Dosage & Administration
By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Susvimo Prescribing Information
SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) is contraindicated in patients with ocular or periocular infections.
In the active comparator period of controlled clinical trials in AMD, the ranibizumab implant has been associated with a 3-fold higher rate of endophthalmitis than monthly intravitreal injections of ranibizumab (1.7% in the SUSVIMO arm vs 0.5% in the intravitreal arm). When including extension phases of clinical trials, 2% (11/555) of patients receiving the ranibizumab implant experienced an episode of endophthalmitis. Reports occurred between days 5 and 853, with a median of 173 days. Many, but not all, of the cases of endophthalmitis reported a preceding or concurrent conjunctival retraction or erosion event.
Endophthalmitis should be treated promptly in an effort to reduce the risk of vision loss and maximize recovery. The SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) dose (refill-exchange) should be delayed until resolution of endophthalmitis
Patients should not have an active or suspected ocular or periocular infection or severe systemic infection at the time of any SUSVIMO implant or refill procedure. Appropriate intraoperative handling followed by secure closure of the conjunctiva and Tenon's capsule, and early detection and surgical repair of conjunctival erosions or retractions and strict/controlled aseptic technique conditions throughout refill-exchange procedures may reduce the risk of endophthalmitis
Indications and Usage, Diabetic Macular Edema (DME) (SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) is indicated for the treatment of patients with Diabetic Macular Edema (DME) who have previously responded to at least two intravitreal injections of a Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) inhibitor medication. | 2/2025 | ||||||||||||||
Indications and Usage, Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) (SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) is indicated for the treatment of patients with Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) who have previously responded to at least two intravitreal injections of a Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) inhibitor medication. | 5/2025 | ||||||||||||||
Dosage and Administration (The recommended dose of SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) is 2 mg (0.02 mL of 100 mg/mL solution) continuously delivered via the SUSVIMO ocular implant with refills administered every 36 weeks (approximately 9 months). For patients with AMD or DME, if a planned dose (refill-exchange) of SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) is missed, it should be administered as soon as possible and the subsequent refill-exchange procedures should be performed 24 weeks (approximately 6 months) thereafter. For patients with DR, if a planned dose (refill-exchange) of SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) is missed, it should be administered as soon as possible and the subsequent refill-exchange procedures should be performed 36 weeks (approximately 9 months) thereafter. Table 1describes dosage modifications for specific adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5)] . No dosage reductions for SUSVIMO are recommended.
| 5/2025 | ||||||||||||||
Warnings and Precautions (In the active comparator period of controlled clinical trials in AMD, the ranibizumab implant has been associated with a 3-fold higher rate of endophthalmitis than monthly intravitreal injections of ranibizumab (1.7% in the SUSVIMO arm vs 0.5% in the intravitreal arm). When including extension phases of clinical trials, 2% (11/555) of patients receiving the ranibizumab implant experienced an episode of endophthalmitis. Reports occurred between days 5 and 853, with a median of 173 days. Many, but not all, of the cases of endophthalmitis reported a preceding or concurrent conjunctival retraction or erosion event. In the active comparator period of the controlled clinical trial in DME, 0% of patients in the SUSVIMO arm compared to 0.3% in the intravitreal arm experienced an episode of endophthalmitis. When including the extension phase of the clinical trial, 0.7% (4/556) of patients receiving the ranibizumab implant experienced an episode of endophthalmitis. Reports occurred between days 625 and 1016, with a median of 824 days. In the period with an observational comparator arm of the clinical trial in DR, there were no patients (0/105) in the SUSVIMO arm who experienced an episode of endophthalmitis [see Clinical Studies (14.3)] . When including the extension phase of the clinical trial 0.8% (1/128) patients receiving the ranibizumab implant experienced an episode of endophthalmitis, with the event reported on day 695.Endophthalmitis should be treated promptly in an effort to reduce the risk of vision loss and maximize recovery. The SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) dose (refill-exchange) should be delayed until resolution of endophthalmitis [see Dosage and Administration (2.10)and Adverse Reactions (6.1)] .Patients should not have an active or suspected ocular or periocular infection or severe systemic infection at the time of any SUSVIMO implant or refill procedure. Appropriate intraoperative handling followed by secure closure of the conjunctiva and Tenon's capsule, and early detection and surgical repair of conjunctival erosions or retractions and strict/controlled aseptic technique conditions throughout refill-exchange procedures may reduce the risk of endophthalmitis [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)and Warnings and Precautions (5.5)] .Vitreous hemorrhages may result in temporary vision loss. Vitrectomy may be needed in the case of a non-clearing vitreous hemorrhage [see Dosage and Administration (2.10)] .In clinical trials of SUSVIMO including the extension phases in patients with AMD, vitreous hemorrhages were reported in 5.2% (23/443) of patients receiving SUSVIMO. In the clinical trial of SUSVIMO including the extension phases in patients with DME, vitreous hemorrhages were reported in 10.1% (56/556) of patients receiving SUSVIMO. In the clinical trial of SUSVIMO including the extension phase in patients with DR, vitreous hemorrhages were reported in 9.4% (12/128) of patients receiving SUSVIMO. The majority of these hemorrhages occurred within the first post-operative month following surgical implantation and the