Get your patient on Tecentriq (Atezolizumab)
Tecentriq prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Tecentriq patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Administer TECENTRIQ intravenously over 60 minutes. If the first infusion is tolerated, all subsequent infusions may be delivered over 30 minutes.
NSCLC
- In the adjuvant setting, administer TECENTRIQ following resection and up to 4 cycles of platinum-based chemotherapy as 840 mg every 2 weeks, 1200 mg every 3 weeks or 1680 mg every 4 weeks for up to 1 year. (2.2 )
- In the metastatic setting, administer TECENTRIQ as 840 mg every 2 weeks, 1200 mg every 3 weeks, or 1680 mg every 4 weeks. (2.2 )
- When administering with chemotherapy with or without bevacizumab, administer TECENTRIQ prior to chemotherapy and bevacizumab when given on the same day. (2.2 )
Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Administer TECENTRIQ as 840 mg every 2 weeks, 1200 mg every 3 weeks, or 1680 mg every 4 weeks. Administer TECENTRIQ prior to chemotherapy when given on the same day. (2.2 )
Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Administer TECENTRIQ as 840 mg every 2 weeks, 1200 mg every 3 weeks, or 1680 mg every 4 weeks. Administer TECENTRIQ prior to bevacizumab when given on the same day. Bevacizumab is administered at 15 mg/kg every 3 weeks. (2.2 )
Melanoma
- Following completion of a 28-day cycle of cobimetinib and vemurafenib, administer TECENTRIQ 840 mg every 2 weeks, 1200 mg every 3 weeks, or 1680 mg every 4 weeks with cobimetinib 60 mg orally once daily (21 days on /7 days off) and vemurafenib 720 mg orally twice daily. (2.2 )
ASPS
Patient Selection for Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Melanoma
Select patients with Stage II to IIIA non-small cell lung cancer for treatment with TECENTRIQ as a single agent based on PD-L1 expression on tumor cells [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ].
Select patients with first-line metastatic non-small cell lung cancer for treatment with TECENTRIQ as a single agent based on the PD-L1 expression on tumor cells or on tumor-infiltrating immune cells [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ].
Information on FDA-approved tests for the determination of PD-L1 expression in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer are available at: http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics.
Select patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma for treatment with TECENTRIQ in combination with cobimetinib and vemurafenib after confirming the presence of a BRAF V600 mutation [see Clinical Studies (14.4) ]. Information on FDA-approved tests for the detection of BRAF V600 mutations in melanoma is available at: http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics.
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosages of TECENTRIQ are presented in Table 1 . Administer TECENTRIQ as an intravenous infusion over 60 minutes. If the first infusion is tolerated, all subsequent infusions may be delivered over 30 minutes.
| Indication | Recommended Dosage of TECENTRIQ | Duration of Therapy |
|---|---|---|
| Metastatic NSCLC |
| Until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity |
| Adjuvant Treatment of NSCLC |
| Up to one year, unless there is disease recurrence or unacceptable toxicity |
| ASPS (adult) |
| Until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity |
| ASPS (pediatric, 2 years of age and older) | 15 mg/kg (up to a maximum 1200 mg) every 3 weeks |
The recommended intravenous dosages of TECENTRIQ in combination with other therapeutic agents are presented in Table 2 . Refer to the respective Prescribing Information for each therapeutic agent administered in combination with TECENTRIQ for the recommended dosage information, as appropriate.
| Indication | Recommended Dosage of TECENTRIQ | Duration of Therapy |
|---|---|---|
| NSCLC |
| Until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity |
| SCLC |
| |
| HCC |
| |
| Melanoma |
Prior to initiating TECENTRIQ, patients should receive a 28-day treatment cycle of cobimetinib 60 mg orally once daily (21 days on and 7 days off) and vemurafenib 960 mg orally twice daily from Days 1-21 and vemurafenib 720 mg orally twice daily from Days 22-28. |
Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
No dose reduction for TECENTRIQ is recommended. In general, withhold TECENTRIQ for severe (Grade 3) immune-mediated adverse reactions. Permanently discontinue TECENTRIQ for life-threatening (Grade 4) immune-mediated adverse reactions, recurrent severe (Grade 3) immune-mediated reactions that require systemic immunosuppressive treatment, or an inability to reduce corticosteroid dose to 10 mg or less of prednisone or equivalent per day within 12 weeks of initiating steroids.
Dosage modifications for TECENTRIQ for adverse reactions that require management different from these general guidelines are summarized in Table 3 .
| Adverse Reaction | Severity Based on Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE), version 4 | Dosage Modification |
|---|---|---|
| ALT = alanine aminotransferase, AST = aspartate aminotransferase, ULN = upper limit normal, DRESS = Drug Rash with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms, SJS = Stevens Johnson syndrome, TEN = toxic epidermal necrolysis | ||
| Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] | ||
| Pneumonitis | Grade 2 | Withhold Resume in patients with complete or partial resolution (Grade 0 to 1) after corticosteroid taper. Permanently discontinue if no complete or partial resolution within 12 weeks of initiating steroids or inability to reduce prednisone to 10 mg per day or less (or equivalent) within 12 weeks of initiating steroids |
| Grades 3 or 4 | Permanently discontinue | |
| Colitis | Grades 2 or 3 | Withhold |
| Grade 4 | Permanently discontinue | |
| Hepatitis with no tumor involvement of the liver | AST or ALT increases to more than 3 and up to 8 times ULN or Total bilirubin increases to more than 1.5 and up to 3 times ULN | Withhold |
| AST or ALT increases to more than 8 times ULN or Total bilirubin increases to more than 3 times ULN | Permanently discontinue | |
| Hepatitis with tumor involvement of the liver If AST and ALT are less than or equal to ULN at baseline, withhold or permanently discontinue TECENTRIQ based on recommendations for hepatitis with no liver involvement | Baseline AST or ALT is more than 1 and up to 3 times ULN and increases to more than 5 and up to 10 times ULN or Baseline AST or ALT is more than 3 and up to 5 times ULN and increases to more than 8 and up to 10 times ULN | Withhold |
| AST or ALT increases to more than 10 times ULN or Total bilirubin increases to more than 3 times ULN | Permanently discontinue | |
| Endocrinopathies | Grades 3 or 4 | Withhold until clinically stable or permanently discontinue depending on severity |
| Nephritis with Renal Dysfunction | Grades 2 or 3 increased blood creatinine | Withhold |
| Grade 4 increased blood creatinine | Permanently discontinue | |
| Exfoliative Dermatologic Conditions | Suspected SJS, TEN, or DRESS | Withhold |
| Confirmed SJS, TEN, or DRESS | Permanently discontinue | |
| Myocarditis or Pericarditis | Grades 2, 3, or 4 | Permanently discontinue |
| Neurological Toxicities | Grade 2 | Withhold |
| Grades 3 or 4 | Permanently discontinue | |
| Other Adverse Reactions | ||
| Infusion-Related Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] | Grades 1 or 2 | Interrupt or slow the rate of infusion |
| Grades 3 or 4 | Permanently discontinue | |
Preparation and Administration
Preparation
Visually inspect drug product for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. Discard the vial if the solution is cloudy, discolored, or visible particles are observed. Do not shake the vial.
Prepare the solution for infusion as follows:
- Select the appropriate vial(s) based on the prescribed dose.
- Withdraw the required volume of TECENTRIQ from the vial(s) using sterile needle and syringe.
- Dilute to a final concentration between 3.2 mg/mL and 16.8 mg/mL in a polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polyethylene (PE), or polyolefin (PO) infusion bag containing 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP.
- Dilute with only 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP.
- Mix diluted solution by gentle inversion. Do not shake.
- Discard used or empty vials of TECENTRIQ.
Storage of Infusion Solution
This product does not contain a preservative.
Administer immediately once prepared. If diluted TECENTRIQ infusion solution is not used immediately, store solution either:
- At room temperature for no more than 6 hours from the time of preparation. This includes room temperature storage of the infusion in the infusion bag and time for administration of the infusion, or
- Under refrigeration at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) for no more than 24 hours from time of preparation.
Do not freeze.
Do not shake.
Administration
Administer the initial infusion over 60 minutes through an intravenous line with or without a sterile, non-pyrogenic, low-protein binding in-line filter (pore size of 0.2–0.22 micron). If the first infusion is tolerated, all subsequent infusions may be delivered over 30 minutes.
Do not coadminister other drugs through the same intravenous line.
Do not administer as an intravenous push or bolus.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Tecentriq prescribing information
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
TECENTRIQ is a programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) blocking antibody indicated:
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
- as adjuvant treatment following resection and platinum-based chemotherapy for adult patients with Stage II to IIIA NSCLC whose tumors have PD-L1 expression on ≥ 1% of tumor cells, as determined by an FDA-approved test. (1.1 , 14.1 )
- for the first-line treatment of adult patients with metastatic NSCLC whose tumors have high PD-L1 expression (PD-L1 stained ≥ 50% of tumor cells [TC ≥ 50%] or PD-L1 stained tumor-infiltrating immune cells [IC] covering ≥ 10% of the tumor area [IC ≥ 10%] ), as determined by an FDA-approved test, with no EGFR or ALK genomic tumor aberrations. (1.1 )
- in combination with bevacizumab, paclitaxel, and carboplatin, for the first-line treatment of adult patients with metastatic non-squamous NSCLC with no EGFR or ALK genomic tumor aberrations. (1.1 )
- in combination with paclitaxel protein-bound and carboplatin for the first-line treatment of adult patients with metastatic non-squamous NSCLC with no EGFR or ALK genomic tumor aberrations (1.1 )
- for the treatment of adult patients with metastatic NSCLC who have disease progression during or following platinum-containing chemotherapy. Patients with EGFR or ALK genomic tumor aberrations should have disease progression on FDA-approved therapy for NSCLC harboring these aberrations prior to receiving TECENTRIQ. (1.1 )
Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC)
- in combination with carboplatin and etoposide, for the first-line treatment of adult patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC). (1.2 )
- in combination with lurbinectedin, for the maintenance treatment of adult patients with ES-SCLC whose disease has not progressed after first-line induction therapy with TECENTRIQ or atezolizumab and hyaluronidase-tqjs, carboplatin and etoposide. (1.2 )
Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
- in combination with bevacizumab for the treatment of adult patients with unresectable or metastatic HCC who have not received prior systemic therapy. (1.3 )
Melanoma
- in combination with cobimetinib and vemurafenib for the treatment of adult patients with BRAF V600 mutation-positive unresectable or metastatic melanoma. (1.4 )
Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma (ASPS)
- for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients 2 years of age and older with unresectable or metastatic ASPS. (1.5 )
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- TECENTRIQ, as a single-agent, is indicated as adjuvant treatment following resection and platinum-based chemotherapy for adult patients with stage II to IIIA [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ] non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose tumors have PD-L1 expression on ≥ 1% of tumor cells, as determined by an FDA-approved test [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) ].
- TECENTRIQ, as a single agent, is indicated for the first-line treatment of adult patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose tumors have high PD-L1 expression (PD-L1 stained ≥ 50% of tumor cells [TC ≥ 50%] or PD-L1 stained tumor-infiltrating immune cells [IC] covering ≥ 10% of the tumor area [IC ≥ 10%]), as determined by an FDA-approved test, with no EGFR or ALK genomic tumor aberrations [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) ].
- TECENTRIQ, in combination with bevacizumab, paclitaxel, and carboplatin, is indicated for the first-line treatment of adult patients with metastatic non-squamous NSCLC with no EGFR or ALK genomic tumor aberrations.
- TECENTRIQ, in combination with paclitaxel protein-bound and carboplatin, is indicated for the first-line treatment of adult patients with metastatic non-squamous NSCLC with no EGFR or ALK genomic tumor aberrations.
- TECENTRIQ, as a single-agent, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with metastatic NSCLC who have disease progression during or following platinum-containing chemotherapy. Patients with EGFR or ALK genomic tumor aberrations should have disease progression on FDA-approved therapy for NSCLC harboring these aberrations prior to receiving TECENTRIQ.
Small Cell Lung Cancer
- TECENTRIQ, in combination with carboplatin and etoposide, is indicated for the first-line treatment of adult patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC).
- TECENTRIQ, in combination with lurbinectedin, is indicated for the maintenance treatment of adult patients with ES-SCLC whose disease has not progressed after first-line induction therapy with TECENTRIQ or atezolizumab and hyaluronidase-tqjs, carboplatin and etoposide.
Hepatocellular Carcinoma
TECENTRIQ, in combination with bevacizumab, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with unresectable or metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) who have not received prior systemic therapy.
Melanoma
TECENTRIQ, in combination with cobimetinib and vemurafenib, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with BRAF V600 mutation-positive unresectable or metastatic melanoma [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) ] .
Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma
TECENTRIQ, as a single agent, is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients 2 years of age and older with unresectable or metastatic alveolar soft part sarcoma (ASPS).
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Administer TECENTRIQ intravenously over 60 minutes. If the first infusion is tolerated, all subsequent infusions may be delivered over 30 minutes.
NSCLC
- In the adjuvant setting, administer TECENTRIQ following resection and up to 4 cycles of platinum-based chemotherapy as 840 mg every 2 weeks, 1200 mg every 3 weeks or 1680 mg every 4 weeks for up to 1 year. (2.2 )
- In the metastatic setting, administer TECENTRIQ as 840 mg every 2 weeks, 1200 mg every 3 weeks, or 1680 mg every 4 weeks. (2.2 )
- When administering with chemotherapy with or without bevacizumab, administer TECENTRIQ prior to chemotherapy and bevacizumab when given on the same day. (2.2 )
Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Administer TECENTRIQ as 840 mg every 2 weeks, 1200 mg every 3 weeks, or 1680 mg every 4 weeks. Administer TECENTRIQ prior to chemotherapy when given on the same day. (2.2 )
Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Administer TECENTRIQ as 840 mg every 2 weeks, 1200 mg every 3 weeks, or 1680 mg every 4 weeks. Administer TECENTRIQ prior to bevacizumab when given on the same day. Bevacizumab is administered at 15 mg/kg every 3 weeks. (2.2 )
Melanoma
- Following completion of a 28-day cycle of cobimetinib and vemurafenib, administer TECENTRIQ 840 mg every 2 weeks, 1200 mg every 3 weeks, or 1680 mg every 4 weeks with cobimetinib 60 mg orally once daily (21 days on /7 days off) and vemurafenib 720 mg orally twice daily. (2.2 )
ASPS
Patient Selection for Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Melanoma
Select patients with Stage II to IIIA non-small cell lung cancer for treatment with TECENTRIQ as a single agent based on PD-L1 expression on tumor cells [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ].
Select patients with first-line metastatic non-small cell lung cancer for treatment with TECENTRIQ as a single agent based on the PD-L1 expression on tumor cells or on tumor-infiltrating immune cells [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ].
Information on FDA-approved tests for the determination of PD-L1 expression in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer are available at: http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics.
Select patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma for treatment with TECENTRIQ in combination with cobimetinib and vemurafenib after confirming the presence of a BRAF V600 mutation [see Clinical Studies (14.4) ]. Information on FDA-approved tests for the detection of BRAF V600 mutations in melanoma is available at: http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics.
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosages of TECENTRIQ are presented in Table 1 . Administer TECENTRIQ as an intravenous infusion over 60 minutes. If the first infusion is tolerated, all subsequent infusions may be delivered over 30 minutes.
| Indication | Recommended Dosage of TECENTRIQ | Duration of Therapy |
|---|---|---|
| Metastatic NSCLC |
| Until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity |
| Adjuvant Treatment of NSCLC |
| Up to one year, unless there is disease recurrence or unacceptable toxicity |
| ASPS (adult) |
| Until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity |
| ASPS (pediatric, 2 years of age and older) | 15 mg/kg (up to a maximum 1200 mg) every 3 weeks |
The recommended intravenous dosages of TECENTRIQ in combination with other therapeutic agents are presented in Table 2 . Refer to the respective Prescribing Information for each therapeutic agent administered in combination with TECENTRIQ for the recommended dosage information, as appropriate.
| Indication | Recommended Dosage of TECENTRIQ | Duration of Therapy |
|---|---|---|
| NSCLC |
| Until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity |
| SCLC |
| |
| HCC |
| |
| Melanoma |
|
Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
No dose reduction for TECENTRIQ is recommended. In general, withhold TECENTRIQ for severe (Grade 3) immune-mediated adverse reactions. Permanently discontinue TECENTRIQ for life-threatening (Grade 4) immune-mediated adverse reactions, recurrent severe (Grade 3) immune-mediated reactions that require systemic immunosuppressive treatment, or an inability to reduce corticosteroid dose to 10 mg or less of prednisone or equivalent per day within 12 weeks of initiating steroids.
Dosage modifications for TECENTRIQ for adverse reactions that require management different from these general guidelines are summarized in Table 3 .
| Adverse Reaction | Severity Based on Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE), version 4 | Dosage Modification |
|---|---|---|
| ALT = alanine aminotransferase, AST = aspartate aminotransferase, ULN = upper limit normal, DRESS = Drug Rash with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms, SJS = Stevens Johnson syndrome, TEN = toxic epidermal necrolysis | ||
| Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] | ||
| Pneumonitis | Grade 2 | Withhold Resume in patients with complete or partial resolution (Grade 0 to 1) after corticosteroid taper. Permanently discontinue if no complete or partial resolution within 12 weeks of initiating steroids or inability to reduce prednisone to 10 mg per day or less (or equivalent) within 12 weeks of initiating steroids |
| Grades 3 or 4 | Permanently discontinue | |
| Colitis | Grades 2 or 3 | Withhold |
| Grade 4 | Permanently discontinue | |
| Hepatitis with no tumor involvement of the liver | AST or ALT increases to more than 3 and up to 8 times ULN or Total bilirubin increases to more than 1.5 and up to 3 times ULN | Withhold |
| AST or ALT increases to more than 8 times ULN or Total bilirubin increases to more than 3 times ULN | Permanently discontinue | |
| Hepatitis with tumor involvement of the liver If AST and ALT are less than or equal to ULN at baseline, withhold or permanently discontinue TECENTRIQ based on recommendations for hepatitis with no liver involvement | Baseline AST or ALT is more than 1 and up to 3 times ULN and increases to more than 5 and up to 10 times ULN or Baseline AST or ALT is more than 3 and up to 5 times ULN and increases to more than 8 and up to 10 times ULN | Withhold |
| AST or ALT increases to more than 10 times ULN or Total bilirubin increases to more than 3 times ULN | Permanently discontinue | |
| Endocrinopathies | Grades 3 or 4 | Withhold until clinically stable or permanently discontinue depending on severity |
| Nephritis with Renal Dysfunction | Grades 2 or 3 increased blood creatinine | Withhold |
| Grade 4 increased blood creatinine | Permanently discontinue | |
| Exfoliative Dermatologic Conditions | Suspected SJS, TEN, or DRESS | Withhold |
| Confirmed SJS, TEN, or DRESS | Permanently discontinue | |
| Myocarditis or Pericarditis | Grades 2, 3, or 4 | Permanently discontinue |
| Neurological Toxicities | Grade 2 | Withhold |
| Grades 3 or 4 | Permanently discontinue | |
| Other Adverse Reactions | ||
| Infusion-Related Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] | Grades 1 or 2 | Interrupt or slow the rate of infusion |
| Grades 3 or 4 | Permanently discontinue | |
Preparation and Administration
Preparation
Visually inspect drug product for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. Discard the vial if the solution is cloudy, discolored, or visible particles are observed. Do not shake the vial.
Prepare the solution for infusion as follows:
- Select the appropriate vial(s) based on the prescribed dose.
- Withdraw the required volume of TECENTRIQ from the vial(s) using sterile needle and syringe.
