Tadliq
(Tadalafil)Dosage & Administration
By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Tadliq Prescribing Information
TADLIQ is a phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5) inhibitor indicated for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) (WHO Group 1) to improve exercise ability. Studies establishing effectiveness included predominately patients with NYHA Functional Class II – III symptoms and etiologies of idiopathic or heritable PAH (61%) or PAH associated with connective tissue diseases (23%). (
TADLIQ®is indicated for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) (WHO Group 1) to improve exercise ability. Studies establishing effectiveness included predominately patients with NYHA Functional Class II – III symptoms and etiologies of idiopathic or heritable PAH (61%) or PAH associated with connective tissue diseases (23%).
- 40 mg (10 mL) once daily, with or without food. ()
2.1 Pulmonary Arterial HypertensionThe recommended dose of TADLIQ is 40 mg (10 mL) taken once daily with or without food.
- Use with ritonavir requires dosage adjustments. ()
2.4 Dose Adjustment for Use with RitonavirCo-administration of TADLIQ in Patients on RitonavirIn patients receiving ritonavir for at least one week, start TADLIQ at 20 mg (5 mL) once daily. Increase to 40 mg (10 mL) once daily based upon individual tolerability
[see Drug Interactions and Clinical Pharmacology ].Co-administration of Ritonavir in Patients on TADLIQAvoid use of TADLIQ during the initiation of ritonavir. Stop TADLIQ at least 24 hours prior to starting ritonavir. After at least one week following the initiation of ritonavir, resume TADLIQ at 20 mg (5 mL) once daily. Increase to 40 mg (10 mL) once daily based upon individual tolerability
[see Drug Interactions and Clinical Pharmacology ].
Oral Suspension: 20 mg/5 mL; white to off-white opaque suspension with a peppermint flavor.
Renal Impairment (
Mild (creatinine clearance 51 to 80 mL/min) or moderate (creatinine clearance 31 to 50 mL/min): Start dosing at 20 mg (5mL) once daily. Increase to 40 mg (10 mL) once daily based on individual tolerability.
Severe (creatinine clearance <30 mL/min and on hemodialysis): Avoid use of TADLIQ because of increased tadalafil exposure (AUC), limited clinical experience, and the lack of ability to influence clearance by dialysis
For patients with mild or moderate renal impairment, start TADLIQ at 20 mg (5 mL) once daily. Increase the dose to 40 mg (10 mL) once daily based upon individual tolerability
In patients with severe renal impairment, avoid use of TADLIQ because of increased tadalafil exposure (AUC), limited clinical experience, and the lack of ability to influence clearance by dialysis
Over a dose range of 2.5 to 20 mg, tadalafil exposure (AUC) increases proportionally with dose in healthy subjects. In PAH patients administered between 20 and 40 mg of tadalafil, an approximately 50% greater AUC was observed indicating a less than proportional increase in exposure over the entire dose range of 2.5 to 40 mg. During tadalafil 20 and 40 mg once daily dosing, steady-state plasma concentrations were attained within 5 days, and exposure was approximately 30% higher than after a single dose.
The rate and extent of absorption of tadalafil are not influenced by food; thus, TADLIQ may be taken with or without food.
In healthy male elderly subjects (65 years or over) after a 10 mg dose, a lower oral clearance of tadalafil, resulting in 25% higher exposure (AUC) with no effect on Cmaxwas observed relative to that in healthy subjects 19 to 45 years of age.
In clinical pharmacology studies using single-dose tadalafil (5 to 10 mg), tadalafil exposure (AUC) doubled in subjects with mild (creatinine clearance 51 to 80 mL/min) or moderate (creatinine clearance 31 to 50 mL/min) renal impairment. In subjects with end-stage renal disease on hemodialysis, there was a doubling in Cmaxand AUC was 2.7- to 4.1 times as high following single-dose administration of 10 or 20 mg tadalafil, respectively. Exposure to total methylcatechol (unconjugated plus glucuronide) was 2- to 4 times as high in subjects with renal impairment, compared to those with normal renal function. Hemodialysis (performed between 24 and 30 hours post-dose) contributed negligibly to tadalafil or metabolite elimination
In clinical pharmacology studies, tadalafil exposure (AUC) in subjects with mild or moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A or B) was comparable to exposure in healthy subjects when a dose of 10 mg was administered. There are no available data for doses higher than 10 mg of tadalafil in patients with hepatic impairment. Insufficient data are available for subjects with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C)
In male patients with diabetes mellitus after a 10 mg tadalafil dose, exposure (AUC) was reduced approximately 19% and Cmaxwas 5% lower than that observed in healthy subjects. No dose adjustment is warranted.
