Get your patient on Tabrecta (Capmatinib)
Tabrecta prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Dosage & administration
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Patient Selection
Select patients for treatment with TABRECTA based on the presence of a mutation that leads to MET exon 14 skipping in tumor or plasma specimens [see Clinical Studies (14)] . If a mutation that leads to MET exon 14 skipping is not detected in a plasma specimen, test tumor tissue if feasible. Information on FDA-approved tests is available at: http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics .
2.2 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of TABRECTA is 400 mg orally twice daily with or without food.
Swallow TABRECTA tablets whole. Do not break, crush or chew the tablets.
If a patient misses or vomits a dose, instruct the patient not to make up the dose, but to take the next dose at its scheduled time.
2.3 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
The recommended dose reductions for the management of adverse reactions are listed in Table 1.
| Dose reduction | Dose and schedule |
| First | 300 mg orally twice daily |
| Second | 200 mg orally twice daily |
Permanently discontinue TABRECTA in patients who are unable to tolerate 200 mg orally twice daily.
The recommended dosage modifications of TABRECTA for adverse reactions are provided in Table 2.
| Abbreviations: ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ILD, interstitial lung disease; ULN, upper limit of normal. Grading according to Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) version 5.0. | ||
| Adverse reaction | Severity | Dosage modification |
| Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)/Pneumonitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] | Any grade | Permanently discontinue TABRECTA. |
| Increased ALT and/or AST without increased total bilirubin [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] | Grade 3 | Withhold TABRECTA until recovery to baseline ALT/AST. If recovered to baseline within 7 days, then resume TABRECTA at the same dose; otherwise resume TABRECTA at a reduced dose. |
| Grade 4 | Permanently discontinue TABRECTA. | |
| Increased ALT and/or AST with increased total bilirubin in the absence of cholestasis or hemolysis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] | ALT and/or AST greater than 3 times ULN with total bilirubin greater than 2 times ULN | Permanently discontinue TABRECTA. |
| Increased total bilirubin without concurrent increased ALT and/or AST [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] | Grade 2 | Withhold TABRECTA until recovery to baseline bilirubin. If recovered to baseline within 7 days, then resume TABRECTA at the same dose; otherwise resume TABRECTA at a reduced dose. |
| Grade 3 | Withhold TABRECTA until recovery to baseline bilirubin. If recovered to baseline within 7 days, then resume TABRECTA at a reduced dose; otherwise permanently discontinue TABRECTA. | |
| Grade 4 | Permanently discontinue TABRECTA. | |
| Increased lipase or amylase [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] | Grade 3 | Withhold TABRECTA until ≤ Grade 2 or baseline. If recovered to baseline or ≤ Grade 2 within 14 days, resume TABRECTA at a reduced dose; otherwise permanently discontinue TABRECTA. |
| Grade 4 | Permanently discontinue TABRECTA. | |
| Pancreatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] | Grade 3 or Grade 4 | Permanently discontinue TABRECTA. |
| Hypersensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] | All Grades | If hypersensitivity is suspected based on clinical judgment, withhold TABRECTA until resolution of the event. Permanently discontinue TABRECTA in patients who develop serious hypersensitivity reactions. |
| Other adverse reactions [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] | Grade 2 | Maintain dose level. If intolerable, consider withholding TABRECTA until resolved, then resume TABRECTA at a reduced dose. |
| Grade 3 | Withhold TABRECTA until resolved, then resume TABRECTA at a reduced dose. | |
| Grade 4 | Permanently discontinue TABRECTA. | |

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Tabrecta prescribing information
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
TABRECTA is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose tumors have a mutation that leads to mesenchymal-epithelial transition (MET) exon 14 skipping as detected by an FDA-approved test.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Patient Selection
Select patients for treatment with TABRECTA based on the presence of a mutation that leads to MET exon 14 skipping in tumor or plasma specimens [see Clinical Studies (14)] . If a mutation that leads to MET exon 14 skipping is not detected in a plasma specimen, test tumor tissue if feasible. Information on FDA-approved tests is available at: http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics .
2.2 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of TABRECTA is 400 mg orally twice daily with or without food.
Swallow TABRECTA tablets whole. Do not break, crush or chew the tablets.
If a patient misses or vomits a dose, instruct the patient not to make up the dose, but to take the next dose at its scheduled time.