majority of vitreous hemorrhages resolved spontaneously. Patients on antithrombotic medication (e.g., oral anticoagulants, aspirin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) may be at increased risk of vitreous hemorrhage. Antithrombotic medications are recommended to be temporarily interrupted prior to the implant insertion procedure. The SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) dose (refill-exchange) should be delayed in the event of sight-threatening vitreous hemorrhage. The use of pars plana laser ablation and scleral cauterization should be performed to reduce the risk of vitreous hemorrhage. A conjunctival erosion is a full thickness degradation or breakdown of the conjunctiva in the area of the implant flange. A conjunctival retraction is a recession or opening of the limbal and/or radial peritomy. Conjunctival erosions or retractions have been associated with an increased risk of endophthalmitis, especially if the implant becomes exposed. Surgical intervention (e.g., conjunctival/Tenon's capsule repair) is recommended to be performed in case of conjunctival erosion or retraction with or without exposure of the implant flange. In clinical trials of SUSVIMO including the extension phases in patients with AMD, 3.6% (16/443) of patients receiving SUSVIMO reported conjunctival erosion and 1.6% (7/443) of patients receiving SUSVIMO reported conjunctival retraction in the study eye. In the clinical trial of SUSVIMO including the extension phases of patients with DME, 2.2% (12/556) of patients receiving SUSVIMO reported conjunctival erosion and 1.3% (7/556) of patients receiving SUSVIMO reported conjunctival retraction in the study eye. In the clinical trial of SUSVIMO including the extension phase in patients with DR, 2.3% (3/128) of patients receiving SUSVIMO reported conjunctival erosion and 1.6% (2/128) of patients receiving SUSVIMO reported conjunctival retraction in the study eye. Appropriate intraoperative handling of conjunctiva and Tenon's capsule to preserve tissue integrity and secure closure of peritomy while ensuring placement of sutures away from implant edge may reduce the risk of conjunctival erosion or retraction. The implant and the tissue overlying the implant flange should be monitored routinely following the implant insertion. A conjunctival bleb is an encapsulated elevation of the conjunctiva above the implant flange, which may be secondary to subconjunctival thickening or fluid. Conjunctival blebs may require surgical management to avoid further complications, especially if the implant septum is no longer identifiable due to the conjunctival bleb. In clinical trials of SUSVIMO including the extension phases in patients with AMD, 5.9% (26/443) of patients receiving SUSVIMO reported conjunctival bleb/conjunctival filtering bleb leak in the study eye. In the clinical trial of SUSVIMO including the extension phases in patients with DME, 9% (50/556) of patients receiving SUSVIMO reported conjunctival bleb/conjunctival filtering bleb leak in the study eye. In the clinical trial of SUSVIMO including the extension phase in patients with DR, 3.9% (5/128) of patients receiving SUSVIMO reported conjunctival bleb/conjunctival filtering bleb leak in the study eye. Strict adherence to the scleral incision length, appropriate intraoperative handling of conjunctiva and Tenon's capsule to preserve tissue integrity and secure closure of peritomy, and proper seating of the refill needle during refill-exchange procedures may reduce the risk of conjunctival bleb. Visual acuity was decreased by 4 letters on average in the first postoperative month and 2 letters on average in the second postoperative month following initial implantation of SUSVIMO in patients with AMD [see Clinical Studies (14.1)] .Visual acuity was decreased by 7 letters on average in the first postoperative month and 3 to 4 letters on average in the second postoperative month following initial implantation of SUSVIMO in patients with DME and DR [see Clinical Studies (14.2and 14.3)] . | 5/2025 | ||||||||||||||
Warnings and Precautions (Postoperative intraocular inflammation has occurred following SUSVIMO implantation. The majority of cases occurred during the first week following implantation and resolved within the first month. | 9/2025 |
SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) is a vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) inhibitor indicated for the treatment of patients with:
- Neovascular (wet) Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD) who have previously responded to at least two intravitreal injections of a VEGF inhibitor ().
1.1 Neovascular (wet) Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD)SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) is indicated for the treatment of patients with Neovascular (wet) Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD) who have previously responded to at least two intravitreal injections of a Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) inhibitor medication.
- Diabetic Macular Edema (DME) who have previously responded to at least two intravitreal injections of a VEGF inhibitor ().
1.2 Diabetic Macular Edema (DME)SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) is indicated for the treatment of patients with Diabetic Macular Edema (DME) who have previously responded to at least two intravitreal injections of a Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) inhibitor medication. - Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) who have previously responded to at least two intravitreal injections of a VEGF inhibitor ().
1.3 Diabetic Retinopathy (DR)SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) is indicated for the treatment of patients with Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) who have previously responded to at least two intravitreal injections of a Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) inhibitor medication.
- For intravitreal use via SUSVIMO ocular implant. ()
2.1 General InformationFor Intravitreal Use via SUSVIMO ocular implant.
The SUSVIMO initial fill and ocular implant insertion and implant removal procedures must be performed under aseptic conditions by a physician experienced in vitreoretinal surgery. The SUSVIMO ocular implant must be surgically implanted in the eye or removed from the eye (if medically necessary) in an operating room using aseptic technique. See SUSVIMO Instructions for Use and the standardized steps to optimize surgical outcomes.
