Rozlytrek - Entrectinib capsule prescribing information
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ROZLYTREK is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of:
- Adult patients with ROS1- positive metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) as detected by an FDA-approved test. (1.1 )
- Adult and pediatric patients older than 1 month of age with solid tumors that:
- have a neurotrophic tyrosine receptor kinase ( NTRK) gene fusion, as detected by an FDA-approved test without a known acquired resistance mutation,
- are metastatic or where surgical resection is likely to result in severe morbidity, and
- have progressed following treatment or have no satisfactory alternative therapy.
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on tumor response rate and durability of response. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in the confirmatory trials. (1.2 )
ROS1 -Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
ROZLYTREK is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with ROS1- positive metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), as detected by an FDA-approved test.
NTRK Gene Fusion-Positive Solid Tumors
ROZLYTREK is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients older than 1 month of age with solid tumors that:
- have a neurotrophic tyrosine receptor kinase (NTRK) gene fusion, as detected by an FDA-approved test without a known acquired resistance mutation,
- are metastatic or where surgical resection is likely to result in severe morbidity, and
- have progressed following treatment or have no satisfactory alternative therapy.
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on tumor response rate and durability of response [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ] . Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in the confirmatory trials.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Select patients for treatment based on the presence of ROS1 rearrangement(s) or NTRK gene fusion. (2.1 )
- Evaluate left ventricular ejection fraction, serum uric acid levels and QT interval and electrolytes prior to ROZLYTREK initiation. (2.2 )
- Select appropriate dosage form: oral capsules, capsules prepared as an oral suspension or oral pellets. (2.3 )
- Use capsules prepared as suspension for enteral tube administration. Do not use pellets for enteral tube administration. (2.3 )
- Administer ROZLYTREK capsules, capsules prepared as a suspension, or pellets once daily, with or without food. (2.4 )
- Adult Dosage for ROS1- Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: 600 mg orally once daily. (2.5 )
- Adult and Pediatric Dosage for NTRK Gene Fusion-Positive Solid Tumors:
- Adults: 600 mg orally once daily. (2.6 )
- Pediatric Patients: Recommended dosage is based on age and body surface area (BSA) as shown below. (2.6 )
Age Recommended Daily Dosage >6 months ≤0.50 m 2 : 300 mg/m 2 0.51 to 0.80 m 2 : 200 mg 0.81 to 1.10 m 2 : 300 mg 1.11 to 1.50 m 2 : 400 mg BSA ≥1.51 m 2 : 600 mg once daily >1 month to ≤6 months 250 mg/m 2 once daily - Modify dosage of ROZLYTREK if coadministration with moderate or strong CYP3A inhibitors cannot be avoided. (2.8 )
- See preparation and administration instructions. (2.9 )
Patient Selection
- Select patients for the treatment of metastatic NSCLC with ROZLYTREK based on the presence of ROS1 rearrangement(s) in tumor or plasma specimens [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ] . Testing using plasma specimens is only appropriate for patients for whom tumor tissue is not available for testing. Information on FDA-approved tests for the detection of ROS1 rearrangement(s) in NSCLC is available at http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics.
- Select patients for treatment of locally advanced or metastatic solid tumors with ROZLYTREK based on the presence of a NTRK gene fusion in tumor or plasma specimens [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ] . Testing using plasma specimens is only appropriate for patients for whom tumor tissue is not available for testing. Information on FDA-approved tests for the detection of NTRK gene fusion(s) in solid tumors is available at http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics.
Recommended Evaluation and Testing Before Initiating ROZLYTREK
Before initiating ROZLYTREK, evaluate:
- left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- serum uric acid levels [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ]
- QT interval and electrolytes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ]
ROZLYTREK Dosage Form Overview
The physician should prescribe the most appropriate dosage form of ROZLYTREK according to the dose required and patient needs.
ROZLYTREK is available in two dosage forms, and can be administered either as capsules swallowed whole, capsules made into an oral suspension (or for enteral tube administration) and as oral pellets swallowed with soft food.
ROZLYTREK Capsules 100 mg and 200 mg
- Whole capsules: For patients who can swallow whole capsules and whose doses are multiples of 100 mg.
- Capsules prepared as an oral suspension:
- For patients who have difficulty or are unable to swallow capsules or who require enteral administration (e.g., gastric or nasogastric tube). [see Dosage and Administration (2.7) ] .
- For dose increments of 10 mg, only use capsules prepared as a suspension.
ROZLYTREK Oral Pellets 50 mg per packet
- Pellets sprinkled on one or more spoonfuls of soft food:
- For patients who have difficulty or are unable to swallow capsules but can swallow soft food and whose doses are multiples of 50 mg. [see Dosage and Administration (2.7) ] .
- Do not use pellets for preparation of suspension.
- Do not attempt to use partial quantities of pellets from 50 mg pellet packets to prepare a dose.
- Do not use the pellet formulation for enteral tube administration as the pellets may clog the tube.
ROZLYTREK Administration Overview
- Administer ROZLYTREK capsules, capsules prepared as a suspension, or pellets once daily, with or without food.
- If a dose of ROZYTREK is missed, make up that dose unless the next dose is due within 12 hours.
- If vomiting occurs immediately after taking a dose of ROZLYTREK, repeat that dose.
ROZLYTREK Recommended Dosage for ROS1 -Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
The recommended dosage of ROZLYTREK is 600 mg orally once daily with or without food until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
ROZLYTREK Recommended Dosage for NTRK Gene Fusion-Positive Solid Tumors
The recommended dosages of ROZLYTREK for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients with NTRK Gene Fusion-Positive Solid Tumors are provided in Table 1 .
Administer the recommended dosage of ROZLYTREK capsules and oral pellets with or without food until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Sprinkle ROZLYTREK oral pellets on one or more spoonfuls of soft food as a vehicle.
| Patient Population | Recommended Dosage of ROZLYTREK | Duration of Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Adults Pediatric patients with BSA ≥ 1.51 m 2 : | 600 mg orally once daily | Until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. |
| Pediatric patients > 6 months: | see Table 2 | |
| Pediatric patients > 1 month to ≤ 6 months: | 250 mg/m 2 orally once daily To enable dosing increments of 10 mg, capsules prepared as an oral suspension must be used [see Dosage and Administration (2.9) ]. |
The recommended dosages of ROZLYTREK for the treatment of pediatric patients older than 6 months with NTRK Gene Fusion-Positive Solid Tumors is provided in Table 2 .
| Body Surface Area (BSA) BSA categories and recommended dosage above are based on closely matching exposures to a target dose of 300 mg/m 2 | Recommended Dosage Orally Once Daily |
|---|---|
| ≤0.50 m 2 | 300 mg/m 2 To enable dosing increments of 10 mg, capsules prepared as an oral suspension must be used [see Dosage and Administration (2.9) ]. |
| 0.51 to 0.80 m 2 | 200 mg |
| 0.81 to 1.10 m 2 | 300 mg |
| 1.11 to 1.50 m 2 | 400 mg |
| ≥ 1.51 m 2 | 600 mg |
ROZLYTREK Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
The recommended dosage reductions of ROZLYTREK for the management of adverse reactions for adults and pediatric patients are provided in Table 3 .
| Starting Dose once daily | First dose reduction | Second dose reduction | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 250 mg/m 2 or 300 mg/m 2 | Reduce the once daily dose to two thirds of the starting dose To enable dosing increments of 10 mg, capsules prepared as an oral suspension must be used [see Dosage and Administration (2.9) ] . | Reduce the once daily dose to one third of the starting dose | Permanently discontinue ROZLYTREK in patients who are unable to tolerate ROZLYTREK after two dose reductions. |
| 200 mg | 150 mg once daily | 100 mg once daily | |
| 300 mg | 200 mg once daily | 100 mg once daily | |
| 400 mg | 300 mg once daily | 200 mg once daily | |
| 600 mg | 400 mg once daily | 200 mg once daily |
Table 4 provides the ROZLYTREK recommended dosage modifications for the management of adverse reactions.
| Adverse Reaction | Severity Severity as defined by National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (NCI CTCAE) version 4.0. | Dosage Modification |
|---|---|---|
| Congestive Heart Failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] | Grade 2 or 3 |
|
| Grade 4 |
| |
| Central Nervous System Effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] | Intolerable Grade 2 |
|
| Grade 3 |
| |
| Grade 4 |
| |
| Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ] | Grade 3 |
|
| Grade 4 |
| |
| ALT or AST greater than 3 times ULN with concurrent total bilirubin greater than 1.5 times ULN (in the absence of cholestasis or hemolysis). |
| |
| Hyperuricemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ] | Symptomatic or Grade 4 |
|
| QT Interval Prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ] | QTc greater than 500 ms |
|
| Torsade de pointes; polymorphic ventricular tachycardia; signs/symptoms of serious arrhythmia |
| |
| Vision Disorders [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ] | Grade 2 or above |
|
| Anemia or Neutropenia [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] | Grade 3 or 4 |
|
| Other Adverse Reactions [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] | Grade 3 or 4 |
|
ROZLYTREK Dosage Modifications for Drug Interactions
Moderate and Strong CYP3A Inhibitors
Adults and Pediatric Patients 2 Years and Older
Avoid coadministration of ROZLYTREK with moderate or strong CYP3A inhibitors. If coadministration cannot be avoided, reduce the ROZLYTREK dose as shown in Table 5 and limit coadministration to 14 days or less.
| Starting dose For pediatric patients with a starting dose less than 200 mg, avoid coadministration with moderate or strong CYP3A inhibitors | Moderate CYP3A inhibitor | Strong CYP3A inhibitor |
|---|---|---|
| 200 mg | 50 mg once daily | 50 mg on alternate days |
| 300 mg | 100 mg once daily | 50 mg once daily |
| 400 mg | 200 mg once daily | 50 mg once daily |
| 600 mg | 200 mg once daily | 100 mg once daily |
After discontinuation of a strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitor for 3 to 5 elimination half-lives, resume the ROZLYTREK dose that was taken prior to initiating the CYP3A inhibitor [see Drug Interactions (7.1) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
ROZLYTREK Preparation and Administration Instructions
ROZLYTREK Capsules
Swallow capsules whole. Do not crush or chew the capsules.
ROZLYTREK Capsules Prepared as a Suspension for Oral or Enteral Tube Administration
It is recommended that a healthcare provider discuss with the patient or caregiver, the volume of water or milk to be added and oral suspension to withdraw, prior to administration of the first dose (see Table 6 ).
