Tibsovo prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Tibsovo patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
500 mg orally once daily with or without food until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity (2.2 ). Avoid a high-fat meal.
Patient Selection
Select patients for treatment with TIBSOVO based on the presence of IDH1 mutations [see Clinical Studies (14.1 , 14.2 , 14.3 , 14.4 )].
Information on FDA-approved tests for the detection of IDH1 mutations in AML, MDS, and cholangiocarcinoma is available at http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics.
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of TIBSOVO is 500 mg taken orally once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity [see Clinical Studies (14.1 , 14.2 , 14.3 , 14.4 )] .
For patients with AML or MDS without disease progression or unacceptable toxicity, continue TIBSOVO for a minimum of 6 months to allow time for clinical response.
- Administer TIBSOVO with or without food.
- Do not administer TIBSOVO with a high-fat meal [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
- Do not split, crush, or chew TIBSOVO tablets.
- Administer TIBSOVO tablets orally about the same time each day.
- If a dose of TIBSOVO is vomited, do not administer a replacement dose; wait until the next scheduled dose is due.
- If a dose of TIBSOVO is missed or not taken at the usual time, administer the dose as soon as possible and at least 12 hours prior to the next scheduled dose. Return to the normal schedule the following day. Do not administer 2 doses within 12 hours.
Newly Diagnosed AML (Combination Regimen)
Start TIBSOVO administration on Cycle 1 Day 1 in combination with azacitidine 75 mg/m 2 subcutaneously or intravenously once daily on Days 1-7 (or Days 1-5 and 8-9) of each 28-day cycle [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ] . Refer to the Prescribing Information for azacitidine for additional dosing information.
Monitoring and Dosage Modifications for Toxicities
Obtain an electrocardiogram (ECG) prior to treatment initiation. Monitor ECGs at least once weekly for the first 3 weeks of therapy and then at least once monthly for the duration of therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] . Manage any abnormalities promptly .
Interrupt dosing or reduce dose for toxicities. See Table 1 for dosage modification guidelines.
| Adverse Reactions | Recommended Action |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| As monotherapy in AML and MDS :
|
Patients with AML or MDS
Assess blood counts and blood chemistries prior to the initiation of TIBSOVO, at least once weekly for the first month, once every other week for the second month, and once monthly for the duration of therapy.
Monitor blood creatine phosphokinase weekly for the first month of therapy.
Dosage Modification for Use with Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors
If a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor must be coadministered, reduce the TIBSOVO dose to 250 mg once daily. If the strong inhibitor is discontinued, increase the TIBSOVO dose (after at least 5 half-lives of the strong CYP3A4 inhibitor) to the recommended dose of 500 mg once daily.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Tibsovo prescribing information
WARNING: DIFFERENTIATION SYNDROME IN AML AND MDS
Patients treated with TIBSOVO have experienced symptoms of differentiation syndrome, which can be fatal. Symptoms may include fever, dyspnea, hypoxia, pulmonary infiltrates, pleural or pericardial effusions, rapid weight gain or peripheral edema, hypotension, and hepatic, renal, or multi-organ dysfunction. If differentiation syndrome is suspected, initiate corticosteroid therapy and hemodynamic monitoring until symptom resolution [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
TIBSOVO is an isocitrate dehydrogenase-1 (IDH1) inhibitor indicated for patients with a susceptible IDH1 mutation as detected by an FDA-approved test with:
Newly Diagnosed Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)
- In combination with azacitidine or as monotherapy for the treatment of newly diagnosed AML in adults 75 years or older, or who have comorbidities that preclude use of intensive induction chemotherapy (1.1 ).
Relapsed or refractory AML
- For the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory AML (1.2 ).
Relapsed or refractory Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS)
- For the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory myelodysplastic syndromes (1.3 ).
Locally Advanced or Metastatic Cholangiocarcinoma
- For the treatment of adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma who have been previously treated (1.4 ).
Newly Diagnosed Acute Myeloid Leukemia
TIBSOVO is indicated in combination with azacitidine or as monotherapy for the treatment of newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with a susceptible isocitrate dehydrogenase-1 (IDH1) mutation as detected by an FDA-approved test in adults 75 years or older, or who have comorbidities that preclude use of intensive induction chemotherapy [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.1) and Clinical Studies (14.1) ].
Relapsed or Refractory Acute Myeloid Leukemia
TIBSOVO is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with a susceptible isocitrate dehydrogenase-1 (IDH1) mutation as detected by an FDA-approved test [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.1) and Clinical Studies (14.2) ] .
Relapsed or Refractory Myelodysplastic Syndromes
TIBSOVO is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) with a susceptible isocitrate dehydrogenase-1 (IDH1) mutation as detected by an FDA-approved test [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.1) and Clinical Studies (14.3) ] .
Locally Advanced or Metastatic Cholangiocarcinoma
TIBSOVO is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with previously treated, locally advanced or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma with an isocitrate dehydrogenase-1 (IDH1) mutation as detected by an FDA-approved test [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.1) , and Clinical Studies (14.4) ] .
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
500 mg orally once daily with or without food until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity (2.2 ). Avoid a high-fat meal.
Patient Selection
Select patients for treatment with TIBSOVO based on the presence of IDH1 mutations [see Clinical Studies (14.1 , 14.2 , 14.3 , 14.4 )].
Information on FDA-approved tests for the detection of IDH1 mutations in AML, MDS, and cholangiocarcinoma is available at http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics.
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of TIBSOVO is 500 mg taken orally once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity [see Clinical Studies (14.1 , 14.2 , 14.3 , 14.4 )] .
For patients with AML or MDS without disease progression or unacceptable toxicity, continue TIBSOVO for a minimum of 6 months to allow time for clinical response.
- Administer TIBSOVO with or without food.
- Do not administer TIBSOVO with a high-fat meal [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
- Do not split, crush, or chew TIBSOVO tablets.
- Administer TIBSOVO tablets orally about the same time each day.
- If a dose of TIBSOVO is vomited, do not administer a replacement dose; wait until the next scheduled dose is due.