SUSVIMO refill-exchange procedures must be performed under aseptic conditions by a physician experienced in ophthalmic surgery
[see Dosage and Administration (2.7)].Do not administer SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) as a bolus intravitreal injection. Do not substitute SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) with other ranibizumab products.
Initial Fill: One SUSVIMO initial fill needle (34-gauge, with integrated 5 μm filter and blue cap) is included. A 5-micron sterile filter needle (19-gauge × 1½ inch), and a 1 mL Luer lock syringe are needed butnot included.Refill-Exchange: One SUSVIMO refill needle (34-gauge with integrated 5 μm filter and clear cap) is included. A 5-micron sterile filter needle (19-gauge × 1½ inch), and a 1 mL Luer lock syringe are needed butnot included. - Neovascular (wet) Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD) and Diabetic Macular Edema (DME)
The recommended dose of SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) is 2 mg (0.02 mL of 100 mg/mL solution) continuously delivered via the SUSVIMO implant with refills every 24 weeks (approximately 6 months). ()2.2 Neovascular (Wet) Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD) and Diabetic Macular Edema (DME)The recommended dose of SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) is 2 mg (0.02 mL of 100 mg/mL solution) continuously delivered via the SUSVIMO ocular implant with refills administered every 24 weeks (approximately 6 months).
- Diabetic Retinopathy (DR)
The recommended dose of SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) is 2 mg (0.02 mL of 100 mg/mL solution) continuously delivered via the SUSVIMO implant with refills every 36 weeks (approximately 9 months). ()2.3 Diabetic Retinopathy (DR)The recommended dose of SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) is 2 mg (0.02 mL of 100 mg/mL solution) continuously delivered via the SUSVIMO ocular implant with refills administered every 36 weeks (approximately 9 months). - Supplemental treatment with 0.5 mg intravitreal ranibizumab injection may be administered in the affected eye if clinically necessary. ()
2.4 Supplemental Treatment with Intravitreal Ranibizumab InjectionSupplemental treatment with 0.5 mg (0.05 mL of 10 mg/mL) intravitreal ranibizumab injection may be administered in the affected eye while the SUSVIMO implant is in place and if clinically necessary
[see Clinical Studies (14)]. - Perform the initial implantation, refill-exchange, and implant removal (if necessary) procedures under strict aseptic conditions. (,
2.5 Ocular Implant Initial FillThe implant initial fill procedure must be performed by a physician experienced in vitreoretinal surgery
[seeDosage and Administration (2.1)].The implant will be filled using aseptic technique with 0.02 mL of SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) prior to insertion of the implant into the patient's eye[see Dosage and Administration (2.6)].Refer to the complete SUSVIMO Instructions for Usefor the initial fill and implant procedure included in the insertion tool assembly carton for further details.
Use aseptic technique to carry out the following preparation steps prior to insertion of the ocular implant into the patient's eye:
Step 1: Gather the supplies needed.- One SUSVIMO ocular implant with insertion tool assembly (included)
- One SUSVIMO initial fill needle (34-gauge with integrated 5 μm filter) with blue cap (included)
- One SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) 100 mg/mL vial (included)
- One sterile 5-micron filter needle (19-gauge × 1½ inch)(not included)
- One sterile 1 mL Luer Lock syringe(not included)
Step 2: Transfer Dose from Vial to SyringeNote:Use the filter needle (not included) to withdraw SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) from the vial. 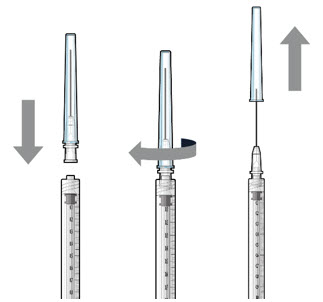 Figure 1Do notuse the SUSVIMO initial fill needle for this step.
Figure 1Do notuse the SUSVIMO initial fill needle for this step.- Prepare SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) vial by removing the flip-off cap and disinfecting the rubber vial septum with alcohol.
- Attach a filter needle to the syringe by screwing it tightly onto the Luer lock (see Figure 1).
- Carefully remove the needle cap by pulling it straight off.
- Using aseptic technique, withdraw all of the contents of the SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) vial through the filter needle into the syringe.
Step 3: Remove Air from Syringe- With the filter needle attached, hold the syringe with the needle pointing up.
- If there are any air bubbles, gently tap the syringe with your finger until the bubbles rise to the top (Figure 2).
- Slowly push the plunger rod just until all air is expelled from the syringe and needle.
– It is important to preserve as much drug as possible in order to completely fill the implant.
- Remove and properly dispose of the filter needle after air is removed from syringe.
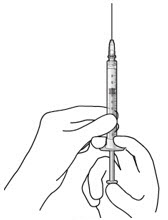 Figure2Step 4: Attach SUSVIMO Initial Fill NeedleDo notuse the filter needle to fill the implant.
Figure2Step 4: Attach SUSVIMO Initial Fill NeedleDo notuse the filter needle to fill the implant.- Attach the SUSVIMO initial fill needle (included) firmly onto the syringe by screwing it tightly onto the Luer lock (see Figure 3). Ensure that the initial fill needle is attached to the syringe.