Pharmacokinetic studies have included subjects from different ethnic groups, and no differences in the typical exposure to tadalafil have been identified. No dose adjustment is warranted.
In healthy female and male subjects following single and multiple-doses of tadalafil, no clinically relevant differences in exposure (AUC and Cmax) were observed. No dose adjustment is warranted.
Tadalafil is a substrate of and predominantly metabolized by CYP3A.
Ketoconazole increased tadalafil exposure relative to the values for tadalafil alone . Although specific interactions have not been studied, other CYP3A inhibitors, such as erythromycin, itraconazole, and grapefruit juice, would likely increase tadalafil exposure.
Ritonavir increased tadalafil 20–mg single-dose exposure relative to the values for tadalafil alone. Ritonavir inhibits and induces CYP3A, the enzyme involved in the metabolism of tadalafil, in a time-dependent manner. The initial inhibitory effect of ritonavir on CYP3A may be mitigated by a more slowly evolving induction effect so that after about 1 week of ritonavir twice daily, the exposure of tadalafil is similar in the presence of and absence of ritonavir
Rifampin (600 mg daily), a CYP3A inducer, reduced tadalafil 10 mg single–dose exposure (AUC) by 88% and Cmaxby 46%, relative to the values for tadalafil 10 mg alone
Bosentan, a substrate of CYP2C9 and CYP3A and a moderate inducer of CYP3A, CYP2C9 and possibly CYP2C19, reduced tadalafil systemic exposure following multiple-dose co-administration . Although specific interactions have not been studied, other CYP3A inducers, such as carbamazepine, phenytoin, and phenobarbital, would likely decrease tadalafil exposure.
Exposure changes of tadalafil following co-administration with other drugs are shown in Figure 2.
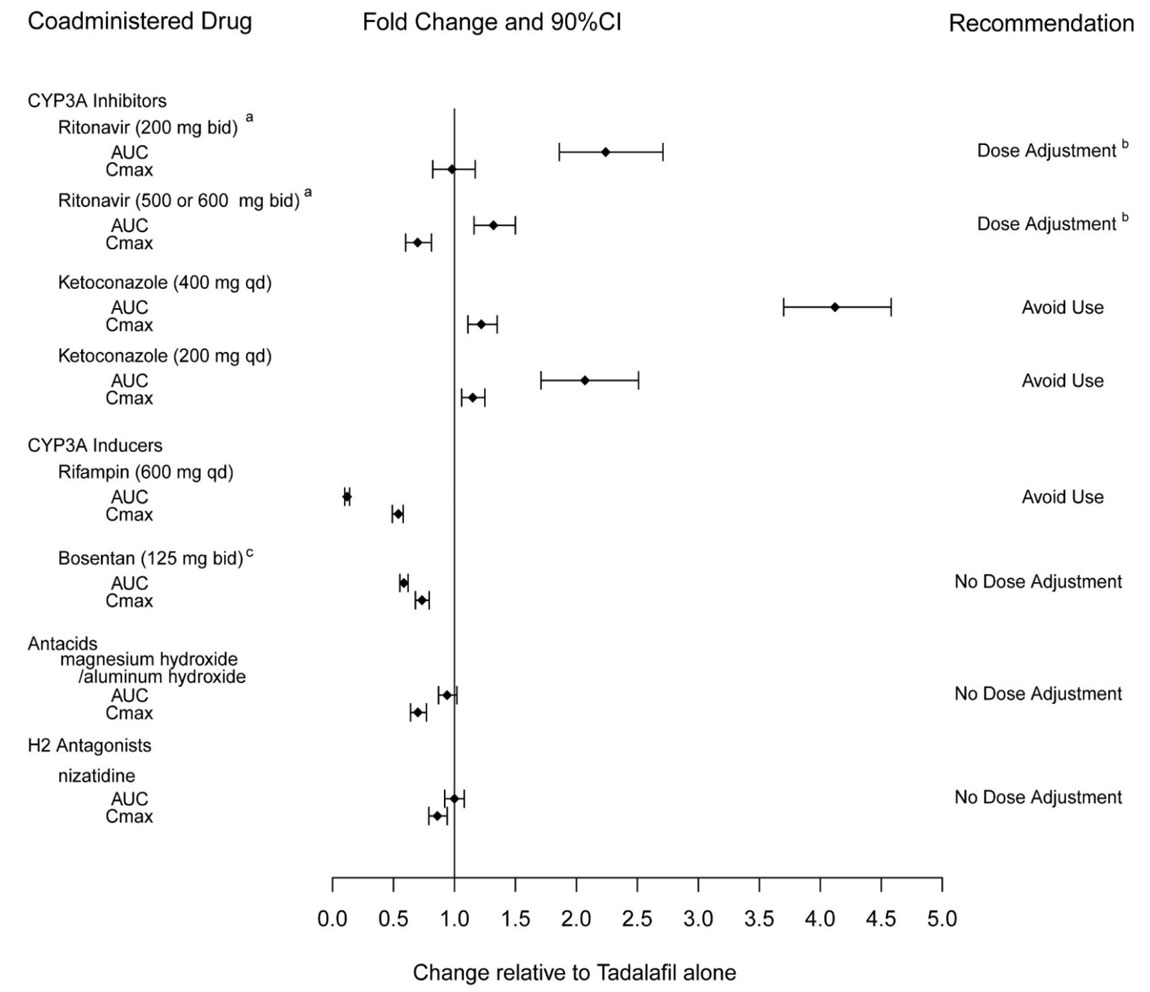 |
| aRitonavir is also a CYP2C9/CYP2C19/CYP2D6 Inhibitor and CYP3A inducer. |
| b [see Dosage and Administration ]. |
| cBosentan is also a CYP2C9/CYP2C19 inducer. |
Figure 2: Impact of Other Drugs on the Pharmacokinetics of Tadalafil |

Tadalafil is not expected to cause clinically significant inhibition or induction of the clearance of drugs metabolized by cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoforms.
Exposure changes of drugs following co-administration with tadalafil are shown in Figure 3.
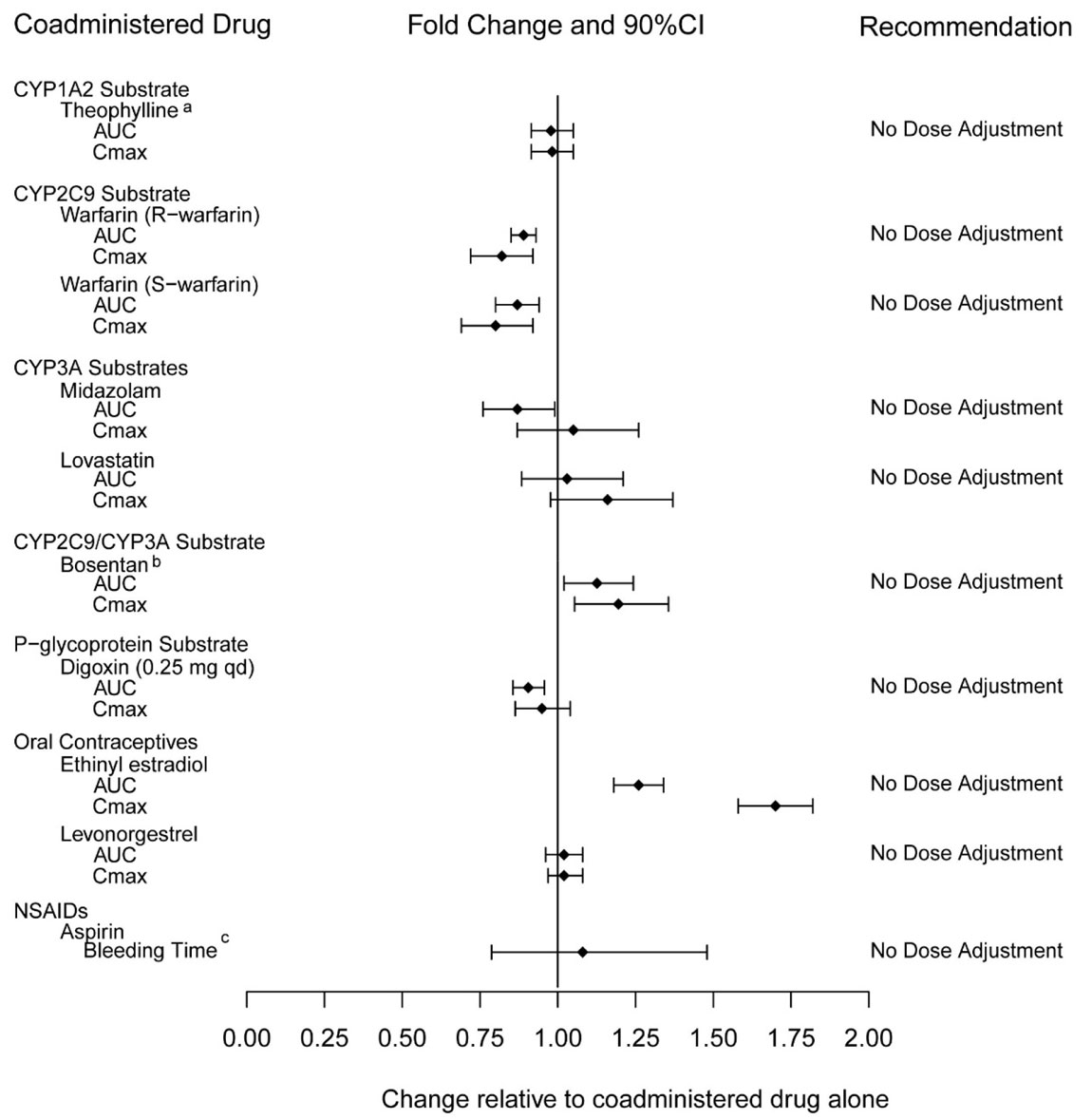 |
| aA small augmentation (increase of 3 beats per minute) in heart rate was observed with theophylline. |
| bTadalafil (40 mg qd) had no clinically significant effect on exposure (AUC and Cmax) of bosentan metabolites. |
| c95% CI |
Figure 3: Impact of Tadalafil on the Pharmacokinetics of Other Drugs |

