.03). In study 2, the median survival time was 37.5 months (95%CI: 29.9, 46.6) in REVLIMID/dexamethasone group and 30.8 months (95%CI: 23.5, 40.3) in placebo/dexamethasone group, with a hazard ratio of 0.86 (95% CI: 0.65-1.14).
Study 1 | Study 2 | |||
REVLIMID/Dex N=177 | Placebo/Dex N=176 | REVLIMID/Dex N=176 | Placebo/Dex N=175 | |
TTP | ||||
Events n (%) | 73 (41) | 120 (68) | 68 (39) | 130 (74) |
Median TTP in months [95% CI] | 13.9 [9.5, 18.5] | 4.7 [3.7, 4.9] | 12.1 [9.5, NE] | 4.7 [3.8, 4.8] |
Hazard Ratio [95% CI] | 0.285 [0.210, 0.386] | 0.324 [0.240, 0.438] | ||
Log-rank Test p-value 3 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
Response | ||||
Complete Response (CR) n (%) | 23 (13) | 1 (1) | 27 (15) | 7 (4) |
Partial Response (RR/PR) n (%) | 84 (48) | 33 (19) | 77 (44) | 34 (19) |
Overall Response n (%) | 107 (61) | 34 (19) | 104 (59) | 41 (23) |
p-value | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
Odds Ratio [95% CI] | 6.38 [3.95, 10.32] | 4.72 [2.98, 7.49] | ||
Kaplan-Meier Estimate of Time to Progression — MM Study 1
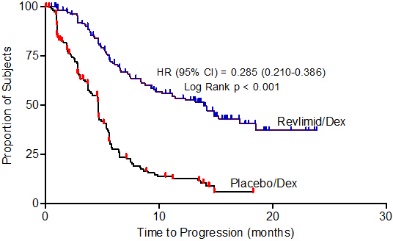
Kaplan-Meier Estimate of Time to Progression — MM Study 2
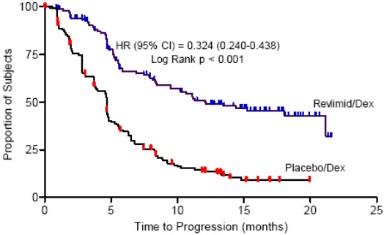
Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS) with a Deletion 5q Cytogenetic Abnormality
The efficacy and safety of REVLIMID were evaluated in patients with transfusion-dependent anemia in low- or intermediate-1- risk MDS with a 5q (q31-33) cytogenetic abnormality in isolation or with additional cytogenetic abnormalities, at a dose of 10 mg once daily or 10 mg once daily for 21 days every 28 days in an open-label, single-arm, multi-center study. The major study was not designed nor powered to prospectively compare the efficacy of the 2 dosing regimens. Sequential dose reductions to 5 mg daily and 5 mg every other day, as well as dose delays, were allowed for toxicity [Dosage and Administration (2.2)] .
This major study enrolled 148 patients who had RBC transfusion dependent anemia. RBC transfusion dependence was defined as having received ≥ 2 units of RBCs within 8 weeks prior to study treatment. The study enrolled patients with absolute neutrophil counts (ANC) ≥ 500/mm 3 , platelet counts ≥ 50,000/mm 3 , serum creatinine ≤ 2.5 mg/dL, serum SGOT/AST or SGPT/ALT ≤ 3 x upper limit of normal (ULN), and serum direct bilirubin ≤ 2 mg/dL. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor was permitted for patients who developed neutropenia or fever in association with neutropenia. Baseline patient and disease-related characteristics are summarized in Table 18.