Table 6 provides the ROZLYTREK dose and volume of room temperature drinking water or milk required to prepare an oral suspension. Instruct patients or caregivers to carefully open capsule(s) and pour the contents into room temperature drinking water or milk to prepare an oral suspension. Let sit for 15 minutes.
| Dose of ROZLYTREK to be administered | Dose needed for suspension (using 100 mg or 200 mg capsules, as appropriate) | Volume of water or milk to be added | Volume of oral suspension to withdraw and administer |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 mg | 100 mg | 5 mL | 1 mL |
| 30 mg | 100 mg | 5 mL | 1.5 mL |
| 40 mg | 100 mg | 5 mL | 2 mL |
| 50 mg | 100 mg | 5 mL | 2.5 mL |
| 60 mg | 100 mg | 5 mL | 3 mL |
| 70 mg | 100 mg | 5 mL | 3.5 mL |
| 80 mg | 100 mg | 5 mL | 4 mL |
| 90 mg | 100 mg | 5 mL | 4.5 mL |
| 100 mg | 100 mg | 5 mL | 5 mL |
| 110 mg | 200 mg | 10 mL | 5.5 mL |
| 120 mg | 200 mg | 10 mL | 6 mL |
| 130 mg | 200 mg | 10 mL | 6.5 mL |
| 140 mg | 200 mg | 10 mL | 7 mL |
| 150 mg | 200 mg | 10 mL | 7.5 mL |
| 200 mg | 200 mg | 10 mL | 10 mL |
| 300 mg | 300 mg | 15 mL | 15 mL |
| 400 mg | 400 mg | 20 mL | 20 mL |
| 600 mg | 600 mg | 30 mL | 30 mL |
Administer ROZLYTREK oral suspension immediately after preparation.
Discard any unused suspension if not used within 2 hours.
Instruct patients to drink water after taking the oral suspension to ensure ROZLYTREK has been completely swallowed.
Enteral Tube Administration
If enteral administration (e.g., gastric or nasogastric tube) is required, administer the oral suspension via the tube. Use an enteral tube that is 8 FR or higher to administer dosing volumes of 3 mL or higher. Instruct patients to divide dosing volumes of 3 mL or higher into at least two aliquots and flush the tube after each administration. Flush the tube with a volume of water or milk that is equal to the aliquot administered. For a dose volume of 30 mL, divide into at least three (10 mL) aliquots. The tube should be flushed with water or milk after delivering each aliquot of ROZLYTREK.
Refer to the Instructions for Use for detailed instructions on preparation and administration of ROZLYTREK capsules as an oral suspension via an enteral tube.
ROZLYTREK Oral Pellets
Sprinkle pellets on one or more spoonfuls of a soft food (e.g., applesauce, yogurt, or pudding) and take within 20 minutes of preparation. Do not crush or chew to avoid a bitter taste.
The patient should drink water after taking the pellets to ensure the drug has been completely swallowed.
Do not attempt to use partial quantities of pellets from 50 mg pellet packets to prepare a dose.
Do not use the pellet formulation for enteral tube administration as the pellets may clog the tube.
Refer to the Instructions for Use for detailed instructions on preparation and administration of ROZLYTREK oral pellets.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Capsules:
- 100 mg: Size 2 yellow opaque body and cap, with "ENT 100" printed in blue ink on body.
- 200 mg: Size 0 orange opaque body and cap, with "ENT 200" printed in blue ink on body.
Pellets:
- 50 mg: Supplied as brownish orange or grayish orange pellets in packets.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Lactation : Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2 )
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on literature reports in humans with congenital mutations leading to changes in TRK signaling, findings from animal studies, and its mechanism of action [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1) ] , ROZLYTREK can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. There are no available data on ROZLYTREK use in pregnant women. Administration of entrectinib to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis resulted in malformations at maternal exposures approximately 2.7 times the human exposure at the 600 mg dose (see Data ) . Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Human Data
Published reports of individuals with congenital mutations in TRK pathway proteins suggest that decreases in TRK-mediated signaling are correlated with obesity, developmental delays, cognitive impairment, insensitivity to pain, and anhidrosis.
Animal Data
Entrectinib administration to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis at a dose of 200 mg/kg [resulting in exposures up to 2.7 times the human exposure (AUC) at the 600 mg dose] resulted in maternal toxicity and fetal malformations including body closure defects (omphalocele and gastroschisis) and malformations of the vertebrae, ribs, and limbs (micromelia and adactyly), but not embryolethality. Lower fetal weights and reduced skeletal ossification occurred at doses ≥ 12.5 and 50 mg/kg [approximately 0.2 and 0.9 times the human exposure (AUC) at the 600 mg dose], respectively.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of entrectinib or its metabolites in human milk or their effects on either the breastfed child or on milk production. Because of the potential serious adverse reactions in breastfed children from ROZLYTREK, advise a lactating woman to discontinue breastfeeding during treatment with ROZLYTREK and for 7 days after the last dose.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Pregnancy Testing
Verify the pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to initiating ROZLYTREK [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ] .
Contraception
ROZLYTREK can cause embryo-fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ].
Females
Advise female patients of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with ROZLYTREK and for at least 5 weeks following the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ] .
Males
Advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with ROZLYTREK and for 3 months following the last dose [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1) ].
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of ROZLYTREK have been established in pediatric patients older than 1 month of age [Clinical Studies (14.2) ]. Use of ROZLYTREK in these age groups is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies of ROZLYTREK in adults and pediatric patients with additional population pharmacokinetic data demonstrating that the exposure of drug substance in pediatric patients greater than 1 month of age is expected to be in the adult range, and that the course of disease is sufficiently similar in adult and pediatric patients to allow extrapolation of data in adults to pediatric patients.
The safety and effectiveness of ROZLYTREK have not been established in pediatric patients with ROS1 -positive NSCLC.
Juvenile Animal Toxicity Data
In a 13-week juvenile rat toxicology study, animals were dosed daily from post-natal day 7 to day 97 (approximately equivalent to neonate to adulthood). Entrectinib resulted in:
- decreased body weight gain and delayed sexual maturation at doses ≥ 4 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.06 times the human exposure (AUC) at the 600 mg dose),
- deficits in neurobehavioral assessments including functional observational battery and learning and memory (at doses ≥ 8 mg/kg/day, approximately 0.14 times the human exposure at the 600 mg dose), and
- decreased femur length at doses ≥ 16 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.18 times the human exposure at the 600 mg dose).
Geriatric Use
Of the 355 patients who received ROZLYTREK across clinical trials, 25% were 65 years or older, and 5% were 75 years of age or older. Clinical studies of ROZLYTREK did not include sufficient numbers of geriatric patients to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients.
Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment is recommended for patients with mild or moderate renal impairment (CLcr 30 to < 90 mL/min calculated by Cockcroft-Gault equation). ROZLYTREK has not been studied in patients with severe renal impairment (CLcr < 30 mL/min) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
Hepatic Impairment
The effect of moderate hepatic impairment (total bilirubin > 1.5 – 3.0 times ULN with any aspartate aminotransferase) or severe hepatic impairment (total bilirubin >3.0 times ULN with any aspartate aminotransferase) on the safety of ROZLYTREK at the recommended dosage is unknown. Consider the risk-benefit profile of ROZLYTREK prior to determining whether to administer ROZLYTREK to patients with moderate to severe hepatic impairment. Monitor for ROZLYTREK adverse reactions in patients with hepatic impairment more frequently since these patients may be at increased risk for adverse reactions [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) : Assess left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) prior to initiation of ROZLYTREK. Monitor patients for clinical signs and symptoms of CHF. For patients with myocarditis, with or without a decreased ejection fraction, MRI or cardiac biopsy may be required to make the diagnosis. For new onset or worsening CHF, withhold ROZLYTREK, reassess LVEF and institute appropriate medical management. Reduce dose or permanently discontinue ROZLYTREK based on severity of CHF or worsening LVEF. (2.7 , 5.1 )
- Central Nervous System (CNS) Effects: CNS adverse reactions including cognitive impairment, mood disorders, dizziness, and sleep disturbances can occur with ROZLYTREK. Withhold and then resume at same or reduced dose upon improvement or permanently discontinue ROZLYTREK based on severity. (2.7 , 5.2 )
- Skeletal Fractures: ROZLYTREK increases the risk of fractures. Promptly evaluate patients with signs or symptoms of fractures. (5.3 )
- Hepatotoxicity : Monitor liver tests, including ALT and AST, every 2 weeks during the first month of treatment, then monthly thereafter, and as clinically indicated. Withhold or permanently discontinue ROZLYTREK based on severity. If withheld, resume ROZLYTREK at same or reduced dose based on severity. (2.7 , 5.4 )
- Hyperuricemia : Assess serum uric acid levels prior to initiation and periodically during treatment with ROZLYTREK. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of hyperuricemia. Initiate treatment with urate-lowering medications as clinically indicated and withhold ROZLYTREK for signs and symptoms of hyperuricemia. Resume at same or reduced dose upon improvement based on severity. (2.7 , 5.5 )
- QT Interval Prolongation : Monitor patients who have or who are at risk for QTc interval prolongation. Assess QT interval and electrolytes at baseline and periodically during treatment. Withhold and then resume at same or reduced dose, or permanently discontinue ROZLYTREK based on severity. (2.7 , 5.6 )
- Vision Disorders : Withhold for new visual changes or changes that interfere with activities of daily living until improvement or stabilization. Conduct an ophthalmological evaluation as appropriate. Resume at same or reduced dose upon improvement or stabilization. (2.7 , 5.7 )
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity : Can cause fetal harm. Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus and use of effective contraception. (5.8 , 8.1 , 8.3 )
Congestive Heart Failure
Among the 355 patients who received ROZLYTREK across clinical trials, congestive heart failure (CHF) occurred in 3.4% of patients, including Grade 3 (2.3%) [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ]. In clinical trials, baseline cardiac function and routine cardiac monitoring other than electrocardiograms (ECGs) were not conducted and eligibility criteria excluded patients with symptomatic CHF, myocardial infarction, unstable angina, and coronary artery bypass graft within 3 months of study entry. Among the 12 patients with CHF, the median time to onset was 2 months (range: 11 days to 12 months). ROZLYTREK was interrupted in 6 of these patients (50%) and discontinued in 2 of these patients (17%). CHF resolved in 6 patients (50%) following interruption or discontinuation of ROZLYTREK and institution of appropriate medical management. In addition, myocarditis in the absence of CHF was documented in 0.3% of patients.