- If a dose of TIBSOVO is missed or not taken at the usual time, administer the dose as soon as possible and at least 12 hours prior to the next scheduled dose. Return to the normal schedule the following day. Do not administer 2 doses within 12 hours.
Newly Diagnosed AML (Combination Regimen)
Start TIBSOVO administration on Cycle 1 Day 1 in combination with azacitidine 75 mg/m 2 subcutaneously or intravenously once daily on Days 1-7 (or Days 1-5 and 8-9) of each 28-day cycle [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ] . Refer to the Prescribing Information for azacitidine for additional dosing information.
Monitoring and Dosage Modifications for Toxicities
Obtain an electrocardiogram (ECG) prior to treatment initiation. Monitor ECGs at least once weekly for the first 3 weeks of therapy and then at least once monthly for the duration of therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] . Manage any abnormalities promptly .
Interrupt dosing or reduce dose for toxicities. See Table 1 for dosage modification guidelines.
| Adverse Reactions | Recommended Action |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| As monotherapy in AML and MDS :
|
Patients with AML or MDS
Assess blood counts and blood chemistries prior to the initiation of TIBSOVO, at least once weekly for the first month, once every other week for the second month, and once monthly for the duration of therapy.
Monitor blood creatine phosphokinase weekly for the first month of therapy.
Dosage Modification for Use with Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors
If a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor must be coadministered, reduce the TIBSOVO dose to 250 mg once daily. If the strong inhibitor is discontinued, increase the TIBSOVO dose (after at least 5 half-lives of the strong CYP3A4 inhibitor) to the recommended dose of 500 mg once daily.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets: 250 mg as a blue oval-shaped film-coated tablet debossed "IVO" on one side and "250" on the other side.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Lactation: Advise women not to breastfeed (8.2) .
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on animal embryo-fetal toxicity studies, TIBSOVO may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. There are no available data on TIBSOVO use in pregnant women to inform a drug-associated risk of major birth defects and miscarriage. In animal embryo-fetal toxicity studies, oral administration of ivosidenib to pregnant rats and rabbits during organogenesis was associated with embryo-fetal mortality and alterations to growth starting at 2 times the steady state clinical exposure based on the AUC at the recommended human dose (see Data ). If this drug is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, advise the patient of the potential risk to a fetus.
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. Adverse outcomes in pregnancy occur regardless of the health of the mother or the use of medications. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2%-4% and 15%-20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
Ivosidenib administered to pregnant rats at a dose of 500 mg/kg/day during organogenesis (gestation days 6-17) was associated with adverse embryo-fetal effects including lower fetal weights, and skeletal variations. These effects occurred in rats at approximately 2 times the human exposure at the recommended dose of 500 mg daily.
In pregnant rabbits treated during organogenesis (gestation days 7-20), ivosidenib was maternally toxic at doses of 180 mg/kg/day (exposure approximately 3.9 times the human exposure at the recommended dose of 500 mg daily) and caused spontaneous abortions as well as decreased fetal weights, skeletal variations, and visceral variations.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of ivosidenib or its metabolites in human milk, the effects on the breastfed child, or the effects on milk production. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for adverse reactions in breastfed children, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with TIBSOVO and for 1 month after the last dose.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of TIBSOVO in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatric Use
Of the 304 patients who received TIBSOVO in the clinical studies for AML and MDS, 75% were 65 years of age or older and 35% were 75 years or older.
Of the 124 patients with cholangiocarcinoma treated with TIBSOVO in Study AG120-C-005, 37% were 65 years of age or older and 11% were 75 years or older.
No overall differences in effectiveness or safety were observed between patients who were 65 years and older compared to younger patients.
Renal Impairment
No modification of the starting dose is recommended for patients with mild or moderate renal impairment (eGFR ≥ 30 mL/min/1.73m 2 , MDRD). The pharmacokinetics and safety of ivosidenib in patients with severe renal impairment (eGFR < 30 mL/min/1.73m 2 , MDRD) or renal impairment requiring dialysis are unknown [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . For patients with pre-existing severe renal impairment or who are requiring dialysis, consider the risks and potential benefits before initiating treatment with TIBSOVO.
Hepatic Impairment
No modification of the starting dose is recommended for patients with mild or moderate (Child-Pugh A or B) hepatic impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . The pharmacokinetics and safety of ivosidenib in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C) are unknown. For patients with pre-existing severe hepatic impairment, consider the risks and potential benefits before initiating treatment with TIBSOVO.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- QTc Interval Prolongation : Monitor electrocardiograms and electrolytes. If QTc interval prolongation occurs, dose reduce or withhold, then resume dose or permanently discontinue TIBSOVO (2.3 , 5.2 ).
- Guillain-Barré Syndrome : Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of new motor and/or sensory findings. Permanently discontinue TIBSOVO in patients who are diagnosed with Guillain-Barré syndrome (2.3 , 5.3 ).
Differentiation Syndrome in AML and MDS
Differentiation syndrome is associated with rapid proliferation and differentiation of myeloid cells and may be life-threatening or fatal.
Symptoms of differentiation syndrome in patients treated with TIBSOVO included noninfectious leukocytosis, peripheral edema, pyrexia, dyspnea, pleural effusion, hypotension, hypoxia, pulmonary edema, pneumonitis, pericardial effusion, rash, fluid overload, tumor lysis syndrome and creatinine increased.
In the combination study AG120-C-009, 15% (11/71) patients with newly diagnosed AML treated with TIBSOVO plus azacitidine experienced differentiation syndrome [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] . Of the 11 patients with newly diagnosed AML who experienced differentiation syndrome with TIBSOVO plus azacitidine 8 (73%) recovered. Differentiation syndrome occurred as early as 3 days after start of therapy and during the first month on treatment.
In the monotherapy clinical trial AG120-C-001, 25% (7/28) of patients with newly diagnosed AML and 19% (34/179) of patients with relapsed or refractory AML treated with TIBSOVO experienced differentiation syndrome [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] . Of the 7 patients with newly diagnosed AML who experienced differentiation syndrome, 6 (86%) patients recovered. Of the 34 patients with relapsed or refractory AML who experienced differentiation syndrome, 27 (79%) patients recovered after treatment or after dose interruption of TIBSOVO. Differentiation syndrome occurred as early as 1 day and up to 3 months after TIBSOVO initiation and has been observed with or without concomitant leukocytosis.