- Carefully remove the needle cap by pulling straight off.
- Do notwipe the needle at any time.
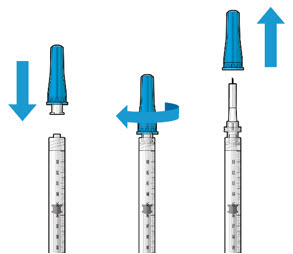 Figure 3Step 5: Remove Any Remaining Air from Syringe
Figure 3Step 5: Remove Any Remaining Air from Syringe- With the initial fill needle attached, hold the syringe with the needle pointing up.
If there are any air bubbles, gently tap the syringe with your finger until the bubbles rise to the top (see Figure 4). - Slowly push the plunger rod just until all air is expelled from the syringe and needle, and a drop of drug solution is seen at the needle tip (see Figure 5).
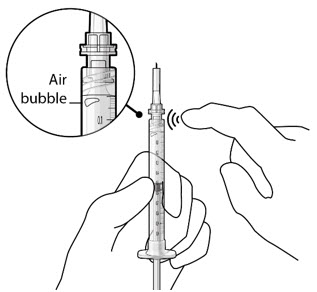 Figure 4
Figure 4 Figure 5Note:
Figure 5Note:It is important to preserve as much drug as possible in order to completely fill the implant. Step 6: Inspect the Syringe for Air Bubbles- Inspect the syringe and the needle hub to ensure that no air bubbles are present (see Figure 6).
- If air bubbles are present, continue to remove air from the syringe and reinspect.
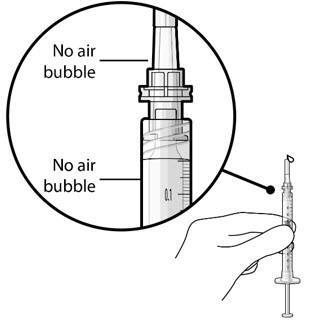 Figure 6Note:
Figure 6Note:Use the syringe within 15 minutesof removing all air to avoid ranibizumab drying in the needle and impeding fluid flow.Do notuse the initial fill needle if the needle is clogged.Step 7: Load Syringe into the CarrierDo nothold or push on the plunger rod of the syringe while inserting the needle into the implant septum.- Retrieve insertion tool carrier with pre-positioned implant from the inner tray.
- Align the syringe Luer lock above the Luer lock slot in the carrier to protect the needle from being damaged.
- Lower the syringe into the carrier (see Figure 7).
- Push the syringe forward until it stops, taking care to avoid touching the plunger rod (see Figure 8)
- With the syringe loaded, (see Figure 9) the initial fill needle should now be penetrating the implant septum.
 Figure 7:Align and lower the syringe into the carrier
Figure 7:Align and lower the syringe into the carrier Figure 8:Push the syringe into the carrier
Figure 8:Push the syringe into the carrier Figure 9:Syringe with initial fill needle inserted through the implant septumStep 8: Fill Ocular Implant with SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) Under Microscope
Figure 9:Syringe with initial fill needle inserted through the implant septumStep 8: Fill Ocular Implant with SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) Under Microscope- Under the microscope,slowlyadminister SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) into the ocular implant by slightly tilting the carrier upwards (see Figure 10).
- The ocular implant should be filled over approximately5 to 10 seconds, to help avoid air entrapment in the implant reservoir.
 Figure 10:Administer ranibizumab into the implant
Figure 10:Administer ranibizumab into the implant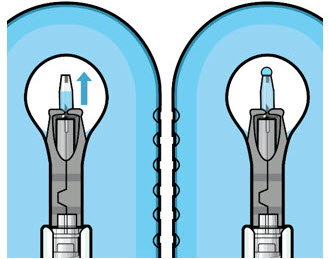 Figure 11:Dome of drug solution forms at tip of implant as viewed under magnificationNote:
Figure 11:Dome of drug solution forms at tip of implant as viewed under magnificationNote:When filling the ocular implant, drug solution should only exit the ocular implant from the release control element. If drug solution is leaking from the implant at a different location, such as the side of the implant, do notuse the ocular implant.
If fluid is leaking from the septum at the needle insertion site, the needle may not be fully penetrating the implant septum. Fully push the syringe forward before continuing to fill the ocular implant.- Continue filling the ocular implant until the implant is completely full of drug solution and all air has been expelled as evidenced by a dome of drug solution formed at the tip of the implant on the release control element (see Figure 11).
Step 9: Inspect the Filled Ocular Implant Under the Microscope- Inspect the ocular implant under the microscope to ensure that the ocular implant is completely full of drug solution (see Figure 12).
