Get your patient on Somavert (Pegvisomant)
Somavert prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Somavert patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Administer a 40 mg loading dose subcutaneously under physician supervision. (2.1 )
- After proper injection instruction, on day after loading dose, patients or caregivers begin daily subcutaneous injections of 10 mg. (2.1 )
- Adjust dosage in 5 mg increments or decrements until serum IGF-1 concentrations are maintained within age-adjusted normal range. Do not adjust dosage based on growth hormone (GH) levels or signs or symptoms of acromegaly. (2.1 )
- Dosage range is 10 mg to 30 mg once daily. (2.1 )
- Perform liver tests prior to first dosage and if greater than 3 times upper limit of normal should work-up prior to SOMAVERT administration. (2.2 )
- Follow reconstitution and injection procedures. (2.3 , 2.4 )
Dosage Information
The recommended loading dose of SOMAVERT is 40 mg given subcutaneously, under healthcare provider supervision. Provide proper training in subcutaneous injection technique to patients or their caregivers so they can receive once daily subcutaneous injections. On the next day following the loading dose, instruct patients or their caregivers to begin daily subcutaneous injections of 10 mg of SOMAVERT.
Titrate the dosage to normalize serum IGF-1 concentrations (serum IGF-1 concentrations should be measured every four to six weeks). The dosage should not be based on growth hormone (GH) concentrations or signs and symptoms of acromegaly. It is unknown whether patients who remain symptomatic while achieving normalized IGF-1 concentrations would benefit from increased SOMAVERT dosage.
- Increase the dosage by 5 mg increments every 4–6 weeks if IGF-1 concentrations are elevated.
- Decrease the dosage by 5 mg decrements every 4–6 weeks if IGF-1 concentrations are below the normal range.
- IGF-1 levels should also be monitored when a SOMAVERT dose given in multiple injections is converted to a single daily injection [see Clinical Pharmacology (12) ] .
The recommended dosage range is between 10 mg to 30 mg given subcutaneously once daily and the maximum daily dosage is 30 mg given subcutaneously once daily.
Assess Liver Tests Prior to Initiation of SOMAVERT
Prior to the start of SOMAVERT, patients should have an assessment of baseline levels of liver tests [serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), serum total bilirubin (TBIL), and alkaline phosphatase (ALP)]. For recommendations regarding initiation of SOMAVERT based on baseline liver tests and recommendations for monitoring of liver tests while on SOMAVERT, refer to Table 1 in Warning and Precautions (5.2) .
Loading Dose Injection Procedure
The following instructions are for the healthcare provider to reconstitute and prepare the 40 mg loading dose. The healthcare provider will need to reconstitute 2 vials of lyophilized powder of SOMAVERT each containing 20 mg of pegvisomant with supplied diluent [two vials of lyophilized powder and two syringes containing 1 mL of diluent (Sterile Water for Injection, USP) will be needed for the 40 mg loading dose]. The healthcare provider will also need to inject the reconstituted SOMAVERT solution twice into the patient's upper arm, upper thigh, abdomen, or buttocks (each injection in a different area).
- Before administering the loading dose, remove 1 vial of lyophilized powder of SOMAVERT containing 20 mg of pegvisomant and one syringe containing 1 mL of diluent from the refrigerator, if refrigerated, about 10 minutes prior to the planned injection time.
- Reconstitute the first 20 mg vial of lyophilized powder of SOMAVERT containing 20 mg of pegvisomant with diluent. When using the diluent in the syringe, inject the contents of the syringe slowly onto the sides of the vial containing lyophilized powder of SOMAVERT. Do not inject the diluent directly on the powder.
- Do not invert the vial or shake the solution as this may cause denaturation of the pegvisomant protein. Slowly swirl the solution to ensure that all of the lyophilized powder has gone into solution. If foaming of the reconstituted SOMAVERT solution is seen, the solution is likely damaged and therefore inappropriate to inject.
- Visually inspect the reconstituted SOMAVERT solution for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. The reconstituted solution should be clear. If the solution is cloudy, do not use it. Once reconstituted, the solution will contain 20 mg of pegvisomant in 1 mL of solution.
- Withdraw the 1 mL reconstituted SOMAVERT solution. The solution must be administered immediately after reconstitution.
- Inject the first reconstituted SOMAVERT solution (20 mg/mL) subcutaneously into the patient's upper arm, upper thigh, abdomen, or buttocks using a 90-degree angle.
- Repeat steps (a) to (e) to reconstitute the second SOMAVERT dose of 20mg.
- Finally, inject the second reconstituted SOMAVERT solution (20 mg/mL) subcutaneously into the patient's upper arm, upper thigh, abdomen, or buttocks using a 90-degree angle (different area than the first injection).
Maintenance Dose Injection Procedure
For patient or caregiver instructions for reconstitution and administration of daily doses (10 mg to 30 mg), see the Patient's Instructions for Use .
- Before administering the dose, remove 1 vial of lyophilized powder of SOMAVERT containing 10 mg, 15 mg, 20 mg, 25 mg or 30 mg of pegvisomant and one syringe containing 1 mL of diluent from the refrigerator, if refrigerated, about 10 minutes prior to the planned injection time.
- Reconstitute the lyophilized powder of SOMAVERT with diluent. When using the diluent in the 2.25 mL syringe, inject the contents of the syringe slowly onto the sides of the vial containing lyophilized powder of SOMAVERT. Do not inject the diluent directly on the powder.
- Do not invert the vial or shake the solution as this may cause denaturation of the pegvisomant protein. Slowly swirl the solution to ensure that all of the lyophilized powder has gone into solution. If foaming of the reconstituted SOMAVERT solution is seen, the solution is likely damaged and therefore inappropriate to inject.
- Visually inspect the reconstituted SOMAVERT solution for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. The reconstituted solution should be clear. If the solution is cloudy, do not use it. Once reconstituted, the solution will contain 10 mg, 15 mg, 20 mg, 25 mg or 30 mg of pegvisomant in 1 mL of solution.
- Withdraw the 1 mL reconstituted SOMAVERT solution. The solution must be administered immediately after reconstitution.
- Inject the reconstituted SOMAVERT solution subcutaneously into the upper arm, upper thigh, abdomen, or buttocks using a 90-degree angle.

Somavert prescribing information
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
SOMAVERT is indicated for the treatment of acromegaly in patients who have had an inadequate response to surgery or radiation therapy, or for whom these therapies are not appropriate. The goal of treatment is to normalize serum insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) levels.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Administer a 40 mg loading dose subcutaneously under physician supervision. (2.1 )
- After proper injection instruction, on day after loading dose, patients or caregivers begin daily subcutaneous injections of 10 mg. (2.1 )
- Adjust dosage in 5 mg increments or decrements until serum IGF-1 concentrations are maintained within age-adjusted normal range. Do not adjust dosage based on growth hormone (GH) levels or signs or symptoms of acromegaly. (2.1 )
- Dosage range is 10 mg to 30 mg once daily. (2.1 )
- Perform liver tests prior to first dosage and if greater than 3 times upper limit of normal should work-up prior to SOMAVERT administration. (2.2 )
- Follow reconstitution and injection procedures. (2.3 , 2.4 )
Dosage Information
The recommended loading dose of SOMAVERT is 40 mg given subcutaneously, under healthcare provider supervision. Provide proper training in subcutaneous injection technique to patients or their caregivers so they can receive once daily subcutaneous injections. On the next day following the loading dose, instruct patients or their caregivers to begin daily subcutaneous injections of 10 mg of SOMAVERT.