| a IPSS Risk Category: Low (combined score = 0), Intermediate-1 (combined score = 0.5 to 1), Intermediate-2 (combined score = 1.5 to 2.0), High (combined score ≥ 2.5); Combined score = (Marrow blast score + Karyotype score + Cytopenia score). b French-American-British (FAB) classification of MDS. | ||
Overall (N=148) | ||
Age (years) | ||
Median | 71 | |
Min, Max | 37, 95 | |
Gender | n | (%) |
Male | 51 | (34.5) |
Female | 97 | (65.5) |
Race | n | (%) |
White | 143 | (96.6) |
Other | 5 | ( 3.4) |
Duration of MDS (years) | ||
Median | 2.5 | |
Min, Max | 0.1, 20.7 | |
Del 5 (q31-33) Cytogenetic Abnormality | n | (%) |
Yes | 148 | (100) |
Other cytogenetic abnormalities | 37 | (25.2) |
IPSS Score a | n | (%) |
Low (0) | 55 | (37.2) |
Intermediate-1 (0.5-1.0) | 65 | (43.9) |
Intermediate-2 (1.5-2.0) | 6 | ( 4.1) |
High (≥2.5) | 2 | ( 1.4) |
Missing | 20 | (13.5) |
FAB Classification b from central review | n | (%) |
RA | 77 | (52) |
RARS | 16 | (10.8) |
RAEB | 30 | (20.3) |
CMML | 3 | ( 2) |
The frequency of RBC transfusion independence was assessed using criteria modified from the International Working Group (IWG) response criteria for MDS. RBC transfusion independence was defined as the absence of any RBC transfusion during any consecutive "rolling" 56 days (8 weeks) during the treatment period.
Transfusion independence was seen in 99/148 (67%) patients (95% CI [59, 74]). The median duration from the date when RBC transfusion independence was first declared (i.e., the last day of the 56-day RBC transfusion-free period) to the date when an additional transfusion was received after the 56-day transfusion-free period among the 99 responders was 44 weeks (range of 0 to >67 weeks). Ninety percent of patients who achieved a transfusion benefit did so by completion of three months in the study.
RBC transfusion independence rates were unaffected by age or gender.
The dose of REVLIMID was reduced or interrupted at least once due to an adverse event in 118 (79.7%) of the 148 patients; the median time to the first dose reduction or interruption was 21 days (mean, 35.1 days; range, 2-253 days), and the median duration of the first dose interruption was 22 days (mean, 28.5 days; range, 2-265 days). A second dose reduction or interruption due to adverse events was required in 50 (33.8%) of the 148 patients. The median interval between the first and second dose reduction or interruption was 51 days (mean, 59.7 days; range, 15-205 days) and the median duration of the second dose interruption was 21 days (mean, 26 days; range, 2-148 days).
Mantle Cell Lymphoma
A multicenter, single-arm, open-label trial of single-agent REVLIMID was conducted to evaluate the safety and efficacy of REVLIMID in patients with mantle cell lymphoma who have relapsed after or were refractory to bortezomib or a bortezomib-containing regimen. Patients with a creatinine clearance ≥60 mL/min were given REVLIMID at a dose of 25 mg once daily for 21 days every 28 days. Patients with a creatinine clearance ≥30 mL/min and <60 mL/min were given REVLIMID at a dose of 10 mg once daily for 21 days every 28 days. Treatment was continued until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or withdrawal of consent.
The trial included patients who were at least 18 years of age with biopsy-proven MCL with measurable disease by CT scan. Patients were required to have received prior treatment with an anthracycline or mitoxantrone, cyclophosphamide, rituximab, and bortezomib, alone or in combination. Patients were required to have documented refractory disease (defined as without any response of PR or better during treatment with bortezomib or a bortezomib-containing regimen), or relapsed disease (defined as progression within one year after treatment with bortezomib or a bortezomib-containing regimen). At enrollment patients were to have an absolute neutrophil counts (ANC) ≥1500/ mm 3 , platelet counts ≥ 60,000/mm 3 , serum SGOT/AST or SGPT/ALT ≤3 x upper limit of normal (ULN) unless there was documented evidence of liver involvement by lymphoma, serum total bilirubin ≤1.5 x ULN except in cases of Gilbert's syndrome or documented liver involvement by lymphoma, and calculated creatinine clearance (Cockcroft-Gault formula) ≥30 mL/min.