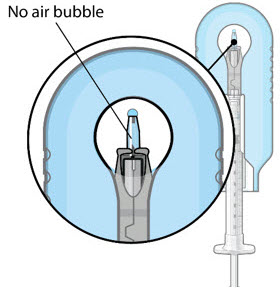 Figure 12:Proper appearance of implant after initial filling with ranibizumabNote:
Figure 12:Proper appearance of implant after initial filling with ranibizumabNote:Minimize air bubbles within the implant reservoir as they may cause slower drug release. If an air bubble is present, it must be no larger than 1/3 of the widest diameter of the implant. If excess air is observed, do notuse the ocular implant.Note:No more thanto ensure that the release control element remains saturated with SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection). If SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) dries in the release control element, the implant may not release the drug properly into the vitreous after insertion.30 minutesshould pass between the initial fill of the implant and the insertion into the patient's eyeStep 10: Remove the Syringe and Guide Sleeve from the Carrier- Remove the syringe and guide sleeve from the carrier by pulling back on the syringe (see Figure 13). The syringe will be locked into the guide sleeve.
- Properly dispose of the used syringe together with the needle and guide sleeve in a sharps disposal container or in accordance with local requirements.
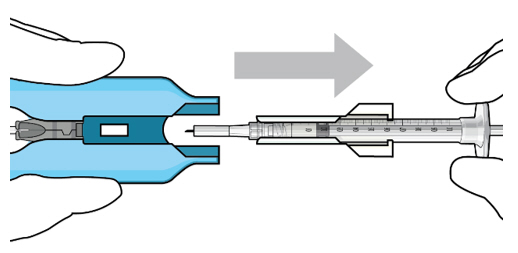 Figure 13:Remove the syringe and guide sleeve from the insertion tool carrierStep 11: Slide the Insertion Tool Handle into the Carrier
Figure 13:Remove the syringe and guide sleeve from the insertion tool carrierStep 11: Slide the Insertion Tool Handle into the Carrier- Slide the insertion tool handle into the guide channel of the carrier, ensuring that both components are facing upwards (see Figure 14).
- Push the handle forward as far as it will go into the gripper tips (see Figure 15).
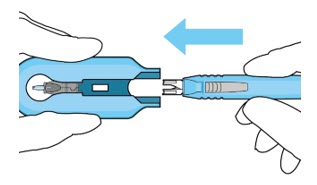 Figure 14:Insert the handle into the insertion tool carrier
Figure 14:Insert the handle into the insertion tool carrier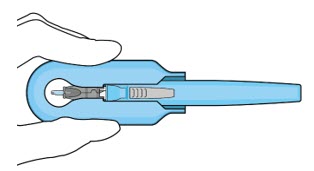 Figure 15:Fully inserted handleNote:Do notwithdraw the handle and implant until the eye is ready for insertion. Contact between the implant and any surface or object – even within the sterile field – may result in the introduction of a foreign body into the vitreous.
Figure 15:Fully inserted handleNote:Do notwithdraw the handle and implant until the eye is ready for insertion. Contact between the implant and any surface or object – even within the sterile field – may result in the introduction of a foreign body into the vitreous.
Figure 1 
Figure 2 
Figure 3 
Figure 4 
Figure 5 
Figure 6 
Figure 7 
Figure 8 
Figure 9 
Figure 10 
Figure 11 
Figure 12 
Figure 13 
Figure 14 
Figure 15 ,2.6 Ocular Implant InsertionSUSVIMO ocular implant insertion is a surgical procedure that is performed in an operating room. The procedure must be performed under aseptic conditions by a physician experienced in vitreoretinal surgery
[see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].The ocular implant is filled with SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) immediately prior to insertion.
No more than 30 minutes should pass between the initial fill of the ocular implant and the insertion into the patient's eye.After placing an infusion line in the eye, create at least a 6×6 mm peritomy of the conjunctiva and Tenon's capsule centered around the selected SUSVIMO implant location in the supero-temporal quadrant. Perform careful conjunctival incision, hemostasis of the underlying sclera, and generous undermining of Tenon's capsule. Using aseptic technique, fill the ocular implant
[see Dosage and Administration (2.5)]. Using an MVR blade, create a full thickness dissection of the sclera 4 mm from the limbus until the pars plana is fully visible, with final target scleral incision length of 3.5 mm. Using a 532 nm laser endoprobe, apply contiguous, overlapping laser spots starting at 300 mW 1000 ms along the full length of the exposed pars plana and repeat until complete ablation is achieved. Pass a 3.2 mm slit knife perpendicularly through the center of the scleral dissection to open the underlying pars plana. Use the insertion tool to slowly insert the SUSVIMO implant into the sclero-pars plana incision perpendicular to the globe, ensuring that the long axis of the implant flange is properly aligned with the sclero-pars plana incision. Using the closed gripper tips of the insertion tool, seat the implant flush against the sclera. Clean any residual vitreous around the implant flange using a vitrector. Suture both Tenon's capsule and conjunctiva, using scleral anchoring at the apex of the peritomy, ensuring complete coverage of the implant flange. Refer to the complete SUSVIMO Instructions for Usefor the initial fill and implant procedure included in the insertion tool assembly carton for further details.,2.7 Ocular Implant RemovalRemoval of the SUSVIMO ocular implant is a surgical procedure that is performed in an operating room. The procedure must be performed under aseptic conditions by a physician experienced in vitreoretinal surgery
[see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].After placing an infusion line in the eye, create at least a 6×6 mm peritomy of the conjunctiva and Tenon's capsule around the SUSVIMO ocular implant flange. Remove any fibrous capsule or scar tissue that may have formed over the implant flange and septum using scalpel and forceps. With the explant tool oriented perpendicular to the globe, align the contoured tips with the long axis of the implant flange and grasp underneath the implant flange. Once the implant is secured in the explant tool, pull the implant from the eye in a perpendicular motion. Clear any vitreous prolapse present within or around the scleral wound using a vitrector. Completely close the scleral incision with multiple non-absorbable sutures. Close the Tenon's capsule and conjunctiva to completely cover the scleral incision. Refer to the complete Instructions for Usefor the implant removal procedure included in the explant tool carton for further details.
