Get your patient on Solosec (Secnidazole)
Solosec prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Solosec patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Bacterial Vaginosis (female patients 12 years of age and older): Administer a single 2-gram packet of granules once orally, without regard to the timing of meals. (2.1 )
- Trichomoniasis (patients 12 years of age and older): Administer a single 2-gram packet of granules once orally, without regard to the timing of meals. Treat sexual partners with the same dose and at the same time. (2.2 )
- Sprinkle entire contents of packet onto applesauce, yogurt or pudding and consume all of the mixture within 30 minutes without chewing or crunching the granules. A glass of water may be taken after the administration of SOLOSEC to aid in swallowing. (2.3 )
- SOLOSEC is not intended to be dissolved in any liquid. (2.3 )
2.1 Recommended Dosage for Bacterial Vaginosis
The recommended dosage of SOLOSEC for the treatment of bacterial vaginosis in female patients 12 years of age and older is a single 2-gram packet of granules taken once orally, without regard to the timing of meals [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )].
2.2 Recommended Dosage for Trichomoniasis
The recommended dosage of SOLOSEC for the treatment of trichomoniasis in patients 12 years of age and older is a single 2-gram packet of granules taken once orally, without regard to the timing of meals [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] . Since trichomoniasis is a sexually transmitted disease, treat sexual partners with the same dose and at the same time [see Indications and Usage (1.2 )] .
Instructions for the Preparation and Administration of SOLOSEC
- Open the SOLOSEC packet by folding over the corner (marked by an arrow) and tearing across the top.
- Sprinkle the entire contents of the SOLOSEC packet onto applesauce, yogurt or pudding [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )]. The granules will not dissolve. Consume all of the mixture within 30 minutes without chewing or crunching the granules. A glass of water may be taken after the administration of SOLOSEC to aid in swallowing.
- The granules are not intended to be dissolved in any liquid.
- Avoid consumption of alcoholic beverages and preparations containing ethanol or propylene glycol during treatment with SOLOSEC and for at least 2 days after completing therapy . [ see Adverse Reactions (6.2 ), Drug Interactions (7.2 ), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] .

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Solosec prescribing information
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
SOLOSEC ® is a nitroimidazole antimicrobial indicated for
- Treatment of bacterial vaginosis in female patients 12 years of age and older. (1.1 )
- Treatment of trichomoniasis in patients 12 years of age and older. (1.2 )
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of SOLOSEC and other antibacterial drugs, SOLOSEC should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria. (1.3 )
1.1 Bacterial Vaginosis
1.2 Trichomoniasis
SOLOSEC is indicated for the treatment of trichomoniasis caused by Trichomonas vaginalis in patients 12 years of age and older. Because trichomoniasis is a sexually transmitted disease with potentially serious sequelae, treat partners of infected patients simultaneously in order to prevent reinfection [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 ) and Clinical Studies (14.2 )] .
Usage
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of SOLOSEC and other antibacterial drugs, SOLOSEC should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Bacterial Vaginosis (female patients 12 years of age and older): Administer a single 2-gram packet of granules once orally, without regard to the timing of meals. (2.1 )
- Trichomoniasis (patients 12 years of age and older): Administer a single 2-gram packet of granules once orally, without regard to the timing of meals. Treat sexual partners with the same dose and at the same time. (2.2 )
- Sprinkle entire contents of packet onto applesauce, yogurt or pudding and consume all of the mixture within 30 minutes without chewing or crunching the granules. A glass of water may be taken after the administration of SOLOSEC to aid in swallowing. (2.3 )
- SOLOSEC is not intended to be dissolved in any liquid. (2.3 )
2.1 Recommended Dosage for Bacterial Vaginosis
The recommended dosage of SOLOSEC for the treatment of bacterial vaginosis in female patients 12 years of age and older is a single 2-gram packet of granules taken once orally, without regard to the timing of meals [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )].