2.3 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
The recommended dose reductions for the management of adverse reactions are listed in Table 1.
| Dose reduction | Dose and schedule |
| First | 300 mg orally twice daily |
| Second | 200 mg orally twice daily |
Permanently discontinue TABRECTA in patients who are unable to tolerate 200 mg orally twice daily.
The recommended dosage modifications of TABRECTA for adverse reactions are provided in Table 2.
| Abbreviations: ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ILD, interstitial lung disease; ULN, upper limit of normal. Grading according to Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) version 5.0. | ||
| Adverse reaction | Severity | Dosage modification |
| Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)/Pneumonitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] | Any grade | Permanently discontinue TABRECTA. |
| Increased ALT and/or AST without increased total bilirubin [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] | Grade 3 | Withhold TABRECTA until recovery to baseline ALT/AST. If recovered to baseline within 7 days, then resume TABRECTA at the same dose; otherwise resume TABRECTA at a reduced dose. |
| Grade 4 | Permanently discontinue TABRECTA. | |
| Increased ALT and/or AST with increased total bilirubin in the absence of cholestasis or hemolysis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] | ALT and/or AST greater than 3 times ULN with total bilirubin greater than 2 times ULN | Permanently discontinue TABRECTA. |
| Increased total bilirubin without concurrent increased ALT and/or AST [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] | Grade 2 | Withhold TABRECTA until recovery to baseline bilirubin. If recovered to baseline within 7 days, then resume TABRECTA at the same dose; otherwise resume TABRECTA at a reduced dose. |
| Grade 3 | Withhold TABRECTA until recovery to baseline bilirubin. If recovered to baseline within 7 days, then resume TABRECTA at a reduced dose; otherwise permanently discontinue TABRECTA. | |
| Grade 4 | Permanently discontinue TABRECTA. | |
| Increased lipase or amylase [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] | Grade 3 | Withhold TABRECTA until ≤ Grade 2 or baseline. If recovered to baseline or ≤ Grade 2 within 14 days, resume TABRECTA at a reduced dose; otherwise permanently discontinue TABRECTA. |
| Grade 4 | Permanently discontinue TABRECTA. | |
| Pancreatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] | Grade 3 or Grade 4 | Permanently discontinue TABRECTA. |
| Hypersensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] | All Grades | If hypersensitivity is suspected based on clinical judgment, withhold TABRECTA until resolution of the event. Permanently discontinue TABRECTA in patients who develop serious hypersensitivity reactions. |
| Other adverse reactions [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] | Grade 2 | Maintain dose level. If intolerable, consider withholding TABRECTA until resolved, then resume TABRECTA at a reduced dose. |
| Grade 3 | Withhold TABRECTA until resolved, then resume TABRECTA at a reduced dose. | |
| Grade 4 | Permanently discontinue TABRECTA. | |
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets:
- 150 mg: pale orange brown, ovaloid, curved film-coated with beveled edges, unscored, debossed with ‘DU’ on one side and ‘NVR’ on the other side
- 200 mg: yellow, ovaloid, curved film-coated with beveled edges, unscored, debossed with ‘LO’ on one side and ‘NVR’ on the other side
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Lactation : Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2 )
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings from animal studies and its mechanism of action [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)] , TABRECTA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. There are no available data on TABRECTA use in pregnant women. Oral administration of capmatinib to pregnant rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis resulted in malformations at maternal exposures less than the human exposure based on AUC at the 400 mg twice daily clinical dose ( see Data ). Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In rats, maternal toxicity (reduced body weight gain and food consumption) occurred at 30 mg/kg/day (approximately 1.4 times the human exposure based on AUC at the 400 mg twice daily clinical dose). Fetal effects included reduced fetal weights, irregular/incomplete ossification, and increased incidences of fetal malformations (e.g., abnormal flexure/inward malrotation of hindpaws/forepaws, thinness of forelimbs, lack of/reduced flexion at the humerus/ulna joints, and narrowed or small tongue) at doses of ≥ 10 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.6 times the human exposure based on AUC at the 400 mg twice daily clinical dose).
