Symdeko
(Tezacaftor And Ivacaftor)Dosage & Administration
By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Symdeko Prescribing Information
Warnings and Precautions, Intracranial Hypertension (Cases of intracranial hypertension (IH) have been reported in the postmarketing setting with the use of drugs containing the same or similar active ingredients as SYMDEKO [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)] . Clinical manifestations of IH include headache, blurred vision, diplopia, and potential vision loss; papilledema can be found on fundoscopy. If an unusual headache or visual disturbances occur during treatment, and IH is suspected, interrupt SYMDEKO and refer for prompt medical evaluation. Consider the benefits and risks for the individual patient to determine whether to resume treatment with SYMDEKO. Patients should be monitored until IH resolution and for recurrence. Patients with elevated vitamin A levels may be at increased risk. | 09/2025 |
SYMDEKO is indicated for the treatment of cystic fibrosis (CF) in patients aged 6 years and older who are homozygous for the
Tezacaftor facilitates the cellular processing and trafficking of select mutant forms of CFTR (including F508del-CFTR) to increase the amount of mature CFTR protein delivered to the cell surface. Ivacaftor is a CFTR potentiator that facilitates increased chloride transport by potentiating the channel-open probability (or gating) of the CFTR protein at the cell surface. For ivacaftor to function CFTR protein must be present at the cell surface. Ivacaftor can potentiate the CFTR protein delivered to the cell surface by tezacaftor, leading to a further enhancement of chloride transport than either agent alone. The combined effect of tezacaftor and ivacaftor is increased quantity and function of CFTR at the cell surface, resulting in increases in chloride transport.
The chloride transport response of mutant CFTR protein to tezacaftor/ivacaftor was determined in Ussing chamber electrophysiology studies using a panel of FRT cell lines transfected with individual
The
Note that splice site mutations cannot be studied in the FRT assay.
Table 6 lists responsive
546insCTA | E92K | G576A | L346P | R117G | S589N |
711+3A→GClinical data for these mutations in Clinical Studies [see Clinical Studies (14.1and 14.2)] . | E116K | G576A;R668CComplex/compound mutations where a single allele of the CFTR gene has multiple mutations; these exist independent of the presence of mutations on the other allele. | L967S | R117H | S737F |
2789+5G→A | E193K | G622D | L997F | R117L | S912L |
3272-26A→G | E403D | G970D | L1324P | R117P | S945L |
3849+10kbC→T | E588V | G1069R | L1335P | R170H | S977F |
A120T | E822K | G1244E | L1480P | R258G | S1159F |
A234D | E831X | G1249R | M152V | R334L | S1159P |
A349V | F191V | G1349D | M265R | R334Q | S1251N |
A455E | F311del | H939R | M952I | R347H | S1255P |
A554E | F311L | H1054D | M952T | R347L | T338I |
A1006E | F508C | H1375P | P5L | R347P | T1036N |
A1067T | F508C;S1251N | I148T | P67L | R352Q | T1053I |
D110E | F508delA patient must have two copies of the F508del mutation or at least one copy of a responsive mutation presented in Table 6 to be indicated. | I175V | P205S | R352W | V201M |
D110H | F575Y | I336K | Q98R | R553Q | V232D |
D192G | F1016S | I601F | Q237E | R668C | V562I |
D443Y | F1052V | I618T | Q237H | R751L | V754M |
D443Y;G576A;R668C | F1074L | I807M | Q359R | R792G | V1153E |
D579G | F1099L | I980K | Q1291R | R933G | V1240G |
D614G | G126D | I1027T | R31L | R1066H | V1293G |
D836Y | G178E | I1139V | R74Q | R1070Q | W1282R |
D924N | G178R | I1269N | R74W | R1070W | Y109N |
D979V | G194R | I1366N | R74W;D1270N | R1162L | Y161S |
D1152H | G194V | K1060T | R74W;V201M | R1283M | Y1014C |
D1270N | G314E | L15P | R74W;V201M;D1270N | R1283S | Y1032C |
E56K | G551D | L206W | R75Q | S549N | |
E60K | G551S | L320V | R117C | S549R |
Dose selection for the clinical program primarily consisted of one double-blind, placebo-controlled, multiple-cohort trial which included 176 patients with CF (homozygous for the
The efficacy of SYMDEKO in patients with CF aged 12 years and older was evaluated in three double-blind, placebo-controlled trials (Trials1, 2, and 3).
Trial 1 was a 24-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, two-arm study in patients with CF who were homozygous for the
Trial 2 was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 2-period, 3-treatment, 8-week crossover study in patients with CF who were heterozygous for the
Trial 3 was a 12-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, two-arm study in patients with CF who were heterozygous for the
Patients in all trials continued on their standard-of-care CF therapies (e.g
Trial 1 evaluated 504 patients (248 SYMDEKO, 256 placebo) with CF aged 12 years and older (mean age 26.3 years). The mean ppFEV1at baseline was 60.0% (range: 27.8% to 96.2%). The primary efficacy endpoint was change in lung function as determined by absolute change from baseline in ppFEV1through Week 24. Treatment with SYMDEKO resulted in a statistically significant improvement in ppFEV1. The treatment difference between SYMDEKO and placebo for the mean absolute change in ppFEV1from baseline through Week 24 was 4.0 percentage points (95% CI: 3.1, 4.8;
Key secondary efficacy variables included relative change from baseline in ppFEV1through Week 24; number of pulmonary exacerbations from baseline through Week 24; absolute change in BMI from baseline at Week 24, and absolute change in CFQ-R Respiratory Domain Score (a measure of respiratory symptoms relevant to patients with CF, such as cough, sputum production, and difficulty breathing) from baseline through Week 24. For the purposes of this trial, a pulmonary exacerbation was defined as a change in antibiotic therapy (IV, inhaled, or oral) as a result of 4 or more of 12 pre-specified sino-pulmonary signs/symptoms. See Table 11for a summary of key secondary outcomes in Trial 1.
| Placebo N=256 | SYMDEKO N=248 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| BMI: body mass index; CI: confidence interval; CFQ-R: Cystic Fibrosis Questionnaire-Revised; IVA: ivacaftor; NA: not applicable; ppFEV1: percent predicted forced expiratory volume in 1 second; | |||
| Relative change in ppFEV1from baseline through Week 24 (%) | Treatment difference (95% CI) | - | 6.8 (5.3, 8.3) |
P value | NA | P< 0.0001Indicates statistical significance confirmed in the hierarchical testing procedure. Other efficacy measures considered not statistically significant. | |
| Number of pulmonary exacerbations from baseline through Week 24 | Number of events (event rate per yearEstimated event rate per year calculated using 48 weeks per year.) Rate ratio (95% CI) | 122 (0.99) | 78 (0.64) 0.65 (0.48, 0.88) |
P value | NA | P =0.0054 | |
| Absolute change in BMI from baseline at Week 24 (kg/m2) | Treatment difference (95% CI) | - | 0.06 (-0.08, 0.19) |
| Absolute change in CFQ-R Respiratory Domain Score from baseline through Week 24 (points) | Treatment difference (95% CI) | - | 5.1 (3.2, 7.0) |
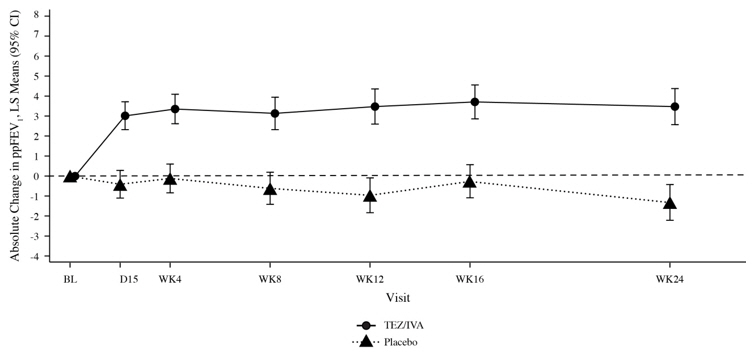

Trial 2 evaluated 244 patients with CF aged 12 years and older (mean age 34.8 years). The mean ppFEV1at baseline was 62.3% (range: 34.6 to 93.5). Of the 244 patients included in the efficacy analysis, 146 patients had a splice mutation and 98 patients had a missense mutation as the second allele. 161 patients received SYMDEKO, 156 patients received ivacaftor, and 161 patients received placebo. The primary efficacy endpoint was the mean absolute change from study baseline in percent predicted FEV1averaged at Weeks 4 and 8 of treatment. The key secondary efficacy endpoint was absolute change in CFQ-R Respiratory Domain Score from study baseline averaged at Weeks 4 and 8 of treatment. For the overall population, treatment with SYMDEKO compared to placebo resulted in significant improvement in ppFEV1(6.8 percentage points [95% CI: 5.7, 7.8];
| Mutation (n) | Absolute Change in percent predicted FEV1Average of Week 4 and 8 values.Absolute change in ppFEV1by individual mutations is an ad hoc analysis. | Absolute Change in CFQ-R Respiratory Domain Score (Points)Absolute change in CFQ-R Respiratory Domain Score and absolute change in sweat chloride by mutation subgroups and by individual mutations are ad hoc analyses. | Absolute Change in Sweat Chloride (mmol/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| (n=) patient numbers analysed. | |||
Splice mutations (n= 93 for TEZ/IVA, n=97 for PBO)Results shown as difference in mean (95% CI) change from study baseline for SYMDEKO vs. placebo-treated patients: | |||
| 7.4 (6.0, 8.7) | 9.5 (6.3, 12.7) | -5.4 (-8.0, -2.7) | |
By individual splice mutation (n). Results shown as mean (minimum, maximum) for change from study baseline for SYMDEKO-treated patients | |||
2789+5G→A (25) | 8.6 (-1.5, 23.4) | 12.0 (-8.3, 38.9) | -3.2 (-16.5, 9.0) |
3272-26A→G (23) | 5.7 (-2.1, 25.9) | 5.7 (-22.2, 44.4) | -3.8 (-22.3, 16.5) |
3849+10kbC→T (43) | 5.8 (-7.2, 22.3) | 8.2 (-25.0, 47.2) | -5.6 (-27.0, 8.5) |
711+3A→G (2) | 4.3 (2.0, 6.7) | -4.2 (-5.6, -2.8) | -15.4 (-21.0, -9.8) |
E831X Patients enrolled did not receive tezacaftor/ivacaftor treatment.(0) | NA | NA | NA |
Missense mutations (n=66 for TEZ/IVA, n=63 for PBO)Results shown as difference in mean (95% CI) change from study baseline for SYMDEKO vs. placebo-treated patients: | |||
| 5.9 (4.2, 7.5) | 13.4 (9.6, 17.3) | -16.3 (-19.7, -12.9) | |
By individual missense mutation (n). Results shown as mean (minimum, maximum) for change from study baseline for SYMDEKO-treated patients | |||
D579G (2) | 8.1 (-0.2, 16.4) | 11.1 (5.6, 16.7) | -23.1 (-24.8, -21.5) |
D110H (1) | -1.0 (-1.0, -1.0) | -11.1 (-11.1, -11.1) | -22.5 (-22.5, -22.5) |
D1152H (21) | 3.8 (-2.5, 12.5) | 15.2 (-8.3, 55.6) | -4.1 (-15.0, 11.5) |
A455E (11) | 8.5 (2.6, 16.1) | 11.6 (-11.1, 44.4) | -0.3 (-8.8, 14.0) |
L206W (4) | 3.0 (-4.5, 10.2) | 12.5 (-2.8, 38.9) | -36.1 (-44.5, -27.5) |
P67L (11) | 9.4 (0.0, 31.9) | 11.7 (-12.5, 72.2) | -29.3 (-50.0, 0.8) |
R1070W (2) | 6.1 (2.0, 10.1) | 29.2 (16.7, 41.7) | -13.8 (-26.8, -0.8) |
R117C (1) | 2.9 (2.9, 2.9) | 16.7 (16.7, 16.7) | -38.8 (-38.8, -38.8) |
R347H (2) | -0.5 (-2.8, 1.7) | 5.6 (-5.6, 16.7) | -13.8 (-19.0, -8.5) |
R352Q (2) | 4.9 (2.6, 7.1) | 8.3 (8.3, 8.3) | -43.3 (-49.8, -36.8) |
S945L (7) | 9.6 (0.7, 19.5) | 11.3 (-4.2, 25.0) | -29.0 (-42.5, -8.0) |
S977F (2) | 10.1 (5.5, 14.7) | -1.4 (-8.3, 5.6) | -13.9 (-22.3, -5.5) |
In an analysis of BMI at Week 8, an exploratory endpoint, patients treated with SYMDEKO had a mean improvement of 0.2 kg/m2(95% CI [0.0, 0.3]), 0.1 kg/m2(95% CI [-0.1, 0.3]), and 0.3 kg/m2(95% CI [0.1, 0.5]) versus placebo for the overall, splice, and missense mutation populations of patients, respectively.
