Dosage & Administration
By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Terlivaz Prescribing Information
Jalan R, et al; Development and validation of a prognostic score to predict mortality in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure. J Hepatol. 2014 Nov;61(5):1038-47.
Obtain baseline oxygen saturation (SpO2) prior to administering the first dose of TERLIVAZ. During treatment, monitor patient oxygen saturation using continuous pulse oximetry. Do not use TERLIVAZ treatment in patients experiencing hypoxia until hypoxia resolves
Assess Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure (ACLF) Grade and volume status before initiating TERLIVAZ
TERLIVAZ is contraindicated in patients experiencing hypoxia or worsening respiratory symptoms.
TERLIVAZ is contraindicated in patients with ongoing coronary, peripheral or mesenteric ischemia.
TERLIVAZ is contraindicated:
In patients experiencing hypoxia or worsening respiratory symptoms. In patients with ongoing coronary, peripheral, or mesenteric ischemia.
In the primary clinical trial
Obtain baseline oxygen saturation and do not initiate TERLIVAZ in hypoxic patients
Patients with fluid overload may be at increased risk of respiratory failure. Manage intravascular volume overload by reducing or discontinuing the administration of albumin and/or other fluids and judicious use of diuretics. Temporarily interrupt, reduce, or discontinue TERLIVAZ treatment until patient volume status improves
Avoid use in patients with ACLF Grade 3 because they are at significant risk for respiratory failure
TERLIVAZ is indicated to improve kidney function in adults with hepatorenal syndrome with rapid reduction in kidney function.
- Prior to initial dosing, assess patients for ACLF Grade 3 and obtain patient baseline oxygenation level. Monitor patient oxygen saturation with pulse oximetry. ()
2.1 Important Considerations Prior to Initiating and During TherapyObtain baseline oxygen saturation (SpO2) prior to administering the first dose of TERLIVAZ. During treatment, monitor patient oxygen saturation using continuous pulse oximetry. Do not use TERLIVAZ treatment in patients experiencing hypoxia until hypoxia resolves
[see Contraindications (4),andWarnings and Precautions (5.1)].Assess Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure (ACLF) Grade and volume status before initiating TERLIVAZ
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)andReferences (15)]. - Recommended Dosage Regimen: ()
2.2 Recommended DosageRecord last available serum creatinine (SCr) value prior to initiating treatment (baseline SCr). The recommended starting dosage is TERLIVAZ 0.85 mg every 6 hours by slow intravenous bolus injection (over 2 minutes) on Days 1 through 3. Adjust the dose on Day 4 based on changes from baseline SCr using the dosing chart (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Dosing Chart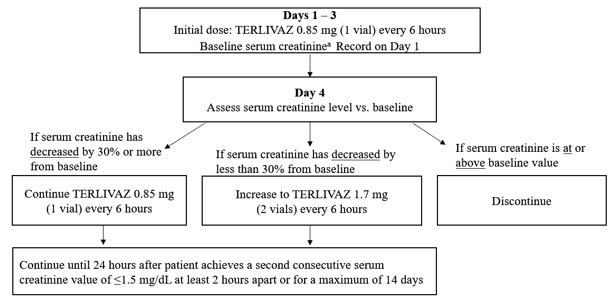
aBaseline SCr is the last available serum creatinine before initiating treatment.

Figure 1 - Days 1 to 3 administer TERLIVAZ 0.85 mg (1 vial) intravenously every 6 hours.
- Day 4: Assess serum creatinine (SCr) versus baseline.
- If SCr has decreased by at least 30% from baseline, continue TERLIVAZ 0.85 mg (1 vial) intravenously every 6 hours.
- If SCr has decreased by less than 30% from baseline, dose may be increased to TERLIVAZ 1.7 mg (2 vials) intravenously every 6 hours.
- If SCr is at or above baseline value, discontinue TERLIVAZ.
- Continue TERLIVAZ until 24 hours after two consecutive SCr ≤1.5 mg/dL values at least 2 hours apart or a maximum of 14 days.
). Flush IV line after administration.2.3 Preparation and AdministrationReconstitute each vial with 5 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection to prepare a 0.85 mg/5 mL solution. Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
Administer TERLIVAZ through a peripheral or central line. A dedicated central line is not required. Flush the line after TERLIVAZ administration.
If not administered immediately, store TERLIVAZ at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) for up to 48 hours. Do not freeze. The reconstituted solution does not need protection from light.
For injection: TERLIVAZ 0.85 mg is a white to off-white lyophilized powder in a single-dose vial for reconstitution.
Based on findings from the published literature and on its mechanism of action, TERLIVAZ may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman
Terlipressin is a synthetic vasopressin analogue with twice the selectivity for vasopressin V1receptors versus V2receptors. Terlipressin acts as both a prodrug for lysine-vasopressin, as well as having pharmacologic activity on its own. Terlipressin is thought to increase renal blood flow in patients with hepatorenal syndrome by reducing portal hypertension and blood circulation in portal vessels and increasing effective arterial volume and mean arterial pressure (MAP).
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
TERLIVAZ is contraindicated in patients experiencing hypoxia or worsening respiratory symptoms.
TERLIVAZ is contraindicated in patients with ongoing coronary, peripheral or mesenteric ischemia.