)2.8 Ocular Implant Refill-Exchange ProcedureThe SUSVIMO ocular implant refill-exchange procedure must be performed under strict aseptic conditions by a physician experienced in ophthalmic surgery
[see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]. This includes the use of a surgical mask, sterile gloves, and a lid speculum.Prior to and after the refill-exchange procedure, perform a dilated slit lamp exam and/or dilated indirect ophthalmoscopy to inspect the implant in the vitreous cavity through the pupil to identify if dislodgement of the implant septum has occurred [
see Figure 33and Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]. If the septum has dislodged, any further refill-exchange procedures should not be performed because normal device functioning cannot be assured. Discontinue treatment with SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) following septum dislodgement and consider implant removal should the benefit of the removal procedure outweigh the risk.Step 1: Gather the supplies needed.- One SUSVIMO Refill Needle (34-gauge with a 5 µm integrated filter) with clear cap (included)
- One SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) 100 mg/mL vial (included)
- One sterile 1 mL Luer Lock syringe(not included)
- One sterile 5-micron filter needle (19-gauge × 1½ inch)(not included)
- Anesthetic ophthalmic solutions
- Ophthalmic broad-spectrum microbicide solution
- Cotton tips and gauze
- Sterile powder free gloves
- Face masks
- Lid speculum
- Magnification such as visor or loupes
- Task lighting
- Indirect ophthalmoscope and lens
- Sterile drape(optional for refill-exchange procedure)
Step 2: Inspect Packaging and Components- Prior to use in the clinic, inspect the packaging of the components for damage.Do notuse if the sterility has been compromised or the contents have been dropped, damaged, or tampered with.
- Check the expiration date printed on the label.
- Remove the vial from the carton.Note: the outside of the vial is not sterile.
- Use aseptic techniqueto open packaging and remove thesterile refill needlefrom the tray.
- Inspect components and place onto sterile field (see Figure 16).
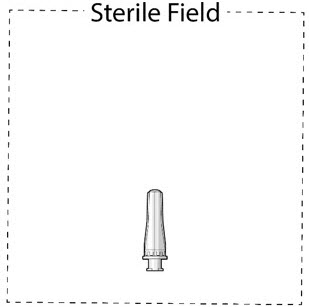 Figure 16Step 3: Inspect SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection)
Figure 16Step 3: Inspect SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection)- Visually inspect the contents of the SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) vial for particulate matter and discoloration.
- SUSVIMO should be colorless to slightly brownish
Do notuse if particulate, cloudiness, or discoloration are visible.Step 4: Patient Preparation- Dilate the pupil of the eye.
- Perform slit lamp examination and/or indirect ophthalmoscopy to inspect the implant and its components in the vitreous cavity through the dilated pupil.
- Position the patient on exam chair in the supine position at approximately 20° to 30° angle for optimal visualization of the implant.
- Apply a broad-spectrum microbicide to the periocular skin, eyelid, and ocular surface prior to the refill-exchange procedure. The use of a sterile drape is up to the physician's discretion.
- Perform the procedure under topical anesthesia.
- If needed, subconjunctival anesthesia may be administered in the nasal quadrant, away from the implant.
Step 5: Transfer Dose from Vial to Syringe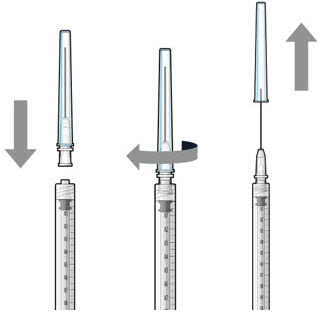 Figure 17Note:
Figure 17Note:Use the filter needle to withdraw SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) from the vial. Do notuse the SUSVIMO refill needle for this step.- Prepare ranibizumab vial by removing the flip-off cap and disinfecting the rubber vial septum with alcohol.
- Attach a filter needle to the syringe by screwing it tightly onto the Luer lock (see Figure 17).
- Carefully remove the needle cap by pulling it straight off.
- Using aseptic technique, withdraw all of the contents of the SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) vial through the filter needle into the syringe.
Step 6: Remove Air from Syringe- With the filter needle attached, hold the syringe with the needle pointing up.
- If there are any air bubbles, gently tap the syringe with your finger until the bubbles rise to the top (Figure 18).
- Slowly push the plunger rod just until the air is expelled from the syringe and needle.
– It is important to preserve as much drug as possible in order to completely refill the implant
- Remove and properly dispose of the filter needle after air is removed from the syringe.
