Get your patient on Semglee - Insulin Glargine - Yfgn injection, Solution (Insulin Glargine-Yfgn)
Semglee - Insulin Glargine - Yfgn injection, Solution prescribing information
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
SEMGLEE is indicated to improve glycemic control in adult and pediatric patients with diabetes mellitus.
Limitations of Use
SEMGLEE is not recommended for the treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Individualize dosage based on metabolic needs, blood glucose monitoring, glycemic control, type of diabetes, and prior insulin use. (2.2 )
- Administer subcutaneously into the abdominal area, thigh, or deltoid once daily at any time of day, but at the same time every day. (2.1 )
- Do not dilute or mix with any other insulin or solution. (2.1 )
- Rotate injection sites to reduce risk of lipodystrophy and localized cutaneous amyloidosis. (2.1 )
See Full Prescribing Information for the recommended starting dosage in patients with type 2 diabetis (2.3 ) and how to change to SEMGLEE from other insulins. (2.4 )
- Closely monitor glucose when switching to SEMGLEE and during initial weeks thereafter. (2.4 )
Important Administration Instructions
- Always check insulin labels before administration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ]
- Visually inspect SEMGLEE vials and prefilled pens for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. Only use if the solution is clear and colorless with no visible particles.
- Administer SEMGLEE subcutaneously into the abdominal area, thigh, or deltoid, and rotate injection sites within the same region from one injection to the next to reduce the risk of lipodystrophy and localized cutaneous amyloidosis. Do not inject into areas of lipodystrophy or localized cutaneous amyloidosis [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) , and Adverse Reactions (6) ].
- During changes to a patient’s insulin regimen, increase the frequency of blood glucose monitoring [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 ) ].
- Do not administer intravenously or via an insulin pump.
- Do not dilute or mix SEMGLEE with any other insulin or solution.
- The SEMGLEE prefilled pen dials in 1-unit increments.
- Use SEMGLEE prefilled pen with caution in patients with visual impairment who may rely on audible clicks to dial their dose.
General Dosing Instructions
- Administer SEMGLEE subcutaneously once daily at any time of day but at the same time every day.
- Individualize and adjust the dosage of SEMGLEE based on the patient’s metabolic needs, blood glucose monitoring results and glycemic control goal.
- Dosage adjustments may be needed with changes in physical activity, changes in meal patterns (i.e., macronutrient content or timing of food intake), during acute illness, or changes in renal or hepatic function. Dosage adjustments should only be made under medical supervision with appropriate glucose monitoring [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ].
- In patients with type 1 diabetes, SEMGLEE must be used concomitantly with short-acting insulin.
Initiation of SEMGLEE Therapy
Recommended Starting Dosage in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes The recommended starting dosage of SEMGLEE in patients with type 1 diabetes is approximately one-third of the total daily insulin requirements. Use short-acting, premeal insulin to satisfy the remainder of the daily insulin requirements.
Recommended Starting Dosage in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes The recommended starting dosage of SEMGLEE in patients with type 2 diabetes who are not currently treated with insulin is 0.2 units/kg or up to 10 units once daily.
Switching to SEMGLEE from Other Insulin Therapies
Dosage adjustments are recommended to lower the risk of hypoglycemia when switching patients to SEMGLEE from other insulin therapies [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 ) ].When switching from:
- Once-daily insulin glargine 300 units/mL to once-daily SEMGLEE (100 units/mL), the recommended starting SEMGLEE dosage is 80% of the insulin glargine, 300 units/mL dosage that is being discontinued.
- Once-daily NPH insulin to once-daily SEMGLEE, the recommended starting SEMGLEE dosage is the same as the dosage of NPH that is being discontinued.
- Twice-daily NPH insulin to once-daily SEMGLEE, the recommended starting SEMGLEE dosage is 80% of the total NPH dosage that is being discontinued.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Injection: 100 units/mL (U-100) clear and colorless solution available as:
- 10 mL multiple-dose vial
- 3 mL single-patient-use prefilled pen
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Published studies with use of insulin glargine products during pregnancy have not reported a clear association with insulin glargine products and adverse developmental outcomes (see Data ). There are risks to the mother and fetus associated with poorly controlled diabetes in pregnancy (see Clinical Considerations ).
Rats and rabbits were exposed to insulin glargine in animal reproduction studies during organogenesis, respectively 50 times and 10 times the human subcutaneous dosage of 0.2 units/kg/day. Overall, the effects of insulin glargine did not generally differ from those observed with regular human insulin (see Data ).
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively. The estimated background risk of major birth defects is 6% to 10% in women with pregestational diabetes with a peri-conceptional HbA1c >7 and has been reported to be as high as 20% to 25% in women with a peri-conceptional HbA1c >10. The estimated background risk of miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-Associated Maternal and/or Embryo-fetal Risk
Hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia occur more frequently during pregnancy in patients with pre-gestational diabetes. Poorly controlled diabetes in pregnancy increases the maternal risk for diabetic ketoacidosis, preeclampsia, spontaneous abortions, preterm delivery, and delivery complications. Poorly controlled diabetes increases the fetal risk for major birth defects, stillbirth, and macrosomia-related morbidity.
Data
Human Data
Published data do not report a clear association with insulin glargine products and major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes when insulin glargine is used during pregnancy. However, these studies cannot definitely establish the absence of any risk because of methodological limitations including small sample size and some lacking comparator groups.
Animal Data
Subcutaneous reproduction and teratology studies have been performed with insulin glargine and regular human insulin in rats and Himalayan rabbits. Insulin glargine was given to female rats before mating, during mating, and throughout pregnancy at doses up to 0.36 mg/kg/day, which is approximately 50 times the recommended human subcutaneous starting dosage of 0.2 units/kg/day (0.007 mg/kg/day), on a mg/kg basis. In rabbits, doses of 0.072 mg/kg/day, which is approximately 10 times the recommended human subcutaneous starting dosage of 0.2 units/kg/day on a mg/kg basis, were administered during organogenesis. The effects of insulin glargine did not generally differ from those observed with regular human insulin in rats or rabbits. However, in rabbits, five fetuses from two litters of the high-dose group exhibited dilation of the cerebral ventricles. Fertility and early embryonic development appeared normal.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There are either no or only limited data on the presence of insulin glargine products in human milk, the effects on breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Endogenous insulin is present in human milk. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for SEMGLEE, and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from SEMGLEE or from the underlying maternal condition.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of SEMGLEE to improve glycemic control in pediatric patients with diabetes mellitus have been established. Use of SEMGLEE for this indication is supported by SEMGLEE’s approval as a biosimilar to insulin glargine and evidence from an adequate and well-controlled study (Study D) in 174 insulin glargine-treated pediatric patients aged 6 to 15 years with type 1 diabetes mellitus and from adequate and well-controlled studies of insulin glargine in adults with diabetes mellitus [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) , Clinical Studies (14.2)] .