Assess left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) prior to initiation of ROZLYTREK. Monitor patients for clinical signs and symptoms of CHF, including shortness of breath and edema. For patients with myocarditis, with or without a decreased ejection fraction, MRI or cardiac biopsy may be required to make the diagnosis. For patients with new onset or worsening CHF, withhold ROZLYTREK, institute appropriate medical management, and reassess LVEF. Based on the severity of CHF or worsening LVEF, resume ROZLYTREK at a reduced dose upon recovery to baseline or permanently discontinue [see Dosage and Administration (2.7) ] .
Central Nervous System Effects
A broad spectrum of central nervous system (CNS) adverse reactions occurred in patients receiving ROZLYTREK, including cognitive impairment, mood disorders, dizziness, and sleep disturbances.
Among the 355 patients who received ROZLYTREK across clinical trials, 96 (27%) experienced cognitive impairment; symptoms occurred within 3 months of starting ROZLYTREK in 74 (77%). Cognitive impairment included cognitive disorders (8%), confusional state (7%), disturbance in attention (4.8%), memory impairment (3.7%), amnesia (2.5%), aphasia (2.3%), mental status changes (2%), hallucinations (1.1%), and delirium (0.8%). Grade 3 cognitive adverse reactions occurred in 4.5% of patients. Among the 96 patients with cognitive impairment, 13% required a dose reduction, 18% required dose interruption and 1% discontinued ROZLYTREK due to cognitive adverse reactions.
Among the 355 patients who received ROZLYTREK across clinical trials, 36 (10%) experienced mood disorders. The median time to onset of mood disorders was 1 month (range: 1 day to 9 months). Mood disorders occurring in ≥ 1% of patients included anxiety (4.8%), depression (2.8%) and agitation (2%). Grade 3 mood disorders occurred in 0.6% of patients. One completed suicide was reported 11 days after treatment had ended. Among the 36 patients who experienced mood disorders, 6% required a dose reduction, 6% required dose interruption and no patients discontinued ROZLYTREK due to mood disorders.
Dizziness occurred in 136 (38%) of the 355 patients. Among the 136 patients who experienced dizziness, Grade 3 dizziness occurred in 2.2% of patients. Ten percent of patients required a dose reduction, 7% required dose interruption and 0.7% discontinued ROZLYTREK due to dizziness.
Among the 355 patients who received ROZLYTREK across clinical trials, 51 (14%) experienced sleep disturbances. Sleep disturbances included insomnia (7%), somnolence (7%), hypersomnia (1.1%), and sleep disorder (0.3%). Grade 3 sleep disturbances occurred in 0.6% of patients. Among the 51 patients who experienced sleep disturbances, 6% required a dose reduction and no patients discontinued ROZLYTREK due to sleep disturbances.
The incidence of CNS adverse reactions was similar in patients with and without CNS metastases; however, the incidence of dizziness (38% vs 31%), headache (21% vs 13%), paresthesia (20% vs 6%), balance disorder (13% vs 4%), and confusional state (11% vs 2%) appeared to be increased in patients with CNS metastases who had received prior CNS irradiation (n = 90) compared to those who did not (n = 48).
Advise patients and caregivers of these risks with ROZLYTREK. Advise patients not to drive or operate hazardous machinery if they are experiencing CNS adverse reactions. Withhold and then resume at same or reduced dose upon improvement, or permanently discontinue ROZLYTREK based on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.7) ] .
Skeletal Fractures
ROZLYTREK increases the risk of fractures. In an expanded safety population that included 338 adult patients and 76 pediatric patients who received ROZLYTREK across clinical trials, 5% of adult patients and 25% of pediatric patients experienced fractures [see Use in Specific Population (8.4) ] . In adult and pediatric patients, some fractures occurred in the setting of a fall or other trauma to the affected area; in pediatric patients some fractures occurred with no trauma. In general, there was inadequate assessment for tumor involvement at the site of fracture; however, radiologic abnormalities possibly indicative of tumor involvement were reported in some adult patients. In both adult and pediatric patients, most fractures were hip or other lower extremity fractures (e.g., femoral or tibial shaft). In two pediatric patients, bilateral femoral neck fractures occurred. A total of 41 fracture events were reported in 19 pediatric patients, with 13 patients who experienced more than one occurrence of fracture. Among the 19 pediatric patients who experienced fractures, 17 patients were less than 12 years of age. Among the 41 fracture events, 27 fracture events resolved, 4 fracture events resolved with sequelae and 3 events were resolving. The median time to fracture was 3.8 months (range 0.3 to 18.5 months) in adults and 4.3 months (range: 2 months to 28.7 months) in pediatric patients. ROZLYTREK was interrupted in 41% of adults and 16% of pediatric patients who experienced fractures. Five pediatric patients discontinued treatment due to fractures.
Promptly evaluate patients with signs or symptoms (e.g., pain, changes in mobility, deformity) of fractures. There are no data on the effects of ROZLYTREK on healing of known fractures and risk of future fractures.
Hepatotoxicity
Among the 355 patients who received ROZLYTREK, increased AST of any grade occurred in 42% of patients and increased ALT of any grade occurred in 36%. Grade 3 – 4 increased AST or ALT occurred in 2.5% and 2.8% of patients, respectively; the incidence may be underestimated as 4.5% of patients had no post-treatment liver function tests [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] . The median time to onset of increased AST was 2 weeks (range: 1 day to 29.5 months). The median time to onset of increased ALT was 2 weeks (range: 1 day to 9.2 months). Increased AST or ALT leading to dose interruptions or reductions occurred in 0.8% and 0.8% of patients, respectively. ROZLYTREK was discontinued due to increased AST or ALT in 0.8% patients.
Monitor liver tests, including ALT and AST, every 2 weeks during the first month of treatment, then monthly thereafter, and as clinically indicated. Withhold or permanently discontinue ROZLYTREK based on the severity. If withheld, resume ROZLYTREK at the same or reduced dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.7) ] .
Hyperuricemia
Among 355 patients who received ROZLYTREK across clinical trials, 32 patients (9%) experienced hyperuricemia reported as adverse reactions with symptoms, as well as elevated uric acid levels. Grade 4 hyperuricemia occurred in 1.7% of patients, including one patient who died due to tumor lysis syndrome. Among the 32 patients with hyperuricemic adverse reactions, 34% required urate-lowering medication to reduce uric acid levels, 6% required dose reduction and 6% required dose interruption. Hyperuricemia resolved in 73% of patients following initiation of urate-lowering medication without interruption or dose reduction of ROZLYTREK. No patients discontinued ROZLYTREK due to hyperuricemia.
Assess serum uric acid levels prior to initiation of ROZLYTREK and periodically during treatment. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of hyperuricemia. Initiate treatment with urate-lowering medications as clinically indicated and withhold ROZLYTREK for signs and symptoms of hyperuricemia. Resume ROZLYTREK at same or reduced dose upon improvement of signs or symptoms based on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.7) ] .
QT Interval Prolongation
Among the 355 patients who received ROZLYTREK across the clinical trials, 3.1% of patients with at least one post-baseline ECG assessment experienced QTcF interval prolongation of > 60 ms after starting ROZLYTREK and 0.6% had a QTcF interval > 500 ms [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.2) ].
Monitor patients who already have or who are at significant risk of developing QTc interval prolongation, including patients with known long QT syndromes, clinically significant bradyarrhythmias, severe or uncontrolled heart failure and those taking other medicinal products associated with QT prolongation. Assess QT interval and electrolytes prior to initiation of ROZLYTREK and periodically during treatment, adjusting frequency based upon risk factors such as congestive heart failure, electrolyte abnormalities, or concomitant medications known to prolong the QTc interval. Based on the severity of QTc interval prolongation, withhold ROZLYTREK and then resume at same or reduced dose, or permanently discontinue [see Dosage and Administration (2.7) ] .
Vision Disorders
Among the 355 patients who received ROZLYTREK across clinical trials, vision changes occurred in 21% of patients, including Grade 1 (17%), Grade 2 (2.8%) and Grade 3 (0.8%) [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] . Vision disorders occurring in ≥ 1% included blurred vision (9%), photophobia (5%), diplopia (3.1%), visual impairment (2%), photopsia (1.1%), cataract (1.1%), and vitreous floaters (1.1%).
For patients with new visual changes or changes that interfere with activities of daily living, withhold ROZLYTREK until improvement or stabilization and conduct an ophthalmological evaluation as clinically appropriate. Upon improvement or stabilization, resume ROZLYTREK at same or reduced dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.7) ] .
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on literature reports in humans with congenital mutations leading to changes in TRK signaling, findings from animal studies, and its mechanism of action, ROZLYTREK can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Administration of entrectinib to pregnant rats resulted in malformations at exposures approximately 2.7 times the human exposure at the 600 mg dose based on area under the curve (AUC).
Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise female patients of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with ROZLYTREK and for 5 weeks following the last dose. Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with ROZLYTREK and for 3 months after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1 , 8.3) ] .
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Congestive Heart Failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- Central Nervous System Effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
- Skeletal Fractures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ]
- Hyperuricemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ]
- QT Interval Prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ]
- Vision Disorders [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ]
Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Data in WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS and below reflect exposure to ROZLYTREK in 355 patients, including 172 (48%) patients exposed for 6 months or longer and 84 (24%) patients exposed for 1 year or longer. ROZLYTREK was studied in one dose-finding trial in adults [ALKA (n = 57)], one dose-finding and activity-estimating trial in adults [STARTRK-1 (n = 76)], one dose-finding and activity-estimating trial in pediatric and adult patients [STARTRK-NG (n = 16)], and one single arm, activity-estimating trial in adults [STARTRK-2 (n = 206)].
The population characteristics were: median age 55 years (range: 4 to 86 years); 5% (n = 17) were less than 18 years of age; 55% were female; and 66% were White, 23% were Asian, and 5% were Black; 3% were Hispanic/Latino. The most common tumors (≥ 5%) were lung (56%), sarcoma (8%), and colon (5%). ROS1 gene fusions were present in 42% and NTRK gene fusions were present in 20%. Most adults (75%) received ROZLYTREK 600 mg orally once daily. The doses ranged from 100 mg/m 2 to 1600 mg/m 2 once daily in adults and 250 mg/m 2 to 750 mg/m 2 once daily in pediatric patients.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 39% of patients. The most frequent serious adverse reactions (≥ 2%) were pneumonia (3.9%), dyspnea (3.7%), pleural effusion (3.4%), sepsis (2.5%), pulmonary embolism (2.3%), respiratory failure (2%), and pyrexia (2%). Grade 3 or 4 adverse reactions occurred in 60% of patients; the most common (≥ 2%) were lung infection (5%), increased weight (7%), dyspnea (6%), fatigue/asthenia (5%), cognitive disorders (4.5%), syncope (2.5%), pulmonary embolism (3.4%), hypoxia (3.4%), pleural effusion (3.1%), hypotension (2.8%), diarrhea (2%), and urinary tract infection (2.5%). Fatal events included dyspnea (0.6%), pneumonia (0.6%), sepsis (0.6%), completed suicide (0.3%), large intestine perforation (0.3%) and tumor lysis syndrome (0.3%). One patient developed Grade 4 myocarditis after one dose of ROZLYTREK which resolved after discontinuation of ROZLYTREK and administration of high-dose corticosteroids.