In rabbits, no maternal effects were detected at doses up to 60 mg/kg/day (approximately 1.5 times the human exposure based on AUC at the 400 mg twice daily clinical dose). Fetal effects included small lung lobe at ≥ 5 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.016 times the human exposure based on AUC at the 400 mg twice daily clinical dose), and reduced fetal weights, irregular/incomplete ossification and increased incidences of fetal malformations (e.g., abnormal flexure/malrotation of hindpaws/forepaws, thinness of forelimbs/hindlimbs, lack of/reduced flexion at the humerus/ulna joints, small lung lobes, narrowed or small tongue) at the dose of 60 mg/kg/day.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of capmatinib or its metabolites in either human or animal milk or its effects on the breastfed child or on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed children, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with TABRECTA and for 1 week after the last dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Based on animal data, TABRECTA can cause malformations at doses less than the human exposure based on AUC at the 400 mg twice daily clinical dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)] .
Pregnancy Testing
Verify pregnancy status for females of reproductive potential prior to starting treatment with TABRECTA.
Contraception
Females
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with TABRECTA and for 1 week after the last dose.
Males
Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with TABRECTA and for 1 week after the last dose.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of TABRECTA in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
In GEOMETRY mono-1, 61% of the 373 patients were 65 years or older and 18% were 75 years or older. No overall differences in the safety or effectiveness were observed between these patients and younger patients.
8.6 Renal Impairment
No dosage adjustment is recommended in patients with mild (baseline creatinine clearance [CLcr] 60 to 89 mL/min by Cockcroft-Gault) or moderate renal impairment (CLcr 30 to 59 mL/min) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] . TABRECTA has not been studied in patients with severe renal impairment (CLcr 15 to 29 mL/min).
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)/Pneumonitis : Monitor for new or worsening pulmonary symptoms indicative of ILD/pneumonitis. Permanently discontinue TABRECTA in patients with ILD/pneumonitis. (2.3 , 5.1 )
- Hepatotoxicity : Monitor liver function tests. Withhold, dose reduce, or permanently discontinue TABRECTA based on severity. (2.3 , 5.2 )
- Pancreatic Toxicity : Monitor amylase and lipase levels. Withhold, dose reduce, or permanently discontinue TABRECTA based on severity. (2.3 , 5.3 )
- Hypersensitivity Reactions : Withhold or permanently discontinue TABRECTA based on severity. (2.3 , 5.4 )
- Risk of Photosensitivity : May cause photosensitivity reactions. Advise patients to limit direct ultraviolet exposure. (5.5 )
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity : Can cause fetal harm. Advise patients of the potential risk to a fetus and to use effective contraception. (5.6 , 8.1 , 8.3 )
5.1 Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)/Pneumonitis
ILD/pneumonitis, which can be fatal, occurred in patients treated with TABRECTA [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] . ILD/pneumonitis occurred in 4.8% of patients treated with TABRECTA in GEOMETRY mono-1, with 1.9% of patients experiencing Grade 3 ILD/pneumonitis and one patient experiencing death (0.3%). Nine patients (2.4%) discontinued TABRECTA due to ILD/pneumonitis. The median time-to-onset of Grade 3 or higher ILD/pneumonitis was 1.8 months (range: 0.2 months to 1.7 years).
Monitor for new or worsening pulmonary symptoms indicative of ILD/pneumonitis (e.g., dyspnea, cough, fever). Immediately withhold TABRECTA in patients with suspected ILD/pneumonitis and permanently discontinue if no other potential causes of ILD/pneumonitis are identified [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)] .
5.2 Hepatotoxicity
Hepatotoxicity occurred in patients treated with TABRECTA [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] . Increased alanine aminotransferase (ALT)/aspartate aminotransferase (AST) occurred in 15% of patients treated with TABRECTA in GEOMETRY mono-1. Grade 3 or 4 increased ALT/AST occurred in 7% of patients. Three patients (0.8%) discontinued TABRECTA due to increased ALT/AST. The median time-to-onset of Grade 3 or higher increased ALT/AST was 1.8 months (range: 0.5 to 46.4 months).
Monitor liver function tests (including ALT, AST, and total bilirubin) prior to the start of TABRECTA, every 2 weeks during the first 3 months of treatment, then once a month or as clinically indicated, with more frequent testing in patients who develop increased transaminases or bilirubin. Based on the severity of the adverse reaction, withhold, dose reduce, or permanently discontinue TABRECTA [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)] .