In the pediatric clinical study, pediatric patients with type 1 diabetes had a higher incidence of severe symptomatic hypoglycemia compared to the adults in studies with type 1 diabetes [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Geriatric Use
Of the total number of subjects in controlled clinical studies of patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes who were treated with insulin glargine, 15% (n=316) were ≥ 65 years of age and 2% (n=42) were ≥ 75 years of age. No overall differecnes in safety or effectiveness of insulin glargine have been observed between patients 65 years of age and older and younger adult patients.
Nevertheless, caution should be exercised when SEMGLEE is administered to geriatric patients. In geriatric patients with diabetes, the initial dosing, dosage increments, and maintenance dosage should be conservative to avoid hypoglycemic reactions. Hypoglycemia may be difficult to recognize in geriatric patients.
Renal Impairment
The effect of kidney impairment on the pharmacokinetics of insulin glargine products has not been studied. Some studies with human insulin have shown increased circulating levels of insulin in patients with kidney failure. Frequent glucose monitoring and dosage adjustment may be necessary for SEMGLEE in patients with kidney impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ].
Hepatic Impairment
The effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of insulin glargine products has not been studied. Frequent glucose monitoring and dosage adjustment may be necessary for SEMGLEE in patients with hepatic impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ] .
CONTRAINDICATIONS
SEMGLEE is contraindicated:
- During episodes of hypoglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ].
- In patients with hypersensitivity to insulin glargine products or any of the excipients in SEMGLEE [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ].
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Never share a SEMGLEE prefilled pen, insulin syringe, or needle between patients, even if the needle is changed. (5.1 )
- Hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia with changes in insulin regimen: Make changes to a patient’s insulin regimen (e.g., insulin strength, manufacturer, type, injection site or method of administration) under close medical supervision with increased frequency of blood glucose monitoring. (5.2 )
- Hypoglycemia: May be life-threatening. Increase frequency of glucose monitoring with changes to: insulin dosage, concomitant drugs, meal pattern, physical activity; and in patients with renal or hepatic impairment and hypoglycemia unawareness. (5.3 )
- Hypoglycemia due to Medication Errors: Accidental mix-ups between insulin products can occur. Instruct patients to check insulin labels before injection. (5.4 )
- Hypersensitivity reactions : Severe, life-threatening, generalized allergy, including anaphylaxis, can occur. Discontinue SEMGLEE. Monitor and treat if indicated. (5.5 )
- Hypokalemia: May be life-threatening. Monitor potassium levels in patients at risk of hypokalemia and treat if indicated. (5.6 )
- Fluid retention and heart failure with concomitant use of thiazolidinediones (TZDs) : Observe for signs and symptoms of heart failure; consider dosage reduction or discontinuation of TZD if heart failure occurs. (5.7 )
Never Share a SEMGLEE Prefilled Pen, Insulin Syringe, or Needle Between Patients
SEMGLEE prefilled pens must never be shared between patients, even if the needle is changed. Patients using SEMGLEE vials must never re-use or share needles or syringes with another person. Sharing poses a risk for transmission of blood-borne pathogens.
Hyperglycemia or Hypoglycemia with Changes in Insulin Regimen
Changes in an insulin regimen (e.g., insulin strength, manufacturer, type, injection site or method of administration) may affect glycemic control and predispose to hypoglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ] or hyperglycemia. Repeated insulin injections into areas of lipodystrophy or localized cutaneous amyloidosis have been reported to result in hyperglycemia; and a sudden change in the injection site (to unaffected area) has been reported to result in hypoglycemia [see Adverse Reactions (6) ] .
Make any changes to a patient’s insulin regimen under close medical supervision with increased frequency of blood glucose monitoring. Advise patients who have repeatedly injected into areas of lipodystrophy or localized cutaneous amyloidosis to change the injection site to unaffected areas and closely monitor for hypoglycemia. For patients with type 2 diabetes, dosage adjustments of concomitant oral and antidiabetic products may be needed.
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia is the most common adverse reaction associated with insulins, including insulin glargine products. Severe hypoglycemia can cause seizures, may be life-threatening or cause death. Hypoglycemia can impair concentration ability and reaction time; this may place the patients and others at risk in situations where these abilities are important (e.g., driving or operating other machinery).
Hypoglycemia can happen suddenly, and symptoms may differ in each patient and change over time in the same patient. Symptomatic awareness of hypoglycemia may be less pronounced in patients with longstanding diabetes, in patients with diabetic neuropathy, using drugs that block the sympathetic nervous system (e.g., beta-blockers) [see Drug Interactions (7) ] , or who experience recurrent hypoglycemia.
The long-acting effect of insulin glargine products may delay recovery from hypoglycemia.
Risk Factors for Hypoglycemia
The risk of hypoglycemia after an injection is related to the duration of action of the insulin and, in general, is highest when the glucose lowering effect of the insulin is maximal. As with all insulins, the glucose lowering effect time course of insulin glargine products may vary in different patients or at different times in the same patient and depends on many conditions, including the area of injection as well as the injection site blood supply and temperature [ see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2 )]. Other factors which may increase the risk of hypoglycemia include changes in meal pattern (e.g., macronutrient content or timing of meals), changes in level of physical activity, or changes to concomitant drugs [ see Drug Interactions (7) ]. Patients with renal or hepatic impairment may be at higher risk of hypoglycemia [ see Use in Specific Populations (8.6, 8.7) ].