- Mild or moderate: Start with 20 mg once daily. (,
2.2 Dose Adjustment in Renal ImpairmentMild (creatinine clearance 51 to 80 mL/min) or moderate (creatinine clearance 31 to 50 mL/min): Start dosing at 20 mg (5mL) once daily. Increase to 40 mg (10 mL) once daily based on individual tolerability.
Severe (creatinine clearance <30 mL/min and on hemodialysis): Avoid use of TADLIQ because of increased tadalafil exposure (AUC), limited clinical experience, and the lack of ability to influence clearance by dialysis
[see Use in Specific Populations ].)8.6 Renal ImpairmentFor patients with mild or moderate renal impairment, start TADLIQ at 20 mg (5 mL) once daily. Increase the dose to 40 mg (10 mL) once daily based upon individual tolerability
[see Dosage and Administration and Clinical Pharmacology ].In patients with severe renal impairment, avoid use of TADLIQ because of increased tadalafil exposure (AUC), limited clinical experience, and the lack of ability to influence clearance by dialysis
[see Clinical Pharmacology ]. - Severe: Avoid use of TADLIQ. (,
2.2 Dose Adjustment in Renal ImpairmentMild (creatinine clearance 51 to 80 mL/min) or moderate (creatinine clearance 31 to 50 mL/min): Start dosing at 20 mg (5mL) once daily. Increase to 40 mg (10 mL) once daily based on individual tolerability.