Permanent discontinuation due to an adverse reaction occurred in 9% of patients who received ROZLYTREK. The most frequent adverse reactions (< 1% each) that resulted in permanent discontinuation were pneumonia, cardio-respiratory arrest, dyspnea, and fatigue.
Dose interruptions due to adverse reactions occurred in 46% of patients. The most frequent adverse reactions (≥ 2%) that resulted in interruption were increased blood creatinine (4%), fatigue (3.7%), anemia (3.1%), diarrhea (2.8%), pyrexia (2.8%), dizziness (2.5%), dyspnea (2.3%), nausea (2.3%), pneumonia (2.3%), cognitive disorder (2%) and neutropenia (2%).
Dose reductions due to adverse reactions occurred in 29% of patients who received ROZLYTREK. The most frequent adverse reactions resulting in dose reductions (≥ 1%) were dizziness (3.9%), increased blood creatinine (3.1%), fatigue (2.3%), anemia (1.7%), and increased weight (1.4%).
The most common adverse reactions (≥ 20%) were fatigue, constipation, dysgeusia, edema, dizziness, diarrhea, nausea, dysesthesia, dyspnea, myalgia, cognitive impairment, increased weight, cough, vomiting, pyrexia, arthralgia and vision disorders.
Table 7 summarizes the adverse reactions observed in these 355 patients.
| Adverse Reactions | ROZLYTREK n = 355 | |
|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) | Grade ≥ 3 Grades 3 – 5, inclusive of fatal adverse reactions, including 2 events of pneumonia and 2 events of dyspnea. (%) | |
| General | ||
| Fatigue Includes fatigue, asthenia | 48 | 5 |
| Edema Includes face edema, fluid retention, generalized edema, localized edema, edema, edema peripheral, peripheral swelling | 40 | 1.1 |
| Pyrexia | 21 | 0.8 |
| Gastrointestinal | ||
| Constipation | 46 | 0.6 |
| Diarrhea | 35 | 2.0 |
| Nausea | 34 | 0.3 |
| Vomiting | 24 | 0.8 |
| Abdominal pain Includes abdominal pain upper, abdominal pain, lower abdominal discomfort, abdominal tenderness | 16 | 0.6 |
| Nervous System | ||
| Dysgeusia | 44 | 0.3 |
| Dizziness Includes dizziness, vertigo, dizziness postural | 38 | 0.8 |
| Dysesthesia Includes paresthesia, hyperesthesia, hypoesthesia, dysesthesia, oral hypoesthesia, palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia, oral paresthesia, genital hypoesthesia | 34 | 0.3 |
| Cognitive impairment Includes amnesia, aphasia, cognitive disorder, confusional state, delirium, disturbance in attention, hallucinations, visual hallucination, memory impairment, mental disorder, mental status changes | 27 | 4.5 |
| Peripheral sensory neuropathy Includes neuralgia, neuropathy peripheral, peripheral motor neuropathy, peripheral sensory neuropathy | 18 | 1.1 |
| Headache | 18 | 0.3 |
| Ataxia Includes ataxia, balance disorder, gait disturbances | 17 | 0.8 |
| Sleep Includes hypersomnia, insomnia, sleep disorder, somnolence | 14 | 0.6 |
| Mood disorders Includes anxiety, affect lability, affective disorder, agitation, depressed mood, euphoric mood, mood altered, mood swings, irritability, depression, persistent depressive disorder, psychomotor retardation | 10 | 0.6 |
| Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal | ||
| Dyspnea | 30 | 6 |
| Cough | 24 | 0.3 |
| Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue | ||
| Myalgia Includes musculoskeletal pain, musculoskeletal chest pain, myalgia, neck pain | 28 | 1.1 |
| Arthralgia | 21 | 0.6 |
| Muscular weakness | 12 | 0.8 |
| Back pain | 12 | 1 |
| Pain in extremity | 11 | 0.3 |
| Metabolism and Nutritional | ||
| Increased weight | 25 | 7 |
| Decreased appetite | 13 | 0.3 |
| Dehydration | 10 | 1.1 |
| Eye | ||
| Vision disorders Includes blindness, cataract, cortical cataract, corneal erosion, diplopia, eye disorder, photophobia, photopsia, retinal hemorrhage, vision blurred, visual impairment, vitreous adhesions, vitreous detachment, vitreous floaters | 21 | 0.8 |
| Infections | ||
| Urinary tract infection | 13 | 2.3 |
| Lung infection Includes lower respiratory tract infection, lung infection, pneumonia, respiratory tract infection | 10 | 6 |
| Vascular | ||
| Hypotension Includes hypotension, orthostatic hypotension | 18 | 2.8 |
| Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue | ||
| Rash Includes rash, rash maculopapular, rash pruritic, rash erythematous, rash papular | 11 | 0.8 |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions occurring in ≤ 10% of patients include dysphagia (10%), fall (8%), pleural effusion (8%), fractures (6%), hypoxia (4.2%), pulmonary embolism (3.9%), syncope (3.9%), congestive heart failure (3.4%), and QT prolongation (3.1%) .
Table 8 summarizes the laboratory abnormalities.
| Laboratory Abnormality | ROZLYTREK NCI CTCAE Grade | |
|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) Denominator for each laboratory parameter is based on the number of patients with a baseline and post-treatment laboratory value available which ranged from 111 to 346 patients. | Grade 3 or 4 (%) | |
| AST: Aspartate Aminotransferase; ALT: Alanine Aminotransferase | ||
| Chemistry | ||
| Increased creatinine Based on NCI CTCAE v5.0 | 73 | 2.1 |
| Hyperuricemia | 52 | 10 |
| Increased AST | 44 | 2.7 |
| Increased ALT | 38 | 2.9 |
| Hypernatremia | 35 | 0.9 |
| Hypocalcemia | 34 | 1.8 |
| Hypophosphatemia | 30 | 7 |
| Increased lipase | 28 | 10 |
| Hypoalbuminemia | 28 | 2.9 |
| Increased amylase | 26 | 5.4 |
| Hyperkalemia | 25 | 1.5 |
| Increased alkaline phosphatase | 25 | 0.9 |
| Hyperglycemia NE = Not evaluable. Grade 1 and 2 could not be determined per NCI CTCAE v5.0, as fasting glucose values were not collected | NE | 3.8 |
| Hematology | ||
| Anemia | 67 | 9 |
| Lymphopenia | 40 | 12 |
| Neutropenia | 28 | 7 |
Safety in Pediatric Patients
The safety of ROZLYTREK was evaluated was evaluated in pediatric patients with unresectable or metastatic solid tumors with a NTRK gene fusion enrolled in one of three multicenter, open-label clinical trials: STARTRK-NG (n=68), TAPISTRY (n=6) and STARTRK-2 (n=2). Patients received ROZLYTREK 20 mg to 600 mg based on body surface area (BSA) orally or via enteral feeding tube once daily in 4-week cycles until unacceptable toxicity or disease progression. Among patients who received ROZLYTREK, 58% were exposed for 6 months or longer and 38% were exposed for greater than one year.
The median age of patients who received ROZLYTREK was 6 years (range: 0 to 17); 51% were females; 68% were White, 18% Asian, 7% Black or African American, and 7% were other races.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 45% of patients who received ROZLYTREK. Serious adverse reactions in > 2% of patients included skeletal fractures (12%), pneumonia (5%), pyrexia (5%), hydrocephalus (5%), device related infection (4%), hypoxia (4%), dyspnea (3%), headache (3%), gait disturbance (3%), pain (3%), upper respiratory infection (3%), and sepsis (3%).
Permanent discontinuation of ROZLYTREK due to an adverse reaction occurred in 13% of patients. Adverse reactions which resulted in permanent discontinuation of ROZLYTREK in > 2% of patients included skeletal fracture.
Dosage interruptions of ROZLYTREK due to an adverse reaction occurred in 39% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dosage interruption in > 5% of patients included decreased neutrophil count, pyrexia, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Dose reductions of ROZLYTREK due to an adverse reaction occurred in 21% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dose reductions in > 2% of patients included increased blood creatinine and increased weight.
Table 9 summarizes the adverse reactions in STARTRK-NG (n=68), TAPISTRY (n=6) and STARTRK-2 (n=2).
| Adverse Reaction | ROZLYTREK (n=76) | |
|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) | |
| General Disorders | ||
| Pyrexia | 43 | 1.3 |
| Fatigue Includes fatigue, asthenia | 30 | 2.6 |
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||
| Constipation | 41 | 1.3 |
| Vomiting | 38 | 0 |
| Diarrhea | 37 | 0 |
| Nausea | 34 | 0 |
| Abdominal Pain | 20 | 2.6 |
| Investigations | ||
| Increased Weight | 39 | 18 |
| Respiratory, Thoracic And Mediastinal Disorders | ||
| Cough | 33 | 1.3 |
| Nasal Congestion | 20 | 0 |
| Musculoskeletal And Connective Tissue Disorders | ||
| Pain in Extremity | 26 | 2.6 |
| Skeletal Fracture Includes clavicle fracture, tibia fracture, femur fracture, fibula fracture, foot fracture, fracture, pathological fracture, limb fracture, lower limb fracture, pelvic fracture, spinal compression fracture, stress fracture, ulna fracture | 25 | 11 |
| Metabolism And Nutrition Disorders | ||
| Decreased Appetite | 24 | 1.3 |
| Nervous System Disorders | ||
| Headache | 22 | 2.6 |
| Infections | ||
| Upper Respiratory Tract Infection | 20 | 1.3 |
| Urinary Tract Infection | 20 | 2.6 |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions in <20% of patients who received ROZLYTREK included pruritus, rash, urinary incontinence, eye pain and photophobia.
