Get your patient on Tafinlar + Mekinist (Dabrafenib)
Tafinlar + Mekinist patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- The recommended dosage of TAFINLAR in adult patients is 150 mg (two 75 mg capsules) orally twice daily. The recommended dosage for TAFINLAR in pediatric patients is based on body weight. Take TAFINLAR at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal. (2 )
Patient Selection
Melanoma
- Confirm the presence of BRAF V600E mutation in tumor specimens prior to initiation of treatment with TAFINLAR as a single agent [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Clinical Studies (14.1)] .
- Confirm the presence of BRAF V600E or V600K mutation in tumor specimens prior to initiation of treatment with TAFINLAR and trametinib [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Clinical Studies (14.2, 14.3)] .
- Information on FDA-approved tests for the detection of BRAF V600 mutations in melanoma is available at: http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics .
NSCLC
- Confirm the presence of BRAF V600E mutation in tumor specimens prior to initiation of treatment with TAFINLAR and trametinib [see Clinical Studies (14.4)] .
- Information on FDA-approved tests for the detection of BRAF V600E mutations in NSCLC is available at: http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics .
ATC
- Confirm the presence of BRAF V600E mutation in tumor specimens prior to initiation of treatment with TAFINLAR and trametinib [see Clinical Studies (14.5)] .
- Information on FDA-approved tests for the detection of BRAF V600E mutations in ATC is available at: http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics .
Solid Tumors
- Confirm the presence of BRAF V600E mutation in tumor specimens prior to initiation of treatment with TAFINLAR and trametinib [see Clinical Studies (14.6)] . An FDA-approved test for the detection of BRAF V600E mutation in solid tumors other than melanoma and NSCLC is not currently available.
Low-Grade Glioma
- Confirm the presence of BRAF V600E mutation in tumor specimens prior to initiation of treatment with TAFINLAR and trametinib [see Clinical Studies (14.7)] . An FDA-approved test for the detection of BRAF V600E mutation in LGG is not currently available.
Recommended Dosage
TAFINLAR Capsules
Adult Patients
The recommended dosage for TAFINLAR capsules in adult patients is 150 mg taken orally twice daily [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)] .
Pediatric Patients
The recommended dosage for TAFINLAR capsules in pediatric patients who weigh at least 26 kg is based on body weight (Table 1) [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)] . A recommended dosage of TAFINLAR capsules has not been established in patients who weigh less than 26 kg.
| Body Weight | Recommended Dosage |
| 26 to 37 kg | 75 mg orally twice daily |
| 38 to 50 kg | 100 mg orally twice daily |
| 51 kg or greater | 150 mg orally twice daily |
TAFINLAR Tablets for Oral Suspension
Adult and Pediatric Patients
The recommended dosage for TAFINLAR tablets for oral suspension for adult and pediatric patients is based on body weight (Table 2) [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)] .
| Body Weight | Recommended Dosage |
| 8 to 9 kg | 20 mg twice daily |
| 10 to 13 kg | 30 mg twice daily |
| 14 to 17 kg | 40 mg twice daily |
| 18 to 21 kg | 50 mg twice daily |
| 22 to 25 kg | 60 mg twice daily |
| 26 to 29 kg | 70 mg twice daily |
| 30 to 33 kg | 80 mg twice daily |
| 34 to 37 kg | 90 mg twice daily |
| 38 to 41 kg | 100 mg twice daily |
| 42 to 45 kg | 110 mg twice daily |
| 46 to 50 kg | 130 mg twice daily |
| ≥ 51 kg | 150 mg twice daily |
Duration of Treatment
- The recommended duration of treatment for patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma or solid tumors, metastatic NSCLC, or locally advanced or metastatic anaplastic thyroid cancer is until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
- The recommended duration of treatment in the adjuvant melanoma setting is until disease recurrence or unacceptable toxicity for up to 1 year.
- The recommended duration of treatment for pediatric patients with LGG is until disease progression or until unacceptable toxicity.
Combination Therapy with Trametinib
Refer to the trametinib prescribing information for recommended trametinib dosing information.
Administration
- Take TAFINLAR at the same time each day, approximately 12 hours apart.
- Do not take a missed dose of TAFINLAR within 6 hours of the next dose of TAFINLAR.
- If vomiting occurs after TAFINLAR administration, do not take an additional dose. Take the next dose at its scheduled time.
TAFINLAR Capsules
- Take TAFINLAR capsules on an empty stomach (at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] .
- Do not open, crush, or break TAFINLAR capsules.
TAFINLAR Tablets for Oral Suspension
- Prior to use of the oral suspension, instruct caregivers (and if appropriate, patients) on proper dosing and administration of TAFINLAR tablets for oral suspension.
- Take the oral suspension on an empty stomach (at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal). Breastfeeding and/or baby formula may be given on demand if a pediatric patient is unable to tolerate the fasting conditions [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] .
- Do not swallow whole, chew or crush TAFINLAR tablets for oral suspension.
Preparation and Administration
- Prepare the oral suspension with approximately 5 mL of water for 1 to 4 tablets, and approximately 10 mL of water for 5 to 15 tablets in the provided dosing cup.
- Gently stir the water and prescribed number of tablets with the handle of a teaspoon until the tablets are fully dissolved. It may take at least 3 minutes to fully dissolve the tablets. Once the tablets are dissolved, the oral suspension will be cloudy white.
- Administer the oral suspension immediately after preparation from a dosing cup, oral syringe or feeding tube (10 French gauge or larger for 1 to 3 tablets; 12 French gauge or larger for 4 to 15 tablets).
- Discard the oral suspension if not administered within 30 minutes after preparation.
Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
Dose reductions for adverse reactions associated with TAFINLAR are presented in Tables 3 and 4.
| Recommended Dosage | 75 mg orally twice daily | 100 mg orally twice daily | 150 mg orally twice daily |
| First dose reduction | 50 mg orally twice daily | 75 mg orally twice daily | 100 mg orally twice daily |
| Second dose reduction | N/A | 50 mg orally twice daily | 75 mg orally twice daily |
| Third dose reduction | N/A | N/A | 50 mg orally twice daily |
| Subsequent modification | Permanently discontinue if unable to tolerate TAFINLAR capsules 50 mg orally twice daily. | ||
| Body Weight (Recommended dosage) | First Dose Reduction | Second Dose Reduction | Third Dose Reduction |
| Tablets for oral suspension twice daily | |||
| 8 to 9 kg (20 mg twice daily) | 10 mg twice daily | N/A | N/A |
| 10 to 13 kg (30 mg twice daily) | 20 mg twice daily | 10 mg twice daily | N/A |
| 14 to 17 kg (40 mg twice daily) | 30 mg twice daily | 20 mg twice daily | 10 mg twice daily |
| 18 to 21 kg (50 mg twice daily) | 30 mg twice daily | 20 mg twice daily | 10 mg twice daily |
| 22 to 25 kg (60 mg twice daily) | 40 mg twice daily | 30 mg twice daily | 20 mg twice daily |
| 26 to 29 kg (70 mg twice daily) | 50 mg twice daily | 40 mg twice daily | 20 mg twice daily |
| 30 to 33 kg (80 mg twice daily) | 50 mg twice daily | 40 mg twice daily | 30 mg twice daily |
| 34 to 37 kg (90 mg twice daily) | 60 mg twice daily | 50 mg twice daily | 30 mg twice daily |
| 38 to 41 kg (100 mg twice daily) | 70 mg twice daily | 50 mg twice daily | 30 mg twice daily |
| 42 to 45 kg (110 mg twice daily) | 70 mg twice daily | 60 mg twice daily | 40 mg twice daily |
| 46 to 50 kg (130 mg twice daily) | 90 mg twice daily | 70 mg twice daily | 40 mg twice daily |
| ≥ 51 kg (150 mg twice daily) | 100 mg twice daily | 80 mg twice daily | 50 mg twice daily |
Dosage modifications for adverse reactions associated with TAFINLAR are presented in Table 5.
| a National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (NCI CTCAE) version 4.0. b See Tables 3 and 4 for recommended dose reductions of TAFINLAR. c Dose modifications are not recommended for TAFINLAR when administered with trametinib for the following adverse reactions of trametinib: retinal vein occlusion (RVO), retinal pigment epithelial detachment (RPED), interstitial lung disease/pneumonitis, and uncomplicated venous thromboembolism. Dose modification of TAFINLAR is not required for new primary cutaneous malignancies. | |
| Severity of Adverse Reaction a | Dosage Modification for TAFINLAR b |
| New Primary Malignancies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] | |
| Non-Cutaneous RAS Mutation-positive Malignancies | Permanently discontinue TAFINLAR. |
| Cardiomyopathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] | |
| Withhold TAFINLAR until LVEF improves to at least the institutional LLN and absolute decrease to less than or equal to 10% compared to baseline, then resume TAFINLAR at same dose. |
| Uveitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)] | |
| For mild or moderate uveitis that does not respond to ocular therapy, or for severe uveitis, withhold TAFINLAR for up to 6 weeks.
|
| Febrile Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)] | |
| Withhold TAFINLAR until fever resolves, then resume TAFINLAR at same or lower dose. |
|
|
| Skin Toxicities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)] | |
| Withhold TAFINLAR for up to 3 weeks.
|
| Permanently discontinue TAFINLAR. |
| Other Adverse Reactions c , including Hemorrhage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] | |
| Withhold TAFINLAR.
|
|
|
| Permanently discontinue TAFINLAR. |
Refer to the trametinib prescribing information for dose modifications for adverse reactions associated with trametinib.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Tafinlar + Mekinist prescribing information
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
TAFINLAR is a kinase inhibitor indicated as a single agent for the treatment of patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma with BRAF V600E mutation as detected by an FDA-approved test. (1.1 , 2.1 )
TAFINLAR is indicated, in combination with trametinib , for:
- the treatment of patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma with BRAF V600E or V600K mutations as detected by an FDA-approved test. (1.2 , 2.1 )
- the adjuvant treatment of patients with melanoma with BRAF V600E or V600K mutations, as detected by an FDA-approved test, and involvement of lymph node(s), following complete resection. (1.3 , 2.1 )
- the treatment of patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with BRAF V600E mutation as detected by an FDA-approved test. (1.4 , 2.1 )
- the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic anaplastic thyroid cancer (ATC) with BRAF V600E mutation, as detected by an FDA-approved test, and with no satisfactory locoregional treatment options. (1.5 , 2.1 )
- the treatment of adult and pediatric patients 1 year of age and older with unresectable or metastatic solid tumors with BRAF V600E mutation who have progressed following prior treatment and have no satisfactory alternative treatment options. This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on overall response rate (ORR) and duration of response (DoR). Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial(s). (1.6 , 2.1 )
- the treatment of pediatric patients 1 year of age and older with low-grade glioma (LGG) with a BRAF V600E mutation who require systemic therapy. (1.7 , 2.1 )
Limitations of Use : TAFINLAR is not indicated for treatment of patients with colorectal cancer because of known intrinsic resistance to BRAF inhibition. (1.8 , 12.1 ) TAFINLAR is not indicated for treatment of patients with wild-type BRAF solid tumors. (5.2 )
BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Unresectable or Metastatic Melanoma
TAFINLAR ® is indicated as a single agent for the treatment of patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma with BRAF V600E mutation as detected by an FDA-approved test.
BRAF V600E or V600K Mutation-Positive Unresectable or Metastatic Melanoma
TAFINLAR is indicated, in combination with trametinib, for the treatment of patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma with BRAF V600E or V600K mutations, as detected by an FDA-approved test [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)] .
Adjuvant Treatment of BRAF V600E or V600K Mutation-Positive Melanoma
TAFINLAR is indicated, in combination with trametinib, for the adjuvant treatment of patients with melanoma with BRAF V600E or V600K mutations, as detected by an FDA-approved test, and involvement of lymph node(s), following complete resection [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)] .
BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Metastatic NSCLC
TAFINLAR is indicated, in combination with trametinib, for the treatment of patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with BRAF V600E mutation as detected by an FDA-approved test [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)] .
BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Locally Advanced or Metastatic Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer
TAFINLAR is indicated, in combination with trametinib, for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic anaplastic thyroid cancer (ATC) with BRAF V600E mutation, as detected by an FDA-approved test, and with no satisfactory locoregional treatment options [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)] .
BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Unresectable or Metastatic Solid Tumors
TAFINLAR is indicated, in combination with trametinib, for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients 1 year of age and older with unresectable or metastatic solid tumors with BRAF V600E mutation who have progressed following prior treatment and have no satisfactory alternative treatment options [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)] . This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on overall response rate (ORR) and duration of response (DoR) [see Clinical Studies (14.6)] . Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial(s).
BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Low-Grade Glioma
TAFINLAR is indicated, in combination with trametinib, for the treatment of pediatric patients 1 year of age and older with low-grade glioma (LGG) with a BRAF V600E mutation who require systemic therapy [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)] .
Limitations of Use
- TAFINLAR is not indicated for treatment of patients with colorectal cancer because of known intrinsic resistance to BRAF inhibition [see Indications and Usage (1.6), Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)] .
- TAFINLAR is not indicated for treatment of patients with wild-type BRAF solid tumors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] .
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- The recommended dosage of TAFINLAR in adult patients is 150 mg (two 75 mg capsules) orally twice daily. The recommended dosage for TAFINLAR in pediatric patients is based on body weight. Take TAFINLAR at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal. (2 )
Patient Selection
Melanoma
- Confirm the presence of BRAF V600E mutation in tumor specimens prior to initiation of treatment with TAFINLAR as a single agent [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Clinical Studies (14.1)] .
- Confirm the presence of BRAF V600E or V600K mutation in tumor specimens prior to initiation of treatment with TAFINLAR and trametinib [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Clinical Studies (14.2, 14.3)] .
- Information on FDA-approved tests for the detection of BRAF V600 mutations in melanoma is available at: http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics .
NSCLC
- Confirm the presence of BRAF V600E mutation in tumor specimens prior to initiation of treatment with TAFINLAR and trametinib [see Clinical Studies (14.4)] .
- Information on FDA-approved tests for the detection of BRAF V600E mutations in NSCLC is available at: http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics .
ATC
- Confirm the presence of BRAF V600E mutation in tumor specimens prior to initiation of treatment with TAFINLAR and trametinib [see Clinical Studies (14.5)] .
- Information on FDA-approved tests for the detection of BRAF V600E mutations in ATC is available at: http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics .
Solid Tumors
- Confirm the presence of BRAF V600E mutation in tumor specimens prior to initiation of treatment with TAFINLAR and trametinib [see Clinical Studies (14.6)] . An FDA-approved test for the detection of BRAF V600E mutation in solid tumors other than melanoma and NSCLC is not currently available.
Low-Grade Glioma
- Confirm the presence of BRAF V600E mutation in tumor specimens prior to initiation of treatment with TAFINLAR and trametinib [see Clinical Studies (14.7)] . An FDA-approved test for the detection of BRAF V600E mutation in LGG is not currently available.
Recommended Dosage
TAFINLAR Capsules
Adult Patients
The recommended dosage for TAFINLAR capsules in adult patients is 150 mg taken orally twice daily [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)] .
Pediatric Patients
The recommended dosage for TAFINLAR capsules in pediatric patients who weigh at least 26 kg is based on body weight (Table 1) [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)] . A recommended dosage of TAFINLAR capsules has not been established in patients who weigh less than 26 kg.
| Body Weight | Recommended Dosage |
| 26 to 37 kg | 75 mg orally twice daily |
| 38 to 50 kg | 100 mg orally twice daily |
| 51 kg or greater | 150 mg orally twice daily |
TAFINLAR Tablets for Oral Suspension
Adult and Pediatric Patients
The recommended dosage for TAFINLAR tablets for oral suspension for adult and pediatric patients is based on body weight (Table 2) [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)] .
| Body Weight | Recommended Dosage |
| 8 to 9 kg | 20 mg twice daily |
| 10 to 13 kg | 30 mg twice daily |
| 14 to 17 kg | 40 mg twice daily |
| 18 to 21 kg | 50 mg twice daily |
| 22 to 25 kg | 60 mg twice daily |
| 26 to 29 kg | 70 mg twice daily |
| 30 to 33 kg | 80 mg twice daily |
| 34 to 37 kg | 90 mg twice daily |
| 38 to 41 kg | 100 mg twice daily |
| 42 to 45 kg | 110 mg twice daily |
| 46 to 50 kg | 130 mg twice daily |
| ≥ 51 kg | 150 mg twice daily |
Duration of Treatment
- The recommended duration of treatment for patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma or solid tumors, metastatic NSCLC, or locally advanced or metastatic anaplastic thyroid cancer is until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
- The recommended duration of treatment in the adjuvant melanoma setting is until disease recurrence or unacceptable toxicity for up to 1 year.