- Dilute to a final concentration between 3.2 mg/mL and 16.8 mg/mL in a polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polyethylene (PE), or polyolefin (PO) infusion bag containing 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP.
- Dilute with only 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP.
- Mix diluted solution by gentle inversion. Do not shake.
- Discard used or empty vials of TECENTRIQ.
Storage of Infusion Solution
This product does not contain a preservative.
Administer immediately once prepared. If diluted TECENTRIQ infusion solution is not used immediately, store solution either:
- At room temperature for no more than 6 hours from the time of preparation. This includes room temperature storage of the infusion in the infusion bag and time for administration of the infusion, or
- Under refrigeration at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) for no more than 24 hours from time of preparation.
Do not freeze.
Do not shake.
Administration
Administer the initial infusion over 60 minutes through an intravenous line with or without a sterile, non-pyrogenic, low-protein binding in-line filter (pore size of 0.2–0.22 micron). If the first infusion is tolerated, all subsequent infusions may be delivered over 30 minutes.
Do not coadminister other drugs through the same intravenous line.
Do not administer as an intravenous push or bolus.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Injection: 840 mg/14 mL (60 mg/mL) and 1200 mg/20 mL (60 mg/mL) colorless to slightly yellow solution in a single-dose vial.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Lactation : Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2 )
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on its mechanism of action [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1) ] , TECENTRIQ can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. There are no available data on the use of TECENTRIQ in pregnant women.
Animal studies have demonstrated that inhibition of the PD-L1/PD-1 pathway can lead to increased risk of immune-related rejection of the developing fetus resulting in fetal death (see Data ) . Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with TECENTRIQ to evaluate its effect on reproduction and fetal development. A literature-based assessment of the effects on reproduction demonstrated that a central function of the PD-L1/PD-1 pathway is to preserve pregnancy by maintaining maternal immune tolerance to a fetus. Blockage of PD-L1 signaling has been shown in murine models of pregnancy to disrupt tolerance to a fetus and to result in an increase in fetal loss; therefore, potential risks of administering TECENTRIQ during pregnancy include increased rates of abortion or stillbirth. As reported in the literature, there were no malformations related to the blockade of PD-L1/PD-1 signaling in the offspring of these animals; however, immune-mediated disorders occurred in PD-1 and PD-L1 knockout mice. Based on its mechanism of action, fetal exposure to atezolizumab may increase the risk of developing immune-mediated disorders or altering the normal immune response.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information regarding the presence of atezolizumab in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. As human IgG is excreted in human milk, the potential for absorption and harm to the infant is unknown. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed infants from TECENTRIQ, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment and for at least 5 months after the last dose.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Pregnancy Testing
Verify pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential prior to initiating TECENTRIQ [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ] .
Contraception
Females
Based on its mechanism of action, TECENTRIQ can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ] . Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with TECENTRIQ and for at least 5 months following the last dose.
Infertility
Females
Based on animal studies, TECENTRIQ may impair fertility in females of reproductive potential while receiving treatment [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1) ] .
Pediatric Use
Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma
The safety and effectiveness of TECENTRIQ for unresectable or metastatic ASPS have been established in pediatric patients aged 2 years and older. Use of TECENTRIQ for this indication is supported by evidence from an adequate and well controlled study of TECENTRIQ in adults and 2 adolescent pediatric patients (≥12 years of age) with ASPS with additional pharmacokinetic and safety data in pediatric patients 2 years to <17 years. These data suggest that atezolizumab exposure in pediatric patients aged 2 years and older is comparable with that of adults and is expected to result in similar safety and efficacy to that of adults [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) , Pharmacokinetics (12.3) , Clinical Studies (14.5) ] . The course of unresectable or metastatic ASPS is sufficiently similar between pediatric patients 2 to 11 years old and that of adults and adolescent patients to allow extrapolation of efficacy and safety to pediatric patients 2 years and older.
The safety and effectiveness of TECENTRIQ for ASPS have not been established in pediatric patients younger than 2 years of age.
Solid Tumors and Lymphomas
The safety and effectiveness of TECENTRIQ in pediatric patients have not been established in non-small cell lung cancer, small-cell lung cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, or melanoma.
The safety and effectiveness of TECENTRIQ were assessed, but not established in a single-arm, multi-center, multi-cohort trial (NCT02541604) in 60 pediatric patients aged 7 months to <17 years with relapsed or progressive solid tumors and lymphomas. No new safety signals were observed in pediatric patients in this study.
Geriatric Use
TECENTRIQ as a Single-Agent
Of 2616 patients with metastatic NSCLC and other tumor types treated with single agent TECENTRIQ in clinical studies, 49% were 65 years and over and 15% were 75 years and over.
No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between patients aged 65 years or older and younger patients.
TECENTRIQ in Combination with Other Antineoplastic Drugs
Of 2421 patients with NSCLC and SCLC treated with TECENTRIQ in combination with other antineoplastic drugs in clinical studies, 48% were 65 years and over and 10% were 75 years and over.
No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between patients aged 65 years or older and younger patients.
TECENTRIQ in Combination with Lurbinectedin
Of the 242 patients with ES-SCLC treated with TECENTRIQ in combination with lurbinectedin in IMforte, 124 (51%) patients were 65 years of age and older, while 29 (12%) patients were 75 years of age and older. No overall differences in effectiveness were observed between older and younger patients. There was a higher incidence of Grade 3 or 4 adverse reactions (45% vs 31%) and treatment discontinuation (11% vs 0.8%) in patients ≥ 65 years of age compared to younger patients, respectively.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions
- Immune-mediated adverse reactions, which may be severe or fatal, can occur in any organ system or tissue, including the following: immune-mediated pneumonitis, immune-mediated colitis, immune-mediated hepatitis, immune-mediated endocrinopathies, immune-mediated dermatologic adverse reactions, immune-mediated nephritis and renal dysfunction, and solid organ transplant rejection. (5.1 )
- Monitor for early identification and management. Evaluate liver enzymes, creatinine, and thyroid function at baseline and periodically during treatment. (5.1 )
- Withhold or permanently discontinue based on severity and type of reaction. (5.1 ).
- Infusion-Related Reactions : Interrupt, slow the rate of infusion, or permanently discontinue based on severity of infusion reactions. (5.2 )
- Complications of Allogeneic HSCT: Fatal and other serious complications can occur in patients who receive allogeneic HSCT before or after being treated with a PD-1/PD-L1 blocking antibody. (5.3 )
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity : Can cause fetal harm. Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus and use of effective contraception. (5.4 , 8.1 , 8.3 )
Severe and Fatal Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions
TECENTRIQ is a monoclonal antibody that belongs to a class of drugs that bind to either the programmed death-receptor 1 (PD-1) or the PD-ligand 1 (PD-L1), blocking the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway, thereby removing inhibition of the immune response, potentially breaking peripheral tolerance and inducing immune-mediated adverse reactions. Important immune-mediated adverse reactions listed under Warnings and Precautions may not include all possible severe and fatal immune-mediated reactions.
Immune-mediated adverse reactions, which may be severe or fatal, can occur in any organ system or tissue. Immune-mediated adverse reactions can occur at any time after starting a PD-1/PD-L1 blocking antibody. While immune-mediated adverse reactions usually manifest during treatment with PD-1/PD-L1 blocking antibodies, immune-mediated adverse reactions can also manifest after discontinuation of PD-1/PD-L1 blocking antibodies.
Early identification and management of immune-mediated adverse reactions are essential to ensure safe use of PD-1/PD-L1 blocking antibodies. Monitor patients closely for symptoms and signs that may be clinical manifestations of underlying immune-mediated adverse reactions. Evaluate liver enzymes, creatinine, and thyroid function at baseline and periodically during treatment. In cases of suspected immune-mediated adverse reactions, initiate appropriate workup to exclude alternative etiologies, including infection. Institute medical management promptly, including specialty consultation as appropriate.
Withhold or permanently discontinue TECENTRIQ depending on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ]. In general, if TECENTRIQ requires interruption or discontinuation, administer systemic corticosteroid therapy (1 to 2 mg/kg/day prednisone or equivalent) until improvement to Grade 1 or less. Upon improvement to Grade 1 or less, initiate corticosteroid taper and continue to taper over at least 1 month. Consider administration of other systemic immunosuppressants in patients whose immune-mediated adverse reactions are not controlled with corticosteroid therapy.
Toxicity management guidelines for adverse reactions that do not necessarily require systemic steroids (e.g., endocrinopathies and dermatologic reactions) are discussed below.
Immune-Mediated Pneumonitis
TECENTRIQ can cause immune-mediated pneumonitis. The incidence of pneumonitis is higher in patients who have received prior thoracic radiation.
TECENTRIQ as a Single Agent:
Immune-mediated pneumonitis occurred in 3% (83/2616) of patients receiving TECENTRIQ as a single agent, including fatal (<0.1%), Grade 4 (0.2%), Grade 3 (0.8%), and Grade 2 (1.1%) adverse reactions. Pneumonitis led to permanent discontinuation of TECENTRIQ in 0.5% and withholding of TECENTRIQ in 1.5% of patients.
Systemic corticosteroids were required in 55% (46/83) of patients with pneumonitis. Pneumonitis resolved in 69% of the 83 patients. Of the 39 patients in whom TECENTRIQ was withheld for pneumonitis, 25 reinitiated TECENTRIQ after symptom improvement; of these, 4% had recurrence of pneumonitis.
In IMpower010 immune-mediated pneumonitis occurred in 3.8% (19/495) of patients receiving TECENTRIQ as a single agent, including fatal (0.2%), Grade 4 (0.2%), and Grade 3 (0.6%) adverse reactions. Pneumonitis led to permanent discontinuation of TECENTRIQ in 2.2% and withholding of TECENTRIQ in 0.8% of patients.
Systemic corticosteroids were required in 63% (12/19) of patients with pneumonitis. Pneumonitis resolved in 84% of the 19 patients.
TECENTRIQ in Combination with Cobimetinib and Vemurafenib:
Immune-mediated pneumonitis occurred in 13% (29/230) of patients receiving TECENTRIQ in combination with cobimetinib and vemurafenib, including Grade 3 (1.3%) and Grade 2 (7%) adverse reactions. Pneumonitis led to permanent discontinuation of TECENTRIQ in 2.6% and withholding of TECENTRIQ in 7.4% of patients.
Systemic corticosteroids were required in 55% (16/29) of patients with pneumonitis. Pneumonitis resolved in 97% of the 29 patients. Of the 17 patients in whom TECENTRIQ was withheld for pneumonitis, 10 reinitiated TECENTRIQ after symptom improvement; of these, 50% had recurrence of pneumonitis.
Immune-Mediated Colitis
TECENTRIQ can cause immune-mediated colitis. Colitis can present with diarrhea, abdominal pain, and lower gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding. Cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection/reactivation has been reported in patients with corticosteroid-refractory immune-mediated colitis. In cases of corticosteroid-refractory colitis, consider repeating infectious workup to exclude alternative etiologies.
TECENTRIQ as a Single Agent:
Immune-mediated colitis occurred in 1% (26/2616) of patients receiving TECENTRIQ as a single agent, including Grade 3 (0.5%) and Grade 2 (0.3%) adverse reactions. Colitis led to permanent discontinuation of TECENTRIQ in 0.2% and withholding of TECENTRIQ in 0.5% of patients.
Systemic corticosteroids were required in 50% (13/26) of patients with colitis. Colitis resolved in 73% of the 26 patients. Of the 12 patients in whom TECENTRIQ was withheld for colitis, 8 reinitiated treatment with TECENTRIQ after symptom improvement; of these, 25% had recurrence of colitis.
Immune-Mediated Hepatitis
TECENTRIQ can cause immune-mediated hepatitis.
Immune-mediated hepatitis occurred in 1.8% (48/2616) of patients receiving TECENTRIQ as a single agent, including fatal (<0.1%), Grade 4 (0.2%), Grade 3 (0.5%), and Grade 2 (0.5%) adverse reactions. Hepatitis led to permanent discontinuation of TECENTRIQ in 0.2% and withholding of TECENTRIQ in 0.2% of patients.
Systemic corticosteroids were required in 25% (12/48) of patients with hepatitis. Hepatitis resolved in 50% of the 48 patients. Of the 6 patients in whom TECENTRIQ was withheld for hepatitis, 4 reinitiated treatment with TECENTRIQ after symptom improvement; of these, none had recurrence of hepatitis.
TECENTRIQ in Combination with Cobimetinib and Vemurafenib:
Immune-mediated hepatitis occurred in 6.1% (14/230) of patients receiving TECENTRIQ in combination with cobimetinib and vemurafenib, including Grade 4 (1.3%), Grade 3 (1.7%) and Grade 2 (1.3%) adverse reactions. Hepatitis led to permanent discontinuation of TECENTRIQ in 2.2% and withholding of TECENTRIQ in 1.7% of patients.
Systemic corticosteroids were required in 50% (7/14) of patients with hepatitis. Hepatitis resolved in 93% of the 14 patients. Of the 4 patients in whom TECENTRIQ was withheld for hepatitis, 3 reinitiated TECENTRIQ after symptom improvement; of these, 33% had recurrence of hepatitis.
Immune-Mediated Endocrinopathies
Adrenal Insufficiency
TECENTRIQ can cause primary or secondary adrenal insufficiency. For Grade 2 or higher adrenal insufficiency, initiate symptomatic treatment, including hormone replacement as clinically indicated. Withhold or permanently discontinue TECENTRIQ depending on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] .
Adrenal insufficiency occurred in 0.4% (11/2616) of patients receiving TECENTRIQ as a single agent, including Grade 3 (<0.1%) and Grade 2 (0.2%) adverse reactions. Adrenal insufficiency led to permanent discontinuation of TECENTRIQ in one patient and withholding of TECENTRIQ in one patient.
Systemic corticosteroids were required in 82% (9/11) of patients with adrenal insufficiency; of these, 3 patients remained on systemic corticosteroids. The single patient in whom TECENTRIQ was withheld for adrenal insufficiency did not reinitiate TECENTRIQ.
In IMpower010 immune-mediated adrenal insufficiency occurred in 1.2% (6/495) of patients receiving TECENTRIQ as a single agent, including Grade 3 (0.4%) adverse reactions. Adrenal insufficiency led to permanent discontinuation of TECENTRIQ in 0.6% and withholding of TECENTRIQ in 0.2% of patients.
Systemic corticosteroids were required in 83% (5/6) of patients with adrenal insufficiency; of these, 4 patients remained on systemic corticosteroids.
Hypophysitis
TECENTRIQ can cause immune-mediated hypophysitis. Hypophysitis can present with acute symptoms associated with mass effect such as headache, photophobia, or visual field cuts. Hypophysitis can cause hypopituitarism. Initiate hormone replacement as clinically indicated. Withhold or permanently discontinue TECENTRIQ depending on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] .
Hypophysitis occurred in <0.1% (2/2616) of patients receiving TECENTRIQ as a single agent, including Grade 2 (1 patient, <0.1%) adverse reactions. Hypophysitis led to permanent discontinuation of TECENTRIQ in one patient and no patients required withholding of TECENTRIQ.
Systemic corticosteroids were required in 50% (1/2) of patients with hypophysitis. Hypophysitis did not resolve in these 2 patients.
Thyroid disorders
TECENTRIQ can cause immune-mediated thyroid disorders. Thyroiditis can present with or without endocrinopathy. Hypothyroidism can follow hyperthyroidism. Initiate hormone replacement for hypothyroidism or medical management for hyperthyroidism as clinically indicated. Withhold or permanently discontinue TECENTRIQ depending on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] .
Thyroiditis:
Thyroiditis occurred in 0.2% (4/2616) of patients receiving TECENTRIQ as a single agent, including Grade 2 (<0.1%) adverse reactions. Thyroiditis did not lead to permanent discontinuation of TECENTRIQ in any of these patients, but led to withholding of TECENTRIQ in one patient.
Hormone replacement therapy was required in 75% (3/4) of patients with thyroiditis. Systemic corticosteroids were required in 25% (1/4) of patients with thyroiditis. Thyroiditis resolved in 50% of patients. The single patient in whom TECENTRIQ was withheld for thyroiditis reinitiated TECENTRIQ; this patient did not have recurrence of thyroiditis.
In IMpower010, thyroiditis occurred in 1.2% (6/495) of patients receiving TECENTRIQ as a single agent, including Grade 2 (0.4%) adverse reactions. Thyroiditis led to withholding of TECENTRIQ in one patient.
Hormone replacement therapy was required in 67% (4/6) of patients with thyroiditis. Systemic corticosteroids were required in 33% (2/6) of patients with thyroiditis. Thyroiditis resolved in 50% of patients.
Hyperthyroidism:
TECENTRIQ as a Single Agent:
Hyperthyroidism occurred in 0.8% (21/2616) of patients receiving TECENTRIQ as a single agent, including Grade 2 (0.4%) adverse reactions. Hyperthyroidism did not lead to permanent discontinuation of TECENTRIQ in any of these patients, but led to withholding of TECENTRIQ in 0.1% of patients.
Antithyroid therapy was required in 29% (6/21) of patients with hyperthyroidism. Of these 6 patients, the majority remained on antithyroid treatment. Of the 3 patients in whom TECENTRIQ was withheld for hyperthyroidism, one patient reinitiated TECENTRIQ; this patient did not have recurrence of hyperthyroidism.
In IMpower010 hyperthyroidism occurred in 6% (32/495) of patients receiving TECENTRIQ as a single agent, including Grade 3 (0.4%) adverse reactions. Hyperthyroidism led to permanent discontinuation of TECENTRIQ in 0.8% and withholding of TECENTRIQ in 2.8% of patients.
Antithyroid therapy was required in 38% (12/32) of patients with hyperthyroidism. Of these 12 patients, the majority remained on antithyroid treatment. Of the 14 patients in whom TECENTRIQ was withheld for hyperthyroidism, 9 patients reinitiated TECENTRIQ.
TECENTRIQ in Combination with Cobimetinib and Vemurafenib:
Hyperthyroidism occurred in 19% (43/230) of patients receiving TECENTRIQ in combination with cobimetinib and vemurafenib, including Grade 3 (0.9%) and Grade 2 (7.8%) adverse reactions. Hyperthyroidism led to permanent discontinuation of TECENTRIQ in 0.4% and withholding of TECENTRIQ in 10% of patients.
Antithyroid therapy was required in 53% (23/43) of patients with hyperthyroidism. Of these 23 patients, the majority remained on antithyroid treatment. Of the 24 patients in whom TECENTRIQ was withheld for hyperthyroidism, 18 patients reinitiated TECENTRIQ; of these, 28% had recurrence of hyperthyroidism.
Hypothyroidism:
TECENTRIQ as a Single Agent:
Hypothyroidism occurred in 4.9% (128/2616) of patients receiving TECENTRIQ as a single agent, including Grade 3 (0.2%) and Grade 2 (3.4%) adverse reactions. Hypothyroidism did not lead to permanent discontinuation of TECENTRIQ in any of these patients, but led to withholding of TECENTRIQ in 0.6% of patients.
Hormone replacement therapy was required in 81% (104/128) of patients with hypothyroidism. The majority of patients with hypothyroidism remained on thyroid hormone replacement. Of the 17 patients in whom TECENTRIQ was withheld for hypothyroidism, 8 reinitiated TECENTRIQ after symptom improvement.
In IMpower010 hypothyroidism occurred in 17% (86/495) of patients receiving TECENTRIQ as a single agent. Hypothyroidism led to permanent discontinuation of TECENTRIQ in 1.6% and withholding of TECENTRIQ in 1.6% of patients.