Trial 3 evaluated 168 patients with CF (83 SYMDEKO and 85 placebo) aged 12 years and older (mean age 26.1 years) who were heterozygous for the
If the patient's genotype is unknown, an FDA-cleared CF mutation test should be used to detect the presence of a
- Pediatric patients aged 6 to less than 12 years weighing less than 30 kg: one tablet (containing tezacaftor 50 mg/ivacaftor 75 mg) in the morning and one tablet (containing ivacaftor 75 mg) in the evening, approximately 12 hours apart. SYMDEKO should be taken with fat-containing food. (,
2.1 General Dosage InformationSwallow the tablets whole.
SYMDEKO should be taken with fat-containing food, such as food recommended in standard nutritional guidelines. Examples of meals or snacks that contain fat are those prepared with butter or oils or those containing eggs, cheeses, nuts, whole milk, or meats, etc.
[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].,2.2 Recommended Dosage in Adults, Adolescents, and Children Aged 6 Years and OlderAdults, adolescents, and children aged 6 years and older should be dosed according to Table 1. The morning and the evening doses should be taken approximately 12 hours apart.
Table 1: Recommended Dosage for Patients Aged 6 Years and Older Age Morning
(one tablet)Evening
(one tablet)6 to <12 years weighing <30 kgtezacaftor 50 mg/ivacaftor 75 mg ivacaftor 75 mg 6 to <12 years weighing ≥30 kgtezacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 150 mg ivacaftor 150 mg ≥12 yearstezacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 150 mg ivacaftor 150 mg Information for Missed Doses:If 6 hours or less have passed since the missed morning or evening dose, the patient should take the missed dose as soon as possible and continue on the original schedule. If more than 6 hours have passed since the missed morning or evening dose, the patient should not take the missed dose. The next scheduled dose can be taken at the usual time. More than one dose should not be taken at the same time.
)12.3 PharmacokineticsThe pharmacokinetics of tezacaftor and ivacaftor are similar between healthy adult volunteers and patients with CF. Following once-daily dosing of tezacaftor and twice-daily dosing of ivacaftor in patients with CF, plasma concentrations of tezacaftor and ivacaftor reach steady-state within 8 days and within 3 to 5 days, respectively, after starting treatment. At steady-state, the accumulation ratio is approximately 1.5 for tezacaftor and 2.2 for ivacaftor. Exposures of tezacaftor (administered alone or in combination with ivacaftor) increase in an approximately dose-proportional manner with increasing doses from 10 mg to 300 mg once daily.
Key pharmacokinetic parameters for tezacaftor and ivacaftor at steady state are shown in Table 7.
Table 7: Mean (SD) Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Tezacaftor and Ivacaftor at Steady State in Patients with CF Drug Cmax
(mcg/mL)Effective t½
(h)AUC0-24hor AUC0-12h
(mcg∙h/mL)AUC0-24hfor tezacaftor and AUC0-12hfor ivacaftorTezacaftor 100 mg once daily/ivacaftor 150 mg every 12 hoursTezacaftor 5.95 (1.50) 15.0 (3.44) 84.5 (27.8) Ivacaftor 1.17 (0.424) 13.7 (6.06) 11.3 (4.60) AbsorptionAfter a single dose in healthy subjects in the fed state, tezacaftor was absorbed with a median (range) time to maximum concentration (tmax) of approximately 4 hours (2 to 6 hours). The median (range) tmaxof ivacaftor was approximately 6 hours (3 to 10 hours) in the fed state.
When a single dose of tezacaftor/ivacaftor was administered with fat-containing foods, tezacaftor exposure was similar and ivacaftor exposure was approximately 3 times higher than when taken in a fasting state.
DistributionTezacaftor is approximately 99% bound to plasma proteins, primarily to albumin. Ivacaftor is approximately 99% bound to plasma proteins, primarily to alpha 1-acid glycoprotein and albumin. After oral administration of tezacaftor 100 mg once daily/ivacaftor 150 mg every 12 hours in patients with CF in the fed state, the mean (±SD) for apparent volume of distribution of tezacaftor and ivacaftor was 271 (157) L and 206 (82.9) L, respectively. Neither tezacaftor nor ivacaftor partition preferentially into human red blood cells.
EliminationAfter oral administration of tezacaftor 100 mg once daily/ivacaftor 150 mg every 12 hours in patients with CF in the fed state, the mean (±SD) for apparent clearance values of tezacaftor and ivacaftor were 1.31 (0.41) and 15.7 (6.38) L/h, respectively. After steady-state dosing of tezacaftor in combination with ivacaftor in patients with CF, the effective half-lives of tezacaftor and ivacaftor were approximately 15 (3.44) and 13.7 (6.06) hours, respectively.
MetabolismTezacaftor is metabolized extensively in humans.
In vitrodata suggested that tezacaftor is metabolized mainly by CYP3A4 and CYP3A5. Following oral administration of a single dose of 100 mg14C-tezacaftor to healthy male subjects, M1, M2, and M5 were the three major circulating metabolites of tezacaftor in humans. M1 has the similar potency to that of tezacaftor and is considered pharmacologically active. M2 is much less pharmacologically active than tezacaftor or M1, and M5 is not considered pharmacologically active. Another minor circulating metabolite, M3, is formed by direct glucuronidation of tezacaftor.Ivacaftor is also metabolized extensively in humans.
In vitroandin vivodata indicate that ivacaftor is metabolized primarily by CYP3A4 and CYP3A5. M1 and M6 are the two major metabolites of ivacaftor in humans. M1 has approximately one-sixth the potency of ivacaftor and is considered pharmacologically active. M6 is not considered pharmacologically active.ExcretionFollowing oral administration of14C-tezacaftor, the majority of the dose (72%) was excreted in the feces (unchanged or as the M2 metabolite) and about 14% was recovered in urine (mostly as M2 metabolite), resulting in a mean overall recovery of 86% up to 21 days after the dose. Less than 1% of the administrated dose was excreted in urine as unchanged tezacaftor, showing that renal excretion is not the major pathway of tezacaftor elimination in humans.
Following oral administration of ivacaftor alone, the majority of ivacaftor (87.8%) is eliminated in the feces after metabolic conversion. There was minimal elimination of ivacaftor and its metabolites in urine (only 6.6% of total radioactivity was recovered in the urine), and there was negligible urinary excretion of ivacaftor as unchanged drug.
Specific PopulationsBased on population PK analyses, the PK exposure parameters of tezacaftor/ivacaftor in children and adolescents (ages 6 to <18 years) are similar to the AUCss range observed in adults when given in combination.
Pediatric patients aged 6 to less than 12 yearsTable 8: Tezacaftor/Ivacaftor Exposure by Age Group, Mean (SD) Age Group Dose Tezacaftor AUCss
mcg∙h/mLAUC0-24hfor tezacaftor and AUC0-12hfor ivacaftorIvacaftor AUCss
mcg∙h/mL6 to <12 yearsExposures in≥30 kg weight range are predictions derived from the population PK model71.3 (28.3) 8.5 (3.34) 6 to <12 years (<30 kg)tezacaftor 50 mg/ivacaftor 75 mg 56.7 (22.3) 6.92 (2.07) 6 to <12 years (≥30 kg)tezacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 150 mg 92.7 (21.9) 10.8 (3.52) Pediatric patients aged 12 to less than 18 yearsFollowing oral administration of SYMDEKO tablets, tezacaftor 100 mg once daily/ivacaftor 150 mg every 12 hours, the mean (±SD) AUCss for tezacaftor and ivacaftor was 97.1 (35.8) mcg∙h/mL and 11.4 (5.50) mcg∙h/mL, respectively, similar to the mean AUCss in adult patients administered SYMDEKO tablets, tezacaftor 100 mg once daily/ivacaftor 150 mg every 12 hours.