2.2 Recommended Dosage for Trichomoniasis
The recommended dosage of SOLOSEC for the treatment of trichomoniasis in patients 12 years of age and older is a single 2-gram packet of granules taken once orally, without regard to the timing of meals [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] . Since trichomoniasis is a sexually transmitted disease, treat sexual partners with the same dose and at the same time [see Indications and Usage (1.2 )] .
Instructions for the Preparation and Administration of SOLOSEC
- Open the SOLOSEC packet by folding over the corner (marked by an arrow) and tearing across the top.
- Sprinkle the entire contents of the SOLOSEC packet onto applesauce, yogurt or pudding [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )]. The granules will not dissolve. Consume all of the mixture within 30 minutes without chewing or crunching the granules. A glass of water may be taken after the administration of SOLOSEC to aid in swallowing.
- The granules are not intended to be dissolved in any liquid.
- Avoid consumption of alcoholic beverages and preparations containing ethanol or propylene glycol during treatment with SOLOSEC and for at least 2 days after completing therapy . [ see Adverse Reactions (6.2 ), Drug Interactions (7.2 ), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] .
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Oral Granules: 2 g, of off-white to slightly yellowish granules with 4.8 g net weight, packed in a unit-of-use child-resistant foil packet.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Lactation : Breastfeeding is not recommended. Discontinue breastfeeding for 96 hours after administration of SOLOSEC. (8.2 )
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Limited available data with SOLOSEC use in pregnant women are insufficient to inform a drug associated risk of adverse developmental outcomes. In animal reproduction studies, there were no adverse developmental outcomes when secnidazole was administered orally to pregnant rats and rabbits during organogenesis at doses up to 4 times the clinical dose (see Data)
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriages in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In animal reproduction studies, pregnant rats were dosed orally with secnidazole during organogenesis (gestational days 6-17) at 100, 300 and 1000 mg/kg/day, up to 4 times the clinical dose based on AUC comparisons. Animals showed no evidence of adverse developmental outcomes, but maternal toxicity (including reduced body weight gain) was observed at and above 300 mg/kg/day. In rabbits, no evidence of adverse developmental outcomes was observed when oral doses of secnidazole were administered to dams during organogenesis (gestational days 7-20) at doses up to 100 mg/kg/day (about 0.1 times the clinical dose, based on AUC comparisons). Secnidazole was associated with maternal toxicity (reduced food consumption and markedly reduced body weight gain) in dams at 100 mg/kg/day.
In a peri- and post-natal development study in rats, secnidazole was administered at 30, 100 and 300 mg/kg/day from Day 6 of gestation through Day 20 of lactation. Secnidazole was not associated with any adverse effects on gestation, parturition, lactation or on subsequent development of first generation (F1) and second generation (F2) offspring at these doses, equivalent to up to 1.4 times the clinical dose based on AUC comparisons. Maternal toxicity (reduced gestational body weight gain) was evident at doses of 100 mg/kg and above (about 0.3 times the clinical dose based on AUC comparisons).
Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information on the presence of secnidazole in human milk, the effects on the breast- fed child, or the effects on milk production. Other nitroimidazole derivatives are present in human milk. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions, including tumorigenicity, advise patients that breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with SOLOSEC and for 96 hours (based on half-life) after administration of SOLOSEC.
Clinical Considerations
A nursing mother may choose to pump and discard her milk during treatment with SOLOSEC and for 96 hours after administration of SOLOSEC and feed her infant stored human milk or formula.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of SOLOSEC for the treatment of bacterial vaginosis have been established in pediatric patients aged 12to 17 years old. Use of SOLOSEC in this age group is supported by evidence from a multicenter, open-label safety study in 40 pediatric female patients with bacterial vaginosis [see Adverse Reactions (6.1 )] and evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies in adult women [see Clinical Studies (14.1 )] .
The safety and effectiveness of SOLOSEC for the treatment of trichomoniasis have been established in pediatric patients aged 12 to 17 years old. Use of SOLOSEC in this group is based on the extrapolation of clinical trial data from adult women with trichomoniasis, four open-label trials in males with trichomoniasis, and an open-label safety study in pediatric female patients with bacterial vaginosis [see Adverse Reactions (6.1 ) and Clinical Studies (14.2 )] .The safety and effectiveness of SOLOSEC in pediatric patients below the age of 12 years have not been established.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies with secnidazole did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
SOLOSEC is contraindicated:
- In patients who have shown hypersensitivity to secnidazole, or other nitroimidazole derivatives.