5.3 Pancreatic Toxicity
Elevations in amylase and lipase levels occurred in patients treated with TABRECTA [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] . Increased amylase/lipase occurred in 14% of patients treated with TABRECTA in GEOMETRY mono-1. Grade 3 and 4 increased amylase/lipase occurred in 7% and 1.9% of patients, respectively. Three patients (0.8%) discontinued TABRECTA due to increased amylase/lipase. The median time-to-onset of Grade 3 or higher increased amylase/lipase was 2 months (range: 0.03 to 31.1 months). Pancreatitis (Grade 3) occurred in one patient (0.3%); TABRECTA was permanently discontinued for this event.
Monitor amylase and lipase at baseline and regularly during treatment with TABRECTA. Based on the severity of the adverse reaction, temporarily withhold, dose reduce, or permanently discontinue TABRECTA [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)] .
5.4 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Serious hypersensitivity reactions occurred in patients treated with TABRECTA in clinical trials other than GEOMETRY mono-1 [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] . Signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity included pyrexia, chills, pruritus, rash, decreased blood pressure, nausea and vomiting. Based on the severity of the adverse reaction, temporarily withhold or permanently discontinue TABRECTA [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)] .
5.5 Risk of Photosensitivity
Based on findings from animal studies, there is a potential risk of photosensitivity reactions with TABRECTA [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.2)] . In GEOMETRY mono-1, it was recommended that patients use precautionary measures against ultraviolet exposure such as use of sunscreen or protective clothing during treatment with TABRECTA. Advise patients to limit direct ultraviolet exposure during treatment with TABRECTA.
5.6 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings from animal studies and its mechanism of action, TABRECTA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Oral administration of capmatinib to pregnant rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis resulted in malformations at exposures less than the human exposure based on area under the curve (AUC) at the 400 mg twice daily clinical dose. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with TABRECTA and for 1 week after the last dose. Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with TABRECTA and for 1 week after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)] .
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- ILD/Pneumonitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Pancreatic Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Hypersensitivity reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
The safety of TABRECTA was evaluated in GEOMETRY mono-1 [see Clinical Studies (14)] . Patients received TABRECTA 400 mg orally twice daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity (N = 373). Among patients who received TABRECTA, 37% were exposed for at least 6 months and 22% were exposed for at least one year.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 53% of patients who received TABRECTA. Serious adverse reactions in ≥ 2% of patients included dyspnea (7%), pneumonia (7%), pleural effusion (4.3%), musculoskeletal pain (3.8%), general physical health deterioration (2.9%), ILD/pneumonitis (2.7%), edema (2.4%), and vomiting (2.4%). Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 0.5% of patients who received TABRECTA, including pneumonitis (0.3%) and death, not otherwise specified (0.3%).
Permanent discontinuation of TABRECTA due to an adverse reaction occurred in 17% of patients. The most frequent adverse reactions (≥ 1%) leading to permanent discontinuation of TABRECTA were ILD/pneumonitis (2.4%), edema (2.4%), fatigue (1.3%), and pneumonia (1.1%).
Dose interruptions due to an adverse reaction occurred in 57% of patients who received TABRECTA. Adverse reactions requiring dosage interruption in > 2% of patients who received TABRECTA included edema, increased blood creatinine, nausea, increased lipase, vomiting, increased ALT, dyspnea, pneumonia, fatigue, increased amylase, increased AST, musculoskeletal pain, abdominal pain, and increased blood bilirubin.
Dose reductions due to an adverse reaction occurred in 26% of patients who received TABRECTA. Adverse reactions requiring dosage reductions in > 2% of patients who received TABRECTA included edema, increased ALT and increased blood creatinine.
The most common adverse reactions (≥ 20%) in patients who received TABRECTA were edema, nausea, musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, vomiting, dyspnea, cough, and decreased appetite.
Table 3 summarizes the adverse reactions in GEOMETRY mono-1.
