Get your patient on Rukobia (Fostemsavir Tromethamine)
Rukobia prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Rukobia patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The recommended dosage of RUKOBIA is one 600-mg tablet taken orally twice daily with or without food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] . Swallow tablets whole. Do not chew, crush, or split tablets.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Rukobia prescribing information
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
RUKOBIA, in combination with other antiretroviral(s), is indicated for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection in heavily treatment-experienced adults with multidrug-resistant HIV-1 infection failing their current antiretroviral regimen due to resistance, intolerance, or safety considerations [see Clinical Studies (14 )].
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The recommended dosage of RUKOBIA is one 600-mg tablet taken orally twice daily with or without food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] . Swallow tablets whole. Do not chew, crush, or split tablets.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Each RUKOBIA extended-release tablet contains 600 mg of fostemsavir (equivalent to 725 mg of fostemsavir tromethamine). The tablets are beige, oval, film-coated, biconvex tablets, debossed with “SV 1V7” on one side.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in individuals exposed to RUKOBIA during pregnancy. Healthcare providers are encouraged to register patients by calling the Antiretroviral Pregnancy Registry (APR) at 1-800-258-4263.
Risk Summary
There are insufficient human data on the use of RUKOBIA during pregnancy to adequately assess a drug-associated risk of birth defects and miscarriage. In animal reproduction studies, oral administration of fostemsavir to pregnant rats and rabbits during organogenesis resulted in no adverse developmental effects at clinically relevant temsavir exposures (see Data) .
The background risk for major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. The background rate for major birth defects in a U.S. reference population of the Metropolitan Atlanta Congenital Defects Program (MACDP) is 2.7%. The estimated background rate of miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies in the U.S. general population is 15% to 20%.
Data
Animal Data: Fostemsavir was administered orally to pregnant rats (50, 200, 600 mg/kg/day) and rabbits (25, 50, or 100 mg/kg/day) during Gestation Days 6 to 15 (rat) and 7 to 19 (rabbit). No fetal abnormalities were observed at temsavir exposures of approximately 180 (rat) and 30 (rabbit) times those in humans at the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD). In rabbits, increased embryonic death associated with maternal toxicity was observed at temsavir exposures approximately 60 times those in humans at the MRHD. In a separate rat study conducted at drug exposures approximately 200 times those in humans at the MRHD, fetal abnormalities (cleft palate, open eyes, shortened snout, microstomia, misaligned mouth/jaw, and protruding tongue) and reductions in fetal body weights occurred in the presence of maternal toxicity.
In a rat pre- and postnatal development study, fostemsavir was administered orally at doses of 10, 50, or 300 mg/kg/day from Gestation Day 6 through Lactation Day 20. Reduced neonatal survival (7 to 14 days after birth) in the absence of other adverse fetal or neonatal effects was observed at maternal temsavir exposures approximately 130 times those in humans at the MRHD. No adverse fetal or neonatal effects were observed at maternal temsavir exposures approximately 35 times those in humans at the MRHD.
In a distribution study in pregnant rats, fostemsavir-related drug materials (i.e., temsavir and/or temsavir-derived metabolites) crossed the placenta and were detectable in fetal tissue.
Lactation
Risk Summary
It is not known whether RUKOBIA is present in human breast milk, affects human milk production, or has effects on the breastfed infant. When administered to lactating rats, fostemsavir-related drug was present in rat milk (see Data) . When a drug is present in animal milk, it is likely that the drug will be present in human milk.
Potential risks of breastfeeding include: (1) HIV-1 transmission (in HIV-1–negative infants), (2) developing viral resistance (in HIV-1–positive infants), and (3) adverse reactions in a breastfed infant similar to those seen in adults.
Data
In a distribution study, fostemsavir-related drug materials (i.e., temsavir and/or temsavir-derived metabolites) were excreted in rat milk following a single dose of fostemsavir administered to lactating rats 7 to 9 days postpartum. In the pre- and postnatal development study in rats, temsavir was present in milk at concentrations similar to those measured in maternal plasma, as determined 11 days postpartum. In addition, lactational exposure was associated with reduced offspring survival at maternal temsavir exposures not thought to be clinically relevant.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of RUKOBIA have not been established in pediatric patients.
Geriatric Use
Clinical trials of RUKOBIA did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and older to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. In general, caution should be exercised in administration of RUKOBIA in elderly patients reflecting greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )]. Elderly patients may be more susceptible to drug-induced QT interval prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 )].
Renal Impairment
No dosage adjustment is required for patients with renal impairment or those on hemodialysis [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] .
Hepatic Impairment
No dosage adjustment is required in patients with mild to severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Score A, B, or C) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] .
CONTRAINDICATIONS
RUKOBIA is contraindicated in patients:
- with previous hypersensitivity to fostemsavir or any of the components of RUKOBIA.
- coadministered strong cytochrome P450 (CYP)3A inducers, as significant decreases in temsavir (the active moiety of fostemsavir) plasma concentrations may occur which may result in loss of virologic response. These drugs include, but are not limited to [see Drug Interactions (7 ), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] :
- Androgen receptor inhibitor: Enzalutamide
- Anticonvulsants: Carbamazepine, phenytoin
- Antimycobacterial: Rifampin
- Antineoplastic: Mitotane
- Herbal product: St John’s wort ( Hypericum perforatum )
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Immune reconstitution syndrome has been reported in patients treated with combination antiretroviral therapies. (5.1 )
- QTc prolongation: Use RUKOBIA with caution in patients with a history of QTc prolongation or with relevant pre-existing cardiac disease or who are taking drugs with a known risk of Torsade de Pointes. (5.2 )
- Elevations in hepatic transaminases in patients with hepatitis B (HBV) or C (HCV) virus co-infection: Elevations in hepatic transaminases were observed in a greater proportion of subjects with HBV and/or HCV co-infection compared with those with HIV mono-infection. (5.3 )
Immune Reconstitution Syndrome
Immune reconstitution syndrome has been reported in patients treated with combination antiretroviral therapy, including RUKOBIA [see Adverse Reactions (6.1 )] . During the initial phase of combination antiretroviral treatment, patients whose immune systems respond may develop an inflammatory response to indolent or residual opportunistic infections (such as Mycobacterium avium infection, cytomegalovirus, Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia [PCP], or tuberculosis), which may necessitate further evaluation and treatment.
Autoimmune disorders (such as Graves’ disease, polymyositis, Guillain-Barré syndrome, and autoimmune hepatitis) have also been reported to occur in the setting of immune reconstitution; however, the time to onset is more variable and can occur many months after initiation of treatment.
QTc Prolongation with Higher than Recommended Dosages
RUKOBIA at 2,400 mg twice daily, 4 times the recommended daily dose, has been shown to significantly prolong the QTc interval of the electrocardiogram [see Drug Interactions (7.4 ), Clinical Pharmacology (12.2 )] . RUKOBIA should be used with caution in patients with a history of QTc interval prolongation, when coadministered with a drug with a known risk of Torsade de Pointes, or in patients with relevant pre-existing cardiac disease. Elderly patients may be more susceptible to drug-induced QT interval prolongation.