- In patients with Cockayne syndrome: Severe irreversible hepatotoxicity/acute liver failure with fatal outcomes have been reported after initiation of metronidazole, another nitroimidazole drug, structurally related to secnidazole, in patients with Cockayne syndrome [see Adverse Reactions (6.2 )] .
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Vulvovaginal Candidiasis : This may develop with SOLOSEC and require treatment with an antifungal agent (5.1 )
- Potential Risk for Carcinogenicity : Carcinogenicity has been seen in mice and rats treated chronically with nitroimidazole derivatives, which are structurally related to secnidazole. It is unclear if the positive tumor findings in lifetime rodent studies indicate a risk to patients taking a single dose of SOLOSEC to treat bacterial vaginosis. Avoid chronic use (5.2 )
Vulvovaginal Candidiasis
The use of SOLOSEC may result in vulvovaginal candidiasis. In controlled clinical trials of non-pregnant women with bacterial vaginosis, vulvovaginal candidiasis developed in 19/197 (9.6%) of patients who received 2 g SOLOSEC and 4/136 (2.9%) subjects who received placebo. In a controlled clinical trial of non-pregnant female patients with trichomoniasis, vulvovaginal candidiasis developed in 2/74 (2.7%) of patients who received 2 g SOLOSEC and 0/73 (0%) subjects who received placebo [see Adverse Reactions (6.1 )]. Symptomatic vulvovaginal candidiasis may require treatment with an antifungal agent.
Potential Risk for Carcinogenicity
Carcinogenicity has been seen in mice and rats treated chronically with nitroimidazole derivatives which are structurally related to secnidazole. It is unclear if the positive tumor findings in lifetime rodent studies of these nitroimidazoles indicate a risk to patients taking a single dose of SOLOSEC to treat bacterial vaginosis. Avoid chronic use of SOLOSEC [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1 )]
Risk of Development of Drug Resistance
Prescribing SOLOSEC in the absence of proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection or a prophylactic indication is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of the development of drug-resistant bacteria.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following important adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of labeling:
- Vulvovaginal Candidiasis [Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Bacterial Vaginosis
The safety data described below reflect exposure to 629 patients, of whom 558 received a 2 g dose of SOLOSEC. SOLOSEC was evaluated in four clinical trials of female patients diagnosed with bacterial vaginosis: two placebo-controlled trials (Trial 1 n=215, Trial 2 n=189) and two uncontrolled safety trials (Trial 3 n=321, Trial 4 n=40).
Most Common Adverse Reactions in Trials 1 and 2
All patients in Trial 1 and Trial 2 received a single oral dose of study medication or placebo. Trial 1 evaluated a 1 g (this dose is not approved) dose (n=71) and a 2 g dose (n=72) of SOLOSEC in patients aged 18 to 54 years. Trial 2 evaluated a 2 g dose (n=125) in patients aged 15 to 54 years. Patients in the placebo-controlled trials were primarily Black or African American (54%) or Caucasian (41%).
Among 197 patients treated with a single 2 g dose of SOLOSEC in the two placebo-controlled trials, Trial 1 and 2, adverse reactions were reported by approximately 29% of patients. Table 1 displays the most common adverse reactions (≥ 2 % in SOLOSEC-treated patients) in these two trials. There were no deaths in the trials.
| Adverse Reaction | SOLOSEC N=197 n (%) | Placebo N=136 n (%) |
| Vulvovaginal candidiasis | 19 (9.6) | 4 (2.9) |
| Headache | 7 (3.6) | 2 (1.5) |
| Nausea | 7 (3.6) | 1 (0.7) |
| Diarrhea | 5 (2.5) | 1 (0.7) |
| Abdominal pain | 4 (2.0) | 2 (1.5) |
| Vulvovaginal pruritus | 4 (2.0) | 2 (1.5) |
Most Common Adverse Reactions in Trial 3
Among the 321 patients in an uncontrolled trial, Trial 3, adverse reactions were reported in 30% of patients. Vulvovaginal candidiasis (8.4%), nausea (5.3%), vomiting (2.5%) and dysgeusia (3.4%) were the most common adverse reactions reported in this trial. Two SOLOSEC-treated patients in Trial 3 discontinued due to vulvovaginal candidiasis.