Risk Mitigation Strategies for Hypoglycemia
Patients and caregivers must be educated to recognize and manage hypoglycemia. Self-monitoring of blood glucose plays an essential role in the prevention and management of hypoglycemia. In patients at higher risk for hypoglycemia and patients who have reduced symptomatic awareness of hypoglycemia, increased frequency of blood glucose monitoring is recommended.
Hypoglycemia Due to Medication Errors
Accidental mix-ups among insulin products have been reported. To avoid medication errors between SEMGLEE and other insulins, instruct patients to always check the insulin label before each injection [see Adverse Reactions (6.3) ] .
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Severe, life-threatening, generalized allergy, including anaphylaxis, can occur with insulins, including insulin glargine products [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] . If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue SEMGLEE; treat per standard of care and monitor until symptoms and signs resolve. SEMGLEE is contraindicated in patients who have had hypersensitivity reactions to insulin glargine products or one of the excipients.
Hypokalemia
All insulins, including insulin glargine products, cause a shift in potassium from the extracellular to intracellular space, possibly leading to hypokalemia. Untreated hypokalemia may cause respiratory paralysis, ventricular arrhythmia, and death. Monitor potassium levels in patients at risk for hypokalemia, if indicated (e.g., patients using potassium-lowering medications, patients taking medications sensitive to serum potassium concentrations).
Fluid Retention and Heart Failure with Concomitant Use of PPAR-gamma Agonists
Thiazolidinediones (TZDs), which are peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)-gamma agonists, can cause dose-related fluid retention, when used in combination with insulin. Fluid retention may lead to or exacerbate heart failure. Patients treated with insulin including SEMGLEE, and a PPAR-gamma agonist should be observed for signs and symptoms of heart failure. If heart failure develops, it should be managed according to current standards of care, and discontinuation or dose reduction of the PPAR-gamma agonist must be considered.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed elsewhere:
Hyperglycemia or Hypoglycemia with Changes in Insulin Regimen [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
Hypoglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
- Hypoglycemia Due to Medication Errors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ]
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ]
- Hypokalemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trial of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data in Table 1 reflect the exposure of 2,327 patients with type 1 diabetes to insulin glargine or NPH in Studies A, B, C, and D [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ] . The type 1 diabetes population had the following characteristics: the mean age was 39 years. 54% were male, and mean body mass index (BMI) was 25.1 Kg/m 2.000000000000000e+00 Ninety-seven percent were White, 2% were Black or African American and less than 1% were Asian. Approximately 3% of the patients instudies B and C were Hispanic.
The data in Table 2 reflect the exposure of 1,563 patients with type 2 diabetes to insulin glargine or NPH in Studies E, F, and G [see Clinical Studies (14.3) ] . The type 2 diabetes population had the following characteristics: the mean age was 59 years, 58% were male, and mean BMI was 29.2 kg/m 2 . Eighty-seven percent were white, 8% were Black or African American and 3% were Asian. Approximately 9% of patients in Study F were Hispanic.
The frequencies of adverse reactions during insulin glargine clinical studies in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus and type 2 diabetes mellitus are listed in the tables below (Tables 1, 2, 3, and 4).
Insulin Glargine, % (n = 1257) | NPH,% (n = 1070) | |
Upper respiratory tract infection | 22.4 | 23.1 |
Infection Body system not specified | 9.4 | 10.3 |
Accidental injury | 5.7 | 6.4 |
Headache | 5.5 | 4.7 |
Insulin Glargine, % (n = 849) | NPH,% (n = 714) | |
Upper respiratory tract infection | 11.4 | 13.3 |
Infection Body system not specified | 10.4 | 11.6 |
Retinal vascular disorder | 5.8 | 7.4 |
Insulin Glargine, % (n = 514) | NPH,% (n = 503) | |
Upper respiratory tract infection | 29.0 | 33.6 |
Edema peripheral | 20.0 | 22.7 |
Hypertension | 19.6 | 18.9 |
Influenza | 18.7 | 19.5 |
Sinusitis | 18.5 | 17.9 |
Cataract | 18.1 | 15.9 |
Bronchitis | 15.2 | 14.1 |
Arthralgia | 14.2 | 16.1 |
Pain in extremity | 13.0 | 13.1 |
Back pain | 12.8 | 12.3 |
Cough | 12.1 | 7.4 |
Urinary tract infection | 10.7 | 10.1 |
Diarrhea | 10.7 | 10.3 |
Depression | 10.5 | 9.7 |
Headache | 10.3 | 9.3 |
Insulin Glargine, % (n = 174) | NPH,% (n = 175) | |
Infection Body system not specified | 13.8 | 17.7 |
Upper respiratory tract infection | 13.8 | 16.0 |
Pharyngitis | 7.5 | 8.6 |
Rhinitis | 5.2 | 5.1 |
Severe Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia was the most commonly observed adverse reaction in patients treated with insulin glargine. Tables 5, 6, and 7 summarize the incidence of severe hypoglycemia in the insulin glargine clinical Studies. Severe symptomatic hypoglycemia was defined as an event with symptoms consistent with hypoglycemia requiring the assistance of another person and associated with either a blood glucose below 50 mg/dL (≤ 56 mg/dL in the 5-year study and ≤ 36 mg/dL in the ORIGIN study) or prompt recovery after oral carbohydrate, intravenous glucose or glucagon administration.
Percentages of insulin glargine-treated adult patients who experienced severe symptomatic hypoglycemia in the insulin glargine clinical studies [see Clinical Studies (14) ] were comparable to percentages of NPH-treated patients for all treatment regimens (see Tables 5 and 6). In the pediatric clinical study, pediatric patients with type 1 diabetes had a higher incidence of severe symptomatic hypoglycemia in the two treatment groups compared to the adult studies with type 1 diabetes.