Patients with Hepatic ImpairmentFollowing multiple doses of tezacaftor and ivacaftor for 10 days, patients with moderately impaired hepatic function (Child-Pugh Class B, score 7-9) had an approximately 36% increase in AUC and a 10% increase in Cmaxfor tezacaftor, and a 1.5-fold increase in ivacaftor AUC compared with healthy subjects matched for demographics. In a separate study, patients with moderately impaired hepatic function (Child-Pugh Class B, score 7-9) had similar ivacaftor Cmax, but an approximately 2.0-fold increase in ivacaftor AUC0-∞compared with healthy subjects matched for demographics.
Pharmacokinetic studies have not been conducted in patients with mild (Child-Pugh Class A, score 5-6) or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C, score 10-15) receiving SYMDEKO. The magnitude of increase in exposure in patients with severe hepatic impairment is unknown but is expected to be higher than that observed in patients with moderate hepatic impairment
[see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Use in Specific Populations (8.6), and Patient Counseling Information (17)].Patients with Renal ImpairmentSYMDEKO has not been studied in patients with moderate or severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance ≤30 mL/min) or in patients with end-stage renal disease. In a human pharmacokinetic study with tezacaftor alone, there was minimal elimination of tezacaftor and its metabolites in urine (only 13.7% of total radioactivity was recovered in the urine with 0.79% as unchanged drug).
In a human pharmacokinetic study with ivacaftor alone, there was minimal elimination of ivacaftor and its metabolites in urine (only 6.6% of total radioactivity was recovered in the urine).
In population pharmacokinetic analysis, data from 665 patients on tezacaftor or tezacaftor in combination with ivacaftor in clinical trials indicated that mild renal impairment (N=147; eGFR 60 to less than 90 mL/min/1.73 m2) and moderate renal impairment (N=7; eGFR 30 to less than 60 mL/min/1.73 m2) did not affect the clearance of tezacaftor significantly
[see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].Male and Female PatientsThe pharmacokinetic parameters of tezacaftor and ivacaftor are similar in males and females.
Drug Interactions StudiesDrug interaction studies were performed with SYMDEKO and other drugs likely to be co-administered or drugs commonly used as probes for pharmacokinetic interaction studies
[see Drug Interactions (7)].Potential for Tezacaftor/Ivacaftor to Affect Other DrugsClinical studies (with rosiglitazone and desipramine – see Table 9) showed that ivacaftor is not an inhibitor of CYP2C8 or CYP2D6. Based on
in vitroresults, ivacaftor has the potential to inhibit CYP3A and P-gp, and may also inhibit CYP2C9.In vitro, ivacaftor was not an inducer of CYP isozymes. Ivacaftor is not an inhibitor of transporters OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OCT1, OCT2, OAT1, or OAT3.Based on
in vitroresults, tezacaftor has a low potential to inhibit CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, and CYP3A4. Tezacaftor has a low potential to induce CYP3A, but it is not an inducer of CYP1A2 and CYP2B6. Tezacaftor has a low potential to inhibit transporters P-gp, BCRP, OATP1B3, OCT2, OAT1, or OAT3.Clinical studies with midazolam showed that SYMDEKO is not an inhibitor of CYP3A. Co-administration of SYMDEKO with digoxin, a sensitive P-gp substrate, increased digoxin exposure by 1.3-fold. Co-administration of SYMDEKO with an ethinyl estradiol/ norethindrone oral contraceptive had no significant effect on the exposures of the hormonal contraceptives. Co-administration of SYMDEKO with pitavastatin, an OATP1B1 substrate, had no clinically relevant effect on the exposure of pitavastatin.
The effects of tezacaftor and ivacaftor (or ivacaftor alone) on the exposure of co-administered drugs are shown in Table 9
[see Drug Interactions (7)].Potential for Other Drugs to Affect Tezacaftor/IvacaftorIn vitrostudies showed that ivacaftor and tezacaftor were substrates of CYP3A enzymes (i.e., CYP3A4 and CYP3A5). Exposure to ivacaftor and tezacaftor will be reduced by concomitant CYP3A inducers and increased by concomitant CYP3A inhibitors.In vitrostudies showed that tezacaftor is a substrate for the uptake transporter OATP1B1, and efflux transporters P-gp and BCRP. Tezacaftor is not a substrate for OATP1B3.In vitrostudies showed that ivacaftor is not a substrate for OATP1B1, OATP1B3, or P-gp.The effects of co-administered drugs on the exposure of tezacaftor and ivacaftor (or ivacaftor alone) are shown in Table 10
[see Dosage and Administration (2.4)and Drug Interactions (7)].Table 9: Impact of Tezacaftor/Ivacaftor or Ivacaftor on Other Drugs Dose and Schedule Mean Ratio (90% CI) of Other Drugs
No Effect=1.0Drug Dose TEZ/IVA or IVA Effect on Drug PK AUC Cmax ↑ = increase, ↓ = decrease, ↔ = no change. CI = Confidence interval; TEZ = tezacaftor; IVA = ivacaftor; PK = Pharmacokinetics Midazolam 2 mg single oral dose TEZ 100 mg/IVA 150 mg every morning + IVA 150 mg every evening ↔ Midazolam 1.12
(1.01, 1.25)1.13
(1.01, 1.25)Digoxin 0.5 mg single dose TEZ 100 mg/IVA 150 mg every morning + IVA 150 mg every evening ↑ Digoxin 1.30
(1.17, 1.45)1.32
(1.07, 1.64)Oral Contraceptive Ethinyl estradiol/ Norethindrone
0.035 mg/1.0 mg once dailyTEZ 100 mg/IVA 150 mg every morning + IVA 150 mg every evening ↔ Ethinyl estradiol 1.12
(1.03, 1.22)1.15
(0.99, 1.33)↔ Norethindrone 1.05
(0.98, 1.12)1.01
(0.87, 1.19)Pitavastatin 2 mg single dose TEZ 100 mg/IVA 150 mg every morning + IVA 150 mg every evening ↑ PitavastatinEffect is not clinically significant – no dosage adjustment is necessary 1.24
(1.17, 1.31)0.977
(0.841, 1.14)Rosiglitazone 4 mg single oral dose IVA 150 mg twice daily ↔ Rosiglitazone 0.975
(0.897, 1.06)0.928
(0.858, 1.00)Desipramine 50 mg single dose IVA 150 mg twice daily ↔ Desipramine 1.04
(0.985, 1.10)1.00
(0.939, 1.07)Table 10: Impact of Other Drugs on Tezacaftor/Ivacaftor or Ivacaftor Dose and Schedule Mean Ratio (90% CI) of Tezacaftor and Ivacaftor
No Effect = 1.0Drug Dose TEZ/IVA or IVA Effect on TEZ/IVA PK AUC Cmax ↑ = increase, ↓ = decrease, ↔ = no change. CI = Confidence interval; TEZ = tezacaftor; IVA = ivacaftor; PK = Pharmacokinetics Itraconazole 200 mg twice a day on Day 1, followed by 200 mg once daily TEZ 25 mg + IVA 50 mg once daily ↑ Tezacaftor 4.02
(3.71, 4.63)2.83
(2.62, 3.07)↑ Ivacaftor 15.6
(13.4, 18.1)8.60
(7.41, 9.98)Ciprofloxacin 750 mg twice daily TEZ 50 mg + IVA 150 mg twice daily ↔ Tezacaftor 1.08
(1.03, 1.13)1.05
(0.99, 1.11)↑ IvacaftorEffect is not clinically significant – no dosage adjustment is necessary 1.17
(1.06, 1.30)1.18
(1.06, 1.31)Oral Contraceptive Norethindrone/ethinyl estradiol 1.0 mg/0.035 mg once daily TEZ 100 mg/IVA 150 mg every morning + IVA 150 mg every evening ↔ Tezacaftor 1.01
(0.963, 1.05)1.01
(0.933, 1.09)↔ Ivacaftor 1.03
(0.960, 1.11)1.03
(0.941, 1.14)Rifampin 600 mg once daily IVA 150 mg single dose ↓ Ivacaftor 0.114
(0.097, 0.136)0.200
(0.168, 0.239)Fluconazole 400 mg single dose on Day 1, followed by 200 mg once daily IVA 150 mg twice daily ↑ Ivacaftor 2.95
(2.27, 3.82)2.47
(1.93, 3.17) - Adults and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older or pediatric patients aged 6 to less than 12 years weighing 30 kg or more: one tablet (containing tezacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 150 mg) in the morning and one tablet (containing ivacaftor 150 mg) in the evening, approximately 12 hours apart. SYMDEKO should be taken with fat-containing food. (,
2.1 General Dosage InformationSwallow the tablets whole.
SYMDEKO should be taken with fat-containing food, such as food recommended in standard nutritional guidelines. Examples of meals or snacks that contain fat are those prepared with butter or oils or those containing eggs, cheeses, nuts, whole milk, or meats, etc.
[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].,2.2 Recommended Dosage in Adults, Adolescents, and Children Aged 6 Years and OlderAdults, adolescents, and children aged 6 years and older should be dosed according to Table 1. The morning and the evening doses should be taken approximately 12 hours apart.
Table 1: Recommended Dosage for Patients Aged 6 Years and Older Age Morning
(one tablet)Evening
(one tablet)6 to <12 years weighing <30 kgtezacaftor 50 mg/ivacaftor 75 mg ivacaftor 75 mg 6 to <12 years weighing ≥30 kgtezacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 150 mg ivacaftor 150 mg ≥12 yearstezacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 150 mg ivacaftor 150 mg Information for Missed Doses:If 6 hours or less have passed since the missed morning or evening dose, the patient should take the missed dose as soon as possible and continue on the original schedule. If more than 6 hours have passed since the missed morning or evening dose, the patient should not take the missed dose. The next scheduled dose can be taken at the usual time. More than one dose should not be taken at the same time.
)12.3 PharmacokineticsThe pharmacokinetics of tezacaftor and ivacaftor are similar between healthy adult volunteers and patients with CF. Following once-daily dosing of tezacaftor and twice-daily dosing of ivacaftor in patients with CF, plasma concentrations of tezacaftor and ivacaftor reach steady-state within 8 days and within 3 to 5 days, respectively, after starting treatment. At steady-state, the accumulation ratio is approximately 1.5 for tezacaftor and 2.2 for ivacaftor. Exposures of tezacaftor (administered alone or in combination with ivacaftor) increase in an approximately dose-proportional manner with increasing doses from 10 mg to 300 mg once daily.