Tables 10 summarizes the laboratory abnormalities in STARTRK-NG (n=68), TAPISTRY (n=6) and STARTRK-2 (n=2).
| Laboratory Abnormality | ROZLYTREK The denominator used to calculate the rate varied from 67 to 76 based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one post-treatment value. All values based on NCI CTCAE v5.0 | |
|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) | |
| AST: Aspartate Aminotransferase; ALT: Alanine Aminotransferase | ||
| Hematology | ||
| Decreased Hemoglobin | 53 | 7 |
| Decreased Neutrophils | 53 | 22 |
| Decreased Leukocytes | 46 | 1.3 |
| Increased Lymphocytes | 33 | 3 |
| Chemistry | ||
| Increased Creatinine | 84 | 5 |
| Increased AST | 61 | 2.7 |
| Increased ALT | 53 | 2.6 |
| Increased Sodium | 38 | 1.4 |
| Increased Magnesium | 32 | 5 |
| Increased Alkaline Phosphatase | 25 | 0 |
| Decreased Glucose | 26 | 0 |
| Increased Potassium | 25 | 2.7 |
| Decreased Albumin | 24 | 9 |
| Increased Calcium | 21 | 8 |
| Increased Bilirubin | 20 | 8 |
Other clinically relevant laboratory abnormalities in patients who received ROZLYTREK included decreased phosphorous.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Effect of Other Drugs on ROZLYTREK
Moderate and Strong CYP3A Inhibitors
Adults and Pediatric Patients 2 Years and Older
Coadministration of ROZLYTREK with a strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitor increases entrectinib plasma concentrations [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ], which could increase the frequency or severity of adverse reactions. Avoid coadministration of strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitors with ROZLYTREK. If coadministration is unavoidable, reduce the ROZLYTREK dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.8) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
Pediatric Patients less than 2 Years
Avoid coadministration of ROZLYTREK with moderate or strong CYP3A inhibitors [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Avoid grapefruit products during treatment with ROZLYTREK, as they contain inhibitors of CYP3A.
Moderate and Strong CYP3A Inducers
Coadministration of ROZLYTREK with a strong or moderate CYP3A inducer decreases entrectinib plasma concentrations [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ], which may reduce ROZLYTREK efficacy. Avoid coadministration of strong and moderate CYP3A inducers with ROZLYTREK .
Drugs That Prolong QTc Interval
QTc interval prolongation can occur with ROZLYTREK. Avoid coadministration of ROZLYTREK with other products with a known potential to prolong QT/QTc interval [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.2) ] .
DESCRIPTION
Entrectinib is a kinase inhibitor. The molecular formula for entrectinib is C 31 H 34 F 2 N 6 O 2 and the molecular weight is 560.64 Daltons. The chemical name is N-[5-(3,5-difluorobenzyl)-1H-indazol-3-yl]-4-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-(tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-ylamino) benzamide. The chemical structure of entrectinib is as follows:

Entrectinib is white to pale pink powder.
Capsules:
ROZLYTREK (entrectinib) capsules for oral use are supplied as printed hard-shell capsules containing 100 mg (yellow opaque HPMC capsule) or 200 mg of entrectinib (orange opaque HPMC capsule). Inactive ingredients are tartaric acid, lactose anhydrous, hypromellose, crospovidone, microcrystalline cellulose, colloidal silicon dioxide, and magnesium stearate.
The yellow opaque capsule shell contains hypromellose, titanium dioxide, and yellow iron oxide. The orange opaque capsule shell contains hypromellose, titanium dioxide, and FD&C yellow #6. The printing ink contains shellac, propylene glycol, strong ammonia solution, and FD&C blue #2 aluminum lake.
Pellets:
ROZLYTREK (entrectinib) oral pellets are supplied as brownish orange or grayish orange, round film-coated pellets in packets. Each packet contains 50 mg of entrectinib and the following inactive ingredients: tartaric acid, microcrystalline cellulose, colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, sodium stearyl fumarate, mannitol, and magnesium stearate.
The film-coating contains polyvinyl alcohol (partially hydrolyzed), titanium dioxide, polyethylene glycol 3350, talc, yellow iron oxide, red iron oxide, and ferrosoferric oxide.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Entrectinib is an inhibitor of the tropomyosin receptor tyrosine kinases (TRK) TRKA, TRKB, and TRKC (encoded by the neurotrophic tyrosine receptor kinase [ NTRK ] genes NTRK1, NTRK2, and NTRK3 , respectively), proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase ROS1 (ROS1), and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) with IC 50 values of 0.1 to 2 nM. Entrectinib also inhibits JAK2 and TNK2 with IC 50 values > 5 nM. The major active metabolite of entrectinib, M5, showed similar in vitro activity against TRK, ROS1, and ALK.
Fusion proteins that include TRK, ROS1, or ALK kinase domains can drive tumorigenic potential through hyperactivation of downstream signaling pathways leading to unconstrained cell proliferation. Entrectinib demonstrated in vitro and in vivo inhibition of cancer cell lines derived from multiple tumor types harboring NTRK , ROS1, and ALK fusion genes.
Entrectinib demonstrated steady-state brain-to-plasma concentration ratios of 0.4 – 2.2 in multiple animal species (mice, rats, and dogs) and demonstrated in vivo anti-tumor activity in mice with intracranial implantation of TRKA- and ALK-driven tumor cell lines.
Pharmacodynamics
Entrectinib exposure-response relationships and the time course of pharmacodynamic responses are unknown.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
Across clinical trials, 3.1% of 355 patients, who received ROZLYTREK at doses ranging from 100 mg to 2600 mg daily under fasting or fed conditions (75% received 600 mg orally once daily) and had at least one post-baseline ECG assessment, experienced QTcF interval prolongation of > 60 ms after starting ROZLYTREK and 0.6% had a QTc interval > 500 ms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ].
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics for entrectinib and its pharmacologically active major circulating metabolite M5 were characterized in adult patients with ROS1 -positive NSCLC, NTRK gene fusion-positive solid tumors, and healthy subjects. The pharmacokinetics of entrectinib and M5 are linear and are not dose-dependent or time-dependent. Steady state is achieved within one week for entrectinib and two weeks for M5 following daily administration of ROZLYTREK. The pharmacokinetic parameters for entrectinib and M5 are described in Table 11 .
| Parameter | Entrectinib Mean Geometric mean (% CV) | M5 Mean(% CV) |
|---|---|---|
| AUC D1 (nM•h) | 31800 (48%) | 10200 (82%) |
| AUC ss (nM•h) | 48000 (77%) | 24000 (97%) |
| C maxD1 (nM) | 2250 (58%) | 622 (79%) |
| C maxss (nM) | 3130 (80%) | 1250 (90%) |
| R acc(AUC) | 1.55 (49%) | 2.84 (93%) |
Absorption
The maximum entrectinib plasma concentration was reached 4 – 6 hours after oral administration of a 600 mg dose.
Entrectinib exposure following a single oral dose (600 mg) of ROZLYTREK oral pellets was not clinically significant compared to ROZLYTREK capsule administered with a light meal (250 calories: 25% fat) in healthy subjects. In STARTRK-2, STARTRK-NG and TAPISTRY studies, ROZLYTREK was administered without regard to food in patients.
Entrectinib exposure of a single dose (600 mg) of ROZLYTREK capsules as a suspension with water or milk, administered orally or through a nasogastric or gastric tube, was not clinically significant compared to administration of intact ROZLYTREK capsules in healthy subjects under fasted conditions.
Effect of Food
A high-fat (approximately 50% of total caloric content), high-calorie (approximately 800 to 1000 calories) meal did not have a significant effect on entrectinib exposure of ROZLYTREK capsules.
Distribution
Entrectinib and its active major metabolite M5 are both > 99% bound to human plasma proteins in vitro.
The estimated apparent volume of distribution (V/F) was 551 L and 81.1 L for entrectinib and M5, respectively.
Elimination
The estimated apparent clearance (CL/F) was 19.6 L/h and 52.4 L/h for entrectinib and M5, respectively. The elimination half-lives of entrectinib and M5 were estimated to be 20 and 40 hours, respectively.
Metabolism
Entrectinib is metabolized primarily by CYP3A4 (~76%). The active metabolite M5 (formed by CYP3A4) is the only major active circulating metabolite identified. M5 has similar pharmacological potency to entrectinib in vitro and circulating M5 exposures at steady-state in patients were 40% of the corresponding entrectinib exposure.
Excretion
Following oral administration of a single oral dose of [ 14 C]-labeled entrectinib, 83% of radioactivity was excreted in feces (36% of the dose as unchanged entrectinib and 22% as M5) with minimal excretion in urine (3%).
Specific Populations
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of entrectinib were observed based on sex, race (White, Asian and Black), mild to moderate renal impairment (CLcr 30 to < 90 mL/min) and mild hepatic impairment (total bilirubin ≤ ULN with aspartate aminotransferase > ULN or total bilirubin > 1.0 – 1.5 times ULN with any aspartate aminotransferase). The impact of severe renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of entrectinib is unknown.
Hepatic Impairment
Following administration of a single oral dose of ROZLYTREK 100 mg (1/6 of the recommended dose), the entrectinib AUC INF was increased by 39% for the mild, 39% for the moderate, and 23% for the severe hepatic impairment groups compared to the normal hepatic function group. The combined AUC last of entrectinib and M5 was increased by 16% for the mild, 16% for the moderate, and 4% for the severe hepatic impairment groups compared to the normal hepatic function group. Large variability in systemic exposure of entrectinib was observed in the hepatic impairment groups.
Pediatric Patients > 6 months
In pediatric patients older than 6 months administered 300 mg/m 2 (based on BSA) of ROZLYTREK once daily, systemic exposure of the sum of entrectinib and M5 in pediatric patients receiving 300 mg/m 2 of ROZLYTREK once daily is within the range of the adults treated with 600 mg of ROZLYTREK once daily.
The available efficacy and safety data also confirm the adequacy of the recommended doses [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4) ] .
Pediatric Patients > 1 to ≤ 6 months
In pediatric patients > 1 to ≤ 6 months administered 250 mg/m 2 (based on BSA) of ROZLYTREK once daily, systemic exposure of the sum of entrectinib and M5 in pediatric patients was at the lower range of the adults administered 600 mg of ROZLYTREK once daily.
The available efficacy and safety data also confirm the adequacy of the recommended doses [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4) ] .
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies
Effect of CYP3A Inhibitors on Entrectinib: Coadministration of itraconazole (a strong CYP3A inhibitor) with a single 100 mg dose of ROZLYTREK capsule increased entrectinib AUC 0-INF by 6-fold and C max by 1.7-fold [see Drug Interactions (7.1) ] . Coadministration of a moderate CYP3A inhibitor with ROZLYTREK capsule is predicted to increase entrectinib AUC 0-Tau by 3-fold and C max by 2.9-fold. Based on physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modelling, a similar magnitude of the effect is expected in children as young as 2 years old.