| a Edema includes edema peripheral, generalized edema, face edema, edema, localized edema, edema genital, eyelid edema, peripheral swelling, scrotal edema, and penile edema. b Musculoskeletal pain includes arthralgia, back pain, bone pain, musculoskeletal chest pain, musculoskeletal pain, myalgia, neck pain, non-cardiac chest pain, pain in extremity, pain in jaw, spinal pain. c Fatigue includes fatigue and asthenia. d Pyrexia includes pyrexia and body temperature increased. e Cough includes cough, upper airway cough syndrome, and productive cough. f Pneumonia includes pneumonia aspiration, pneumonia, pneumonia influenzal, pneumonia bacterial, lower respiratory tract infection, and lung abscess. g Rash includes rash, dermatitis acneiform, rash maculo-papular, eczema, erythema multiforme, rash macular, dermatitis, rash erythematous, rash pustular, dermatitis bullous, and rash vesicular. h Dizziness includes dizziness, vertigo, and vertigo positional. | ||
| Adverse reactions | TABRECTA (N = 373) | |
| Grades 1 to 4 (%) | Grades 3 to 4 (%) | |
| General disorders and administration-site conditions | ||
| Edema a | 59 | 13 |
| Musculoskeletal pain b | 40 | 4.3 |
| Fatigue c | 34 | 8 |
| Pyrexia d | 14 | 0.8 |
| Weight decreased | 11 | 0.5 |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||
| Nausea | 46 | 2.4 |
| Vomiting | 28 | 2.4 |
| Constipation | 19 | 0.8 |
| Diarrhea | 19 | 0.5 |
| Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders | ||
| Dyspnea | 25 | 7 |
| Cough e | 21 | 0.5 |
| Pneumonia f | 13 | 6 |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders | ||
| Decreased appetite | 21 | 1.1 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||
| Rash g | 13 | 0.5 |
| Nervous system disorders | ||
| Dizziness h | 13 | 0.5 |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions occurring in < 10% of patients treated with TABRECTA included pruritus (including allergic pruritus), ILD/pneumonitis, cellulitis, acute kidney injury (including renal failure), urticaria, and acute pancreatitis.
Table 4 summarizes the laboratory abnormalities in GEOMETRY mono-1.
| a The denominator used to calculate the rate varied from 359 to 364 based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one post-treatment value. | ||
| Laboratory abnormalities | TABRECTA a | |
| Grades 1 to 4 (%) | Grades 3 to 4 (%) | |
| Chemistry | ||
| Decreased albumin | 72 | 1.9 |
| Increased creatinine | 65 | 0.5 |
| Increased alanine aminotransferase | 39 | 9 |
| Increased amylase | 34 | 4.7 |
| Increased alkaline phosphatase | 32 | 0.6 |
| Increased gamma-glutamyltransferase | 30 | 6 |
| Increased lipase | 29 | 9 |
| Increased aspartate aminotransferase | 28 | 6 |
| Decreased phosphate | 26 | 4.4 |
| Increased potassium | 25 | 4.1 |
| Decreased sodium | 24 | 6 |
| Decreased glucose | 23 | 0.3 |
| Hematology | ||
| Decreased lymphocytes | 45 | 14 |
| Decreased leukocytes | 25 | 1.7 |
| Decreased hemoglobin | 24 | 2.8 |
Other Clinical Trials Experience
The following adverse reactions have been reported following administration of TABRECTA: hypersensitivity and thrombocytopenia.
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
Strong and Moderate CYP3A Inducers : Avoid concomitant use. (7.1 )
7.1 Effect of Other Drugs on TABRECTA
Strong CYP3A Inhibitors
Coadministration of TABRECTA with a strong CYP3A inhibitor increased capmatinib exposure, which may increase the incidence and severity of adverse reactions of TABRECTA [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] . Closely monitor patients for adverse reactions during coadministration of TABRECTA with strong CYP3A inhibitors.
Strong and Moderate CYP3A Inducers
Coadministration of TABRECTA with a strong CYP3A inducer decreased capmatinib exposure. Coadministration of TABRECTA with a moderate CYP3A inducer may also decrease capmatinib exposure. Decreases in capmatinib exposure may decrease TABRECTA anti-tumor activity [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] . Avoid coadministration of TABRECTA with strong and moderate CYP3A inducers.
7.2 Effect of TABRECTA on Other Drugs
CYP1A2 Substrates
Coadministration of TABRECTA increased the exposure of a CYP1A2 substrate, which may increase the adverse reactions of these substrates [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] . If coadministration is unavoidable between TABRECTA and CYP1A2 substrates where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious adverse reactions, decrease the CYP1A2 substrate dosage in accordance with the approved prescribing information.
P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and Breast Cancer Resistance Protein (BCRP) Substrates
Coadministration of TABRECTA increased the exposure of a P-gp substrate and a BCRP substrate, which may increase the adverse reactions of these substrates [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] . If coadministration is unavoidable between TABRECTA and P-gp or BCRP substrates where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious adverse reactions, decrease the P-gp or BCRP substrate dosage in accordance with the approved prescribing information.