The median age was 67 years (43-83), 81% were male and 96% were Caucasian. The table below summarizes the baseline disease-related characteristics and prior anti-lymphoma therapy in the Mantle Cell Lymphoma trial.
| a ECOG = Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. b MIPI = MCL International Prognostic Index. c High tumor burden is defined as at least one lesion that is ≥5 cm in diameter or 3 lesions that are ≥3 cm in diameter. d Bulky disease is defined as at least one lesion that is ≥7cm in the longest diameter. | |
Baseline Disease Characteristics and Prior Anti -Lymphoma Treatment | Total Patients (N=134) |
ECOG Performance Status a n (%) | |
0 | 43 (32) |
1 | 73 (54) |
2 | 17 (13) |
3 | 1 (<1) |
Advanced MCL Stage, n (%) | |
III | 27 (20) |
IV | 97 (72) |
High or Intermediate MIPI Score b , n (%) | 90 (67) |
High Tumor Burden c , n (%) | 77 (57) |
Bulky Disease d , n (%) | 44 (33) |
Extranodal Disease, n (%) | 101 (75) |
Number of Prior Systemic Anti-Lymphoma Therapies, n (%) | |
Median (range) | 4 (2, 10) |
1 | 0 (0) |
2 | 29 (22) |
3 | 34 (25) |
≥ 4 | 71 (53) |
Number of Subjects Who Received Prior Regimen Containing, n (%): | |
Anthracycline/mitoxantrone | 133 (99) |
Cyclophosphamide | 133 (99) |
Rituximab | 134 (100) |
Bortezomib | 134 (100) |
Refractory to Prior Bortezomib, n (%) | 81 (60) |
Refractory to Last Prior Therapy, n (%) | 74 (55) |
Prior Autologous Bone Marrow or Stem Cell Transplant, n (%) | 39 (29) |
The efficacy endpoints in the MCL trial were overall response rate (ORR) and duration of response (DOR). Response was determined based on review of radiographic scans by an independent review committee according to a modified version of the International Workshop Lymphoma Response Criteria (Cheson, 1999). The DOR is defined as the time from the initial response (at least PR) to documented disease progression. The efficacy results for the MCL population were based on all evaluable patients who received at least one dose of study drug and are presented in Table 20. The median time to response was 2.2 months (range 1.8 to 13 months).
Response Analyses (N = 133) | N (%) | 95% CI | |
Overall Response Rate (IWRC) (CR + CRu +PR) | 34 (26) | (18.4, 33.9) | |
Complete Response (CR + CRu) | 9 (7) | (3.1, 12.5) | |
CR | 1 (1) | ||
CRu | 8 (6) | ||
Partial Response (PR) | 25 (19) | ||
Duration of Response (months) | Median | 95% CI | |
Duration of Overall Response (CR + CRu + PR) | (N = 34) | 16.6 | (7.7, 26.7) |
Follicular and Marginal Zone Lymphoma
The efficacy of REVLIMID with rituximab in patients with relapsed or refractory follicular and marginal zone lymphoma was evaluated in the AUGMENT (NCT01938001) and MAGNIFY (NCT01996865) trials.
AUGMENT is a randomized, double-blind, multicenter trial (n=358) in which patients with relapsed or refractory follicular or marginal zone lymphoma were randomized 1:1 to receive REVLIMID and rituximab or rituximab and placebo. AUGMENT included patients diagnosed with Grade 1, 2, or 3a follicular lymphoma, who received at least 1 prior systemic therapy, were refractory or relapsed, not rituximab-refractory, had at least one measurable nodal or extranodal lesion by CT or MRI scan, and had adequate bone marrow, liver, and renal function. Randomization was stratified by follicular versus marginal zone lymphoma, previous rituximab therapy, and time since other anti-lymphoma therapy. In AUGMENT, REVLIMID was administered orally 20 mg once daily for Days 1 to 21 of repeating 28-day cycles for a maximum of 12 cycles or until unacceptable toxicity. The dose of rituximab was 375 mg/m 2 every week in Cycle 1 (Days 1, 8, 15, and 22) and on Day 1 of every 28-day cycle from Cycles 2 through 5. All dosage calculations for rituximab were based on the patient's body surface area (BSA), using actual patient weight. Dose adjustments for REVLIMID were allowed based on clinical and laboratory findings. A patient with moderate renal insufficiency (≥30 to <60 mL/minute) received a lower REVLIMID starting dose of 10 mg daily on the same schedule. After 2 cycles, the REVLIMID dose could be increased to 15 mg once daily on Days 1 to 21 of each 28-day cycle if the patient tolerated the medication.