Titrate the dosage to normalize serum IGF-1 concentrations (serum IGF-1 concentrations should be measured every four to six weeks). The dosage should not be based on growth hormone (GH) concentrations or signs and symptoms of acromegaly. It is unknown whether patients who remain symptomatic while achieving normalized IGF-1 concentrations would benefit from increased SOMAVERT dosage.
- Increase the dosage by 5 mg increments every 4–6 weeks if IGF-1 concentrations are elevated.
- Decrease the dosage by 5 mg decrements every 4–6 weeks if IGF-1 concentrations are below the normal range.
- IGF-1 levels should also be monitored when a SOMAVERT dose given in multiple injections is converted to a single daily injection [see Clinical Pharmacology (12) ] .
The recommended dosage range is between 10 mg to 30 mg given subcutaneously once daily and the maximum daily dosage is 30 mg given subcutaneously once daily.
Assess Liver Tests Prior to Initiation of SOMAVERT
Prior to the start of SOMAVERT, patients should have an assessment of baseline levels of liver tests [serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), serum total bilirubin (TBIL), and alkaline phosphatase (ALP)]. For recommendations regarding initiation of SOMAVERT based on baseline liver tests and recommendations for monitoring of liver tests while on SOMAVERT, refer to Table 1 in Warning and Precautions (5.2) .
Loading Dose Injection Procedure
The following instructions are for the healthcare provider to reconstitute and prepare the 40 mg loading dose. The healthcare provider will need to reconstitute 2 vials of lyophilized powder of SOMAVERT each containing 20 mg of pegvisomant with supplied diluent [two vials of lyophilized powder and two syringes containing 1 mL of diluent (Sterile Water for Injection, USP) will be needed for the 40 mg loading dose]. The healthcare provider will also need to inject the reconstituted SOMAVERT solution twice into the patient's upper arm, upper thigh, abdomen, or buttocks (each injection in a different area).
- Before administering the loading dose, remove 1 vial of lyophilized powder of SOMAVERT containing 20 mg of pegvisomant and one syringe containing 1 mL of diluent from the refrigerator, if refrigerated, about 10 minutes prior to the planned injection time.
- Reconstitute the first 20 mg vial of lyophilized powder of SOMAVERT containing 20 mg of pegvisomant with diluent. When using the diluent in the syringe, inject the contents of the syringe slowly onto the sides of the vial containing lyophilized powder of SOMAVERT. Do not inject the diluent directly on the powder.
- Do not invert the vial or shake the solution as this may cause denaturation of the pegvisomant protein. Slowly swirl the solution to ensure that all of the lyophilized powder has gone into solution. If foaming of the reconstituted SOMAVERT solution is seen, the solution is likely damaged and therefore inappropriate to inject.
- Visually inspect the reconstituted SOMAVERT solution for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. The reconstituted solution should be clear. If the solution is cloudy, do not use it. Once reconstituted, the solution will contain 20 mg of pegvisomant in 1 mL of solution.
- Withdraw the 1 mL reconstituted SOMAVERT solution. The solution must be administered immediately after reconstitution.
- Inject the first reconstituted SOMAVERT solution (20 mg/mL) subcutaneously into the patient's upper arm, upper thigh, abdomen, or buttocks using a 90-degree angle.
- Repeat steps (a) to (e) to reconstitute the second SOMAVERT dose of 20mg.
- Finally, inject the second reconstituted SOMAVERT solution (20 mg/mL) subcutaneously into the patient's upper arm, upper thigh, abdomen, or buttocks using a 90-degree angle (different area than the first injection).
Maintenance Dose Injection Procedure
For patient or caregiver instructions for reconstitution and administration of daily doses (10 mg to 30 mg), see the Patient's Instructions for Use .
- Before administering the dose, remove 1 vial of lyophilized powder of SOMAVERT containing 10 mg, 15 mg, 20 mg, 25 mg or 30 mg of pegvisomant and one syringe containing 1 mL of diluent from the refrigerator, if refrigerated, about 10 minutes prior to the planned injection time.
- Reconstitute the lyophilized powder of SOMAVERT with diluent. When using the diluent in the 2.25 mL syringe, inject the contents of the syringe slowly onto the sides of the vial containing lyophilized powder of SOMAVERT. Do not inject the diluent directly on the powder.
- Do not invert the vial or shake the solution as this may cause denaturation of the pegvisomant protein. Slowly swirl the solution to ensure that all of the lyophilized powder has gone into solution. If foaming of the reconstituted SOMAVERT solution is seen, the solution is likely damaged and therefore inappropriate to inject.
- Visually inspect the reconstituted SOMAVERT solution for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. The reconstituted solution should be clear. If the solution is cloudy, do not use it. Once reconstituted, the solution will contain 10 mg, 15 mg, 20 mg, 25 mg or 30 mg of pegvisomant in 1 mL of solution.
- Withdraw the 1 mL reconstituted SOMAVERT solution. The solution must be administered immediately after reconstitution.
- Inject the reconstituted SOMAVERT solution subcutaneously into the upper arm, upper thigh, abdomen, or buttocks using a 90-degree angle.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
For injection: 10 mg, 15 mg, 20 mg, 25 mg or 30 mg white lyophilized powder in a single-dose vial for reconstitution supplied with a prefilled syringe containing 1 mL of diluent (Sterile Water for Injection, USP).
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential: Advise premenopausal females of the potential for an unintended pregnancy. (8.3 )
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Postmarketing reports of SOMAVERT use in pregnant women are insufficient to establish a drug-associated risk for major birth defects, miscarriage or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Acromegaly may improve during pregnancy (see Clinical Considerations ) . In animal reproduction studies, fetotoxicity was observed at a dose that was 6 times the maximum recommended human dose based on body surface area following subcutaneous administration of pegvisomant during organogenesis or during the preimplantation period (see Data ) .
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2–4% and 15–20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-associated maternal and/or embryofetal risk
Published data from case reports, case series, and a small interventional study in pregnant women with acromegaly have demonstrated that acromegaly may improve or stabilize without treatment during pregnancy, particularly if acromegaly is treated before pregnancy. In rare cases, acromegaly may worsen during pregnancy. Since IGF-1 levels may change physiologically during pregnancy and interpreting IGF-1 and growth hormone levels in pregnant women with acromegaly may be unreliable, clinical monitoring is recommended.
Data
Animal Data
The effects of pegvisomant on early embryonic development and embryo-fetal development were evaluated in two separate studies, which were conducted in pregnant rabbits with pegvisomant at subcutaneous doses of 1, 3, and 10 mg/kg/day. There was no evidence of teratogenic effects associated with pegvisomant administration during organogenesis. At the 10-mg/kg/day dose (6 times the maximum human therapeutic dose based on body surface area), a reproducible, slight increase in post-implantation loss was observed in both studies.