Elevations in Hepatic Transaminases in Patients with Hepatitis B or C Virus Co-Infection
Monitoring of liver chemistries is recommended in patients with hepatitis B (HBV) and/or C (HCV) virus co-infection. Elevations in hepatic transaminases were observed in a greater proportion of subjects with HBV and/or HCV co-infection compared with those with HIV mono-infection. Some of these elevations in transaminases were consistent with hepatitis B reactivation, particularly in the setting where anti-hepatitis therapy was withdrawn [see Adverse Reactions (6.1 )] . Particular diligence should be applied in initiating or maintaining effective hepatitis B therapy (referring to treatment guidelines) when starting RUKOBIA in patients co-infected with hepatitis B.
Risk of Adverse Reactions or Loss of Virologic Response Due to Drug Interactions
The concomitant use of RUKOBIA and certain other drugs may result in known or potentially significant drug interactions, some of which may lead to [see Contraindications (4 ), Warnings and Precautions (5.2 ), Drug Interactions (7.3 ), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] :
- Loss of therapeutic effect of RUKOBIA and possible development of resistance due to reduced exposure of temsavir.
- Possible prolongation of QTc interval from increased exposure to temsavir [see Drug Interactions (7.4 )] .
See Table 3 for steps to prevent or manage these possible and known significant drug interactions, including dosing recommendations. Consider the potential for drug interactions prior to and during therapy with RUKOBIA, review concomitant medications during therapy with RUKOBIA, and monitor for the adverse reactions associated with the concomitant drugs.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared with rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
A total of 620 subjects with HIV-1 infection received at least one dose of RUKOBIA as part of a controlled clinical trial.
The primary safety assessment of RUKOBIA is based on 96 weeks of data from a Phase 3 partially randomized, international, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (BRIGHTE) conducted in 371 heavily treatment-experienced adult subjects [see Clinical Studies (14 )] . In the randomized cohort, 203 subjects received at least one dose of blinded RUKOBIA 600 mg twice daily and 69 subjects received placebo in addition to their current failing regimen for 8 days of functional monotherapy. Beyond Day 8, all randomized subjects except one received open-label RUKOBIA 600 mg twice daily plus an optimized background therapy (OBT). In the nonrandomized cohort, 99 subjects received open-label RUKOBIA 600 mg twice daily plus OBT from Day 1 onward.
A total of 370 subjects (271 randomized and 99 nonrandomized) received at least 1 dose of RUKOBIA 600 mg twice daily in the BRIGHTE trial. Overall, most (81%) of the adverse reactions reported with RUKOBIA were mild or moderate in severity. The proportion of subjects who discontinued treatment with RUKOBIA due to an adverse event was 7% at Week 96 (randomized: 5% and nonrandomized: 12%). The most common adverse events leading to discontinuation were related to infections (3% of subjects receiving RUKOBIA). Serious drug reactions occurred in 3% of subjects and included 3 cases of severe immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome.
Data from the randomized cohort form the basis of the safety assessment of RUKOBIA because the presence of significant comorbid illness in the nonrandomized cohort (associated with advanced HIV infection) may confound the assessment of causality. Adverse reactions (all grades) reported in ≥2% of subjects in the randomized cohort in the Week 96 analysis are listed in Table 1 .
| OBT = Optimized background therapy. | |
| a Frequencies of adverse reactions are based on all treatment-emergent adverse events attributed to study drug by the investigator. b Of the 272 subjects enrolled in the randomized cohort, 1 subject who received placebo withdrew from the trial prior to receiving RUKOBIA in the open-label phase of the trial. c Includes pooled terms: abdominal discomfort, abdominal pain, and abdominal pain upper. d Includes pooled terms: fatigue and asthenia. e Includes pooled terms: rash, rash generalized, rash maculo-papular, rash pruritic, and dermatitis allergic. f Includes pooled terms: insomnia, sleep deficit, sleep disorder, abnormal dreams. | |
Adverse Reaction | RUKOBIA plus OBT (n = 271) b |
Nausea | 10% |
Diarrhea | 4% |
Headache | 4% |
Abdominal pain c | 3% |
Dyspepsia | 3% |
Fatigue d | 3% |
Rash e | 3% |
Sleep disturbance f | 3% |
Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome | 2% |
Somnolence | 2% |
Vomiting | 2% |
Adverse reactions in the nonrandomized cohort were similar to those observed in the randomized cohort. The most common adverse reactions reported in nonrandomized subjects were fatigue (7%), nausea (6%), and diarrhea (6%).
Less Common Adverse Reactions
The following adverse reactions occurred in <2% of subjects receiving RUKOBIA in the randomized cohort of the BRIGHTE trial. These events have been included based on the assessment of potential causal relationship and were also reported in the nonrandomized cohort.
Cardiac Disorders: Electrocardiogram QT prolonged. All reports were asymptomatic.
Musculoskeletal Disorders: Myalgia.
Nervous System Disorders: Dizziness, d ysgeusia, neuropathy peripheral (includes pooled terms: neuropathy peripheral and peripheral sensory neuropathy).
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Pruritus.
Laboratory Abnormalities
Selected laboratory abnormalities (Grades 3 to 4) with a worsening grade from baseline and representing the worst-grade toxicity in ≥2% of subjects in the randomized cohort of the BRIGHTE trial are presented in Table 2 .
| OBT = Optimized background therapy; ULN = Upper limit of normal. a Percentages were calculated based on the number of subjects with post-baseline toxicity grades for each laboratory parameter (n = 221 for cholesterol and triglycerides, n = 216 for LDL cholesterol, and n = 268 for all other parameters). b Grade 3 only (no Grade 4 values reported). | |
Laboratory Parameter Preferred Term | RUKOBIA plus OBT (n = 271 a ) |
ALT (>5.0 x ULN) | 5% |
AST (>5.0 x ULN) | 4% |
Direct bilirubin (>ULN) b | 7% |
Bilirubin (≥2.6 x ULN) | 3% |
Cholesterol (≥300 mg/dL) b | 5% |
Creatinine (>1.8 x ULN or 1.5 x baseline) | 19% |
Creatine kinase (≥10 x ULN) | 2% |
Hemoglobin (<9.0 g/dL) | 6% |
Hyperglycemia (>250 mg/dL) | 4% |
Lipase (>3.0 x ULN) | 5% |
LDL cholesterol (≥190 mg/dL) | 4% |
Neutrophils (≤599 cells/mm 3 ) | 4% |
Triglycerides (>500 mg/dL) | 5% |
Urate (>12 mg/dL) | 3% |
The incidence of selected laboratory abnormalities (Grades 3 to 4) in the nonrandomized cohort were overall consistent with those of the randomized cohort, with the exception of direct bilirubin (14% versus 7%), bilirubin (6% versus 3%), lipase (10% versus 5%), triglycerides (10% versus 5%), neutrophils (7% versus 4%), and leukocytes (6% versus 1%), respectively.
Changes in Serum Creatinine: Clinically relevant increases in serum creatinine have primarily occurred in patients with identifiable risk factors for reduced renal function, including pre-existing medical history of renal disease and/or concomitant medications known to cause increases in creatinine. A causal association between RUKOBIA and elevation in serum creatinine has not been established.