Most Common Adverse Reactions in Trial 4
In Trial 4, the safety of SOLOSEC was evaluated in a multicenter, uncontrolled, open-label study evaluating the safety and tolerability of SOLOSEC in 40 pediatric patients between the ages of 12 and less than 18 years old all of whom were treated with a 2 g single dose of SOLOSEC. Most patients in this study were either White (60%) or Black/African-American (38%). The overall safety findings of a SOLOSEC 2 g dose in patients aged 12 to 17 years are consistent with findings in adult patients aged 18 to 65 years old. There were no deaths, severe adverse reactions, or discontinuations due to adverse reactions. Adverse reactions occurring in at least one SOLOSEC-treated pediatric patient included: nausea and abdominal pain.
Trichomoniasis
The safety of SOLOSEC was evaluated in 147 female patients with trichomoniasis who participated in Trial 5, a placebo controlled, double blind trial, of whom 143 (97.3%) patients completed the 'Test of Cure' (TOC) visit. In this trial, 74 patients received a single 2-gram oral dose of SOLOSEC, and 73 patients received placebo. The mean age of the patients in this study was 37.7 years, with a range of 15 to 65 years. Most of the patients were Black or African American (134/147; 91.2%). In the primary phase of Trial 5, i.e., baseline to TOC visit, one SOLOSEC-treated patient was discontinued from the study due to nausea and productive cough.
Most Common Adverse Reactions
A total of 11 patients (14.9%) who received SOLOSEC and 16 patients (21.9%) in the placebo group reported adverse reactions, respectively. Vulvovaginal candidiasis was reported in 2 patients (2.7%) in the SOLOSEC-treated group and in none of the patients in the placebo group.
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been reported during use of SOLOSEC and other 2 g formulations of secnidazole outside of the United States. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Adverse Reactions with SOLOSEC
Nervous System Disorders: Dysgeusia
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, dizziness, and headache have been reported when SOLOSEC was taken concomitantly with alcohol. [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 ), Drug Interactions (7.2 ) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )].
Metronidazole, Another Nitroimidazole Agent, Structurally Related to Secnidazole
Cases of severe irreversible hepatotoxicity/acute liver failure, including cases with fatal outcomes with very rapid onset after initiation of systemic use of metronidazole, another nitroimidazole agent structurally related to secnidazole, have been reported in patients with Cockayne syndrome (latency from drug start to signs of liver failure as short as 2 days) [see Contraindications (4 )] .
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Oral Contraceptives
There was no clinically significant drug interaction between secnidazole and the combination oral contraceptive, ethinyl estradiol plus norethindrone [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )]. SOLOSEC can be co-administered with combination oral contraceptives (e.g., ethinyl estradiol plus norethindrone).
Alcohol
Alcoholic beverages and preparations containing ethanol or propylene glycol should be avoided during SOLOSEC therapy and for 2 days after treatment is stopped.
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, dizziness, and headache have been reported when SOLOSEC was taken concomitantly with alcohol. [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 ), Adverse Reactions (6.2 ) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )].
DESCRIPTION
The active ingredient in SOLOSEC Oral Granules is secnidazole (also named 1-(2- hydroxypropyl)-2-methyl-5-nitroimidazole and 1-(2-methyl-5-nitro-1 H -imidazol-1-yl) propan-2- ol), a nitroimidazole antimicrobial.