MAGNIFY is an open-label, multicenter trial (n=232) in which patients with relapsed or refractory follicular, marginal zone, or mantle cell lymphoma received 12 induction cycles of REVLIMID and rituximab. MAGNIFY included patients diagnosed with Grade 1, 2,3a, 3b follicular (including transformed), marginal zone, or mantle cell lymphoma Stage I to IV who were previously treated for their lymphoma, had been refractory or had a relapse after their last treatment, had at least one measurable nodal or extranodal lesion by CT or MRI scan, and had adequate bone marrow, liver, and renal function. Patients refractory to rituximab were also included. The information from the subjects who received at least 1 dose of initial therapy in the first 12 induction cycles (n=222) in the MAGNIFY trial was included in the evaluation of the efficacy of REVLIMID/rituximab in patients with relapsed or refractory follicular and marginal zone lymphoma. In MAGNIFY, REVLIMID 20 mg was given on Days 1-21 of repeated 28-day cycles for up to 12 cycles or until unacceptable toxicity, progression, or withdrawal of consent. The dose of rituximab was 375 mg/m 2 every week in Cycle 1 (Days 1, 8, 15, and 22) and on Day 1 of every other 28-day cycle (Cycles 3,5,7,9, and 11) up to 12 cycles therapy. All dosage calculations for rituximab were based on the patient BSA and actual weight. Dose adjustments were allowed based on clinical and laboratory findings.
The demographic and disease-related baseline characteristics in the AUGMENT and MAGNIFY trials are shown in the following table.
| Data Cutoff: 22 June 2018 (AUGMENT) and 1 May 2017 (MAGNIFY). a Defined by GELF criteria. b Patient had either 0 (n=2) or 1 prior systemic therapy. ECOG = Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group; FLIPI = follicular lymphoma international prognostic index | |||
Parameter | AUGMENT Trial | MAGNIFY Trial | |
REVLIMID + Rituximab (N=178) | Rituximab + Placebo (Control Arm) (N=180) | REVLIMID + Rituximab (N=222) | |
Age (years) | |||
Median (Max, Min) | 64 (26, 86) | 62 (35, 88) | 65 (35, 91) |
Age distribution, n (%) | |||
<65 years | 96 (54) | 107 (59) | 103 (46) |
≥65 years | 82 (46) | 73 (41) | 119 (54) |
Sex, n (%) | |||
Male | 75 (42) | 97 (54) | 122 (55) |
Female | 103 (58) | 83 (46) | 100 (45) |
Race | |||
White | 118 (66) | 115 (64) | 206 (93) |
Other races | 54 (30) | 64 (36) | 14 (6) |
Not collected or reported | 6 (3) | 1 (0.6) | 2 (1) |
Body Surface Area (BSA, m 2 ) | |||
Median (Max, Min) | 1.8 (1.4, 3.1) | 1.8 (1.3, 2.7) | 2 (1.3, 2.6) |
Disease Type FL or MZL | |||
Follicular lymphoma | 147 (83) | 148 (82) | 177 (80) |
Marginal zone lymphoma | 31 (17) | 32 (18) | 45 (20) |
MZL subtype at diagnosis (investigator), n (%) | |||