Study A Type 1 Diabetes Adults 28 weeks In combination with regular insulin | Study B Type 1 Diabetes Adults 28 weeks In combination with regular insulin | Study C Type 1 Diabetes Adults 16 weeks In combination with insulin lispro | Study D Type 1 Diabetes Pediatrics 26 weeks In combination with regular insulin | |||||
Insulin Glargine n = 292 | NPH n = 293 | Insulin Glargine n = 264 | NPH n = 270 | Insulin Glargine n = 310 | NPH n = 309 | Insulin Glargine n = 174 | NPH n = 175 | |
Percent of patients | 10.6 | 15.0 | 8.7 | 10.4 | 6.5 | 5.2 | 23.0 | 28.6 |
Study E Type 2 Diabetes Adults 52 weeks In combination with oral agents | Study F Type 2 Diabetes Adults 28 weeks In combination with regular insulin | Study G Type 2 Diabetes Adults 5 years In combination with regular insulin | ||||
Insulin Glargine n = 289 | NPH n = 281 | Insulin Glargine n = 259 | NPH n = 259 | Insulin Glargine n = 513 | NPH n = 504 | |
Percent of patients | 1.7 | 1.1 | 0.4 | 2.3 | 7.8 | 11.9 |
Table 7 displays the proportion of patients who experienced severe symptomatic hypoglycemia in the insulin glargine and Standard Care groups in the ORIGIN study [see Clinical Studies (14) ] .
ORIGIN Study Medium duration of follow-up: 6.2 years | ||
Insulin Glargine n = 6231 | Standard Care n = 6273 | |
Percent of patients | 5.6 | 1.8 |
Peripheral Edema
Some patients taking insulin glargine products have experienced sodium retention and edema, particularly if previously poor metabolic control was improved by intensified insulin therapy.
Lipodystrophy
Administration of insulin subcutaneously, including insulin glargine products, has resulted in lipoatrophy (depression in the skin) or lipohypertrophy (enlargement or thickening of tissue) in some patients [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) ] .
Insulin Initiation and Intensification of Glucose Control
Intensification or rapid improvement in glucose control has been associated with a transitory, reversible ophthalmologic refraction disorder, worsening of diabetic retinopathy, and acute painful peripheral neuropathy. However, long-term glycemic control decreases the risk of diabetic retinopathy and neuropathy.
Weight Gain
Weight gain has occurred with insulin including insulin glargine products and has been attributed to the anabolic effects of insulin and the decrease in glucosuria.
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Local Reactions
Patients taking insulin glargine experienced injection site reactions, including redness, pain, itching, urticaria, edema, and inflammation. In clinical studies in adult patients, there was a higher incidence of treatment-emergent injection site pain in insulin glargine-treated patients (2.7%) compared to NPH insulin-treated patients (0.7%). The reports of pain at the injection site did not result in discontinuation of therapy.
Systemic Reactions
Severe, life-threatening, generalized allergy, including anaphylaxis, generalized skin reactions, angioedema, bronchospasm, hypotension, and shock have occured with insulin, including insulin glargine products and may be life threatening.
Immunogenicity
As with all therapeutic proteins, there is potential for immunogenicity. The detection of antibody formation is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Additionally, the observed incidence of antibody (including neutralizing antibody) positivity in an assay may be influenced by several factors, including assay methodology, sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant medications, and underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of the incidence of antibodies in the studies described below with the incidence of antibodies in other studies or to other insulin glargine products may be misleading.
All insulin products can elicit the formation of insulin antibodies. The presence of such insulin antibodies may increase or decrease the efficacy of insulin and may require adjustment of the insulin dose. In clinical studies of insulin glargine, increases in titers of antibodies to insulin were observed in NPH insulin and insulin glargine treatment groups with similar incidences.
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of insulin glargine products. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Medication errors have been reported in which rapid-acting insulins and other insulins have been accidentally administered instead of insulin glargine products.
Localized cutaneous amyloidosis at the injection site has occurred. Hyperglycemia has been reported with repeated insulin injections into areas of localized cutaneous amyloidosis; hypoglycemia has been reported with a sudden change to an unaffected injection site.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Table 8 includes clinically significant drug interactions with SEMGLEE.
Drugs that May Increase the Risk of Hypoglycemia | |
Drugs: | Antidiabetic agents, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blocking agents, disopyramide, fibrates, fluoxetine, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, pentoxifylline, pramlintide, salicylates, somatostatin analogs (e.g., octreotide), sulfonamide antibiotics,GLP-1 receptor agonists, DPP-4 inhibitors, and SGLT-2 inhibitors. |
Intervention: | Dosage reductions and increased frequency of glucose monitoring may be required when SEMGLEE is coadministered with these drugs. |
Drugs that May Decrease the Blood Glucose Lowering Effect of SEMGLEE | |
Drugs: | Atypical antipsychotics (e.g., olanzapine and clozapine), corticosteroids, danazol, diuretics, estrogens, glucagon, isoniazid, niacin, oral contraceptives, phenothiazines, progestogens (e.g., in oral contraceptives), protease inhibitors, somatropin, sympathomimetic agents (e.g., albuterol, epinephrine, terbutaline), and thyroid hormones. |
Intervention: | Dosage increases and increased frequency of glucose monitoring may be required when SEMGLEE is coadministered with these drugs. |
Drugs that May Increase or Decrease the Blood Glucose Lowering Effect of SEMGLEE | |
Drugs: | Alcohol, beta-blockers, clonidine, and lithium salts. Pentamidine may cause hypoglycemia, which may sometimes be followed by hyperglycemia. |
Intervention: | Dosage adjustment and increased frequency of glucose monitoring may be required when SEMGLEE is coadministered with these drugs. |
Drugs that May Blunt Signs and Symptoms of Hypoglycemia | |
Drugs: | Beta-blockers, clonidine, guanethidine, and reserpine |
Intervention: | Increased frequency of glucose monitoring may be required when SEMGLEE is coadministered with these drugs. |
DESCRIPTION
Insulin glargine-yfgn is a long-acting human insulin analog produced by recombinant DNA technology utilizing a recombinant yeast strain, Pichia pastoris . Insulin glargine-yfgn differs from human insulin in that the amino acid asparagine at position A21 is replaced by glycine and two arginines are added to the C-terminus of the B-chain. Insulin glargine-yfgn has a molecular weight of 6063 Da.
SEMGLEE (insulin glargine-yfgn) injection is a sterile, clear and colorless solution for subcutaneous use in a 10 mL multiple-dose vial and a 3 mL single-patient-use prefilled pen.