Hormone replacement was required in 57% (49/86) of patients with hypothyroidism. The majority of patients with hypothyroidism remained on thyroid hormone replacement. Of the 8 patients in whom TECENTRIQ was withheld for hypothyroidism, 3 reinitiated TECENTRIQ after symptom improvement.
TECENTRIQ in Combination with Platinum-based Chemotherapy:
Hypothyroidism occurred in 11% (277/2421) of patients with NSCLC and SCLC receiving TECENTRIQ in combination with platinum-based chemotherapy, including Grade 4 (<0.1%), Grade 3 (0.3%), and Grade 2 (5.7%) adverse reactions. Hypothyroidism led to permanent discontinuation of TECENTRIQ in 0.1% and withholding of TECENTRIQ in 1.6% of patients.
Hormone replacement therapy was required in 71% (198/277) of patients with hypothyroidism. The majority of patients with hypothyroidism remained on thyroid hormone replacement. Of the 39 patients in whom TECENTRIQ was withheld for hypothyroidism, 9 reinitiated TECENTRIQ after symptom improvement.
TECENTRIQ in Combination with Cobimetinib and Vemurafenib:
Hypothyroidism occurred in 26% (60/230) of patients receiving TECENTRIQ in combination with cobimetinib and vemurafenib, including Grade 2 (9.1%) adverse reactions. Hypothyroidism did not lead to permanent discontinuation of TECENTRIQ in any of these patients, but led to withholding of TECENTRIQ in 2.6% of patients.
Hormone replacement therapy was required in 52% (31/60) of patients with hypothyroidism. The majority of patients with hypothyroidism remained on thyroid hormone replacement. Of the 6 patients in whom TECENTRIQ was withheld for hypothyroidism, 4 reinitiated TECENTRIQ after symptom improvement. The majority of patients with hypothyroidism required long term thyroid replacement.
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus, which can present with Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Monitor patients for hyperglycemia or other signs and symptoms of diabetes. Initiate treatment with insulin as clinically indicated. Withhold or permanently discontinue TECENTRIQ depending on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] .
Type 1 diabetes mellitus occurred in 0.3% (7/2616) of patients receiving TECENTRIQ, including Grade 3 (0.2%) and Grade 2 (<0.1%) adverse reactions. Type 1 diabetes mellitus led to permanent discontinuation of TECENTRIQ in one patient and withholding of TECENTRIQ in two patients.
Treatment with insulin was required for all patients with confirmed Type 1 diabetes mellitus and insulin therapy was continued long-term. Of the 2 patients in whom TECENTRIQ was withheld for Type 1 diabetes mellitus, both re-initiated TECENTRIQ treatment.
Immune-Mediated Nephritis with Renal Dysfunction
TECENTRIQ can cause immune-mediated nephritis.
TECENTRIQ as a Single Agent:
Immune-mediated nephritis with renal dysfunction occurred in <0.1% (1/2616) of patients receiving TECENTRIQ as a single agent, and this adverse reaction was a Grade 3 (<0.1%) adverse reaction. Nephritis led to permanent discontinuation of TECENTRIQ in this patient.
This patient required systemic corticosteroids. In this patient, nephritis did not resolve.
TECENTRIQ in Combination with Cobimetinib and Vemurafenib:
Immune-mediated nephritis with renal dysfunction occurred in 1.3% (3/230) of patients receiving TECENTRIQ in combination with cobimetinib and vemurafenib, including Grade 2 (1.3%) adverse reactions. Nephritis led to permanent discontinuation of TECENTRIQ in 0.4% and withholding of TECENTRIQ in 0.9% of patients.
Systemic corticosteroids were required in 67% (2/3) of patients with nephritis. Nephritis resolved in all 3 of these patients. Of the 2 patients in whom TECENTRIQ was withheld for nephritis, both reinitiated TECENTRIQ after symptom improvement and neither had recurrence of nephritis.
Immune-Mediated Dermatologic Adverse Reactions
TECENTRIQ can cause immune-mediated rash or dermatitis. Exfoliative dermatitis, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), DRESS, and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), has occurred with PD-1/PD-L1 blocking antibodies. Topical emollients and/or topical corticosteroids may be adequate to treat mild to moderate non-exfoliative rashes. Withhold or permanently discontinue TECENTRIQ depending on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] .
Immune-mediated dermatologic adverse reactions occurred in 0.6% (15/2616) of patients receiving TECENTRIQ as a single agent, including Grade 3 (<0.1%) and Grade 2 (0.2%) adverse reactions. Dermatologic adverse reactions led to permanent discontinuation of TECENTRIQ in 0.1% and withholding of TECENTRIQ in 0.2% of patients.
Systemic corticosteroids were required in 20% (3/15) of patients with dermatologic adverse reactions. Dermatologic adverse reactions resolved in 87% of the 15 patients. Of the 4 patients in whom TECENTRIQ was withheld for immune-mediated dermatologic adverse reactions, none re-initiated TECENTRIQ.
Other Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions
The following clinically significant immune-mediated adverse reactions occurred at an incidence of < 1% (unless otherwise noted) in patients who received TECENTRIQ or were reported with the use of other PD-1/PD-L1 blocking antibodies. Severe or fatal cases have been reported for some of these adverse reactions.
Cardiac/Vascular : Myocarditis, pericarditis, vasculitis.
Nervous System : Meningitis, encephalitis, myelitis and demyelination, myasthenic syndrome/myasthenia gravis (including exacerbation), Guillain-Barré syndrome, nerve paresis, autoimmune neuropathy.
Ocular : Uveitis, iritis, and other ocular inflammatory toxicities can occur. Some cases can be associated with retinal detachment. Various grades of visual impairment, including blindness, can occur. If uveitis occurs in combination with other immune-mediated adverse reactions, consider a Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada-like syndrome, as this may require treatment with systemic steroids to reduce the risk of permanent vision loss.
Gastrointestinal: Pancreatitis to include increases in serum amylase and lipase levels, gastritis, duodenitis.
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue : Myositis/polymyositis, rhabdomyolysis and associated sequelae including renal failure, arthritis, polymyalgia rheumatic.
Endocrine: Hypoparathyroidism.
Other (Hematologic/Immune) : Hemolytic anemia, aplastic anemia, hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, systemic inflammatory response syndrome, histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis (Kikuchi lymphadenitis), sarcoidosis, immune thrombocytopenic purpura, solid organ transplant rejection, other transplant (including corneal graft) rejection.
Infusion-Related Reactions
TECENTRIQ can cause severe or life-threatening infusion-related reactions, including anaphylaxis. Monitor for signs and symptoms of infusion-related reactions. Interrupt, slow the rate of, or permanently discontinue TECENTRIQ based on the severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] . For Grade 1 or 2 infusion-related reactions, consider using pre-medications with subsequent doses.
In clinical studies enrolling 2616 patients with various cancers who received TECENTRIQ as a single-agent [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] , infusion-related reactions occurred in 1.3% of patients, including Grade 3 (0.2%). The frequency and severity of infusion-related reactions were similar whether TECENTRIQ was given as a single-agent in patients with various cancers, in combination with other antineoplastic drugs in NSCLC and SCLC, and across the recommended dose range (840 mg Q2W to 1680 mg Q4W).
Complications of Allogeneic HSCT after PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors
Fatal and other serious complications can occur in patients who receive allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) before or after being treated with a PD-1/PD-L1 blocking antibody. Transplant-related complications include hyperacute graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), acute GVHD, chronic GVHD, hepatic veno-occlusive disease (VOD) after reduced intensity conditioning, and steroid-requiring febrile syndrome (without an identified infectious cause). These complications may occur despite intervening therapy between PD-1/PD-L1 blockage and allogeneic HSCT.
Follow patients closely for evidence of transplant-related complications and intervene promptly. Consider the benefits versus risks of treatment with a PD-1/PD-L1 blocking antibody prior to or after an allogeneic HSCT.
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on its mechanism of action, TECENTRIQ can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. There are no available data on the use of TECENTRIQ in pregnant women. Animal studies have demonstrated that inhibition of the PD-L1/PD-1 pathway can lead to increased risk of immune-related rejection of the developing fetus resulting in fetal death.
Verify pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to initiating TECENTRIQ. Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with TECENTRIQ and for at least 5 months after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1 , 8.3) ].
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Severe and Fatal Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- Infusion-Related Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
- Complications of Allogeneic HSCT after PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data described in WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS reflect exposure to TECENTRIQ as a single-agent in 2616 patients in two randomized, active-controlled studies (POPLAR, OAK) and three open-label, single arm studies (PCD4989g, BIRCH, FIR) which enrolled 1636 patients with metastatic NSCLC, and 980 patients with other tumor types. TECENTRIQ was administered at a dose of 1200 mg intravenously every 3 weeks in all studies except PCD4989g. Among the 2616 patients who received a single-agent TECENTRIQ, 36% were exposed for longer than 6 months and 20% were exposed for longer than 12 months. Using the dataset described for patients who received TECENTRIQ as a single-agent, the most common adverse reactions in ≥ 20% of patients were fatigue/asthenia (48%), decreased appetite (25%), nausea (24%), cough (22%), and dyspnea (22%). In addition, the data reflect exposure to TECENTRIQ as a single agent as adjuvant therapy in 495 patients with early-stage NSCLC enrolled in a randomized study (IMpower010).
In addition, the data reflect exposure to TECENTRIQ in combination with other antineoplastic drugs in 2421 patients with NSCLC (N = 2223) or SCLC (N = 198) enrolled in five randomized, active-controlled trials, including IMpower150, IMpower130 and IMpower133. Among the 2421 patients, 53% were exposed to TECENTRIQ for longer than 6 months and 29% were exposed to TECENTRIQ for longer than 12 months. Among the 2421 patients with NSCLC and SCLC who received TECENTRIQ in combination with other antineoplastic drugs, the most common adverse reactions in ≥20% of patients were fatigue/asthenia (49%), nausea (38%), alopecia (35%), constipation (29%), diarrhea (28%) and decreased appetite (27%).
The data also reflect exposure to TECENTRIQ administered in combination with cobimetinib and vemurafenib in 230 patients enrolled in IMspire150. Among the 230 patients, 62% were exposed to TECENTRIQ for longer than 6 months and 42% were exposed to TECENTRIQ for longer than 12 months.
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
Adjuvant Treatment of Early-stage NSCLC
IMpower010
The safety of TECENTRIQ was evaluated in IMpower010, a multicenter, open-label, randomized trial for the adjuvant treatment of patients with stage IB (tumors ≥ 4 cm) - IIIA NSCLC who had complete tumor resection and received up to 4 cycles of cisplatin-based adjuvant chemotherapy. Patients received TECENTRIQ 1200 mg every 3 weeks (n=495) for 1 year (16 cycles), unless disease progression or unacceptable toxicity occurred, or best supportive care [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ] . The median number of cycles received was 16 (range: 1, 16).
Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 1.8% of patients receiving TECENTRIQ; these included multiple organ dysfunction syndrome, pneumothorax, interstitial lung disease, arrhythmia, acute cardiac failure, myocarditis, cerebrovascular accident, death of unknown cause, and acute myeloid leukemia (1 patient each).
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 18% of patients receiving TECENTRIQ. The most frequent serious adverse reactions (>1%) were pneumonia (1.8%), pneumonitis (1.6%), and pyrexia (1.2%).
TECENTRIQ was discontinued due to adverse reactions in 18% of patients ; the most common adverse reactions (≥1%) leading to TECENTRIQ discontinuation were pneumonitis (2.2%), hypothyroidism (1.6%), increased aspartate aminotransferase (1.4%), arthralgia (1.0%), and increased alanine aminotransferase (1.0%).
Adverse reactions leading to interruption of TECENTRIQ occurred in 29% of patients; the most common (>1%) were rash (3.0%), hyperthyroidism (2.8%), hypothyroidism (1.6%), increased AST (1.6%), pyrexia (1.6%), increased ALT (1.4%), upper respiratory tract infection (1.4%), headache (1.2%), peripheral neuropathy (1.2%), and pneumonia (1.2%).
Tables 4 and 5 summarize adverse reactions and selected laboratory abnormalities in patients receiving TECENTRIQ in IMpower010.
| Adverse Reaction Graded per NCI CTCAE v4.0 | TECENTRIQ N = 495 | Best Supportive Care N = 495 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) | Grades 3–4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3–4 (%) | |
| Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue | ||||
| Rash Includes rash, dermatitis, genital rash, skin exfoliation, rash maculo-papular, rash erythematous, rash papular, lichen planus, eczema asteatotic, dermatitis exfoliative, palmar-plantar erythrodysaesthesia syndrome, dyshidrotic eczema, eczema, drug eruption, rash pruritic, toxic skin eruption, dermatitis acneiform | 17 | 1.2 | 1.4 | 0 |
| Pruritus | 10 | 0 | 0.6 | 0 |
| Endocrine Disorders | ||||
| Hypothyroidism Includes hypothyroidism, autoimmune hypothyroidism, primary hypothyroidism, blood thyroid stimulating hormone increased | 14 | 0 | 0.6 | 0 |
| Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal | ||||
| Cough Productive cough, upper airway cough syndrome, cough | 16 | 0 | 11 | 0 |
| General | ||||
| Pyrexia Includes pyrexia, body temperature increased, hyperthermia | 14 | 0.8 | 2.2 | 0.2 |
| Fatigue Includes fatigue, asthenia | 14 | 0.6 | 5 | 0.2 |
| Nervous System Disorders | ||||
| Peripheral neuropathy Includes paraesthesia, neuropathy peripheral, peripheral sensory neuropathy, hypoaesthesia, polyneuropathy, dysaesthesia, neuralgia, axonal neuropathy | 12 | 0.4 | 7 | 0.2 |
| Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue | ||||
| Musculoskeletal pain Includes myalgia, bone pain, back pain, spinal pain, musculoskeletal chest pain, pain in extremity, neck pain, non-cardiac chest pain, musculoskeletal discomfort, musculoskeletal stiffness, musculoskeletal pain | 14 | 0.8 | 9 | 0.2 |
| Arthralgia Includes arthralgia, arthritis | 11 | 0.6 | 6 | 0 |
| Laboratory Abnormality Graded per NCI CTCAE v4.0, except for increased creatinine which only includes patients with creatinine increase based on upper limit of normal definition for Grade 1 events (NCI CTCAE v5.0). | TECENTRIQ The denominators used to calculate the rate varied from 78-480 for BSC arm and 483 for TECENTRIQ are for all tests of interest based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one post-treatment value. | Best Supportive Care | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) | Grades 3–4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3–4 (%) | |
| Chemistry | ||||
| Increased aspartate aminotransferase | 34 | 2.5 | 18 | 0 |
| Increased alanine aminotransferase | 30 | 3.3 | 19 | 0.4 |
| Hyperkalemia | 24 | 3.5 | 15 | 2.5 |
| Increased blood creatinine | 31 | 0.2 | 23 | 0.2 |
Metastatic Chemotherapy-Naïve NSCLC
IMpower110
The safety of TECENTRIQ was evaluated in IMpower110, a multicenter, international, randomized, open-label study in 549 chemotherapy-naïve patients with stage IV NSCLC, including those with EGFR or ALK genomic tumor aberrations. Patients received TECENTRIQ 1200 mg every 3 weeks (n=286) or platinum-based chemotherapy consisting of carboplatin or cisplatin with either pemetrexed or gemcitabine (n=263) until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ] . IMpower110 enrolled patients whose tumors express PD-L1 (PD-L1 stained ≥ 1% of tumor cells [TC] or PD-L1 stained tumor-infiltrating immune cells [IC] covering ≥ 1% of the tumor area). The median duration of exposure to TECENTRIQ was 5.3 months (0 to 33 months).
Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 3.8% of patients receiving TECENTRIQ; these included death (reported as unexplained death and death of unknown cause), aspiration, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, pulmonary embolism, acute myocardial infarction, cardiac arrest, mechanical ileus, sepsis, cerebral infarction, and device occlusion (1 patient each).
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 28% of patients receiving TECENTRIQ. The most frequent serious adverse reactions (>2%) were pneumonia (2.8%), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (2.1%) and pneumonitis (2.1%).
TECENTRIQ was discontinued due to adverse reactions in 6% of patients ; the most common adverse reactions (≥2 patients) leading to TECENTRIQ discontinuation were peripheral neuropathy and pneumonitis.
Adverse reactions leading to interruption of TECENTRIQ occurred in 26% of patients; the most common (>1%) were ALT increased (2.1%), AST increased (2.1%), pneumonitis (2.1%), pyrexia (1.4%), pneumonia (1.4%) and upper respiratory tract infection (1.4%).
Tables 6 and 7 summarize adverse reactions and selected laboratory abnormalities in patients receiving TECENTRIQ in IMpower110.
| Adverse Reaction | TECENTRIQ N = 286 | Platinum-Based Chemotherapy N = 263 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) | Grades 3–4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3–4 (%) | |
| Graded per NCI CTCAE v4.0 | ||||
| Gastrointestinal | ||||
| Nausea | 14 | 0.3 | 34 | 1.9 |
| Constipation | 12 | 1.0 | 22 | 0.8 |
| Diarrhea | 11 | 0 | 12 | 0.8 |
| General | ||||
| Fatigue/asthenia | 25 | 1.4 | 34 | 4.2 |
| Pyrexia | 14 | 0 | 9 | 0.4 |
| Metabolism and Nutrition | ||||
| Decreased appetite | 15 | 0.7 | 19 | 0 |
| Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal | ||||
| Dyspnea | 14 | 0.7 | 10 | 0 |
| Cough | 12 | 0.3 | 10 | 0 |
| Laboratory Abnormality | TECENTRIQ | Platinum-Based Chemotherapy | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) | Grades 3–4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3–4 (%) | |
| Each test incidence is based on the number of patients who had at least one on-study laboratory measurement available: TECENTRIQ (range: 278-281); platinum-based chemotherapy (range: 256-260). Graded per NCI CTCAE v4.0. Increased blood creatinine only includes patients with test results above the normal range. | ||||
| Hematology | ||||
| Anemia | 69 | 1.8 | 94 | 20 |
| Lymphopenia | 47 | 9 | 59 | 17 |
| Chemistry | ||||
| Hypoalbuminemia | 48 | 0.4 | 39 | 2 |
| Increased alkaline phosphatase | 46 | 2.5 | 42 | 1.2 |
| Hyponatremia | 44 | 9 | 36 | 7 |
| Increased ALT | 38 | 3.2 | 32 | 0.8 |
| Increased AST | 36 | 3.2 | 32 | 0.8 |
| Hyperkalemia | 29 | 3.9 | 36 | 2.7 |
| Hypocalcemia | 24 | 1.4 | 24 | 2.7 |
| Increased blood creatinine | 24 | 0.7 | 33 | 1.5 |
| Hypophosphatemia | 23 | 3.6 | 21 | 2 |
IMpower150
The safety of TECENTRIQ with bevacizumab, paclitaxel and carboplatin was evaluated in IMpower150, a multicenter, international, randomized, open-label trial in which 393 chemotherapy-naïve patients with metastatic non-squamous NSCLC received TECENTRIQ 1200 mg with bevacizumab 15 mg/kg, paclitaxel 175 mg/m 2 or 200 mg/m 2 , and carboplatin AUC 6 mg/mL/min intravenously every 3 weeks for a maximum of 4 or 6 cycles, followed by TECENTRIQ 1200 mg with bevacizumab 15 mg/kg intravenously every 3 weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ] . The median duration of exposure to TECENTRIQ was 8.3 months in patients receiving TECENTRIQ with bevacizumab, paclitaxel, and carboplatin.
Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 6% of patients receiving TECENTRIQ; these included hemoptysis, febrile neutropenia, pulmonary embolism, pulmonary hemorrhage, death, cardiac arrest, cerebrovascular accident, pneumonia, aspiration pneumonia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, intracranial hemorrhage, intestinal angina, intestinal ischemia, intestinal obstruction and aortic dissection.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 44%. The most frequent serious adverse reactions (>2%) were febrile neutropenia, pneumonia, diarrhea, and hemoptysis.
TECENTRIQ was discontinued due to adverse reactions in 15% of patients; the most common adverse reaction leading to discontinuation was pneumonitis (1.8%).
Adverse reactions leading to interruption of TECENTRIQ occurred in 48%; the most common (>1%) were neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, fatigue/asthenia, diarrhea, hypothyroidism, anemia, pneumonia, pyrexia, hyperthyroidism, febrile neutropenia, increased ALT, dyspnea, dehydration and proteinuria.
Tables 8 and 9 summarize adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities in patients receiving TECENTRIQ with bevacizumab, paclitaxel, and carboplatin in IMpower150.
| Adverse Reaction | TECENTRIQ with Bevacizumab, Paclitaxel, and Carboplatin N = 393 | Bevacizumab, Paclitaxel and Carboplatin N = 394 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) | Grades 3–4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3–4 (%) | |
| Graded per NCI CTCAE v4.0 | ||||
| Nervous System | ||||
| Neuropathy Includes neuropathy peripheral, peripheral sensory neuropathy, hypoesthesia, paraesthesia, dysesthesia, polyneuropathy | 56 | 3 | 47 | 3 |
| Headache | 16 | 0.8 | 13 | 0 |
| General | ||||
| Fatigue/Asthenia | 50 | 6 | 46 | 6 |
| Pyrexia | 19 | 0.3 | 9 | 0.5 |
| Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue | ||||
| Alopecia | 48 | 0 | 46 | 0 |
| Rash Includes rash, rash maculo-papular, drug eruption, eczema, eczema asteatotic, dermatitis, contact dermatitis, rash erythematous, rash macular, pruritic rash, seborrheic dermatitis, dermatitis psoriasiform | 23 | 2 | 10 | 0.3 |
| Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue | ||||
| Myalgia/Pain Includes pain in extremity, musculoskeletal chest pain, musculoskeletal discomfort, neck pain, back pain, myalgia, and bone pain | 42 | 3 | 34 | 2 |
| Arthralgia | 26 | 1 | 22 | 1 |
| Gastrointestinal | ||||
| Nausea | 39 | 4 | 32 | 2 |
| Diarrhea Includes diarrhea, gastroenteritis, colitis, enterocolitis | 33 | 6 | 25 | 0.5 |
| Constipation | 30 | 0.3 | 23 | 0.3 |
| Vomiting | 19 | 2 | 18 | 1 |
| Metabolism and Nutrition | ||||
| Decreased appetite | 29 | 4 | 21 | 0.8 |
| Vascular | ||||
| Hypertension | 25 | 9 | 22 | 8 |
| Respiratory | ||||
| Cough | 20 | 0.8 | 19 | 0.3 |
| Epistaxis | 17 | 1 | 22 | 0.3 |
| Renal | ||||
| Proteinuria Data based on Preferred Terms since laboratory data for proteinuria were not systematically collected | 16 | 3 | 15 | 3 |
| Laboratory Abnormality | TECENTRIQ with Bevacizumab, Paclitaxel, and Carboplatin | Bevacizumab, Paclitaxel and Carboplatin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) | Grades 3–4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3–4 (%) | |
| Each test incidence is based on the number of patients who had both baseline and at least one on-study laboratory measurement available: TECENTRIQ with bevacizumab, paclitaxel, and carboplatin range: 337-380); bevacizumab, paclitaxel, and carboplatin (range: 337-382). Graded per NCI CTCAE v4.0 | ||||
| Hematology | ||||
| Anemia | 83 | 10 | 83 | 9 |
| Neutropenia | 52 | 31 | 45 | 26 |
| Lymphopenia | 48 | 17 | 38 | 13 |
| Chemistry | ||||
| Hyperglycemia | 61 | 0 | 60 | 0 |
| Increased BUN | 52 | NA NA = Not applicable. NCI CTCAE does not provide a Grades 3-4 definition for these laboratory abnormalities | 44 | NA |
| Hypomagnesemia | 42 | 2 | 36 | 1 |
| Hypoalbuminemia | 40 | 3 | 31 | 2 |
| Increased AST | 40 | 4 | 28 | 0.8 |
| Hyponatremia | 38 | 10 | 36 | 9 |
| Increased Alkaline Phosphatase | 37 | 2 | 32 | 1 |
| Increased ALT | 37 | 6 | 28 | 0.5 |
| Increased TSH | 30 | NA | 20 | NA |
| Hyperkalemia | 28 | 3 | 25 | 2 |
| Increased Creatinine | 28 | 1 | 19 | 2 |
| Hypocalcemia | 26 | 3 | 21 | 3 |
| Hypophosphatemia | 25 | 4 | 18 | 4 |
| Hypokalemia | 23 | 7 | 14 | 4 |
| Hyperphosphatemia | 25 | NA | 19 | NA |
IMpower130
The safety of TECENTRIQ with paclitaxel protein-bound and carboplatin was evaluated in IMpower130, a multicenter, international, randomized, open-label trial in which 473 chemotherapy-naïve patients with metastatic non-squamous NSCLC received TECENTRIQ 1200 mg and carboplatin AUC 6 mg/mL/min intravenously on Day 1 and paclitaxel protein-bound 100 mg/m 2 intravenously on Day 1, 8, and 15 of each 21-day cycle for a maximum of 4 or 6 cycles, followed by TECENTRIQ 1200 mg intravenously every 3 weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ] . Among patients receiving TECENTRIQ, 55% were exposed for 6 months or longer and 3.5% were exposed for greater than one year.
Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 5.3% of patients receiving TECENTRIQ; these included pneumonia (1.1%), pulmonary embolism (0.8%), myocardial infarction (0.6%), cardiac arrest (0.4%), pneumonitis (0.4%) and sepsis, septic shock, staphylococcal sepsis, aspiration, respiratory distress, cardiorespiratory arrest, ventricular tachycardia, death (not otherwise specified), and hepatic cirrhosis (0.2% each).
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 51% of patients receiving TECENTRIQ. The most frequent serious adverse reactions (≥2%) were pneumonia (6%), diarrhea (3%), lung infection (3%), pulmonary embolism (3%), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbation (2.5%), dyspnea (2.3%), and febrile neutropenia (1.9%).
TECENTRIQ was discontinued due to adverse reactions in 13% of patients; the most common adverse reactions leading to discontinuation were pneumonia (0.8%), pulmonary embolism (0.8%), fatigue (0.6%), dyspnea (0.6%), pneumonitis (0.6%), neutropenia (0.4%), nausea (0.4%), renal failure (0.4%), cardiac arrest (0.4%), and septic shock (0.4%).
Adverse reactions leading to interruption of TECENTRIQ occurred in 62% of patients; the most common (>1%) were neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia, diarrhea, fatigue/asthenia, pneumonia, dyspnea, pneumonitis, pyrexia, nausea, acute kidney injury, vomiting, pulmonary embolism, arthralgia, infusion-related reaction, abdominal pain, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbation, dehydration, and hypokalemia.
Tables 10 and 11 summarize adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities in patients receiving TECENTRIQ with paclitaxel protein-bound and carboplatin in IMpower130.
| Adverse Reaction | TECENTRIQ with Paclitaxel Protein-Bound and Carboplatin N = 473 | Paclitaxel Protein-Bound and Carboplatin N = 232 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) | Grades 3–4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3–4 (%) | |
| Graded per NCI CTCAE v4.0 | ||||
| General | ||||
| Fatigue/Asthenia | 61 | 11 | 60 | 8 |
| Gastrointestinal | ||||
| Nausea | 50 | 3.4 | 46 | 2.2 |
| Diarrhea Includes diarrhea, colitis, and gastroenteritis | 43 | 6 | 32 | 6 |
| Constipation | 36 | 1.1 | 31 | 0 |
| Vomiting | 27 | 2.7 | 19 | 2.2 |
| Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue | ||||
| Myalgia/Pain Includes back pain, pain in extremity, myalgia, musculoskeletal chest pain, bone pain, neck pain and musculoskeletal discomfort | 38 | 3 | 22 | 0.4 |
| Nervous System | ||||
| Neuropathy Includes neuropathy peripheral, peripheral sensory neuropathy, hypoesthesia, paresthesia, dysesthesia, polyneuropathy | 33 | 2.5 | 28 | 2.2 |
| Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal | ||||
| Dyspnea Includes dyspnea, dyspnea exertional and wheezing | 32 | 4.9 | 25 | 1.3 |
| Cough | 27 | 0.6 | 17 | 0 |
| Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue | ||||
| Alopecia | 32 | 0 | 27 | 0 |
| Rash Includes rash, rash maculo-papular, eczema, rash pruritic, rash erythematous, dermatitis, dermatitis contact, drug eruption, seborrheic dermatitis and rash macular. | 20 | 0.6 | 11 | 0.9 |
| Metabolism and Nutrition | ||||
| Decreased appetite | 30 | 2.1 | 26 | 2.2 |
| Laboratory Abnormality | TECENTRIQ with Paclitaxel Protein-Bound and Carboplatin N = 473 | Paclitaxel Protein-Bound and Carboplatin N = 232 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) | Grades 3–4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3–4 (%) | |
| Each test incidence is based on the number of patients who had both baseline and at least one on-study laboratory measurement available: TECENTRIQ with paclitaxel protein-bound and carboplatin (range: 423 - 467); paclitaxel protein-bound and carboplatin (range: 218 - 229). Graded per NCI CTCAE v4.0. | ||||
| Hematology | ||||
| Anemia | 92 | 33 | 87 | 25 |
| Neutropenia | 75 | 50 | 67 | 39 |
| Thrombocytopenia | 73 | 19 | 59 | 13 |
| Lymphopenia | 71 | 23 | 61 | 16 |
| Chemistry | ||||
| Hyperglycemia | 75 | 8 | 66 | 8 |
| Hypomagnesemia | 50 | 3.4 | 42 | 3.2 |
| Hyponatremia | 37 | 9 | 28 | 7 |
| Hypoalbuminemia | 35 | 1.3 | 31 | 0 |
| Increased ALT | 31 | 2.8 | 24 | 3.9 |
| Hypocalcemia | 31 | 2.6 | 27 | 1.8 |
| Hypophosphatemia | 29 | 6 | 20 | 3.2 |
| Increased AST | 28 | 2.2 | 24 | 1.8 |
| Increased TSH | 26 | NA NA = Not applicable. NCI CTCAE does not provide a Grades 3-4 definition for these laboratory abnormalities | 5 | NA |
| Hypokalemia | 26 | 6 | 24 | 4.4 |
| Increased Alkaline Phosphatase | 25 | 2.6 | 22 | 1.3 |
| Increased Blood Creatinine | 23 | 2.8 | 16 | 0.4 |
| Hyperphosphatemia | 21 | NA | 13 | NA |
Previously Treated Metastatic NSCLC
OAK
The safety of TECENTRIQ was evaluated in OAK, a multicenter, international, randomized, open-label trial in patients with metastatic NSCLC who progressed during or following a platinum-containing regimen, regardless of PD-L1 expression [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ] . A total of 609 patients received TECENTRIQ 1200 mg intravenously every 3 weeks until unacceptable toxicity, radiographic progression, or clinical progression or docetaxel (n=578) 75 mg/m 2 intravenously every 3 weeks until unacceptable toxicity or disease progression. The study excluded patients with active or prior autoimmune disease or with medical conditions that required systemic corticosteroids. The median duration of exposure was 3.4 months (0 to 26 months) in TECENTRIQ-treated patients and 2.1 months (0 to 23 months) in docetaxel-treated patients.
The study population characteristics were: median age of 63 years (25 to 85 years), 46% age 65 years or older, 62% male, 71% White, 20% Asian, 68% former smoker, 16% current smoker, and 63% had Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status of 1.
Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 1.6% of patients; these included pneumonia, sepsis, septic shock, dyspnea, pulmonary hemorrhage, sudden death, myocardial ischemia or renal failure.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 33.5% of patients. The most frequent serious adverse reactions (>1%) were pneumonia, sepsis, dyspnea, pleural effusion, pulmonary embolism, pyrexia and respiratory tract infection.
TECENTRIQ was discontinued due to adverse reactions in 8% of patients. The most common adverse reactions leading to TECENTRIQ discontinuation were fatigue, infections and dyspnea. Adverse reactions leading to interruption of TECENTRIQ occurred in 25% of patients; the most common (>1%) were pneumonia, liver function test abnormality, dyspnea, fatigue, pyrexia, and back pain.
Tables 12 and 13 summarize adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities, respectively, in OAK.
| Adverse Reaction | TECENTRIQ N = 609 | Docetaxel N = 578 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) | Grades 3–4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3–4 (%) | |
| Graded per NCI CTCAE v4.0 | ||||
| General | ||||
| Fatigue/Asthenia Includes fatigue and asthenia | 44 | 4 | 53 | 6 |
| Pyrexia | 18 | <1 | 13 | <1 |
| Respiratory | ||||
| Cough Includes cough and exertional cough | 26 | <1 | 21 | <1 |
| Dyspnea | 22 | 2.8 | 21 | 2.6 |
| Metabolism and Nutrition | ||||
| Decreased appetite | 23 | <1 | 24 | 1.6 |
| Musculoskeletal | ||||
| Myalgia/Pain Includes musculoskeletal pain, musculoskeletal stiffness, musculoskeletal chest pain, myalgia | 20 | 1.3 | 20 | <1 |
| Arthralgia | 12 | 0.5 | 10 | 0.2 |
| Gastrointestinal | ||||
| Nausea | 18 | <1 | 23 | <1 |
| Constipation | 18 | <1 | 14 | <1 |
| Diarrhea | 16 | <1 | 24 | 2 |
| Skin | ||||
| Rash Includes rash, erythematous rash, generalized rash, maculopapular rash, papular rash, pruritic rash, pustular rash, pemphigoid | 12 | <1 | 10 | 0 |
| Laboratory Abnormality | TECENTRIQ | Docetaxel | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) | Grades 3–4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3–4 (%) | |
| Each test incidence is based on the number of patients who had both baseline and at least one on-study laboratory measurement available: TECENTRIQ (range: 546–585) and docetaxel (range: 532–560). Graded according to NCI CTCAE version 4.0 | ||||
| Hematology | ||||
| Anemia | 67 | 3 | 82 | 7 |
| Lymphocytopenia | 49 | 14 | 60 | 21 |
| Chemistry | ||||
| Hypoalbuminemia | 48 | 4 | 50 | 3 |
| Hyponatremia | 42 | 7 | 31 | 6 |
| Increased Alkaline Phosphatase | 39 | 2 | 25 | 1 |
| Increased AST | 31 | 3 | 16 | 0.5 |
| Increased ALT | 27 | 3 | 14 | 0.5 |
| Hypophosphatemia | 27 | 5 | 23 | 4 |
| Hypomagnesemia | 26 | 1 | 21 | 1 |
| Increased Creatinine | 23 | 2 | 16 | 1 |
Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC)
IMpower133
The safety of TECENTRIQ with carboplatin and etoposide was evaluated in IMpower133, a randomized, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in which 198 patients with ES-SCLC received TECENTRIQ 1200 mg and carboplatin AUC 5 mg/mL/min on Day 1 and etoposide 100 mg/m 2 intravenously on Days 1, 2 and 3 of each 21-day cycle for a maximum of 4 cycles, followed by TECENTRIQ 1200 mg every 3 weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ] . Among 198 patients receiving TECENTRIQ, 32% were exposed for 6 months or longer and 12% were exposed for 12 months or longer.
Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 2% of patients receiving TECENTRIQ. These included pneumonia, respiratory failure, neutropenia, and death (1 patient each).
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 37% of patients receiving TECENTRIQ. Serious adverse reactions in >2% were pneumonia (4.5%), neutropenia (3.5%), febrile neutropenia (2.5%), and thrombocytopenia (2.5%).
TECENTRIQ was discontinued due to adverse reactions in 11% of patients. The most frequent adverse reaction requiring permanent discontinuation in >2% of patients was infusion-related reactions (2.5%).
Adverse reactions leading to interruption of TECENTRIQ occurred in 59% of patients; the most common (>1%) were neutropenia (22%), anemia (9%), leukopenia (7%), thrombocytopenia (5%), fatigue (4.0%), infusion-related reaction (3.5%), pneumonia (2.0%), febrile neutropenia (1.5%), increased ALT (1.5%), and nausea (1.5%).
Tables 14 and 15 summarize adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities, respectively, in patients who received TECENTRIQ with carboplatin and etoposide in IMpower133.
| Adverse Reaction | TECENTRIQ with Carboplatin and Etoposide N = 198 | Placebo with Carboplatin and Etoposide N = 196 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) | Grades 3–4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3–4 (%) | |
| Graded per NCI CTCAE v4.0 | ||||
| General | ||||
| Fatigue/asthenia | 39 | 5 | 33 | 3 |
| Gastrointestinal | ||||
| Nausea | 38 | 1 | 33 | 1 |
| Constipation | 26 | 1 | 30 | 1 |
| Vomiting | 20 | 2 | 17 | 3 |
| Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue | ||||
| Alopecia | 37 | 0 | 35 | 0 |
| Metabolism and Nutrition | ||||
| Decreased appetite | 27 | 1 | 18 | 0 |
| Laboratory Abnormality | TECENTRIQ with Carboplatin and Etoposide | Placebo with Carboplatin and Etoposide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) | Grades 3–4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3–4 (%) | |
| Each test incidence is based on the number of patients who had both baseline and at least one on-study laboratory measurement available: TECENTRIQ (range: 181-193); Placebo (range: 181-196). Graded per NCI CTCAE v4.0 | ||||
| Hematology | ||||
| Anemia | 94 | 17 | 93 | 19 |
| Neutropenia | 73 | 45 | 76 | 48 |
| Thrombocytopenia | 58 | 20 | 53 | 17 |
| Lymphopenia | 46 | 14 | 38 | 11 |
| Chemistry | ||||
| Hyperglycemia | 67 | 10 | 65 | 8 |
| Increased Alkaline Phosphatase | 38 | 1 | 35 | 2 |
| Hyponatremia | 34 | 15 | 33 | 11 |
| Hypoalbuminemia | 32 | 1 | 30 | 0 |
| Decreased TSH TSH = thyroid-stimulating hormone. NCI CTCAE v4.0 does not include these laboratories. | 28 | NA NA = Not applicable. | 15 | NA |
| Hypomagnesemia | 31 | 5 | 35 | 6 |
| Hypocalcemia | 26 | 3 | 28 | 5 |
| Increased ALT | 26 | 3 | 31 | 1 |
| Increased AST | 22 | 1 | 21 | 2 |
| Increased Blood Creatinine | 22 | 4 | 15 | 1 |
| Hyperphosphatemia | 21 | NA | 23 | NA |
| Increased TSH | 21 | NA | 7 | NA |
IMforte
The safety of TECENTRIQ in combination with lurbinectedin was evaluated in IMforte [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ]. Patients received TECENTRIQ 1200 mg IV and lurbinectedin 3.2 mg/m 2 IV, on Day 1 of each 21-day cycle until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Primary prophylaxis of G-CSF was administered to 84% of patients. Among 242 patients receiving TECENTRIQ with lurbinectedin, the median duration of exposure to TECENTRIQ was 4.2 months, with 34% of patients exposed for 6 months or longer and 8% of patients exposed for 12 months or longer.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 31% of patients receiving TECENTRIQ with lurbinectedin. Serious adverse reactions in >2% of patients were pneumonia (2.5%), respiratory tract infection (2.1%), dyspnea (2.1%), and decreased platelet count (2.1%). Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 5% of patients receiving TECENTRIQ with lurbinectedin including pneumonia (3 patients), sepsis (3 patients), cardio-respiratory arrest (2 patients), myocardial infarction (2 patients) and febrile neutropenia (1 patient).