Severe (creatinine clearance <30 mL/min and on hemodialysis): Avoid use of TADLIQ because of increased tadalafil exposure (AUC), limited clinical experience, and the lack of ability to influence clearance by dialysis
[see Use in Specific Populations ].)8.6 Renal ImpairmentFor patients with mild or moderate renal impairment, start TADLIQ at 20 mg (5 mL) once daily. Increase the dose to 40 mg (10 mL) once daily based upon individual tolerability
[see Dosage and Administration and Clinical Pharmacology ].In patients with severe renal impairment, avoid use of TADLIQ because of increased tadalafil exposure (AUC), limited clinical experience, and the lack of ability to influence clearance by dialysis
[see Clinical Pharmacology ].
Hepatic Impairment (
Mild (creatinine clearance 51 to 80 mL/min) or moderate (creatinine clearance 31 to 50 mL/min): Start dosing at 20 mg (5mL) once daily. Increase to 40 mg (10 mL) once daily based on individual tolerability.
Severe (creatinine clearance <30 mL/min and on hemodialysis): Avoid use of TADLIQ because of increased tadalafil exposure (AUC), limited clinical experience, and the lack of ability to influence clearance by dialysis
Because of limited clinical experience in patients with mild to moderate hepatic cirrhosis (Child-Pugh Class A or B), consider a starting dose of TADLIQ 20 mg (5 mL) once daily. Patients with severe hepatic cirrhosis (Child-Pugh Class C) have not been studied, thus avoid use of TADLIQ in such patients
Over a dose range of 2.5 to 20 mg, tadalafil exposure (AUC) increases proportionally with dose in healthy subjects. In PAH patients administered between 20 and 40 mg of tadalafil, an approximately 50% greater AUC was observed indicating a less than proportional increase in exposure over the entire dose range of 2.5 to 40 mg. During tadalafil 20 and 40 mg once daily dosing, steady-state plasma concentrations were attained within 5 days, and exposure was approximately 30% higher than after a single dose.
The rate and extent of absorption of tadalafil are not influenced by food; thus, TADLIQ may be taken with or without food.
In healthy male elderly subjects (65 years or over) after a 10 mg dose, a lower oral clearance of tadalafil, resulting in 25% higher exposure (AUC) with no effect on Cmaxwas observed relative to that in healthy subjects 19 to 45 years of age.
In clinical pharmacology studies using single-dose tadalafil (5 to 10 mg), tadalafil exposure (AUC) doubled in subjects with mild (creatinine clearance 51 to 80 mL/min) or moderate (creatinine clearance 31 to 50 mL/min) renal impairment. In subjects with end-stage renal disease on hemodialysis, there was a doubling in Cmaxand AUC was 2.7- to 4.1 times as high following single-dose administration of 10 or 20 mg tadalafil, respectively. Exposure to total methylcatechol (unconjugated plus glucuronide) was 2- to 4 times as high in subjects with renal impairment, compared to those with normal renal function. Hemodialysis (performed between 24 and 30 hours post-dose) contributed negligibly to tadalafil or metabolite elimination
In clinical pharmacology studies, tadalafil exposure (AUC) in subjects with mild or moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A or B) was comparable to exposure in healthy subjects when a dose of 10 mg was administered. There are no available data for doses higher than 10 mg of tadalafil in patients with hepatic impairment. Insufficient data are available for subjects with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C)
In male patients with diabetes mellitus after a 10 mg tadalafil dose, exposure (AUC) was reduced approximately 19% and Cmaxwas 5% lower than that observed in healthy subjects. No dose adjustment is warranted.
Pharmacokinetic studies have included subjects from different ethnic groups, and no differences in the typical exposure to tadalafil have been identified. No dose adjustment is warranted.
In healthy female and male subjects following single and multiple-doses of tadalafil, no clinically relevant differences in exposure (AUC and Cmax) were observed. No dose adjustment is warranted.
Tadalafil is a substrate of and predominantly metabolized by CYP3A.
Ketoconazole increased tadalafil exposure relative to the values for tadalafil alone . Although specific interactions have not been studied, other CYP3A inhibitors, such as erythromycin, itraconazole, and grapefruit juice, would likely increase tadalafil exposure.