- The recommended duration of treatment for pediatric patients with LGG is until disease progression or until unacceptable toxicity.
Combination Therapy with Trametinib
Refer to the trametinib prescribing information for recommended trametinib dosing information.
Administration
- Take TAFINLAR at the same time each day, approximately 12 hours apart.
- Do not take a missed dose of TAFINLAR within 6 hours of the next dose of TAFINLAR.
- If vomiting occurs after TAFINLAR administration, do not take an additional dose. Take the next dose at its scheduled time.
TAFINLAR Capsules
- Take TAFINLAR capsules on an empty stomach (at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] .
- Do not open, crush, or break TAFINLAR capsules.
TAFINLAR Tablets for Oral Suspension
- Prior to use of the oral suspension, instruct caregivers (and if appropriate, patients) on proper dosing and administration of TAFINLAR tablets for oral suspension.
- Take the oral suspension on an empty stomach (at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal). Breastfeeding and/or baby formula may be given on demand if a pediatric patient is unable to tolerate the fasting conditions [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] .
- Do not swallow whole, chew or crush TAFINLAR tablets for oral suspension.
Preparation and Administration
- Prepare the oral suspension with approximately 5 mL of water for 1 to 4 tablets, and approximately 10 mL of water for 5 to 15 tablets in the provided dosing cup.
- Gently stir the water and prescribed number of tablets with the handle of a teaspoon until the tablets are fully dissolved. It may take at least 3 minutes to fully dissolve the tablets. Once the tablets are dissolved, the oral suspension will be cloudy white.
- Administer the oral suspension immediately after preparation from a dosing cup, oral syringe or feeding tube (10 French gauge or larger for 1 to 3 tablets; 12 French gauge or larger for 4 to 15 tablets).
- Discard the oral suspension if not administered within 30 minutes after preparation.
Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
Dose reductions for adverse reactions associated with TAFINLAR are presented in Tables 3 and 4.
| Recommended Dosage | 75 mg orally twice daily | 100 mg orally twice daily | 150 mg orally twice daily |
| First dose reduction | 50 mg orally twice daily | 75 mg orally twice daily | 100 mg orally twice daily |
| Second dose reduction | N/A | 50 mg orally twice daily | 75 mg orally twice daily |
| Third dose reduction | N/A | N/A | 50 mg orally twice daily |
| Subsequent modification | Permanently discontinue if unable to tolerate TAFINLAR capsules 50 mg orally twice daily. | ||
| Body Weight (Recommended dosage) | First Dose Reduction | Second Dose Reduction | Third Dose Reduction |
| Tablets for oral suspension twice daily | |||
| 8 to 9 kg (20 mg twice daily) | 10 mg twice daily | N/A | N/A |
| 10 to 13 kg (30 mg twice daily) | 20 mg twice daily | 10 mg twice daily | N/A |
| 14 to 17 kg (40 mg twice daily) | 30 mg twice daily | 20 mg twice daily | 10 mg twice daily |
| 18 to 21 kg (50 mg twice daily) | 30 mg twice daily | 20 mg twice daily | 10 mg twice daily |
| 22 to 25 kg (60 mg twice daily) | 40 mg twice daily | 30 mg twice daily | 20 mg twice daily |
| 26 to 29 kg (70 mg twice daily) | 50 mg twice daily | 40 mg twice daily | 20 mg twice daily |
| 30 to 33 kg (80 mg twice daily) | 50 mg twice daily | 40 mg twice daily | 30 mg twice daily |
| 34 to 37 kg (90 mg twice daily) | 60 mg twice daily | 50 mg twice daily | 30 mg twice daily |
| 38 to 41 kg (100 mg twice daily) | 70 mg twice daily | 50 mg twice daily | 30 mg twice daily |
| 42 to 45 kg (110 mg twice daily) | 70 mg twice daily | 60 mg twice daily | 40 mg twice daily |
| 46 to 50 kg (130 mg twice daily) | 90 mg twice daily | 70 mg twice daily | 40 mg twice daily |
| ≥ 51 kg (150 mg twice daily) | 100 mg twice daily | 80 mg twice daily | 50 mg twice daily |
Dosage modifications for adverse reactions associated with TAFINLAR are presented in Table 5.
| a National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (NCI CTCAE) version 4.0. b See Tables 3 and 4 for recommended dose reductions of TAFINLAR. c Dose modifications are not recommended for TAFINLAR when administered with trametinib for the following adverse reactions of trametinib: retinal vein occlusion (RVO), retinal pigment epithelial detachment (RPED), interstitial lung disease/pneumonitis, and uncomplicated venous thromboembolism. Dose modification of TAFINLAR is not required for new primary cutaneous malignancies. | |
| Severity of Adverse Reaction a | Dosage Modification for TAFINLAR b |
| New Primary Malignancies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] | |
| Non-Cutaneous RAS Mutation-positive Malignancies | Permanently discontinue TAFINLAR. |
| Cardiomyopathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] | |
| Withhold TAFINLAR until LVEF improves to at least the institutional LLN and absolute decrease to less than or equal to 10% compared to baseline, then resume TAFINLAR at same dose. |
| Uveitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)] | |
| For mild or moderate uveitis that does not respond to ocular therapy, or for severe uveitis, withhold TAFINLAR for up to 6 weeks.
|
| Febrile Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)] | |
| Withhold TAFINLAR until fever resolves, then resume TAFINLAR at same or lower dose. |
|
|
| Skin Toxicities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)] | |
| Withhold TAFINLAR for up to 3 weeks.
|
| Permanently discontinue TAFINLAR. |
| Other Adverse Reactions c , including Hemorrhage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] | |
| Withhold TAFINLAR.
|
|
|
| Permanently discontinue TAFINLAR. |
Refer to the trametinib prescribing information for dose modifications for adverse reactions associated with trametinib.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
TAFINLAR Capsules:
- 50 mg: Dark red capsule imprinted with ‘GS TEW’ and ‘50 mg’.
- 75 mg: Dark pink capsule imprinted with ‘GS LHF’ and ‘75 mg’.
TAFINLAR Tablets for Oral Suspension:
- 10 mg: White to slightly yellow, round, biconvex 6 mm tablet debossed with “D” on one side and “NVR” on the other, contains berry flavor.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings from animal reproduction studies and its mechanism of action [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)] , TAFINLAR can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. There is insufficient data in pregnant women exposed to TAFINLAR to assess the risks. Dabrafenib was teratogenic and embryotoxic in rats at doses three times greater than the human exposure at the recommended adult clinical dose of 150 mg twice daily (see Data) . Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In a combined female fertility and embryo-fetal development study in rats conducted during the period of organogenesis, developmental toxicity consisted of embryo-lethality, ventricular septal defects, and variation in thymic shape at a dabrafenib dose of 300 mg/kg/day [approximately three times the human exposure at the recommended adult dose based on area under the curve (AUC)]. At doses of 20 mg/kg/day or greater (equivalent to the human exposure at the recommended adult dose based on AUC), rats demonstrated delays in skeletal development and reduced fetal body weight.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of dabrafenib in human milk, or the effects of dabrafenib on the breastfed child or on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed children, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with TAFINLAR and for 2 weeks following the last dose.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Pregnancy Testing
Verify pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential prior to initiating TAFINLAR.
Contraception
Based on data from animal studies and its mechanism of action, TAFINLAR can cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1 )].
Females
Advise female patients of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with TAFINLAR and for 2 weeks after the last dose. Counsel patients to use a non-hormonal method of contraception since TAFINLAR can render hormonal contraceptives ineffective [see Drug Interactions (7.2)] .
Males
To avoid potential drug exposure to pregnant partners and female partners of reproductive potential, advise male patients (including those who have had vasectomies) with female partners of reproductive potential to use condoms during treatment with TAFINLAR and for 2 weeks after the last dose.
Infertility
Females
Advise female patients of reproductive potential that TAFINLAR may impair fertility. A reduction in fertility was observed in female rats at dose exposures equivalent to the human exposure at the recommended adult dose. A reduction in the number of corpora lutea was noted in pregnant rats at dose exposures approximately three times the human exposure at the recommended adult dose [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
Males
Advise male patients of the potential risk for impaired spermatogenesis which may be irreversible. Effects on spermatogenesis have been observed in animals treated with dabrafenib at dose exposures up to three times the human exposure at the recommended adult dose [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
Pediatric Use
BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Unresectable or Metastatic Solid Tumors and LGG
The safety and effectiveness of TAFINLAR in combination with trametinib have been established in pediatric patients 1 year of age and older with unresectable or metastatic solid tumors with BRAF V600E mutation who have progressed following prior treatment and have no satisfactory alternative treatment options; or with LGG with BRAF V600E mutation who require systemic therapy. Use of TAFINLAR in combination with trametinib for these indications is supported by evidence from studies X2101 and G2201 that enrolled 171 patients (1 to < 18 years of age) with BRAF V600 mutation-positive advanced solid tumors, of which 4 (2.3%) patients were 1 to < 2 years of age, 39 (23%) patients were 2 to < 6 years of age, 54 (32%) patients were 6 to < 12 years of age, and 74 (43%) patients were 12 to < 18 years of age [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), Clinical Studies (14.6, 14.7)] .
The safety and effectiveness of TAFINLAR in combination with trametinib have not been established for these indications in pediatric patients less than 1 year old.
The safety and effectiveness of TAFINLAR as a single agent in pediatric patients have not been established.
Juvenile Animal Toxicity Data
In a repeat-dose toxicity study in juvenile rats, an increased incidence of kidney cysts and tubular deposits were noted at doses as low as 0.2 times the human exposure at the recommended adult dose based on AUC. Additionally, forestomach hyperplasia, decreased bone length, and early vaginal opening were noted at doses as low as 0.8 times the human exposure at the recommended adult dose based on AUC.
Geriatric Use
Of the 586 patients with various solid tumors who received single agent TAFINLAR, 22% were aged 65 years and older. Of the 187 patients with melanoma who received single-agent TAFINLAR in the BREAK-3 study, 21% were aged 65 years and older [see Clinical Studies (14.1)] . No overall differences in the effectiveness or safety of TAFINLAR were observed between geriatric patients as compared to younger adults in the BREAK-3 study.
Of the 994 patients with melanoma who received TAFINLAR plus trametinib in the COMBI-d, COMBI-v, and COMBI-AD studies [see Clinical Studies (14.2, 14.3)] , 21% were aged 65 years and older and 5% were aged 75 years and older. No overall differences in the effectiveness of TAFINLAR plus trametinib were observed in geriatric patients as compared to younger adults across these melanoma studies. The incidences of peripheral edema (26% vs. 12%) and anorexia (21% vs. 9%) were increased in geriatric patients as compared to younger adults in these studies.
Of the 171 patients with NSCLC who received TAFINLAR in Study BRF113928, there were insufficient numbers of geriatric patients to determine whether they respond differently from younger adults [see Clinical Studies (14.4)] .
Of the 26 patients with ATC who received TAFINLAR in Study BRF117019, 77% were aged 65 years and older, and 31% were aged 75 years and older [see Clinical Studies (14.5)] . This study in ATC did not include sufficient numbers of younger adults to determine whether they respond differently compared to geriatric patients.
Hepatic Impairment
Dose adjustment is not recommended for patients with mild (bilirubin ≤ upper limit of normal (ULN) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) > ULN or bilirubin > 1x to 1.5x ULN and any AST) hepatic impairment. As hepatic metabolism and biliary secretion are the primary routes of elimination of dabrafenib and its metabolites, patients with moderate (bilirubin > 1.5x to 3x ULN and any AST) to severe (bilirubin > 3x to 10x ULN and any AST) hepatic impairment may have increased exposure. An appropriate dosage has not been established for patients with moderate to severe hepatic impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] .
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
New Primary Malignancies
Cutaneous Malignancies
TAFINLAR Monotherapy (Adult) : In the pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] , cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas (cuSCC), and keratoacanthomas occurred in 11% and 4% of patients, respectively. Basal cell carcinoma and new primary melanoma occurred in 4% and 1% of patients, respectively.
TAFINLAR Administered with Trametinib (Adult) : In the pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] , the incidence of cuSCC (including keratoacanthomas) occurred in 2% of patients. Basal cell carcinoma and new primary melanoma occurred in 3% and < 1% of patients, respectively.
TAFINLAR Administered with Trametinib (Pediatric) : In the pooled safety population, new primary melanoma occurred in < 1% of patients.
Perform dermatologic evaluations prior to initiation of TAFINLAR, every 2 months while on therapy, and for up to 6 months following discontinuation of TAFINLAR.
Non-Cutaneous Malignancies
Based on its mechanism of action, TAFINLAR may promote the growth and development of malignancies with activation of RAS through mutation or other mechanisms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] .
In the pooled adult safety populations of TAFINLAR monotherapy and TAFINLAR administered with trametinib [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] , non-cutaneous malignancies occurred in 1% of patients.
Monitor patients receiving TAFINLAR for signs or symptoms of non-cutaneous malignancies. Permanently discontinue TAFINLAR for RAS mutation-positive non-cutaneous malignancies [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)] .
Tumor Promotion in BRAF Wild-Type Tumors
In vitro experiments have demonstrated paradoxical activation of MAP-kinase signaling and increased cell proliferation in BRAF wild-type cells which are exposed to BRAF inhibitors. Confirm evidence of BRAF V600E or V600K mutation status prior to initiation of TAFINLAR as a single agent or in combination with trametinib [see Indications and Usage (1.6), Dosage and Administration (2.1)] .
Hemorrhage
Hemorrhage, including major hemorrhage defined as symptomatic bleeding in a critical area or organ, can occur when TAFINLAR is administered with trametinib. Fatal cases have been reported.
TAFINLAR Administered with Trametinib (Adult) : In the pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] , hemorrhagic events occurred in 17% of patients; gastrointestinal hemorrhage occurred in 3% of patients; intracranial hemorrhage occurred in 0.6% of patients; fatal hemorrhage occurred in 0.5% of patients. The fatal events were cerebral hemorrhage and brainstem hemorrhage.
TAFINLAR Administered with Trametinib (Pediatric) : In the pooled safety population, hemorrhagic events occurred in 25% of patients; the most common type of bleeding was epistaxis (16%). Serious events of bleeding occurred in 3.6% of patients and included gastrointestinal hemorrhage (1.2%), cerebral hemorrhage (0.6%), uterine hemorrhage (0.6%), post-procedural hemorrhage (0.6%), and epistaxis (0.6%).
Permanently discontinue TAFINLAR for all Grade 4 hemorrhagic events and for any Grade 3 hemorrhagic events that do not improve. Withhold TAFINLAR for Grade 3 hemorrhagic events; if improved, resume TAFINLAR at the next lower dose level.
Cardiomyopathy
TAFINLAR Administered with Trametinib (Adult) : In the pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] , cardiomyopathy, defined as a decrease in left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) ≥ 10% from baseline and below the institutional lower limit of normal (LLN), occurred in 6% of patients. Development of cardiomyopathy resulted in dose interruption or discontinuation of TAFINLAR in 3% and < 1% of patients, respectively. Cardiomyopathy resolved in 45 of 50 patients who received TAFINLAR administered with trametinib.