The molecular formula of secnidazole is C 7 H 11 N 3 O 3 , the molecular weight is 185.18 and the chemical structure is:
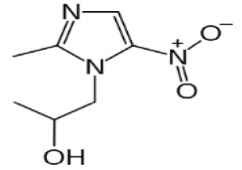
Figure 1: Structure of Secnidazole
Each packet of SOLOSEC contains 4.8 g of off-white to slightly yellowish granules, which contain 2 g of secnidazole and the following inactive ingredients: Eudragit NE30D (ethyl acrylate methyl methacrylate copolymer), polyethylene glycol 4000, povidone, sugar spheres, and talc. Contains no ingredient made from a gluten-containing grain (wheat, barley, or rye).
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
SOLOSEC is a nitroimidazole antimicrobial drug [See Microbiology (12.4 )].
Pharmacodynamics
Secnidazole exposure-response relationships and the time course of pharmacodynamic response are unknown.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
The effect of secnidazole on the QTc interval was evaluated in a Phase 1 randomized, double blind, placebo- and positive-controlled four-period crossover thorough QTc study in 52 healthy adult subjects following single oral granule doses of 2 g and 6 g (3-times the recommended dose). Although there was a positive relationship of the QTc interval with secnidazole concentrations, there was no clinically relevant increase in the QTc interval following either dose.
Pharmacokinetics
A single oral dose of 2 g of SOLOSEC in healthy adult female subjects, following an overnight fast and admixed with (4 oz) of applesauce, resulted in a mean (SD) secnidazole peak plasma concentration (C max ) of 45.4 (7.64) mcg/mL and mean (SD) systemic exposure (AUC 0-inf ) of 1331.6 (230.16) mcg•hr/mL. Median (range) time to peak concentration (T max ) was 4.0 (3.0-4.0) hours. Following administration of the 2 g dose, mean secnidazole plasma concentrations decreased to 22.1 mcg/mL at 24 hours, 9.2 mcg/mL at 48 hours, 3.8 mcg/mL at 72 hours, and 1.4 mcg/mL at 96 hours.
Absorption
Effect of Food
Administration of 2 g of SOLOSEC admixed with applesauce followed by ingestion of a high-fat meal (approximately 150 protein calories, 250 carbohydrate calories, and 500-600 fat calories) resulted in no significant change in the rate (C max ) and extent (AUC) of secnidazole exposure as compared to administration when admixed with applesauce and taken under fasted conditions. There was no effect of admixing SOLOSEC with pudding and yogurt as compared to admixing with applesauce (Table 2). [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 )]
• Median (range) | ||||
† Admixed with applesauce | ||||
| C max (mcg/mL) | T max (hr) • | AUC (mcg•hr/mL) | ||
| Fasted † (N=23) | Mean (SD) | 41.2 (5.5) | 4.0 (3.0 - 6.0) | 1261.5 (236.5) |
| Range | 32.7 – 56.2 | 874.3 – 1750.4 | ||
| High fat meal † (N=23) | Mean (SD) | 40.1 (4.9) | 6.0 (4.0 - 8.0) | 1248.2 (291.6) |
| Range | 31.0 – 47.7 | 762.0 – 1769.4 | ||
| Mixed with applesauce (N=24) | Mean (SD) | 44.1 (4.6) | 4.0 (3.0 – 6.1) | 1523 (372.2) |
| Range | 37.4 – 55.6 | 1040 - 2350 | ||
| Mixed with pudding (N=23) | Mean (SD) | 45.6 (5.1) | 4.0 (4.0 – 6.0) | 1447 (331.0) |
| Range | 38.6 – 60.4 | 997 - 2130 | ||
| Mixed with yogurt (N=24) | Mean (SD) | 43.4 (5.4) | 4.0 (4.0 – 8.0) | 1478 (335.0) |
| Range | 36.3 – 59.3 | 965 - 2240 | ||
Distribution
The apparent volume of distribution of secnidazole is approximately 42 L. The plasma protein binding of secnidazole is <5%.
Elimination
The total body clearance of secnidazole is approximately 25 mL/min. The renal clearance of secnidazole is approximately 3.9 mL/min.
The plasma elimination half-life for secnidazole is approximately 17 hours.