MALT | 14 (45) | 16 (50) | 10 (22) |
Nodal | 8 (26) | 10 (31) | 25 (56) |
Splenic | 9 (29) | 6 (19) | 10 (22) |
FL stage at diagnosis (investigator), n (%) | |||
FL Grade 1-2 | 125 (85) | 123 (83) | 149 (84) |
FL Grade 3a | 22 (15) | 25 (17) | 28 (16) |
FLIPI score at baseline (calculated), n (%) | Not Collected | ||
Low risk (0,1) | 52 (29) | 67 (37) | |
Intermediate risk (2) | 55 (31) | 58 (32) | |
High risk (≥3) | 69 (39) | 54 (30) | |
Missing | 2 (1) | 1 (0.6) | |
ECOG score at baseline, n (%) | |||
0 | 116 (65) | 128 (71) | 102 (46) |
1 | 60 (34) | 50 (28) | 113 (51) |
2 | 2 (1) | 2 (1) | 7 (3) |
High tumor burden a at baseline, n (%) | |||
Yes | 97 (54) | 86 (48) | 148 (67) |
No | 81 (46) | 94 (52) | 74 (33) |
Number of prior systemic antilymphoma therapies | |||
1 | 102 (57) | 97 (54) | 94 (42) b |
>1 | 76 (43) | 83 (46) | 128 (58) |
In AUGMENT, efficacy was established in the intent-to-treat (ITT) population based on progression-free survival by Independent Review Committee using modified 2007 International Working Group response criteria. Efficacy results are summarized in Table 22.
| a Median estimate is from Kaplan-Meier analysis. b hazard ratio and its CI were estimated from Cox proportional hazard model adjusting for the stratification 3: previous rituximab treatment (yes, no), time since last antilymphoma therapy (≤ 2, > 2 years), and disease histology (FL, MZL). c p-value from log-rank test stratified by 3 factors noted above: previous rituximab treatment (yes, no), time since last antilymphoma therapy (≤ 2, > 2 years), and disease histology (FL, MZL). d Exact confidence interval for binomial distribution. | ||
Parameter | REVLIMID + Rituximab (N=178) | Rituximab + Placebo (N=180) |
PFS | ||
Patients with event, n (%) | 68 (38.2) | 115 (63.9) |
Death | 6 (8.8) | 2 (1.7) |
Progression of disease | 62 (91.2) | 113 (98.3) |
PFS, median a [95% CI] (months) | 39.4 [ 22.9, NE] | 14.1 [11.4, 16.7] |
HR b [95% CI] | 0.46 [ 0.34, 0.62] | |
p-value c | <0.0001 | |
Objective response (CR+PR) , n(%) [95% CI] d | 138 (77.5) [70.7, 83.4] | 96 (53.3) [45.8, 60.8] |
Kaplan-Meier Curves of Progression-free Survival by IRC Assessment Between Arms in AUGMENT Trial (ITT FL and MZL Population)
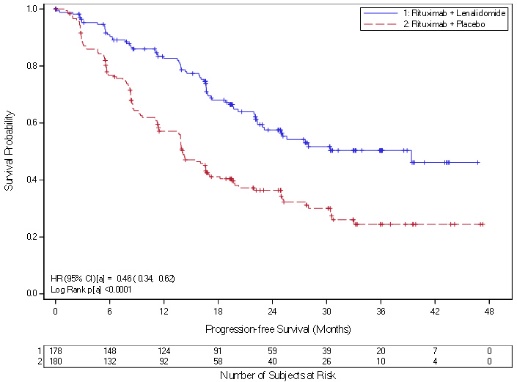
a = Stratification factors included: previous rituximab treatment (y/n), time since last anti-lymphoma therapy (≤2 years, >2years), and disease histology (FL or MZL). CI = confidence interval; HR = hazard ratio; KM = Kaplan-Meier; PFS = progression-free survival
Follicular Lymphoma
In AUGMENT, the objective response by IRC assessment for patients with follicular lymphoma was 80% (118/147) [95% CI: 73%, 86%]) in REVLIMID with rituximab arm compared to 55% (82/148) [95% CI: 47, 64] in control arm.