Prefilled pen and Vial: Each mL contains 100 units of insulin glargine-yfgn and the inactive ingredients: glycerol (20 mg), metacresol (2.7 mg), zinc chloride (content adjusted to provide 30 mcg zinc ion), and Water for Injection, USP. The vial also contains polysorbate 20 (20 mcg). The pH is adjusted by addition of aqueous solutions of hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide. SEMGLEE has a pH of approximately 4.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
The primary activity of insulin, including insulin glargine products, is regulation of glucose metabolism. Insulin and its analogs lower blood glucose by stimulating peripheral glucose uptake, especially by skeletal muscle and fat, and by inhibiting hepatic glucose production. Insulin inhibits lipolysis and proteolysis and enhances protein synthesis.
Pharmacodynamics
In clinical studies, the glucose-lowering effect on a molar basis (i.e., when given at the same doses) of intravenous insulin glargine is approximately the same as that for human insulin. Figure 1 shows results from a study in patients with type 1 diabetes conducted for a maximum of 24 hours after subcutaneous injection of insulin glargine or NPH insulin. The median time between subcutaneous injection and the end of pharmacological effect was 14.5 hours (range: 9.5 to 19.3 hours) for NPH insulin, and 24 hours (range: 10.8 to > 24 hours) (24 hours was the end of the observation period) for insulin glargine.
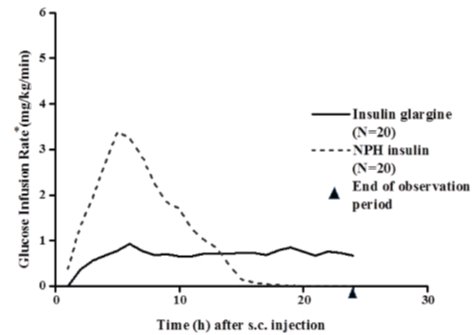
• Determined as amount of glucose infused to maintain constant plasma glucose levels
The duration of action after abdominal, deltoid, or thigh subcutaneous administration of insulin glargine was similar. The time course of action of insulins, including insulin glargine products, may vary between patients and within the same patient.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
After subcutaneous injection of insulin glargine in healthy subjects and in patients with diabetes, the insulin serum concentrations indicated a slower, more prolonged absorption and a relatively constant concentration/time profile over 24 hours with no pronounced peak in comparison to NPH insulin.
Elimination
Metabolism A metabolism study in humans indicates that insulin glargine is partly metabolized at the carboxyl terminus of the B chain in the subcutaneous depot to form two active metabolites with in vitro activity similar to that of human insulin, M1 (21 A -Gly-insulin) and M2 (21 A -Gly-des- 30 B -Thr-insulin). Unchanged drug and these degradation products are also present in the circulation.
Specific Populations
Age, Race, Body Mass Index and Gender
Effect of age, race, body mass index (BMI) and gender on the pharmacokinetics of insulin glargine products has not been evaluated. However, in controlled clinical studies in adults (n = 3,890) and a controlled clinical study in pediatric patients (n = 349), subgroup analyses based on age, race, BMI and gender did not show differences in safety and efficacy between insulin glargine and NPH insulin [see Clinical Studies (14) ] .
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In mice and rats, standard two-year carcinogenicity studies with insulin glargine were performed at doses up to 0.455 mg/kg, which was for the rat approximately 65 times the recommended human subcutaneous starting dosage of 0.2 units/kg/day (0.007 mg/kg/day) on a mg/kg basis. Histiocytomas were found at injection sites in male rats and mice in acid vehicle containing groups and are considered a response to chronic tissue irritation and inflammation in rodents. These tumors were not found in female animals, in saline control, or insulin comparator groups using a different vehicle.
Insulin glargine was not mutagenic in tests for detection of gene mutations in bacteria and mammalian cells (Ames and HGPRT-test) and in tests for detection of chromosomal aberrations (cytogenetics in vitro in V79 cells and in vivo in Chinese hamsters).
In a combined fertility and prenatal and postnatal study in male and female rats at subcutaneous doses up to 0.36 mg/kg/day, which was approximately 50 times the recommended human subcutaneous starting dosage of 0.2 units/kg/day (0.007 mg/kg/day) maternal toxicity due to dose-dependent hypoglycemia, including some deaths, was observed. Consequently, a reduction of the rearing rate occurred in the high-dose group only. Similar effects were observed with NPH insulin.
CLINICAL STUDIES
Overview of Clinical Studies
The safety and effectiveness of insulin glargine given once-daily at bedtime was compared to that of once-daily and twice-daily NPH insulin in open-label, randomized, active-controlled, parallel studies of 2,327 adult patients and 349 pediatric patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus and 1,563 adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (see Tables 9-11). In general, the reduction in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) with insulin glargine was similar to that with NPH insulin.
Clinical Studies in Adult and Pediatric Patients with Type 1 Diabetes
Adult Patients with Type 1 Diabetes In two clinical studies (Studies A and B), adult patients with type 1 diabetes (Study A; n = 585, Study B n = 534) were randomized to 28 weeks of basal-bolus treatment with insulin glargine or NPH insulin. Regular human insulin was administered before each meal. Insulin glargine was administered at bedtime. NPH insulin was administered either as once daily at bedtime or in the morning and at bedtime when used twice daily.
In Study A, the average age was 39 years. The majority of patients were White (99%) and 56% were male. The mean BMI was approximately 24.9 kg/m 2 . The mean duration of diabetes was 16 years.
In Study B, the average age was 39 years. The majority of patients were White (95%) and 51% were male. The mean BMI was approximately 25.8 kg/m 2 . The mean duration of diabetes was 17 years.
In another clinical study (Study C), patients with type 1 diabetes (n = 619) were randomized to 16 weeks of basal-bolus treatment with insulin glargine or NPH insulin. Insulin lispro was used before each meal. Insulin glargine was administered once daily at bedtime and NPH insulin was administered once or twice daily. The average age was 39 years. The majority of patients were White (97%) and 51% were male. The mean BMI was approximately 25.6 kg/m 2 . The mean duration of diabetes was 19 years.