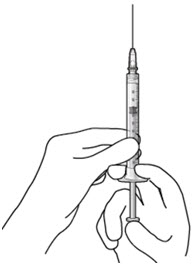 Figure 18Step 7: Attach SUSVIMO Refill NeedleDo notuse the filter needle to fill the implant.
Figure 18Step 7: Attach SUSVIMO Refill NeedleDo notuse the filter needle to fill the implant.- Attach the SUSVIMO refill needle firmly onto the syringe by screwing it tightly onto the Luer lock (see Figure 19). Ensure that the refill needle is attached to the syringe.
- Carefully remove the needle cap, pulling straight off to avoid damage to the needle cannula.
- Do notwipe the needle at any time.
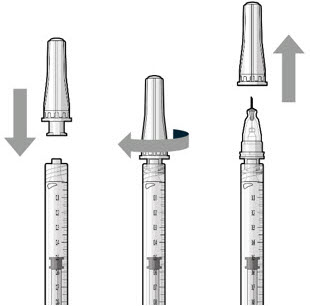 Figure 19Step 8: Remove Any Remaining Air from Syringe and Adjust Drug Dose
Figure 19Step 8: Remove Any Remaining Air from Syringe and Adjust Drug Dose- With the refill needle attached, hold the syringe with the needle pointing up.
- If there are any air bubbles, gently tap the syringe with your finger until the bubbles rise to the top (see Figure 20).
- Slowly push the plunger rod until all air is expelled from the syringe and needle and the uppermost edge of the black plunger tip is aligned with the0.1 mLdose mark (see Figure 21).
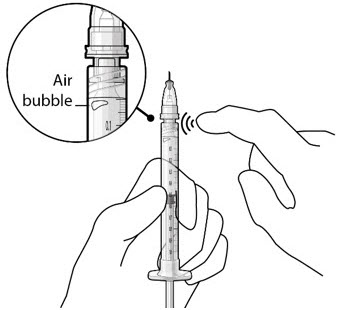 Figure 20
Figure 20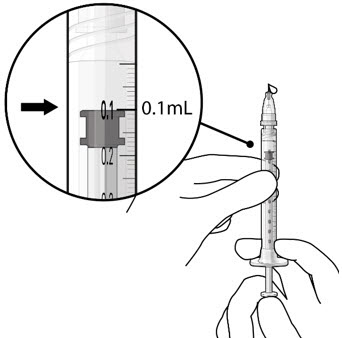 Figure 21Step 9: Inspect the Syringe for Air Bubbles
Figure 21Step 9: Inspect the Syringe for Air Bubbles Figure 22Note:
Figure 22Note:Ensure no air bubbles are present in the syringe and needle hub. Air injected into the implant could result in slower drug release. - Inspect the syringe and the needle hub using magnification to ensure that no air bubbles are present (see Figure 22).
Note:Use the syringe within 15 minutesof removing all air and adjusting the drug dose to avoid drug solution drying in the needle and impeding fluid flow.Do notuse the refill needle or syringe if the needle is clogged.Step 10: Stabilize the globe and orient the refill needle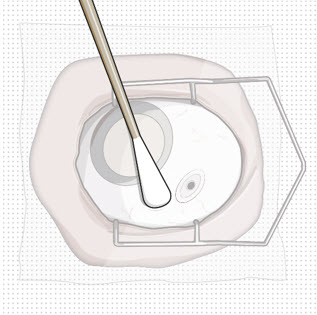 Figure 23
Figure 23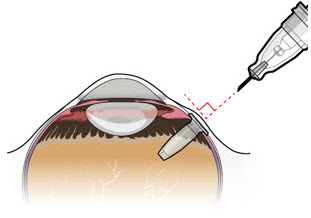 Figure 24Note:
Figure 24Note:Perform the refill-exchange procedure using magnification (e.g., loupes, reading glasses, magnifiers) for visual assistance. - After placing the lid speculum in the eye, stabilize the globe with a cotton-tipped applicator to minimize eye movement (see Figure 23).
– Recommend standing on the contralateral side of the implanted eye, with the patient looking down and toward their nose to optimally expose the implant.
- Orient the refill needle perpendicular to the globe (see Figure 24).
Step 11: Insert the Refill Needle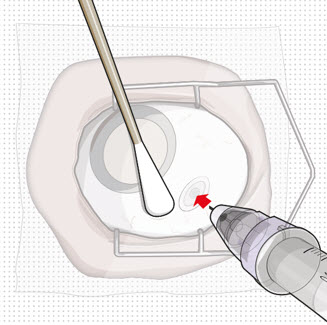 Figure 25
Figure 25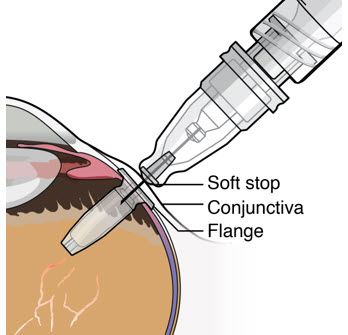 Figure 26Note:
Figure 26Note:Insert needle at the very center of the implant septum and perpendicular to the implant to ensure the needle inserts fully. Do notmaneuver if there is resistance as it will bend the needle.Do notuse a bent refill needle; replace if bent or if damage is suspected.- Targeting the center of the implant septum, insert the refill needle perpendicularly through the conjunctiva and into the implant septum (see Figure 25).