In the monotherapy clinical trial AG120-C-001, 11% (2/19) of patients with relapsed or refractory MDS treated with TIBSOVO experienced differentiation syndrome [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] . Of the 2 patients who experienced differentiation syndrome, both recovered after treatment or after dose interruption of TIBSOVO. Differentiation syndrome occurred as early as 1 day and up to 3 months after TIBSOVO initiation and has been observed with or without concomitant leukocytosis.
If differentiation syndrome is suspected, initiate dexamethasone 10 mg IV every 12 hours (or an equivalent dose of an alternative oral or IV corticosteroid) and hemodynamic monitoring until improvement [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] . If concomitant noninfectious leukocytosis is observed, initiate treatment with hydroxyurea or leukapheresis, as clinically indicated. Taper corticosteroids and hydroxyurea after resolution of symptoms and administer corticosteroids for a minimum of 3 days. Symptoms of differentiation syndrome may recur with premature discontinuation of corticosteroid and/or hydroxyurea treatment. If severe signs and/or symptoms persist for more than 48 hours after initiation of corticosteroids, interrupt TIBSOVO until signs and symptoms are no longer severe [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ].
QTc Interval Prolongation
Patients treated with TIBSOVO can develop QT (QTc) prolongation and ventricular arrhythmias [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2) ].
Of the 71 patients with newly diagnosed AML treated with TIBSOVO in combination with azacitidine in the clinical trial (Study AG120-C-009), 10 (14%) were found to have a heart-rate corrected QT interval (using Fridericia's method) (QTcF) greater than 500 msec and 15 out of 69 (22%) had an increase from baseline QTcF greater than 60 msec [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] . The clinical trial excluded patients with a QTcF ≥ 470 msec or other factors that increased the risk of QT prolongation or arrhythmic events (e.g. NYHA Class III or IV congestive heart failure, hypokalemia, family history of long QT interval syndrome).
Of the 265 patients with hematological malignancies, including patients with AML and MDS, treated with TIBSOVO monotherapy in the clinical trial (AG120-C-001), 9% were found to have a QTc interval greater than 500 msec and 14% of patients had an increase from baseline QTc greater than 60 msec [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] . One patient developed ventricular fibrillation attributed to TIBSOVO. The clinical trial excluded patients with baseline QTc of ≥ 450 msec (unless the QTc ≥ 450 msec was due to a pre-existing bundle branch block) or with a history of long QT syndrome or uncontrolled or significant cardiovascular disease.
Of the 123 patients with cholangiocarcinoma treated with TIBSOVO in the clinical trial (Study AG120-C-005), 2% were found to have a QTc interval greater than 500 msec and 5% of patients had an increase from baseline QTc greater than 60 msec [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] . The clinical trial excluded patients with a heart-rate corrected QT interval (using Fridericia's formula) (QTcF) ≥ 450 msec or other factors that increased the risk of QT prolongation or arrhythmic events (e.g., heart failure, hypokalemia, family history of long QT interval syndrome).
Concomitant use of TIBSOVO with drugs known to prolong the QTc interval (e.g., anti-arrhythmic medicines, fluoroquinolones, triazole anti-fungals, 5-HT 3 receptor antagonists) and CYP3A4 inhibitors may increase the risk of QTc interval prolongation [see Drug Interactions (7.1) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.2) ]. Conduct monitoring of electrocardiograms (ECGs) and electrolytes [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] .
In patients with congenital long QTc syndrome, congestive heart failure, electrolyte abnormalities, or those who are taking medications known to prolong the QTc interval, more frequent monitoring may be necessary.
Interrupt TIBSOVO if QTc increases to greater than 480 msec and less than 500 msec. Interrupt and reduce TIBSOVO if QTc increases to greater than 500 msec. Permanently discontinue TIBSOVO in patients who develop QTc interval prolongation with signs or symptoms of life-threatening arrhythmia [See Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] .
Guillain-Barré Syndrome
Guillain-Barré syndrome can develop in patients treated with TIBSOVO. Guillain-Barré syndrome occurred in 0.8% (2/265) of patients treated with TIBSOVO in study AG120-C-001 [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
Monitor patients taking TIBSOVO for onset of new signs or symptoms of motor and/or sensory neuropathy such as unilateral or bilateral weakness, sensory alterations, paresthesias, or difficulty breathing. Permanently discontinue TIBSOVO in patients who are diagnosed with Guillain-Barré syndrome [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ].
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Differentiation Syndrome in AML and MDS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- QTc Interval Prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
- Guillain-Barré Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Acute Myeloid Leukemia
In AML, the safety population reflects exposure to TIBSOVO at 500 mg daily in combination with azacitidine or as monotherapy in patients in Studies AG120-C-009 (N=71) and AG120-C-001 (N=213), respectively [see Clinical Studies (14.1 and 14.2) ] . In this safety population, the most common adverse reactions including laboratory abnormalities (≥ 25% in either trial) were leukocytes decreased, diarrhea, hemoglobin decreased, platelets decreased, glucose increased, fatigue, alkaline phosphatase increased, edema, potassium decreased, nausea, vomiting, phosphatase decreased, decreased appetite, sodium decreased, leukocytosis, magnesium decreased, aspartate aminotransferase increased, arthralgia, dyspnea, uric acid increased, abdominal pain, creatinine increased, mucositis, rash, electrocardiogram QT prolonged, differentiation syndrome, calcium decreased, neutrophils decreased, and myalgia.
Newly Diagnosed AML
TIBSOVO in Combination with Azacitidine
The safety of TIBSOVO was evaluated in AML patients treated in combination with azacitidine, in Study AG120-C-009 [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ] . Patients received at least one dose of either TIBSOVO 500 mg daily (N=71) or placebo (N=73). Among patients who received TIBSOVO in combination with azacitidine, the median duration of exposure to TIBSOVO was 6 months (range 0 to 33 months). Thirty-four patients (48%) were exposed to TIBSOVO for at least 6 months and 22 patients (31%) were exposed for at least 1 year.