MATE1 and MATE2K Substrates
Coadministration of TABRECTA may increase the exposure of MATE1 and MATE2K substrates, which may increase the adverse reactions of these substrates [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] . If coadministration is unavoidable between TABRECTA and MATE1 or MATE2K substrates where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious adverse reactions, decrease the MATE1 or MATE2K substrate dosage in accordance with the approved prescribing information.
11 DESCRIPTION
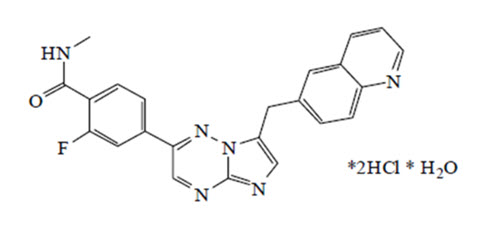
Capmatinib is a kinase inhibitor. The chemical name is 2-Fluoro- N -methyl-4-[7-(quinolin-6-ylmethyl)imidazo[1,2- b ][1,2,4]triazin-2-yl]benzamide—hydrogen chloride—water (1/2/1). The molecular formula for capmatinib dihydrochloride monohydrate is C 23 H 21 Cl 2 FN 6 O 2 . The relative molecular mass is 503.36 g/mol for the dihydrochloride monohydrate salt and 412.43 g/mol for the free base. The chemical structure for capmatinib dihydrochloride monohydrate is shown below:
Capmatinib dihydrochloride monohydrate is a yellow powder with a pKa 1 of 0.9 (calculated) and pKa 2 of 4.5 (experimentally). Capmatinib dihydrochloride monohydrate is slightly soluble in acidic aqueous solutions at pH 1 and 2 and of further decreasing solubility towards neutral condition. The log of the distribution coefficient (n-octanol/acetate buffer pH 4.0) is 1.2.
TABRECTA is supplied for oral use as ovaloid, curved film-coated tablets with beveled edges, unscored containing 150 mg (pale orange brown color) or 200 mg (yellow color) capmatinib (equivalent to 183.00 mg or 244.00 mg respectively of capmatinib dihydrochloride monohydrate). Each tablet strength contains colloidal silicon dioxide; crospovidone; magnesium stearate; mannitol; microcrystalline cellulose; povidone; and sodium lauryl sulfate as inactive ingredients.
The 150 mg tablet coating contains ferric oxide, red; ferric oxide, yellow; ferrosoferric oxide; hypromellose; polyethylene glycol (PEG) 4000; talc; and titanium dioxide. The 200 mg tablet coating contains ferric oxide, yellow; hypromellose; polyethylene glycol (PEG) 4000; talc; and titanium dioxide.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Capmatinib is a kinase inhibitor that targets MET, including the mutant variant produced by exon 14 skipping. MET exon 14 skipping results in a protein with a missing regulatory domain that reduces its negative regulation leading to increased downstream MET signaling. Capmatinib inhibited cancer cell growth driven by a mutant MET variant lacking exon 14 at clinically achievable concentrations and demonstrated anti-tumor activity in murine tumor xenograft models derived from human lung tumors with either a mutation leading to MET exon 14 skipping or MET amplification. Capmatinib inhibited the phosphorylation of MET triggered by binding of hepatocyte growth factor or by MET amplification, as well as MET-mediated phosphorylation of downstream signaling proteins and proliferation and survival of MET-dependent cancer cells.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Exposure-Response
Capmatinib exposure-response relationships and the time course of pharmacodynamics response are unknown.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
No large mean increase in QTc (i.e. > 20 ms) was detected following treatment with TABRECTA at the recommended dosage of 400 mg orally twice daily.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Capmatinib exposure (AUC 0-12h and C max ) increased approximately proportionally over a dose range of 200 mg (0.5 times the recommended dosage) to 400 mg. Capmatinib reached steady-state by day 3 following twice daily dosing, with a mean (% coefficient of variation [%CV]) accumulation ratio of 1.5 (41%).
Absorption
After administration of TABRECTA 400 mg orally in patients with cancer, capmatinib peak plasma concentrations (C max ) were reached in approximately 1 to 2 hours (T max ). The absorption of capmatinib after oral administration is estimated to be greater than 70%.