Changes in Direct Bilirubin: Increases in direct (conjugated) bilirubin have been observed following treatment with RUKOBIA (Table 2 ). Cases of clinical significance were uncommon and were confounded by the presence of intercurrent serious comorbid events (e.g., sepsis, cholangiocarcinoma, or other complications of viral hepatitis co-infection). In the remaining cases, elevations in direct bilirubin (without clinical jaundice) were typically transient, occurred without increases in liver transaminases, and resolved on continued RUKOBIA.
Changes in ALT and AST in Subjects with Hepatitis B and/or Hepatitis C Virus Co-Infection: A total of 29 subjects with Hepatitis B and/or Hepatitis C co-infection were enrolled in the BRIGHTE trial (randomized and nonrandomized cohorts combined). Grade 3 and 4 elevations in ALT and AST occurred in 14% of these subjects compared with 3% (ALT) and 2% (AST) of subjects without viral hepatitis co-infection. Some of these elevations in transaminases were consistent with hepatitis B reactivation particularly in the setting where anti-hepatitis therapy was withdrawn [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 )] .
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Potential for RUKOBIA to Affect Other Drugs
Temsavir may increase plasma concentrations of grazoprevir or voxilaprevir to a clinically relevant extent due to organic anion transporting polypeptide (OATP)1B1/3 inhibition [see Drug Interactions (7.3 )] .
When RUKOBIA was coadministered with oral contraceptives, temsavir increased concentrations of ethinyl estradiol (Table 3 ) [see Drug Interactions (7.3 ), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] .
Potential for Other Drugs to Affect RUKOBIA
Coadministration of RUKOBIA with rifampin, a strong CYP3A4 inducer, significantly decreases temsavir plasma concentrations. The use of RUKOBIA with drugs that are strong inducers of CYP3A4 can significantly decrease temsavir plasma concentrations which may lead to loss of virologic response [see Contraindications (4 ), Drug Interactions (7.3 ), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] .
Established and Other Potentially Significant Drug Interactions
Information regarding potential drug interactions with RUKOBIA is provided in Table 3 . These recommendations are based on either drug interaction trials or predicted interactions due to the expected magnitude of interaction and potential for serious adverse events or loss of efficacy [see Contraindications (4 ), Warnings and Precautions (5.4 ), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] .
| ↑ = Increase; ↓ = Decrease; HCV = Hepatitis C virus. a This table is not all inclusive. b See Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 ) for magnitude of interaction. | ||
Concomitant Drug Class: Drug Name | Effect on Concentration of Temsavir and/or Concomitant Drug | Clinical Comment |
Androgen receptor inhibitor: Enzalutamide | ↓Temsavir | Coadministration is contraindicated due to potential for loss of therapeutic effect to RUKOBIA [see Contraindications (4 )] . |
Anticonvulsants: Carbamazepine Phenytoin | ↓Temsavir | |
Antimycobacterial: Rifampin b | ↓Temsavir | |
Antineoplastic: Mitotane | ↓Temsavir | |
Herbal product: St John’s wort ( Hypericum perforatum ) | ↓Temsavir | |
Hepatitis C virus direct-acting antivirals: Grazoprevir Voxilaprevir | ↑Grazoprevir ↑Voxilaprevir | Coadministration may increase exposures of grazoprevir or voxilaprevir; however, the magnitude of increase in exposure is unknown. Increased exposures of grazoprevir may increase the risk of ALT elevations. Use an alternative HCV regimen if possible. |
Oral contraceptive: Ethinyl estradiol b | ↑Ethinyl estradiol | Ethinyl estradiol daily dose should not exceed 30 mcg . Caution is advised particularly in patients with additional risk factors for thromboembolic events. |
Statins: Rosuvastatin b Atorvastatin Fluvastatin Pitavastatin Simvastatin | ↑Rosuvastatin ↑Atorvastatin ↑Fluvastatin ↑Pitavastatin ↑Simvastatin | Use the lowest possible starting dose for statins and monitor for statin-associated adverse events. |
Drugs that Prolong QT Interval
Drugs without Clinically Significant Interactions with RUKOBIA
Based on drug interaction study results, the following drugs can be coadministered with RUKOBIA without a dose adjustment: atazanavir/ritonavir, buprenorphine/naloxone, cobicistat, darunavir/cobicistat, darunavir/ritonavir with and without etravirine, etravirine, famotidine, maraviroc, methadone, norethindrone, raltegravir, ritonavir, rifabutin with and without ritonavir, tenofovir disoproxil fumarate [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] .
DESCRIPTION
Fostemsavir tromethamine is a prodrug of temsavir, an HIV-1 gp120-directed attachment inhibitor.
The chemical name of fostemsavir tromethamine is (3-((4-benzoyl-1-piperazinyl)(oxo)acetyl)-4-methoxy-7-(3-methyl-1 H -1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-1 H -pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-1-yl)methyl dihydrogen phosphate, 2-amino-2-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-propanediol (1:1). The empirical formula is C 25 H 26 N 7 O 8 P•C 4 H 11 NO 3 . The molecular weight is 704.6 g/mol (583.5 as free acid). It has the following structural formula:
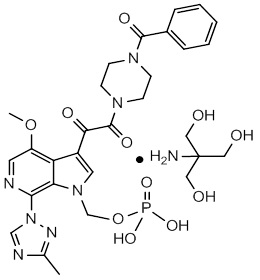
Fostemsavir tromethamine is a white powder and is soluble to greater than 250 mg/mL in aqueous solutions with a pH greater than 3.7.
RUKOBIA extended-release tablets are for oral administration. Each film-coated tablet contains 600 mg of fostemsavir (equivalent to 725 mg fostemsavir tromethamine), and the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose, and magnesium stearate. The tablet film-coating contains the inactive ingredients iron oxide red, iron oxide yellow, polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol, talc, and titanium dioxide.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
RUKOBIA is an HIV-1 antiretroviral agent [see Microbiology (12.4 )].
Pharmacodynamics
Cardiac Electrophysiology
At therapeutic doses, RUKOBIA does not prolong the QT interval to any clinically relevant extent. At 4 times the recommended dose, the mean (upper 90% confidence interval) QTcF increase was 11.2 milliseconds (13.3 milliseconds). The observed increase in QTcF was temsavir concentration-dependent [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 )] .
Exposure-Response Relationship
In the Phase 3 trial evaluating the recommended dosing regimen of RUKOBIA (600 mg twice daily) in subjects with multidrug resistant HIV-1 infection on their failing regimen, no relationship was observed between plasma temsavir C trough and change in plasma HIV-1 RNA from Day 1 to Day 8.
Pharmacokinetics
Fostemsavir is a prodrug of temsavir, its active moiety. Fostemsavir was generally not detectable in plasma following oral administration. However, temsavir was readily absorbed (Table 4 ). Following oral administration, increases in plasma temsavir exposure (C max and AUC tau ) appeared dose proportional or slightly greater than dose proportional, over the range of 600 mg to 1,800 mg of RUKOBIA. The pharmacokinetics of temsavir following administration of RUKOBIA are similar between healthy and HIV-1–infected subjects.
Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion
The pharmacokinetic properties of temsavir following administration of RUKOBIA are provided in Table 4 . The multiple-dose pharmacokinetic parameters are provided in Table 5 .
| HSA = Human serum albumin; UGT = Uridine diphosphate glucuronosyl transferases. a Dosing in absolute bioavailability study: single-dose administration of fostemsavir extended-release tablet 600 mg followed by single IV infusion of [ 13 C] temsavir 100 mcg. b Geometric mean ratio (fed/fasted) in pharmacokinetic parameters and (90% confidence interval). Standard meal = ~423 kcal, 36% fat, 47% carbohydrates, and 17% protein. High-calorie/high-fat meal = ~985 kcal, 60% fat, 28% carbohydrates, and 12% protein. c Volume of distribution at steady state (Vss) following IV administration. d Apparent clearance. e In vitro studies have shown that temsavir is biotransformed into 2 predominant circulating inactive metabolites: BMS-646915 (hydrolysis metabolite) and BMS-930644 (N-dealkylated metabolite). f Dosing in mass balance study: single-dose administration of [ 14 C] fostemsavir oral solution 300 mg containing 100 microCi (3.7 MBq) of total radioactivity. | |
Absorption | |
% Absolute bioavailability a | 26.9 |
T max (h) | 2.0 |
Effect of standard meal (relative to fasting) b | AUC ratio =1.10 (0.95, 1.26) |
Effect of high-fat meal (relative to fasting) b | AUC ratio =1.81 (1.54, 2.12) |
Distribution | |
% Plasma protein binding | 88.4 (primarily to HSA) |
Blood-to-plasma ratio | 0.74 |
Steady-state volume of distribution (Vss, L) c | 29.5 |
Elimination | |
Major route of elimination | Metabolism |
Clearance (CL and CL/F d , L/h) | 17.9 and 66.4 |
Half-life (h) | 11 |
Metabolism | |
Metabolic pathways e | Hydrolysis (esterases) [36.1% of oral dose] Oxidation (CYP3A4) [21.2% of oral dose] UGT [<1% of oral dose] |
Excretion | |
% of dose excreted in urine (unchanged drug) f | 51 (<2) |
% of dose excreted in feces (unchanged drug) f | 33 (1.1) |
| CV = Coefficient of variation; C max = Maximum concentration; AUC = Area under the time concentration curve; C 12 = Concentration at 12 hours. a Based on population pharmacokinetic analyses in heavily treatment-experienced adult subjects with HIV-1 infection receiving 600 mg of RUKOBIA twice daily with or without food in combination with other antiretroviral drugs. | |
Parameter Mean (CV%) | Temsavir a |
C max (ng/mL) | 1,770 (39.9) |
AUC tau (ng.h/mL) | 12,900 (46.4) |
C trough or C 12 (ng/mL) | 478 (81.5) |
Specific Populations
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of temsavir were observed based on age, sex, race/ethnicity (White, Black/African American, Asian, or other). The effect of hepatitis B and/or C virus co-infection on the pharmacokinetics of temsavir is unknown.
The pharmacokinetics of temsavir has not been studied in pediatric subjects and data are limited in subjects aged 65 years or older.
Population pharmacokinetic analyses of subjects with HIV-1 infection aged up to 73 years from studies with RUKOBIA indicated age had no clinically relevant effect on the pharmacokinetics of temsavir [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4 , 8.5 )] .
Patients with Renal Impairment: No clinically relevant differences in total and unbound temsavir pharmacokinetics were observed in patients with mild to severe renal impairment. No clinically relevant differences in temsavir pharmacokinetics were observed in patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) on hemodialysis compared with the same patients with ESRD off hemodialysis. Temsavir was not readily cleared by hemodialysis with approximately 12.3% of the administered dose removed during the 4-hour hemodialysis session [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6 )] .
Patients with Hepatic Impairment: No clinically relevant differences in total and unbound temsavir pharmacokinetics were observed in patients with mild to severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Score A, B, or C) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7 )] .
Drug Interaction Studies
Temsavir is a substrate of CYP3A, esterases, P-glycoprotein (P-gp), and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP). Drugs that induce or inhibit CYP3A, P-gp, and BCRP may affect temsavir plasma concentrations. Coadministration of fostemsavir with drugs that are strong CYP3A inducers result in decreased concentrations of temsavir. Coadministration of fostemsavir with drugs that are moderate CYP3A inducers and/or strong CYP3A, P-gp and/or BCRP inhibitors are not likely to have a clinically relevant effect on the plasma concentrations of temsavir.
Temsavir is an inhibitor of OATP1B1 and OATP1B3. Additionally, temsavir and 2 metabolites (Table 4 ) are inhibitors of BCRP. Thus, temsavir is expected to affect the pharmacokinetics of drugs that are substrates of OATP1B1/3 and/or BCRP [see Drug Interactions (7.3 )] .
At clinically relevant concentrations, significant interactions are not expected when RUKOBIA is coadministered with substrates of CYP1A2, 2A6, 2B6, 2C8, 2C9, 2C19, 2E1, 2D6, and 3A4; UGT1A1, 1A4, 1A6, 1A9, 2B7; P-gp; multidrug resistance protein (MRP)2; bile salt export pump (BSEP); sodium taurocholate co-transporting polypeptide (NTCP); multidrug and toxin extrusion protein (MATE)1/2K; organic anion transporters (OAT)1 and OAT3; organic cation transporters (OCT)1 and OCT2 based on in vitro and clinical drug interaction results (Table 6 ).
Drug interaction studies were performed with RUKOBIA and other drugs likely to be coadministered for pharmacokinetic interactions. The effects of temsavir on the pharmacokinetics of coadministered drugs are summarized in Table 6 and the effects of coadministration of other drugs on the pharmacokinetics of temsavir are summarized in Table 7 .
Dosing recommendations as a result of established and other potentially significant drug-drug interactions with RUKOBIA are provided in Table 3 [see Drug Interactions (7.3 )] .