Key pharmacokinetic parameters for tezacaftor and ivacaftor at steady state are shown in Table 7.
Table 7: Mean (SD) Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Tezacaftor and Ivacaftor at Steady State in Patients with CF Drug Cmax
(mcg/mL)Effective t½
(h)AUC0-24hor AUC0-12h
(mcg∙h/mL)AUC0-24hfor tezacaftor and AUC0-12hfor ivacaftorTezacaftor 100 mg once daily/ivacaftor 150 mg every 12 hoursTezacaftor 5.95 (1.50) 15.0 (3.44) 84.5 (27.8) Ivacaftor 1.17 (0.424) 13.7 (6.06) 11.3 (4.60) AbsorptionAfter a single dose in healthy subjects in the fed state, tezacaftor was absorbed with a median (range) time to maximum concentration (tmax) of approximately 4 hours (2 to 6 hours). The median (range) tmaxof ivacaftor was approximately 6 hours (3 to 10 hours) in the fed state.
When a single dose of tezacaftor/ivacaftor was administered with fat-containing foods, tezacaftor exposure was similar and ivacaftor exposure was approximately 3 times higher than when taken in a fasting state.
DistributionTezacaftor is approximately 99% bound to plasma proteins, primarily to albumin. Ivacaftor is approximately 99% bound to plasma proteins, primarily to alpha 1-acid glycoprotein and albumin. After oral administration of tezacaftor 100 mg once daily/ivacaftor 150 mg every 12 hours in patients with CF in the fed state, the mean (±SD) for apparent volume of distribution of tezacaftor and ivacaftor was 271 (157) L and 206 (82.9) L, respectively. Neither tezacaftor nor ivacaftor partition preferentially into human red blood cells.
EliminationAfter oral administration of tezacaftor 100 mg once daily/ivacaftor 150 mg every 12 hours in patients with CF in the fed state, the mean (±SD) for apparent clearance values of tezacaftor and ivacaftor were 1.31 (0.41) and 15.7 (6.38) L/h, respectively. After steady-state dosing of tezacaftor in combination with ivacaftor in patients with CF, the effective half-lives of tezacaftor and ivacaftor were approximately 15 (3.44) and 13.7 (6.06) hours, respectively.
MetabolismTezacaftor is metabolized extensively in humans.
In vitrodata suggested that tezacaftor is metabolized mainly by CYP3A4 and CYP3A5. Following oral administration of a single dose of 100 mg14C-tezacaftor to healthy male subjects, M1, M2, and M5 were the three major circulating metabolites of tezacaftor in humans. M1 has the similar potency to that of tezacaftor and is considered pharmacologically active. M2 is much less pharmacologically active than tezacaftor or M1, and M5 is not considered pharmacologically active. Another minor circulating metabolite, M3, is formed by direct glucuronidation of tezacaftor.Ivacaftor is also metabolized extensively in humans.
In vitroandin vivodata indicate that ivacaftor is metabolized primarily by CYP3A4 and CYP3A5. M1 and M6 are the two major metabolites of ivacaftor in humans. M1 has approximately one-sixth the potency of ivacaftor and is considered pharmacologically active. M6 is not considered pharmacologically active.ExcretionFollowing oral administration of14C-tezacaftor, the majority of the dose (72%) was excreted in the feces (unchanged or as the M2 metabolite) and about 14% was recovered in urine (mostly as M2 metabolite), resulting in a mean overall recovery of 86% up to 21 days after the dose. Less than 1% of the administrated dose was excreted in urine as unchanged tezacaftor, showing that renal excretion is not the major pathway of tezacaftor elimination in humans.
Following oral administration of ivacaftor alone, the majority of ivacaftor (87.8%) is eliminated in the feces after metabolic conversion. There was minimal elimination of ivacaftor and its metabolites in urine (only 6.6% of total radioactivity was recovered in the urine), and there was negligible urinary excretion of ivacaftor as unchanged drug.
Specific PopulationsBased on population PK analyses, the PK exposure parameters of tezacaftor/ivacaftor in children and adolescents (ages 6 to <18 years) are similar to the AUCss range observed in adults when given in combination.
Pediatric patients aged 6 to less than 12 yearsTable 8: Tezacaftor/Ivacaftor Exposure by Age Group, Mean (SD) Age Group Dose Tezacaftor AUCss
mcg∙h/mLAUC0-24hfor tezacaftor and AUC0-12hfor ivacaftorIvacaftor AUCss
mcg∙h/mL6 to <12 yearsExposures in≥30 kg weight range are predictions derived from the population PK model71.3 (28.3) 8.5 (3.34) 6 to <12 years (<30 kg)tezacaftor 50 mg/ivacaftor 75 mg 56.7 (22.3) 6.92 (2.07) 6 to <12 years (≥30 kg)tezacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 150 mg 92.7 (21.9) 10.8 (3.52) Pediatric patients aged 12 to less than 18 yearsFollowing oral administration of SYMDEKO tablets, tezacaftor 100 mg once daily/ivacaftor 150 mg every 12 hours, the mean (±SD) AUCss for tezacaftor and ivacaftor was 97.1 (35.8) mcg∙h/mL and 11.4 (5.50) mcg∙h/mL, respectively, similar to the mean AUCss in adult patients administered SYMDEKO tablets, tezacaftor 100 mg once daily/ivacaftor 150 mg every 12 hours.
Patients with Hepatic ImpairmentFollowing multiple doses of tezacaftor and ivacaftor for 10 days, patients with moderately impaired hepatic function (Child-Pugh Class B, score 7-9) had an approximately 36% increase in AUC and a 10% increase in Cmaxfor tezacaftor, and a 1.5-fold increase in ivacaftor AUC compared with healthy subjects matched for demographics. In a separate study, patients with moderately impaired hepatic function (Child-Pugh Class B, score 7-9) had similar ivacaftor Cmax, but an approximately 2.0-fold increase in ivacaftor AUC0-∞compared with healthy subjects matched for demographics.
Pharmacokinetic studies have not been conducted in patients with mild (Child-Pugh Class A, score 5-6) or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C, score 10-15) receiving SYMDEKO. The magnitude of increase in exposure in patients with severe hepatic impairment is unknown but is expected to be higher than that observed in patients with moderate hepatic impairment
[see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Use in Specific Populations (8.6), and Patient Counseling Information (17)].Patients with Renal ImpairmentSYMDEKO has not been studied in patients with moderate or severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance ≤30 mL/min) or in patients with end-stage renal disease. In a human pharmacokinetic study with tezacaftor alone, there was minimal elimination of tezacaftor and its metabolites in urine (only 13.7% of total radioactivity was recovered in the urine with 0.79% as unchanged drug).
In a human pharmacokinetic study with ivacaftor alone, there was minimal elimination of ivacaftor and its metabolites in urine (only 6.6% of total radioactivity was recovered in the urine).
In population pharmacokinetic analysis, data from 665 patients on tezacaftor or tezacaftor in combination with ivacaftor in clinical trials indicated that mild renal impairment (N=147; eGFR 60 to less than 90 mL/min/1.73 m2) and moderate renal impairment (N=7; eGFR 30 to less than 60 mL/min/1.73 m2) did not affect the clearance of tezacaftor significantly
[see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].Male and Female PatientsThe pharmacokinetic parameters of tezacaftor and ivacaftor are similar in males and females.
Drug Interactions StudiesDrug interaction studies were performed with SYMDEKO and other drugs likely to be co-administered or drugs commonly used as probes for pharmacokinetic interaction studies
[see Drug Interactions (7)].Potential for Tezacaftor/Ivacaftor to Affect Other DrugsClinical studies (with rosiglitazone and desipramine – see Table 9) showed that ivacaftor is not an inhibitor of CYP2C8 or CYP2D6. Based on
in vitroresults, ivacaftor has the potential to inhibit CYP3A and P-gp, and may also inhibit CYP2C9.In vitro, ivacaftor was not an inducer of CYP isozymes. Ivacaftor is not an inhibitor of transporters OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OCT1, OCT2, OAT1, or OAT3.Based on
in vitroresults, tezacaftor has a low potential to inhibit CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, and CYP3A4. Tezacaftor has a low potential to induce CYP3A, but it is not an inducer of CYP1A2 and CYP2B6. Tezacaftor has a low potential to inhibit transporters P-gp, BCRP, OATP1B3, OCT2, OAT1, or OAT3.Clinical studies with midazolam showed that SYMDEKO is not an inhibitor of CYP3A. Co-administration of SYMDEKO with digoxin, a sensitive P-gp substrate, increased digoxin exposure by 1.3-fold. Co-administration of SYMDEKO with an ethinyl estradiol/ norethindrone oral contraceptive had no significant effect on the exposures of the hormonal contraceptives. Co-administration of SYMDEKO with pitavastatin, an OATP1B1 substrate, had no clinically relevant effect on the exposure of pitavastatin.