Effect of CYP3A Inducers on Entrectinib: Coadministration of rifampin (a strong CYP3A inducer) with a single 600 mg dose of ROZLYTREK capsule reduced entrectinib AUC 0-INF by 77% and C max by 56% [see Drug Interactions (7.1) ]. Coadministration of a moderate CYP3A inducer with ROZLYTREK capsule is predicted to reduce entrectinib AUC 0-Tau by 56% and C max by 43%.
Effect of Gastric Acid Reducing Drugs on Entrectinib : Coadministration of a proton pump inhibitor (PPI), lansoprazole with a single 600 mg dose of ROZLYTREK capsule reduced entrectinib AUC by 25% and C max by 23%.
Coadministration of lansoprazole, with a single 600 mg dose of ROZLYTREK capsule as oral suspension in water increased entrectinib AUC by 25% and C max by 17%. These changes are not likely to be clinically significant.
Effect of Entrectinib on CYP Substrates : Coadministration of 600 mg dose of ROZLYTREK capsule once daily with oral midazolam (a sensitive CYP3A substrate) in patients increased the midazolam AUC by 50% but reduced midazolam C max by 21% [see Drug Interactions (7.1) ] .
Effect of Entrectinib on Transporters: Coadministration of a single 600 mg dose of ROZLYTREK capsule with digoxin [a sensitive P-glycoprotein (P-gp) substrate] increased digoxin C max by 28% and AUC by 18%.
In Vitro Studies
Entrectinib is not a substrate of P-gp or BCRP, but M5 is a substrate of P-gp and BCRP. Entrectinib and M5 are not substrates of OATP1B1 or OATP1B3.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies were not conducted with entrectinib. Entrectinib was not mutagenic in vitro in the bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assay; however, an in vitro assay in cultured human peripheral blood lymphocytes did demonstrate a potential for abnormal chromosome segregation (aneugenicity). Entrectinib was not clastogenic or aneugenic in the in vivo micronucleus assay in rats and did not induce DNA damage in a comet assay in rats.
Dedicated fertility studies were not conducted with entrectinib. With the exception of dose-dependent decreases in prostate weight in male dogs, there were no effects on male and female reproductive organs observed in general toxicology studies conducted in rats and dogs at doses resulting in exposures of up to approximately 3.2-fold the human exposure (AUC) at the 600 mg dose.
CLINICAL STUDIES
ROS1 -Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
The efficacy of ROZLYTREK was evaluated in a pooled subgroup of patients with ROS1 -positive metastatic NSCLC who received ROZLYTREK at various doses and schedules (90% received ROZLYTREK 600 mg orally once daily) and were enrolled in one of three multicenter, single-arm, open-label clinical trials: ALKA, STARTRK-1 (NCT02097810) and STARTRK-2 (NCT02568267). To be included in this pooled subgroup, patients were required to have histologically confirmed, recurrent or metastatic, ROS1 -positive NSCLC, ECOG performance status ≤ 2, measurable disease per RECIST v 1.1, ≥ 18 months of follow-up from first post-treatment tumor assessment, and no prior therapy with a ROS1 inhibitor. Identification of ROS1 gene fusion in tumor specimens was prospectively determined in local laboratories using either a fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), next-generation sequencing (NGS), or polymerase chain reaction (PCR) laboratory-developed tests. All patients were assessed for CNS lesions at baseline. The major efficacy outcome measures were overall response rate (ORR) and duration of response (DOR) according to RECIST v1.1 as assessed by Blinded Independent Central Review (BICR). Intracranial response according to Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST v1.1) was assessed by BICR. Tumor assessments with imaging were performed every 8 weeks.
Efficacy was assessed in 92 patients with ROS1 -positive NSCLC. The median age was 53 years (range: 27 to 86); female (65%); White (48%), Asian (45%), and Black (5%); and Hispanic or Latino (2.4%); never smoked (59%); and ECOG performance status 0 or 1 (88%). Ninety-nine percent of patients had metastatic disease, including 42% with CNS metastases; 96% had adenocarcinoma; 65% received prior platinum-based chemotherapy for metastatic or recurrent disease and no patient had progressed in less than 6 months following platinum-based adjuvant or neoadjuvant therapy. ROS1 positivity was determined by NGS in 79%, FISH in 16%, and PCR in 4%. Twenty-five percent had central laboratory confirmation of ROS1 positivity using an analytically validated NGS test.
Efficacy results are summarized in Table 12 .
| Efficacy Parameters | ROZLYTREK n = 92 |
|---|---|
| Confidence Interval (CI) calculated using the Clopper-Pearson method. | |
| Overall Response Rate (95% CI) | 74% (64, 83) |
| Complete Response | 15% |
| Partial Response | 59% |
| Duration of Response (DOR) Observed DOR | n = 68 |
| Range (months) | 2.4, 55.2 denotes ongoing response |
| % DOR ≥ 9 months | 75% |
| % DOR ≥ 12 months | 57% |
| % DOR ≥ 18 months | 38% |
Among the 92 patients, 10 had measurable CNS metastases at baseline as assessed by BICR and had not received radiation therapy to the brain within 2 months prior to study entry. Responses in intracranial lesions were observed in 7 of these 10 patients.
NTRK Gene Fusion-Positive Solid Tumors
Efficacy in Adult Patients
The efficacy of ROZLYTREK was evaluated in a pooled subgroup of adult patients with unresectable or metastatic solid tumors with a NTRK gene fusion enrolled in one of three multicenter, single-arm, open-label clinical trials: ALKA, STARTRK-1 (NCT02097810) and STARTRK-2 (NCT02568267). To be included in this pooled subgroup, patients were required to have progressed following systemic therapy for their disease, if available, or would have required surgery causing significant morbidity for locally advanced disease; measurable disease per RECIST v1.1; at least 2 years of follow-up from first post-treatment tumor assessment; and no prior therapy with a TRK inhibitor. Patients received ROZLYTREK at various doses and schedules (94% received ROZLYTREK 600 mg orally once daily) until unacceptable toxicity or disease progression. Identification of positive NTRK gene fusion status was prospectively determined in local laboratories or a central laboratory using various nucleic acid-based tests. The major efficacy outcome measures were ORR and DOR, as determined by a BICR according to RECIST v1.1. Intracranial response according to RECIST v1.1 as evaluated by BICR. Tumor assessments with imaging were performed every 8 weeks.
Efficacy was assessed in the first 54 adult patients with solid tumors with an NTRK gene fusion enrolled into these trials. The median age was 58 years (range: 21 to 83); female (59%); White (80%), Asian (13%) and Hispanic or Latino (7%); and ECOG performance status 0 (43%) or 1 (46%). Ninety-six percent of patients had metastatic disease, including 22% with CNS metastases, and 4% had locally advanced, unresectable disease. All patients had received prior treatment for their cancer including surgery (n = 43), radiotherapy (n = 36), or systemic therapy (n = 48). Forty patients (74%) received prior systemic therapy for metastatic disease with a median of 1 prior systemic regimen and 17% (n = 9) received 3 or more prior systemic regimens. The most common cancers were sarcoma (24%), lung cancer (19%), salivary gland tumors (13%), breast cancer (11%), thyroid cancer (9%), and colorectal cancer (7%). A total of 52 (96%) patients had an NTRK gene fusion detected by NGS and 2 (4%) had an NTRK gene fusion detected by other nucleic acid-based tests. Eighty-three percent of patients had central laboratory confirmation of NTRK gene fusion using an analytically validated NGS test.
Efficacy results are summarized in Tables 13 , 14 , and 15 .
| Efficacy Parameter | ROZLYTREK n = 54 |
|---|---|
| Overall Response Rate (95% CI) | 59% (45, 72) |
| Complete Response | 13% |
| Partial Response | 46% |
| Duration of Response Observed DOR | n = 32 |
| Range (months) | 2.8, 47.8 denotes ongoing response |
| % with duration ≥ 6 months | 72% |
| % with duration ≥ 9 months | 66% |
| % with duration ≥ 12 months | 56% |
| Tumor Type | Patients n = 54 | ORR | DOR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | 95% CI | Range (months) | ||
| MASC: mammary analogue secretory carcinoma; NA = not applicable due to small numbers or lack of response; PR = partial response. | ||||
| Sarcoma | 13 | 46% | 19%, 75% | 2.8, 33.6 denotes ongoing response |
| Non-small cell lung cancer | 10 | 60% | 26%, 88% | 3.7, 47.8 |
| Salivary (MASC) | 7 | 86% | 42%, 100% | 2.8, 38.5 |
| Breast cancer | 6 | 83% | 36%, 100% | 4.2, 42.3 |
| Thyroid cancer | 5 | 60% | NA | 7.9, 31.5 |
| Colorectal cancer | 4 | 25% | NA | 15.1 |
| Neuroendocrine cancers | 3 | CR | NA | 32.9 |
| Pancreatic cancer | 3 | PR, PR | NA | 7.1, 12.9 |
| Gynecological cancers | 2 | PR | NA | 38.2 |
| Cholangiocarcinoma | 1 | PR | NA | 9.3 |
| NTRK Partner | Patients n = 54 | ORR | DOR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | 95% CI | Range (months) | ||
| PR = partial response; PD = progressive disease; SD = stable disease; NA = not applicable due to small numbers or lack of response; NE = not evaluable. | ||||
| ETV6 – NTRK3 | 25 | 72% | 51%, 88% | 2.8, 47.8 denotes ongoing response |
| TPM3 – NTRK1 | 4 | 50% | 7%, 93% | 2.8, 15.1 |
| TPR – NTRK1 | 4 | 100% | 40%, 100% | 5.6, 33.6 |
| LMNA – NTRK1 | 2 | PR, PD | NA | 4.2 |
| SQSTM1 – NTRK1 | 2 | PR, PD | NA | 18.8 |
| PEAR1 – NTRK1 | 2 | SD, NE | NA | NA |
| EML4 – NTRK3 | 2 | PR, NE | NA | 13.2 |
| CD74 – NTRK1 | 1 | PR | NA | 10.4 |
| PLEKHA6 – NTRK1 | 1 | PR | NA | 9.3 |
| CDC42BPA – NTRK1 | 1 | PR | NA | 29.4 |
| EPS15L1 – NTRK1 | 1 | PR | NA | 3.7 |
| RBPMS – NTRK3 | 1 | PR | NA | 4.6 |
| ERC1 – NTRK1 | 1 | SD | NA | NA |
| PDIA3 – NTRK1 | 1 | SD | NA | NA |
| TRIM33 – NTRK1 | 1 | SD | NA | NA |
| AKAP13 – NTRK3 | 1 | SD | NA | NA |
| KIF7 – NTRK3 | 1 | SD | NA | NA |
| FAM19A2 – NTRK3 | 1 | PD | NA | NA |
| CGN – NTRK1 | 1 | NE | NA | NA |
| SQSTM1 – NTRK2 | 1 | NE | NA | NA |
Among the subset of patients who received prior systemic therapy for metastatic disease, the ORR was 53%, similar to that seen in the overall population. Among the 54 adult patients, 4 had measurable CNS metastases at baseline as assessed by BICR and had not received radiation therapy to the brain within 2 months of study entry. Responses in intracranial lesions were observed in 3 of these 4 patients.