TAFINLAR Administered with Trametinib (Pediatric) : In the pooled safety population, cardiomyopathy, defined as a decrease in LVEF ≥ 10% from baseline and below the institutional LLN, occurred in 9% of patients.
Assess LVEF by echocardiogram or multigated acquisition (MUGA) scan before initiation of TAFINLAR in combination with trametinib, one month after initiation, and then at 2- to 3-month intervals while on treatment. Withhold TAFINLAR for symptomatic cardiomyopathy or an absolute decrease in LVEF of greater than 20% from baseline that is below the institutional LLN. Resume TAFINLAR at the same dose level upon recovery of cardiac function to at least the institutional LLN for LVEF and absolute decrease to less than or equal to 10% compared to baseline [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)] .
Uveitis
TAFINLAR Monotherapy (Adult) : In the pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] , uveitis occurred in 1% of patients.
Cases of biocular panuveitis or biocular iridocyclitis have been reported in the post-marketing setting.
TAFINLAR Administered with Trametinib (Adult) : In the pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] , uveitis occurred in 2% of patients.
TAFINLAR Administered with Trametinib (Pediatric) : In the pooled safety population, uveitis occurred in 1.2% of patients.
Treatment employed in clinical trials included steroid and mydriatic ophthalmic drops. Monitor patients for visual signs and symptoms of uveitis (e.g., change in vision, photophobia, eye pain). If iritis is diagnosed, administer ocular therapy and continue TAFINLAR without dose modification. If severe uveitis (i.e., iridocyclitis) or if mild or moderate uveitis does not respond to ocular therapy, withhold TAFINLAR and treat as clinically indicated. Resume TAFINLAR at the same or lower dose if improves to Grade 0 or 1. Permanently discontinue TAFINLAR for persistent Grade 2 or greater uveitis of > 6 weeks [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)] .
Serious Febrile Reactions
Serious febrile reactions and fever of any severity complicated by hypotension, rigors or chills, dehydration, or renal failure, can occur with TAFINLAR.
The incidence and severity of pyrexia are increased when TAFINLAR is administered with trametinib compared with TAFINLAR as a single agent [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] .
TAFINLAR Monotherapy (Adult) : In the pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] , fever (serious and non-serious) occurred in 30% of patients. Approximately 13% of these patients experienced 3 or more discrete episodes. Serious febrile reactions and fever of any severity complicated by hypotension, rigors or chills occurred in 6% of patients.
TAFINLAR Administered with Trametinib (Adult) : In the pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] , fever occurred in 58% of patients. Serious febrile reactions and fever of any severity complicated by hypotension, rigors or chills, dehydration or renal failure occurred in 5% of patients. Fever was complicated by hypotension in 4%, dehydration in 3%, syncope in 2%, renal failure in 1%, and severe chills/rigors in < 1% of patients.
TAFINLAR Administered with Trametinib (Pediatric) : In the pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] , pyrexia occurred in 66% of patients.
Withhold TAFINLAR when used as monotherapy, and both TAFINLAR and trametinib when used in combination, if the patient’s temperature is ≥ 100.4°F. In case of recurrence, therapy can also be interrupted at the first symptom of pyrexia [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] . Fever may be complicated by hypotension, rigors or chills, dehydration, or renal failure. Evaluate for signs and symptoms of infection and monitor serum creatinine and other evidence of renal function during and following severe pyrexia. If appropriate, TAFINLAR, or both TAFINLAR and trametinib when used in combination, may be restarted if the patient has recovered from the febrile reaction for at least 24 hours, either at the same or lower dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)] . Administer antipyretics as secondary prophylaxis when resuming TAFINLAR if patient had a prior episode of severe febrile reaction or fever associated with complications. Administer corticosteroids (e.g., prednisone 10 mg daily) for at least 5 days for second or subsequent pyrexia if temperature does not return to baseline within 3 days of onset of pyrexia, or for pyrexia associated with complications, such as dehydration, hypotension, renal failure, or severe chills/rigors, and there is no evidence of active infection.
Serious Skin Toxicities
Severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCARs), including Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), which can be life-threatening or fatal, have been reported during treatment with TAFINLAR administered with trametinib [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)] .
TAFINLAR Administered with Trametinib (Adult): In the pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] , other serious skin toxicity occurred in < 1% of patients.
TAFINLAR Administered with Trametinib (Pediatric): In the pooled safety population, serious adverse events of skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders occurred in 1.8% of patients.
Monitor for new or worsening serious skin reactions. Permanently discontinue TAFINLAR for SCARs [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)] . For other skin toxicities, withhold TAFINLAR for intolerable or severe skin toxicity. Resume TAFINLAR at a lower dose in patients with improvement or recovery from skin toxicity within 3 weeks. Permanently discontinue TAFINLAR if skin toxicity has not improved within 3 weeks [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)] .
Hyperglycemia
TAFINLAR Monotherapy (Adult) : In the pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] , 14% of patients with a history of diabetes that received TAFINLAR required more intensive hypoglycemic therapy. Grade 3 and Grade 4 hyperglycemia occurred in 3% of patients.
TAFINLAR Administered with Trametinib (Adult) : In the pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] , 15% of patients with a history of diabetes who had received TAFINLAR with trametinib required more intensive hypoglycemic therapy. Grade 3 and Grade 4 hyperglycemia occurred in 2% of patients.
TAFINLAR Administered with Trametinib (Pediatric) : In the pooled safety population, Grade 3 and Grade 4 hyperglycemia events occurred in < 1% of patients.
Monitor serum glucose levels upon initiation and as clinically appropriate when TAFINLAR is administered in patients with preexisting diabetes or hyperglycemia. Initiate or optimize anti-hyperglycemic medications as clinically indicated.
Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficiency
TAFINLAR, which contains a sulfonamide moiety, confers a potential risk of hemolytic anemia in patients with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency. Monitor patients with G6PD deficiency for signs of hemolytic anemia while taking TAFINLAR.
Risks Associated with Combination Treatment
TAFINLAR is indicated for use in combination with trametinib. Review the prescribing information for trametinib for information on the serious risks of trametinib prior to initiation of TAFINLAR with trametinib.
Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis
Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) has been observed in the post-marketing setting when TAFINLAR was administered with trametinib. If HLH is suspected, interrupt treatment. If HLH is confirmed, discontinue treatment and initiate appropriate management of HLH.
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings from animal studies and its mechanism of action, TAFINLAR can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Dabrafenib was teratogenic and embryotoxic in rats at doses three times greater than the human exposure at the recommended adult clinical dose. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise female patients of reproductive potential to use effective non-hormonal contraception, since TAFINLAR can render hormonal contraceptives ineffective, during treatment with TAFINLAR and for 2 weeks after the last dose [see Drug Interactions (7.2), Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)] .
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- New Primary Malignancies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Tumor Promotion in BRAF Wild-Type Tumors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Hemorrhage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Cardiomyopathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Uveitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Serious Febrile Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Serious Skin Toxicities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Hyperglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficiency [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
There are additional adverse reactions associated with trametinib. Refer to the trametinib prescribing information for additional information.
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adult Safety Pools
The pooled safety population described in the WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS reflects exposure to TAFINLAR 150 mg orally, twice daily as a single agent in 586 patients with various solid tumors, including BRAF V600 mutation-positive unresectable or metastatic melanoma, enrolled in BREAK-2, BREAK-3, BREAK-MB, BRF113220, and BRF112680. Among these 586 patients who received TAFINLAR as a single agent, 46% were exposed for 6 months or longer and 15% were exposed for greater than one year.
The pooled safety population described in the WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS reflects exposure to TAFINLAR 150 mg orally, twice daily, administered in combination with trametinib 2 mg orally, once daily, in 1087 patients enrolled in COMBI-d, COMBI-v, COMBI-AD, and BRF113928 with unresectable or metastatic melanoma, adjuvant melanoma, or NSCLC. Among these 1087 patients who received TAFINLAR administered with trametinib, 70% were exposed for 6 months or longer and 21% were exposed for greater than one year.
Pediatric Safety Pool
The pediatric pooled safety population described in the WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS reflects exposure to weight-based TAFINLAR orally, twice daily administered in combination with trametinib in 166 pediatric patients across two trials: a multi-center, open-label, multi-cohort study in pediatric patients with BRAF V600E mutation-positive glioma requiring systemic therapy (Study G2201; n = 123) and a multi-center, open-label, multi-cohort study in pediatric patients with refractory or recurrent solid tumors with MAPK pathway activation (Study X2101; n = 43) [see Clinical Studies (14.6, 14.7)] . Among 166 patients who received TAFINLAR administered with trametinib, 84% were exposed for 6 months or longer and 70% were exposed for greater than one year. The most common (> 20%) adverse reactions were pyrexia (66%), rash (54%), headache (40%), vomiting (38%), musculoskeletal pain (36%), fatigue (31%), dry skin (31%), diarrhea (30%), nausea (26%), epistaxis and other bleeding events (25%), abdominal pain (24%), and dermatitis acneiform (23%). The most common (> 2%) Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities were decreased neutrophil count (20%), increased alanine aminotransferase (3.1%), and increased aspartate aminotransferase (3.1%).
Unresectable or Metastatic BRAF V600E or V600K Mutation-Positive Melanoma
TAFINLAR as a Single Agent
The safety of TAFINLAR was evaluated in BREAK-3, a multi-center, international, open-label, randomized (3:1), controlled trial that allocated 250 patients with unresectable or metastatic BRAF V600E mutation-positive melanoma to receive TAFINLAR 150 mg orally twice daily (n = 187) or dacarbazine 1000 mg/m 2 intravenously every 3 weeks (n = 63) [see Clinical Studies (14.1)] . The trial excluded patients with abnormal LVEF or cardiac valve morphology (≥ Grade 2), corrected QT interval ≥ 480 milliseconds on electrocardiogram, or a known history of G6PD deficiency. The median duration on treatment was 4.9 months for patients treated with TAFINLAR and 2.8 months for dacarbazine-treated patients. The population exposed to TAFINLAR was 60% male, 99% White, and had a median age of 53 years.
The most common adverse reactions (≥ 20%) in patients treated with TAFINLAR were, in order of decreasing frequency: hyperkeratosis, headache, pyrexia, arthralgia, papilloma, alopecia, and palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome (PPES).
The incidence of adverse events resulting in permanent discontinuation of study medication in the BREAK-3 study was 3% for patients treated with TAFINLAR and 3% for patients treated with dacarbazine. The most frequent (≥ 2%) adverse reactions leading to dose reduction of TAFINLAR were pyrexia (9%), PPES (3%), chills (3%), fatigue (2%), and headache (2%). Table 6 and Table 7 present adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities, respectively, of TAFINLAR as a single agent in the BREAK-3 study.
| Abbreviations: cuSCC, cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma, includes squamous cell carcinoma of the skin and keratoacanthoma; NA, not applicable. a Adverse reactions, reported using MedDRA and graded using NCI CTCAE version 4.0 for assessment of toxicity. b Grade 4 adverse reactions limited to hyperkeratosis (n = 1) and constipation (n = 1). c Includes skin papilloma and papilloma. d Cases of cuSCC were required to be reported as Grade 3 per protocol. | ||||
| TAFINLAR N = 187 | Dacarbazine N = 59 | |||
| Adverse Reactions | All Grades (%) | Grades 3 and 4 b (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3 and 4 (%) |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue | ||||
| Hyperkeratosis | 37 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Alopecia | 22 | NA | 2 | NA |
| Palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome | 20 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| Rash | 17 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Nervous system | ||||
| Headache | 32 | 0 | 8 | 0 |
| General | ||||
| Pyrexia | 28 | 3 | 10 | 0 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue | ||||
| Arthralgia | 27 | 1 | 2 | 0 |
| Back pain | 12 | 3 | 7 | 0 |
| Myalgia | 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Neoplasms | ||||
| Papilloma c | 27 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| cuSCC d | 7 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| Respiratory system | ||||
| Cough | 12 | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| Gastrointestinal | ||||
| Constipation | 11 | 2 | 14 | 0 |
| Infections and infestations | ||||
| Nasopharyngitis | 10 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| a Adverse reactions, reported using MedDRA and graded using NCI CTCAE version 4.0 for assessment of toxicity. b Grade 4 laboratory abnormality limited to hypophosphatemia (n = 1). | ||||
| TAFINLAR N = 187 | Dacarbazine N = 59 | |||
| Laboratory Abnormality | All Grades (%) | Grades 3 and 4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3 and 4 (%) |
| Hyperglycemia | 50 | 6 | 43 | 0 |
| Hypophosphatemia | 37 | 6 b | 14 | 2 |
| Increased alkaline phosphatase | 19 | 0 | 14 | 2 |
| Hyponatremia | 8 | 2 | 3 | 0 |
Other clinically important adverse reactions for TAFINLAR in a pool of TAFINLAR monotherapy clinical studies observed in less than 10% of patients who received TAFINLAR were:
Gastrointestinal: Pancreatitis
Immune System: Hypersensitivity manifesting as bullous rash
Nervous System: Peripheral neuropathy
Renal and Urinary: Interstitial nephritis
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue: Photosensitivity
TAFINLAR with Trametinib
The safety of TAFINLAR when administered with trametinib was evaluated in 559 patients with previously untreated, unresectable or metastatic, BRAF V600E or V600K mutation-positive melanoma who received TAFINLAR in two trials, the COMBI-d study (n = 209), a multi-center, double-blind, randomized (1:1), active-controlled trial and the COMBI-v study (n = 350), a multi-center, open-label, randomized (1:1), active-controlled trial. In both trials, patients received TAFINLAR 150 mg orally twice daily and trametinib 2 mg orally once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Both trials excluded patients with abnormal LVEF, history of acute coronary syndrome within 6 months, history of Class II or greater congestive heart failure (New York Heart Association), history of retinal vein occlusion (RVO) or retinal pigment epithelial detachment (RPED), QTcB interval ≥ 480 msec, treatment refractory hypertension, uncontrolled arrhythmias, active brain metastases, or known history of G6PD deficiency [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
Among these 559 patients, 199 (36%) were exposed to TAFINLAR for > 6 months to 12 months while 185 (33%) were exposed to TAFINLAR for ≥ 1 year. The median age was 55 years (range: 18 to 91), 57% were male, 98% were White, 72% had baseline ECOG performance status of 0 and 28% had ECOG performance status of 1, 64% had M1c disease, 35% had elevated lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) at baseline, and 0.5% had a history of brain metastases.
The most common adverse reactions (≥ 20%) for TAFINLAR in patients who received TAFINLAR plus trametinib in the COMBI-d and COMBI-v studies were: pyrexia, rash, chills, headache, arthralgia, and cough. The demographics and baseline tumor characteristics of patients enrolled in the COMBI-d study are summarized in Clinical Studies [see Clinical Studies (14.2)] . Patients who received TAFINLAR plus trametinib had a median duration of exposure of 11 months (range: 3 days to 30 months) to TAFINLAR. Among the 209 patients who received TAFINLAR plus trametinib, 26% were exposed to TAFINLAR for > 6 months to 12 months while 46% were exposed to TAFINLAR for > 1 year.
In the COMBI-d study, adverse reactions leading to discontinuation of TAFINLAR occurred in 11% of patients who received TAFINLAR plus trametinib; the most frequent was pyrexia (1.9%). Adverse reactions leading to dose reductions of TAFINLAR occurred in 26% of patients who received TAFINLAR plus trametinib; the most frequent were pyrexia (14%), neutropenia (1.9%), rash (1.9%), and chills (1.9%). Adverse reactions leading to dose interruptions of TAFINLAR occurred in 56% of patients who received TAFINLAR plus trametinib; the most frequent were pyrexia (35%), chills (11%), vomiting (7%), nausea (5%), and decreased ejection fraction (5%).