Lactation
Risk Summary
Limited information from a case report in published literature reported that the level of pegvisomant in human milk was below the level of detection. There is no information available on the effects of the drug on the breastfed infant or the effects of the drug on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for SOMAVERT and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from SOMAVERT or from the underlying maternal condition.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Discuss the potential for unintended pregnancy with premenopausal women as the therapeutic benefits of a reduction in growth hormone (GH) levels and normalization of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) concentration in acromegalic females treated with pegvisomant may lead to improved fertility.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of SOMAVERT in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of SOMAVERT did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
Renal Impairment
SOMAVERT was not studied in patients with renal impairment and the safety and efficacy in these patients is not known.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Hypoglycemia : Monitor blood glucose in patients with diabetes mellitus and reduce anti-diabetic drug therapy as necessary. (5.1 )
- Liver Toxicity: Should have more frequent liver tests and/or discontinue SOMAVERT. (5.2 )
- Systemic Hypersensitivity : Monitor closely when re-initiating SOMAVERT in patients with systemic hypersensitivity. (5.5 )
Hypoglycemia Associated With GH Lowering in Patients With Diabetes Mellitus
GH opposes the effects of insulin on carbohydrate metabolism by decreasing insulin sensitivity; thus, glucose tolerance may improve in some patients treated with SOMAVERT. Patients should be carefully monitored and doses of anti-diabetic drugs reduced as necessary to avoid hypoglycemia in patients with diabetes mellitus.
Liver Toxicity
Baseline serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), serum total bilirubin (TBIL), and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) levels should be obtained prior to initiating therapy with SOMAVERT. Table 1 lists recommendations regarding initiation of treatment with SOMAVERT, based on the results of these liver tests (LTs).
Asymptomatic, transient elevations in transaminases up to 15 times ULN have been observed in <2% of subjects among two open-label trials (with a total of 147 patients). These reports were not associated with an increase in bilirubin. Transaminase elevations normalized with time, most often after suspending treatment. Postmarketing reports have identified elevations in serum hepatic transaminases up to greater than 20 times ULN associated with elevation in total bilirubin greater than 2 times ULN. In many of these cases, discontinuation of SOMAVERT therapy resulted in improvement or resolution of hepatic laboratory abnormalities.
SOMAVERT should be used in accordance with the information presented in Table 2 with respect to liver test abnormalities while on SOMAVERT treatment.
| Baseline LT Levels | Recommendations |
|---|---|
Normal |
|
Elevated, but less than or equal to 3 times ULN | May treat with SOMAVERT; however, monitor LTs monthly for at least one year after initiation of therapy and then bi-annually for the next year. |
Greater than 3 times ULN |
|
If a patient develops LT elevations, or any other signs or symptoms of liver dysfunction while receiving SOMAVERT, the following patient management is recommended (Table 2).
Table 2. Clinical Recommendations Based on Liver Test Results While on SOMAVERT
| LT Levels and Clinical Signs/Symptoms | Recommendations |
|---|---|
Greater than or equal to 3 but less than 5 times ULN (without signs/symptoms of hepatitis or other liver injury, or increase in serum TBIL) |
|
At least 5 times ULN, or transaminase elevations at least 3 times ULN associated with any increase in serum TBIL (with or without signs/symptoms of hepatitis or other liver injury) |
|
Signs or symptoms suggestive of hepatitis or other liver injury (e.g., jaundice, bilirubinuria, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, right upper quadrant pain, ascites, unexplained edema, easy bruisability) |
|
Cross-Reactivity With GH Assays
SOMAVERT has significant structural similarity to growth hormone (GH) which causes it to cross-react in commercially available GH assays. Since serum concentrations of therapeutically effective doses of SOMAVERT are generally 100 to 1000 times higher than the actual serum GH concentrations seen in patients with acromegaly, measurements of serum GH concentrations will appear falsely elevated.
Lipohypertrophy
There have been cases of lipohypertrophy in patients treated with SOMAVERT. In a double-blind, 12-week, placebo-controlled study, there was one case (1.3%) of injection site lipohypertrophy reported in a subject receiving 10 mg/day. The subject recovered while on treatment. Among two open-label trials (with a total of 147 patients), there were two subjects, both receiving 10 mg/day, who developed lipohypertrophy. One case recovered while on treatment, and one case resulted in a discontinuation of treatment. Injection sites should be rotated daily to help prevent lipohypertrophy (different area than the last injection).
Systemic Hypersensitivity
In patients with systemic hypersensitivity reactions, caution and close monitoring should be exercised when re-initiating SOMAVERT therapy [see Adverse Reactions (6.2) ] .
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Clinically significant adverse reactions that appear in other section of the labeling include:
- Hypoglycemia Associated with GH Lowering in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- Liver Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
- Cross-Reactivity with GH Assays [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
- Lipohypertrophy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ]
- Systemic Hypersensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ]
Elevations of serum concentrations of ALT and AST greater than ten times the ULN were reported in two patients (0.8%) exposed to SOMAVERT in pre-approval clinical studies. One patient was rechallenged with SOMAVERT, and the recurrence of elevated transaminase levels suggested a probable causal relationship between administration of the drug and the elevation in liver enzymes. A liver biopsy performed on the second patient was consistent with chronic hepatitis of unknown etiology. In both patients, the transaminase elevations normalized after discontinuation of the drug.
Elevations in ALT and AST levels were not associated with increased levels of TBIL and ALP, with the exception of two patients with minimal associated increases in ALP levels (i.e., less than 3 times ULN). The transaminase elevations did not appear to be related to the dose of SOMAVERT administered, generally occurred within 4 to 12 weeks of initiation of therapy, and were not associated with any identifiable biochemical, phenotypic, or genetic predictors.
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
In a 12-week randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, fixed-dose study of SOMAVERT in subjects with acromegaly, 32 subjects received placebo and 80 subjects received SOMAVERT once daily [see Clinical Studies (14) ] . A total of 108 subjects (30 placebo, 78 SOMAVERT) completed 12 weeks of study treatment.
Overall, eight patients with acromegaly (5.3%) withdrew from pre-marketing clinical studies because of adverse events, including two patients with marked transaminase elevations, one patient with lipohypertrophy at the injection sites, and one patient with substantial weight gain. Most adverse events did not appear to be dose-dependent. Table 3 shows the incidence of adverse events that were reported in at least two patients treated with SOMAVERT and at frequencies greater than placebo during the 12-week, placebo-controlled study.
| Placebo n=32 | SOMAVERT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mg/day n=26 | 15 mg/day n=26 | 20 mg/day N=28 | ||
Infection The 6 events coded as "infection" in the group treated with SOMAVERT 10 mg were reported as cold symptoms (3), upper respiratory infection (1), blister (1), and ear infection (1). The 2 events in the placebo group were reported as cold symptoms (1) and chest infection (1). | 2 (6%) | 6 (23%) | 0 | 0 |
Pain | 2 (6%) | 2 (8%) | 1 (4%) | 4 (14%) |
Nausea | 1 (3%) | 0 | 2 (8%) | 4 (14%) |
Diarrhea | 1 (3%) | 1 (4%) | 0 | 4 (14%) |
Abnormal liver function tests | 1 (3%) | 3 (12%) | 1 (4%) | 1 (4%) |
Flu syndrome | 0 | 1 (4%) | 3 (12%) | 2 (7%) |
Injection site reaction | 0 | 2 (8%) | 1 (4%) | 3 (11%) |
Dizziness | 2 (6%) | 2 (8%) | 1 (4%) | 1 (4%) |
Accidental injury | 1 (3%) | 2 (8%) | 1 (4%) | 0 |
Back pain | 1 (3%) | 2 (8%) | 0 | 1 (4%) |
Sinusitis | 1 (3%) | 2 (8%) | 0 | 1 (4%) |
Chest pain | 0 | 1 (4%) | 2 (8%) | 0 |
Peripheral edema | 0 | 2 (8%) | 0 | 1 (4%) |
Hypertension | 0 | 0 | 2 (8%) | 0 |
Paresthesia | 2 (6%) | 0 | 0 | 2 (7%) |
Postmarketing Experience
Adverse Reactions from Postmarketing Spontaneous Reports
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of SOMAVERT. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Systemic hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylactic reactions, laryngospasm, angioedema, generalized skin reactions (rash, erythema, pruritus, urticaria) have been reported in post-marketing use. Some patients required hospitalization. Symptoms did not re-occur in all patients after re-challenge [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ] .