| CI = Confidence Interval; n = Maximum number of subjects with data; NA = Not available. AUC = AUC tau for repeat-dose studies and AUC (0-inf) for single-dose study. a Temsavir is the active moiety. | ||||||
Coadministered Drug(s) and Dose(s) | Dose of RUKOBIA | n | Geometric Mean Ratio (90% CI) of Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Coadministered Drugs with/without RUKOBIA No Effect = 1.00 | |||
C max | AUC | C tau | ||||
Atazanavir + | 300 mg once daily/ | 600 mg twice daily | 18 | 1.03 (0.96, 1.10) | 1.09 (1.03, 1.15) | 1.19 (1.10, 1.30) |
Ritonavir | 100 mg once daily | 1.02 (0.96, 1.09) | 1.07 (1.03, 1.10) | 1.22 (1.12, 1.32) | ||
Darunavir + | 600 mg twice daily/ | 600 mg twice daily | 13 | 0.98 (0.93, 1.04) | 0.94 (0.89, 1.00) | 0.95 (0.87, 1.04) |
Ritonavir | 100 mg twice daily | 1.00 (0.86, 1.16) | 1.15 (0.99, 1.33) | 1.19 (1.06, 1.35) | ||
Darunavir + | 600 mg twice daily/ | 600 mg twice daily | 13 | 0.95 (0.90, 1.01) | 0.94 (0.89, 0.99) | 0.88 (0.77, 1.01) |
Ritonavir + | 100 mg twice daily/ | 1.14 (0.96, 1.35) | 1.09 (0.98, 1.22) | 1.07 (0.97, 1.17) | ||
Etravirine | 200 mg twice daily | 1.18 (1.10, 1.27) | 1.28 (1.20, 1.36) | 1.28 (1.18, 1.39) | ||
Etravirine | 200 mg twice daily | 600 mg twice daily | 14 | 1.11 (1.04, 1.19) | 1.11 (1.05, 1.17) | 1.14 (1.08, 1.21) |
Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate | 300 mg once daily | 600 mg twice daily | 18 | 1.18 (1.12, 1.25) | 1.19 (1.12, 1.25) | 1.28 (1.20, 1.38) |
Rosuvastatin | 10-mg single dose | 600 mg twice daily | 18 | 1.78 (1.52, 2.09) | 1.69 (1.44, 1.99) | NA |
Ethinyl estradiol/ | 0.030 mg once daily/ | 600 mg twice daily | 26 | 1.39 (1.28, 1.51) | 1.40 (1.29, 1.51) | NA |
Norethindrone | 1.5 mg once daily | 1.08 (1.01, 1.16) | 1.08 (1.03, 1.14) | NA | ||
Maraviroc | 300 mg twice daily | 600 mg twice daily | 13 | 1.01 (0.84, 1.20) | 1.25 (1.08, 1.44) | 1.37 (1.26, 1.48) |
Methadone | 40 to 120 mg | 600 mg | 16 | |||
R(-) Methadone | once daily | twice daily | 1.15 (1.11, 1.20) | 1.13 (1.07, 1.19) | 1.09 (1.01, 1.17) | |
S(+) Methadone | 1.15 (1.10, 1.19) | 1.15 (1.09, 1.21) | 1.10 (1.02, 1.19) | |||
Total Methadone | 1.15 (1.11, 1.19) | 1.14 (1.09, 1.20) | 1.10 (1.02, 1.18) | |||
Buprenorphine/ Naloxone | 8/2 to 24/6 mg once daily | 600 mg twice daily | 16 | |||
Buprenorphine | 1.24 (1.06, 1.46) | 1.30 (1.17, 1.45) | 1.39 (1.18, 1.63) | |||
Norbuprenorph- ine | 1.24 (1.03, 1.51) | 1.39 (1.16, 1.67) | 1.36 (1.10, 1.69) | |||
| CI = Confidence Interval; n = Maximum number of subjects with data; NA = Not available. AUC = AUC tau for repeat-dose studies and AUC (0-inf) for single-dose study. C tau = C 12 for single-dose study. a Temsavir is the active moiety. | ||||||
Coadministered Drug(s) and Dose(s) | Dose of RUKOBIA | n | Geometric Mean Ratio (90% CI) of Temsavir Pharmacokinetic Parameters with/without Coadministered Drugs No Effect = 1.00 | |||
C max | AUC | C tau | ||||
Atazanavir + | 300 mg once daily/ | 600 mg twice daily | 36 | 1.68 (1.58, 1.79) | 1.54 (1.44, 1.65) | 1.57 (1.28, 1.91) |
Ritonavir | 100 mg once daily | |||||
Darunavir + | 600 mg twice daily/ | 600 mg twice daily | 14 | 1.52 (1.28, 1.82) | 1.63 (1.42, 1.88) | 1.88 (1.09, 3.22) |
Ritonavir | 100 mg twice daily | |||||
Darunavir + | 600 mg twice daily/ | 600 mg twice daily | 18 | 1.53 (1.32, 1.77) | 1.34 (1.17, 1.53) | 1.33 (0.98, 1.81) |
Ritonavir + | 100 mg twice daily/ | |||||
Etravirine | 200 mg twice daily | |||||
Etravirine | 200 mg twice daily | 600 mg twice daily | 14 | 0.52 (0.45, 0.59) | 0.50 (0.44, 0.57) | 0.48 (0.32, 0.72) |
Ritonavir | 100 mg once daily | 600 mg twice daily | 18 | 1.53 (1.31, 1.79) | 1.45 (1.29, 1.61) | 1.44 (1.00, 2.08) |
Raltegravir + | 400 mg twice daily/ | 1,200 mg once daily | 17 | 1.23 (0.92, 1.64) | 1.07 (0.84, 1.34) | 1.17 (0.59, 2.32) |
Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate | 300 mg once daily | |||||
Rifabutin + | 150 mg once daily/ | 600 mg twice daily | 23 | 1.50 (1.38, 1.64) | 1.66 (1.52, 1.81) | 2.58 (1.95, 3.42) |
Ritonavir | 100 mg once daily | |||||
Rifabutin | 300 mg once daily | 600 mg twice daily | 22 | 0.73 (0.65, 0.83) | 0.70 (0.64, 0.76) | 0.59 (0.46, 0.77) |
Rifampin | 600 mg once daily | 1,200-mg single dose | 15 | 0.24 (0.21, 0.28) | 0.18 (0.16, 0.2) | NA |
Cobicistat | 150 mg once daily | 600 mg twice daily | 16 | 1.71 (1.54, 1.90) | 1.93 (1.75, 2.12) | 2.36 (2.03, 2.75) |
Darunavir + | 800 mg once daily/ | 600 mg twice daily | 15 | 1.79 (1.62, 1.98) | 1.97 (1.78, 2.18) | 2.24 (1.75, 2.88) |
Cobicistat | 150 mg once daily | |||||
Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate | 300 mg once daily | 600 mg twice daily | 18 | 0.99 (0.86, 1.13) | 1.00 (0.91, 1.11) | 1.13 (0.77, 1.66) |
Maraviroc | 300 mg twice daily | 600 mg twice daily | 14 | 1.13 (0.96, 1.32) | 1.10 (0.99, 1.23) | 0.90 (0.69, 1.17) |
Famotidine | 40-mg single dose | 600-mg single dose | 24 | 1.01 (0.85, 1.21) | 1.04 (0.87, 1.25) | 0.90 (0.64, 1.28) |
Microbiology
Mechanism of Action
Fostemsavir is a prodrug without significant biochemical or antiviral activity that is hydrolyzed to the active moiety, temsavir, which is an HIV-1 attachment inhibitor. Temsavir binds directly to the gp120 subunit within the HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein gp160 and selectively inhibits the interaction between the virus and cellular CD4 receptors, thereby preventing attachment. Additionally, temsavir can inhibit gp120-dependent post-attachment steps required for viral entry into host cells. Temsavir inhibited the binding of soluble CD4 to surface immobilized gp120 with an IC 50 value of 14 nM using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
Antiviral Activity in Cell Culture
Temsavir exhibited antiviral activity against 3 CCR5-tropic laboratory strains of subtype B HIV‑1, with EC 50 values ranging from 0.4 to 1.7 nM. The range of susceptibility to temsavir was broader for CXCR4-tropic laboratory strains with 2 strains having EC 50 values of 0.7 and 2.2 nM and 3 strains having EC 50 values of 14.8, 16.2, and >2,000 nM. Antiviral activity of temsavir against HIV-1 subtype B clinical isolates varied depending on tropism with median EC 50 values against the CCR5-tropic viruses, CXCR4-tropic viruses, and dual/mixed viruses of 3.7 nM (n = 9; range: 0.3 to 345 nM), 40.9 nM (n = 4; range: 0.6 to >2,000 nM), and 0.8 nM (n = 2; range: 0.3 to 1.3), respectively, showing a broad range of EC 50 values for temsavir across the different tropic strains.