Table 8 and Table 9 present adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities, respectively, observed in the COMBI-d study.
| a NCI CTCAE version 4.0. b Grade 4 adverse reactions limited to headache (n = 1). c Includes rash generalized, rash pruritic, rash erythematous, rash papular, rash vesicular, rash macular, rash maculo-papular, and rash follicular. | ||||||
| Pooled TAFINLAR plus Trametinib N = 559 | COMBI-d Study | |||||
| TAFINLAR plus Trametinib N = 209 | TAFINLAR N = 211 | |||||
| Adverse Reactions | All Grades (%) | Grades 3 and 4 b (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3 and 4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3 and 4 (%) |
| General | ||||||
| Pyrexia | 54 | 5 | 57 | 7 | 33 | 1.9 |
| Chills | 31 | 0.5 | 31 | 0 | 17 | 0.5 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue | ||||||
| Rash c | 32 | 1.1 | 42 | 0 | 27 | 1.4 |
| Dry skin | 10 | 0 | 12 | 0 | 16 | 0 |
| Nervous system | ||||||
| Headache | 30 | 0.9 | 33 | 0.5 | 30 | 1.4 |
| Dizziness | 11 | 0.2 | 14 | 0 | 7 | 0 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue | ||||||
| Arthralgia | 25 | 0.9 | 26 | 0.9 | 31 | 0 |
| Myalgia | 15 | 0.2 | 13 | 0.5 | 13 | 0 |
| Respiratory system | ||||||
| Cough | 20 | 0 | 21 | 0 | 21 | 0 |
| Gastrointestinal | ||||||
| Constipation | 13 | 0.2 | 13 | 0.5 | 10 | 0 |
| Infections and infestations | ||||||
| Nasopharyngitis | 12 | 0 | 12 | 0 | 10 | 0 |
Other clinically important adverse reactions for TAFINLAR across the COMBI-d and COMBI-v studies (N = 559) observed in less than 10% of patients who received TAFINLAR administered with trametinib were:
Cardiac: Atrioventricular block, bundle branch block
Gastrointestinal: Colitis, gastrointestinal perforation, pancreatitis
Immune System: Sarcoidosis
Nervous System: Peripheral neuropathy, Guillain-Barré syndrome
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue: Panniculitis, photosensitivity
| a For these laboratory tests, the denominator is 556. b For these laboratory tests, the denominator is 208 for the combination arm, 208-209 for the TAFINLAR arm. c Grade 4 adverse reactions limited to hyperglycemia (n = 4), hyponatremia and hypophosphatemia (each n = 1) in the pooled combination arm; hyperglycemia (n = 1) in the COMBI-d study combination arm; hypophosphatemia (n = 1) in the TAFINLAR arm. | ||||||
| Laboratory Abnormalities | Pooled TAFINLAR plus T rametinib N = 559 a | COMBI-d Study | ||||
| TAFINLAR plus Trametinib N = 209 b | TAFINLAR N = 211 b | |||||
| All Grades (%) | Grades 3 and 4 c (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3 and 4 c (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3 and 4 c (%) | |
| Chemistry | ||||||
| Hyperglycemia | 60 | 4.7 | 65 | 6 | 57 | 4.3 |
| Hypophosphatemia | 38 | 6 | 38 | 3.8 | 35 | 7 |
| Hyponatremia | 25 | 8 | 24 | 6 | 14 | 2.9 |
| Hepatic | ||||||
| Increased blood alkaline phosphatase | 49 | 2.7 | 50 | 1.0 | 25 | 0.5 |
Adjuvant Treatment of BRAF V600E or V600K Mutation-Positive Melanoma
The safety of TAFINLAR when administered with trametinib was evaluated in 435 patients with Stage III melanoma with BRAF V600E or V600K mutations following complete resection who received at least one dose of study therapy in the COMBI-AD study [see Clinical Studies (14.3)] . Patients received TAFINLAR 150 mg orally twice daily and trametinib 2 mg orally once daily for 12 months. The trial excluded patients with abnormal LVEF; history of acute coronary syndromes, coronary angioplasty, or stenting within 6 months; Class II or greater congestive heart failure (New York Heart Association); QTc interval ≥ 480 msec; treatment refractory hypertension; uncontrolled arrhythmias; or history of RVO.
Patients who received TAFINLAR in combination with trametinib had a median duration of exposure of 11 months (range: 0 to 12) to TAFINLAR. Among the 435 patients receiving TAFINLAR in combination with trametinib, 71% were exposed to TAFINLAR for > 6 months. The median age of patients who received TAFINLAR administered with trametinib was 50 years (range: 18 to 89), 56% were male, 99% were White, 92% had baseline ECOG performance status of 0, and 8% had baseline ECOG performance status of 1.
The most common adverse reactions (≥ 20%) in patients who received TAFINLAR administered with trametinib were: pyrexia, fatigue, nausea, headache, rash, chills, diarrhea, vomiting, arthralgia, and myalgia.
Adverse reactions resulting in discontinuation, dose reduction, or dose interruption of TAFINLAR occurred in 25%, 35%, and 66% of patients, respectively; the most frequent for each were pyrexia and chills.
Table 10 summarizes the adverse reactions that occurred in at least 20% of patients who received TAFINLAR administered with trametinib.
| a NCI CTCAE version 4.0. b Includes pyrexia and hyperpyrexia. c Includes fatigue, asthenia, and malaise. d Includes headache and tension headache. e Includes rash, rash maculo-papular, rash macular, rash generalized, rash erythematous, rash papular, rash pruritic, nodular rash, rash vesicular, and rash pustular. f Includes myalgia, musculoskeletal pain, and musculoskeletal chest pain. | ||||
| Adverse Reactions | TAFINLAR plus Trametinib N = 435 | Placebo N = 432 | ||
| All Grades (%) | Grades 3 and 4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3 and 4 (%) | |
| General | ||||
| Pyrexia b | 63 | 5 | 11 | < 1 |
| Fatigue c | 59 | 5 | 37 | < 1 |
| Chills | 37 | 1 | 4 | 0 |
| Gastrointestinal | ||||
| Nausea | 40 | < 1 | 20 | 0 |
| Diarrhea | 33 | < 1 | 15 | < 1 |
| Vomiting | 28 | < 1 | 10 | 0 |
| Nervous system | ||||
| Headache d | 39 | 1 | 24 | 0 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue | ||||
| Rash e | 37 | < 1 | 16 | < 1 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue | ||||
| Arthralgia | 28 | < 1 | 14 | 0 |
| Myalgia f | 20 | < 1 | 14 | 0 |
Other clinically important adverse reactions for TAFINLAR in the COMBI-AD study observed in less than 20% of patients who received TAFINLAR administered with trametinib were: blurred vision (6%), decreased ejection fraction (5%), peripheral neuropathy (2.5%), rhabdomyolysis (< 1%), atrioventricular block (< 1%), Guillain-Barré syndrome (< 1%), and sarcoidosis (< 1%).
The laboratory abnormalities are summarized in Table 11.
| Abbreviations: ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase. a The incidence is based on the number of patients who had both a baseline and at least one on-study laboratory measurement: TAFINLAR plus Trametinib (range: 429 to 431) and Placebo arm (range: 426 to 428). | ||||
| Laboratory Abnormality | TAFINLAR plus Trametinib a N = 435 | Placebo a N = 432 | ||
| All Grades (%) | Grades 3 and 4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3 and 4 (%) | |
| Chemistry | ||||
| Hyperglycemia | 63 | 3 | 47 | 2 |
| Hypophosphatemia | 42 | 7 | 10 | < 1 |
| Hypoalbuminemia | 25 | < 1 | < 1 | 0 |
| Hepatic | ||||
| Increased AST | 57 | 6 | 11 | < 1 |
| Increased ALT | 48 | 5 | 18 | < 1 |
| Increased blood alkaline phosphatase | 38 | 1 | 6 | < 1 |
| Hematology | ||||
| Neutropenia | 47 | 6 | 12 | < 1 |
| Lymphopenia | 26 | 5 | 6 | < 1 |
| Anemia | 25 | < 1 | 6 | < 1 |
Trial COMBI-aPlus (Pyrexia Management Study)
COMBI-aPlus evaluated the impact of pyrexia-related outcomes of a revised pyrexia management algorithm in patients who received dabrafenib administered with trametinib in the adjuvant treatment of BRAF V600 mutation-positive melanoma after complete resection. The pyrexia management algorithm interrupted both dabrafenib and trametinib when patient’s temperature is ≥ 100.4°F.
Grade 3-4 pyrexia occurred in 4.3% of patients, hospitalizations due to pyrexia occurred in 5.1% of patients, pyrexia with complications (dehydration, hypotension, renal dysfunction, syncope, severe chills) occurred in 2.2% of patients, and treatment discontinuation due to pyrexia occurred in 2.5% of patients.
Metastatic, BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
The safety of TAFINLAR when administered with trametinib was evaluated in 93 patients with previously untreated (n = 36) and previously treated (n = 57) metastatic BRAF V600E mutation-positive NSCLC in a multi-center, multi-cohort, non-randomized, open-label trial (Study BRF113928). Patients received TAFINLAR 150 mg orally twice daily and trametinib 2 mg orally once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The trial excluded patients with abnormal LVEF, history of acute coronary syndrome within 6 months, history of Class II or greater congestive heart failure (New York Heart Association), QTc interval ≥ 480 msec, treatment refractory hypertension, uncontrolled arrhythmias, active brain metastases, history of interstitial lung disease or pneumonitis, or history or current RVO [see Clinical Studies (14.4)].
Among these 93 patients, 53 (57%) were exposed to TAFINLAR and trametinib for > 6 months and 27 (29%) were exposed to TAFINLAR and trametinib for ≥ 1 year. The median age was 65 years (range: 41 to 91); 46% were male; 85% were White; 32% had baseline ECOG performance status of 0 and 61% had ECOG performance status of 1; 98% had non-squamous histology; and 12% were current smokers, 60% were former smokers, and 28% had never smoked.
The most common adverse reactions (≥ 20%) in these 93 patients were: pyrexia, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dry skin, decreased appetite, edema, rash, chills, hemorrhage, cough, and dyspnea.
Adverse reactions leading to discontinuation of TAFINLAR occurred in 18% of patients; the most frequent were pyrexia (2.2%), decreased ejection fraction (2.2%), and respiratory distress (2.2%). Adverse reactions leading to dose reductions of TAFINLAR occurred in 35% of patients; the most frequent were pyrexia (10%), diarrhea (4.3%), nausea (4.3%), vomiting (4.3%), and neutropenia (3.2%). Adverse reactions leading to dose interruptions of TAFINLAR occurred in 62% of patients; the most frequent were pyrexia (27%), vomiting (11%), neutropenia (8%), and chills (6%).
Table 12 and Table 13 present adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities, respectively, of TAFINLAR administered with trametinib in Study BRF113928.
| a NCI CTCAE version 4.0. b Includes fatigue, malaise, and asthenia. c Includes peripheral edema, edema, and generalized edema. d Includes rash, rash generalized, rash papular, rash macular, rash maculo-papular, and rash pustular. e Includes hemoptysis, hematoma, epistaxis, purpura, hematuria, subarachnoid hemorrhage, gastric hemorrhage, urinary bladder hemorrhage, contusion, hematochezia, injection site hemorrhage, pulmonary hemorrhage, and retroperitoneal hemorrhage. | ||
| Adverse Reactions | TAFINLAR plus T rametinib N = 93 | |
| All Grades (%) | Grades 3 and 4 (%) | |
| General | ||
| Pyrexia | 55 | 5 |
| Fatigue b | 51 | 5 |
| Edema c | 28 | 0 |
| Chills | 23 | 1.1 |
| Gastrointestinal | ||
| Nausea | 45 | 0 |
| Vomiting | 33 | 3.2 |
| Diarrhea | 32 | 2.2 |
| Decreased appetite | 29 | 0 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue | ||
| Dry skin | 31 | 1.1 |
| Rash d | 28 | 3.2 |
| Vascular | ||
| Hemorrhage e | 23 | 3.2 |
| Respiratory system | ||
| Cough | 22 | 0 |
| Dyspnea | 20 | 5 |
Other clinically important adverse reactions for TAFINLAR in Study BRF113928 observed in less than 20% of patients who received TAFINLAR administered with trametinib were:
Cardiac: Atrioventricular block
Gastrointestinal: Pancreatitis
Nervous System: Peripheral neuropathy
Renal and Urinary: Tubulointerstitial nephritis
| Abbreviations: ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase. a For these laboratory tests, the denominator is 90. b For these laboratory tests, the denominator is 91. | ||
| Laboratory Abnormality | TAFINLAR plus Trametinib N = 93 | |
| All Grades (%) | Grades 3 and 4 (%) | |
| Chemistry a | ||
| Hyperglycemia | 71 | 9 |
| Hyponatremia | 57 | 17 |
| Hypophosphatemia | 36 | 7 |
| Increased creatinine | 21 | 1.1 |
| Hepatic a | ||
| Increased blood alkaline phosphatase | 64 | 0 |
| Increased AST | 61 | 4.4 |
| Increased ALT | 32 | 6 |
| Hematology b | ||
| Leukopenia | 48 | 8 |
| Anemia | 46 | 10 |
| Neutropenia | 44 | 8 |
| Lymphopenia | 42 | 14 |
Advanced BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Tumors
Study BRF117019
The safety of TAFINLAR when administered with trametinib was evaluated in a multi-cohort, multi-center, non-randomized, open-label study in adult patients with cancers with the BRAF V600E mutation (Study BRF117019). A total of 206 patients were enrolled in the trial, 36 of whom were enrolled in the ATC cohort, 105 were enrolled in specific solid tumor cohorts, and 65 in other malignancies [see Clinical Studies (14.5, 14.6)] . Patients received TAFINLAR 150 mg orally twice daily and trametinib 2 mg orally once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Among these 206 patients, 103 (50%) were exposed to TAFINLAR for ≥ 1 year and 101 (49%) were exposed to trametinib for ≥ 1 year. The median age was 60 years (range: 18 to 89); 56% were male; 79% were White; and 34% had baseline ECOG performance status of 0 and 60% had ECOG performance status of 1.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 45% of patients who received TAFINLAR in combination with trametinib. Serious adverse reactions in > 5% of patients included pyrexia (11%) and pneumonia (6%). Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 3.9% of patients who received TAFINLAR in combination with trametinib. Fatal adverse reactions that occurred in > 1% of patients included sepsis (1.9%).
Permanent treatment discontinuation due to an adverse reaction occurred in 13% of patients. Adverse reactions which resulted in permanent treatment discontinuation in > 1% of patients included nausea (1.5%).
Dosage interruptions due to an adverse reaction occurred in 55% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dosage interruption in > 5% of patients included pyrexia (22%), chills (9%), fatigue (6%), neutropenia (6%), and nausea (5%).
Dose reductions due to an adverse reaction occurred in 44% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dose reductions in > 5% of patients included pyrexia (18%), chills (8%), and fatigue (6%).
The most common (≥ 20%) adverse reactions, including laboratory abnormalities, are listed in Table 14 and Table 15.
Table 14 summarizes the adverse reactions in Study BRF117019.
| a NCI CTCAE version 4.0. b Includes fatigue, asthenia, and malaise. c Includes peripheral edema and peripheral swelling. d Includes rash, rash maculo-papular, rash erythematous, rash pustular, and rash papular. e Includes epistaxis, hematuria, contusion, hematoma, hemoptysis, conjunctival hemorrhage, hematochezia, rectal hemorrhage, hemorrhoidal hemorrhage, melena, purpura, eye contusion, eye hemorrhage, gastric hemorrhage, gingival bleeding, hematemesis, hemorrhage intracranial, hemorrhagic stroke, hemothorax, increased tendency to bruise, large intestinal hemorrhage, mouth hemorrhage, petechiae, pharyngeal hemorrhage, prothrombin time prolonged, pulmonary hematoma, retinal hemorrhage, vaginal hemorrhage, and vitreous hemorrhage. f Includes cough and productive cough. g Includes myalgia, musculoskeletal chest pain, and musculoskeletal pain. | ||
| Adverse Reactions | TAFINLAR plus Trametinib a (N = 206) | |
| All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) | |
| General | ||
| Pyrexia | 55 | 4.9 |
| Fatigue b | 50 | 5 |
| Chills | 30 | 0.5 |
| Peripheral edema c | 22 | 0 |
| Gastrointestinal | ||
| Nausea | 40 | 1.5 |
| Constipation | 27 | 0 |
| Vomiting | 27 | 1.5 |
| Diarrhea | 26 | 2.9 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue | ||
| Rash d | 40 | 2.4 |
| Nervous system | ||
| Headache | 30 | 1.5 |
| Vascular | ||
| Hemorrhage e | 29 | 4.4 |
| Respiratory system | ||
| Cough f | 29 | 0 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue | ||
| Myalgia g | 24 | 0.5 |
| Arthralgia | 23 | 0.5 |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions for TAFINLAR in Study BRF117019 observed in less than 20% of patients who received TAFINLAR in combination with trametinib were: peripheral neuropathy (9%), decreased ejection fraction (8%), atrioventricular block (2.9%), uveitis (1.9%), hypersensitivity (1.9%), and Guillain-Barré syndrome (< 1%).