Common (≥ 5%) serious adverse reactions in patients who received TIBSOVO in combination with azacitidine included differentiation syndrome (8%).
Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 4% of patients who received TIBSOVO in combination with azacitidine, due to differentiation syndrome (3%) and one case of cerebral ischemia.
Adverse reactions leading to discontinuation of TIBSOVO in ≥2% of patients were differentiation syndrome (3%) and pulmonary embolism (3%).
The most common (>5%) adverse reactions leading to dose interruption of TIBSOVO were neutropenia (25%), electrocardiogram QT prolonged (7%), and thrombocytopenia (7%).
Adverse reactions leading to dose reduction of TIBSOVO included electrocardiogram QT prolonged (8%), neutropenia (8%), and thrombocytopenia (1%).
The most common adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities observed in Study AG120-C-009 are shown in Tables 2 and 3.
| TIBSOVO + Azacitidine N=71 | Placebo + Azacitidine N=73 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body System Adverse Reaction | All Grades n (%) | Grade ≥3 n (%) | All Grades n (%) | Grade ≥3 n (%) |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||||
| Nausea | 30 (42) | 2 (3) | 28 (38) | 3 (4) |
| Vomiting Grouped term includes vomiting and retching. | 29 (41) | 0 | 20 (27) | 1 (1) |
| Investigations | ||||
| Electrocardiogram QT prolonged | 14 (20) | 7 (10) | 5 (7) | 2 (3) |
| Psychiatric Disorders | ||||
| Insomnia | 13 (18) | 1 (1) | 9 (12) | 0 |
| Blood system and lymphatic system disorders | ||||
| Differentiation Syndrome Differentiation syndrome can be associated with other commonly reported events such as peripheral edema, leukocytosis, pyrexia, dyspnea, pleural effusion, hypotension, hypoxia, pulmonary edema, pneumonia, pericardial effusion, rash, fluid overload, tumor lysis syndrome, and creatinine increased. | 11 (15) | 7 (10) | 6 (8) | 6 (8) |
| Leukocytosis Grouped term includes leukocytosis, white blood cell count increased. | 9 (13) | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 |
| Vascular disorders | ||||
| Hematoma Grouped term includes hematoma, eye hematoma, catheter site hematoma, oral mucosa hematoma, spontaneous hematoma, application site hematoma, injection site hematoma, periorbital hematoma. | 11 (15) | 0 | 3 (4) | 0 |
| Hypertension Grouped term includes blood pressure increased, essential hypertension, and hypertension. | 9 (13) | 3 (4) | 6 (8) | 4 (5) |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||||
| Arthralgia Grouped term includes pain in extremity, arthralgia, back pain, musculoskeletal stiffness, cancer pain, and neck pain. | 21 (30) | 3 (4) | 6 (8) | 1 (1) |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | ||||
| Dyspnea Grouped term includes dyspnea, dyspnea exertional, hypoxia, respiration failure. | 14 (20) | 2 (3) | 11 (15) | 4 (5) |
| Nervous system disorders | ||||
| Headache | 8 (11) | 0 | 2 (3) | 0 |
| TIBSOVO + Azacitidine N=71 | Placebo + Azacitidine N=73 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | All Grades n (%) | Grade ≥ 3 n (%) | All Grades n (%) | Grade ≥ 3 n (%) |
| Hematology Parameters | ||||
| Leukocytes decreased | 46 (65) | 39 (55) | 47 (64) | 42 (58) |
| Platelets decreased | 41 (58) | 30 (42) | 52 (71) | 42 (58) |
| Hemoglobin decreased | 40 (56) | 33 (46) | 48 (66) | 42 (58) |
| Neutrophils decreased | 18 (25) | 16 (23) | 25 (35) | 23 (32) |
| Lymphocytes increased | 17 (24) | 1 (1) | 7 (10) | 1 (1) |
| Chemistry Parameters | ||||
| Glucose increased | 40 (56) | 9 (13) | 34 (47) | 8 (11) |
| Phosphate decreased | 29 (41) | 7 (10) | 25 (34) | 9 (12) |
| Aspartate Aminotransferase increased | 26 (37) | 0 | 17 (23) | 0 |
| Magnesium decreased | 25 (35) | 0 | 19 (26) | 0 |
| Alkaline Phosphatase increased | 23 (32) | 0 | 21 (29) | 0 |
| Potassium increased | 17 (24) | 2 (3) | 9 (12) | 1 (1) |
TIBSOVO Monotherapy
The safety profile of single-agent TIBSOVO was studied in 28 adults with newly diagnosed AML treated with 500 mg daily [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ] . The median duration of exposure to TIBSOVO was 4.3 months (range 0.3 to 40.9 months). Ten patients (36%) were exposed to TIBSOVO for at least 6 months and 6 patients (21%) were exposed for at least 1 year.
Common (≥ 5%) serious adverse reactions included differentiation syndrome (18%), electrocardiogram QT prolonged (7%), and fatigue (7%). There was one case of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES).
Common (≥ 10%) adverse reactions leading to dose interruption included electrocardiogram QT prolonged (14%) and differentiation syndrome (11%). Two (7%) patients required a dose reduction due to electrocardiogram QT prolonged. One patient each required permanent discontinuation due to diarrhea and PRES.