Analysis of data from 1,337 clinical samples from the fostemsavir clinical development program (881 subtype B samples, 156 subtype C samples, 43 subtype A samples, 17 subtype A1 samples, 48 subtype F1 samples, 29 subtype BF1 samples, 19 subtype BF samples, 5 CRF01_AE samples, and 139 other) showed temsavir susceptibility is highly variable across subtypes with a wide range in EC 50 values from 0.018 nM to >5,000 nM. The majority of subtype B isolates (84%, 740/881) had EC 50 values below 10 nM, with 6% of isolates having EC 50 values >100 nM. Of all isolates from all subtypes tested, 9% exhibited EC 50 values >100 nM. Subtypes BF, F1 and BF1 had higher proportions (21% to 38%) of isolates with EC 50 values >100 nM, and all 5 of 5 subtype AE isolates had EC 50 values >100 nM. From an additional panel of clinical isolates with non-B subtypes, temsavir EC 50 values were greater than the upper limits of the concentrations tested (>1,800 nM) in all subtype E (AE; 3 of 3), Group O (2 of 2), and HIV-2 (1 of 1) isolates, and some subtype D (1 of 4) and subtype G (1 of 3) isolates.
Reduced Antiviral Activity against Subtype AE
Temsavir showed reduced antiviral activity against 14 different subtype AE isolates in peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) assays and the Phenosense Entry assay indicating that subtype AE (or E) viruses are inherently less sensitive to temsavir. Genotyping of subtype AE viruses identified polymorphisms at amino acid positions S375H and M475I in gp120, which have been associated with reduced susceptibility to fostemsavir. Subtype AE is a predominant subtype in Southeast Asia, but it is not found in high frequencies elsewhere throughout the world.
There were 2 subjects with subtype AE virus at screening in the randomized cohort of the clinical trial. One subject (EC 50 fold change >4,747-fold and gp120 substitutions at S375H and M475I at baseline) did not respond to RUKOBIA at Day 8. A second subject (EC 50 fold change 298-fold and gp120 substitution at S375N at baseline) received placebo during functional monotherapy. Both subjects were virologically suppressed at Week 96 while receiving OBT (with dolutegravir) plus RUKOBIA.
Antiviral Activity in Combination with Other Antiviral Agents
The antiviral activity of temsavir was not antagonistic in cell culture when combined with the CD4-directed post-attachment HIV-1 inhibitor ibalizumab, the CCR5 co-receptor antagonist maraviroc, the gp41 fusion inhibitor enfuvirtide, integrase strand transfer inhibitors (INSTIs) (dolutegravir, raltegravir), non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) (delavirdine, efavirenz, nevirapine, rilpivirine), nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) (abacavir, didanosine, emtricitabine, lamivudine, stavudine, tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, zidovudine), or protease inhibitors (PIs) (amprenavir, atazanavir, darunavir, indinavir, lopinavir, nelfinavir, ritonavir, saquinavir). In addition, temsavir antiviral activity was not antagonistic in cell culture with the anti-HBV drug entecavir and the anti-HCV drug ribavirin.
Resistance in Cell Culture
HIV-1 variants with reduced susceptibility to temsavir were selected following 14 to 49 days passage in cell culture of NL4-3, LAI, and BaL viruses in a T-cell line. Selected viruses exhibited 18- to 159-fold decreased temsavir susceptibility and genotypic analysis identified the following emerging amino acid substitutions in gp120: L116P/Q, L175P, A204D, V255I, A281V, M426L, M434I, and M475I (S375 substitutions were identified based on in vivo data with a related attachment inhibitor). In general, most substitutions mapped to the conserved regions (C1, C2, C4, and C5) of the gp120 envelope, confirming temsavir targets the viral envelope protein during infection.
Single-substitution recombinant viruses at these amino acid positions were engineered into the HIV-1 LAI viral background and the resultant recombinants demonstrated reduced susceptibility to temsavir (L116P [>340-fold], A204D [>340-fold], S375M [47-fold], S375V [5.5-fold], S375Y [>10,000-fold], M426L [81-fold], M426V [3.3-fold], M434I [11-fold], M434T [15-fold], M475I [5-fold], M475L [17-fold], and M475V [9.5-fold]).
Temsavir remained active against laboratory-derived CD4-independent viruses and temsavir-resistant viruses showed no evidence of a CD4-independent phenotype. Therefore, treatment with RUKOBIA is unlikely to promote resistance to temsavir via generation of CD4-independent virus.
Response at Day 8 by Genotype
The effect of the gp120 resistance-associated polymorphisms (RAPs) on response to fostemsavir functional monotherapy at Day 8 was assessed in an as-treated analysis by censoring the subjects who had a >0.4 log 10 decline in HIV-1 RNA from screening to baseline or <400 copies/mL at screening (n = 47 subjects were censored). The presence of gp120 RAPs at key sites S375, M426, M434, or M475 was associated with a lower overall decline in HIV-1 RNA and fewer subjects achieving >0.5 log 10 decline in HIV-1 RNA compared with subjects with no changes at these sites (Table 8 ). However, the presence of the gp120 RAPs did not preclude some subjects from achieving a response of >0.5 log 10 copies/mL at Day 8. Baseline gp120 RAPs most associated with decreased response of <0.5 log 10 copies/mL at Day 8 were S375M, M426L, and M475V (Table 8 ). There was no difference in response rates and median decline in viral load for subjects with more than one gp120 RAP.
| RAPs = Resistance-associated polymorphisms. | ||
| a Removed subjects who had <400 copies/mL at screening or >0.4 log 10 decline from screening to baseline. | ||
Envelope RAPs | Response Rate at Day 8 (>0.5 log 10 decline) n = 151 | Median Log 10 Decline in Viral Load: Baseline to Day 8 n = 151 |
Overall | 107/151 (71%) | 1.05 |
No gp120 RAPs (at predefined sites) | 70/83 (84%) | 1.11 |
Predefined gp120 RAPs: | ||
S375I/M/N/T, M426L, M434I, or M475I/V | 37/68 (54%) | 0.66 |
S375M | 1/5 (20%) | 0.32 |
M426L | 6/17 (35%) | 0.19 |
M434I | 3/6 (50%) | 0.66 |
M475V | 0/1 (0%) | 0 |
1 gp120 RAP | 38/62 (61%) | 1.03 |
2 or 3 gp120 RAPs | 18/26 (69%) | 1.09 |
Response at Day 8 by Phenotype
The fold change in susceptibility to temsavir for subject isolates at screening was highly variable ranging from 0.06 to 6,651. The effect of screening fostemsavir phenotype on response of >0.5 log 10 decline at Day 8 was assessed in the as-treated analysis. The majority of these subjects (55%, 83/151) had a screening temsavir EC 50 fold change normalized to a reference virus of <2‑fold. The response rate for fostemsavir phenotypes ≤2 was 80% (66/83) (Table 9 ). Response rates for fostemsavir phenotypic fold changes of >2 to 200 were moderately decreased to 69% (29/42). Phenotypic fold changes of >200 resulted in lower response rates to fostemsavir (29%, 5/17). Five subjects, despite having >200-fold decreased fostemsavir susceptibility and the presence of screening gp120 RAPs, had over 1 log 10 declines in HIV-1 RNA at Day 8. Lack of resistance to background drugs or higher fostemsavir concentrations do not explain the >1 log 10 response of these 5 subjects.