Table 15 summarizes the laboratory abnormalities in Study BRF117019.
| Abbreviations: ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase. a The denominator used to calculate the rate varied from 199 to 202 based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one post-treatment value. | ||
| Laboratory Abnormality | TAFINLAR plus Trametinib a | |
| All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) | |
| Chemistry | ||
| Hyperglycemia | 61 | 8 |
| Decreased sodium | 35 | 10 |
| Decreased magnesium | 24 | 0 |
| Increased creatinine | 21 | 1.5 |
| Hepatic | ||
| Increased alkaline phosphatase | 51 | 5 |
| Increased AST | 51 | 4.6 |
| Increased ALT | 39 | 3 |
| Hematology | ||
| Decreased hemoglobin | 44 | 9 |
BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Solid Tumors in Pediatric Patients Study CTMT212X2101 (X2101)
The safety of TAFINLAR when administered with trametinib was evaluated in Study X2101, a multi-center, open-label, multi-cohort study in pediatric patients (n = 48) with refractory or recurrent solid tumors [see Clinical Studies (14.6)] . The median duration of exposure to TAFINLAR in Parts C (dose escalation) and D (cohort expansion) was 20.8 and 24.9 months, respectively. The median duration of exposure to trametinib in Parts C and D was 20.8 and 24.4 months, respectively. The median age of pediatric patients who received TAFINLAR with trametinib was 9 years (range: 1 to 17).
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 46% of patients who received TAFINLAR in combination with trametinib. Serious adverse reactions in > 5% of patients included pyrexia (25%) and decreased ejection fraction (6%). Permanent treatment discontinuation due to an adverse reaction occurred in 21% of patients. Adverse reactions which resulted in permanent treatment discontinuation in > 3% of patients included increased ALT (6%), increased AST (4.2%) and decreased ejection fraction (4.2%). Dosage interruptions due to an adverse reaction occurred in 73% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dosage interruption in > 5% of patients included pyrexia (56%), vomiting (19%), neutropenia (13%), rash (13%), decreased ejection fraction (6%), and uveitis (6%). Dose reductions due to an adverse reaction occurred in 25% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dose reductions in > 5% of patients included pyrexia (13%).
The most common (≥ 20%) adverse reactions, including laboratory abnormalities, are listed in Table 16 and Table 17.
Table 16 summarizes the adverse reactions in Study X2101.
| a NCI CTCAE version 4.0. b Includes fatigue, asthenia, and malaise. c Includes rash, rash maculo-papular, rash erythematous, rash papular, rash pustular, and rash macular. d Includes dermatitis acneiform and acne. e Includes abdominal pain and abdominal pain upper. f Includes epistaxis, hematuria, contusion, hematoma, petechiae, rectal hemorrhage, and red blood cell count decreased. | ||
| Adverse Reactions | TAFINLAR plus Trametinib a (N = 48) | |
| All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) | |
| General | ||
| Pyrexia | 75 | 17 |
| Fatigue b | 48 | 0 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue | ||
| Rash c | 73 | 2.1 |
| Dry skin | 48 | 0 |
| Dermatitis acneiform d | 40 | 0 |
| Gastrointestinal | ||
| Vomiting | 52 | 4.2 |
| Diarrhea | 42 | 2.1 |
| Abdominal pain e | 33 | 4.2 |
| Nausea | 33 | 2.1 |
| Constipation | 23 | 0 |
| Respiratory system | ||
| Cough | 44 | 0 |
| Nervous system | ||
| Headache | 35 | 0 |
| Vascular | ||
| Hemorrhage f | 33 | 0 |
| Infections and infestations | ||
| Paronychia | 23 | 0 |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions for TAFINLAR in Study X2101 observed in less than 20% of patients (N=48) who received TAFINLAR in combination with trametinib were: atrioventricular block (2.1%).
Table 17 summarizes the laboratory abnormalities in Study X2101.
| Abbreviations: ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase. a The denominator used to calculate the rate varied from 39 to 48 based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one post-treatment value. | ||
| Laboratory Abnormality | TAFINLAR plus Trametinib a | |
| All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) | |
| Chemistry | ||
| Hyperglycemia | 65 | 2.2 |
| Hypoalbuminemia | 48 | 2.1 |
| Hypocalcemia | 40 | 2.1 |
| Decreased phosphate | 38 | 0 |
| Decreased magnesium | 33 | 2.1 |
| Hypernatremia | 27 | 0 |
| Hypokalemia | 21 | 2.1 |
| Hepatic | ||
| Increased AST | 55 | 4.2 |
| Increased ALT | 40 | 6 |
| Increased alkaline phosphatase | 28 | 6 |
| Increased total bilirubin | 21 | 2.1 |
| Hematology | ||
| Decreased hemoglobin | 60 | 6 |
| Decreased neutrophils | 49 | 28 |
BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Low-Grade Glioma in Pediatric Patients
Study CDRB436G2201 (G2201)
The safety of TAFINLAR in combination with trametinib was evaluated in pediatric patients 1 to < 18 years of age in Study G2201. Patients with low-grade glioma (LGG) who required first systemic therapy were randomized (2:1) to TAFINLAR plus trametinib (n = 73) or carboplatin plus vincristine (n = 33). Nine patients crossed over from the carboplatin plus vincristine arm to the TAFINLAR and trametinib arm. Pediatric patients received weight-based TAFINLAR orally twice daily administered in combination with trametinib until disease progression or intolerable toxicity. Patients in the control arm received carboplatin and vincristine at doses of 175 mg/m 2 and 1.5 mg/m 2 , respectively in 10-week induction course followed by eight 6-week cycles of maintenance therapy or until disease progression or intolerable toxicity. Among patients with low-grade glioma who were randomized to TAFINLAR plus trametinib (n = 73), 95% were exposed for 6 months or longer and 71% were exposed for greater than one year.
The median age of these patients was 10 years (range: 1 to 17); 60% female; 75% White, 7% Asian, 2.7% Black or African American, 4% other race, and 11% where race was unknown or not reported.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 40% of these patients. Serious adverse reactions in > 3% of patients included pyrexia (14%) and vomiting (4%).
Permanent discontinuation of TAFINLAR due to an adverse reaction occurred in 4% of patients. Adverse reactions which resulted in permanent discontinuation of TAFINLAR included chills, fatigue, pyrexia, weight increased, and headache.
Dosage interruptions of TAFINLAR due to an adverse reaction occurred in 73% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dosage interruption in > 5% of patients included pyrexia (53%).
Dose reductions of TAFINLAR due to an adverse reaction occurred in 48% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dose reductions in > 2% of patients included rash (2.7%). The most common (≥ 15%) adverse reactions were pyrexia (68%), rash (51%), headache (47%), vomiting (34%), musculoskeletal pain (34%), fatigue (33%), diarrhea (29%), dry skin (26%), nausea (25%), hemorrhage (25%), abdominal pain (25%), dermatitis acneiform (22%), dizziness (15%), upper respiratory tract infection (15%), and weight increased (15%).
The most common (≥ 20%) laboratory abnormalities that worsened from baseline were leukopenia (59%), increased alkaline phosphatase (55%), anemia (46%), decreased neutrophils (44%), increased AST (37%), decreased magnesium (34%), increased magnesium (32%), decreased platelets (30%), increased ALT (29%), and increased lymphocytes (24%).
Table 18 summarizes the adverse reactions in Study G2201.
| a NCI CTCAE version 4.03. b Includes diarrhea, colitis, enterocolitis, and enteritis. c Includes abdominal pain and upper abdominal pain. d Includes stomatitis, cheilitis, mouth ulceration, aphthous ulcer, and glossitis. e Includes pyrexia and body temperature increased. f Includes fatigue and asthenia. g Includes headache and migraine with aura. h Includes dizziness and vertigo. i Includes peripheral neuropathy, peripheral motor neuropathy, peripheral sensorimotor neuropathy, paresthesia, neuralgia, hypoaesthesia, and peripheral sensory neuropathy. j Includes epistaxis, post-procedural hemorrhage, hematuria, upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage, and hemorrhage intracranial. k Includes rash, rash macular, rash maculo-papular, rash pustular, rash papular, rash erythematous, eczema, erythema multiforme, dermatitis, dermatitis exfoliative, skin exfoliation, palmar-plantar erythrodysaesthesia syndrome, and dermatitis bullous. l Includes dermatitis acneiform, acne, and acne pustular. m Includes back pain, myalgia, pain in extremity, arthralgia, bone pain, non-cardiac chest pain, neck pain, and musculoskeletal stiffness. | ||||
| Adverse Reactions | TAFINLAR plus Trametinib N = 73 | Carboplatin plus Vincristine N = 33 | ||
| All Grades (%) | Grade ≥ 3 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade ≥ 3 (%) | |
| Gastrointestinal | ||||
| Vomiting | 34 | 1 | 48 | 3 |
| Diarrhea b | 29 | 0 | 18 | 6 |
| Nausea | 25 | 0 | 45 | 0 |
| Abdominal pain c | 25 | 0 | 24 | 0 |
| Constipation | 12 | 0 | 36 | 0 |
| Stomatitis d | 10 | 0 | 18 | 0 |
| General | ||||
| Pyrexia e | 68 | 8 | 18 | 3 |
| Fatigue f | 33 | 0 | 39 | 0 |
| Nervous system | ||||
| Headache g | 47 | 1 | 33 | 3 |
| Dizziness h | 15 | 0 | 9 | 3 |
| Peripheral neuropathy i | 7 | 0 | 45 | 6 |
| Vascular | ||||
| Hemorrhage j | 25 | 0 | 12 | 0 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue | ||||
| Rash k | 51 | 2.7 | 18 | 3 |
| Dry skin | 26 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| Dermatitis acneiform l | 22 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Alopecia | 3 | 0 | 24 | 0 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue | ||||
| Musculoskeletal pain m | 34 | 0 | 30 | 0 |
| Pain in jaw | 1.4 | 0 | 18 | 0 |
| Metabolism and nutrition | ||||
| Decreased appetite | 5 | 0 | 24 | 0 |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal | ||||
| Oropharyngeal pain | 11 | 0 | 18 | 0 |
| Psychiatric | ||||
| Anxiety | 1.4 | 0 | 15 | 3 |
| Immune system | ||||
| Hypersensitivity | 0 | 0 | 15 | 3 |
| Infections and infestations | ||||
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 15 | 0 | 6 | 0 |
| Injury, poisoning and procedural complications | ||||
| Infusion-related reaction | 0 | 0 | 15 | 3 |
| Investigations | ||||
| Weight increased | 15 | 7 | 0 | 0 |
Table 19 summarizes the laboratory abnormalities in Study G2201.
| Abbreviations: ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase. a The denominator used to calculate the rate varied from 70 to 73 in D + T arm and 9 to 33 in C + V arm based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one post-treatment value. | ||||
| Laboratory Abnormality | TAFINLAR plus Trametinib N = 73 | Carboplatin plus Vincristine N = 33 | ||
| All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) | |
| Hepatic | ||||
| Increased alkaline phosphatase | 55 | 0 | 13 | 0 |
| Increased AST | 37 | 1.4 | 55 | 0 |
| Increased ALT | 29 | 3 | 61 | 9 |
| Chemistry | ||||
| Decreased magnesium | 34 | 4.1 | 76 | 6 |
| Increased magnesium | 32 | 0 | 24 | 3 |
| Increased potassium | 15 | 4.2 | 21 | 6 |
| Decreased calcium | 14 | 4.1 | 22 | 9 |
| Decreased potassium | 8 | 1.4 | 70 | 0 |
| Decreased phosphate | 7 | 2.7 | 33 | 3 |
| Decreased sodium | 5 | 1.4 | 27 | 6 |
| Increased serum fasting glucose | 0 | 0 | 44 | 0 |
| Hematology | ||||
| Decreased leukocytes | 59 | 0 | 91 | 18 |
| Decreased hemoglobin | 46 | 0 | 94 | 36 |
| Decreased neutrophils | 44 | 17 | 84 | 75 |
| Decreased platelets | 30 | 0 | 73 | 18 |
| Increased lymphocytes | 24 | 0 | 13 | 3.1 |
| Decreased lymphocytes | 16 | 1.4 | 56 | 6 |
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of TAFINLAR in combination with trametinib. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Cardiac: Atrioventricular block complete
Immune System: Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue: SCAR (including DRESS and SJS) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
Effects of Other Drugs on TAFINLAR
Strong inhibitors of CYP3A4 or CYP2C8 may increase the concentration of dabrafenib [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] . Substitution of strong inhibitors of CYP3A4 or CYP2C8 is recommended during treatment with TAFINLAR. If concomitant use of strong inhibitors of CYP3A4 or CYP2C8 is unavoidable, monitor patients closely for adverse reactions when taking strong inhibitors.
Effects of TAFINLAR on Other Drugs
Dabrafenib decreased the systemic exposures of midazolam (a CYP3A4 substrate), S-warfarin (a CYP2C9 substrate), and R-warfarin (a CYP3A4/CYP1A2 substrate) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] . Monitor international normalized ratio (INR) levels more frequently in patients receiving warfarin during initiation or discontinuation of dabrafenib. Coadministration of TAFINLAR with other substrates of these enzymes, including dexamethasone or hormonal contraceptives , can result in decreased concentrations and loss of efficacy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8. 3 )] . Substitute for these medications or monitor patients for loss of efficacy if use of these medications is unavoidable.
11 DESCRIPTION
Dabrafenib mesylate is a kinase inhibitor. The chemical name for dabrafenib mesylate is N-{3-[5-(2-amino-4-pyrimidinyl)-2-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]-2-fluorophenyl}-2,6-difluorobenzene sulfonamide, methanesulfonate salt. It has the molecular formula C 23 H 20 F 3 N 5 O 2 S 2 •CH 4 O 3 S and a molecular weight of 615.68 g/mol. Dabrafenib mesylate has the following chemical structure:
Dabrafenib mesylate is a white to slightly colored solid with three pK a s: 6.6, 2.2, and -1.5. It is very slightly soluble at pH 1 and practically insoluble above pH 4 in aqueous media.
TAFINLAR (dabrafenib) capsules for oral use are supplied as 50 mg and 75 mg capsules for oral administration. Each 50 mg capsule contains 59.25 mg dabrafenib mesylate equivalent to 50 mg of dabrafenib free base. Each 75 mg capsule contains 88.88 mg dabrafenib mesylate equivalent to 75 mg of dabrafenib free base. The inactive ingredients of TAFINLAR capsules are colloidal silicon dioxide, magnesium stearate, and microcrystalline cellulose. Capsule shells contain hypromellose, red iron oxide (E172), and titanium dioxide (E171).