Ritonavir increased tadalafil 20–mg single-dose exposure relative to the values for tadalafil alone. Ritonavir inhibits and induces CYP3A, the enzyme involved in the metabolism of tadalafil, in a time-dependent manner. The initial inhibitory effect of ritonavir on CYP3A may be mitigated by a more slowly evolving induction effect so that after about 1 week of ritonavir twice daily, the exposure of tadalafil is similar in the presence of and absence of ritonavir
Rifampin (600 mg daily), a CYP3A inducer, reduced tadalafil 10 mg single–dose exposure (AUC) by 88% and Cmaxby 46%, relative to the values for tadalafil 10 mg alone
Bosentan, a substrate of CYP2C9 and CYP3A and a moderate inducer of CYP3A, CYP2C9 and possibly CYP2C19, reduced tadalafil systemic exposure following multiple-dose co-administration . Although specific interactions have not been studied, other CYP3A inducers, such as carbamazepine, phenytoin, and phenobarbital, would likely decrease tadalafil exposure.
Exposure changes of tadalafil following co-administration with other drugs are shown in Figure 2.
 |
| aRitonavir is also a CYP2C9/CYP2C19/CYP2D6 Inhibitor and CYP3A inducer. |
| b [see Dosage and Administration ]. |
| cBosentan is also a CYP2C9/CYP2C19 inducer. |
Figure 2: Impact of Other Drugs on the Pharmacokinetics of Tadalafil |

Tadalafil is not expected to cause clinically significant inhibition or induction of the clearance of drugs metabolized by cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoforms.
Exposure changes of drugs following co-administration with tadalafil are shown in Figure 3.
 |
| aA small augmentation (increase of 3 beats per minute) in heart rate was observed with theophylline. |
| bTadalafil (40 mg qd) had no clinically significant effect on exposure (AUC and Cmax) of bosentan metabolites. |
| c95% CI |
Figure 3: Impact of Tadalafil on the Pharmacokinetics of Other Drugs |

- Mild or moderate: Consider starting dose of 20 mg once daily. (,
2.3 Dose Adjustment in Hepatic ImpairmentMild or moderate (Child Pugh Class A or B): Because of limited clinical experience in patients with mild to moderate hepatic cirrhosis, consider a starting dose of 20 mg (5 mL) once per day.
Severe (Child Pugh Class C): Patients with severe hepatic cirrhosis have not been studied. Avoid use of TADLIQ
[see Use in Specific Populations ].)8.7 Hepatic ImpairmentBecause of limited clinical experience in patients with mild to moderate hepatic cirrhosis (Child-Pugh Class A or B), consider a starting dose of TADLIQ 20 mg (5 mL) once daily. Patients with severe hepatic cirrhosis (Child-Pugh Class C) have not been studied, thus avoid use of TADLIQ in such patients
[see Dosage and Administration and Clinical Pharmacology ]. - Severe: Avoid use of TADLIQ. (,
2.3 Dose Adjustment in Hepatic ImpairmentMild or moderate (Child Pugh Class A or B): Because of limited clinical experience in patients with mild to moderate hepatic cirrhosis, consider a starting dose of 20 mg (5 mL) once per day.
Severe (Child Pugh Class C): Patients with severe hepatic cirrhosis have not been studied. Avoid use of TADLIQ
[see Use in Specific Populations ].)8.7 Hepatic ImpairmentBecause of limited clinical experience in patients with mild to moderate hepatic cirrhosis (Child-Pugh Class A or B), consider a starting dose of TADLIQ 20 mg (5 mL) once daily. Patients with severe hepatic cirrhosis (Child-Pugh Class C) have not been studied, thus avoid use of TADLIQ in such patients
[see Dosage and Administration and Clinical Pharmacology ].
- Concomitant organic nitrates ()
4.1 Concomitant Organic NitratesTADLIQ is contraindicated in patients who are using any form of organic nitrate, either regularly or intermittently. Do not use nitrates within 48 hours of the last dose of TADLIQ. TADLIQ potentiates the hypotensive effect of nitrates. This potentiation is thought to result from the combined effects of nitrates and TADLIQ on the nitric oxide/cGMP pathway
[see Clinical Pharmacology ]. - Concomitant Guanylate Cyclase (GC) Stimulators ()
4.2 Concomitant Guanylate Cyclase (GC) StimulatorsCoadministration of GC stimulators such as riociguat with TADLIQ is contraindicated. TADLIQ may potentiate the hypotensive effects of GC stimulators.