Metabolism
Secnidazole is metabolized in vitro via oxidation by human hepatic CYP450 enzyme system with ≤ 1% conversion to metabolites.
Excretion
Approximately 15% of a 2 g oral dose of SOLOSEC is excreted as unchanged secnidazole in the urine.
Drug Interaction Studies
Oral Contraceptives
Concomitant administration of 2 g of SOLOSEC with the combination oral contraceptive (OC), ethinyl estradiol (EE) plus norethindrone (NE), to healthy adult female subjects resulted in a decrease in mean C max of EE of 29%, and no significant effect on the mean AUC of EE. Administration of 2 g of SOLOSEC 1 day before combination OC administration resulted in no significant effect on mean C max or AUC of EE.
Concomitant administration of 2 g of SOLOSEC with the combination OC resulted in no significant effect on mean C max and AUC of NE (increases of 13% and 16%, respectively). Administration of 2 g of SOLOSEC 1 day before combination OC administration also resulted in no significant effect on mean C max and AUC of NE. [see Drug Interactions (7.1 )]
Ethanol Metabolism
In vitro studies showed that secnidazole had no effect on aldehyde dehydrogenase activity.
However, postmarketing observations of adverse reactions of nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, dizziness, and headache with concomitant use of SOLOSEC and alcohol have been reported [see, Dosage and Administration (2.3 ), Adverse Reactions (6.2 ), and Drug Interactions (7.2 )].
Microbiology
Mechanism of Action
Secnidazole, like other 5‑nitroimidazoles, enters the bacterial and Trichomonas cells where the nitro group is reduced by nitroreductase enzyme(s) leading to the production of radical anions and a series of intermediates, depletion of thiols, DNA damage, and death of susceptible isolates of Gram positive bacteria, Gram negative bacteria and T. vaginalis .
Resistance
The potential for development of resistance to secnidazole by bacteria and T. vaginalis associated with bacterial vaginosis and trichomoniasis, respectively, was not examined. The mechanism of resistance, like for other nitroimidazoles, appears to be multifactorial that include decreased uptake of the drug, higher efflux activity, and/or altered nitroreductase activity.
Bacterial and T. vaginalis isolates exhibiting reduced in vitro susceptibility to metronidazole also show reduced susceptibility to secnidazole. The clinical significance of such an effect is unknown.
Antibacterial Activity
Culture and sensitivity testing of bacteria are not routinely performed to establish the diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis [see Indications and Usage (1.1 )] ; standard methodology for the susceptibility testing of potential bacterial pathogens, Gardnerella vaginalis or Mobiluncus spp. has not been defined.
The following in vitro data are available, but their clinical significance is unknown. Secnidazole is active in vitro against most isolates of the following organisms reported to be associated with bacterial vaginosis:
Bacteroides spp.
Gardnerella vaginalis
Prevotella spp.
Mobiluncus spp.
Megasphaera -like type I/II
Anti-protozoal Activity
Trichomonas vaginalis
Standardized susceptibility tests do not exist for use in clinical microbiology laboratories.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis Mutagenesis & Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Nitroimidazoles, which have similar chemical structures to secnidazole, have been associated with tumors affecting the liver, lungs, mammary, and lymphatic tissues in animals after lifetime exposures. It is unclear if these positive tumor findings in lifetime rodent studies of these nitroimidazoles indicate a risk to patients taking a single dose of secnidazole to treat bacterial vaginosis or trichomoniasis.
Mutagenesis
Secnidazole was positive in the Bacterial Reverse Mutation Assay but was negative for the rat micronucleus test and mouse lymphoma test.
Impairment of Fertility
In a rat fertility study, females were dosed for two weeks prior to mating until Day 7 of gestation with males that were dosed for a minimum of 28 days before cohabitation. No parental toxicity or adverse effects on mating performance, estrous cycles, fertility or conception was observed at doses of up to the maximum tolerated dose (300 mg/kg/day, approximately 1.4 times the recommended dose based on AUC comparisons).