The effects of tezacaftor and ivacaftor (or ivacaftor alone) on the exposure of co-administered drugs are shown in Table 9
[see Drug Interactions (7)].Potential for Other Drugs to Affect Tezacaftor/IvacaftorIn vitrostudies showed that ivacaftor and tezacaftor were substrates of CYP3A enzymes (i.e., CYP3A4 and CYP3A5). Exposure to ivacaftor and tezacaftor will be reduced by concomitant CYP3A inducers and increased by concomitant CYP3A inhibitors.In vitrostudies showed that tezacaftor is a substrate for the uptake transporter OATP1B1, and efflux transporters P-gp and BCRP. Tezacaftor is not a substrate for OATP1B3.In vitrostudies showed that ivacaftor is not a substrate for OATP1B1, OATP1B3, or P-gp.The effects of co-administered drugs on the exposure of tezacaftor and ivacaftor (or ivacaftor alone) are shown in Table 10
[see Dosage and Administration (2.4)and Drug Interactions (7)].Table 9: Impact of Tezacaftor/Ivacaftor or Ivacaftor on Other Drugs Dose and Schedule Mean Ratio (90% CI) of Other Drugs
No Effect=1.0Drug Dose TEZ/IVA or IVA Effect on Drug PK AUC Cmax ↑ = increase, ↓ = decrease, ↔ = no change. CI = Confidence interval; TEZ = tezacaftor; IVA = ivacaftor; PK = Pharmacokinetics Midazolam 2 mg single oral dose TEZ 100 mg/IVA 150 mg every morning + IVA 150 mg every evening ↔ Midazolam 1.12
(1.01, 1.25)1.13
(1.01, 1.25)Digoxin 0.5 mg single dose TEZ 100 mg/IVA 150 mg every morning + IVA 150 mg every evening ↑ Digoxin 1.30
(1.17, 1.45)1.32
(1.07, 1.64)Oral Contraceptive Ethinyl estradiol/ Norethindrone
0.035 mg/1.0 mg once dailyTEZ 100 mg/IVA 150 mg every morning + IVA 150 mg every evening ↔ Ethinyl estradiol 1.12
(1.03, 1.22)1.15
(0.99, 1.33)↔ Norethindrone 1.05
(0.98, 1.12)1.01
(0.87, 1.19)Pitavastatin 2 mg single dose TEZ 100 mg/IVA 150 mg every morning + IVA 150 mg every evening ↑ PitavastatinEffect is not clinically significant – no dosage adjustment is necessary 1.24
(1.17, 1.31)0.977
(0.841, 1.14)Rosiglitazone 4 mg single oral dose IVA 150 mg twice daily ↔ Rosiglitazone 0.975
(0.897, 1.06)0.928
(0.858, 1.00)Desipramine 50 mg single dose IVA 150 mg twice daily ↔ Desipramine 1.04
(0.985, 1.10)1.00
(0.939, 1.07)Table 10: Impact of Other Drugs on Tezacaftor/Ivacaftor or Ivacaftor Dose and Schedule Mean Ratio (90% CI) of Tezacaftor and Ivacaftor
No Effect = 1.0Drug Dose TEZ/IVA or IVA Effect on TEZ/IVA PK AUC Cmax ↑ = increase, ↓ = decrease, ↔ = no change. CI = Confidence interval; TEZ = tezacaftor; IVA = ivacaftor; PK = Pharmacokinetics Itraconazole 200 mg twice a day on Day 1, followed by 200 mg once daily TEZ 25 mg + IVA 50 mg once daily ↑ Tezacaftor 4.02
(3.71, 4.63)2.83
(2.62, 3.07)↑ Ivacaftor 15.6
(13.4, 18.1)8.60
(7.41, 9.98)Ciprofloxacin 750 mg twice daily TEZ 50 mg + IVA 150 mg twice daily ↔ Tezacaftor 1.08
(1.03, 1.13)1.05
(0.99, 1.11)↑ IvacaftorEffect is not clinically significant – no dosage adjustment is necessary 1.17
(1.06, 1.30)1.18
(1.06, 1.31)Oral Contraceptive Norethindrone/ethinyl estradiol 1.0 mg/0.035 mg once daily TEZ 100 mg/IVA 150 mg every morning + IVA 150 mg every evening ↔ Tezacaftor 1.01
(0.963, 1.05)1.01
(0.933, 1.09)↔ Ivacaftor 1.03
(0.960, 1.11)1.03
(0.941, 1.14)Rifampin 600 mg once daily IVA 150 mg single dose ↓ Ivacaftor 0.114
(0.097, 0.136)0.200
(0.168, 0.239)Fluconazole 400 mg single dose on Day 1, followed by 200 mg once daily IVA 150 mg twice daily ↑ Ivacaftor 2.95
(2.27, 3.82)2.47
(1.93, 3.17) - Reduce dosage in patients with moderate and severe hepatic impairment. (,
2.3 Recommended Dosage for Patients with Hepatic ImpairmentFor dosage adjustment for patients with hepatic impairment, refer to Table 2.
Studies have not been conducted in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C), but exposure of tezacaftor and ivacaftor is expected to be higher than in patients with moderate hepatic impairment. Therefore, SYMDEKO should be used with caution at an adjusted dosage after weighing the risks and benefits of treatment in these patients
[see Use in Specific Populations (8.6), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), and Patient Counseling Information (17)].Table 2: Recommended Dosage for Patients with Hepatic Impairment Hepatic Impairment Morning Evening Patients Aged 6 to <12 Years Weighing <30 kg Patients Aged 6 to <12 Years Weighing ≥30 kg and Patients Age ≥12 Years All Patients Mild (Child-Pugh Class A)No dose adjustment No dose adjustment No dose adjustment Moderate (Child-Pugh Class B)One tablet of tezacaftor 50 mg/ivacaftor 75 mg once daily One tablet of tezacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 150 mg once daily No ivacaftor dose Severe (Child-Pugh Class C)One tablet of tezacaftor 50 mg/ivacaftor 75 mg once daily
(or less frequently)One tablet of tezacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 150 mg once daily
(or less frequently),8.6 Hepatic ImpairmentNo dosage adjustment is necessary for patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A). A reduced dosage of SYMDEKO is recommended in patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B). There is no experience in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C), but tezacaftor/ivacaftor exposure is expected to be higher than in patients with moderate hepatic impairment. Therefore, use with caution at a reduced dosage in patients with severe hepatic impairment after weighing the risks and benefits of treatment
[see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), and Patient Counseling Information (17)].)12.3 PharmacokineticsThe pharmacokinetics of tezacaftor and ivacaftor are similar between healthy adult volunteers and patients with CF. Following once-daily dosing of tezacaftor and twice-daily dosing of ivacaftor in patients with CF, plasma concentrations of tezacaftor and ivacaftor reach steady-state within 8 days and within 3 to 5 days, respectively, after starting treatment. At steady-state, the accumulation ratio is approximately 1.5 for tezacaftor and 2.2 for ivacaftor. Exposures of tezacaftor (administered alone or in combination with ivacaftor) increase in an approximately dose-proportional manner with increasing doses from 10 mg to 300 mg once daily.
Key pharmacokinetic parameters for tezacaftor and ivacaftor at steady state are shown in Table 7.
Table 7: Mean (SD) Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Tezacaftor and Ivacaftor at Steady State in Patients with CF Drug Cmax
(mcg/mL)Effective t½
(h)AUC0-24hor AUC0-12h
(mcg∙h/mL)AUC0-24hfor tezacaftor and AUC0-12hfor ivacaftorTezacaftor 100 mg once daily/ivacaftor 150 mg every 12 hoursTezacaftor 5.95 (1.50) 15.0 (3.44) 84.5 (27.8) Ivacaftor 1.17 (0.424) 13.7 (6.06) 11.3 (4.60) AbsorptionAfter a single dose in healthy subjects in the fed state, tezacaftor was absorbed with a median (range) time to maximum concentration (tmax) of approximately 4 hours (2 to 6 hours). The median (range) tmaxof ivacaftor was approximately 6 hours (3 to 10 hours) in the fed state.
When a single dose of tezacaftor/ivacaftor was administered with fat-containing foods, tezacaftor exposure was similar and ivacaftor exposure was approximately 3 times higher than when taken in a fasting state.
DistributionTezacaftor is approximately 99% bound to plasma proteins, primarily to albumin. Ivacaftor is approximately 99% bound to plasma proteins, primarily to alpha 1-acid glycoprotein and albumin. After oral administration of tezacaftor 100 mg once daily/ivacaftor 150 mg every 12 hours in patients with CF in the fed state, the mean (±SD) for apparent volume of distribution of tezacaftor and ivacaftor was 271 (157) L and 206 (82.9) L, respectively. Neither tezacaftor nor ivacaftor partition preferentially into human red blood cells.
EliminationAfter oral administration of tezacaftor 100 mg once daily/ivacaftor 150 mg every 12 hours in patients with CF in the fed state, the mean (±SD) for apparent clearance values of tezacaftor and ivacaftor were 1.31 (0.41) and 15.7 (6.38) L/h, respectively. After steady-state dosing of tezacaftor in combination with ivacaftor in patients with CF, the effective half-lives of tezacaftor and ivacaftor were approximately 15 (3.44) and 13.7 (6.06) hours, respectively.
MetabolismTezacaftor is metabolized extensively in humans.
In vitrodata suggested that tezacaftor is metabolized mainly by CYP3A4 and CYP3A5. Following oral administration of a single dose of 100 mg14C-tezacaftor to healthy male subjects, M1, M2, and M5 were the three major circulating metabolites of tezacaftor in humans. M1 has the similar potency to that of tezacaftor and is considered pharmacologically active. M2 is much less pharmacologically active than tezacaftor or M1, and M5 is not considered pharmacologically active. Another minor circulating metabolite, M3, is formed by direct glucuronidation of tezacaftor.Ivacaftor is also metabolized extensively in humans.
In vitroandin vivodata indicate that ivacaftor is metabolized primarily by CYP3A4 and CYP3A5. M1 and M6 are the two major metabolites of ivacaftor in humans. M1 has approximately one-sixth the potency of ivacaftor and is considered pharmacologically active. M6 is not considered pharmacologically active.ExcretionFollowing oral administration of14C-tezacaftor, the majority of the dose (72%) was excreted in the feces (unchanged or as the M2 metabolite) and about 14% was recovered in urine (mostly as M2 metabolite), resulting in a mean overall recovery of 86% up to 21 days after the dose. Less than 1% of the administrated dose was excreted in urine as unchanged tezacaftor, showing that renal excretion is not the major pathway of tezacaftor elimination in humans.
Following oral administration of ivacaftor alone, the majority of ivacaftor (87.8%) is eliminated in the feces after metabolic conversion. There was minimal elimination of ivacaftor and its metabolites in urine (only 6.6% of total radioactivity was recovered in the urine), and there was negligible urinary excretion of ivacaftor as unchanged drug.
Specific PopulationsBased on population PK analyses, the PK exposure parameters of tezacaftor/ivacaftor in children and adolescents (ages 6 to <18 years) are similar to the AUCss range observed in adults when given in combination.
Pediatric patients aged 6 to less than 12 yearsTable 8: Tezacaftor/Ivacaftor Exposure by Age Group, Mean (SD) Age Group Dose Tezacaftor AUCss
mcg∙h/mLAUC0-24hfor tezacaftor and AUC0-12hfor ivacaftorIvacaftor AUCss
mcg∙h/mL6 to <12 yearsExposures in≥30 kg weight range are predictions derived from the population PK model71.3 (28.3) 8.5 (3.34) 6 to <12 years (<30 kg)tezacaftor 50 mg/ivacaftor 75 mg 56.7 (22.3) 6.92 (2.07) 6 to <12 years (≥30 kg)tezacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 150 mg 92.7 (21.9) 10.8 (3.52) Pediatric patients aged 12 to less than 18 yearsFollowing oral administration of SYMDEKO tablets, tezacaftor 100 mg once daily/ivacaftor 150 mg every 12 hours, the mean (±SD) AUCss for tezacaftor and ivacaftor was 97.1 (35.8) mcg∙h/mL and 11.4 (5.50) mcg∙h/mL, respectively, similar to the mean AUCss in adult patients administered SYMDEKO tablets, tezacaftor 100 mg once daily/ivacaftor 150 mg every 12 hours.