The most common adverse reactions reported in the trial are shown in Table 4.
| TIBSOVO (500 mg daily) N=28 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Body System Adverse Reaction | All Grades n (%) | Grade ≥ 3 n (%) |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||
| Diarrhea | 17 (61) | 2 (7) |
| Nausea | 10 (36) | 2 (7) |
| Abdominal pain Grouped term includes abdominal pain, upper abdominal pain, abdominal discomfort, and abdominal tenderness. | 8 (29) | 1 (4) |
| Constipation | 6 (21) | 1 (4) |
| Vomiting | 6 (21) | 1 (4) |
| Mucositis Grouped term includes aphthous ulcer, esophageal pain, esophagitis, gingival pain, gingivitis, mouth ulceration, mucosal inflammation, oral pain, oropharyngeal pain, proctalgia, and stomatitis. | 6 (21) | 0 |
| Dyspepsia | 3 (11) | 0 |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | ||
| Fatigue Grouped term includes asthenia and fatigue. | 14 (50) | 4 (14) |
| Edema Grouped term includes edema, face edema, fluid overload, fluid retention, hypervolemia, peripheral edema, and swelling face. | 12 (43) | 0 |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders | ||
| Decreased appetite | 11 (39) | 1 (4) |
| Blood system and lymphatic system disorders | ||
| Leukocytosis Grouped term includes leukocytosis, hyperleukocytosis, and increased white blood cell count. | 10 (36) | 2 (7) |
| Differentiation Syndrome Differentiation syndrome can be associated with other commonly reported events such as peripheral edema, leukocytosis, pyrexia, dyspnea, pleural effusion, hypotension, hypoxia, pulmonary edema, pneumonia, pericardial effusion, rash, fluid overload, tumor lysis syndrome, and creatinine increased. | 7 (25) | 3 (11) |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||
| Arthralgia Grouped term includes arthralgia, back pain, musculoskeletal stiffness, neck pain, and pain in extremity. | 9 (32) | 1 (4) |
| Myalgia Grouped term includes myalgia, muscular weakness, musculoskeletal pain, musculoskeletal chest pain, musculoskeletal discomfort, and myalgia intercostal. | 7 (25) | 1 (4) |
| Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders | ||
| Dyspnea Grouped term includes dyspnea, dyspnea exertional, hypoxia, and respiratory failure. | 8 (29) | 1 (4) |
| Cough Grouped term includes cough, productive cough, and upper airway cough syndrome. | 4 (14) | 0 |
| Investigations | ||
| Electrocardiogram QT prolonged | 6 (21) | 3 (11) |
| Weight decreased | 3 (11) | 0 |
| Nervous system disorders | ||
| Dizziness | 6 (21) | 0 |
| Neuropathy Grouped term includes burning sensation, lumbosacral plexopathy, neuropathy peripheral, paresthesia, and peripheral motor neuropathy. | 4 (14) | 0 |
| Headache | 3 (11) | 0 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||
| Pruritus | 4 (14) | 1 (4) |
| Rash Grouped term includes dermatitis acneiform, dermatitis, rash, rash maculo-papular, urticaria, rash erythematous, rash macular, rash pruritic, rash generalized, rash papular, skin exfoliation, and skin ulcer. | 4 (14) | 1 (4) |
Changes in selected post-baseline laboratory values that were observed in patients with newly diagnosed AML are shown in Table 5.
| TIBSOVO (500 mg daily) N=28 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Parameter | All Grades n (%) | Grade ≥ 3 n (%) |
| Hemoglobin decreased | 15 (54) | 12 (43) |
| Alkaline phosphatase increased | 13 (46) | 0 |
| Potassium decreased | 12 (43) | 3 (11) |
| Sodium decreased | 11 (39) | 1 (4) |
| Uric acid increased | 8 (29) | 1 (4) |
| Aspartate aminotransferase increased | 8 (29) | 1 (4) |
| Creatinine increased | 8 (29) | 0 |
| Magnesium decreased | 7 (25) | 0 |
| Calcium decreased | 7 (25) | 1 (4) |
| Phosphate decreased | 6 (21) | 2 (7) |
| Alanine aminotransferase increased | 4 (14) | 1 (4) |
Relapsed or Refractory AML
The safety profile of single-agent TIBSOVO was studied in 179 adults with relapsed or refractory AML treated with 500 mg daily [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ] .
The median duration of exposure to TIBSOVO was 3.9 months (range 0.1 to 39.5 months). Sixty-five patients (36%) were exposed to TIBSOVO for at least 6 months and 16 patients (9%) were exposed for at least 1 year.
Serious adverse reactions (≥ 5%) were differentiation syndrome (10%), leukocytosis (10%), and electrocardiogram QT prolonged (7%). There was one case of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML).
The most common adverse reactions leading to dose interruption were electrocardiogram QT prolonged (7%), differentiation syndrome (3%), leukocytosis (3%) and dyspnea (3%). Five out of 179 patients (3%) required a dose reduction due to an adverse reaction.
Adverse reactions leading to a dose reduction included electrocardiogram QT prolonged (1%), diarrhea (1%), nausea (1%), decreased hemoglobin (1%), and increased transaminases (1%).
Adverse reactions leading to permanent discontinuation included Guillain-Barré syndrome (1%), rash (1%), stomatitis (1%), and creatinine increased (1%).
The most common adverse reactions reported in the trial are shown in Table 6.