In these 3 adult studies, insulin glargine and NPH insulin had similar effects on HbA1c (Table 9) with a similar overall rate of severe symptomatic hypoglycemia [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
Treatment duration Treatment in combination with | Study A 28 weeks Regular insulin | Study B 28 weeks Regular insulin | Study C 16 weeks Insulin lispro | |||
Insulin Glargine | NPH | Insulin Glargine | NPH | Insulin Glargine | NPH | |
Number of subjects treated | 292 | 293 | 264 | 270 | 310 | 309 |
HbA1c | ||||||
Baseline HbA1c | 8.0 | 8.0 | 7.7 | 7.7 | 7.6 | 7.7 |
Adjusted mean change at study end | +0.2 | +0.1 | -0.2 | -0.2 | -0.1 | -0.1 |
Treatment Difference (95% CI) | +0.1 (0.0; +0.2) | +0.1 (-0.1; +0.2) | 0.0 (-0.1; +0.1) | |||
Basal insulin dose | ||||||
Baseline mean | 21 | 23 | 29 | 29 | 28 | 28 |
Mean change from baseline | -2 | 0 | -4 | +2 | -5 | +1 |
Total insulin dose | ||||||
Baseline mean | 48 | 52 | 50 | 51 | 50 | 50 |
Mean change from baseline | -1 | 0 | 0 | +4 | -3 | 0 |
Fasting blood glucose (mg/dL) | ||||||
Baseline mean | 167 | 166 | 166 | 175 | 175 | 173 |
Adj. mean change from baseline | -21 | -16 | -20 | -17 | -29 | -12 |
Body weight (kg) | ||||||
Baseline mean | 73.2 | 74.8 | 75.5 | 75.0 | 74.8 | 75.6 |
Mean change from baseline | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.7 | 1.0 | 0.1 | 0.5 |
Pediatric Patients with Type 1 Diabetes
In a randomized, controlled clinical study (Study D), pediatric patients (age range 6 to 15 years) with type 1 diabetes (n = 349) were treated for 28 weeks with a basal-bolus insulin regimen where regular human insulin was used before each meal. Insulin glargine was administered once daily at bedtime and NPH insulin was administered once or twice daily. The average age was 11.7 years. The majority of patients were White (97%) and 52% were male. The mean BMI was approximately 18.9 kg/m 2 . The mean duration of diabetes was 5 years. Similar effects on HbA1c (Table 10) were observed in both treatment groups [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
Treatment duration Treatment in combination with | Study D 28 weeks Regular insulin | |
Insulin Glargine + Regular insulin | NPH+ Regular insulin | |
Number of subjects treated | 174 | 175 |
HbA1c | ||
Baseline mean | 8.5 | 8.8 |
Change from baseline (adjusted mean) | +0.3 | +0.3 |
Difference from NPH (adjusted mean) | 0.0 | |
(95% CI) | (-0.2; +0.3) | |
Basal insulin dose | ||
Baseline mean | 19 | 19 |
Mean change from baseline | -1 | +2 |
Total insulin dose | ||
Baseline mean | 43 | 43 |
Mean change from baseline | +2 | +3 |
Fasting blood glucose (mg/dL) | ||
Baseline mean | 194 | 191 |
Mean change from baseline | -23 | -12 |
Body weight (kg) | ||
Baseline mean | 45.5 | 44.6 |
Mean change from baseline | 2.2 | 2.5 |
Clinical Studies in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes
In a randomized, controlled clinical study (Study E) in 570 adults with type 2 diabetes, insulin glargine was evaluated for 52 weeks in combination with oral anti-diabetic medications (a sulfonylurea, metformin, acarbose, or combinations of these drugs). The average age was 60 years old. The majority of patients were White (93%) and 54% were male. The mean BMI was approximately 29.1 kg/m 2 . The mean duration of diabetes was 10 years. Insulin glargine administered once daily at bedtime was as effective as NPH insulin administered once daily at bedtime in reducing HbA1c and fasting glucose (Table 11). The rate of severe symptomatic hypoglycemia was similar in insulin glargine and NPH insulin treated patients [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
In a randomized, controlled clinical study (Study F), in adult patients with type 2 diabetes not using oral antidiabetic medications (n = 518), a basal-bolus regimen of insulin glargine once daily at bedtime or NPH insulin administered once or twice daily was evaluated for 28 weeks. Regular human insulin was used before meals, as needed. The average age was 59 years. The majority of patients were White (81%) and 60% were male. The mean BMI was approximately 30.5 kg/m 2 . The mean duration of diabetes was 14 years. Insulin glargine had similar effectiveness as either once- or twice-daily NPH insulin in reducing HbA1c and fasting glucose (Table 11) with a similar incidence of hypoglycemia [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
In a randomized, controlled clinical study (Study G), adult patients with type 2 diabetes were randomized to 5 years of treatment with once-daily insulin glargine or twice-daily NPH insulin. For patients not previously treated with insulin, the starting dosage of insulin glargine or NPH insulin was 10 units daily. Patients who were already treated with NPH insulin either continued on the same total daily NPH insulin dose or started insulin glargine at a dosage that was 80% of the total previous NPH insulin dosage. The primary endpoint for this study was a comparison of the progression of diabetic retinopathy by 3 or more steps on the Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study (ETDRS) scale. HbA1c change from baseline was a secondary endpoint. Similar glycemic control in the 2 treatment groups was desired in order to not confound the interpretation of the retinal data. Patients or study personnel used an algorithm to adjust the insulin glargine and NPH insulin dosages to a target fasting plasma glucose ≤ 100 mg/dL. After the insulin glargine or NPH insulin dosage was adjusted, other anti-diabetic agents, including premeal insulin were to be adjusted or added. The average age was 55 years. The majority of patients were White (85%) and 54% were male. The mean BMI was approximately 34.3 kg/m 2 . The mean duration of diabetes was 11 years. The insulin glargine group had a smaller mean reduction from baseline in HbA1c compared to the NPH insulin group, which may be explained by the lower daily basal insulin doses in the insulin glargine group (Table 11). The incidences of severe symptomatic hypoglycemia were similar between groups [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
Treatment duration Treatment in combination with | Study E 52 weeks Oral agents | Study F 28 weeks Regular insulin | Study G 5 years Regular insulin | |||
Insulin Glargine | NPH | Insulin Glargine | NPH | Insulin Glargine | NPH | |
Number of subjects treated | 289 | 281 | 259 | 259 | 513 | 504 |