CLINICAL STUDIES
Bacterial Vaginosis
Two randomized placebo-controlled clinical trials (Trial 1 and Trial 2) with similar designs were conducted to evaluate the efficacy of SOLOSEC 2 gram for the treatment of bacterial vaginosis. A diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis was defined as all of (a) the presence of an off-white (milky or gray), thin, homogeneous vaginal discharge; (b) a vaginal pH ≥ 4.7; (c) the presence of Clue cells ≥ 20% of the total epithelial cells on a microscopic examination of the vaginal saline wet mount; (d) a positive "whiff" test (detection of amine odor on addition of 10% KOH solution to a sample of the vaginal discharge); and (e) a Nugent score ≥ 4.
Trial 1 enrolled 144 non-pregnant female patients aged 19 to 54 years and Trial 2 enrolled 189 non-pregnant females aged 18 to 54 years. Black or African American subjects in both trials were 54%. Efficacy was assessed by clinical outcome evaluated 21 to 30 days following a single dose of SOLOSEC. A clinical responder was defined as "normal" vaginal discharge, negative "whiff" test, and clue cells <20%. Additional endpoints included Nugent score cure (Nugent score of 0-3) and therapeutic outcome. A therapeutic responder was defined as a clinical responder with a Nugent score cure. In Trial 2, the endpoints were also assessed at Day 7-14.
In both trials, a statistically significantly greater percentage of patients experienced clinical response, Nugent score cure, and therapeutic response at 21 to 30 days following a single dose of SOLOSEC compared to placebo. Statistically significant results for the endpoints were also achieved at Day 7-14 in Trial 2.
The percentage of patients with clinical response was also consistently higher in both trials in the SOLOSEC arm compared to placebo among all subsets of patients: number of prior episodes of bacterial vaginosis (≤ 3 episodes and ≥ 4 episodes) in past 12 months, baseline Nugent score (score 4-6 and score 7-10), and race (Black/African American and White). Tables 3 and 4 describe the efficacy of SOLOSEC in the treatment of bacterial vaginosis.
• N=number of patients in treatment group (modified intent-to-treat population defined as all patients randomized who had a baseline Nugent score ≥4 and were negative for other sexually transmitted infections at baseline). | ||||
† Patients missing one or more of the clinical assessments were considered as non-responders/not cured. | ||||
‡ Difference in response (SOLOSEC – placebo) and 95% confidence interval | ||||
§ Patients with missing Nugent scores were considered Nugent score failures. | ||||
| Trial 1 | Trial 2 | |||
| SOLOSEC (N=62) • n (%) | Placebo (N=62) • n (%) | SOLOSEC (N=107) • n (%) | Placebo (N=57) • n (%) | |
| Clinical Responder † | 42 (67.7) | 11 (17.7) | 57 (53.3) | 11 (19.3) |
| 50.0 (33.4, 66.7) ‡ p<0.001 | 34.0 (18.7, 49.3) ‡ p<0.001 | |||
| Nugent Score Cure § | 25 (40.3) | 4 (6.5) | 47 (43.9) | 3 (5.3) |
| 33.8 (18.5, 49.1) ‡ p<0.001 | 38.6 (26.2, 51.0) ‡ p<0.001 | |||
| Therapeutic Responder | 25 (40.3) | 4 (6.5) | 37 (34.6) | 2 (3.5) |
| 33.8 (18.5, 49.1) ‡ p<0.001 | 31.1 (19.6, 42.6) ‡ p<0.001 | |||
• N=number of patients in treatment group (modified intent-to-treat population defined as all patients randomized who had a baseline Nugent | ||
score ≥4 and were negative for other sexually transmitted infections at baseline). | ||
† Patients missing one or more of the clinical assessments were considered as non-responders/not cured. | ||
‡ Difference in response (SOLOSEC – placebo) and 95% confidence interval | ||
§ Patients with missing Nugent scores were considered Nugent score failures. | ||
| Trial 2 | ||
| SOLOSEC (N=107) • n (%) | Placebo (N=57) • n (%) | |
| Clinical Responder † | 62 (57.9) | 14 (24.6) |
| 33.3 (17.4, 49.2) ‡ p<0.001 | ||
| Nugent Score Cure § | 49 (45.8) | 2(3.5) |