| TIBSOVO (500 mg daily) N=179 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Body System Adverse Reaction | All Grades n (%) | Grade ≥ 3 n (%) |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | ||
| Fatigue Grouped term includes asthenia and fatigue. | 69 (39) | 6 (3) |
| Edema Grouped term includes peripheral edema, edema, fluid overload, fluid retention, and face edema. | 57 (32) | 2 (1) |
| Pyrexia | 41 (23) | 2 (1) |
| Chest pain Grouped term includes angina pectoris, chest pain, chest discomfort, and non-cardiac chest pain | 29 (16) | 5 (3) |
| Blood system and lymphatic system disorders | ||
| Leukocytosis Grouped term includes leukocytosis, hyperleukocytosis, and increased white blood cell count. | 68 (38) | 15 (8) |
| Differentiation Syndrome Differentiation syndrome can be associated with other commonly reported events such as peripheral edema, leukocytosis, pyrexia, dyspnea, pleural effusion, hypotension, hypoxia, pulmonary edema, pneumonia, pericardial effusion, rash, fluid overload, tumor lysis syndrome, and creatinine increased. | 34 (19) | 23 (13) |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||
| Arthralgia Grouped term includes arthralgia, back pain, musculoskeletal stiffness, neck pain, and pain in extremity. | 64 (36) | 8 (4) |
| Myalgia Grouped term includes myalgia, muscular weakness, musculoskeletal pain, musculoskeletal chest pain, musculoskeletal discomfort, and myalgia intercostal. | 33 (18) | 1 (1) |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||
| Diarrhea | 60 (34) | 4 (2) |
| Nausea | 56 (31) | 1 (1) |
| Mucositis Grouped term includes aphthous ulcer, esophageal pain, esophagitis, gingival pain, gingivitis, mouth ulceration, mucosal inflammation, oral pain, oropharyngeal pain, proctalgia, and stomatitis. | 51 (28) | 6 (3) |
| Constipation | 35 (20) | 1 (1) |
| Vomiting Grouped term includes vomiting and retching. | 32 (18) | 2 (1) |
| Abdominal pain Grouped term includes abdominal pain, upper abdominal pain, abdominal discomfort, and abdominal tenderness. | 29 (16) | 2 (1) |
| Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders | ||
| Dyspnea Grouped term includes dyspnea, respiratory failure, hypoxia, and dyspnea exertional. | 59 (33) | 16 (9) |
| Cough Grouped term includes cough, productive cough, and upper airway cough syndrome. | 40 (22) | 1 (<1) |
| Pleural effusion | 23 (13) | 5 (3) |
| Investigations | ||
| Electrocardiogram QT prolonged | 46 (26) | 18 (10) |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||
| Rash Grouped term includes dermatitis acneiform, dermatitis, rash, rash maculo-papular, urticaria, rash erythematous, rash macular, rash pruritic, rash generalized, rash papular, skin exfoliation, and skin ulcer. | 46 (26) | 4 (2) |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders | ||
| Decreased appetite | 33 (18) | 3 (2) |
| Tumor lysis syndrome | 14 (8) | 11 (6) |
| Nervous system disorders | ||
| Headache | 28 (16) | 0 |
| Neuropathy Grouped term includes ataxia, burning sensation, gait disturbance, Guillain-Barré syndrome, neuropathy peripheral, paresthesia, peripheral sensory neuropathy, peripheral motor neuropathy, and sensory disturbance. | 21 (12) | 2 (1) |
| Vascular disorders | ||
| Hypotension Grouped term includes hypotension and orthostatic hypotension. | 22 (12) | 7 (4) |
Changes in selected post-baseline laboratory values that were observed in patients with relapsed or refractory AML are shown in Table 7.
| TIBSOVO (500 mg daily) N=179 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Parameter | All Grades n (%) | Grade ≥ 3 n (%) |
| Hemoglobin decreased | 108 (60) | 83 (46) |
| Sodium decreased | 69 (39) | 8 (4) |
| Magnesium decreased | 68 (38) | 0 |
| Uric acid increased | 57 (32) | 11 (6) |
| Potassium decreased | 55 (31) | 11 (6) |
| Alkaline phosphatase increased | 49 (27) | 1 (1) |
| Aspartate aminotransferase increased | 49 (27) | 1 (1) |
| Phosphate decreased | 45 (25) | 15 (8) |
| Creatinine increased | 42 (23) | 2 (1) |
| Alanine aminotransferase increased | 26 (15) | 2 (1) |
| Bilirubin increased | 28 (16) | 1 (1) |
Relapsed or Refractory Myelodysplastic Syndromes
The safety of TIBSOVO was evaluated in 19 adults with relapsed or refractory MDS treated with 500 mg daily in AG120-C-001 [see Clinical Studies (14.3) ] . The median duration of exposure to TIBSOVO was 9.3 months (range 3.3 to 78.8 months). Fourteen patients (74%) were exposed to TIBSOVO for at least 6 months and 8 patients (42%) were exposed for at least 1 year.
Serious adverse reactions in ≥ 5% included differentiation syndrome (11%), fatigue (5%), and rash (5%).
Permanent discontinuation of TIBSOVO due to an adverse reaction occurred in 5% of patients. The adverse reaction which resulted in permanent discontinuation of TIBSOVO was fatigue.
Adverse reactions leading to dosage interruption of TIBSOVO occurred in 16% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dosage interruption in ≥ 5% were differentiation syndrome, leukocytosis, and rash.
Dose reductions of TIBSOVO due to an adverse reaction occurred in 16% of patients. Adverse reactions which required a dose reduction in ≥ 5% included differentiation syndrome, fatigue, and rash.
The most common (≥ 25%) adverse reactions, including laboratory abnormalities, were creatinine increased, hemoglobin decrease, arthralgia, albumin decreased, aspartate aminotransferase increased, fatigue, diarrhea, cough, sodium decreased, mucositis, decreased appetite, myalgia, phosphate decreased, pruritus, and rash.
Table 8 summarizes the adverse reactions in AG120-C-001.
| TIBSOVO (500 mg daily) N=19 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Body System Adverse Reaction | All Grades % | Grade 3 or 4 % |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||
| Arthralgia Grouped term includes arthralgia, back pain, pain in extremity, flank pain, joint swelling, and neck pain. | 42 | 16 |
| Myalgia Grouped term includes myalgia, muscle spasms, muscle discomfort, and musculoskeletal chest pain. | 26 | 0 |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | ||
| Fatigue Grouped term includes fatigue and asthenia. | 37 | 11 |
| Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders | ||
| Cough | 32 | 0 |
| Dyspnea Grouped term includes dyspnea and dyspnea exertional. | 21 | 0 |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||
| Diarrhea | 32 | 0 |
| Mucositis Grouped term includes oropharyngeal pain, gingivitis, mouth ulceration, stomatitis. | 26 | 5 |
| Constipation | 16 | 0 |
| Nausea | 16 | 0 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||
| Pruritus | 26 | 0 |
| Rash Grouped term includes rash, catheter site erythema, and urticaria. | 26 | 0 |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders | ||
| Decreased appetite | 26 | 0 |
| Blood system and lymphatic system disorders | ||
| Leukocytosis Grouped term includes leukocytosis, hyperleukocytosis, and white blood cell count increased. | 16 | 5 |
| Differentiation Syndrome | 11 | 0 |
| Nervous system disorders | ||
| Headache | 16 | 0 |
| Vascular disorders | ||
| Hypertension | 16 | 16 |
| Investigations | ||
| Electrocardiogram QT prolonged | 11 | 0 |
Table 9 summarizes laboratory abnormalities in AG120-C-001.