| a Removed subjects who had <400 copies/mL at screening or >0.4 log 10 decline from screening to baseline. | |
Fostemsavir Phenotypic Fold Change | Response Rate at Day 8 (>0.5 log 10 decline) As-Treated Analysis a n = 151 |
Not Reported | 9 |
0 - 2 | 66/83 (80%) |
>2 - 10 | 17/25 (68%) |
10 - 200 (Range 11 - 104) | 12/17 (71%) |
>200 (Range 234 - 6,651) | 5/17 (29%) |
Resistance in Clinical Subjects
The percentage of subjects who experienced virologic failure through the Week 96 analysis was 25% (69/272) in the randomized cohort (including 25% [51/203] among subjects who received blinded fostemsavir functional monotherapy and 26% [18/69] among subjects who received blinded placebo during the 8‑day double-blind period) (Table 10 ). Virologic failure = confirmed ≥400 copies/mL after prior confirmed suppression to <400 copies/mL, ≥400 copies/mL at last available prior to discontinuation, or >1 log 10 copies/mL increase in HIV-1 RNA at any time above nadir level (≥40 copies/mL). Overall, 55% (29/53) of evaluable subjects with virologic failure in the randomized cohorts had treatment-emergent gp120 genotypic substitutions at 4 key sites (S375, M426, M434, and M475) (Table 10 ). One subject in the randomized cohort receiving fostemsavir plus OBT (but did not receive ibalizumab) experienced loss of virologic response and had an emergent K202E substitution in gp120. The glutamic acid (E) substitution at position 202 in gp120 was found to confer reduced susceptibility to both fostemsavir and ibalizumab (see Cross-Resistance) .
The median temsavir EC 50 fold change at failure in randomized evaluable subject isolates with emergent gp120 substitutions at positions 375, 426, 434, or 475 (n = 29) was 1,142-fold. In randomized evaluable subject isolates with no emergent gp120 substitutions at those positions (n = 24), the median temsavir EC 50 fold change at failure was 0.92-fold.
Forty-one percent (28/69) of the virologic failures in the randomized groups combined had genotypic or phenotypic resistance to at least one drug in the OBT at screening, and 48% (31/64) of the virologic failures with post-baseline data had emergent resistance to at least one drug in the OBT.
Rates of virologic failure were higher in the nonrandomized cohort at 51% (50/99) (Table 10 ). While the proportion of virologic failures with gp120 RAPs at screening was similar between subjects in the randomized and nonrandomized cohorts, the proportion of subjects with emergent gp120 resistance-associated substitutions at the time of failure was higher among nonrandomized subjects (Table 10 ). The median temsavir EC 50 fold change at failure in nonrandomized evaluable subject isolates with emergent substitutions at positions 375, 426, 434, or 475 (n = 33) was 4,216-fold and was 767-fold among failure subject isolates without emergent resistance-associated substitutions (n = 12).
Consistent with the nonrandomized group of subjects having fewer antiretroviral options, 90% (45/50) of the virologic failures in this group had genotypic or phenotypic resistance to at least one drug in the OBT at screening, and 55% (27/49) of the virologic failures with post-baseline data in the nonrandomized group had emergent resistance to at least one drug in the OBT.
| RAPs = Resistance-associated polymorphisms; RAS = Resistance-associated substitutions. | ||
Randomized Cohort Total | Nonrandomized Cohort Total | |
Number of virologic failures | 69/272 (25%) | 50/99 (51%) |
With gp120 RAPs at screening (of those with genotypic data) | 43/68 (63%) | 26/48 (54%) |
Virologic failures with post-baseline data | 53 | 45 |
With emergent gp120 RAS | 29/53 (55%) | 33/45 (73%) |
S375H/I/M/N/T | 19/53 (36%) | 21/45 (47%) |
M426L/I | 18/53 (34%) | 23/45 (51%) |
M434I/L | 6/53 (11%) | 5/45 (11%) |
M475I/L/V | 8/53 (15%) | 5/45 (11%) |
Cross-Resistance
There was no evidence of cross-resistance to representative agents from other antiretroviral (ARV) classes including INSTIs, NNRTIs, NRTIs, and PIs. Temsavir retained wild-type activity against viruses resistant to the INSTI raltegravir, the NNRTIs (efavirenz, rilpivirine), the NRTIs (abacavir, lamivudine, tenofovir, zidovudine), and the PIs (atazanavir and darunavir).
Additionally, the INSTI raltegravir, the NNRTIs (efavirenz, rilpivirine), the NRTIs (abacavir, tenofovir), and the PIs (atazanavir, darunavir), retained activity against site-directed mutants with reduced temsavir susceptibility (i.e., S375M, M426L, or M426L plus M475I).
Both the CD4-directed post-attachment inhibitor ibalizumab and the gp120-directed attachment inhibitor fostemsavir develop reduced susceptibility in gp120. Ibalizumab retained activity against site-directed mutants that had reduced susceptibility to temsavir (i.e., S375M, M426L, or M426L plus M475I). Temsavir was active against several ibalizumab-resistant viruses. However, HIV-1 gp120 E202 was identified as a treatment-emergent substitution seen in a single subject in BRIGHTE that can reduce susceptibility to temsavir, and, depending on the sequence context of the envelope, can result in reduced susceptibility to ibalizumab.
Temsavir was active against viruses with resistance to enfuvirtide. Temsavir had reduced activity against some CCR5-tropic, maraviroc-resistant viruses, but no absolute correlation between maraviroc resistance and reduced temsavir susceptibility has been identified. Maraviroc and enfuvirtide retained activity against clinical envelopes that had reduced susceptibility to temsavir and contained S375H, M426L, or M426L plus M475I substitutions.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
In a 2-year carcinogenicity study conducted in rats and a 26-week carcinogenicity study conducted in transgenic mice, fostemsavir produced no statistically significant increases in tumors over controls. The maximum daily exposures in rats were approximately 5 times (males) and 16 times (females) greater than those in humans at the MRHD.
Mutagenesis
Fostemsavir was not genotoxic in the bacterial reverse mutation assay (Ames test in Salmonella and E. coli), a chromosome aberration test in human lymphocytes, and rat bone marrow micronucleus test.
Impairment of Fertility
Oral administration of fostemsavir had no adverse effects on male or female fertility in rats at exposures approximately 10 times (males) and 186 times (females) of those in humans at the MRHD. At higher exposures (>80 times those in humans at the MRHD) in male rats, decreases in prostate gland/seminal vesicle weights, sperm density/motility, and increased abnormal sperm were observed.