Patients with Hepatic ImpairmentFollowing multiple doses of tezacaftor and ivacaftor for 10 days, patients with moderately impaired hepatic function (Child-Pugh Class B, score 7-9) had an approximately 36% increase in AUC and a 10% increase in Cmaxfor tezacaftor, and a 1.5-fold increase in ivacaftor AUC compared with healthy subjects matched for demographics. In a separate study, patients with moderately impaired hepatic function (Child-Pugh Class B, score 7-9) had similar ivacaftor Cmax, but an approximately 2.0-fold increase in ivacaftor AUC0-∞compared with healthy subjects matched for demographics.
Pharmacokinetic studies have not been conducted in patients with mild (Child-Pugh Class A, score 5-6) or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C, score 10-15) receiving SYMDEKO. The magnitude of increase in exposure in patients with severe hepatic impairment is unknown but is expected to be higher than that observed in patients with moderate hepatic impairment
[see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Use in Specific Populations (8.6), and Patient Counseling Information (17)].Patients with Renal ImpairmentSYMDEKO has not been studied in patients with moderate or severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance ≤30 mL/min) or in patients with end-stage renal disease. In a human pharmacokinetic study with tezacaftor alone, there was minimal elimination of tezacaftor and its metabolites in urine (only 13.7% of total radioactivity was recovered in the urine with 0.79% as unchanged drug).
In a human pharmacokinetic study with ivacaftor alone, there was minimal elimination of ivacaftor and its metabolites in urine (only 6.6% of total radioactivity was recovered in the urine).
In population pharmacokinetic analysis, data from 665 patients on tezacaftor or tezacaftor in combination with ivacaftor in clinical trials indicated that mild renal impairment (N=147; eGFR 60 to less than 90 mL/min/1.73 m2) and moderate renal impairment (N=7; eGFR 30 to less than 60 mL/min/1.73 m2) did not affect the clearance of tezacaftor significantly
[see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].Male and Female PatientsThe pharmacokinetic parameters of tezacaftor and ivacaftor are similar in males and females.
Drug Interactions StudiesDrug interaction studies were performed with SYMDEKO and other drugs likely to be co-administered or drugs commonly used as probes for pharmacokinetic interaction studies
[see Drug Interactions (7)].Potential for Tezacaftor/Ivacaftor to Affect Other DrugsClinical studies (with rosiglitazone and desipramine – see Table 9) showed that ivacaftor is not an inhibitor of CYP2C8 or CYP2D6. Based on
in vitroresults, ivacaftor has the potential to inhibit CYP3A and P-gp, and may also inhibit CYP2C9.In vitro, ivacaftor was not an inducer of CYP isozymes. Ivacaftor is not an inhibitor of transporters OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OCT1, OCT2, OAT1, or OAT3.Based on
in vitroresults, tezacaftor has a low potential to inhibit CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, and CYP3A4. Tezacaftor has a low potential to induce CYP3A, but it is not an inducer of CYP1A2 and CYP2B6. Tezacaftor has a low potential to inhibit transporters P-gp, BCRP, OATP1B3, OCT2, OAT1, or OAT3.Clinical studies with midazolam showed that SYMDEKO is not an inhibitor of CYP3A. Co-administration of SYMDEKO with digoxin, a sensitive P-gp substrate, increased digoxin exposure by 1.3-fold. Co-administration of SYMDEKO with an ethinyl estradiol/ norethindrone oral contraceptive had no significant effect on the exposures of the hormonal contraceptives. Co-administration of SYMDEKO with pitavastatin, an OATP1B1 substrate, had no clinically relevant effect on the exposure of pitavastatin.
The effects of tezacaftor and ivacaftor (or ivacaftor alone) on the exposure of co-administered drugs are shown in Table 9
[see Drug Interactions (7)].Potential for Other Drugs to Affect Tezacaftor/IvacaftorIn vitrostudies showed that ivacaftor and tezacaftor were substrates of CYP3A enzymes (i.e., CYP3A4 and CYP3A5). Exposure to ivacaftor and tezacaftor will be reduced by concomitant CYP3A inducers and increased by concomitant CYP3A inhibitors.In vitrostudies showed that tezacaftor is a substrate for the uptake transporter OATP1B1, and efflux transporters P-gp and BCRP. Tezacaftor is not a substrate for OATP1B3.In vitrostudies showed that ivacaftor is not a substrate for OATP1B1, OATP1B3, or P-gp.The effects of co-administered drugs on the exposure of tezacaftor and ivacaftor (or ivacaftor alone) are shown in Table 10
[see Dosage and Administration (2.4)and Drug Interactions (7)].Table 9: Impact of Tezacaftor/Ivacaftor or Ivacaftor on Other Drugs Dose and Schedule Mean Ratio (90% CI) of Other Drugs
No Effect=1.0Drug Dose TEZ/IVA or IVA Effect on Drug PK AUC Cmax ↑ = increase, ↓ = decrease, ↔ = no change. CI = Confidence interval; TEZ = tezacaftor; IVA = ivacaftor; PK = Pharmacokinetics Midazolam 2 mg single oral dose TEZ 100 mg/IVA 150 mg every morning + IVA 150 mg every evening ↔ Midazolam 1.12
(1.01, 1.25)1.13
(1.01, 1.25)Digoxin 0.5 mg single dose TEZ 100 mg/IVA 150 mg every morning + IVA 150 mg every evening ↑ Digoxin 1.30
(1.17, 1.45)1.32
(1.07, 1.64)Oral Contraceptive Ethinyl estradiol/ Norethindrone
0.035 mg/1.0 mg once dailyTEZ 100 mg/IVA 150 mg every morning + IVA 150 mg every evening ↔ Ethinyl estradiol 1.12
(1.03, 1.22)1.15
(0.99, 1.33)↔ Norethindrone 1.05
(0.98, 1.12)1.01
(0.87, 1.19)Pitavastatin 2 mg single dose TEZ 100 mg/IVA 150 mg every morning + IVA 150 mg every evening ↑ PitavastatinEffect is not clinically significant – no dosage adjustment is necessary 1.24
(1.17, 1.31)0.977
(0.841, 1.14)Rosiglitazone 4 mg single oral dose IVA 150 mg twice daily ↔ Rosiglitazone 0.975
(0.897, 1.06)0.928
(0.858, 1.00)Desipramine 50 mg single dose IVA 150 mg twice daily ↔ Desipramine 1.04
(0.985, 1.10)1.00
(0.939, 1.07)Table 10: Impact of Other Drugs on Tezacaftor/Ivacaftor or Ivacaftor Dose and Schedule Mean Ratio (90% CI) of Tezacaftor and Ivacaftor
No Effect = 1.0Drug Dose TEZ/IVA or IVA Effect on TEZ/IVA PK AUC Cmax ↑ = increase, ↓ = decrease, ↔ = no change. CI = Confidence interval; TEZ = tezacaftor; IVA = ivacaftor; PK = Pharmacokinetics Itraconazole 200 mg twice a day on Day 1, followed by 200 mg once daily TEZ 25 mg + IVA 50 mg once daily ↑ Tezacaftor 4.02
(3.71, 4.63)2.83
(2.62, 3.07)↑ Ivacaftor 15.6
(13.4, 18.1)8.60
(7.41, 9.98)Ciprofloxacin 750 mg twice daily TEZ 50 mg + IVA 150 mg twice daily ↔ Tezacaftor 1.08
(1.03, 1.13)1.05
(0.99, 1.11)↑ IvacaftorEffect is not clinically significant – no dosage adjustment is necessary 1.17
(1.06, 1.30)1.18
(1.06, 1.31)Oral Contraceptive Norethindrone/ethinyl estradiol 1.0 mg/0.035 mg once daily TEZ 100 mg/IVA 150 mg every morning + IVA 150 mg every evening ↔ Tezacaftor 1.01
(0.963, 1.05)1.01
(0.933, 1.09)↔ Ivacaftor 1.03
(0.960, 1.11)1.03
(0.941, 1.14)Rifampin 600 mg once daily IVA 150 mg single dose ↓ Ivacaftor 0.114
(0.097, 0.136)0.200
(0.168, 0.239)Fluconazole 400 mg single dose on Day 1, followed by 200 mg once daily IVA 150 mg twice daily ↑ Ivacaftor 2.95
(2.27, 3.82)2.47
(1.93, 3.17) - See full prescribing information for dosage modifications due to drug interactions with SYMDEKO. (,
2.4 Dosage Adjustment for Patients Taking Drugs that are CYP3A InhibitorsThe dosing regimen of SYMDEKO should be adjusted when co-administered with moderate and strong CYP3A inhibitors.