TAFINLAR (dabrafenib) tablets for oral suspension are supplied as 10 mg tablets for oral administration. Each 10 mg tablet contains 11.85 mg dabrafenib mesylate equivalent to 10 mg of dabrafenib base. The inactive ingredients of TAFINLAR tablets are acesulfame potassium, artificial berry flavor, colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, mannitol, microcrystalline cellulose.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Dabrafenib is an inhibitor of some mutated forms of BRAF kinases with in vitro IC 50 values of 0.65, 0.5, and 1.84 nM for BRAF V600E, BRAF V600K, and BRAF V600D enzymes, respectively. Dabrafenib also inhibits wild-type BRAF and CRAF kinases with IC 50 values of 3.2 and 5.0 nM, respectively, and other kinases, such as SIK1, NEK11, and LIMK1 at higher concentrations. Some mutations in the BRAF gene, including those that result in BRAF V600E, can result in constitutively activated BRAF kinases that may stimulate tumor cell growth [see Indications and Usage (1)] . Dabrafenib inhibits cell growth of various BRAF V600 mutation-positive tumors in vitro and in vivo.
Dabrafenib and trametinib target two different kinases in the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK pathway. Use of dabrafenib and trametinib in combination resulted in greater growth inhibition of BRAF V600 mutation-positive tumor cell lines in vitro and prolonged inhibition of tumor growth in BRAF V600 mutation-positive tumor xenografts compared with either drug alone.
In the setting of BRAF-mutant colorectal cancer, induction of EGFR-mediated MAPK pathway re-activation has been identified as a mechanism of intrinsic resistance to BRAF inhibitors [see Indications and Usage (1.8)].
Pharmacodynamics
Cardiac Electrophysiology
The potential effect of TAFINLAR on QT interval was assessed in a dedicated multiple-dose study in 32 patients with BRAF V600 mutation-positive tumors. No large changes in the mean QT interval (i.e., > 20 ms) were detected with dabrafenib 300 mg administered twice daily (two times the recommended dosage).
In clinical trials, QTc (heart rate-corrected QT) prolongation to ≥ 500 ms occurred in 0.8% of 264 patients who received TAFINLAR with trametinib and in 1.5% of patients who received TAFINLAR as a single agent. The QTc was increased > 60 ms from baseline in 3.8% of patients who received TAFINLAR with trametinib and 3% of patients treated with TAFINLAR as a single agent.
Pharmacokinetics
Following administration of TAFINLAR capsules, dabrafenib C max and AUC increased in a dose-proportional manner across the dose range of 12 mg (0.08 times the approved recommended adult dose) to 300 mg (2 times the approved recommended adult dose), but the increase was less than dose-proportional after steady state twice-daily dosing. After twice-daily dosing, the mean accumulation ratio was 0.7, and the intersubject variability (CV%) of AUC at steady-state was 38%.
Absorption
The median time to achieve peak plasma concentration (T max ) is 2 hours. Mean absolute bioavailability of TAFINLAR capsules is 95% and TAFINLAR tablets for oral suspension is 76%.
Effect of Food
Following administration of TAFINLAR capsules, a high-fat meal (approximately 1000 calories, 58-75 grams fat, 58 grams carbohydrates, and 33 grams protein) decreased C max by 51%, decreased AUC by 31%, and delayed median T max by 3.6 hours as compared with the fasted state.
Administration of a single 150 mg dose of TAFINLAR tablets for the oral suspension with a low-fat, low-calorie meal (approximately 500 calories, 14 grams fat, 80 grams carbohydrates, and 12 grams protein) decreased dabrafenib C max by 35% and AUC by 29% as compared with the fasted state.
Distribution
Dabrafenib is 99.7% bound to human plasma proteins. The apparent volume of distribution (V c /F) is 70.3 L.
Elimination
The mean terminal half-life is 8 hours. Hydroxy-dabrafenib terminal half-life (10 hours) parallels that of dabrafenib while the carboxy- and desmethyl-dabrafenib metabolites exhibit longer half-lives (21 to 22 hours). The apparent clearance of dabrafenib is 17 L/h after a single dose and 34 L/h after twice-daily dosing for 2 weeks.
Metabolism
The metabolism of dabrafenib is primarily mediated by CYP2C8 and CYP3A4 to form hydroxy-dabrafenib. Hydroxy-dabrafenib is further oxidized via CYP3A4 to form carboxy-dabrafenib and subsequently excreted in bile and urine. Carboxy-dabrafenib is decarboxylated to form desmethyl-dabrafenib; desmethyl-dabrafenib may be reabsorbed from the gut. Desmethyl-dabrafenib is further metabolized by CYP3A4 to oxidative metabolites. Mean metabolite-to-parent AUC ratios following repeat-dose administration are 0.9, 11, and 0.7 for hydroxy-, carboxy-, and desmethyl-dabrafenib, respectively. Based on systemic exposure, relative potency, and pharmacokinetic properties, both hydroxy- and desmethyl-dabrafenib are likely to contribute to the clinical activity of dabrafenib.
Excretion
Fecal excretion is the major route of elimination accounting for 71% of radioactive dose while urinary excretion accounted for 23% of total radioactivity as metabolites only.
Specific Populations
Age (18 to 93 years), sex, weight (36 to 170 kg), and renal impairment (eGFR 15 to 89 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ) have no clinically relevant effect on the pharmacokinetics of dabrafenib.
Pediatric Patients
The pharmacokinetics of dabrafenib in glioma and other solid tumors were evaluated in 243 patients aged 1 to < 18 years following a single dose or multiple doses. Pharmacokinetic parameters in patients aged 1 to < 18 years are within range of values previously observed in adults given the same dose based on weight. Weight (6 to 156 kg) had a statistically significant effect on dabrafenib oral clearance in this population.
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
Mild hepatic impairment (bilirubin ≤ ULN and AST > ULN or bilirubin > 1x to 1.5x ULN and any AST) has no effect on systemic exposure to dabrafenib and its metabolites. No data are available in patients with moderate (bilirubin > 1.5x to 3x ULN and any AST) or severe (bilirubin > 3x to 10x ULN and any AST) hepatic impairment.
Drug Interaction Studies
Effect of Trametinib on Dabrafenib: Coadministration of TAFINLAR 75 mg twice daily with trametinib 2 mg daily resulted in a 23% increase in AUC of dabrafenib, a 33% increase in AUC of desmethyl-dabrafenib, and no change in AUC of hydroxy-dabrafenib as compared with administration of dabrafenib.
Effect of Strong Inhibitors of CYP3A4 or CYP2C8 on Dabrafenib: Coadministration of TAFINLAR 75 mg twice daily and ketoconazole (a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor) for 4 days increased dabrafenib AUC by 71%, hydroxy-dabrafenib AUC by 82%, and desmethyl-dabrafenib AUC by 68%.
Coadministration of TAFINLAR 75 mg twice daily and gemfibrozil (a strong CYP2C8 inhibitor) for 4 days increased dabrafenib AUC by 47%, with no change in the AUC of dabrafenib metabolites.
Effect of Strong Inducers of CYP3A4 or Moderate Inducers of CYP2C8 on Dabrafenib: Coadministration of TAFINLAR 150 mg twice daily and rifampin (a strong CYP3A4 and moderate CYP2C8 inducer) for 10 days decreased dabrafenib AUC by 34% and desmethyl-dabrafenib AUC by 30%, and had no effect on hydroxy-dabrafenib AUC.
Effect of Acid Reducing Agents on Dabrafenib: Coadministration of TAFINLAR 150 mg twice daily and rabeprazole for 4 days did not result in clinically relevant changes in exposures to dabrafenib and its metabolites.
Effect of Dabrafenib on CYP Substrates: Coadministration of TAFINLAR 150 mg twice daily for 15 days and a single dose of midazolam (a CYP3A4 substrate) decreased midazolam AUC by 65%. Coadministration of TAFINLAR 150 mg twice daily for 15 days and a single dose of warfarin decreased the AUC of S-warfarin (a CYP2C9 substrate) by 37% and the AUC of R-warfarin (CYP3A4/CYP1A2 substrate) by 33%.
In vitro data demonstrate that dabrafenib is an inducer of CYP3A4 and CYP2B6 via activation of the pregnane X receptor (PXR) and constitutive androstane receptor (CAR) nuclear receptors. Dabrafenib may also induce CYP2C enzymes via the same mechanism.
Effect of Transporters on Dabrafenib: Dabrafenib and its metabolites, hydroxyl-dabrafenib and desmethyl-dabrafenib, are substrates of human P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP) but are not substrates of organic cation transporter (OCT1) or organic anion transporting polypeptide (OATP1A2, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OATP2B1) in vitro.
Effect of Dabrafenib on Transporters: Coadministration of TAFINLAR 150 mg twice daily with a single dose of rosuvastatin (a sensitive OATP1B1 and OATP1B3 substrate) increased rosuvastatin C max by 2.6-fold but did not change its AUC.
Dabrafenib and its metabolites, hydroxy-dabrafenib, carboxy-dabrafenib, and desmethyl-dabrafenib, are inhibitors of organic anion transporter (OAT1 and OAT3) in vitro. Dabrafenib and desmethyl-dabrafenib are inhibitors of OCT2 and BCRP in vitro.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies with dabrafenib have not been conducted. TAFINLAR increased the risk of cuSCCs in patients in clinical trials.
Dabrafenib was not mutagenic in vitro in the bacterial reverse mutation assay (Ames test) or the mouse lymphoma assay and was not clastogenic in an in vivo rat bone marrow micronucleus test.
In a combined female fertility and embryo-fetal development study in rats, a reduction in fertility was noted at doses greater than or equal to 20 mg/kg/day (equivalent to the human exposure at the recommended adult dose based on AUC). A reduction in the number of ovarian corpora lutea was noted in pregnant females at 300 mg/kg/day (which is approximately three times the human exposure at the recommended adult dose based on AUC).
Male fertility studies with dabrafenib have not been conducted; however, in repeat-dose studies, testicular degeneration/depletion was seen in rats and dogs at doses equivalent to and three times the human exposure at the recommended adult dose based on AUC, respectively.
Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Adverse cardiovascular effects were noted in dogs at dabrafenib doses of 50 mg/kg/day (approximately five times the human exposure at the recommended adult dose based on AUC) or greater, when administered for up to 4 weeks. Adverse effects consisted of coronary arterial degeneration/necrosis and hemorrhage, as well as cardiac atrioventricular valve hypertrophy/hemorrhage.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Unresectable or Metastatic Melanoma – TAFINLAR as a Single Agent
BREAK-3 Study
The safety and efficacy of TAFINLAR as a single agent were evaluated in an international, multi-center, randomized (3:1), open-label, active-controlled trial (the BREAK-3 study; NCT01227889) conducted in 250 patients with previously untreated BRAF V600E mutation-positive, unresectable or metastatic melanoma. Patients with any prior use of BRAF inhibitors or MEK inhibitors were excluded. Patients were randomized to receive TAFINLAR 150 mg orally twice daily (n = 187) or dacarbazine 1000 mg/m 2 intravenously every 3 weeks (n = 63). Randomization was stratified by disease stage at baseline [unresectable Stage III (regional nodal or in-transit metastases), M1a (distant skin, subcutaneous, or nodal metastases), or M1b (lung metastases) versus M1c melanoma (all other visceral metastases or elevated serum LDH)]. The main efficacy outcome measure was progression-free survival (PFS) as assessed by the investigator. In addition, an independent radiology review committee (IRRC) assessed the following efficacy outcome measures in pre-specified supportive analyses: PFS, confirmed overall response rate (ORR), and duration of response (DoR).
The median age of patients in the BREAK-3 study was 52 years. The majority of the trial population was male (60%), White (99%), had an ECOG performance status of 0 (67%), had M1c disease (66%), and had normal LDH (62%). All patients had tumor tissue with mutations in BRAF V600E as determined by a clinical trial assay at a centralized testing site. Tumor samples from 243 patients (97%) were tested retrospectively using an FDA-approved companion diagnostic test, tHxID™-BRAF assay.
The median durations of follow-up prior to initiation of alternative treatment in patients randomized to receive TAFINLAR was 5.1 months and in the dacarbazine arm was 3.5 months. Twenty-eight (44%) patients crossed over from the dacarbazine arm at the time of disease progression to receive TAFINLAR.
The BREAK-3 study demonstrated a statistically significant increase in PFS in the patients treated with TAFINLAR. Table 20 and Figure 1 summarize the PFS results.
| Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; DoR, duration of response; HR, hazard ratio; NR, not reached. a Pike estimator, stratified by disease state. b Stratified log-rank test. | ||
| Investigator-Assessed Endpoints | TAFINLAR N = 187 | Dacarbazine N = 63 |
| Progression- F ree Survival | ||
| Number of events (%) | 78 (42%) | 41 (65%) |
| Progressive disease | 76 | 41 |
| Death | 2 | 0 |
| Median, months (95% CI) | 5.1 (4.9, 6.9) | 2.7 (1.5, 3.2) |
| HR a (95% CI) | 0.33 (0.20, 0.54) | |
| P value b | < 0.0001 | |
| Confirmed Tumor Responses | ||
| Overall response rate (95% CI) | 52% (44%, 59%) | 17% (9%, 29%) |
| Complete response, n (%) | 6 (3%) | 0 |
| Partial response, n (%) | 91 (48%) | 11 (17%) |
| Duration of response | ||
| Median DoR, months (95% CI) | 5.6 (5.4, NR) | NR (5.0, NR) |

In supportive analyses based on IRRC assessment and in an exploratory subgroup analysis of patients with retrospectively confirmed V600E mutation-positive melanoma with the tHxID™-BRAF assay, the PFS results were consistent with those of the primary efficacy analysis.
BREAK-MB Study
The activity of TAFINLAR for the treatment of BRAF V600E mutation-positive melanoma, metastatic to the brain was evaluated in a single-arm, open-label, two-cohort multi-center trial (the BREAK-MB study; NCT01266967). All patients received TAFINLAR 150 mg twice daily. Patients in Cohort A (n = 74) had received no prior local therapy for brain metastases, while patients in Cohort B (n = 65) had received at least one local therapy for brain metastases, including, but not limited to, surgical resection, whole brain radiotherapy, or stereotactic radiosurgery, such as gamma knife, linear-accelerated-based radiosurgery, or charged particles. In addition, patients in Cohort B were required to have evidence of disease progression in a previously treated lesion or an untreated lesion. Additional eligibility criteria were at least one measurable lesion of 0.5 cm or greater in largest diameter on contrast-enhanced MRI, stable or decreasing corticosteroid dose, and no more than two prior systemic regimens for treatment of metastatic disease. The major efficacy outcome measure was estimation of the overall intracranial response rate (OIRR) in each cohort.
The median age of patients in Cohort A was 50 years, 72% were male, 100% were White, 59% had a pre-treatment ECOG performance status of 0, and 57% had elevated LDH at baseline. The median age of patients in Cohort B was 51 years, 63% were male, 98% were White, 66% had a pre-treatment ECOG performance status of 0, and 54% had elevated LDH at baseline. The intracranial response rate as determined by an independent radiology review committee, masked to investigator response assessments, was 18% (95% CI: 10%, 28%) in Cohort A and 18% (95% CI: 10%, 30%) in Cohort B. The median duration of intracranial response was 4.6 months in both cohorts.
BRAF V600E or V600K Unresectable or Metastatic Melanoma – TAFINLAR With Trametinib
COMBI-d Study and COMBI-v Study
The safety and efficacy of TAFINLAR administered with trametinib were evaluated in two international, randomized, active-controlled trials: one double-blind trial (the COMBI-d study; NCT01584648) and one open-label trial (the COMBI-v study; NCT01597908).
The COMBI-d study compared TAFINLAR plus trametinib to TAFINLAR plus placebo as first-line therapy for patients with unresectable (Stage IIIC) or metastatic (Stage IV) BRAF V600E or V600K mutation-positive cutaneous melanoma. Patients were randomized (1:1) to receive TAFINLAR 150 mg twice daily plus trametinib 2 mg once daily or TAFINLAR 150 mg twice daily plus matching placebo. Randomization was stratified by LDH level (> ULN vs. ≤ ULN) and BRAF mutation subtype (V600E vs. V600K). The major efficacy outcome measure was investigator-assessed progression-free survival (PFS) per RECIST v1.1 with additional efficacy outcome measures of overall survival (OS) and confirmed overall response rate (ORR).