Efficacy in Pediatric Patients
The efficacy of ROZLYTREK was evaluated in pediatric patients with unresectable or metastatic solid tumors with a NTRK gene fusion enrolled in one of two multicenter, open-label clinical trials: STARTRK-NG (NCT02650401) and TAPISTRY (NCT04589845). To be included in the analysis, patients were required to have received at least 1 dose of ROZLYTREK; measurable or evaluable disease at baseline; at least 6 months of follow-up; and no prior therapy with a TRK inhibitor. Patients received ROZLYTREK 20 mg to 600 mg based on body surface area (BSA) orally or via enteral feeding tube once daily in 4-week cycles until unacceptable toxicity or disease progression. The major efficacy outcome measure was overall response rate (ORR) as assessed by BICR according to RECIST v1.1 for extracranial tumors and according to Response Assessment in Neuro-Oncology (RANO) for primary central nervous system (CNS) tumors. An additional efficacy outcome measure was DOR as evaluated by BICR.
Efficacy was assessed in 33 pediatric patients with NTRK fusion-positive solid tumors treated with ROZLYTREK. The median age was 4 years (range: 2 months to 15 years); male (52%); White (58%), Asian (30%), other races (9%), Black or African American (3.0%), and Hispanic or Latino (9%). Seventy-one percent of patients had locally advanced disease and 29% had metastatic disease. Eighty-five percent of patients had received prior treatment for their cancer including surgery (n=20), radiotherapy (n=7) and/or systemic therapy (n=22). The sites for metastatic disease included other (4 patients), brain (3 patients) and lung (2 patients).
Efficacy results are summarized in Tables 16 and 17 .
| Efficacy Parameter Includes patients with measurable and evaluable disease. BICR analysis by RECIST v1.1 for solid tumors (16 patients) and by RANO criteria for primary CNS tumors (17 patients) | ROZLYTREK n = 33 |
|---|---|
| NE = not estimable | |
| Overall Response Rate (95% CI) | 70% (51, 84) |
| Complete Response | 42% |
| Partial Response | 27% |
| Duration of Response Observed DOR | n = 23 |
| Median in months (95% CI) | 25.4 (14.3, NE) |
| % with duration ≥ 12 months | 43% |
| Tumor Type | Patients n = 33 | ORR | DOR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | 95% CI | Range (months) | ||
| NA = not applicable due to small numbers or lack of response | ||||
| Primary CNS Median time to first objective response for patients with primary CNS tumors was 1.9 months | 17 | 53% | 28%, 77% | 5.5, 30.4 denotes ongoing response |
| Infantile fibrosarcoma | 8 | 88% | 47%, 100% | 3.7, 24 |
| Spindle Cell | 6 | 100% | 54%, 100% | 3.7, 12.9 |
| Sarcoma (other) | 1 | 0% Patient with evaluable but non-measurable disease at baseline | NA | NA |
| Melanoma | 1 | 100% | NA | 42.4 |
| NTRK Partner | Patients n = 33 | ORR | DOR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | 95% CI | Range (months) | ||
| PR = partial response; PD = progressive disease; SD = stable disease; NA = not applicable due to small numbers or lack of response | ||||
| ETV6 – NTRK3 | 7 | 86% | 42%, 100% | 11.9- 42.4 denotes ongoing response |
| LMNA – NTRK1 | 5 | 80% | 28%, 99% | 7.4- 12.9 |
| TPM3 – NTRK1 | 3 | 100% | 29%, 100% | 3.7- 24.0 |
| TPR – NTRK1 | 3 | 67% | 9%, 99% | 8.1- 14.3 |
| EML4-NTRK3 | 2 | 50% | 1.3%, 99% | 13.8 |
| BCAN-NTRK1 | 1 | CR | NA | 11.8 |
| EML1-NTRK2 | 1 | CR | NA | 11.8 |
| QKI-NTRK2 | 1 | CR | NA | 11.1 |
| TFG-NTRK3 | 1 | CR | NA | 3.7 |
| KANK1-NTRK2 | 1 | PR | NA | 5.5 |
| KIF5B-NTRK2 | 1 | PR | NA | 12.9 |
| TNS3-NRTK2 | 1 | PR | NA | 9.5 |
| ARHGEF2-NTRK1 | 1 | SD | NA | NA |
| KIF21B-NTRK1 | 1 | SD | NA | NA |
| BCR-NTRK2 | 1 | SD | NA | NA |
| GKAP1-NTRK2 | 1 | SD | NA | NA |
| DNM3-NTRK2 | 1 | PD | NA | NA |
| PARP6-NTRK3 | 1 | PD | NA | NA |
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Capsules
How Supplied
- 100 mg hard capsules: Size 2 yellow opaque, with "ENT 100" printed in blue ink; available in HDPE bottles of 30 capsules: NDC 50242-091-30
- 200 mg hard capsules: Size 0 orange opaque, with "ENT 200" printed in blue ink; available in HDPE bottles of 90 capsules: NDC 50242-094-90
Storage:
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature] .
Store ROZLYTREK capsules in the original container and keep the bottle tightly closed in order to protect from moisture.
Storage time should not exceed 2 hours (below 30°C (86°F)) if capsules are prepared as an oral suspension using drinking water or milk. Discard any unused suspension if not used within 2 hours of preparation.
Pellets
How Supplied
- ROZLYTREK oral pellets are supplied as brownish orange to grayish orange, round pellets, available in: 42-count carton (each packet contains 50 mg entrectinib): NDC 50242-623-42
Storage :
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature] .
Store ROZLYTREK oral pellets in the original container in order to protect from moisture.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE ROZLYTREK ® [roz lye trek] (entrectinib) capsules, for oral use
This Instructions for Use contains information on how to prepare and take or give ROZLYTREK capsules.
| Before Starting |
Read this Instructions for Use before giving ROZLYTREK capsules for the first time and each time you get a refill. There may be new information.
ROZLYTREK capsules can be swallowed whole or prepared as a suspension and taken or given by mouth or through a nasogastric tube (NG tube) or gastrostomy tube (G tube) feeding tube.
| Important Information You Need to Know Before Taking or Giving ROZLYTREK Capsules |
- Your healthcare provider or pharmacist should show you how to correctly prepare and take or give a dose of ROZLYTREK capsules. Always take or give ROZLYTREK capsules exactly as your healthcare provider tells you.
- Do not take or give ROZLYTREK to someone else until you have been shown how to properly prepare and take or give ROZLYTREK.
- Wash your hands before and after preparing, taking, or giving ROZLYTREK.
- Check the expiration date and check the product for damage before use. Do not use if expired or damaged.
| Dosing of ROZLYTREK capsules to be swallowed whole |
- Your healthcare provider will decide the right dose of ROZLYTREK for you or your child.
- Your healthcare provider will tell you what your daily dose of ROZLYTREK is.
- Swallow ROZLYTREK capsules whole, with or without food.
- Swallow whole capsules with drinking water, as directed by your healthcare provider.
- Do not crush or chew the capsules.
| Dosing of ROZLYTREK capsules prepared as a suspension to be taken by mouth or through a feeding tube |
If you or your child cannot swallow capsules whole, ROZLYTREK capsules can be prepared as a suspension and taken or given by mouth or through a feeding tube. For doses of 3 mL or higher, a NG or G feeding tube size 8 French or larger should be used.
Your healthcare provider or pharmacist will show you how to prepare and take or give a dose of ROZLYTREK capsules prepared as a suspension.
Table 1 shows the prescribed dose, the number and strength of capsules needed, the amount of water or milk needed to mix the capsules, and the amount of suspension needed to give for the prescribed dose.
Your healthcare provider will tell you the number of capsules to use, the amount of liquid needed to mix the capsules, and the amount of suspension (mL) to take or give to get the correct dose of ROZLYTREK.
You may need to measure a smaller amount of suspension than you prepared to take or give the correct prescribed dose of ROZLYTREK.
| Prescribed dose of ROZLYTREK to be given | Number of 100 mg or 200 mg capsules needed | Amount of water or milk needed to mix the capsules | Amount of suspension to take or give |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 mg | One 100 mg | 5 mL | 1 mL |
| 30 mg | One 100 mg | 5 mL | 1.5 mL |
| 40 mg | One 100 mg | 5 mL | 2 mL |
| 50 mg | One 100 mg | 5 mL | 2.5 mL |
| 60 mg | One 100 mg | 5 mL | 3 mL |
| 70 mg | One 100 mg | 5 mL | 3.5 mL |
| 80 mg | One 100 mg | 5 mL | 4 mL |
| 90 mg | One 100 mg | 5 mL | 4.5 mL |
| 100 mg | One 100 mg | 5 mL | 5 mL |
| 110 mg | One 200 mg | 10 mL | 5.5 mL |
| 120 mg | One 200 mg | 10 mL | 6 mL |
| 130 mg | One 200 mg | 10 mL | 6.5 mL |
| 140 mg | One 200 mg | 10 mL | 7 mL |
| 150 mg | One 200 mg | 10 mL | 7.5 mL |
| 200 mg | One 200 mg | 10 mL | 10 mL |
| 300 mg | Three 100 mg | 15 mL | 15 mL |
| 400 mg | Two 200 mg | 20 mL | 20 mL |
| 600 mg | Three 200 mg | 30 mL | 30 mL |
Supplies needed to prepare and take or give ROZLYTREK as a suspension :
- the number of capsules needed for your prescribed dose
- a clean empty cup
- a paper towel
- a cup of room temperature drinking water or milk
- an oral syringe (provided by your healthcare provider or pharmacist)
| Preparing ROZLYTREK capsules as a suspension |
| Step 1. Wash your hands. | |
| Step 2. Count the number of capsules you will need to give the prescribed dose. | |
| Step 3. Place a clean empty cup on a paper towel. | 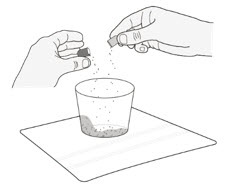 Figure A Figure A |
| Step 4. Tap the capsules to loosen the contents inside (medicine). | |
| Step 5. While holding each capsule above the clean cup, open the capsule by gently pressing in on the capsule and twisting both sides apart. Pour the medicine into the clean cup (Figure A ). | |
Step 6. Tap both sides of the capsule shell and check to make sure all the medicine has gone into the cup.