Moderate CYP3A inhibitors:When co-administered with moderate CYP3A inhibitors (e.g., fluconazole, erythromycin), the dosing regimen should be adjusted as in Table 3
[see Drug Interactions (7.2), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), and Patient Counseling Information (17)].Table 3: Dosing Schedule for Concomitant Use of SYMDEKO with Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4Continue dosing with tezacaftor/ivacaftor or ivacaftor tablets on alternate days. Patients Aged 6 to <12 Years Weighing <30 kgMorningTezacaftor 50 mg/ivacaftor 75 mg tablet ✓ - ✓ - Ivacaftor 75 mg tablet - ✓ - ✓ EveningIvacaftor 75 mg tablet - - - - Patients Aged 6 to <12 Years Weighing ≥30 kg and Patients Age ≥12 YearsMorningTezacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 150 mg tablet ✓ - ✓ - Ivacaftor 150 mg tablet - ✓ - ✓ EveningIvacaftor 150 mg tablet - - - - Strong CYP3A inhibitors:When co-administered with strong CYP3A inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole, posaconazole, voriconazole, telithromycin, and clarithromycin), the dosing regimen should be adjusted as in Table 4
[see Drug Interactions (7.2), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), and Patient Counseling Information (17)].Table 4: Dosing Schedule for Concomitant Use of SYMDEKO with Strong CYP3A Inhibitors Day 1 Day 2 and Day 3 Day 4Continue dosing with tezacaftor/ivacaftor tablets twice a week, taken approximately 3 to 4 days apart. Patients Aged 6 to <12 Years Weighing <30 kgMorningTezacaftor 50 mg/ivacaftor 75 mg tablet ✓ - ✓ EveningThe evening dose of ivacaftor should not be taken on any day.Ivacaftor 75 mg tablet - - - Patients Aged 6 to <12 Years Weighing ≥30 kg and Patients Age ≥12 YearsMorningTezacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 150 mg tablet ✓ - ✓ EveningIvacaftor 150 mg tablet - - - Food or drink containing grapefruit should be avoided during treatment with SYMDEKO
[see Drug Interactions (7.2)and Patient Counseling Information (17)].,7.2 Inhibitors of CYP3ACo-administration with itraconazole, a strong CYP3A inhibitor, increased tezacaftor exposure (AUC) by 4.0-fold and ivacaftor by 15.6-fold. When co-administered with strong CYP3A inhibitors, the dosing regimen of SYMDEKO should be adjusted
[see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), and Patient Counseling Information (17)].Examples of strong CYP3A inhibitors include:
- ketoconazole, itraconazole, posaconazole, and voriconazole
- telithromycin and clarithromycin
Co-administration of fluconazole increased ivacaftor exposure (AUC) by 3.0-fold. Simulation suggested co-administration with fluconazole, a moderate CYP3A inhibitor, may increase tezacaftor exposure (AUC) by approximately 2.0-fold. When co-administered with moderate CYP3A inhibitors, the dosing regimen of SYMDEKO should be adjusted
[see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), and Patient Counseling Information (17)].Examples of moderate CYP3A inhibitors include:
- fluconazole
- erythromycin
Co-administration of SYMDEKO with grapefruit juice, which contains one or more components that moderately inhibit CYP3A, may increase exposure of tezacaftor and ivacaftor; therefore, food or drink containing grapefruit should be avoided during treatment with SYMDEKO
[see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), and Patient Counseling Information (17)].)12.3 PharmacokineticsThe pharmacokinetics of tezacaftor and ivacaftor are similar between healthy adult volunteers and patients with CF. Following once-daily dosing of tezacaftor and twice-daily dosing of ivacaftor in patients with CF, plasma concentrations of tezacaftor and ivacaftor reach steady-state within 8 days and within 3 to 5 days, respectively, after starting treatment. At steady-state, the accumulation ratio is approximately 1.5 for tezacaftor and 2.2 for ivacaftor. Exposures of tezacaftor (administered alone or in combination with ivacaftor) increase in an approximately dose-proportional manner with increasing doses from 10 mg to 300 mg once daily.
Key pharmacokinetic parameters for tezacaftor and ivacaftor at steady state are shown in Table 7.
Table 7: Mean (SD) Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Tezacaftor and Ivacaftor at Steady State in Patients with CF Drug Cmax
(mcg/mL)Effective t½
(h)AUC0-24hor AUC0-12h
(mcg∙h/mL)AUC0-24hfor tezacaftor and AUC0-12hfor ivacaftorTezacaftor 100 mg once daily/ivacaftor 150 mg every 12 hoursTezacaftor 5.95 (1.50) 15.0 (3.44) 84.5 (27.8) Ivacaftor 1.17 (0.424) 13.7 (6.06) 11.3 (4.60) AbsorptionAfter a single dose in healthy subjects in the fed state, tezacaftor was absorbed with a median (range) time to maximum concentration (tmax) of approximately 4 hours (2 to 6 hours). The median (range) tmaxof ivacaftor was approximately 6 hours (3 to 10 hours) in the fed state.
When a single dose of tezacaftor/ivacaftor was administered with fat-containing foods, tezacaftor exposure was similar and ivacaftor exposure was approximately 3 times higher than when taken in a fasting state.
DistributionTezacaftor is approximately 99% bound to plasma proteins, primarily to albumin. Ivacaftor is approximately 99% bound to plasma proteins, primarily to alpha 1-acid glycoprotein and albumin. After oral administration of tezacaftor 100 mg once daily/ivacaftor 150 mg every 12 hours in patients with CF in the fed state, the mean (±SD) for apparent volume of distribution of tezacaftor and ivacaftor was 271 (157) L and 206 (82.9) L, respectively. Neither tezacaftor nor ivacaftor partition preferentially into human red blood cells.
EliminationAfter oral administration of tezacaftor 100 mg once daily/ivacaftor 150 mg every 12 hours in patients with CF in the fed state, the mean (±SD) for apparent clearance values of tezacaftor and ivacaftor were 1.31 (0.41) and 15.7 (6.38) L/h, respectively. After steady-state dosing of tezacaftor in combination with ivacaftor in patients with CF, the effective half-lives of tezacaftor and ivacaftor were approximately 15 (3.44) and 13.7 (6.06) hours, respectively.
MetabolismTezacaftor is metabolized extensively in humans.
In vitrodata suggested that tezacaftor is metabolized mainly by CYP3A4 and CYP3A5. Following oral administration of a single dose of 100 mg14C-tezacaftor to healthy male subjects, M1, M2, and M5 were the three major circulating metabolites of tezacaftor in humans. M1 has the similar potency to that of tezacaftor and is considered pharmacologically active. M2 is much less pharmacologically active than tezacaftor or M1, and M5 is not considered pharmacologically active. Another minor circulating metabolite, M3, is formed by direct glucuronidation of tezacaftor.Ivacaftor is also metabolized extensively in humans.
In vitroandin vivodata indicate that ivacaftor is metabolized primarily by CYP3A4 and CYP3A5. M1 and M6 are the two major metabolites of ivacaftor in humans. M1 has approximately one-sixth the potency of ivacaftor and is considered pharmacologically active. M6 is not considered pharmacologically active.ExcretionFollowing oral administration of14C-tezacaftor, the majority of the dose (72%) was excreted in the feces (unchanged or as the M2 metabolite) and about 14% was recovered in urine (mostly as M2 metabolite), resulting in a mean overall recovery of 86% up to 21 days after the dose. Less than 1% of the administrated dose was excreted in urine as unchanged tezacaftor, showing that renal excretion is not the major pathway of tezacaftor elimination in humans.
Following oral administration of ivacaftor alone, the majority of ivacaftor (87.8%) is eliminated in the feces after metabolic conversion. There was minimal elimination of ivacaftor and its metabolites in urine (only 6.6% of total radioactivity was recovered in the urine), and there was negligible urinary excretion of ivacaftor as unchanged drug.
Specific PopulationsBased on population PK analyses, the PK exposure parameters of tezacaftor/ivacaftor in children and adolescents (ages 6 to <18 years) are similar to the AUCss range observed in adults when given in combination.
Pediatric patients aged 6 to less than 12 yearsTable 8: Tezacaftor/Ivacaftor Exposure by Age Group, Mean (SD) Age Group Dose Tezacaftor AUCss
mcg∙h/mLAUC0-24hfor tezacaftor and AUC0-12hfor ivacaftorIvacaftor AUCss
mcg∙h/mL6 to <12 yearsExposures in≥30 kg weight range are predictions derived from the population PK model71.3 (28.3) 8.5 (3.34) 6 to <12 years (<30 kg)tezacaftor 50 mg/ivacaftor 75 mg 56.7 (22.3) 6.92 (2.07) 6 to <12 years (≥30 kg)tezacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 150 mg 92.7 (21.9) 10.8 (3.52) Pediatric patients aged 12 to less than 18 yearsFollowing oral administration of SYMDEKO tablets, tezacaftor 100 mg once daily/ivacaftor 150 mg every 12 hours, the mean (±SD) AUCss for tezacaftor and ivacaftor was 97.1 (35.8) mcg∙h/mL and 11.4 (5.50) mcg∙h/mL, respectively, similar to the mean AUCss in adult patients administered SYMDEKO tablets, tezacaftor 100 mg once daily/ivacaftor 150 mg every 12 hours.
Patients with Hepatic ImpairmentFollowing multiple doses of tezacaftor and ivacaftor for 10 days, patients with moderately impaired hepatic function (Child-Pugh Class B, score 7-9) had an approximately 36% increase in AUC and a 10% increase in Cmaxfor tezacaftor, and a 1.5-fold increase in ivacaftor AUC compared with healthy subjects matched for demographics. In a separate study, patients with moderately impaired hepatic function (Child-Pugh Class B, score 7-9) had similar ivacaftor Cmax, but an approximately 2.0-fold increase in ivacaftor AUC0-∞compared with healthy subjects matched for demographics.
Pharmacokinetic studies have not been conducted in patients with mild (Child-Pugh Class A, score 5-6) or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C, score 10-15) receiving SYMDEKO. The magnitude of increase in exposure in patients with severe hepatic impairment is unknown but is expected to be higher than that observed in patients with moderate hepatic impairment
[see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Use in Specific Populations (8.6), and Patient Counseling Information (17)].Patients with Renal ImpairmentSYMDEKO has not been studied in patients with moderate or severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance ≤30 mL/min) or in patients with end-stage renal disease. In a human pharmacokinetic study with tezacaftor alone, there was minimal elimination of tezacaftor and its metabolites in urine (only 13.7% of total radioactivity was recovered in the urine with 0.79% as unchanged drug).
In a human pharmacokinetic study with ivacaftor alone, there was minimal elimination of ivacaftor and its metabolites in urine (only 6.6% of total radioactivity was recovered in the urine).
In population pharmacokinetic analysis, data from 665 patients on tezacaftor or tezacaftor in combination with ivacaftor in clinical trials indicated that mild renal impairment (N=147; eGFR 60 to less than 90 mL/min/1.73 m2) and moderate renal impairment (N=7; eGFR 30 to less than 60 mL/min/1.73 m2) did not affect the clearance of tezacaftor significantly
[see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].Male and Female PatientsThe pharmacokinetic parameters of tezacaftor and ivacaftor are similar in males and females.