Effect of Food
A high-fat meal (containing approximately 1000 calories and 50% fat) in healthy subjects increased capmatinib AUC 0-INF by 46% with no change in C max compared to under fasted conditions. A low-fat meal (containing approximately 300 calories and 20% fat) in healthy subjects had no clinically meaningful effect on capmatinib exposure. When capmatinib was administered at 400 mg orally twice daily in cancer patients, exposure (AUC 0-12h ) was similar after administration of capmatinib with food and under fasted conditions.
Distribution
Capmatinib plasma protein binding is 96%, independent of capmatinib concentration. The apparent mean volume of distribution at steady-state is 164 L.
The blood-to-plasma ratio was 1.5, but decreased at higher concentrations to 0.9.
Elimination
The effective elimination half-life of capmatinib is 6.5 hours. The mean (%CV) steady-state apparent clearance of capmatinib is 24 L/hr (82%).
Metabolism
Capmatinib is primarily metabolized by CYP3A4 and aldehyde oxidase.
Excretion
Following a single oral administration of radiolabeled-capmatinib to healthy subjects, 78% of the total radioactivity was recovered in feces with 42% as unchanged and 22% was recovered in urine with negligible as unchanged.
Specific Populations
No clinically significant effects on the pharmacokinetic parameters of capmatinib were identified for the following covariates assessed: age (26 to 90 years), sex, race (White, Asian, Native American, Black, unknown), body weight (35 to 131 kg), mild to moderate renal impairment (baseline CLcr 30 to 89 mL/min by Cockcroft-Gault) and mild, moderate or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh classification). The effect of severe renal impairment (baseline CLcr 15 to 29 mL/min) on capmatinib pharmacokinetics has not been studied.
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies and Model-Informed Approaches
Strong CYP3A Inhibitors: Coadministration with itraconazole (a strong CYP3A inhibitor) increased capmatinib AUC 0-INF by 42% with no change in capmatinib C max .
Strong CYP3A Inducers: Coadministration with rifampicin (a strong CYP3A inducer) decreased capmatinib AUC 0-INF by 67% and decreased C max by 56%.
Moderate CYP3A Inducers: Coadministration with efavirenz (a moderate CYP3A inducer) was predicted to decrease capmatinib AUC 0-12h by 44% and decrease C max by 34%.
Proton Pump Inhibitors: Coadministration with rabeprazole (a proton pump inhibitor) decreased capmatinib AUC 0-INF by 25% and decreased C max by 38%.
Substrates of CYP Enzymes: Coadministration of capmatinib increased caffeine (a CYP1A2 substrate) AUC 0-INF by 134% with no change in its C max . Coadministration of capmatinib had no clinically meaningful effect on exposure of midazolam (a CYP3A substrate).
P-gp Substrates: Coadministration of capmatinib increased digoxin (a P-gp substrate) AUC 0-INF by 47% and increased C max by 74%.
BCRP Substrates: Coadministration of capmatinib increased rosuvastatin (a BCRP substrate) AUC 0-INF by 108% and increased C max by 204%.
In Vitro Studies
Transporter Systems: Capmatinib is a substrate of P-gp, but not a substrate of BCRP or MRP2. Capmatinib reversibly inhibits MATE1 and MATE2K, but does not inhibit OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OCT1, OAT1, OAT3, or MRP2.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies were not conducted with capmatinib. Capmatinib was not mutagenic in an in vitro bacterial reverse mutation assay and did not cause chromosomal aberrations in an in vitro chromosome aberration assay in human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Capmatinib was not clastogenic in an in vivo bone marrow micronucleus test in rats.
Dedicated fertility studies were not conducted with capmatinib. No effects on male and female reproductive organs occurred in general toxicology studies conducted in rats and monkeys at doses resulting in exposures of up to approximately 3.6 times the human exposure based on AUC at the 400 mg twice daily clinical dose.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
In rats, capmatinib administration resulted in vacuolation of white matter of the brain in both 4- and 13-week studies at doses ≥ 2.2 times the human exposure (AUC) at the 400 mg twice daily clinical dose. In some cases, the brain lesions were associated with early death and/or convulsions or tremors. Concentrations of capmatinib in the brain tissue of rats was approximately 9% of the corresponding concentrations in plasma.