In MAGNIFY, the overall response by investigator assessment was 59% (104/177) [95% CI: 51, 66] for patients with follicular lymphoma. Median duration of response was not reached with a median follow-up time of 7.9 months [95% CI: 4.6, 9.2].
Marginal Zone Lymphoma
In AUGMENT, the objective response by IRC assessment for patients with marginal zone lymphoma was 65% (20/31) [95% CI: 45%, 81%] in REVLIMID with rituximab arm compared to 44% (14/32) [95% CI: 26%, 62%] in control arm.
In MAGNIFY, the overall response by investigator assessment was 51% (23/45) [95% CI: 36, 66] for patients with marginal zone lymphoma. Median duration of response was not reached with a median follow-up time of 11.5 months [95% CI: 8.0, 18.9].
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
White and blue-green opaque hard capsules imprinted "REV" on one half and "2.5 mg" on the other half in black ink:
2.5 mg bottles of 28 | (NDC 59572-402-28) |
2.5 mg bottles of 100 | (NDC 59572-402-00) |
White opaque capsules imprinted "REV" on one half and "5 mg" on the other half in black ink:
5 mg bottles of 28 | (NDC 59572-405-28) |
5 mg bottles of 100 | (NDC 59572-405-00) |
Blue/green and pale yellow opaque capsules imprinted "REV" on one half and "10 mg" on the other half in black ink:
10 mg bottles of 28 | (NDC 59572-410-28) |
10 mg bottles of 100 | (NDC 59572-410-00) |
Powder blue and white opaque capsules imprinted "REV" on one half and "15 mg" on the other half in black ink:
15 mg bottles of 21 | (NDC 59572-415-21) |
15 mg bottles of 100 | (NDC 59572-415-00) |
Powder blue and blue-green opaque hard capsules imprinted "REV" on one half and "20 mg" on the other half in black ink.
20 mg bottles of 21 | (NDC 59572-420-21) |
20 mg bottles of 100 | (NDC 59572-420-00) |
White opaque capsules imprinted "REV" on one half and "25 mg" on the other half in black ink:
25 mg bottles of 21 | (NDC 59572-425-21) |
25 mg bottles of 100 | (NDC 59572-425-00) |
Storage
Store at 20°C - 25°C (68°F - 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C - 30°C (59°F - 86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Handling and Disposal
Care should be exercised in the handling of REVLIMID. REVLIMID capsules should not be opened or broken. If powder from REVLIMID contacts the skin, wash the skin immediately and thoroughly with soap and water. If REVLIMID contacts the mucous membranes, flush thoroughly with water.
Procedures for the proper handling and disposal of anticancer drugs should be considered. Several guidelines on the subject have been published. 1
Dispense no more than a 28-day supply.
Mechanism of Action
Lenalidomide is an analogue of thalidomide with immunomodulatory, antiangiogenic, and antineoplastic properties. Cellular activities of lenalidomide are mediated through its target cereblon, a component of a cullin ring E3 ubiquitin ligase enzyme complex. In vitro, in the presence of drug, substrate proteins (including Aiolos, Ikaros, and CK1α) are targeted for ubiquitination and subsequent degradation leading to direct cytotoxic and immunomodulatory effects. Lenalidomide inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of certain hematopoietic tumor cells including MM, mantle cell lymphoma, and del (5q) myelodysplastic syndromes, follicular lymphoma and marginal zone lymphoma in vitro . Lenalidomide causes a delay in tumor growth in some in vivo nonclinical hematopoietic tumor models including MM. Immunomodulatory properties of lenalidomide include increased number and activation of T cells and natural killer (NK) cells leading to direct and enhanced antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) via increased secretion of interleukin-2 and interferon-gamma, increased numbers of NKT cells, and inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α and IL-6) by monocytes. In MM cells, the combination of lenalidomide and dexamethasone synergizes the inhibition of cell proliferation and the induction of apoptosis. The combination of lenalidomide and rituximab increases ADCC and direct tumor apoptosis in follicular lymphoma cells and increases ADCC in marginal zone lymphoma cells compared to rituximab alone in vitro .