Permanent discontinuation of TECENTRIQ due to an adverse reaction occurred in 2.5% of patients. The adverse reactions requiring permanent discontinuation in ≥ 1% of patients who received TECENTRIQ were immune-mediated nephritis, peripheral neuropathy, nephropathy, pneumonitis, anemia, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia.
Dosage interruptions of TECENTRIQ due to an adverse reaction occurred in 29% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dosage interruption in ≥ 2% of patients included anemia, fatigue, decreased neutrophil count, pneumonitis, and decreased platelet count.
Tables 16 and 17 summarize adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities, respectively, in patients who received TECENTRIQ with lurbinectedin in IMforte.
| Adverse Reaction | TECENTRIQ with Lurbinectedin N = 242 | TECENTRIQ N = 240 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) | Grades 3 or 4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3 or 4 (%) | |
| Graded per NCI CTCAE v5.0 | ||||
| Gastrointestinal | ||||
| Nausea | 36 | 3 | 4 | 1 |
| Diarrhea Includes diarrhea and colitis. | 15 | 0 | 8 | 0 |
| Vomiting | 14 | 1 | 3 | 0 |
| Constipation | 12 | 0 | 6 | 1 |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | ||||
| Fatigue Includes fatigue and asthenia. | 32 | 5 | 13 | 2 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||||
| Musculoskeletal Pain Includes arthralgia, arthritis, back pain, bone pain, musculoskeletal chest pain, musculoskeletal discomfort, musculoskeletal pain, myalgia, neck pain, non-cardiac chest pain, and pain in extremity. | 19 | 2 | 16 | 1 |
| Metabolism and Nutrition | ||||
| Decreased appetite | 17 | 0 | 7 | 0 |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | ||||
| Cough Includes cough, productive cough, and upper-airway cough syndrome. | 12 | 0 | 8 | 0 |
| Dyspnea Includes dyspnea and dyspnea exertional. | 11 | 2 | 10 | 2 |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions in < 10% of patients who received TECENTRIQ in combination with lurbinectedin included pneumonia, phlebitis, extravasation resulting in skin necrosis, hypersensitivity and increased creatine phosphokinase.
| Laboratory Abnormality | TECENTRIQ with Lurbinectedin N = 242 | TECENTRIQ N = 240 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) | Grades 3 or 4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3 or 4 (%) | |
| Graded per NCI CTCAE v5.0 | ||||
| Hematology | ||||
| Lymphopenia | 55 | 17 | 31 | 11 |
| Thrombocytopenia | 54 | 15 | 15 | 3 |
| Anemia | 51 | 13 | 12 | 3 |
| Neutropenia | 36 | 18 | 7 | 4 |
| Chemistry | ||||
| Increased alkaline phosphatase | 29 | 1 | 14 | 0 |
| Decreased sodium | 27 | 4 | 30 | 5 |
| Increased ALT | 25 | 3 | 18 | 2 |
| Increased AST | 24 | 3 | 22 | 1 |
| Decreased calcium | 24 | 3 | 8 | 1 |
| Increased creatinine | 21 | 3 | 14 | 0 |
Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
IMbrave150
The safety of TECENTRIQ in combination with bevacizumab was evaluated in IMbrave150, a multicenter, international, randomized, open-label trial in patients with locally advanced or metastatic or unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma who have not received prior systemic treatment [see Clinical Studies (14.3) ] . Patients received 1,200 mg of TECENTRIQ intravenously followed by 15 mg/kg bevacizumab (n=329) every 3 weeks, or 400 mg of sorafenib (n=156) given orally twice daily, until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The median duration of exposure to TECENTRIQ was 7.4 months (range: 0-16 months) and to bevacizumab was 6.9 months (range: 0-16 months).
Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 4.6% of patients in the TECENTRIQ and bevacizumab arm. The most common adverse reactions leading to death were gastrointestinal and esophageal varices hemorrhage (1.2%) and infections (1.2%).
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 38% of patients in the TECENTRIQ and bevacizumab arm. The most frequent serious adverse reactions (≥ 2%) were gastrointestinal hemorrhage (7%), infections (6%), and pyrexia (2.1%).
Adverse reactions leading to discontinuation of TECENTRIQ occurred in 9% of patients in the TECENTRIQ and bevacizumab arm. The most common adverse reactions leading to TECENTRIQ discontinuation were hemorrhages (1.2%), including gastrointestinal, subarachnoid, and pulmonary hemorrhages; increased transaminases or bilirubin (1.2%); infusion-related reaction/cytokine release syndrome (0.9%); and autoimmune hepatitis (0.6%).
Adverse reactions leading to interruption of TECENTRIQ occurred in 41% of patients in the TECENTRIQ and bevacizumab arm; the most common (≥ 2%) were liver function laboratory abnormalities including increased transaminases, bilirubin, or alkaline phosphatase (8%); infections (6%); gastrointestinal hemorrhages (3.6%); thrombocytopenia/decreased platelet count (3.6%); hyperthyroidism (2.7%); and pyrexia (2.1%).
Immune-related adverse reactions requiring systemic corticosteroid therapy occurred in 12% of patients in the TECENTRIQ and bevacizumab arm.
Tables 18 and 19 summarize adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities, respectively, in patients who received TECENTRIQ and bevacizumab in IMbrave150.
| Adverse Reaction | TECENTRIQ in combination with Bevacizumab (n = 329) | Sorafenib (n=156) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades Graded per NCI CTCAE v4.0 (%) | Grades 3–4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3–4 (%) | |
| Vascular Disorders | ||||
| Hypertension | 30 | 15 | 24 | 12 |
| General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions | ||||
| Fatigue/asthenia Includes fatigue and asthenia | 26 | 2 | 32 | 6 |
| Pyrexia | 18 | 0 | 10 | 0 |
| Renal and Urinary Disorders | ||||
| Proteinuria | 20 | 3 | 7 | 0.6 |
| Investigations | ||||
| Weight Decreased | 11 | 0 | 10 | 0 |
| Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders | ||||
| Pruritus | 19 | 0 | 10 | 0 |
| Rash | 12 | 0 | 17 | 2.6 |
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||||
| Diarrhea | 19 | 1.8 | 49 | 5 |
| Constipation | 13 | 0 | 14 | 0 |
| Abdominal Pain | 12 | 0 | 17 | 0 |
| Nausea | 12 | 0 | 16 | 0 |
| Vomiting | 10 | 0 | 8 | 0 |
| Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders | ||||
| Decreased Appetite | 18 | 1.2 | 24 | 3.8 |
| Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders | ||||
| Cough | 12 | 0 | 10 | 0 |
| Epistaxis | 10 | 0 | 4.5 | 0 |
| Injury, Poisoning and Procedural Complications | ||||
| Infusion-Related Reaction | 11 | 2.4 | 0 | 0 |
| Laboratory Abnormality | TECENTRIQ in combination with Bevacizumab (n = 329) | Sorafenib (n=156) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades Graded per NCI CTCAE v4.0 (%) | Grades 3–4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3–4 (%) | |
| Each test incidence is based on the number of patients who had both baseline and at least one on-study laboratory measurement available: TECENTRIQ plus bevacizumab (222-323) and sorafenib (90-153) | ||||
| Chemistry | ||||
| Increased AST | 86 | 16 | 90 | 16 |
| Increased Alkaline Phosphatase | 70 | 4 | 76 | 4.6 |
| Increased ALT | 62 | 8 | 70 | 4.6 |
| Decreased Albumin | 60 | 1.5 | 54 | 0.7 |
| Decreased Sodium | 54 | 13 | 49 | 9 |
| Increased Glucose | 48 | 9 | 43 | 4.6 |
| Decreased Calcium | 30 | 0.3 | 35 | 1.3 |
| Decreased Phosphorus | 26 | 4.7 | 58 | 16 |
| Increased Potassium | 23 | 1.9 | 16 | 2 |
| Hypomagnesemia | 22 | 0 | 22 | 0 |
| Hematology | ||||
| Decreased Platelet | 68 | 7 | 63 | 4.6 |
| Decreased Lymphocytes | 62 | 13 | 58 | 11 |
| Decreased Hemoglobin | 58 | 3.1 | 62 | 3.9 |
| Increased Bilirubin | 57 | 8 | 59 | 14 |
| Decreased Leukocyte | 32 | 3.4 | 29 | 1.3 |
| Decreased Neutrophil | 23 | 2.3 | 16 | 1.1 |
Melanoma
IMspire150
The safety of TECENTRIQ, administered with cobimetinib and vemurafenib was evaluated in IMspire150, a double-blind, randomized (1:1), placebo-controlled study conducted in patients with previously untreated BRAF V600 mutation-positive metastatic or unresectable melanoma [see Clinical Studies (14.4) ] . Patients received TECENTRIQ with cobimetinib and vemurafenib (N=230) or placebo with cobimetinib and vemurafenib (n=281).
Among the 230 patients who received TECENTRIQ administered with cobimetinib and vemurafenib, the median duration of exposure to TECENTRIQ was 9.2 months (range: 0-30 months) to cobimetinib was 10.0 months (range: 1-31 months) and to vemurafenib was 9.8 months (range: 1-31 months).
Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 3% of patients in the TECENTRIQ plus cobimetinib and vemurafenib arm. Adverse reactions leading to death were hepatic failure, fulminant hepatitis, sepsis, septic shock, pneumonia, and cardiac arrest.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 45% of patients in the TECENTRIQ plus cobimetinib and vemurafenib arm. The most frequent (≥ 2%) serious adverse reactions were hepatotoxicity (7%), pyrexia (6%), pneumonia (4.3%), malignant neoplasms (2.2%), and acute kidney injury (2.2%).
Adverse reactions leading to discontinuation of TECENTRIQ occurred in 21% of patients in the TECENTRIQ plus cobimetinib and vemurafenib arm. The most frequent (≥ 2%) adverse reactions leading to TECENTRIQ discontinuation were increased ALT (2.2%) and pneumonitis (2.6%).
Adverse reactions leading to interruption of TECENTRIQ occurred in 68% of patients in the TECENTRIQ plus cobimetinib and vemurafenib arm. The most frequent (≥ 2%) adverse reactions leading to TECENTRIQ interruption were pyrexia (14%), increased ALT (13%), hyperthyroidism (10%), increased AST (10%), increased lipase (9%), increased amylase (7%), pneumonitis (5%), increased CPK (4.3%), diarrhea (3.5%), pneumonia (3.5%), asthenia (3%), rash (3%), influenza (3%), arthralgia (2.6%), fatigue (2.2%), dyspnea (2.2%), cough (2.2%), peripheral edema (2.2%), uveitis (2.2%), bronchitis (2.2%), hypothyroidism (2.2%), and respiratory tract infection (2.2%).
Tables 20 and 21 summarize the incidence of adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities in Study IMspire150.
| Adverse Reaction | TECENTRIQ in combination with Cobimetinib and Vemurafenib (n=230) | Placebo with Cobimetinib and Vemurafenib (n=281) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) | Grade 3–4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade 3–4 (%) | |
| Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders | ||||
| Rash Includes rash, rash maculo-papular, dermatitis acneiform, rash macular, rash erythematous, eczema, skin exfoliation, rash papular, rash pustular, palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome, dermatitis, dermatitis contact, erythema multiforme, rash pruritic, drug eruption, nodular rash, dermatitis allergic, exfoliative rash, dermatitis exfoliative generalized and rash morbilliform | 75 | 27 | 72 | 23 |
| Pruritus | 26 | <1 | 17 | <1 |
| Photosensitivity reaction | 21 | <1 | 25 | 3.2 |
| General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions | ||||
| Fatigue Includes fatigue, asthenia and malaise | 51 | 3 | 45 | 1.8 |
| Pyrexia Includes pyrexia and hyperpyrexia | 49 | 1.7 | 35 | 2.1 |
| Edema Includes edema peripheral, lymphoedema, edema, face edema, eyelid edema, periorbital edema, lip edema and generalized edema | 26 | <1 | 21 | 0 |
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||||
| Hepatotoxicity Includes alanine aminotransferase increased, aspartate aminotransferase increased, blood bilirubin increased, transaminases increased, hepatitis, hepatic enzyme increased, hepatotoxicity, hypertransaminasemia, bilirubin conjugated increased, hepatocellular injury, hyperbilirubinemia, liver function test increased, hepatic failure, hepatitis fulminant and liver function test abnormal | 50 | 21 | 36 | 13 |
| Nausea | 30 | <1 | 32 | 2.5 |
| Stomatitis Includes stomatitis, mucosal inflammation, aphthous ulcer, mouth ulceration, cheilitis and glossitis | 23 | 1.3 | 15 | <1 |
| Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders | ||||
| Musculoskeletal pain Includes arthralgia, myalgia, pain in extremity, back pain, musculoskeletal pain, arthritis, neck pain, musculoskeletal chest pain, musculoskeletal stiffness, bone pain, spinal pain, immune-mediated arthritis, joint stiffness and non-cardiac chest pain | 62 | 4.3 | 48 | 3.2 |
| Endocrine Disorders | ||||
| Hypothyroidism Includes hypothyroidism and blood thyroid stimulating hormone increased | 22 | 0 | 10 | 0 |
| Hyperthyroidism | 18 | <1 | 8 | 0 |
| Injury, Poisoning and Procedural Complications | ||||
| Infusion-related reaction Includes infusion related reaction and hypersensitivity | 10 | 2.6 | 8 | <1 |
| Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders | ||||
| Pneumonitis Includes pneumonitis and interstitial lung disease | 12 | 1.3 | 6 | <1 |
| Vascular Disorders | ||||
| Hypertension Includes hypertension, blood pressure increased, hypertensive crisis | 17 | 10 | 18 | 7 |
Clinically important adverse reactions in < 10% of patients who received TECENTRIQ plus cobimetinib and vemurafenib were:
Cardiac Disorders : Arrhythmias, ejection fraction decreased, electrocardiogram QT prolonged
Eye Disorders : Uveitis
Gastrointestinal disorders : Pancreatitis
Infections and infestations: Pneumonia, urinary tract infection
Metabolism and nutrition disorders: Hyperglycemia
Nervous system Disorders : Dizziness, dysgeusia, syncope
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders : Dyspnea, oropharyngeal pain
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders : Vitiligo
| Laboratory Abnormality | TECENTRIQ in combination with Cobimetinib and Vemurafenib (n=230) | Placebo with Cobimetinib and Vemurafenib (n=281) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) | Grade 3–4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade 3–4 (%) | |
| Graded per NCI CTCAE v4.0. | ||||
| Each test incidence is based on the number of patients who had both baseline and at least one on-study laboratory measurement available: TECENTRIQ plus cobimetinib and vemurafenib (28-277), placebo plus cobimetinib and vemurafenib arm (25-230). | ||||
| Hematology | ||||
| Decreased Lymphocytes | 80 | 24 | 72 | 17 |
| Decreased Hemoglobin | 77 | 2.6 | 72 | 2.2 |
| Decreased Platelet | 34 | 1.3 | 24 | 0.4 |
| Decreased Neutrophils | 26 | 2.2 | 19 | 1.5 |
| Chemistry | ||||
| Increased Creatine Kinase | 88 | 22 | 81 | 18 |
| Increased AST | 80 | 13 | 68 | 6 |
| Increased ALT | 79 | 18 | 62 | 12 |
| Increased Triacylglycerol Lipase | 75 | 46 | 62 | 35 |
| Increased Alkaline Phosphatase | 73 | 6 | 63 | 2.9 |
| Decreased Phosphorus | 67 | 22 | 64 | 14 |
| Increased Amylase | 51 | 13 | 45 | 13 |
| Increased Blood Urea Nitrogen | 47 | NA NA= Not applicable. NCI CTCAE v4.0 does not include these laboratories. | 37 | NA |
| Decreased Albumin | 43 | 0.9 | 34 | 1.5 |
| Increased Bilirubin | 42 | 3.1 | 33 | 0.7 |
| Decreased Calcium | 41 | 1.3 | 28 | 0 |
| Decreased Sodium | 40 | 5 | 34 | 7 |
| Decreased Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone | 38 | NA | 23 | NA |
| Increased Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone Increased Thyroid Stimulating Hormone has a difference <5% (All Grades) between arms and is included for clinical completeness. | 37 | NA | 33 | NA |
| Decreased Potassium | 36 | 5 | 22 | 4.3 |
| Increased Triiodothyronine | 33 | NA | 18 | NA |
| Increased Free Thyroxine | 32 | NA | 21 | NA |
| Decreased Total Triiodothyronine | 32 | NA | 8 | NA |
| Increased Potassium | 29 | 1.3 | 19 | 1.4 |
| Decreased Triiodothyronine | 27 | NA | 21 | NA |
| Increased Sodium | 20 | 0 | 13 | 0.4 |
Unresectable or Metastatic Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma (ASPS)
ML39345 Study
The safety of TECENTRIQ was evaluated in 47 adult and 2 pediatric patients enrolled in Study ML39345 [see Clinical Studies (14.5) ]. Adult patients received TECENTRIQ 1200 mg every 3 weeks and pediatric patients received 15 mg/kg up to a maximum 1200 mg every 3 weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The median duration of exposure to TECENTRIQ was 8.9 months (1 to 40 months).
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 41% of patients receiving TECENTRIQ. The most frequent serious adverse reactions (>2%) were fatigue, pain in extremity, pulmonary hemorrhage, and pneumonia (4.1% each).
Dosage interruptions of TECENTRIQ due to an adverse reaction occurred in 35% of patients. The most common adverse reactions (≥3%) leading to dose interruptions were pneumonitis and pain in extremity (4.1% each).