| 42.3 (30.4, 54.2) ‡ p<0.001 | ||
| Therapeutic Responder | 37 (34.6) | 2(3.5) |
| 31.1 (19.6, 42.6) ‡ p<0.001 | ||
Trichomoniasis
The efficacy of a single 2-gram oral dose of SOLOSEC for the treatment of trichomoniasis was evaluated in a multi-center, prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled, delayed treatment, double-blind, trial (Trial 4, NCT03935217). A total of 147 female patients from the United States aged 15 to 65 years were enrolled and randomized 1:1 to receive either SOLOSEC or placebo. The modified intent-to-treat (mITT) population included all randomized patients who were culture positive for T. vaginalis and negative for other sexually transmitted infections. Of the 131 female patients in the mITT population, the median age was 36 years, and 90.8% were African American. Baseline clinical symptoms of vaginal itching, discharge, or odor were reported in 111 (84.7%) patients. Following initial dosing, the test of cure (TOC) visit occurred 6 to 12 days later. At the TOC visit, patients received the opposite treatment (placebo patients received SOLOSEC and vice versa) with a return visit 7 to 12 days later.
Results for microbiological cure, defined as testing negative for T. vaginalis, for the mITT population are presented in Table 5. The microbiological cure rate at the TOC visit was significantly higher in the SOLOSEC treatment group compared to the placebo group.
CI = confidence interval; TOC = Test of Cure | |||
a InPouch TM TV test negative for T. vaginalis . | |||
b Subjects with no test results are assumed to be positive (1 SOLOSEC and 3 placebo subjects). | |||
c Exact CI from the Score Method. | |||
d P-value <0.001 versus placebo from a CMH test adjusted for clinical symptoms (present/absent) of trichomoniasis at baseline. | |||
e In placebo subjects with positive T. vaginalis culture at TOC, receiving delayed SOLOSEC treatment showed a comparable microbiological cure rate 7-12 days later (56/63 (88.9%), 95% CI: 78.4%, 95.4%) to the 92.2% cure rate for the initially SOLOSEC treated subjects. | |||
•N: number of patients in treatment group. For microbiological cure, included all subjects in the modified intent-to-treat (mITT) population, defined as all randomized patients who were culture positive for Trichomonas vaginalis and negative for other sexually transmitted infections. | |||
| Endpoint | SOLOSEC 2 g n/N (%) • | Placebo n/N (%) •,e | Treatment Difference (95% CI) |
| Microbiological Cure a,b | 59/64 (92.2) | 1/67 (1.5) | 90.7 (80.7, 96.5) c,d |
The single oral 2 g secnidazole dose was also assessed in four open-label trials in males (one comparative study with metronidazole and ornidazole in males only 1 and three single-arm studies in males and females 2,3,4 ). Parasitological evaluation was performed both pre- and post-treatment and reported cure rates ranged from 91.7% (165/180) to 100% (30/30) at time points ranging from 2 to 20 days (n=437, 211 males and 226 females). In addition, the natural history of trichomoniasis in men was evaluated in one study. 5 The spontaneous resolution during a mean follow-up of 16 ± 12 days was noted in 36% (5/14) (95% CI: 12.8%, 64.9%) of untreated men.
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
SOLOSEC (secnidazole) Oral Granules, 2 g, consists of off-white to slightly yellowish granules containing secnidazole. SOLOSEC is supplied in one unit-of-use child-resistant foil packet of granules in an individual carton. Each packet contains 4.8 g of granules containing 2 g secnidazole. SOLOSEC is supplied as follows:
NDC 27437-051-01 carton containing one unit-of-use child-resistant 2 g foil packet
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30ºC (59ºF to 86ºF) [See USP Controlled Room temperature].
Mechanism of Action
SOLOSEC is a nitroimidazole antimicrobial drug [See Microbiology (12.4 )].