– If excessive resistance, withdraw the refill needle. Orient and insert again.– Do nottwist when encountering conjunctiva and Tenon's capsule to gain access to the septum, as damage to the overlying tissue and to the septum of the device may result.
- Continue inserting the needle until the soft stop of the refill needle makes physical contact with the conjunctiva (see Figure 26) to provide a tactile cue that optimal contact has been made.
Step 12: Refill the SUSVIMO Implant- Refill the implantslowly, by delivering the entire contents of the syringe into the implant, over approximately5 to 10 seconds, to avoid pressure build-up in the implant reservoir. The soft stop of the refill needle must remain in contact with the conjunctiva throughout the procedure.
- As ranibizumab is administered into the implant, existing solution from the implant should immediately begin to fill the refill needle fluid collection chamber (see Figure 27).
- If fluid is not observed collecting in the refill needle fluid collection reservoir, stop injecting and ensure the refill needle is inserted into the center of the implant septum at a perpendicular angle and the soft stop is in contact with the conjunctiva.
- Administer all of the syringe contents in order to achieve the target replacement ranibizumab concentration in the implant reservoir.
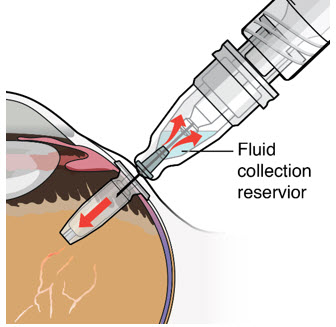 Figure 27Step 13: Withdraw the Syringe
Figure 27Step 13: Withdraw the Syringe- Withdraw the syringe perpendicular to the globe to avoid damaging the septum (see Figure 28).
- A cotton-tipped applicator may be used to provide counter traction to the conjunctiva during needle withdrawal.
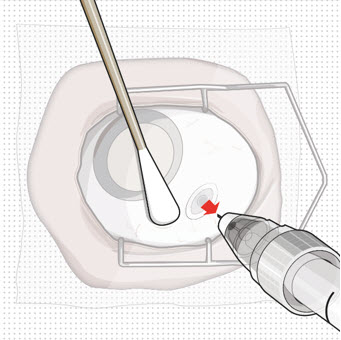 Figure 28Step 14: Dispose of the Used Components
Figure 28Step 14: Dispose of the Used Components- Do notrecap the needle or detach it from the syringe. Dispose of the used syringe together with the refill needle in a sharps disposal container or in accordance with local requirements.
Step 15: Perform Indirect Ophthalmoscopy- Perform dilated indirect ophthalmoscopy (and slit lamp exam as needed) to ensure continued proper position of the implant and its components (e.g., septum) in the vitreous cavity and to examine for complications.

Figure 16 
Figure 17 
Figure 18 
Figure 19 
Figure 20 
Figure 21 
Figure 22 
Figure 23 
Figure 24 
Figure 25 
Figure 26 
Figure 27 
Figure 28
Injection: 100 mg/mL, clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to slightly brownish solution in a single-dose vial
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) administration in pregnant women. Administration of ranibizumab to pregnant monkeys throughout the period of organogenesis resulted in a low incidence of skeletal abnormalities at intravitreal doses up to 41 times the human exposure (based on serum levels following the recommended clinical dose). No skeletal abnormalities were observed at serum trough levels similar to the human exposure after a single eye treatment at the recommended clinical dose (
An embryo-fetal developmental toxicity study was performed on pregnant cynomolgus monkeys. Pregnant animals received intravitreal injections of ranibizumab every 14 days starting on Day 20 of gestation, until Day 62 at doses of 0, 0.125, and 1 mg/eye. Skeletal abnormalities including incomplete and/or irregular ossification of bones in the skull, vertebral column, and hindlimbs and shortened supernumerary ribs were seen at a low incidence in fetuses from animals treated with 1 mg/eye of ranibizumab. The 1 mg/eye dose resulted in trough serum ranibizumab levels up to 41 times higher than observed human Cmaxlevels of SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) after treatment of a single eye.
No skeletal abnormalities were seen at the lower dose of 0.125 mg/eye, a dose which resulted in trough exposures similar to single eye treatment with SUSVIMO (ranibizumab injection) in humans. No effect on the weight or structure of the placenta, maternal toxicity, or embryotoxicity was observed.
Animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, and it is not known whether ranibizumab can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Based on the anti-VEGF mechanism of action for ranibizumab
Ranibizumab binds to the receptor binding site of multiple biologically active forms of VEGF-A, including VEGF110. VEGF-A has been shown to cause neovascularization and leakage in models of ocular angiogenesis and vascular occlusion and is thought to contribute to pathophysiology of neovascular AMD. The binding of ranibizumab to VEGF-A prevents the interaction of VEGF-A with its receptors (VEGFR1 and VEGFR2) on the surface of endothelial cells, reducing endothelial cell proliferation, vascular leakage, and new blood vessel formation.
All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defects, loss, and other adverse outcomes. The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects is 2% – 4% and of miscarriage is 15% – 20% of clinically recognized pregnancies.