| TIBSOVO Laboratory abnormality is defined as new or worsened by at least one grade from baseline, or if baseline is unknown. N=19 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Laboratory Abnormality | All Grades % | Grade 3 or 4 % |
| Creatinine increased | 95 | 5 |
| Hemoglobin decreased | 42 | 32 |
| Albumin decreased | 37 | 0 |
| Aspartate Aminotransferase increased | 37 | 5 |
| Sodium decreased | 32 | 5 |
| Phosphate decreased | 26 | 5 |
| Alanine Aminotransferase increased | 21 | 5 |
| Bilirubin increased | 21 | 0 |
| Magnesium decreased | 21 | 0 |
| Alkaline Phosphatase increased | 16 | 0 |
| Potassium increased | 16 | 0 |
Locally Advanced or Metastatic Cholangiocarcinoma
The safety of TIBSOVO was studied in patients with previously treated, locally advanced or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma in Study AG120-C-005 [see Clinical Studies (14.4) ] . Patients received at least one dose of either TIBSOVO 500 mg daily (N=123) or placebo (N=59). The median duration of treatment was 2.8 months (range 0.1 to 34.4 months) with TIBSOVO.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 34% of patients receiving TIBSOVO. Serious adverse reactions in ≥2% of patients in the TIBSOVO arm were pneumonia, ascites, hyperbilirubinemia, and jaundice cholestatic.
Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 4.9% of patients receiving TIBSOVO, including sepsis (1.6%) and pneumonia, intestinal obstruction, pulmonary embolism, and hepatic encephalopathy (each 0.8%).
TIBSOVO was permanently discontinued in 7% of patients. The most common adverse reactions leading to permanent discontinuation was acute kidney injury (1.6%).
Dose interruptions due to adverse reactions occurred in 29% of patients treated with TIBSOVO. The most common (>2%) adverse reactions leading to dose interruption were hyperbilirubinemia, alanine aminotransferase increased, aspartate aminotransferase increased, ascites, and fatigue.
Dose reductions of TIBSOVO due to an adverse reaction occurred in 4.1% of patients. Adverse reactions leading to dose reduction were electrocardiogram QT prolonged (3.3%) and neuropathy peripheral (0.8%).
The most common adverse reactions (≥15%) were fatigue, nausea, abdominal pain, diarrhea, cough, decreased appetite, ascites, vomiting, anemia, and rash.
Adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities observed in Study AG120-C-005 are shown in Tables 10 and 11.
| TIBSOVO (500 mg daily) N=123 | Placebo N=59 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body System Adverse Reaction | All Grades n (%) | Grade ≥ 3 n (%) | All Grades n (%) | Grade ≥ 3 n (%) |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | ||||
| Fatigue Grouped term includes asthenia and fatigue. | 53 (43) | 4 (3) | 18 (31) | 3 (5) |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||||
| Nausea | 51 (41) | 3 (2) | 17 (29) | 1 (2) |
| Diarrhea | 43 (35) | 0 | 10 (17) | 0 |
| Abdominal pain Grouped term includes abdominal pain, abdominal pain upper, abdominal discomfort, abdominal pain lower, epigastric discomfort, abdominal tenderness, and gastrointestinal pain. | 43 (35) | 3 (2) | 13 (22) | 2 (3) |
| Ascites | 28 (23) | 11 (9) | 9 (15) | 4 (7) |
| Vomiting Grouped term includes vomiting and retching. | 28 (23) | 3 (2) | 12 (20) | 0 |
| Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders | ||||
| Cough Grouped term includes cough and productive cough. | 33 (27) | 0 | 5 (9) | 0 |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders | ||||
| Decreased appetite | 30 (24) | 2 (2) | 11 (19) | 0 |
| Blood and lymphatic system disorders | ||||
| Anemia | 22 (18) | 8 (7) | 3 (5) | 0 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||||
| Rash Grouped term includes rash, rash maculo-papular, erythema, rash macular, dermatitis exfoliative generalized, drug eruption, and drug hypersensitivity. | 19 (15) | 1 (1) | 4 (7) | 0 |
| Nervous system disorders | ||||
| Headache | 16 (13) | 0 | 4 (7) | 0 |
| Neuropathy peripheral Grouped term includes neuropathy peripheral, peripheral sensory neuropathy, and paresthesia. | 13 (11) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Investigations | ||||
| Electrocardiogram QT prolonged | 12 (10) | 2 (2) | 2 (3) | 0 |
| TIBSOVO (500 mg daily) N=123 | Placebo N=59 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | All Grades n (%) | Grade ≥ 3 n (%) | All Grades n (%) | Grade ≥ 3 n (%) |
| AST increased | 41 (34) | 5 (4) | 14 (24) | 1 (2) |
| Bilirubin increased | 36 (30) | 15 (13) | 11 (19) | 2 (3) |
| Hemoglobin decreased | 48 (40) | 8 (7) | 14 (25) | 0 |
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Strong or Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors: Reduce TIBSOVO dose with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. Monitor patients for increased risk of QTc interval prolongation (2.4 , 5.2 , 7.1 , 12.3 ).
- Strong CYP3A4 Inducers: Avoid concomitant use with TIBSOVO (7.1 , 12.3 ).
- Sensitive CYP3A4 substrates: Avoid concomitant use with TIBSOVO (7.2 , 12.3 ).
- QTc Prolonging Drugs: Avoid concomitant use with TIBSOVO. If co-administration is unavoidable, monitor patients for increased risk of QTc interval prolongation (5.2 , 7.1 ).