In vitro and in vivo assays demonstrated that capmatinib has some potential for photosensitization; however, the no-observed-adverse-effect level for in vivo photosensitization was 30 mg/kg/day (C max of 14000 ng/mL), about 2.9 times the human C max at the 400 mg twice daily clinical dose.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Metastatic NSCLC with a Mutation that Leads to MET Exon 14 Skipping
The efficacy of TABRECTA was evaluated in GEOMETRY mono-1, a multicenter, non-randomized, open-label, multi-cohort study (NCT02414139). Eligible patients were required to have NSCLC with a mutation that leads to MET exon 14 skipping, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) wild-type and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) negative status, and at least one measurable lesion as defined by Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) version 1.1. Patients with symptomatic CNS metastases, clinically significant uncontrolled cardiac disease, or who received treatment with any MET or hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) inhibitor were not eligible for the study.
Out of the first 97 patients enrolled in GEOMETRY mono-1 following the central confirmation of MET exon 14 skipping by a RNA-based clinical trial assay, 78 patient samples were retested with the FDA-approved FoundationOne ® CDx (22 treatment-naïve and 56 previously treated patients) to detect mutations that lead to MET exon 14 skipping. Out of 78 samples retested with FoundationOne ® CDx, 73 samples were evaluable (20 treatment-naïve and 53 previously treated patients), 72 (20 treatment-naïve and 52 previously treated patients) of which were confirmed to have a mutation that leads to MET exon 14 skipping, demonstrating an estimated positive percentage agreement of 99% (72/73) between the clinical trial assay and the FDA-approved assay.
Patients received TABRECTA 400 mg orally twice daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The major efficacy outcome measure was overall response rate (ORR) as determined by a Blinded Independent Review Committee (BIRC) according to RECIST 1.1. An additional efficacy outcome measure was duration of response (DOR) by BIRC.
The efficacy population included 60 treatment-naïve patients and 100 previously treated patients. The median age was 71 years (range: 48 to 90 years); 61% female; 77% White; 25% had Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) Performance Status (PS) 0 and 74% had ECOG PS 1; 61% never smoked; 83% had adenocarcinoma; and 16% had CNS metastases. Among previously treated patients, 81% received one, 16% received two and 3% received three prior lines of systemic therapy. Amongst previously treated patients, 86% received prior platinum-based chemotherapy.
Efficacy results are presented in Table 5.
| Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; NE, not estimable. a Blinded Independent Review Committee (BIRC) review. b Confirmed response. c Clopper and Pearson exact binomial 95% CI. d Based on Kaplan-Meier estimate. | ||
| Efficacy parameters | Treatment-naïve N = 60 | Previously treated N = 100 |
| Overall response rate a,b (95% CI) c | 68% (55, 80) | 44% (34, 54) |
| Complete response | 5% | 0 |
| Partial response | 63% | 44% |
| Duration of response (DOR) a | ||
| Median (months) (95% CI) d | 16.6 (8.4, 22.1) | 9.7 (5.6, 13.0) |
| Patients % with DOR ≥ 12 months | 49% | 36% |
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
| Strength | Description | Tablets per bottle | NDC number |
| 150 mg | Pale orange brown, ovaloid, curved film-coated tablet with beveled edges, unscored, debossed with ‘DU’ on one side and ‘NVR’ on the other side. | 56 | 0078-0709-56 |
| 200 mg | Yellow, ovaloid, curved film-coated tablet with beveled edges, unscored, debossed with ‘LO’ on one side and ‘NVR’ on the other side. | 56 | 0078-0716-56 |
Storage
Dispense in the original package with the desiccant cartridge. Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F), excursions permitted between 15°C and 30°C (59°F and 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Protect from moisture.
Discard any unused TABRECTA remaining after 6 weeks of first opening the bottle.
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Capmatinib is a kinase inhibitor that targets MET, including the mutant variant produced by exon 14 skipping. MET exon 14 skipping results in a protein with a missing regulatory domain that reduces its negative regulation leading to increased downstream MET signaling. Capmatinib inhibited cancer cell growth driven by a mutant MET variant lacking exon 14 at clinically achievable concentrations and demonstrated anti-tumor activity in murine tumor xenograft models derived from human lung tumors with either a mutation leading to MET exon 14 skipping or MET amplification. Capmatinib inhibited the phosphorylation of MET triggered by binding of hepatocyte growth factor or by MET amplification, as well as MET-mediated phosphorylation of downstream signaling proteins and proliferation and survival of MET-dependent cancer cells.