Tables 22 and 23 summarize adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities in Study ML39345.
| Adverse Reaction | TECENTRIQ N = 49 | |
|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) | Grades 3–4 (%) | |
| Graded per NCI CTCAE v4.0 | ||
| General disorders and administration site conditions | ||
| Fatigue | 55 | 2 |
| Pyrexia | 25 | 2 |
| Influenza like illness | 18 | 0 |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||
| Nausea | 43 | 0 |
| Vomiting | 37 | 0 |
| Constipation | 33 | 0 |
| Diarrhea | 27 | 2 |
| Abdominal pain Includes abdominal pain and abdominal pain upper | 25 | 0 |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders | ||
| Decreased appetite | 22 | 2 |
| Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal | ||
| Cough Includes cough, upper-airway cough syndrome, and productive cough | 45 | 0 |
| Dyspnea | 33 | 0 |
| Rhinitis allergic | 16 | 0 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||
| Musculoskeletal pain Includes arthralgia, pain in extremity, myalgia, non-cardiac chest pain, neck pain, musculoskeletal chest pain, and back pain | 67 | 8 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||
| Rash Includes rash maculo-papular, rash, dermatitis acneiform, eczema, skin exfoliation, and drug eruption | 47 | 2 |
| Nervous system disorders | ||
| Headache | 43 | 4 |
| Dizziness Includes vertigo and dizziness | 29 | 4 |
| Vascular disorders | ||
| Hypertension | 43 | 6 |
| Hemorrhage Includes pulmonary hemorrhage, hemoptysis, conjunctival hemorrhage, epistaxis, hematuria, rectal hemorrhage, and laryngeal hemorrhage | 29 | 2 |
| Psychiatric disorders | ||
| Insomnia | 27 | 0 |
| Anxiety | 25 | 0 |
| Cardiac Disorders | ||
| Arrhythmia Includes atrial fibrillation, sinus bradycardia, ventricular tachycardia, and sinus tachycardia | 22 | 2 |
| Endocrine disorders | ||
| Hypothyroidism Includes hypothyroidism and blood thyroid stimulating hormone increased | 25 | 0 |
| Investigations | ||
| Weight decreased | 18 | 0 |
| Weight increased | 16 | 6 |
| Laboratory Abnormality Laboratory tests which do not have NCI CTCAE grading criteria are also included for All Grade assessments, which were performed by comparing to respective lab normal ranges. | TECENTRIQ The denominators used to calculate the rate varied from 4-49 for all tests of interest based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one on-study laboratory measurement available. | |
|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) | Grades 3–4 (%) | |
| Hematology | ||
| Decreased Hemoglobin | 63 | 0 |
| Decreased Platelets | 27 | 0 |
| Increased Platelets | 29 | 0 |
| Chemistry | ||
| Increased Alkaline Phosphatase | 29 | 0 |
| Decreased Amylase | 40 | 0 |
| Increased Amylase | 20 | 20 |
| Decreased Bilirubin | 49 | 0 |
| Decreased Calcium | 47 | 0 |
| Increased Calcium | 25 | 14 |
| Decreased Glucose | 33 | 0 |
| Increased Glucose | 78 | 0 |
| Decreased Glucose (fasting) | 25 | 0 |
| Decreased Magnesium | 21 | 0 |
| Increased Magnesium | 26 | 26 |
| Increased AST | 39 | 2 |
| Increased ALT | 33 | 2 |
| Decreased Sodium | 43 | 0 |
| Increased Lipase | 25 | 25 |
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of TECENTRIQ. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Cardiac: pericarditis, pericardial effusion, cardiac tamponade
- Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue: tenosynovitis
DESCRIPTION
Atezolizumab is a programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) blocking antibody. Atezolizumab is an Fc-engineered, humanized, non-glycosylated IgG1 kappa immunoglobulin that has a calculated molecular mass of 145 kDa.
TECENTRIQ (atezolizumab) injection for intravenous use is a sterile, preservative-free, colorless to slightly yellow solution in single-dose vials. Each 20 mL vial contains 1200 mg of atezolizumab and is formulated in glacial acetic acid (16.5 mg), L-histidine (62 mg), polysorbate 20 (8 mg), and sucrose (821.6 mg), with a pH of 5.8. Each 14 mL vial contains 840 mg of atezolizumab and is formulated in glacial acetic acid (11.5 mg), L-histidine (43.4 mg), polysorbate 20 (5.6 mg), and sucrose (575.1 mg) with a pH of 5.8.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
PD L1 may be expressed on tumor cells and/or tumor infiltrating immune cells and can contribute to the inhibition of the anti-tumor immune response in the tumor microenvironment. Binding of PD L1 to the PD 1 and B7.1 receptors found on T cells and antigen presenting cells suppresses cytotoxic T-cell activity, T-cell proliferation and cytokine production.
Atezolizumab is a monoclonal antibody that binds to PD L1 and blocks its interactions with both PD 1 and B7.1 receptors. This releases the PD L1/PD 1 mediated inhibition of the immune response, including activation of the anti-tumor immune response without inducing antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. In syngeneic mouse tumor models, blocking PD L1 activity resulted in decreased tumor growth.
In mouse models of cancer, dual inhibition of the PD-1/PD-L1 and MAPK pathways suppresses tumor growth and improves tumor immunogenicity through increased antigen presentation and T cell infiltration and activation compared to targeted therapy alone.
Pharmacodynamics
The exposure-response relationship and time course of pharmacodynamic response for the safety and effectiveness of atezolizumab have not been fully characterized.
Pharmacokinetics
Atezolizumab exposure increased dose proportionally over the dose range of 1 mg/kg to 20 mg/kg (0.07 to 1.33 times of the approved recommended doses), including a dose of 1200 mg administered every 3 weeks. Steady state was achieved after 6 to 9 weeks following multiple doses. The systemic accumulation ratio for every 2 weeks administration and every 3 weeks administration is 3.3- and 1.9- fold, respectively.
Distribution
The volume of distribution at steady state is 6.9 L.
Elimination
The clearance (CV%) is 0.2 L/day (29%) and the terminal half-life is 27 days. Atezolizumab clearance was found to decrease over time, with a mean maximal reduction (CV%) from baseline value of 17% (41%); however, the decrease in clearance was not considered clinically relevant.
Specific Populations
The following factors had no clinically significant effect on the systemic exposure of atezolizumab: age (2 to 89 years), body weight, sex, albumin levels, tumor burden, region or race, mild or moderate renal impairment [estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) 30 to 89 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ], mild hepatic impairment (bilirubin ≤ ULN and AST > ULN or bilirubin > 1 to 1.5 × ULN and any AST), moderate hepatic impairment (bilirubin >1.5 to 3 × ULN and any AST), level of PD-L1 expression, or performance status.
Pediatric Patients
Atezolizumab serum concentrations with weight-based dosing at 15 mg/kg up to a maximum of 1200 mg every 3 weeks, in pediatric patients (2 years to <17 years) with relapsed or progressive solid tumors and lymphomas, are comparable to those of adult patients receiving 1200 mg every 3 weeks; while the exposure tended to be lower in pediatric patients less than 12 years old, this is not considered to be clinically relevant.
Immunogenicity
The observed incidence of anti-drug antibodies (ADA) is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Differences in assay methods preclude meaningful comparisons of the incidence of ADA in the studies described below with the incidence of ADA in other products.
During the first year of treatment with TECENTRIQ across 8 clinical studies, 13% to 36% of patients developed anti-atezolizumab antibodies. Median atezolizumab clearance in patients who tested positive for ADA was 19% (minimum 18%, maximum 49%) higher as compared to atezolizumab clearance in patients who tested negative for ADA; this change in clearance is not expected to be clinically significant.
In OAK and IMbrave150, exploratory analyses showed that the subset of patients who were ADA-positive appeared to have less efficacy (effect on overall survival) as compared to patients who tested negative for ADA [see Clinical Studies (14.1 , 14.3) ] . In study IMpower150 and IMforte, the impact of ADA on efficacy did not appear to be clinically significant [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ] . In the remaining studies, there is insufficient information to characterize the effect of ADA on efficacy.
The presence of ADA did not have a clinically significant effect on the incidence or severity of adverse reactions.
Across clinical studies, the incidence of neutralizing antibodies (NAb) in ADA-positive patients was 24% to 83%. The effect of NAb on atezolizumab exposure and safety did not appear to be clinically significant. The effect of NAb on key efficacy endpoints is uncertain due to small sample sizes.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No studies have been performed to test the potential of atezolizumab for carcinogenicity or genotoxicity.
Animal fertility studies have not been conducted with atezolizumab; however, an assessment of the male and female reproductive organs was included in a 26-week, repeat-dose toxicity study in cynomolgus monkeys. Weekly administration of atezolizumab to female monkeys at the highest dose tested caused an irregular menstrual cycle pattern and a lack of newly formed corpora lutea in the ovaries. This effect occurred at an estimated AUC approximately 6 times the AUC in patients receiving the recommended dose and was reversible. There was no effect on the male monkey reproductive organs.
Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
In animal models, inhibition of PD-L1/PD-1 signaling increased the severity of some infections and enhanced inflammatory responses. M. tuberculosis-infected PD-1 knockout mice exhibit markedly decreased survival compared with wild-type controls, which correlated with increased bacterial proliferation and inflammatory responses in these animals. PD-L1 and PD-1 knockout mice and mice receiving PD-L1 blocking antibody have also shown decreased survival following infection with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus.
CLINICAL STUDIES
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Adjuvant Treatment of Stage II-IIIA NSCLC with PD-L1 Expression ≥ 1%
The efficacy of TECENTRIQ was evaluated in IMpower010 (NCT02486718), a multi-center, randomized, open-label trial for the adjuvant treatment of patients with NSCLC who had complete tumor resection and were eligible to receive cisplatin-based adjuvant chemotherapy. Eligible patients were required to have Stage IB (tumors ≥ 4 cm) – Stage IIIA NSCLC per the Union for International Cancer Control/American Joint Committee on Cancer staging system, 7th edition. Patients were excluded if they had a history of autoimmune disease; a history of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, organizing pneumonia, drug-induced pneumonitis, idiopathic pneumonitis, or evidence of active pneumonitis; administration of a live, attenuated vaccine within 28 days prior to randomization; administration of systemic immunostimulatory agents within 4 weeks or systemic immunosuppressive medications within 2 weeks prior to randomization.
A total of 1005 patients who had complete tumor resection and received cisplatin-based adjuvant chemotherapy were randomized (1:1) to receive TECENTRIQ 1200 mg intravenous infusion every 3 weeks for 16 cycles, unless disease recurrence or unacceptable toxicity occurred, or best supportive care (BSC). Randomization was stratified by sex, stage of disease, histology, and PD-L1 expression.
Tumor assessments were conducted at baseline of the randomization phase and every 4 months for the first year following Cycle 1, Day 1 and then every 6 months until year five, then annually thereafter.
The median age was 62 years (range: 26 to 84), and 67% of patients were male. The majority of patients were White (73%) and Asian (24%). Most patients were current or previous smokers (78%) and baseline Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status in patients was 0 (55%) or 1 (44%). Overall, 12% of patients had Stage IB, 47% had Stage II and 41% had Stage IIIA disease. PD-L1 expression, defined as the percentage of tumor cells expressing PD-L1 as measured by the VENTANA PD-L1 (SP263) assay, was ≥ 1% in 53% of patients, <1% in 44% and unknown in 2.6%.
The primary efficacy outcome measure was disease-free survival (DFS) as assessed by the investigator. The primary efficacy analysis population (n = 476) was patients with Stage II – IIIA NSCLC with PD-L1 expression on ≥ 1% of tumor cells (PD-L1 ≥ 1% TC). DFS was defined as the time from the date of randomization to the date of occurrence of any of the following: first documented recurrence of disease, new primary NSCLC, or death due to any cause, whichever occurred first. A key secondary efficacy outcome measure was overall survival (OS) in the intent-to-treat population.
At the time of the interim DFS analysis, the study demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in DFS in the PD-L1 ≥ 1% TC, Stage II – IIIA patient population.
Efficacy results are presented in Table 24 and Figure 1 .
| Arm A: TECENTRIQ N = 248 | Arm B: Best Supportive Care N = 228 | |
|---|---|---|
| CI = Confidence interval, NE = Not estimable, NR = Not reached | ||
| Disease-Free Survival | ||
| Number of events (%) | 88 (35) | 105 (46) |
| Median, months | NR | 35.3 |
| (95% CI) | (36.1, NE) | (29.0, NE) |
| Hazard ratio Stratified by stage, sex, and histology (95% CI) | 0.66 (0.50, 0.88) | |
| p-value | 0.004 | |
In a pre-specified secondary subgroup analysis of patients with PD-L1 TC ≥ 50% Stage II – IIIA NSCLC (n=229), the median DFS was not reached (95% CI: 42.3 months, NE) for patients in the TECENTRIQ arm and was 35.7 months (95% CI: 29.7, NE) for patients in the best supportive care arm, with a HR of 0.43 (95% CI: 0.27, 0.68). In an exploratory subgroup analysis of patients with PD-L1 TC 1-49% Stage II – IIIA NSCLC (n=247), the median DFS was 32.8 months (95% CI: 29.4, NE) for patients in the TECENTRIQ arm and 31.4 months (95% CI: 24.0, NE) for patients in the best supportive care arm, with a HR of 0.87 (95% CI: 0.60, 1.26).
Figure 1: Kaplan-Meier Plot of Disease-Free Survival in IMpower010 in Patients with Stage II – IIIA NSCLC with PD-L1 expression ≥ 1% TC

At the time of the DFS interim analysis, 19% of patients in the PD-L1 ≥1% TC Stage II – IIIA patient population had died. An exploratory analysis of OS in this population resulted in a stratified HR of 0.77 (95% CI: 0.51, 1.17).
Metastatic Chemotherapy-Naïve NSCLC with High PD-L1 Expression
The efficacy of TECENTRIQ was evaluated in IMpower110 (NCT02409342), a multicenter, international, randomized, open-label trial in patients with stage IV NSCLC whose tumors express PD-L1 (PD-L1 stained ≥ 1% of tumor cells [TC ≥ 1%] or PD-L1 stained tumor-infiltrating immune cells [IC] covering ≥ 1% of the tumor area [IC ≥ 1%]), who had received no prior chemotherapy for metastatic disease. PD-L1 tumor status was determined based on immunohistochemistry (IHC) testing using the VENTANA PD-L1 (SP142) Assay. The evaluation of efficacy is based on the subgroup of patients with high PD-L1 expression (TC ≥ 50% or IC ≥ 10%), excluding those with EGFR or ALK genomic tumor aberrations. The trial excluded patients with a history of autoimmune disease, administration of a live attenuated vaccine within 28 days prior to randomization, active or untreated CNS metastases, administration of systemic immunostimulatory agents within 4 weeks or systemic immunosuppressive medications within 2 weeks prior to randomization.
Randomization was stratified by sex, ECOG performance status, histology (non-squamous vs. squamous) and PD-L1 expression (TC ≥ 1% and any IC vs. TC < 1% and IC ≥ 1%). Patients were randomized (1:1) to receive one of the following treatment arms:
- Arm A: TECENTRIQ 1200 mg every 3 weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity
- Arm B: Platinum-based chemotherapy
Arm B platinum-based chemotherapy regimens for non-squamous NSCLC consisted of cisplatin (75 mg/m 2 ) and pemetrexed (500 mg/m 2 ) OR carboplatin (AUC 6 mg/mL/min) and pemetrexed (500 mg/m 2 ) on Day 1 of each 21-day cycle for a maximum of 4 or 6 cycles followed by pemetrexed (500 mg/m 2 ) until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Arm B platinum-based chemotherapy regimens for squamous NSCLC consisted of cisplatin (75 mg/m 2 ) on Day 1 with gemcitabine (1250 mg/m 2 ) on Days 1 and 8 of each 21-day cycle OR carboplatin (AUC 5 mg/mL/min) on Day 1 with gemcitabine (1000 mg/m 2 ) on Days 1 and 8 of each 21-day cycle for a maximum of 4 or 6 cycles followed by best supportive care until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Administration of TECENTRIQ was permitted beyond RECIST-defined disease progression. Tumor assessments were conducted every 6 weeks for the first 48 weeks following Cycle 1, Day 1 and then every 9 weeks thereafter. Tumor specimens were evaluated prospectively using the VENTANA PD-L1 (SP142) Assay at a central laboratory and the results were used to define subgroups for pre-specified analyses.
The major efficacy outcome measure was overall survival (OS) sequentially tested in the following subgroups of patients, excluding those with EGFR or ALK genomic tumor aberrations: TC ≥50% or IC ≥10%; TC ≥5% or IC ≥5%; and TC ≥1% or IC ≥1%.
Among the 205 chemotherapy-naïve patients with stage IV NSCLC with high PD-L1 expression (TC ≥ 50% or IC ≥ 10%) excluding those with EGFR or ALK genomic tumor aberrations, the median age was 65.0 years (range: 33 to 87), and 70% of patients were male. The majority of patients were White (82%) and Asian (17%). Baseline ECOG performance status was 0 (36%) or 1 (64%); 88% were current or previous smokers; and 76% of patients had non-squamous disease while 24% of patients had squamous disease.
The trial demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in OS for patients with high PD-L1 expression (TC ≥50% or IC ≥10%) at the time of the OS interim analysis. There was no statistically significant difference in OS for the other two PD-L1 subgroups (TC ≥5% or IC ≥5%; and TC ≥1% or IC ≥1%) at the interim or final analyses. Efficacy results for patients with NSCLC with high PD-L1 expression are presented in Table 25 and Figure 2 .
| Arm A: TECENTRIQ N = 107 | Arm B: Platinum-Based Chemotherapy N = 98 | |
|---|---|---|
| CI=confidence interval; NE=not estimable | ||
| Overall Survival Based on OS interim analysis. The median survival follow-up time in patients was 15.7 months. | ||
| Deaths (%) | 44 (41%) | 57 (58%) |
| Median, months | 20.2 | 13.1 |
| (95% CI) | (16.5, NE) | (7.4, 16.5) |
| Hazard ratio Stratified by sex and ECOG performance status (95% CI) | 0.59 (0.40, 0.89) | |
| p-value Based on the stratified log-rank test compared to Arm A | 0.0106 Compared to the allocated alpha of 0.0413 (two-sided) for this interim analysis. | |
Figure 2: Kaplan-Meier Plot of Overall Survival in IMpower110 in Patients with NSCLC with High PD-L1 Expression (TC ≥ 50% or IC ≥ 10%) and without EGFR or ALK Genomic Tumor Aberrations

Investigator-assessed PFS showed an HR of 0.63 (95% CI: 0.45, 0.88), with median PFS of 8.1 months (95% CI: 6.8, 11.0) in the TECENTRIQ arm and 5 months (95% CI: 4.2, 5.7) in the platinum-based chemotherapy arm. The investigator-assessed confirmed ORR was 38% (95% CI: 29%, 48%) in the TECENTRIQ arm and 29% (95% CI: 20%, 39%) in the platinum-based chemotherapy arm.
Metastatic Chemotherapy-Naive Non-Squamous NSCLC
IMpower150
The efficacy of TECENTRIQ with bevacizumab, paclitaxel, and carboplatin was evaluated in IMpower150 (NCT02366143), a multicenter, international, randomized (1:1:1), open-label trial in patients with metastatic non-squamous NSCLC. Patients with stage IV non-squamous NSCLC who had received no prior chemotherapy for metastatic disease but could have received prior EGFR or ALK kinase inhibitor if appropriate, regardless of PD-L1 or T-effector gene (tGE) status and ECOG performance status 0 or 1 were eligible. The trial excluded patients with a history of autoimmune disease, administration of a live attenuated vaccine within 28 days prior to randomization, active or untreated CNS metastases, administration of systemic immunostimulatory agents within 4 weeks or systemic immunosuppressive medications within 2 weeks prior to randomization, or clear tumor infiltration into the thoracic great vessels or clear cavitation of pulmonary lesions as seen on imaging. Randomization was stratified by sex, presence of liver metastases, and PD-L1 expression status on tumor cells (TC) and tumor-infiltrating immune cells (IC) as follows: TC3 and any IC vs. TC0/1/2 and IC2/3 vs. TC0/1/2 and IC0/1. Patients were randomized to one of the following three treatment arms:
- Arm A: TECENTRIQ 1200 mg, paclitaxel 175 mg/m 2 or 200 mg/m 2 and carboplatin AUC 6 mg/mL/min on Day 1 of each 21-day cycle for a maximum of 4 or 6 cycles
- Arm B: TECENTRIQ 1200 mg, bevacizumab 15 mg/kg, paclitaxel 175 mg/m 2 or 200 mg/m 2 , and carboplatin AUC 6 mg/mL/min on Day 1 of each 21-day cycle for a maximum of 4 or 6 cycles
- Arm C: bevacizumab 15 mg/kg, paclitaxel 175 mg/m 2 or 200 mg/m 2 , and carboplatin AUC 6 mg/mL/min on Day 1 of each 21-day cycle for a maximum of 4 or 6 cycles
Patients who had not experienced disease progression following the completion or cessation of platinum-based chemotherapy, received:
- Arm A: TECENTRIQ 1200 mg intravenously on Day 1 of each 21-day cycle until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity
- Arm B: TECENTRIQ 1200 mg and bevacizumab 15 mg/kg intravenously on Day 1 of each 21-day cycle until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity
- Arm C: bevacizumab 15 mg/kg intravenously on Day 1 of each 21-day cycle until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity
Tumor assessments were conducted every 6 weeks for the first 48 weeks following Cycle 1, Day 1 and then every 9 weeks thereafter. Tumor specimens were evaluated prior to randomization for PD-L1 tumor expression using the VENTANA PD-L1 (SP142) assay at a central laboratory. Tumor tissue was collected at baseline for expression of tGE signature and evaluation was performed using a clinical trial assay in a central laboratory prior to the analysis of efficacy outcome measures.