HbA1c | ||||||
Baseline mean | 9.0 | 8.9 | 8.6 | 8.5 | 8.4 | 8.3 |
Adjusted mean change from baseline | -0.5 | -0.4 | -0.4 | -0.6 | -0.6 | -0.8 |
Insulin Glargine ‒ NPH | -0.1 | +0.2 | +0.2 | |||
95% CI for Treatment difference | (-0.3; +0.1) | (0.0; +0.4) | (+0.1; +0.4) | |||
Basal insulin dose In Study G, the baseline dose of basal or total insulin was the first available on-treatment dose prescribed during the study (on visit month 1.5) | ||||||
Baseline mean | 14 | 15 | 44.1 | 45.5 | 39 | 44 |
Mean change from baseline | +12 | +9 | -1 | +7 | +23 | +30 |
Total insulin dose | ||||||
Baseline mean | 14 | 15 | 64 | 67 | 48 | 53 |
Mean change from baseline | +12 | +9 | +10 | +13 | +41 | +40 |
Fasting blood glucose (mg/dL) | ||||||
Baseline mean | 179 | 180 | 164 | 166 | 190 | 180 |
Adj. mean change from baseline | -49 | -46 | -24 | -22 | -45 | -44 |
Body weight (kg) | ||||||
Baseline mean | 83.5 | 82.1 | 89.6 | 90.7 | 100 | 99 |
Adj. mean change from baseline | 2.0 | 1.9 | 0.4 | 1.4 | 3.7 | 4.8 |
Additional Clinical Studies in Adults with Diabetes Type 1 and Type 2
Different Timing of Insulin Glargine Administration in Diabetes Type 1 and Diabetes Type 2 The safety and efficacy of once daily insulin glargine administered either at pre-breakfast, pre-dinner, or at bedtime were evaluated in a randomized, controlled clinical study in adult patients with type 1 diabetes (Study H, n = 378). Patients were also treated with insulin lispro at mealtime. The average age was 41 years. All patients were White (100%) and 54% were male. The mean BMI was approximately 25.3 kg/m 2 . The mean duration of diabetes was 17 years.
Insulin glargine administered at pre-breakfast or at pre-dinner (both once daily) resulted in similar reductions in HbA1c compared to that with bedtime administration (see Table 12). In these patients, data are available from 8-point home glucose monitoring. The maximum mean blood glucose was observed just prior to insulin glargine injection regardless of time of administration. In this study, 5% of patients in the insulin glargine-breakfast group discontinued treatment because of lack of efficacy. No patients in the other two groups (pre-dinner, bedtime) discontinued for this reason.
The safety and efficacy of once daily lnsulin glargine administered pre-breakfast or at bedtime were also evaluated in a randomized, active-controlled clinical study (Study I, n = 697) in patients with type 2 diabetes not adequately controlled on oral anti-diabetic therapy. All patients in this study also received glimepiride 3 mg daily. The average age was 61 years. The majority of patients were White (97%) and 54% were male. The mean BMI was approximately 28.7 kg/m 2 . The mean duration of diabetes was 10 years. Insulin glargine given before breakfast was at least as effective in lowering HbA1c as insulin glargine given at bedtime or NPH insulin given at bedtime (see Table 12).
Treatment duration Treatment in combination with | Study H 24 weeks Insulin lispro | Study I 24 weeks Glimepiride | ||||
Insulin Glargine Before Breakfast | Insulin Glargine Before Dinner | Insulin Glargine Bedtime | Insulin Glargine Before Breakfast | Insulin Glargine Bedtime | NPH Bedtime | |
Number of subjects treated Intent-to-treat | 112 | 124 | 128 | 234 | 226 | 227 |
HbA1c | ||||||
Baseline mean | 7.6 | 7.5 | 7.6 | 9.1 | 9.1 | 9.1 |
Mean change from baseline | -0.2 | -0.1 | 0.0 | -1.3 | -1.0 | -0.8 |
Basal insulin dose (Units) | ||||||
Baseline mean | 22 | 23 | 21 | 19 | 20 | 19 |
Mean change from baseline | 5 | 2 | 2 | 11 | 18 | 18 |
Total insulin dose (Units) | NA | NA | NA | |||
Baseline mean | 52 | 52 | 49 | |||
Mean change from baseline | 2 | 3 | 2 | |||
Body weight (kg) | ||||||
Baseline mean | 77.1 | 77.8 | 74.5 | 80.7 | 82 | 81 |
Mean change from baseline | 0.7 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 3.9 | 3.7 | 2.9 |
Progression of Retinopathy Evaluation in adults with Diabetes Type 1 and Diabetes Type 2
Insulin glargine was compared to NPH insulin in a 5-year randomized clinical study that evaluated the progression of retinopathy as assessed with fundus photography using a grading protocol derived from the Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Scale (ETDRS). Patients had type 2 diabetes (mean age 55 years) with no (86%) or mild (14%) retinopathy at baseline. Mean baseline HbA1c was 8.4%. The primary outcome was progression by 3 or more steps on the ETDRS scale at study endpoint. Patients with pre-specified post-baseline eye procedures (pan-retinal photocoagulation for proliferative or severe nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy, local photocoagulation for new vessels, and vitrectomy for diabetic retinopathy) were also considered as 3-step progressors regardless of actual change in ETDRS score from baseline. Retinopathy graders were blinded to treatment group assignment.
The results for the primary endpoint are shown in Table 13 for both the per-protocol and intent-to-treat populations and indicate similarity of insulin glargine to NPH in the progression of diabetic retinopathy as assessed by this outcome. In this study, the numbers of retinal adverse events reported for insulin glargine and NPH insulin treatment groups were similar for adult patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
Insulin Glargine (%) | NPH (%) | Difference Difference = Insulin Glargine – NPH , Using a generalized linear model (SAS GENMOD) with treatment and baseline HbA1c strata (cutoff 9.0%) as the classified independent variables, and with binomial distribution and identity link function (SE) | 95% CI for difference | |
Per-protocol | 53/374 (14.2%) | 57/363 (15.7%) | -2.0% (2.6%) | -7.0% to +3.1% |
Intent-to-Treat | 63/502 (12.5%) | 71/487 (14.6%) | -2.1% (2.1%) | -6.3% to +2.1% |
The ORIGIN Study of Major Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Established CV Disease or CV Risk Factors
The Outcome Reduction with Initial Glargine Intervention study (i.e., ORIGIN) was an open-label, randomized, 2-by-2, factorial design study. One intervention in ORIGIN compared the effect of insulin glargine to standard care on major adverse cardiovascular (CV) outcomes in 12,537 adults ≥ 50 years of age with;
Abnormal glucose levels (i.e., impaired fasting glucose [IFG] and/or impaired glucose tolerance [IGT]) or early type 2 diabetes mellitus and
Established CV disease or CV risk factors at baseline.