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared with rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
A total of 620 subjects with HIV-1 infection received at least one dose of RUKOBIA as part of a controlled clinical trial.
The primary safety assessment of RUKOBIA is based on 96 weeks of data from a Phase 3 partially randomized, international, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (BRIGHTE) conducted in 371 heavily treatment-experienced adult subjects [see Clinical Studies (14 )] . In the randomized cohort, 203 subjects received at least one dose of blinded RUKOBIA 600 mg twice daily and 69 subjects received placebo in addition to their current failing regimen for 8 days of functional monotherapy. Beyond Day 8, all randomized subjects except one received open-label RUKOBIA 600 mg twice daily plus an optimized background therapy (OBT). In the nonrandomized cohort, 99 subjects received open-label RUKOBIA 600 mg twice daily plus OBT from Day 1 onward.
A total of 370 subjects (271 randomized and 99 nonrandomized) received at least 1 dose of RUKOBIA 600 mg twice daily in the BRIGHTE trial. Overall, most (81%) of the adverse reactions reported with RUKOBIA were mild or moderate in severity. The proportion of subjects who discontinued treatment with RUKOBIA due to an adverse event was 7% at Week 96 (randomized: 5% and nonrandomized: 12%). The most common adverse events leading to discontinuation were related to infections (3% of subjects receiving RUKOBIA). Serious drug reactions occurred in 3% of subjects and included 3 cases of severe immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome.
Data from the randomized cohort form the basis of the safety assessment of RUKOBIA because the presence of significant comorbid illness in the nonrandomized cohort (associated with advanced HIV infection) may confound the assessment of causality. Adverse reactions (all grades) reported in ≥2% of subjects in the randomized cohort in the Week 96 analysis are listed in Table 1 .
| OBT = Optimized background therapy. | |
| a Frequencies of adverse reactions are based on all treatment-emergent adverse events attributed to study drug by the investigator. b Of the 272 subjects enrolled in the randomized cohort, 1 subject who received placebo withdrew from the trial prior to receiving RUKOBIA in the open-label phase of the trial. c Includes pooled terms: abdominal discomfort, abdominal pain, and abdominal pain upper. d Includes pooled terms: fatigue and asthenia. e Includes pooled terms: rash, rash generalized, rash maculo-papular, rash pruritic, and dermatitis allergic. f Includes pooled terms: insomnia, sleep deficit, sleep disorder, abnormal dreams. | |
Adverse Reaction | RUKOBIA plus OBT (n = 271) b |
Nausea | 10% |
Diarrhea | 4% |
Headache | 4% |
Abdominal pain c | 3% |
Dyspepsia | 3% |
Fatigue d | 3% |
Rash e | 3% |
Sleep disturbance f | 3% |
Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome | 2% |
Somnolence | 2% |
Vomiting | 2% |
Adverse reactions in the nonrandomized cohort were similar to those observed in the randomized cohort. The most common adverse reactions reported in nonrandomized subjects were fatigue (7%), nausea (6%), and diarrhea (6%).
Less Common Adverse Reactions
The following adverse reactions occurred in <2% of subjects receiving RUKOBIA in the randomized cohort of the BRIGHTE trial. These events have been included based on the assessment of potential causal relationship and were also reported in the nonrandomized cohort.
Cardiac Disorders: Electrocardiogram QT prolonged. All reports were asymptomatic.
Musculoskeletal Disorders: Myalgia.
Nervous System Disorders: Dizziness, d ysgeusia, neuropathy peripheral (includes pooled terms: neuropathy peripheral and peripheral sensory neuropathy).
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Pruritus.
Laboratory Abnormalities
Selected laboratory abnormalities (Grades 3 to 4) with a worsening grade from baseline and representing the worst-grade toxicity in ≥2% of subjects in the randomized cohort of the BRIGHTE trial are presented in Table 2 .
| OBT = Optimized background therapy; ULN = Upper limit of normal. a Percentages were calculated based on the number of subjects with post-baseline toxicity grades for each laboratory parameter (n = 221 for cholesterol and triglycerides, n = 216 for LDL cholesterol, and n = 268 for all other parameters). b Grade 3 only (no Grade 4 values reported). | |
Laboratory Parameter Preferred Term | RUKOBIA plus OBT (n = 271 a ) |
ALT (>5.0 x ULN) | 5% |
AST (>5.0 x ULN) | 4% |
Direct bilirubin (>ULN) b | 7% |
Bilirubin (≥2.6 x ULN) | 3% |
Cholesterol (≥300 mg/dL) b | 5% |
Creatinine (>1.8 x ULN or 1.5 x baseline) | 19% |
Creatine kinase (≥10 x ULN) | 2% |
Hemoglobin (<9.0 g/dL) | 6% |
Hyperglycemia (>250 mg/dL) | 4% |
Lipase (>3.0 x ULN) | 5% |
LDL cholesterol (≥190 mg/dL) | 4% |
Neutrophils (≤599 cells/mm 3 ) | 4% |
Triglycerides (>500 mg/dL) | 5% |
Urate (>12 mg/dL) | 3% |
The incidence of selected laboratory abnormalities (Grades 3 to 4) in the nonrandomized cohort were overall consistent with those of the randomized cohort, with the exception of direct bilirubin (14% versus 7%), bilirubin (6% versus 3%), lipase (10% versus 5%), triglycerides (10% versus 5%), neutrophils (7% versus 4%), and leukocytes (6% versus 1%), respectively.
Changes in Serum Creatinine: Clinically relevant increases in serum creatinine have primarily occurred in patients with identifiable risk factors for reduced renal function, including pre-existing medical history of renal disease and/or concomitant medications known to cause increases in creatinine. A causal association between RUKOBIA and elevation in serum creatinine has not been established.
Changes in Direct Bilirubin: Increases in direct (conjugated) bilirubin have been observed following treatment with RUKOBIA (Table 2 ). Cases of clinical significance were uncommon and were confounded by the presence of intercurrent serious comorbid events (e.g., sepsis, cholangiocarcinoma, or other complications of viral hepatitis co-infection). In the remaining cases, elevations in direct bilirubin (without clinical jaundice) were typically transient, occurred without increases in liver transaminases, and resolved on continued RUKOBIA.
Changes in ALT and AST in Subjects with Hepatitis B and/or Hepatitis C Virus Co-Infection: A total of 29 subjects with Hepatitis B and/or Hepatitis C co-infection were enrolled in the BRIGHTE trial (randomized and nonrandomized cohorts combined). Grade 3 and 4 elevations in ALT and AST occurred in 14% of these subjects compared with 3% (ALT) and 2% (AST) of subjects without viral hepatitis co-infection. Some of these elevations in transaminases were consistent with hepatitis B reactivation particularly in the setting where anti-hepatitis therapy was withdrawn [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 )] .
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
RUKOBIA extended-release tablets, 600 mg, are beige, oval, film-coated, biconvex tablets debossed with “SV 1V7” on one side.
Bottle of 60 tablets with child-resistant closure. NDC 49702-250-18.
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C and 30°C (59°F and 86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
RUKOBIA extended-release tablets may have a slight vinegar-like odor.
Mechanism of Action
RUKOBIA is an HIV-1 antiretroviral agent [see Microbiology (12.4 )].