Adverse Reactions from an Observational Study
ACROSTUDY was an international observational registry that captured long term safety data in 2221 patients with acromegaly treated with SOMAVERT for a mean treatment duration of 8.5 years. Patients could also receive other therapy for acromegaly during the registry period. Treatment dose and schedule were at the discretion of each treating healthcare provider. Although safety monitoring as per the recommended schedule was mandatory, not all assessments were performed at all time points for every patient. Because of this, comparison of rates of adverse events to those in the original clinical trial is not appropriate. Of the 1327 patients who had a normal AST and ALT at baseline, 20 (1.5%) patients had elevated tests >3-5 times ULN, and 22 (1.7%) patients had elevated tests >5 times ULN. Lipohypertrophy was reported in 35 (1.6%) patients. Of the 1795 patients who had a MRI reported at baseline and at least once during follow up in the study, MRI results showed that 128 (7.1%) were reported to have an increase, 310 (17.3%) were reported to have a decrease, 81 (4.5%) had both increase and decrease, and 1276 (71.1%) had no change.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Insulin and/or Oral hypoglycemic Agents: Patients with acromegaly and with diabetes mellitus may require careful monitoring and dose reductions of insulin and/or oral hypoglycemic agents. (5.2 , 7.1 )
- Opioids: Patients on opioids may need higher SOMAVERT doses to achieve appropriate IGF-1 suppression. (7.2 )
Insulin and/or Oral Hypoglycemic Agents
After initiation of SOMAVERT, patients with acromegaly and diabetes mellitus treated with insulin and/or oral hypoglycemic agents may require dose reductions of insulin and/or oral hypoglycemic agents [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
Opioids
In clinical studies, patients taking opioids often needed higher SOMAVERT doses to normalize IGF-1 concentrations compared with patients not receiving opioids. The mechanism of this interaction is not known.
DESCRIPTION
Pegvisomant is an analog of human growth hormone (GH) of recombinant DNA origin that acts as a GH receptor antagonist.
It contains 191 amino acid residues. The molecular weight of pegvisomant is 22 kDa. The molecular weight of the PEG portion of pegvisomant is approximately 5 kDa. The predominant molecular weights of pegvisomant are thus approximately 42, 47, and 52 kDa. The schematic shows the amino acid sequence of the pegvisomant protein (PEG polymers are shown attached to the 5 most probable attachment sites). Pegvisomant is synthesized by a specific strain of Escherichia coli bacteria that has been genetically modified by the addition of a plasmid that carries a gene for GH receptor antagonist.
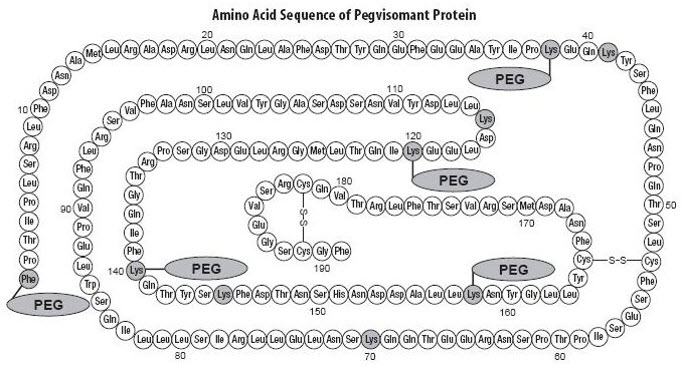 |
Stippled residues indicate PEG attachment sites (Phe 1 , Lys 38 , Lys 41 , Lys 70 , Lys 115 , Lys 120 , Lys 140 , Lys 145 , Lys 158 ) |
Shown below are the amino acid substitutions in pegvisomant, relative to human GH.
| hGH | Pegvisomant |
|---|---|
His 18 | Asp 18 |
Ala 21 | Asn 21 |
Gly 120 | Lys 120 |
Arg 167 | Asn 167 |
Lys 168 | Ala 168 |
Asp 171 | Ser 171 |
Lys 172 | Arg 172 |
Glu 174 | Ser 174 |
Ile 179 | Thr 179 |
SOMAVERT (pegvisomant) for injection is a sterile, white lyophilized powder intended for subcutaneous injection after reconstitution. SOMAVERT is supplied in packages that include a single-dose prefilled syringe containing 1 mL of Sterile Water for Injection, USP, that is a sterile, nonpyrogenic preparation of water for injection that contains no bacteriostat, antimicrobial agent, or added buffer, to be used as a diluent.
SOMAVERT is available in single-dose sterile vials containing 10 mg, 15 mg, 20 mg, 25 mg or 30 mg of pegvisomant. SOMAVERT 10 mg, 15 mg, and 20 mg vials also contain glycine (1.36 mg), mannitol (36 mg), sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate (0.36 mg), and sodium phosphate dibasic anhydrous (1.04 mg). After reconstitution with 1 mL of Water for Injection, USP, the resulting concentration is 10 mg/mL, 15 mg/mL and 20 mg/mL, respectively, with a pH of 7.1 – 7.7.
SOMAVERT 25 mg vial also contains glycine (1.7 mg), mannitol (45 mg), sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate (0.45 mg), and sodium phosphate dibasic anhydrous (1.3 mg). After reconstitution with 1 mL of Water for Injection, USP, the resulting concentration is 25 mg/mL with a pH of 7.1 – 7.7.
SOMAVERT 30 mg vial also contains glycine (2.04 mg), mannitol (54 mg), sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate (0.54 mg), and sodium phosphate dibasic anhydrous (1.56 mg). After reconstitution with 1 mL of Water for Injection, USP, the resulting concentration is 30 mg/mL with a pH of 7.1 – 7.7.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Pegvisomant selectively binds to growth hormone (GH) receptors on cell surfaces, where it blocks the binding of endogenous GH, and thus interferes with GH signal transduction.
Inhibition of GH action results in decreased serum concentrations of IGF-1, as well as other GH-responsive serum proteins such as free IGF-1, the acid-labile subunit of IGF-1 (ALS), and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3).
Pharmacodynamics
Pegvisomant binds selectively to the GH receptor, and does not cross-react with 19 other cytokine receptors tested, including prolactin. Pegvisomant leads to decreased serum concentrations of IGF-1, free IGF-1, ALS, and IGFBP-3 [see Clinical Studies (14, Figure 1) ] .
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption: Following subcutaneous administration, peak serum pegvisomant concentrations are not generally attained until 33 to 77 hours after administration. The mean extent of absorption of a 20-mg subcutaneous dose was 57%, relative to a 10-mg intravenous dose.