| |
| Step 7. Push the syringe plunger all the way down to remove any air in the oral syringe (Figure B ) . | 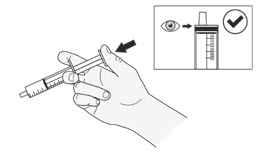 Figure B Figure B |
| Step 8. Place the syringe tip into the room temperature cup of drinking water or milk. Measure the proper amount of liquid (mL) by pulling up on the syringe plunger to draw the liquid into the syringe (Figure C ). Your healthcare provider will tell you how much liquid to use. Do not use any other type of liquid. | 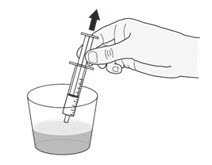 Figure C Figure C |
| Step 9. Check that the correct amount of liquid (mL) is in the syringe (Figure D ). | 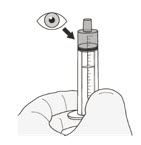 Figure D Figure D |
| Step 10. Add the liquid to the cup that contains the medicine by holding the barrel of the syringe and pushing the syringe plunger all the way down (Figure E ). | 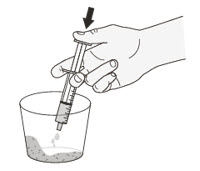 Figure E Figure E |
| Step 11. Let the mixture sit for 15 minutes (Figure F ). Note: It is important to do this to get an even mixture, otherwise you may not get the correct dose. | 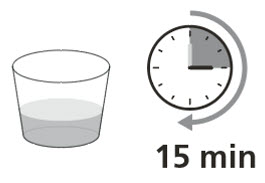 Figure F Figure F |
| Step 12. Swirl the cup several times to evenly mix the medicine in the liquid (Figure G ). Note : The medicine does not dissolve in the liquid and the suspension will be cloudy if you have used water. | 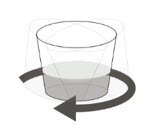 Figure G Figure G |
| Step 13. Push the syringe plunger all the way down to remove any air in the syringe (Figure H ) . | 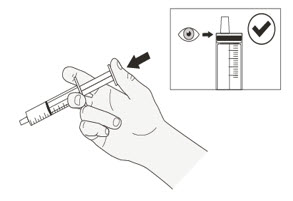 Figure H Figure H |
| Step 14. Swirl the cup of medicine again before placing the syringe in the cup (Figure I ). | 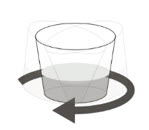 Figure I Figure I |
| Step 15. Place the syringe tip right away into the cup and slowly pull up the plunger to draw up the correct amount (mL) of suspension (Figure J ). Do not wait to draw up the suspension. If it sits for too long, the medicine may settle to the bottom, and you may not get the correct dose. | 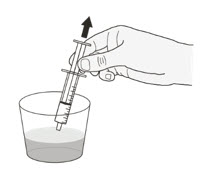 Figure J Figure J |
| Step 16. Check that the correct amount of suspension (mL) is in the syringe (Figure K ). | 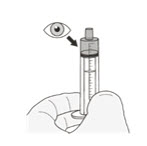 Figure K Figure K |
Step 17. With the tip of the syringe pointing up, check that:
| 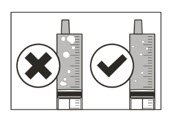 Figure L Figure L |
| Giving ROZLYTREK capsules prepared as a suspension by mouth | |
| Step A1. Sit your child upright when you give a dose of ROZLYTREK by mouth (Figure M ). Place the oral syringe into the mouth with the tip along either cheek. Slowly push the plunger all the way down. Giving ROZLYTREK too fast may cause choking. | 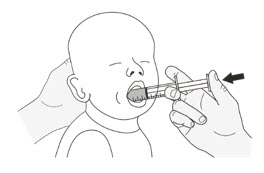 Figure M Figure M |
| Step A2. Check that there is no suspension left in the oral syringe (Figure N ). If suspension remains in the oral syringe, repeat step A1. | 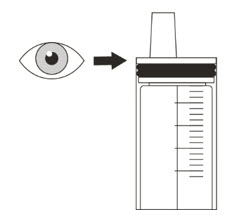 Figure N Figure N |
| Step A3. Give sips of water right after taking or giving the prescribed dose of ROZLYTREK (Figure O ). You can breastfeed or give your child milk if they still taste the medicine after you give the dose. Go to Step D1 for clean-up instructions. | 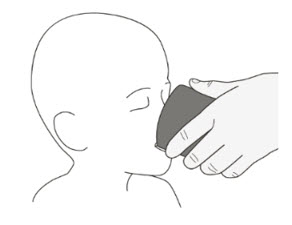 Figure O Figure O |
| Giving ROZLYTREK capsules prepared as a suspension through a gastrostomy tube (G tube) | |
| To take or give ROZLYTREK through a G tube review the manufacturer's instructions and consult your healthcare provider. Make sure that the tube is at least 8 French or larger to prevent clogging of the tube if your dose (amount of suspension) is 3 mL or higher. To take or give ROZLYTREK doses of 3 mL or higher, split the dose in half and give it in 2 parts. Flush the tube with the same amount of water or milk after giving each part. To take or give ROZLYTREK doses of 30 mL, split the dose into at least three 10 mL parts. Flush the tube with the same amount of water or milk after giving each part. | |
| Step B1 Place the oral syringe tip into the G tube. Slowly push the plunger all the way down to give ROZLYTREK (Figure P ). | 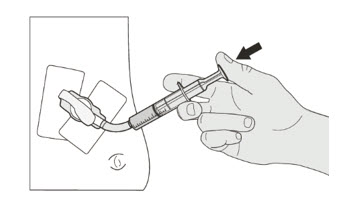 Figure P Figure P |
| Step B2 Check that there is no suspension left in the oral syringe (Figure Q ). If suspension remains in the oral syringe, repeat step B1. | 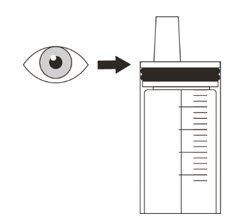 Figure Q Figure Q |
| Step B3 Flush the G tube with water or milk right after giving ROZLYTREK (Figure R ). If you need to split the amount of suspension to give it through the G tube, also split the amount of water or milk you use to flush the tube in the same way. Ask your healthcare provider if you are not sure how much water or milk to use to flush the G tube. Go to Step D1 for clean up instructions. | 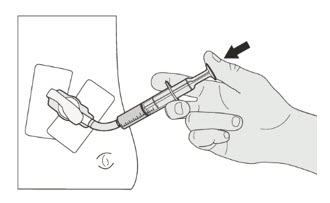 Figure R Figure R |
| Giving ROZLYTREK capsules prepared as a suspension through a nasogastric tube (NG tube) | |
| If you are giving ROZLYTREK through an NG tube, review the manufacturer instructions and consult your healthcare provider. Make sure that the tube is at least 8 French or larger to prevent clogging of the tube if your dose (amount of suspension) is 3 mL or higher. To take or give ROZLYTREK doses of 3 mL or higher, split the dose in half and give it in 2 parts. Flush the tube with the same amount of water or milk after giving each part. To take or give ROZLYTREK doses of 30 mL, split the dose into at least three 10 mL parts. Flush the tube with the same amount of water or milk after giving each part. | |
| Step C1 Place the syringe tip into the NG tube. Slowly press the plunger all the way down to give ROZLYTREK (Figure S ). | 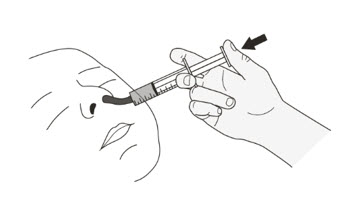 Figure S Figure S |
| Step C2 Check that there is no suspension left in the syringe (Figure T ). If suspension remains in the syringe, repeat step C1. |  Figure T Figure T |
| Step C3 Flush the NG tube with water or milk right after giving ROZLYTREK (Figure U ). If you need to split the amount of suspension to give it through the NG tube, also split the amount of water or milk you use to flush the tube in the same way. Ask your healthcare provider if you are not sure how much water or milk to use to flush the NG tube. Go to Step D1 for clean up instructions. | 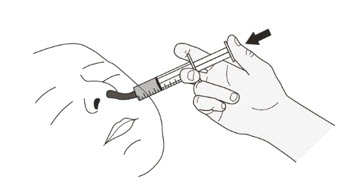 Figure U Figure U |
| Cleaning up and disposing of ROZLYTREK | |
Step D1
| |
| Storing ROZLYTREK | |
| |
Distributed by: Genentech USA, Inc. A Member of the Roche Group 1 DNA Way South San Francisco, CA 94080-4990
ROZLYTREK ® is a registered trademark of Genentech, Inc.
©2023 Genentech, Inc.
For more information, go to www.ROZLYTREK.com or call 1-877-436-3683.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Issued: 10/2023
Mechanism of Action
Entrectinib is an inhibitor of the tropomyosin receptor tyrosine kinases (TRK) TRKA, TRKB, and TRKC (encoded by the neurotrophic tyrosine receptor kinase [ NTRK ] genes NTRK1, NTRK2, and NTRK3 , respectively), proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase ROS1 (ROS1), and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) with IC 50 values of 0.1 to 2 nM. Entrectinib also inhibits JAK2 and TNK2 with IC 50 values > 5 nM. The major active metabolite of entrectinib, M5, showed similar in vitro activity against TRK, ROS1, and ALK.
Fusion proteins that include TRK, ROS1, or ALK kinase domains can drive tumorigenic potential through hyperactivation of downstream signaling pathways leading to unconstrained cell proliferation. Entrectinib demonstrated in vitro and in vivo inhibition of cancer cell lines derived from multiple tumor types harboring NTRK , ROS1, and ALK fusion genes.
Entrectinib demonstrated steady-state brain-to-plasma concentration ratios of 0.4 – 2.2 in multiple animal species (mice, rats, and dogs) and demonstrated in vivo anti-tumor activity in mice with intracranial implantation of TRKA- and ALK-driven tumor cell lines.