The COMBI-v study compared TAFINLAR and trametinib to vemurafenib as first-line treatment therapy for patients with unresectable (Stage IIIC) or metastatic (Stage IV) BRAF V600E or V600K mutation-positive cutaneous melanoma. Patients were randomized (1:1) to receive TAFINLAR 150 mg twice daily and trametinib 2 mg once daily or vemurafenib 960 mg twice daily. Randomization was stratified by lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) level (> ULN vs. ≤ ULN) and BRAF mutation subtype (V600E vs. V600K). The major efficacy outcome measure was OS. Additional efficacy outcome measures were PFS and ORR as assessed by investigator per RECIST v1.1.
In the COMBI-d study, 423 patients were randomized to TAFINLAR plus trametinib (n = 211) or TAFINLAR plus placebo (n = 212). The median age was 56 years (range: 22 to 89), 53% were male, > 99% were White, 72% had ECOG performance status of 0, 4% had Stage IIIC, 66% had M1c disease, 65% had normal LDH, and 2 patients had a history of brain metastases. All patients had tumor containing BRAF V600E or V600K mutations as determined by centralized testing with the FDA-approved companion diagnostic test; 85% with BRAF V600E mutation positive melanoma and 15% with BRAF V600K mutation positive melanoma.
In the COMBI-v study, 704 patients were randomized to TAFINLAR plus trametinib (n = 352) or single-agent vemurafenib (n = 352). The median age was 55 years (range: 18 to 91), 96% were White, 55% were male, 6% had Stage IIIC, 61% had M1c disease, 67% had normal LDH, 70% had ECOG performance status of 0, 89% had BRAF V600E mutation-positive melanoma, and one patient had a history of brain metastases.
The COMBI-d and COMBI-v studies demonstrated statistically significant improvements in OS and PFS. Table 21 and Figures 2 and 3 summarize the efficacy results.
| Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; DoR, duration of response; HR, hazard ratio; NR, not reached; ORR, overall response rate. a P -value is comparing with the allocated alpha of 0.021 for the interim analysis based on 77% information. b PFS and ORR were assessed by investigator. | ||||
| Endpoint | COMBI-d Study | COMBI-v Study | ||
| TAFINLAR plus Trametinib N = 211 | TAFINLAR plus Placebo N = 212 | TAFINLAR plus Trametinib N = 352 | Vemurafenib N = 352 | |
| Overall Survival | ||||
| Number of deaths (%) | 99 (47%) | 123 (58%) | 100 (28%) | 122 (35%) |
| Median, months (95% CI) | 25.1 (19.2, NR) | 18.7 (15.2, 23.1) | NR (18.3, NR) | 17.2 (16.4, NR) |
| HR (95% CI) | 0.71 (0.55, 0.92) | 0.69 (0.53, 0.89) | ||
| P value (log-rank test) | 0.01 | 0.005 a | ||
| Progression-Free Survival b | ||||
| Number of events (%) | 102 (48%) | 109 (51%) | 166 (47%) | 217 (62%) |
| Median, months (95% CI) | 9.3 (7.7, 11.1) | 8.8 (5.9, 10.9) | 11.4 (9.9, 14.9) | 7.3 (5.8, 7.8) |
| HR (95% CI) | 0.75 (0.57, 0.99) | 0.56 (0.46, 0.69) | ||
| P value (log-rank test) | 0.035 | < 0.001 | ||
| Overall Response Rate b | ||||
| ORR (95% CI) | 66% (60%, 73%) | 51% (44%, 58%) | 64% (59%, 69%) | 51% (46%, 56%) |
| P value | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | ||
| Complete response | 10% | 8% | 13% | 8% |
| Partial response | 56% | 42% | 51% | 43% |
| Median DoR, months (95% CI) | 9.2 (7.4, NR) | 10.2 (7.5, NR) | 13.8 (11.0, NR) | 7.5 (7.3, 9.3) |


COMBI-MB Study
The activity of TAFINLAR with trametinib for the treatment of BRAF V600E or V600K mutation-positive melanoma, metastatic to the brain, was evaluated in a non-randomized, open-label, multi-center, multi-cohort trial (the COMBI-MB study; NCT02039947). Eligible patients were required to have at least one measurable intracranial lesion and to have no leptomeningeal disease, parenchymal brain metastasis greater than 4 cm in diameter, ocular melanoma, or primary mucosal melanoma. Patients received TAFINLAR 150 mg orally twice daily and trametinib 2 mg orally once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The major efficacy outcome measure was intracranial response rate, defined as the percentage of patients with a confirmed intracranial response per RECIST v1.1, modified to allow up to five intracranial target lesions at least 5 mm in diameter, as assessed by independent review.
The COMBI-MB study enrolled 121 patients with a BRAF V600E (85%) or V600K (15%) mutation. The median age was 54 years (range: 23 to 84), 58% were male, 100% were White, 8% were from the United States, 65% had normal LDH at baseline, and 97% had an ECOG performance status of 0 or 1. Intracranial metastases were asymptomatic in 87% and symptomatic in 13% of patients, 22% received prior local therapy for brain metastases, and 87% also had extracranial metastases.
The intracranial response rate was 50% (95% CI: 41, 60), with a complete response rate of 4.1% and a partial response rate of 46%. The median duration of intracranial response was 6.4 months (range: 1 to 31). Of the patients with an intracranial response, 9% had stable or progressive disease as their best overall response.
Adjuvant Treatment of BRAF V600E or V600K Mutation-Positive Melanoma
The efficacy of TAFINLAR administered with trametinib was evaluated in an international, multi-center, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (COMBI AD; NCT01682083) that enrolled patients with Stage III melanoma with BRAF V600E or V600K mutations as detected by the tHxID ™ -BRAF assay and pathologic involvement of regional lymph node(s). Enrollment required complete resection of melanoma with complete lymphadenectomy within 12 weeks prior to randomization. The trial excluded patients with mucosal or ocular melanoma, unresectable in-transit metastases, distant metastatic disease, or prior systemic anti-cancer treatment, including radiotherapy. Patients were randomized (1:1) to receive TAFINLAR 150 mg twice daily and trametinib 2 mg once daily or two placebos for up to 1 year. Randomization was stratified by BRAF mutation status (V600E or V600K) and American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC; 7 th Edition) Stage (IIIA, IIIB, or IIIC). The major efficacy outcome measure was relapse-free survival (RFS), defined as the time from randomization to disease recurrence (local, regional, or distant metastasis), new primary melanoma, or death from any cause, whichever occurred first as assessed by the investigator. Patients underwent imaging for tumor recurrence every 3 months for the first two years and every 6 months thereafter.
In COMBI-AD, a total of 870 patients were randomized: 438 to TAFINLAR in combination with trametinib and 432 to placebo. Median age was 51 years (range: 18 to 89), 55% were male, 99% were White, and 91% had an ECOG performance status of 0. Disease characteristics were AJCC Stage IIIA (18%), Stage IIIB (41%), Stage IIIC (40%), stage unknown (1%); BRAF V600E mutation (91%), BRAF V600K mutation (9%); macroscopic lymph nodes (65%); and tumor ulceration (41%).
The median duration of follow-up at the time of the primary analysis was 2.8 years.
COMBI-AD showed a statistically significant improvement in RFS in patients randomized to TAFINLAR in combination with trametinib compared to those randomized to placebo. Efficacy results are presented in Table 22 and Figure 4.
| Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; HR, hazard ratio; NE, not estimable. a Pike estimator obtained from the stratified log-rank test. b Log-rank test stratified by disease stage (IIIA vs. IIIB vs. IIIC) and BRAF V600 mutation type (V600E vs. V600K). | ||
| Investigator-Assessed Endpoint | TAFINLAR plus Trametinib N = 438 | Placebo N = 432 |
| Relapse-Free Survival | ||
| Number of events (%) | 166 (38) | 248 (57) |
| Median, months (95% CI) | NE (44.5, NE) | 16.6 (12.7, 22.1) |
| HR (95% CI) a | 0.47 (0.39, 0.58) | |
| P value b | < 0.0001 | |

The median duration of follow-up at the time of the final overall survival analysis was 8.0 years. The estimated hazard ratio for overall survival was 0.80 (95% CI: 0.62, 1.01; p = 0.063) with 125 events (29%) in the combination arm and 136 events (31%) in the placebo arm. Median overall survival was not estimable in both arms.
BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
The safety and efficacy of TAFINLAR alone or administered with trametinib were evaluated in a multi-center, three-cohort, non-randomized, activity-estimating, open-label trial (Study BRF113928, NCT01336634). Key eligibility criteria were locally confirmed BRAF V600E mutation-positive metastatic NSCLC, no prior exposure to BRAF or MEK-inhibitor, and absence of EGFR mutation or ALK rearrangement (unless patients had progression on prior tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy). Patients enrolled in Cohorts A and B were required to have received at least one previous platinum-based chemotherapy regimen for NSCLC with demonstrated disease progression but no more than three prior systemic regimens. Patients enrolled in Cohort C could not have received prior systemic therapy for metastatic NSCLC. Patients in Cohort A received TAFINLAR 150 mg twice daily. Patients in Cohorts B and C received TAFINLAR 150 mg twice daily and trametinib 2 mg once daily. The major efficacy outcome measure was overall response rate (ORR) per RECIST v1.1 as assessed by independent review committee (IRC) and duration of response (DoR).
There were a total of 171 patients enrolled which included 78 patients enrolled in Cohort A, 57 patients enrolled in Cohort B, and 36 patients enrolled in Cohort C. The characteristics of the study population were: a median age of 66 years, 48% male; 81% White, 14% Asian, 3% Black, and 2% Hispanic; 60% former smokers, 32% never smokers, and 8% current smokers; 27% had ECOG performance status (PS) of 0, 63% had ECOG PS of 1, and 11% had ECOG PS of 2; 99% had metastatic disease of which 6% had brain metastasis at baseline and 14% had liver metastasis at baseline; 11% had systemic anti-cancer therapy in the adjuvant setting and 58% of the 135 previously treated patients had only one line of prior systemic therapy for metastatic disease; 98% had non-squamous histology.
Efficacy results are summarized in Table 23.
| Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; DoR, duration of response; ORR, overall response rate. a Represents final analysis results (cutoff date of 24 Feb 2021) for the primary analysis responder cohorts. | |||
| Treatment | TAFINLAR | TAFINLAR plus Trametinib | |
| Population | Previously Treated N = 78 | Previously Treated N = 57 | Treatment Naïve N = 36 |
| Overall Response Rate a | |||
| ORR (95% CI) | 27% (18%, 38%) | 61% (48%, 74%) | 61% (44%, 77%) |
| Complete response | 1% | 5% | 8% |
| Partial response | 26% | 56% | 53% |
| Duration of Response a | n = 21 | n = 35 | n = 22 |
| Median DoR, months (95% CI) | 18.0 (4.2, 40.1) | 9.0 (5.8, 26.2) | 15.2 (7.8, 23.5) |
In a subgroup analysis of patients with retrospectively, centrally confirmed BRAF V600E mutation-positive NSCLC with the Oncomine ™ Dx Target Test, the ORR results were similar to those presented in Table 22.
BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Locally Advanced or Metastatic Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer
The safety and efficacy of TAFINLAR administered with trametinib was evaluated in an activity-estimating, nine-cohort, multi-center, non-randomized, open-label trial (Study BRF117019; NCT02034110) in patients with rare cancers with the BRAF V600E mutation, including locally advanced, unresectable, or metastatic ATC with no standard locoregional treatment options. Trial BRF117019 excluded patients who could not swallow or retain the medication; who received prior treatment with BRAF or MEK inhibitors; with symptomatic or untreated CNS metastases; or who had airway obstruction. Patients received TAFINLAR 150 mg twice daily and trametinib 2 mg once daily. The major efficacy outcome measure was overall response rate (ORR) per RECIST v1.1 as assessed by independent review committee (IRC) and duration of response (DoR).
Thirty-six patients were enrolled and were evaluable for response in the ATC cohort. The median age was 71 years (range: 47 to 85); 44% were male, 50% White, 44% Asian; and 94% had ECOG performance status of 0 or 1. Prior anti-cancer treatments included surgery and external beam radiotherapy (83% each), and systemic therapy (67%).
Efficacy results are summarized in Table 24.
| Abbreviations: ATC, anaplastic thyroid cancer; CI, confidence interval; DoR, duration of response; NE, not estimable; ORR, overall response rate. | |
| ATC Cohort Population | N = 36 |
| Overall Response Rate | |
| ORR (95% CI) | 53% (35.5%, 69.6%) |
| Complete response | 6% |
| Partial response | 47% |
| Duration of Response | n = 19 |
| Median DoR, months (95% CI) | 13.6 (3.8, NE) |
| % with DoR ≥ 6 months | 68% |
| % with DoR ≥ 12 months | 53% |
BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Unresectable or Metastatic Solid Tumors
The safety and efficacy of TAFINLAR in combination with trametinib for the treatment of BRAF V600E mutation-positive unresectable or metastatic solid tumors were evaluated in Trials BRF117019, NCI-MATCH, and CTMT212X2101, and supported by results in COMBI-d, COMBI-v [see Clinical Studies (14.2)] , and BRF113928 [see Clinical Studies (14.4)] . In adult studies, patients received TAFINLAR 150 mg twice daily and trametinib 2 mg once daily. The major efficacy outcome measures were ORR per RECIST v1.1, RANO [HGG] or modified RANO [LGG] criteria and duration of response (DoR).
BRF117019 Study and NCI-MATCH Study
Study BRF117019 (NCT02034110) [see Clinical Studies (14.5)] is a multi-cohort, multi-center, non-randomized, open-label trial in adult patients with selected tumors with the BRAF V600E mutation, including high-grade glioma (HGG) (n = 45), biliary tract cancer (BTC) (n = 43), low-grade glioma (LGG) (n = 13), adenocarcinoma of small intestine (ASI) (n = 3), gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) (n = 1), and anaplastic thyroid cancer [see Clinical Studies (14.5)] . Patients were enrolled based on local assessments of BRAF V600E mutation status; a central laboratory confirmed the BRAF V600E mutation in 93 of 105 patients.
Arm H (EAY131-H) of the NCI-MATCH study (NCT02465060) is a single-arm, open-label study that enrolled patients with a BRAF V600E mutation. Patients with melanoma, thyroid cancer, or CRC were excluded. BRAF V600E mutation status for enrollment was determined either by central or local laboratory test. The study included adult patients with solid tumors including gastrointestinal tumors (n = 14), lung tumors (n = 7), gynecologic or peritoneal tumors (n = 6), CNS tumors (n = 4), and ameloblastoma of mandible (n = 1).
Among the 131 patients enrolled in BRF117019 and NCI-MATCH with the tumor types shown in Table 25, the baseline characteristics were: median age of 51 years with 20% age 65 or older; 56% female; 85% White, 9% Asian, 3% Black, 3% other; and 37% ECOG PS of 0, 56% ECOG PS of 1, and 6% ECOG PS of 2. Of the 131 patients, 90% received prior systemic therapy.