Distribution: The mean apparent volume of distribution of pegvisomant is 7 L (12% coefficient of variation), suggesting that pegvisomant does not distribute extensively into tissues. After a single subcutaneous administration, exposure (C max , AUC) to pegvisomant increases disproportionately with increasing dose. Mean ± SEM serum pegvisomant concentrations after 12 weeks of therapy with daily doses of 10, 15, and 20 mg were 6600 ± 1330; 16,000 ± 2200; and 27,000 ± 3100 ng/mL, respectively.
The relative bioavailability of 1 × 30 mg pegvisomant was compared to 2 × 15 mg pegvisomant in a single-dose study. The AUC inf and C max of pegvisomant when administered as one injection of 30 mg strength was approximately 6% and 4% greater, respectively, as compared to when administered as two injections of 15 mg strengths.
Metabolism and Elimination: The pegvisomant molecule contains covalently bound polyethylene glycol polymers in order to reduce the clearance rate. Clearance of pegvisomant following multiple doses is lower than seen following a single-dose. The mean total body systemic clearance of pegvisomant following multiple doses is estimated to range between 36 to 28 mL/h for subcutaneous doses ranging from 10 to 20 mg/day, respectively. Clearance of pegvisomant was found to increase with body weight. Pegvisomant is eliminated from serum with a mean half-life estimates ranging from 60 to 138 hours following either single or multiple doses. Less than 1% of administered drug is recovered in the urine over 96 hours. The elimination route of pegvisomant has not been studied in humans.
Drug Interaction Studies
In clinical studies, patients on opioids often needed higher serum pegvisomant concentrations to achieve appropriate IGF-1 suppression compared with patients not receiving opioids. The mechanism of this interaction is not known [see Drug Interactions (7.2) ] .
Specific Populations
No pharmacokinetic studies have been conducted in patients with renal impairment, patients with hepatic impairment, geriatric patients, or pediatric patients and the effects of race on the pharmacokinetics of pegvisomant has not been studied. No gender effect on the pharmacokinetics of pegvisomant was found in a population pharmacokinetic analysis.
Immunogenicity
The observed incidence of anti-drug antibodies is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Differences in assay methods preclude meaningful comparisons of the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in the studies described below with the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in other studies, including those of SOMAVERT or other growth hormone analogs.
In pre-marketing clinical studies, approximately 17% of the SOMAVERT-treated patients developed low titer, non‑neutralizing anti-GH antibodies. Although the presence of these antibodies did not appear to impact the efficacy of SOMAVERT, the long term clinical significance of these antibodies is not known. No assay for anti-pegvisomant antibodies is commercially available for patients receiving SOMAVERT.
The data above reflect the percentage of patients whose test results were considered positive for antibodies to SOMAVERT. The detection of antibody formation is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Additionally, the observed incidence of antibody positivity in an assay may be influenced by several factors including sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant medications, and underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of the incidence of antibodies to SOMAVERT with the incidence of antibodies to other products may be misleading.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Pegvisomant was administered subcutaneously to rats daily for 2 years at doses of 2, 8, and 20 mg/kg (about 2, 9, and 22-fold a single 30 mg dose in humans on an AUC basis). Long term treatment with pegvisomant at 8 and 20 mg/kg caused an increase in malignant fibrous histiocytoma at injection sites in males. Injection site tumors were not seen in female rats at the same doses. The increased incidence of injection site tumors was most probably caused by irritation and the high sensitivity of the rat to repeated subcutaneous injections.
Mutagenesis
Pegvisomant did not cause genetic damage in standard in vitro assays (bacterial mutation, human lymphocyte chromosome aberration).
Impairment of Fertility
Fertility studies have not been conducted with pegvisomant.
CLINICAL STUDIES
A total of one hundred twelve patients (63 men and 49 women) with acromegaly participated in a 12-week, randomized, double-blind, multi-center study comparing placebo and SOMAVERT. The mean ±SD age was 48±14 years, and the mean duration of acromegaly was 8±8 years. Ninety three had undergone previous pituitary surgery, of which 57 had also been treated with conventional radiation therapy. Six patients had undergone irradiation without surgery, nine had received only drug therapy, and four had received no previous therapy. At study start, the mean ± SD time since the subjects' last surgery and/or irradiation therapy, respectively, was 6.8 ± 0.93 years (n=63) and 5.6 ± 0.57 years (n=93).
Subjects were qualified for enrollment if their serum IGF-1, drawn after the required drug washout period, was ≥1.3 times the upper limit of the age-adjusted normal range. They were randomly assigned at the baseline visit to one of four treatment groups: placebo (n=32), 10 mg/day (n=26), 15 mg/day (n= 26), or 20 mg/day (n=28) of SOMAVERT subcutaneously IGF-1. The primary efficacy endpoint was IGF-1 percent change in IGF-1 concentrations from baseline to week 12. The three groups that received SOMAVERT showed statistically significant (p<0.01) reductions in serum levels of IGF-1 compared with the placebo group (Table 4).
| Placebo n=31 | SOMAVERT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mg/day n=26 | 15 mg/day n=26 | 20 mg/day n=28 | ||
Mean baseline IGF-1 (ng/ml) (SD) | 670 (288) | 627 (251) | 649 (293) | 732 (205) |
Mean percent change from baseline in IGF-1 (SD) | -4.0 (17) | -27 (28) | -48 (26) | -63 (21) |
SOMAVERT minus Placebo (95% CI for treatment difference) | -23 P<0.01; n=number of patients; SD = standard deviation (-35, -11) | -44 (-56, -33) | -59 (-68, -49) | |
There were also reductions in serum levels of free IGF-1, IGFBP-3, and ALS compared with placebo at all post-baseline visits (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Effects of SOMAVERT on Serum Markers (Mean ± Standard Error)
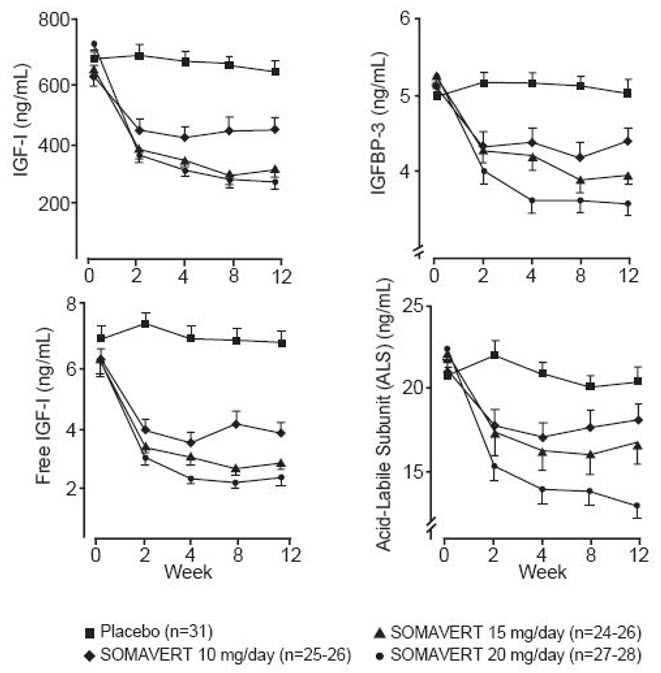 |
After 12 weeks of treatment, the following percentages of patients had normalized IGF-1 (Figure 2):
Figure 2. Percent of Patients Whose IGF-1 Levels Normalized at Week 12
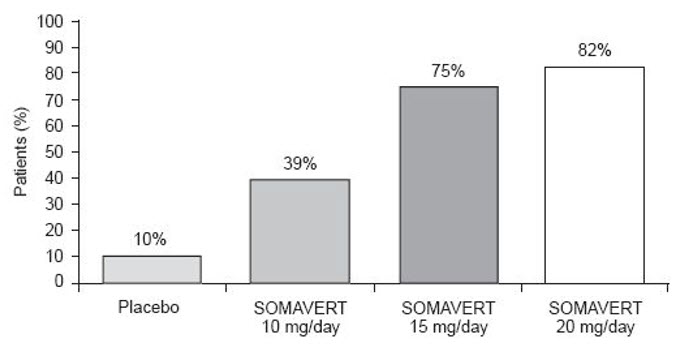 |
Table 5 shows the effect of treatment with SOMAVERT on ring size (standard jeweler's sizes converted to a numeric score ranging from 1 to 63), and on signs and symptoms of acromegaly. Each individual score for a sign or symptom of acromegaly (for soft-tissue swelling, arthralgia, headache, perspiration and fatigue) was based on a nine-point ordinal rating scale (0 = absent and 8 = severe and incapacitating), and the total score for signs or symptoms of acromegaly was derived from the sum of the individual scores. Mean baseline scores were as follows: ring size = 47.1; total signs and symptoms = 15.2; soft tissue swelling = 2.5; arthralgia = 3.2; headache = 2.4; perspiration = 3.3; and fatigue = 3.7.