Major efficacy outcome measures for comparison of Arms B and C were progression free survival (PFS) by RECIST v1.1 in the tGE-WT (patients with high expression of T-effector gene signature [tGE], excluding those with EGFR- and ALK-positive NSCLC [WT]) and in the ITT-WT subpopulations and overall survival (OS) in the ITT-WT subpopulation. Additional efficacy outcome measures for comparison of Arms B and C or Arms A and C were PFS and OS in the ITT population, OS in the tGE-WT subpopulation, and ORR/DoR in the tGE-WT and ITT-WT subpopulations.
A total of 1202 patients were enrolled across the three arms of whom 1045 were in the ITT-WT subpopulation and 447 were in the tGE-WT subpopulation. The demographic information is limited to the 800 patients enrolled in Arms B and C where efficacy has been demonstrated. The median age was 63 years (range: 31 to 90), and 60% of patients were male. The majority of patients were White (82%), 13% of patients were Asian, 10% were Hispanic, and 2% of patients were Black. Clinical sites in Asia (enrolling 13% of the study population) received paclitaxel at a dose of 175 mg/m 2 while the remaining 87% received paclitaxel at a dose of 200 mg/m 2 . Approximately 14% of patients had liver metastases at baseline, and most patients were current or previous smokers (80%). Baseline ECOG performance status was 0 (43%) or 1 (57%). PD-L1 was TC3 and any IC in 12%, TC0/1/2 and IC2/3 in 13%, and TC0/1/2 and IC0/1 in 75%. The demographics for the 696 patients in the ITT-WT subpopulation were similar to the ITT population except for the absence of patients with EGFR- or ALK- positive NSCLC.
The trial demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in PFS between Arms B and C in both the tGE-WT and ITT-WT subpopulations, but did not demonstrate a significant difference for either subpopulation between Arms A and C based on the final PFS analyses. In the interim analysis of OS, a statistically significant improvement was observed for Arm B compared to Arm C, but not for Arm A compared to Arm C. Efficacy results for the ITT-WT subpopulation are presented in Table 26 and Figure 3 .
| Arm C: Bevacizumab, Paclitaxel and Carboplatin | Arm B: TECENTRIQ with Bevacizumab, Paclitaxel, and Carboplatin | Arm A: TECENTRIQ with Paclitaxel, and Carboplatin | |
|---|---|---|---|
| N = 337 | N = 359 | N = 349 | |
| CI=confidence interval | |||
| Overall Survival Based on OS interim analysis | |||
| Deaths (%) | 197 (59%) | 179 (50%) | 179 (51%) |
| Median, months | 14.7 | 19.2 | 19.4 |
| (95% CI) | (13.3, 16.9) | (17.0, 23.8) | (15.7, 21.3) |
| Hazard ratio Stratified by sex, presence of liver metastases, and PD-L1 expression status on TC and IC (95% CI) | --- | 0.78 (0.64, 0.96) | 0.84 (0.72, 1.08) |
| p-value Based on the stratified log-rank test compared to Arm C | --- | 0.016 Compared to the allocated α=0.0174 (two sided) for this interim analysis | 0.204 Compared to the allocated α=0.0128 (two sided) for this interim analysis |
| Progression-Free Survival As determined by independent review facility (IRF) per RECIST v1.1 (Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors v1.1) | |||
| Number of events (%) | 247 (73%) | 247 (69%) | 245 (70%) |
| Median, months | 7.0 | 8.5 | 6.7 |
| (95% CI) | (6.3, 7.9) | (7.3, 9.7) | (5.6, 6.9) |
| Hazard ratio(95% CI) | --- | 0.71 (0.59, 0.85) | 0.94 (0.79, 1.13) |
| p-value | --- | 0.0002 Compared to the allocated α=0.006 (two sided) for the final PFS analysis | 0.5219 |
| Objective Response Rate | |||
| Number of responders (%) | 142 (42%) | 196 (55%) | 150 (43%) |
| (95% CI) | (37, 48) | (49, 60) | (38, 48) |
| Complete Response | 3 (1%) | 14 (4%) | 9 (3%) |
| Partial Response | 139 (41%) | 182 (51%) | 141 (40%) |
| Duration of Response | n = 142 | n = 196 | n = 150 |
| Median, months | 6.5 | 10.8 | 9.5 |
| (95% CI) | (5.6, 7.6) | (8.4, 13.9) | (7.0, 13.0) |
Figure 3: Kaplan-Meier Curves for Overall Survival in ITT-WT Population in IMpower150

Exploratory analyses showed that the subset of patients in the four drug regimen arm who were ADA positive by week 4 (30%) appeared to have similar efficacy (effect on overall survival) as compared to patients who tested negative for treatment-emergent ADA by week 4 (70%) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.6) ] . In an exploratory analysis, propensity score matching was conducted to compare ADA positive patients in the TECENTRIQ, bevacizumab, paclitaxel, and carboplatin arm with a matched population in the bevacizumab, paclitaxel, and carboplatin arm. Similarly ADA negative patients in the TECENTRIQ, bevacizumab, paclitaxel, and carboplatin arm were compared with a matched population in the bevacizumab, paclitaxel, and carboplatin arm. Propensity score matching factors were: baseline sum of longest tumor size (BSLD), baseline ECOG, baseline albumin, baseline LDH, sex, tobacco history, metastatic site, TC level, and IC level. The hazard ratio comparing the ADA-positive subgroup with its matched control was 0.69 (95% CI: 0.44, 1.07). The hazard ratio comparing the ADA-negative subgroup with its matched control was 0.64 (95% CI: 0.46, 0.90).
IMpower130
The efficacy of TECENTRIQ with paclitaxel protein-bound and carboplatin was evaluated in IMpower130 (NCT02367781), a multicenter, randomized (2:1), open-label trial in patients with stage IV non-squamous NSCLC. Patients with Stage IV non-squamous NSCLC who had received no prior chemotherapy for metastatic disease, but could have received prior EGFR or ALK kinase inhibitor, if appropriate, were eligible. The trial excluded patients with history of autoimmune disease, administration of live attenuated vaccine within 28 days prior to randomization, administration of immunostimulatory agents within 4 weeks or systemic immunosuppressive medications within 2 weeks prior to randomization, and active or untreated CNS metastases. Randomization was stratified by sex, presence of liver metastases, and PD-L1 tumor expression according to the VENTANA PD-L1 (SP142) assay as follows: TC3 and any IC vs. TC0/1/2 and IC2/3 vs. TC0/1/2 and IC0/1. Patients were randomized to one of the following treatment regimens:
- TECENTRIQ 1200 mg on Day 1, paclitaxel protein-bound 100 mg/m 2 on Days 1, 8, and 15, and carboplatin AUC 6 mg/mL/min on Day 1 of each 21-day cycle for a maximum of 4 or 6 cycles followed by TECENTRIQ 1200 mg once every 3 weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity, or
- Paclitaxel protein-bound 100 mg/m 2 on Days 1, 8 and 15 and carboplatin AUC 6 mg/mL/min on Day 1 of each 21-day cycle for a maximum of 4 or 6 cycles followed by best supportive care or pemetrexed.
Tumor assessments were conducted every 6 weeks for the first 48 weeks, then every 9 weeks thereafter. Major efficacy outcome measures were PFS by RECIST v1.1 and OS in the subpopulation of patients evaluated for and documented to have no EGFR or ALK genomic tumor aberrations (ITT-WT).
A total of 724 patients were enrolled; of these, 681 (94%) were in the ITT-WT population. The median age was 64 years (range: 18 to 86) and 59% were male. The majority of patients were white (90%), 2% of patients were Asian, 5% were Hispanic, and 4% were Black. Baseline ECOG performance status was 0 (41%) or 1 (58%). Most patients were current or previous smokers (90%). PD-L1 tumor expression was TC0/1/2 and IC0/1 in 73%; TC3 and any IC in 14%; and TC0/1/2 and IC2/3 in 13%.
Efficacy results for the ITT-WT population are presented in Table 27 and Figure 4 .
| TECENTRIQ with Paclitaxel Protein-Bound and Carboplatin | Paclitaxel Protein-Bound and Carboplatin | |
|---|---|---|
| CI=confidence interval | ||
| Overall Survival Based on OS interim analysis | n=453 | n=228 |
| Deaths (%) | 228 (50%) | 131 (57%) |
| Median, months | 18.6 | 13.9 |
| (95% CI) | (15.7, 21.1) | (12.0, 18.7) |
| Hazard ratio Stratified by sex and PD-L1 tumor expression on tumor cells (TC) and tumor infiltrating cells (IC) (95% CI) | 0.80 (0.64, 0.99) | |
| p-value Based on the stratified log-rank test | 0.0384 Compared to the allocated α=0.0428 (two sided) for this interim analysis | |
| Progression-Free Survival As determined by independent review facility (IRF) per RECIST v1.1 (Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors v1.1) | n=453 | n=228 |
| Number of events (%) | 330 (73%) | 177 (78%) |
| Median, months | 7.2 | 6.5 |
| (95% CI) | (6.7, 8.3) | (5.6, 7.4) |
| Hazard ratio(95% CI) | 0.75 (0.63, 0.91) | |
| p-value | 0.0024 Compared to the allocated α=0.006 (two sided) for the final PFS analysis | |
| Overall Response Rate , Confirmed response | n=453 | n=228 |
| Number of responders (%) | 207 (46%) | 74 (32%) |
| (95% CI) | (41, 50) | (26, 39) |
| Complete Response | 22 (5%) | 2 (1%) |
| Partial Response | 185 (41%) | 72 (32%) |
| Duration of Response , | n=207 | n=74 |
| Median, months | 10.8 | 7.8 |
| (95% CI) | (9.0, 14.4) | (6.8, 10.9) |
Figure 4: Kaplan-Meier Curves for Overall Survival in IMpower130

Previously Treated Metastatic NSCLC
OAK
The efficacy of TECENTRIQ was evaluated in a multicenter, international, randomized (1:1), open-label study (OAK; NCT02008227) conducted in patients with locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC whose disease progressed during or following a platinum-containing regimen. Patients with a history of autoimmune disease, symptomatic or corticosteroid-dependent brain metastases, or requiring systemic immunosuppression within 2 weeks prior to enrollment were ineligible. Randomization was stratified by PD-L1 expression tumor-infiltrating immune cells (IC), the number of prior chemotherapy regimens (1 vs. 2), and histology (squamous vs. non-squamous).
Patients were randomized to receive TECENTRIQ 1200 mg intravenously every 3 weeks until unacceptable toxicity, radiographic progression, or clinical progression or docetaxel 75 mg/m 2 intravenously every 3 weeks until unacceptable toxicity or disease progression. Tumor assessments were conducted every 6 weeks for the first 36 weeks and every 9 weeks thereafter. Major efficacy outcome measure was overall survival (OS) in the first 850 randomized patients and OS in the subgroup of patients with PD-L1-expressing tumors (defined as ≥ 1% PD-L1 expression on tumor cells [TC] or immune cells [IC]). Additional efficacy outcome measures were OS in all randomized patients (n = 1225), OS in subgroups based on PD-L1 expression, overall response rate (ORR), and progression free survival as assessed by the investigator per RECIST v.1.1.
Among the first 850 randomized patients, the median age was 64 years (33 to 85 years) and 47% were ≥ 65 years old; 61% were male; 70% were White and 21% were Asian; 15% were current smokers and 67% were former smokers; and 37% had baseline ECOG performance status (PS) of 0 and 63% had a baseline ECOG PS of 1. Nearly all (94%) had metastatic disease, 74% had non-squamous histology, 75% had received only one prior platinum-based chemotherapy regimen, and 55% of patients had PD-L1-expressing tumors.
Efficacy results are presented in Table 28 and Figure 5 .
| TECENTRIQ | Docetaxel | |
|---|---|---|
| CI=confidence interval; NE=not estimable | ||
| Overall Survival in first 850 patients | ||
| Number of patients | N=425 | N=425 |
| Deaths (%) | 271 (64%) | 298 (70%) |
| Median, months | 13.8 | 9.6 |
| (95% CI) | (11.8, 15.7) | (8.6, 11.2) |
| Hazard ratio Stratified by PD-L1 expression in tumor infiltrating immune cells, the number of prior chemotherapy regimens, and histology (95% CI) | 0.74 (0.63, 0.87) | |
| p-value Based on the stratified log-rank test | 0.0004 Compared to the pre-specified allocated α of 0.03 for this analysis | |
| Progression-Free Survival | ||
| Number of Patients | N=425 | N=425 |
| Events (%) | 380 (89%) | 375 (88%) |
| Progression (%) | 332 (78%) | 290 (68%) |
| Deaths (%) | 48 (11%) | 85 (20%) |
| Median, months | 2.8 | 4.0 |
| (95% CI) | (2.6, 3.0) | (3.3, 4.2) |
| Hazard ratio(95% CI) | 0.95 (0.82, 1.10) | |
| Overall Response Rate Per RECIST v1.1 (Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors v1.1) | ||
| Number of Patients | N=425 | N=425 |
| ORR, n (%) | 58 (14%) | 57 (13%) |
| (95% CI) | (11%, 17%) | (10%, 17%) |
| Complete Response | 6 (1%) | 1 (0.2%) |
| Partial Response | 52 (12%) | 56 (13%) |
| Duration of Response | N=58 | N=57 |
| Median, months | 16.3 | 6.2 |
| (95% CI) | (10.0, NE) | (4.9, 7.6) |
| Overall Survival in all 1225 patients | ||
| Number of patients | N=613 | N=612 |
| Deaths (%) | 384 (63%) | 409 (67%) |
| Median, months | 13.3 | 9.8 |
| (95% CI) | (11.3, 14.9) | (8.9, 11.3) |
| Hazard ratio(95% CI) | 0.79 (0.69, 0.91) | |
| p-value | 0.0013 Compared to the allocated α of 0.0177 for this interim analysis based on 86% information using O'Brien-Fleming boundary | |
| Figure 5: Kaplan-Meier Curves of Overall Survival in the First 850 Patients Randomized in OAK |
|
Tumor specimens were evaluated prospectively using the VENTANA PD-L1 (SP142) Assay at a central laboratory and the results were used to define the PD-L1 expression subgroups for pre-specified analyses. Of the 850 patients, 16% were classified as having high PD-L1 expression, defined as having PD-L1 expression on ≥ 50% of TC or ≥ 10% of IC. In an exploratory efficacy subgroup analysis of OS based on PD-L1 expression, the hazard ratio was 0.41 (95% CI: 0.27, 0.64) in the high PD-L1 expression subgroup and 0.82 (95% CI: 0.68, 0.98) in patients who did not have high PD-L1 expression.
Exploratory analyses showed that the subset of patients who were ADA positive by week 4 (21%) appeared to have less efficacy (effect on overall survival) as compared to patients who tested negative for treatment-emergent ADA by week 4 (79%) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.6) ] . ADA positive patients by week 4 appeared to have similar OS compared to docetaxel-treated patients. In an exploratory analysis, propensity score matching was conducted to compare ADA positive patients in the TECENTRIQ arm with a matched population in the docetaxel arm and ADA negative patients in the TECENTRIQ arm with a matched population in the docetaxel arm. Propensity score matching factors were: baseline sum of longest tumor size (BSLD), baseline ECOG, histology (squamous vs. non-squamous), baseline albumin, baseline LDH, gender, tobacco history, metastases status (advanced or local), metastatic site, TC level, and IC level. The hazard ratio comparing the ADA positive subgroup with its matched control was 0.89 (95% CI: 0.61, 1.3). The hazard ratio comparing the ADA negative subgroup with its matched control was 0.68 (95% CI: 0.55, 0.83).
Small Cell Lung Cancer
IMpower133
The efficacy of TECENTRIQ with carboplatin and etoposide was investigated in IMpower133 (NCT02763579), a randomized (1:1), multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in 403 patients with ES-SCLC. IMpower133 enrolled patients with ES-SCLC who had received no prior chemotherapy for extensive stage disease and ECOG performance status 0 or 1. The trial excluded patients with active or untreated CNS metastases, history of autoimmune disease, administration of a live, attenuated vaccine within 4 weeks prior to randomization, or administration of systemic immunosuppressive medications within 1 week prior to randomization. Randomization was stratified by sex, ECOG performance status, and presence of brain metastases. Patients were randomized to receive one of the following two treatment arms:
- TECENTRIQ 1200 mg and carboplatin AUC 5 mg/mL/min on Day 1 and etoposide 100 mg/m 2 intravenously on Days 1, 2 and 3 of each 21-day cycle for a maximum of 4 cycles followed by TECENTRIQ 1200 mg once every 3 weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity, or
- placebo and carboplatin AUC 5 mg/mL/min on Day 1 and etoposide 100 mg/m 2 intravenously on Days 1, 2, and 3 of each 21-day cycle for a maximum of 4 cycles followed by placebo once every 3 weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Administration of TECENTRIQ was permitted beyond RECIST-defined disease progression. Tumor assessments were conducted every 6 weeks for the first 48 weeks following Cycle 1, Day 1 and then every 9 weeks thereafter. Patients treated beyond disease progression had tumor assessment conducted every 6 weeks until treatment discontinuation.
Major efficacy outcome measures were OS and PFS as assessed by investigator per RECIST v1.1 in the intent-to-treat population. Additional efficacy outcome measures included ORR and DoR as assessed by investigator per RECIST v1.1.
A total of 403 patients were randomized, including 201 to the TECENTRIQ arm and 202 to the chemotherapy alone arm. The median age was 64 years (range 26 to 90) and 65% were male. The majority of patients were White (80%); 17% were Asian, 4% were Hispanic and 1% were Black. Baseline ECOG performance status was 0 (35%) or 1 (65%); 9% of patients had a history of brain metastases, and 97% were current or previous smokers.
Efficacy results are presented in Table 29 and Figure 6 .
| TECENTRIQ with Carboplatin and Etoposide | Placebo with Carboplatin and Etoposide | |
|---|---|---|
| CI=confidence interval | ||
| Overall Survival | N=201 | N=202 |
| Deaths (%) | 104 (52%) | 134 (66%) |
| Median, months | 12.3 | 10.3 |
| (95% CI) | (10.8, 15.9) | (9.3, 11.3) |
| Hazard ratio Stratified by sex and ECOG performance status (95% CI) | 0.70 (0.54, 0.91) | |
| p-value Based on the stratified log-rank test , Compared to the allocated α of 0.0193 for this interim analysis based on 78% information using O'Brien-Fleming boundary | 0.0069 | |
| Progression-Free Survival As determined by investigator assessment , per RECIST v1.1 (Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors v1.1) | N=201 | N=202 |
| Number of events (%) | 171 (85%) | 189 (94%) |
| Median, months | 5.2 | 4.3 |
| (95% CI) | (4.4, 5.6) | (4.2, 4.5) |
| Hazard ratio(95% CI) | 0.77 (0.62, 0.96) | |
| p-value , Compared to the allocated α of 0.05 for this analysis | 0.0170 | |
| Objective Response Rate , , Confirmed response | N=201 | N=202 |
| Number of responders (%) | 121 (60%) | 130 (64%) |
| (95% CI) | (53, 67) | (57, 71) |
| Complete Response (%) | 5 (2%) | 2 (1%) |
| Partial Response (%) | 116 (58%) | 128 (63%) |
| Duration of Response , , | N=121 | N=130 |
| Median, months | 4.2 | 3.9 |
| (95% CI) | (4.1, 4.5) | (3.1, 4.2) |
Figure 6: Kaplan-Meier Plot of Overall Survival in IMpower133

IMforte
The efficacy of TECENTRIQ in combination with lurbinectedin as maintenance treatment was evaluated in IMforte (NCT05091567), a randomized, multicenter, open-label study in patients with ES-SCLC. Patients were eligible if their disease had not progressed after completion of four cycles of TECENTRIQ, carboplatin and etoposide (induction treatment) and they had an ECOG performance status of 0 or 1. The trial excluded patients with CNS metastases, history of autoimmune disease, or administration of systemic immunosuppressive medications within 1 week prior to enrollment. Unless contraindicated, primary prophylaxis with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) was mandated for patients assigned to the TECENTRIQ with lurbinectedin arm.