Efficacy results in patients with solid tumors are summarized in Table 25.
| Abbreviations: NA, not applicable; PR, partial response. a Excludes NSCLC (n = 6) and ATC (n = 36) (previously approved tumor types for TAFINLAR in combination with trametinib). b Median DoR 9.8 months (95% CI: 5.3, 20.4). c Median DoR 13.6 months (95% CI: 5.5, 26.7). d Denotes a right-censored DoR. | ||||
| Tumor Type a | N | Objective Response Rate | Duration of Response | |
| % | 95% CI | Range (months) | ||
| Biliary tract cancer b | 48 | 46 | (31, 61) | 1.8 d , 40 d |
| High-grade glioma c | 48 | 33 | (20, 48) | 3.9, 44 |
| Glioblastoma | 32 | 25 | (12, 43) | 3.9, 27 |
| Anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma | 6 | 67 | (22, 96) | 6, 43 |
| Anaplastic astrocytoma | 5 | 20 | (0.5, 72) | 15 |
| Astroblastoma | 2 | 100 | (16, 100) | 15, 23 d |
| Undifferentiated | 1 | PR | (2.5, 100) | 6 |
| Anaplastic ganglioglioma | 1 | 0 | NA | NA |
| Anaplastic oligodendroglioma | 1 | 0 | NA | NA |
| Low-grade glioma | 14 | 50 | (23, 77) | 6, 29 d |
| Astrocytoma | 4 | 50 | (7, 93) | 7, 23 |
| Ganglioglioma | 4 | 50 | (7, 93) | 6, 13 |
| Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma | 2 | 50 | (1.3, 99) | 6 |
| Pilocytic astrocytoma | 2 | 0 | NA | NA |
| Choroid plexus papilloma | 1 | PR | (2.5, 100) | 29 d |
| Gangliocytoma/ganglioglioma | 1 | PR | (2.5, 100) | 18 d |
| Low-grade serous ovarian carcinoma | 5 | 80 | (28, 100) | 12, 42 d |
| Adenocarcinoma small intestine | 4 | 50 | (7, 93) | 7, 8 |
| Adenocarcinoma pancreas | 3 | 0 | NA | NA |
| Mixed ductal/adenoneuroendocrine carcinoma | 2 | 0 | NA | NA |
| Neuroendocrine carcinoma of colon | 2 | 0 | NA | NA |
| Ameloblastoma of mandible | 1 | PR | (2.5, 100) | 30 |
| Combined small cell-squamous carcinoma of lung | 1 | PR | (2.5, 100) | 5 |
| Mucinous-papillary serous adenocarcinoma of peritoneum | 1 | PR | (2.5, 100) | 8 |
| Adenocarcinoma of anus | 1 | 0 | NA | NA |
| Gastrointestinal stromal tumor | 1 | 0 | NA | NA |
CTMT212X2101 (X2101) Study
Study X2101 (NCT02124772) was a multi-center, open-label, multi-cohort study in pediatric patients with refractory or recurrent solid tumors. Part C was a dose escalation of TAFINLAR in combination with trametinib in patients with a BRAF V600E mutation. Part D was a cohort expansion phase of TAFINLAR in combination with trametinib in patients with LGG with a BRAF V600E mutation. The major efficacy outcome measure was ORR as assessed by independent review committee per RANO criteria.
The efficacy of TAFINLAR in combination with trametinib was evaluated in 48 pediatric patients, including 34 patients with LGG and 2 patients with HGG.
For patients with BRAF V600E mutation positive LGG and HGG in Parts C and D, the median age was 10 years (range: 1 to 17); 50% were male, 75% White, 8% Asian, 3% Black; and 58% had Karnofsky/Lansky performance status of 100. Prior anti-cancer treatments included surgery (83%), external beam radiotherapy (2.8%), and systemic therapy (92%). The ORR was 25% (95% CI: 12%, 42%). For the 9 patients who responded, DoR was ≥ 6 months for 78% of patients and ≥ 24 months for 44% of patients.
CDRB436G2201 (G2201) Study – High-Grade Glioma Cohort
Study G2201 (NCT02684058) was a multi-center, randomized, open-label, Phase II study of dabrafenib and trametinib in chemotherapy-naïve pediatric patients with BRAF V600E mutant low-grade glioma (LGG) and patients with relapsed or progressive BRAF V600E mutant HGG. Patients with HGG were enrolled in a single-arm cohort. The major efficacy outcome measure for the HGG cohort was ORR as assessed by independent review committee per RANO 2010 criteria.
The efficacy of TAFINLAR in combination with trametinib was evaluated in 41 pediatric patients with relapsed or progressive HGG.
For patients with BRAF V600E mutant HGG enrolled in the HGG cohort, the median age was 13 years (range: 2 to 17); 56% were female, 61% White, 27% Asian, 2.4% Black, and 37% had Karnofsky/Lansky performance status of 100. Prior anti-cancer treatments included surgery (98%), radiotherapy (90%), and chemotherapy (81%). The ORR was 56% (95% CI: 40, 72). The median DoR was not reached (95% CI: 9.2, NE). For the 23 patients who responded in the HGG cohort, DoR was ≥ 6 months for 78% of patients, ≥ 12 months for 48% of patients, and ≥ 24 months for 22% of patients.
BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Low-Grade Glioma
CDRB436G2201 (G2201) Study – Low-Grade Glioma Cohort
The safety and efficacy of TAFINLAR in combination with trametinib for the treatment of BRAF V600E mutation-positive low-grade glioma (LGG) in pediatric patients aged 1 to < 18 years of age were evaluated in the multi-center, open-label trial (Study CDRB436G2201; NCT02684058). Patients with LGG (WHO grades 1 and 2) who required first systemic therapy were randomized in a 2:1 ratio to dabrafenib plus trametinib (D + T) or carboplatin plus vincristine (C + V).
BRAF mutation status was identified prospectively via a local assessment or a central laboratory test. In addition, retrospective testing of available tumor samples by the central laboratory was performed to evaluate BRAF V600E mutation status.
Patients received age- and weight-based dosing of TAFINLAR and trametinib until loss of clinical benefit or until unacceptable toxicity. Carboplatin and vincristine were dosed based on body surface area at doses 175 mg/m 2 and 1.5 mg/m 2 (0.05 mg/kg for patients < 12 kg), respectively, as one 10-week induction course followed by eight 6-week cycles of maintenance therapy.
The major efficacy outcome measure was overall response rate (ORR) by independent review based on RANO LGG (2017) criteria. Additional efficacy outcome measures were progression-free survival and overall survival. The primary analysis was performed when all patients had completed at least 32 weeks of therapy.
In the LGG cohort, 110 patients were randomized to D + T (n = 73) or C + V (n = 37). Median age was 9.5 years (range: 1 to 17); 60% were female. Study G2201 showed a statistically significant improvement in ORR and PFS in LGG patients randomized to D + T compared to those randomized to C + V. Efficacy results are shown in Table 26.
| Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; DoR, duration of response; NE, not estimable; ORR, overall response rate. a Based on Clopper-Pearson exact confidence interval. b Based on Kaplan-Meier method. c Based on proportional hazards model. | ||||
| TAFINLAR plus Trametinib N = 73 | Carboplatin plus Vincristine N = 37 | |||
| Overall Response Rate | ||||
| ORR% (95% CI) a | 46.6 (34.8, 58.6) | 10.8 (3.0, 25.4) | ||
| P -value | < 0.001 | |||
| Complete response, n (%) | 2 (2.7) | 1 (2.7) | ||
| Partial response, n (%) | 32 (44) | 3 (8) | ||
| Duration of Response | ||||
| Median (95% CI) b , months | 23.7 (14.5, NE) | NE (6.6, NE) | ||
| % with observed DoR ≥ 12 months | 56 | 50 | ||
| % with observed DoR ≥ 24 months | 15 | 25 | ||
| Progression-Free Survival | ||||
| Median (95% CI) b , months | 20.1 (12.8, NE) | 7.4 (3.6, 11.8) | ||
| Hazard ratio (95% CI) c | 0.31 (0.17, 0.55) | |||
| P -value | < 0.001 | |||

At the time of the interim analysis of overall survival (OS), conducted when all patients had completed at least 32 weeks of treatment or had discontinued earlier, there was one death on the C + V arm. The OS results at interim analysis did not reach statistical significance.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
TAFINLAR Capsules:
50 mg capsules: Dark red capsule imprinted with ‘GS TEW’ and ‘50 mg’ available in bottles of 120 with child-resistant closures (NDC 0078-0682-66). Each bottle contains a silica gel desiccant.
75 mg capsules: Dark pink capsule imprinted with ‘GS LHF’ and ‘75 mg’ available in bottles of 120 with child-resistant closures (NDC 0078-0681-66). Each bottle contains a silica gel desiccant.
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C and 30°C (59°F and 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Store and dispense in the original bottle with the desiccant.
TAFINLAR Tablets for Oral Suspension:
10 mg tablets for oral suspension: white to slightly yellow, round biconvex 6 mm tablet debossed with “D” on one side and “NVR” on the other side. Available in bottles of 210 with child-resistant closures (NDC 0078-1154-21). Each bottle contains 2 silica gel desiccants.
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C and 30°C (59°F and 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Store and dispense in the original bottle with the desiccant.
| This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Revised: March 2024 |
| INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE TAFINLAR ® (TAFF-in-lar) (dabrafenib) tablets for oral suspension | |
| This “Instructions for Use” contains information on how to prepare and take or give TAFINLAR tablets for oral suspension. | |
| Important information you need to know before taking or giving TAFINLAR tablets for oral suspension | |
| |
| The TAFINLAR pack should contain: | |
 | |
| You will also need drinking water. For taking or giving a dose of the TAFINLAR oral suspension by swallowing, go to Section A. For taking or giving a dose of the TAFINLAR oral suspension through a feeding tube or using an oral syringe, go to Section B. | |
| Section A. Preparing and taking or giving a dose of the TAFINLAR oral suspension by swallowing directly from the dosing cup | |
If any of the TAFINLAR oral suspension comes into contact with your skin or eyes when you are following the steps below, follow instructions in the section “Important information you need to know before taking or giving TAFINLAR tablets for oral suspension”. To prepare and take or give a dose of TAFINLAR oral suspension, you will need:
| |
Step 1. Wash and dry your hands before preparing TAFINLAR tablets as an oral suspension.
| 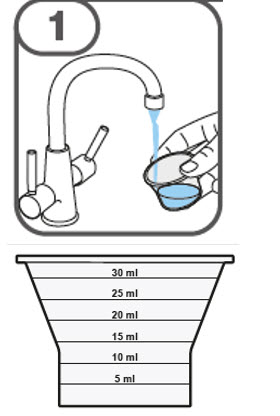 |
Step 2. Remove the bottle cap by pushing down and turning counter-clockwise in the direction of the arrow, as shown.
|  |
| Step 3. Count out the prescribed number of tablets into your hand. | 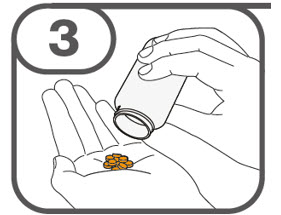 |
|  |
|  |
| Step 4. Place the cap back onto the bottle and turn it clockwise in the direction of the arrow, as shown to close it. |  |
Step 5. With one hand, tilt the dosing cup.
|  |
| Step 6. Drink the TAFINLAR oral suspension from the dosing cup. Important: After swallowing, there will be some medicine residue still inside the dosing cup. The medicine residue may be difficult to see. Follow Steps 7 through 9 to take or give any medicine residue still in the dosing cup so that you give the full dose of TAFINLAR. |  |
| Step 7. Add about 5 mL of water to the empty dosing cup. |  |
| Step 8. Stir with the handle of a teaspoon to loosen the remaining medicine residue. | 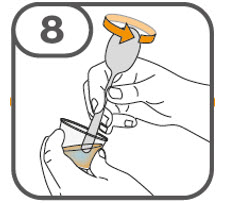 |
| Step 9. Drink the water and medicine residue mixture. |  |
| |
| Step 10. Go to Section C. “Cleaning the dosing cup and oral syringe (if used)”. | |
| Section B. Preparing and giving TAFINLAR tablets as an oral suspension via feeding tube or oral syringe | |
Important administration information Make sure all the tablets are dispersed before taking or giving the TAFINLAR oral suspension. The minimum feeding tube size you may use to give the TAFINLAR oral suspension:
| |
| Step 1. Follow Steps 1 through 5 in Section A to disperse the TAFINLAR tablets. If using a feeding tube, flush the feeding tube with drinking water then continue with Step 2 below. | |
| Step 2. Draw up all of the TAFINLAR oral suspension from the dosing cup into an oral syringe by pulling back on the plunger. Be sure to use an oral syringe that can be used with the feeding tube or that can be used to give the TAFINLAR oral suspension by mouth. Ask your healthcare provider if you are not sure what oral syringe to use. |  |
| Step 3. If giving the dose through a feeding tube, give the TAFINLAR oral suspension into the feeding tube according to the feeding tube manufacturer’s instructions. If giving a dose of TAFINLAR oral suspension using an oral syringe, place the open end of the oral syringe inside the mouth with the tip pointing toward the inside of either cheek. If you are giving a dose of the TAFINLAR oral suspension to a child, make sure they are sitting upright. Slowly push the plunger all the way down to give the full dose of TAFINLAR oral suspension. Warning: Giving TAFINLAR oral suspension directly into the throat or pushing down on the plunger too fast may cause choking. |  |
| Step 4. Add about 5 mL of water to the empty dosing cup. |  |
| Step 5. Stir with the handle of a teaspoon to loosen the remaining medicine residue inside the dosing cup. |  |
| Step 6. Draw up the water and medicine residue mixture. | 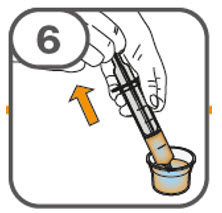 |
| Step 7. Give the water and medicine residue mixture through the feeding tube or into the inside of the cheek. |  |
| |
| Step 8. After repeating Steps 4 through 7 three times, flush the feeding tube with drinking water. Then go to the cleaning steps in Section C. | |
| Section C. Cleaning the dosing cup and oral syringe (if used) | |
| Use only clean water to rinse the dosing cup. Do not use soap or dishwashing liquid when cleaning the dosing cup. | |
Step 1. Rinse the dosing cup under clean cool water right away after dosing.
|  |
Step 2. Rinse the teaspoon in clean cold water then wash in warm soapy water and dry using clean paper towels.
|  |
| Step 3. Clean the used oral syringe, as instructed by your healthcare provider, or according to the manufacturer’s instructions. |  |
| Section D. How to throw away TAFINLAR tablets or oral suspension that are expired or no longer needed, or old dosing cups | |
| |
| Section E. How to clean up any spilled TAFINLAR oral suspension | |
| If you accidentally spill any TAFINLAR oral suspension, clean up the spill as follows: 1. Put on plastic gloves. 2. Soak up the spilled TAFINLAR oral suspension completely using an absorbent material, such as paper towels soaked with either a mixture of water and household disinfectant or with ethanol 70% (or higher grade). 3. Repeat the cleaning with fresh soaked absorbent material at least three times until the area is clean. 4. Dry the area with paper towels. 5. Throw away all the disposable materials used to clean the spillage into a sealable plastic bag. 6. Throw away the bags into the trash. 7. Wash your hands well with soap and water. | |
| How should I store TAFINLAR tablets for oral suspension? | |
| |
| Distributed by: Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation East Hanover, New Jersey 07936 © Novartis | |
T2024-24
Mechanism of Action
Dabrafenib is an inhibitor of some mutated forms of BRAF kinases with in vitro IC 50 values of 0.65, 0.5, and 1.84 nM for BRAF V600E, BRAF V600K, and BRAF V600D enzymes, respectively. Dabrafenib also inhibits wild-type BRAF and CRAF kinases with IC 50 values of 3.2 and 5.0 nM, respectively, and other kinases, such as SIK1, NEK11, and LIMK1 at higher concentrations. Some mutations in the BRAF gene, including those that result in BRAF V600E, can result in constitutively activated BRAF kinases that may stimulate tumor cell growth [see Indications and Usage (1)] . Dabrafenib inhibits cell growth of various BRAF V600 mutation-positive tumors in vitro and in vivo.
Dabrafenib and trametinib target two different kinases in the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK pathway. Use of dabrafenib and trametinib in combination resulted in greater growth inhibition of BRAF V600 mutation-positive tumor cell lines in vitro and prolonged inhibition of tumor growth in BRAF V600 mutation-positive tumor xenografts compared with either drug alone.
In the setting of BRAF-mutant colorectal cancer, induction of EGFR-mediated MAPK pathway re-activation has been identified as a mechanism of intrinsic resistance to BRAF inhibitors [see Indications and Usage (1.8)].