| Placebo n=30 | SOMAVERT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mg/day n=26 | 15 mg/day n=24–25 | 20 mg/day n=26–27 | ||
Ring size | -0.1 (2.3) | -0.8 (1.6) | -1.9 (2.0) | -2.5 (3.3) |
Total score for signs and symptoms of acromegaly | 1.3 (6.0) | -2.5 (4.3) | -4.4 (5.9) | -4.7 (4.7) |
Soft-tissue swelling | 0.3 (2.3) | -0.7 (1.6) | -1.2 (2.3) | -1.3 (1.3) |
Arthralgia | 0.1 (1.8) | -0.3 (1.8) | -0.5 (2.5) | -0.4 (2.1) |
Headache | 0.1 (1.7) | -0.4 (1.6) | -0.3 (1.4) | -0.3 (2.0) |
Perspiration | 0.1 (1.7) | -0.6 (1.6) | -1.1 (1.3) | -1.7 (1.6) |
Fatigue | 0.7 (1.5) | -0.5 (1.4) | -1.3 (1.7) | -1.0 (1.6) |
Serum growth hormone (GH) concentrations, as measured by research assays using antibodies that do not cross-react with pegvisomant, rose within two weeks of beginning treatment with SOMAVERT. The largest increase in GH concentration was seen in patients treated with doses of SOMAVERT 20 mg/day. This effect is presumably the result of diminished inhibition of GH secretion as IGF-1 levels fall. As shown in Figure 3, when patients with acromegaly were given a loading dose of SOMAVERT followed by a fixed daily dose, the rise in GH was inversely proportional to the fall in IGF-1 and generally stabilized by week 2. Serum GH concentrations remained stable in patients treated with SOMAVERT for the average of 43 weeks (range, 0–82 weeks).
Figure 3. Percent Change in Serum GH and IGF-1 Concentrations
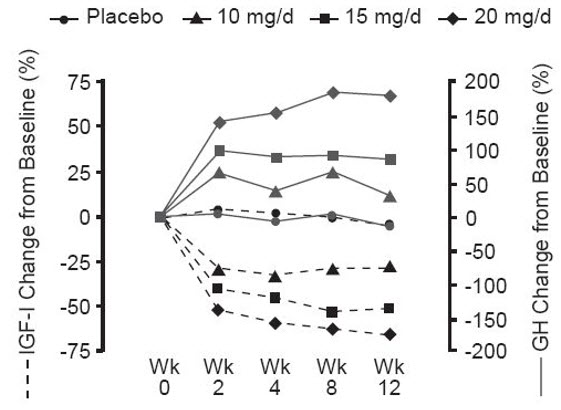 |
In the open-label extension to the clinical study, 109 subjects (including 6 new patients) with mean treatment exposure of 42.6 weeks (range 1 day – 82 weeks), 93 (85.3%) subjects had an adverse event, 16 (14.7%) had an SAE, and 4 (3.7%) discontinued due to an AE (headaches, elevated liver function tests, pancreatic cancer, and weight gain). A total of 100 (92.6%) of the 108 subjects with available IGF-1 data had a normal IGF-1 concentration at any visit during the study.
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
SOMAVERT (pegvisomant) for injection is a white lyophilized powder supplied in the following strengths and package configurations:
One Day Package Configuration | ||
Strength | NDC | Description |
10 mg per vial | 0009-7166-01 | One single-dose vial with one prefilled syringe containing 1 mL of diluent (Sterile Water for Injection, USP) and a separate 27 -gauge ½ inch safety needle per carton |
15 mg per vial | 0009-7168-01 | |
20 mg per vial | 0009-7188-01 | |
25 mg per vial | 0009-7199-01 | |
30 mg per vial | 0009-7200-01 | |
30-Day Package Configuration | ||
Strength | NDC | Description |
10 mg per vial | 0009-7166-30 | Each outer carton contains three intermediate cartons, 30 prefilled syringes containing 1 mL of diluent (Sterile Water for Injection, USP), and 30 separate 27-gauge ½ inch safety needles. Each intermediate carton contains ten single-dose vials of Somavert. |
15 mg per vial | 0009-7168-30 | |
20 mg per vial | 0009-7188-30 | |
25 mg per vial | 0009-7199-30 | |
30 mg per vial | 0009-7200-30 | |
Storage
Prior to reconstitution:
- The One Day Package of SOMAVERT should be stored in a refrigerator at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F).
- For the 30-Day Package, remove the three intermediate cartons containing the SOMAVERT vials and store in a refrigerator at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F).
- For convenience, the One Day Package and intermediate cartons in the 30-Day Package containing the SOMAVERT vial(s), may be stored at room temperature up to 25°C (77°F) for a single period of up to 30 days.
- In the space provided on the carton, record the date when the carton was removed from the refrigerator and the discard date (30 days after removal from the refrigerator).
- Once the carton has been stored at room temperature, it should not be placed back into the refrigerator. If not used within 30 days at room temperature, the vial(s) should be discarded.
Discard the SOMAVERT vial(s) after the expiration date printed on the carton or the discard date, whichever is sooner.
The prefilled syringe(s) may be stored at a temperature up to 30°C (86°F) until the expiration date printed on the carton, at which point they should be discarded.
Do not freeze.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
SOMAVERT ® (SOM-ah-vert) (pegvisomant) for injection, for subcutaneous use
Read these Instructions for Use before you start using SOMAVERT and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This leaflet does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment. Your healthcare provider should show you or a caregiver how to inject SOMAVERT the right way before you inject it for the first time.
SOMAVERT is available in two types of packaging:
- One Day Package (containing one single-dose vial of SOMAVERT powder, a prefilled syringe, and a safety needle)
- 30-Day Package (containing three intermediate cartons of 10 single-dose vials of SOMAVERT powder, 30 prefilled syringes, and 30 safety needles)
- Before you mix the SOMAVERT powder and the liquid:
- Store SOMAVERT in a refrigerator at 36 ºF to 46 ºF (2 ºC to 8 ºC).