- History of known serious hypersensitivity reaction to TADLIQ, ADCIRCA® or CIALIS® ()
4.3 Hypersensitivity ReactionsTADLIQ is contraindicated in patients with a known serious hypersensitivity to tadalafil (TADLIQ, ADCIRCA®or CIALIS®). Hypersensitivity reactions have been reported, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome and exfoliative dermatitis
[see Adverse Reactions ].
- Hypotension: Carefully consider whether patients with certain underlying cardiovascular disease could be adversely affected by vasodilatory effects of TADLIQ. Not recommended in patients with pulmonary veno-occlusive disease. (,
5.1 HypotensionTADLIQ has vasodilatory properties that may result in transient decreases in blood pressure. Prior to prescribing TADLIQ, carefully consider whether patients with underlying cardiovascular disease could be affected adversely by such vasodilatory effects. Patients with preexisting hypotension, with autonomic dysfunction, with left ventricular outflow obstruction, may be particularly sensitive to the actions of vasodilators.
)5.2 Worsening Pulmonary Vascular Occlusive DiseasePulmonary vasodilators may significantly worsen the cardiovascular status of patients with pulmonary veno-occlusive disease (PVOD). Since there are no clinical data on administration of TADLIQ to patients with veno-occlusive disease, administration of TADLIQ to such patients is not recommended. Should signs of pulmonary edema occur when TADLIQ is administered, the possibility of associated PVOD should be considered.
- Effects on the eye: Sudden loss of vision could be a sign of non-arteritic ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION) and may be permanent. ()
5.3 Visual LossWhen used to treat erectile dysfunction, non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION), a cause of decreased vision including permanent loss of vision, has been reported postmarketing in temporal association with the use of phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE-5) inhibitors, including tadalafil. Most, but not all, of these patients had underlying anatomic or vascular risk factors for development of NAION, including but not necessarily limited to: low cup to disc ratio (“crowded disc”), age over 50, diabetes, hypertension, coronary artery disease, hyperlipidemia, and smoking. Based on published literature, the annual incidence of NAION is 2.5-11.8 cases per 100,000 in males aged ≥50 in the general population. An observational case-crossover study evaluated the risk of NAION when PDE5 inhibitor use, as a class, typical of erectile dysfunction treatment, occurred immediately before NAION onset (within 5 half-lives), compared to PDE5 inhibitor use in a prior time period. The results suggest an approximate doubling in the risk of NAION. Other risk factors for NAION, such as the presence of “crowded” optic disc, may have contributed to the occurrence of NAION in these studies.
Patients with known hereditary degenerative retinal disorders, including retinitis pigmentosa, were not included in the clinical trials, and use in these patients is not recommended.
- Hearing impairment: Cases of sudden decrease or loss of hearing have been reported with tadalafil. ()
5.4 Hearing ImpairmentCases of sudden decrease or loss of hearing, which may be accompanied by tinnitus and dizziness, have been reported in patients taking tadalafil. It is not possible to determine whether these events are related directly to the use of PDE5 inhibitors or to other factors
[see Adverse Reactions ]. - Concomitant PDE5 inhibitors: Avoid use with CIALIS, ADCIRCA or other PDE5 inhibitors. ()
5.5 Combination with Other PDE5 InhibitorsTadalafil is also marketed for erectile dysfunction. The safety and efficacy of taking TADLIQ together with another PDE5 inhibitor has not been studied. Inform patients taking TADLIQ not to take other PDE5 inhibitors.
- Prolonged erection: Advise patients to seek emergency treatment if an erection lasts >4 hours. ()
5.6 Prolonged ErectionThere have been reports of prolonged erections greater than 4 hours and priapism (painful erections greater than 6 hours in duration) for this class of compounds. Patients with conditions that might predispose them to priapism (such as sickle cell anemia, multiple myeloma, or leukemia), or in patients with anatomical deformation of the penis (such as angulation, cavernosal fibrosis, or Peyronie's disease) are at an increased risk. Priapism, if not treated promptly, can result in irreversible damage to the erectile tissue. Patients who have an erection lasting greater than 4 hours, whether painful or not, should seek emergency medical attention.