The trial randomized 483 patients who had not experienced disease progression following the completion of four cycles of TECENTRIQ with carboplatin and etoposide to one of the following two treatment arms:
- TECENTRIQ 1200 mg IV in combination with lurbinectedin 3.2 mg/m 2 IV once every 3 weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity, or
- TECENTRIQ 1200 mg IV once every 3 weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity
Randomization was stratified by ECOG performance status prior to randomization (0 vs. 1), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) (≤ ULN vs. > ULN) prior to randomization, presence of liver metastases prior to initial study enrollment (yes vs. no), and prior receipt of prophylactic cranial irradiation (yes vs. no).
The major efficacy outcome measures were OS and PFS by Independent Review Facility (IRF) per RECIST v1.1.
A total of 483 patients were randomized, including 242 to the TECENTRIQ with lurbinectedin arm and 241 to the TECENTRIQ arm. The median age was 66 years (range 35 to 85 years); 63% male; 82% White; 13% Asian; 0.8% were Black or African American; 7% were of Hispanic or Latino ethnicity and 98% were current or previous smokers. Baseline ECOG performance status was 0 (43%) or 1 (57%).
Efficacy results are presented in Table 30 and Figures 7 and 8 .
| TECENTRIQ with Lurbinectedin N=242 | TECENTRIQ N=241 | |
|---|---|---|
| CI=confidence interval | ||
| Overall Survival Measured from the time of randomization | ||
| Deaths (%) | 113 (47%) | 136 (56%) |
| Median, months | 13.2 | 10.6 |
| (95% CI) | (11.9, 16.4) | (9.5, 12.2) |
| Hazard ratio Stratified by ECOG performance status, LDH level, presence of liver metastases and prior receipt of prophylactic cranial irradiation (95% CI) | 0.73 (0.57, 0.95) | |
| p-value Based on the stratified log-rank test , Compared to the allocated alpha of 0.0313 (two-sided) for this interim OS analysis. | 0.0174 | |
| Progression-Free Survival , As determined by an IRF , per RECIST v1.1 (Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors v1.1) | ||
| Number of events (%) | 174 (72%) | 202 (84%) |
| Median, months | 5.4 | 2.1 |
| (95% CI) | (4.2, 5.8) | (1.6, 2.7) |
| Hazard ratio(95% CI) | 0.54 (0.43, 0.67) | |
| p-value , Compared to the allocated alpha of 0.001 (two- sided) for this final PFS analysis. | <0.0001 | |
Figure 7: Kaplan-Meier Plot of IRF-assessed Progression-Free Survival in IMforte

Figure 8: Kaplan-Meier Plot of Overall Survival in IMforte

Hepatocellular Carcinoma
The efficacy of TECENTRIQ in combination with bevacizumab was investigated in IMbrave150 (NCT03434379), a multicenter, international, open-label, randomized trial in patients with locally advanced unresectable and/or metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma who have not received prior systemic therapy. Randomization was stratified by geographic region (Asia excluding Japan vs. rest of world), macrovascular invasion and/or extrahepatic spread (presence vs. absence), baseline AFP (<400 vs. ≥400 ng/mL), and by ECOG performance status (0 vs. 1).
A total of 501 patients were randomized (2:1) to receive either TECENTRIQ as an intravenous infusion of 1200 mg, followed by 15 mg/kg bevacizumab, on the same day every 3 weeks or sorafenib 400 mg given orally twice daily, until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Patients could discontinue either TECENTRIQ or bevacizumab (e.g., due to adverse events) and continue on single-agent therapy until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity associated with the single-agent.
The study enrolled patients who were ECOG performance score 0 or 1 and who had not received prior systemic treatment. Patients were required to be evaluated for the presence of varices within 6 months prior to treatment, and were excluded if they had variceal bleeding within 6 months prior to treatment, untreated or incompletely treated varices with bleeding, or high risk of bleeding. Patients with Child-Pugh B or C cirrhosis, moderate or severe ascites; history of hepatic encephalopathy; a history of autoimmune disease; administration of a live, attenuated vaccine within 4 weeks prior to randomization; administration of systemic immunostimulatory agents within 4 weeks or systemic immunosuppressive medications within 2 weeks prior to randomization; or untreated or corticosteroid-dependent brain metastases were excluded. Tumor assessments were performed every 6 weeks for the first 54 weeks and every 9 weeks thereafter.
The demographics and baseline disease characteristics of the study population were balanced between the treatment arms. The median age was 65 years (range: 26 to 88) and 83% of patients were male. The majority of patients were Asian (57%) or White (35%); 40% were from Asia (excluding Japan). Approximately 75% of patients presented with macrovascular invasion and/or extrahepatic spread and 37% had a baseline AFP ≥400 ng/mL. Baseline ECOG performance status was 0 (62%) or 1 (38%). HCC risk factors were Hepatitis B in 48% of patients, Hepatitis C in 22%, and 31% of patients had non-viral liver disease. The majority of patients had BCLC stage C (82%) disease at baseline, while 16% had stage B, and 3% had stage A.
The major efficacy outcome measures were overall survival (OS) and independent review facility (IRF)-assessed progression free survival (PFS) per RECIST v1.1. Additional efficacy outcome measures were IRF-assessed overall response rate (ORR) per RECIST and mRECIST.
Efficacy results are presented in Table 31 and Figure 9 .
| TECENTRIQ in combination with Bevacizumab (N= 336) | Sorafenib (N=165) | |
|---|---|---|
| CI=confidence interval; HCC mRECIST=Modified RECIST Assessment for Hepatocellular Carcinoma; NE=not estimable; RECIST 1.1=Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors v1.1 | ||
| Overall Survival | ||
| Number of deaths (%) | 96 (29) | 65 (39) |
| Median OS in months (95% CI) | NE (NE, NE) | 13.2 (10.4, NE) |
| Hazard ratio Stratified by geographic region (Asia excluding Japan vs. rest of world), macrovascular invasion and/or extrahepatic spread (presence vs. absence), and baseline AFP (<400 vs. ≥400 ng/mL) (95% CI) | 0.58 (0.42, 0.79) | |
| p-value Based on two-sided stratified log-rank test; as compared to significance level 0.004 (2-sided) based on 161/312=52% information using the OBF method | 0.0006 | |
| Progression-Free Survival Per independent radiology review | ||
| Number of events (%) | 197 (59) | 109 (66) |
| Median PFS in months (95% CI) | 6.8 (5.8, 8.3) | 4.3 (4.0, 5.6) |
| Hazard ratio(95% CI) | 0.59 (0.47, 0.76) | |
| p-value | <0.0001 | |
| Overall Response Rate , Confirmed responses (ORR), RECIST 1.1 | ||
| Number of responders (%) | 93 (28) | 19 (12) |
| (95% CI) | (23, 33) | (7,17) |
| p-value Based on two-sided Cochran-Mantel-Haesnszel test | <0.0001 | |
| Complete responses, n (%) | 22 (7) | 0 |
| Partial responses, n (%) | 71 (21) | 19 (12) |
| Duration of Response , (DOR) RECIST 1.1 | ||
| (n=93) | (n=19) | |
| Median DOR in months (95% CI) | NE (NE, NE) | 6.3 (4.7, NE) |
| Range (months) | (1.3 Denotes a censored value , 13.4) | (1.4, 9.1) |
| Overall Response Rate , (ORR), HCC mRECIST | ||
| Number of responders (%) | 112 (33) | 21 (13) |
| (95% CI) | (28, 39) | (8, 19) |
| p-value | <0.0001 | |
| Complete responses, n (%) | 37 (11) | 3 (1.8) |
| Partial responses, n (%) | 75 (22) | 18 (11) |
| Duration of Response , (DOR) HCC mRECIST | ||
| (n=112) | (n=21) | |
| Median DOR in months (95% CI) | NE (NE, NE) | 6.3 (4.9, NE) |
| Range (months) | (1.3, 13.4) | (1.4, 9.1) |
Figure 9: Kaplan-Meier Plot of Overall Survival in IMbrave150
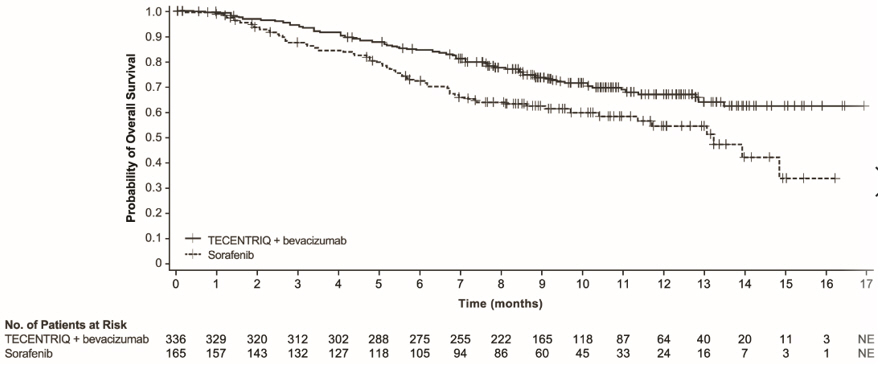
Exploratory analyses showed that the subset of patients (20%) who were ADA-positive by week 6 appeared to have reduced efficacy (effect on OS) as compared to patients (80%) who tested negative for treatment-emergent ADA by week 6 [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.6) ] . ADA-positive patients by week 6 appeared to have similar overall survival compared to sorafenib-treated patients. In an exploratory analysis, inverse probability weighting was conducted to compare ADA-positive patients and ADA-negative patients in the TECENTRIQ and bevacizumab arm to the sorafenib arm. Inverse probability weighting factors were: baseline sum of longest tumor size (BSLD), baseline ECOG, baseline albumin, baseline LDH, sex, age, race, geographic region, weight, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, AFP (<400 ng/mL vs ≥400 ng/mL), number of metastatic sites, MVI and/or EHS present at study entry, etiology (HBV vs. HCV vs. non-viral) and Child-Pugh Score (A5 vs. A6). The OS hazard ratio comparing the ADA-positive subgroup of the TECENTRIQ and bevacizumab arm to sorafenib was 0.93 (95% CI: 0.57, 1.53). The OS hazard ratio comparing the ADA-negative subgroup to sorafenib was 0.39 (95% CI: 0.26, 0.60).
Melanoma
The efficacy of TECENTRIQ in combination with cobimetinib and vemurafenib was evaluated in a double-blind, randomized (1:1), placebo-controlled, multicenter trial (IMspire150; NCT02908672) conducted in 514 patients. Randomization was stratified by geographic location (North America vs. Europe vs. Australia, New Zealand, and others) and baseline lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) [less than or equal to upper limit of normal (ULN) vs. greater than ULN]. Eligible patients were required to have previously untreated unresectable or metastatic BRAF V600 mutation-positive melanoma as detected by a locally available test and centrally confirmed with the FoundationOne™ assay. Patients were excluded if they had history of autoimmune disease; administration of a live, attenuated vaccine within 28 days prior to randomization; administration of systemic immunostimulatory agents within 4 weeks or systemic immunosuppressive medications within 2 weeks prior to randomization; and active or untreated CNS metastases.
TECENTRIQ was initiated after patients received a 28-day treatment cycle of cobimetinib 60 mg orally once daily (21 days on / 7 days off) and vemurafenib 960 mg orally twice daily Days 1-21 and 720 mg orally twice daily Days 22-28. Patients received TECENTRIQ 840 mg intravenous infusion over 60 minutes every 2 weeks in combination with cobimetinib 60 mg orally once daily and vemurafenib 720 mg orally twice daily, or placebo in combination with cobimetinib 60 mg orally once daily and vemurafenib 960 mg orally twice daily. Treatment continued until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. There was no crossover at the time of disease progression. Tumor assessments were performed every 8 weeks (± 1 week) for the first 24 months and every 12 weeks (± 1 week) thereafter.
The major efficacy outcome measure was investigator-assessed progression-free survival (PFS) per RECIST v1.1. Additional efficacy outcomes included PFS assessed by an independent central review, investigator-assessed ORR, OS, and DOR.
The median age of the study population was 54 years (range: 22-88), 58% of patients were male, 95% were White, a baseline ECOG performance status of 0 (77%) or 1 (23%), 33% had elevated LDH, 94% had metastatic disease, 60% were Stage IV (M1C), 56% had less than three metastatic sites at baseline, 3% had prior treatment for brain metastases, 30% had liver metastases at baseline, and 14% had received prior adjuvant systemic therapy. Based on central testing, 74% were identified as having a V600E mutation, 11% as having V600K mutation, and 1% as having V600D or V600R mutations.
Efficacy results are summarized in Table 32 and Figure 10 . Patients had a median survival follow up time of 18.9 months.
| TECENTRIQ + Cobimetinib + Vemurafenib N=256 | Placebo + Cobimetinib + Vemurafenib N=258 | |
|---|---|---|
| Progression-Free Survival As determined by investigator assessment with Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors v1.1.; CI=confidence interval; | ||
| Number of events (%) | 148 (58) | 179 (69) |
| Median, months | 15.1 | 10.6 |
| (95% CI) | (11.4, 18.4) | (9.3, 12.7) |
| Hazard ratio Stratified by baseline LDH (95% CI) | 0.78 (0.63, 0.97) | |
| p-value Based on the stratified log-rank test | 0.0249 | |
| Overall Response Rate , Confirmed Responses | ||
| Number of responders (%) | 170 (66) | 168 (65) |
| (95% CI) | (60, 72) | (59, 71) |
| Complete responses, n (%) | 41 (16) | 46 (18) |
| Partial response, n (%) | 129 (50) | 122 (47) |
| Duration of Response , | n=170 | n=168 |
| Median, months | 20.4 | 12.5 |
| (95% CI) | (15.1, NE) | (10.7, 16.6) |
Figure 10: Kaplan-Meier Plot for Progression-Free Survival in IMspire150
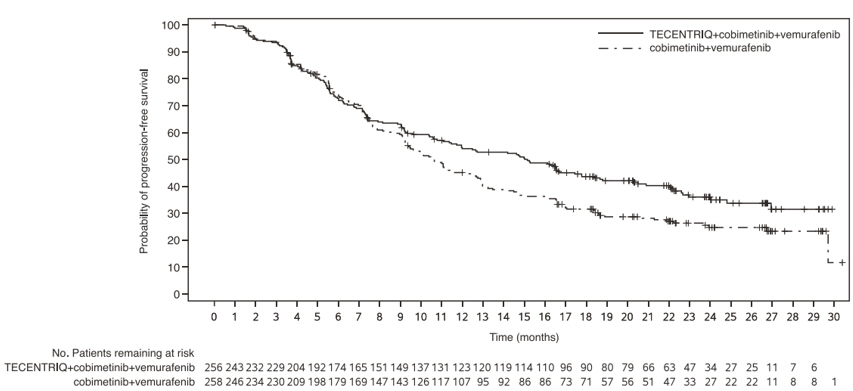
At a pre-specified analysis at the time of the primary analysis of PFS, the OS data were not mature. The median OS was 28.8 months with 93 (36%) deaths in the TECENTRIQ plus cobimetinib and vemurafenib arm, and 25.1 months with 112 (43%) deaths in the placebo plus cobimetinib and vemurafenib arm. The hazard ratio for OS was 0.85 (95% CI: 0.64, 1.11) and the p-value was 0.2310.
Alveolar soft part sarcoma (ASPS)
The efficacy of TECENTRIQ was evaluated in study ML39345 (NCT03141684), an open-label, single-arm study, in 49 adult and pediatric patients aged 2 years and older with unresectable or metastatic ASPS. Eligible patients were required to have histologically or cytologically confirmed ASPS that was not curable by surgery, and an ECOG performance status of ≤ 2.
Patients were excluded if they had known primary central nervous system (CNS) malignancy or symptomatic CNS metastases, known clinically significant liver disease, or history of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, pneumonitis, organizing pneumonia, or evidence of active pneumonitis on screening chest computed tomography (CT) scan.
Adult patients received 1200 mg intravenously and pediatric patients received 15 mg/kg (up to a maximum of 1200 mg) intravenously once every 21 days until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
The major efficacy outcomes were Overall Response Rate (ORR) and Duration of Response (DOR) by Independent Review Committee according to Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) v1.1.
A total of 49 patients were enrolled. The median age of patients was 31 years (range: 12-70); 2% of adult patients (n=47) were ≥65 years of age and the pediatric patients (n=2) were ≥12 years of age; 51% of patients were female, 55% White, 29% Black or African American, 10% Asian; 53% had an ECOG performance status of 0 and 45% had an ECOG performance status of 1. All patients had prior surgery for ASPS and 55% received at least one prior line of treatment for ASPS; 55% received radiotherapy and 53% received chemotherapy. Of the patients who reported staging at initial diagnosis, all were Stage IV.
Efficacy results of this study are summarized in Table 33 .
| Endpoint | All Patients (N=49) |
|---|---|
| CI: confidence interval; N: number of patients; +: Censored | |
| Overall response rate (95% CI) 95% CI based on Clopper–Pearson exact method. | 24% (13, 39) |
| Complete Responses, n | 0 |
| Partial Responses, n (%) | 12 (24) |
| Duration of response | |
| Median, month | NE |
| (95% CI) | (17.0, NE) |
| Range | 1+, 41+ |
| Durability of Response | |
| ≥6 months, n (%) | 8 (67%) |
| ≥12 months, n (%) | 5 (42%) |
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
TECENTRIQ injection is a sterile, preservative-free, and colorless to slightly yellow solution for intravenous infusion supplied as a carton containing one 840 mg/14 mL single-dose vial (NDC 50242-918-01) or 1,200 mg/20 mL single-dose vial (NDC 50242-917-01).
Store vials under refrigeration at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) in original carton to protect from light. Do not freeze. Do not shake.
Mechanism of Action
PD L1 may be expressed on tumor cells and/or tumor infiltrating immune cells and can contribute to the inhibition of the anti-tumor immune response in the tumor microenvironment. Binding of PD L1 to the PD 1 and B7.1 receptors found on T cells and antigen presenting cells suppresses cytotoxic T-cell activity, T-cell proliferation and cytokine production.
Atezolizumab is a monoclonal antibody that binds to PD L1 and blocks its interactions with both PD 1 and B7.1 receptors. This releases the PD L1/PD 1 mediated inhibition of the immune response, including activation of the anti-tumor immune response without inducing antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. In syngeneic mouse tumor models, blocking PD L1 activity resulted in decreased tumor growth.
In mouse models of cancer, dual inhibition of the PD-1/PD-L1 and MAPK pathways suppresses tumor growth and improves tumor immunogenicity through increased antigen presentation and T cell infiltration and activation compared to targeted therapy alone.