- The One Day Package and intermediate cartons in the 30-Day Package containing the SOMAVERT vials, may be stored at room temperature up to 77°F (25°C) for a single period of up to 30 days.
- In the space provided on the carton, record the date when the carton was removed from the refrigerator and the discard date (30 days after removal from the refrigerator).
- After the carton has been stored at room temperature, it should not be placed back into the refrigerator. If not used within 30 days at room temperature, the vials should be thrown away.
- Throw away the SOMAVERT vials after the expiration date printed on the carton or the discard date, whichever is sooner.
- The prefilled syringes may be stored at a temperature up to 86°F (30°C) until the expiration date printed on the carton. After that time, they should be thrown away.
- Do not freeze SOMAVERT.
Important:
- Do not share your SOMAVERT syringes or needles with other people. You may give other people a serious infection, or get an infection from them.
- SOMAVERT comes in a vial as a white block of powder. You must mix SOMAVERT with a liquid (diluent) before you can use it. The liquid comes in a single-dose prefilled syringe labeled 'Sterile Water for Injection'. Do not use any other liquid to mix with SOMAVERT.
- You must use the mixed SOMAVERT immediately after you mix it. If you have not used the mixed SOMAVERT immediately, throw it away.
Step 1. Things you need
- A vial of SOMAVERT powder.
- A prefilled syringe.
- A safety needle.
You will also need:
- A cotton ball.
- An alcohol swab.
- A sharps disposal container. See " Dispose " at the end of these instructions.
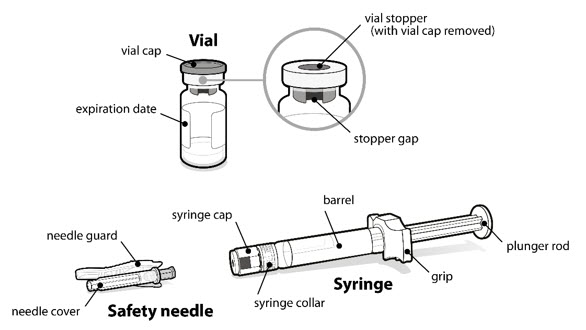
Step 2. Getting ready
Before you start:
- Only mix SOMAVERT and the liquid when you are ready to inject your dose.
- SOMAVERT One Day Package: If refrigerated, remove the package and allow it to come to room temperature in a safe place for at least 10 minutes before you need to use it.
- SOMAVERT 30-Day Package: If refrigerated, remove a single vial from the intermediate carton and allow it to come to room temperature in a safe place for at least 10 minutes before you need to use it.
- Do not heat the vial or syringe by using a heat source such as hot water or microwave. Let it warm up on its own.
- Wash your hands with soap and water, and dry completely.
- Peel open the packaging of the syringe and safety needle to make it easier to pick up each item as you prepare for your injection.
- Do not use the syringe or vial if:
- they are damaged or faulty
- the expiration date has passed
- it has been frozen, even if it has now thawed (syringe only)
Step 3. Choose injection area
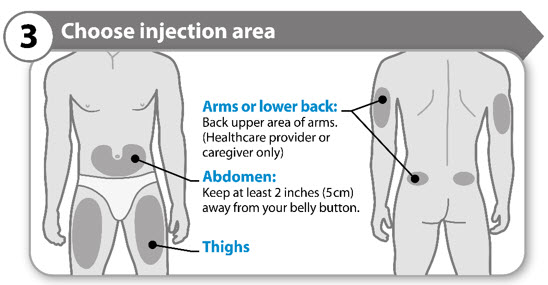
- Choose a different location within an area for each injection.
- Avoid bony areas or areas that are bruised, red, sore or hard, or areas that have scars or skin conditions.
- Clean the injection area with the alcohol swab as instructed by your healthcare provider.
- Allow the injection area to dry.
Step 4. Remove vial cap
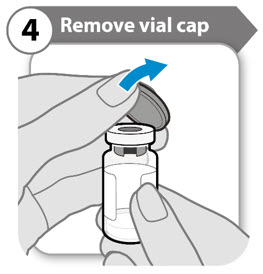
- Remove the cap from the vial.
- Throw the cap away. It is not needed again. Caution: Do not let anything touch the vial stopper.
Step 5. Remove syringe cap
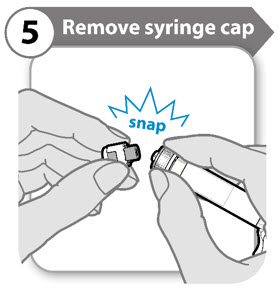
- Snap off the syringe cap leaving the syringe collar in place. It may take more effort to snap off than you might expect.
- Throw the syringe cap away. It is not needed again.
- Keep the syringe upright to avoid leakage. Caution: Do not let the end of the syringe touch anything when the syringe cap is off.
Step 6. Attach safety needle
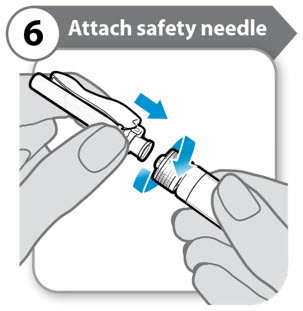
- Push down and twist the safety needle firmly onto the syringe as far as it will go.
Step 7. Remove needle cover
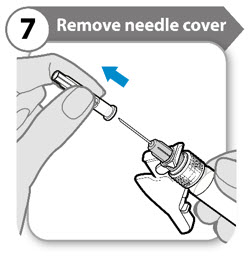
- Fold the needle guard out of the way of the needle cover.
- Carefully pull the needle cover straight off.
- Throw the needle cover away. It is not needed again. Caution: Do not let the needle touch anything.
Step 8. Insert needle
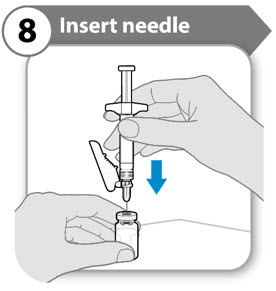
- Push the needle through the center of vial stopper, as shown.
- Support the syringe while the needle is in the vial stopper to prevent bending the needle.
Step 9. Add liquid
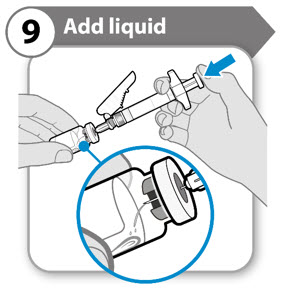
- Tilt both the vial and syringe at an angle, as shown.
- Push the plunger rod down slowly until all the liquid has emptied into the vial.
- Caution: Do not squirt the liquid directly onto the powder. This creates foam. Foam makes the medicine unusable.
- Do not withdraw the needle yet.
Step 10. Swirl vial
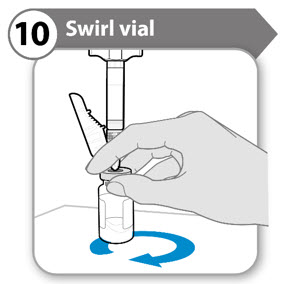
- Support both the syringe and vial in 1 hand, as shown.
- Gently and slowly swirl the liquid, sliding the vial in a circular motion on a flat surface.