The objective of the study was to demonstrate that insulin glargine use could significantly lower the risk of major CV outcomes compared to standard care. There were two coprimary composite CV endpoints.
The first coprimary endpoint was the time to first occurrence of a major adverse CV event defined as the composite of CV death, nonfatal myocardial infarction and nonfatal stroke.
The second coprimary endpoint was the time to the first occurrence of CV death or nonfatal myocardial infarction or nonfatal stroke or revascularization procedure or hospitalization for heart failure.
Patients were randomized to either insulin glargine (N = 6,264) titrated to a goal fasting plasma glucose of ≤ 95 mg/dL or to standard care (N = 6,273). Anthropometric and disease characteristics were balanced at baseline. The mean age was 64 years and 8% of patients were 75 years of age or older. The majority of patients were male (65%). Fifty nine percent were White, 25% were Latin, 10% were Asian and 3% were Black or African American. The median baseline BMI was 29 kg/m 2 . Approximately 12% of patients had abnormal glucose levels (IGT and/or IFG) at baseline and 88% had type 2 diabetes. For patients with type 2 diabetes, 59% were treated with a single oral antidiabetic drug, 23% had known diabetes but were on no antidiabetic drug and 6% were newly diagnosed during the screening procedure. The mean HbA1c (SD) at baseline was 6.5% (1.0). Fifty-nine percent of patients had a prior CV event and 39% had documented coronary artery disease or other CV risk factors.
Vital status was available for 99.9% and 99.8% of patients randomized to insulin glargine and standard care respectively at end of study. The median duration of follow-up was 6.2 years (range: 8 days to 7.9 years). The mean HbA1c (SD) at the end of the study was 6.5% (1.1) and 6.8% (1.2) in the insulin glargine and standard care group respectively. The median dose of insulin glargine at end of study was 0.45 U/kg. Eighty-one percent of patients randomized to insulin glargine were using insulin glargine at end of the study. The mean change in body weight from baseline to the last treatment visit was 2.2 kg greater in the insulin glargine group than in the standard care group.
Overall, the incidence of major adverse CV outcomes was similar between groups (see Table 14). All-cause mortality was also similar between groups.
Insulin Glargine N = 6,264 | Standard Care N = 6,273 | Insulin Glargine vs Standard Care | |
n (Events per 100 PY) | n (Events per 100 PY) | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | |
Coprimary endpoints | |||
CV death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or nonfatal stroke | 1041 (2.9) | 1013 (2.9) | 1.02 (0.94, 1.11) |
CV death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, nonfatal stroke, hospitalization for heart failure or revascularization procedure | 1792 (5.5) | 1727 (5.3) | 1.04 (0.97, 1.11) |
Components of coprimary endpoints | |||
CV death | 580 | 576 | 1.00 (0.89, 1.13) |
Myocardial Infarction (fatal or nonfatal) | 336 | 326 | 1.03 (0.88, 1.19) |
Stroke (fatal or nonfatal) | 331 | 319 | 1.03 (0.89, 1.21) |
Revascularizations | 908 | 860 | 1.06 (0.96, 1.16) |
Hospitalization for heart failure | 310 | 343 | 0.90 (0.77, 1.05) |
In the ORIGIN study, the overall incidence of cancer (all types combined) or death from cancer (Table 15) was similar between treatment groups.
Insulin Glargine N = 6,264 | Standard Care N = 6,273 | Insulin Glargine vs Standard Care | |
n (Events per 100 PY) | n (Events per 100 PY) | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | |
Cancer endpoints | |||
Any cancer event (new or recurrent) | 559 (1.56) | 561 (1.56) | 0.99 (0.88, 1.11) |
New cancer events | 524 (1.46) | 535 (1.49) | 0.96 (0.85, 1.09) |
Death due to Cancer | 189 (0.51) | 201 (0.54) | 0.94 (0.77, 1.15) |
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
SEMGLEE (insulin glargine-yfgn) injection is supplied as a clear and colorless solution containing 100 units/mL (U-100) available as follows:
| SEMGLEE | NDC Number | Package Size |
| 10 mL multiple-dose vial | 83257-011-11 | 1 vial per carton |
| 3 mL single-patient-use prefilled pen | 83257-012-31 | 1 pen per carton |
| 83257-012-32 | 3 pens per carton | |
| 83257-012-33 | 5 pens per carton |
Additional Information about SEMGLEE:
The SEMGLEE prefilled pen dials in 1-unit increments.
Needles are not included in the packs.
Embecta Ultra-Fine needles are compatible with this pen.
Storage
Dispense in the original sealed carton with the enclosed Instructions for Use.
Store unused SEMGLEE in a refrigerator between 2° to 8°C (36° to 46°F). Do not freeze. Discard SEMGLEE if it has been frozen. Protect SEMGLEE from direct heat and light.
Storage conditions are summarized in the following table:
Not in-use (unopened) Refrigerated (2° to 8°C [36° to 46°F]) | Not in-use (unopened) Room Temperature (up to 30°C [86°F]) | In-use (opened) (see temperature below) | |
10 mL multiple-dose vial | Until expiration date | 28 days | 28 days Refrigerated or room temperature |
3 mL single-patient-use prefilled pen | Until expiration date | 28 days | 28 days Room temperature only (Do not refrigerate) |
Mechanism of Action
The primary activity of insulin, including insulin glargine products, is regulation of glucose metabolism. Insulin and its analogs lower blood glucose by stimulating peripheral glucose uptake, especially by skeletal muscle and fat, and by inhibiting hepatic glucose production. Insulin inhibits lipolysis and proteolysis and enhances protein synthesis.