Drug Interactions StudiesDrug interaction studies were performed with SYMDEKO and other drugs likely to be co-administered or drugs commonly used as probes for pharmacokinetic interaction studies
[see Drug Interactions (7)].Potential for Tezacaftor/Ivacaftor to Affect Other DrugsClinical studies (with rosiglitazone and desipramine – see Table 9) showed that ivacaftor is not an inhibitor of CYP2C8 or CYP2D6. Based on
in vitroresults, ivacaftor has the potential to inhibit CYP3A and P-gp, and may also inhibit CYP2C9.In vitro, ivacaftor was not an inducer of CYP isozymes. Ivacaftor is not an inhibitor of transporters OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OCT1, OCT2, OAT1, or OAT3.Based on
in vitroresults, tezacaftor has a low potential to inhibit CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, and CYP3A4. Tezacaftor has a low potential to induce CYP3A, but it is not an inducer of CYP1A2 and CYP2B6. Tezacaftor has a low potential to inhibit transporters P-gp, BCRP, OATP1B3, OCT2, OAT1, or OAT3.Clinical studies with midazolam showed that SYMDEKO is not an inhibitor of CYP3A. Co-administration of SYMDEKO with digoxin, a sensitive P-gp substrate, increased digoxin exposure by 1.3-fold. Co-administration of SYMDEKO with an ethinyl estradiol/ norethindrone oral contraceptive had no significant effect on the exposures of the hormonal contraceptives. Co-administration of SYMDEKO with pitavastatin, an OATP1B1 substrate, had no clinically relevant effect on the exposure of pitavastatin.
The effects of tezacaftor and ivacaftor (or ivacaftor alone) on the exposure of co-administered drugs are shown in Table 9
[see Drug Interactions (7)].Potential for Other Drugs to Affect Tezacaftor/IvacaftorIn vitrostudies showed that ivacaftor and tezacaftor were substrates of CYP3A enzymes (i.e., CYP3A4 and CYP3A5). Exposure to ivacaftor and tezacaftor will be reduced by concomitant CYP3A inducers and increased by concomitant CYP3A inhibitors.In vitrostudies showed that tezacaftor is a substrate for the uptake transporter OATP1B1, and efflux transporters P-gp and BCRP. Tezacaftor is not a substrate for OATP1B3.In vitrostudies showed that ivacaftor is not a substrate for OATP1B1, OATP1B3, or P-gp.The effects of co-administered drugs on the exposure of tezacaftor and ivacaftor (or ivacaftor alone) are shown in Table 10
[see Dosage and Administration (2.4)and Drug Interactions (7)].Table 9: Impact of Tezacaftor/Ivacaftor or Ivacaftor on Other Drugs Dose and Schedule Mean Ratio (90% CI) of Other Drugs
No Effect=1.0Drug Dose TEZ/IVA or IVA Effect on Drug PK AUC Cmax ↑ = increase, ↓ = decrease, ↔ = no change. CI = Confidence interval; TEZ = tezacaftor; IVA = ivacaftor; PK = Pharmacokinetics Midazolam 2 mg single oral dose TEZ 100 mg/IVA 150 mg every morning + IVA 150 mg every evening ↔ Midazolam 1.12
(1.01, 1.25)1.13
(1.01, 1.25)Digoxin 0.5 mg single dose TEZ 100 mg/IVA 150 mg every morning + IVA 150 mg every evening ↑ Digoxin 1.30
(1.17, 1.45)1.32
(1.07, 1.64)Oral Contraceptive Ethinyl estradiol/ Norethindrone
0.035 mg/1.0 mg once dailyTEZ 100 mg/IVA 150 mg every morning + IVA 150 mg every evening ↔ Ethinyl estradiol 1.12
(1.03, 1.22)1.15
(0.99, 1.33)↔ Norethindrone 1.05
(0.98, 1.12)1.01
(0.87, 1.19)Pitavastatin 2 mg single dose TEZ 100 mg/IVA 150 mg every morning + IVA 150 mg every evening ↑ PitavastatinEffect is not clinically significant – no dosage adjustment is necessary 1.24
(1.17, 1.31)0.977
(0.841, 1.14)Rosiglitazone 4 mg single oral dose IVA 150 mg twice daily ↔ Rosiglitazone 0.975
(0.897, 1.06)0.928
(0.858, 1.00)Desipramine 50 mg single dose IVA 150 mg twice daily ↔ Desipramine 1.04
(0.985, 1.10)1.00
(0.939, 1.07)Table 10: Impact of Other Drugs on Tezacaftor/Ivacaftor or Ivacaftor Dose and Schedule Mean Ratio (90% CI) of Tezacaftor and Ivacaftor
No Effect = 1.0Drug Dose TEZ/IVA or IVA Effect on TEZ/IVA PK AUC Cmax ↑ = increase, ↓ = decrease, ↔ = no change. CI = Confidence interval; TEZ = tezacaftor; IVA = ivacaftor; PK = Pharmacokinetics Itraconazole 200 mg twice a day on Day 1, followed by 200 mg once daily TEZ 25 mg + IVA 50 mg once daily ↑ Tezacaftor 4.02
(3.71, 4.63)2.83
(2.62, 3.07)↑ Ivacaftor 15.6
(13.4, 18.1)8.60
(7.41, 9.98)Ciprofloxacin 750 mg twice daily TEZ 50 mg + IVA 150 mg twice daily ↔ Tezacaftor 1.08
(1.03, 1.13)1.05
(0.99, 1.11)↑ IvacaftorEffect is not clinically significant – no dosage adjustment is necessary 1.17
(1.06, 1.30)1.18
(1.06, 1.31)Oral Contraceptive Norethindrone/ethinyl estradiol 1.0 mg/0.035 mg once daily TEZ 100 mg/IVA 150 mg every morning + IVA 150 mg every evening ↔ Tezacaftor 1.01
(0.963, 1.05)1.01
(0.933, 1.09)↔ Ivacaftor 1.03
(0.960, 1.11)1.03
(0.941, 1.14)Rifampin 600 mg once daily IVA 150 mg single dose ↓ Ivacaftor 0.114
(0.097, 0.136)0.200
(0.168, 0.239)Fluconazole 400 mg single dose on Day 1, followed by 200 mg once daily IVA 150 mg twice daily ↑ Ivacaftor 2.95
(2.27, 3.82)2.47
(1.93, 3.17)
Tablets: Tezacaftor 50 mg/ivacaftor 75 mg fixed-dose combination tablets co-packaged with ivacaftor 75 mg tablets
- Tezacaftor 50 mg/ivacaftor 75 mg tablets are white, oblong-shaped, and debossed with "V50" on one side and plain on the other.
- Ivacaftor 75 mg tablets are light blue, oblong-shaped, and printed with "V 75" in black ink on one side and plain on the other.
Tablets: Tezacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 150 mg fixed-dose combination tablets co-packaged with ivacaftor 150 mg tablets
- Tezacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 150 mg tablets are yellow, oblong-shaped, and debossed with "V100" on one side and plain on the other.
- Ivacaftor 150 mg tablets are light blue, oblong-shaped, and printed with "V 150" in black ink on one side and plain on the other.
There are limited and incomplete human data from clinical trials and postmarketing reports on the use of SYMDEKO or its individual components, tezacaftor and ivacaftor, in pregnant women to inform a drug-associated risk. Although there are no animal reproduction studies with the concomitant administration of tezacaftor and ivacaftor, separate reproductive and developmental studies were conducted with tezacaftor and ivacaftor in pregnant rats and rabbits. In animal reproduction studies, oral administration of tezacaftor to pregnant rats and rabbits during organogenesis demonstrated no teratogenicity or adverse developmental effects at doses that produced maternal exposures up to approximately 3 times the exposure at the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) in rats and 0.2 times the MRHD in rabbits (based on summed AUCs for tezacaftor and M1 metabolite). Oral administration of ivacaftor to pregnant rats and rabbits during organogenesis demonstrated no teratogenicity or adverse developmental effects at doses that produced maternal exposures up to approximately 6 and 16 times the exposure at the MRHD, respectively. No adverse developmental effects were observed after oral administration of either tezacaftor or ivacaftor to pregnant rats from the period of organogenesis through lactation at doses that produced maternal exposures approximately 1 and 4 times the exposures at the MRHD, respectively (
Tezacaftor
In an embryo-fetal development study in pregnant rats dosed during the period of organogenesis from gestation Days 6-17, tezacaftor was not teratogenic and did not affect fetal development or survival at exposures up to 3 times the MRHD (based on summed AUCs for tezacaftor and M1 metabolite at maternal oral doses up to 100 mg/kg/day). In an embryo-fetal development study in pregnant rabbits dosed during the period of organogenesis from gestation Days 7-20, tezacaftor was not teratogenic and did not affect fetal development or survival at exposures up to 0.2 times the MRHD (based on summed AUCs for tezacaftor and M1 metabolite at maternal oral doses up to 25 mg/kg/day). Lower fetal body weights were observed in rabbits at a maternally toxic dose that produced exposures approximately 1 times the MRHD (at a maternal dose of 50 mg/kg/day). In a pre- and postnatal development (PPND) study in pregnant rats dosed from gestation Day 6 through lactation Day 18, tezacaftor had no adverse developmental effects on pups at an exposure of approximately 1 times the MRHD (based on summed AUCs for tezacaftor and M1 metabolite at a maternal dose of 25 mg/kg/day). Decreased fetal body weights and early developmental delays in pinna detachment, eye opening, and righting reflex occurred at a maternally toxic dose (based on maternal weight loss) that produced exposures approximately 2 times the exposure at the MRHD (based on summed AUCs for tezacaftor and M1 metabolite at a maternal oral dose of 50 mg/kg/day). Placental transfer of tezacaftor was observed in pregnant rats.
Ivacaftor
In an embryo-fetal development study in pregnant rats dosed during the period of organogenesis from gestation Days 7-17, ivacaftor was not teratogenic and did not affect fetal survival at exposures up to 6 times the MRHD (based on summed AUCs for ivacaftor and its metabolites at a maternal oral dose of 200 mg/kg/day). In an embryo-fetal development study in pregnant rabbits dosed during the period of organogenesis from gestation Days 7-19, ivacaftor was not teratogenic and did not affect fetal development or survival at exposures up to 16 times the MRHD (on an ivacaftor AUC basis at maternal oral doses up to 100 mg/kg/day). In a PPND study in pregnant rats dosed from gestation Day 7 through lactation Day 20, ivacaftor had no effects on delivery or growth and development of offspring at exposures up to 4 times the MRHD (based on summed AUCs for ivacaftor and its metabolites at maternal oral doses up to 100 mg/kg/day). Decreased fetal body weights were observed at a maternally toxic dose that produced exposures 6 times the MRHD. Placental transfer of ivacaftor was observed in pregnant rats and rabbits.
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
None.