- Continue swirling the liquid until all the powder has fully dissolved. Note: This may take up to 5 minutes. Do not shake.
Step 11. Check medicine
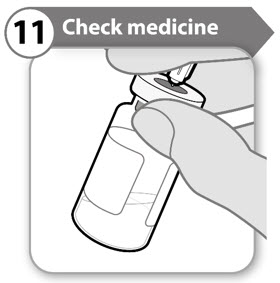
- Keeping the needle in the vial, look carefully at the medicine. It must be clear and free of particles.
- Do not use if:
- the medicine is cloudy or hazy
- the medicine has any color at all
- there are any particles or foam in the vial
- If you have any doubts about your medication go to www.SOMAVERT.com or call 1-800-645-1280.
Step 12. Reposition needle
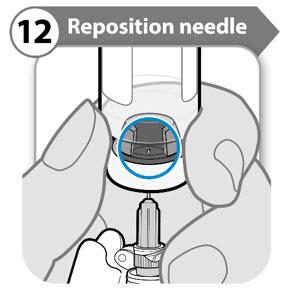
- Turn the vial so that you can see the stopper gap, as shown.
- Pull the needle down so that the needle tip is at the lowest point in the liquid. This will help you to draw off as much liquid as possible.
- Check that the plunger rod has not moved. If the plunger rod has moved, then push it back all the way into the syringe. This ensures that all air is removed from the syringe before you draw off the dose.
Step 13. Draw off dose
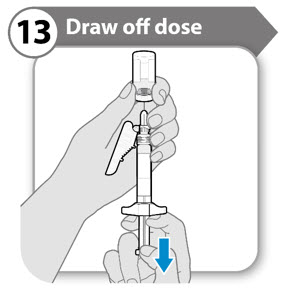
- Slowly pull back the plunger rod to withdraw as much medicine as possible from the vial. Note: If you see air in the syringe, tap the barrel to float the bubbles to the top, and then gently push the bubbles out into the vial .
- Pull the needle out of the vial.
Step 14. Insert needle
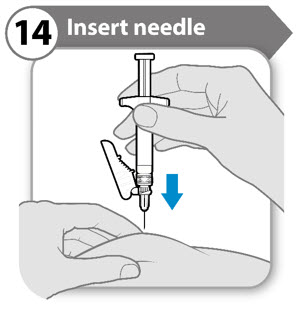
- Gently pinch the skin at the site of injection.
- Insert the needle to its full depth into the pinched skin.
Step 15. Inject medicine
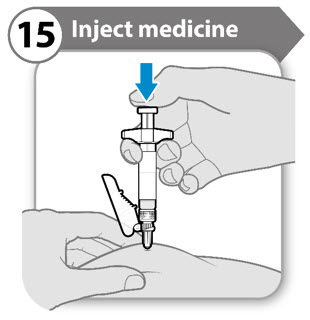
- Push the plunger rod down slowly until the barrel is empty. Note: Make sure you keep the needle in at full depth.
- Release the pinched skin and pull the needle straight out.
Step 16. Make needle safe
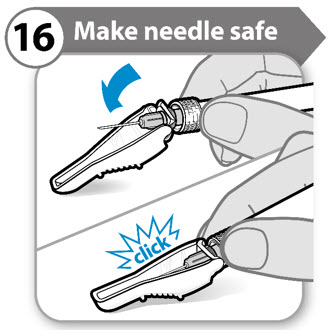
- Fold the needle guard over the needle. Gently apply pressure using a hard surface to lock the needle guard in place.
- Note: You will hear a click when the needle guard has been locked.
Step 17. Dispose
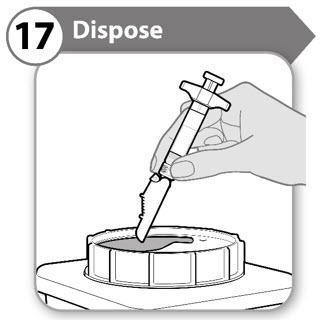
- Put your used syringes in a FDA cleared sharps disposal container right away after use.
- Do not throw away (dispose of) syringes in your household trash. Note: If you do not have a FDA cleared sharps disposal container, please refer to the safe syringe disposal information on the right hand side of this leaflet.
Step 18. After injection
- If necessary, use a clean cotton ball and press lightly on the injection area.
- Do not rub the area.
QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
What should I do if anything has accidentally touched the vial stopper?
- Clean the vial stopper with a fresh alcohol wipe, and leave it to dry completely. If you are unable to clean the stopper, do not use the vial.
What should I do with the syringe if it has been dropped?
- Do not use it even if it looks undamaged. Dispose of the syringe in the same way as a used syringe. You will need a replacement syringe.
How many times can I safely insert the needle into the vial stopper?
- Only 1 time. Withdrawing and reinserting greatly increases the risk of needle damage, and will blunt the needle. This can cause discomfort and increases risk of skin damage and infection. There is also a risk you may lose some of the medicine.
Is it okay to shake the vial if the powder is not dissolving?
- No. Never shake the vial. Shaking can destroy the medicine and create foam. The powder may take a few minutes to dissolve fully, so continue swirling the vial gently until the liquid is completely clear.
How can I tell if there is any foam in the vial?
- Foam looks like a mass of small bubbles that float as a layer to the top of the liquid. Do not inject SOMAVERT if it has foamed.
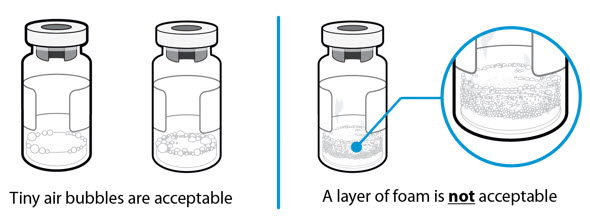
How can I prevent the medicine from foaming?
- Press the plunger very slowly so that the liquid gently runs down the inside of the vial. Do not spray the liquid directly onto the powder, because this creates foam. This will also reduce the swirling time and allow more of the medicine to be drawn off.
I can see some air in the syringe. Is this okay?
- Tiny air bubbles in the liquid are normal and are safe to inject. However, it is possible to accidently draw air into the syringe, which should be removed before injecting. Bubbles or air gaps that float to the top of the liquid should be pushed back out into the vial.
Why can I not get all of the medicine out of the vial?
- The shape of the vial means that a very small amount of the medicine will be left behind in the vial. This is normal. To ensure that only a trace of medicine remains, make sure the needle tip is as low as it can be in the vial when drawing off your dose.
What should I do if I have any doubts about my medicine?
- For more information, go to www.SOMAVERT.com or call 1-800-645-1280.
Safe syringe disposal information
If you do not have a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
- made of heavy-duty plastic,
- can be closed with a tight-fitting, puncture-resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out,
- upright and stable during use, leak-resistant, and
- properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container.
When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used needles and syringes.
For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA's website at: http://www.fda.gov/safesharpdisposal
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.

U.S. License No. 1216 LAB-0784-3.0 Revised: July 2023
Mechanism of Action
Pegvisomant selectively binds to growth hormone (GH) receptors on cell surfaces, where it blocks the binding of endogenous GH, and thus interferes with GH signal transduction.
Inhibition of GH action results in decreased serum concentrations of IGF-1, as well as other GH-responsive serum proteins such as free IGF-1, the acid-labile subunit of IGF-1 (ALS), and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3).