Effect of Other Drugs on Ivosidenib
| Strong or Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors | |
| Clinical Impact |
|
| Prevention or Management |
|
| Strong CYP3A4 Inducers | |
| Clinical Impact |
|
| Prevention or Management |
|
| QTc Prolonging Drugs | |
| Clinical Impact |
|
| Prevention or Management |
|
Effect of Ivosidenib on Other Drugs
Ivosidenib induces CYP3A4 and may induce CYP2C9. Co-administration will decrease concentrations of drugs that are sensitive CYP3A4 substrates and may decrease concentrations of drugs that are sensitive CYP2C9 substrates [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . Use alternative therapies that are not sensitive substrates of CYP3A4 and CYP2C9 during TIBSOVO treatment. If co-administration of TIBSOVO with sensitive CYP3A4 substrates or CYP2C9 substrates is unavoidable, monitor patients for loss of therapeutic effect of these drugs.
Do not administer TIBSOVO with anti-fungal agents that are substrates of CYP3A4 due to expected loss of antifungal efficacy.
Co-administration of TIBSOVO may decrease the concentrations of hormonal contraceptives, consider alternative methods of contraception in patients receiving TIBSOVO.
DESCRIPTION
TIBSOVO (ivosidenib) is an inhibitor of isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH1) enzyme. The chemical name is (2 S )- N -{(1 S )-1-(2-chlorophenyl)-2-[(3,3-difluorocyclobutyl)-amino]-2-oxoethyl}-1-(4-cyanopyridin-2-yl)- N -(5-fluoropyridin-3-yl)-5-oxopyrrolidine-2-carboxamide. The chemical structure is:
The molecular formula is C 28 H 22 ClF 3 N 6 O 3 and the molecular weight is 583.0 g/mol. Ivosidenib is practically insoluble in aqueous solutions between pH 1.2 and 7.4.
TIBSOVO (ivosidenib) is available as a film-coated 250 mg tablet for oral administration. Each tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, hypromellose acetate succinate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and sodium lauryl sulfate. The tablet coating includes FD&C blue #2, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, titanium dioxide, and triacetin.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Ivosidenib is a small molecule inhibitor that targets the mutant isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH1) enzyme. In patients with AML, susceptible IDH1 mutations are defined as those leading to increased levels of 2-hydroxyglutarate (2-HG) in the leukemia cells and where efficacy is predicted by 1) clinically meaningful remissions with the recommended dose of ivosidenib and/or 2) inhibition of mutant IDH1 enzymatic activity at concentrations of ivosidenib sustainable at the recommended dosage according to validated methods. The most common of such mutations in patients with AML are R132H and R132C substitutions.
Ivosidenib was shown to inhibit selected IDH1 R132 mutants at much lower concentrations than wild-type IDH1 in vitro. Inhibition of the mutant IDH1 enzyme by ivosidenib led to decreased 2-HG levels and induced myeloid differentiation in vitro and in vivo in mouse xenograft models of IDH1-mutated AML. In blood samples from patients with AML with mutated IDH1, ivosidenib decreased 2-HG levels ex-vivo, reduced blast counts, and increased percentages of mature myeloid cells.
In a patient-derived xenograft intra-hepatic cholangiocarcinoma mouse model with IDH1 R132C, ivosidenib reduced 2-HG levels.
Pharmacodynamics
Multiple doses of ivosidenib 500 mg daily were observed to decrease plasma 2-HG concentrations in patients with hematological malignancies and cholangiocarcinoma to levels similar to those observed at baseline in healthy subjects. In bone marrow of patients with hematological malignancies and in tumor biopsy of patients with cholangiocarcinoma, the mean [% coefficient of variation (%CV)] reduction in 2-HG concentrations were 93.1% (11.1%) and 82.2% (32.4%), respectively.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
The mean increase in QTc was 17 msec (UCI: 20 msec) following administration of TIBSOVO 500 mg in patients with newly diagnosed AML and patients with relapsed or refractory AML. The increase in QTc interval was concentration-dependent [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] . A similar mean increase following administration of TIBSOVO 500 mg daily was observed in patients with relapsed or refractory MDS and in patients with solid tumors, including patients with cholangiocarcinoma. Co-administration with moderate or strong CYP3A inhibitors is expected to further increase QTc interval prolongation from baseline.
Pharmacokinetics
The AUC and C max of ivosidenib increase in a less than dose-proportional manner from 200 mg to 1,200 mg daily (0.4 to 2.4 times the approved recommended dosage). The following ivosidenib pharmacokinetic parameters (Table 12) were observed following administration of ivosidenib 500 mg as a single dose or daily dose (for steady state), unless otherwise specified. The steady-state pharmacokinetics of ivosidenib 500 mg were comparable between patients with newly diagnosed AML, relapsed or refractory AML, and relapsed or refractory MDS, and were lower in patients with cholangiocarcinoma.
| Newly diagnosed AML treated with a combination of TIBSOVO and azacitidine | Relapsed or refractory AML treated with TIBSOVO | Relapsed or refractory MDS treated with TIBSOVO | Cholangiocarcinoma treated with TIBSOVO | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PK parameters | ||||
| Single dose C max (ng/mL) PK parameters expressed as mean (%CV). | 4,820 (39%) | 4,503 (38%) | 4,020 (31%) | 4,060 (45%) |
| Steady state C max (ng/mL) | 6,145 (34%) | 6,551 (44%) | 5,820 (37%) | 4,799 (33%) |
| Steady state AUC (ng∙hr/mL) | 106,326 (41%) | 117,348 (50%) | 103,770 (40%) | 86,382 (34%) |
| Steady state PK | Within 14 days | |||
| Accumulation | ||||
| C max | 1.2 | 1.5 | 1.4 | 1.2 |
| AUC | 1.6 | 1.9 | 2 | 1.5 |
| Absorption | ||||
| Median T max (hr) | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 |
| Effect of Food Following administration of a single dose in healthy subjects, a high-fat meal (approximately 900 to 1,000 calories, 500 to 600 fat calories, 250 carbohydrate calories and 150 protein calories). | ||||
| C max | 1.98-fold (90% CI: 1.79, 2.19) | |||
| AUC | 1.24-fold (90% CI: 1.16, 1.33) | |||
| Distribution | ||||
| In vitro protein binding | 92 to 96% | |||
| Apparent volume of distribution at steady state (L) | 504 (22%) | 403 (35%) | 552 (26%) | 706 (45%) |
| Elimination | ||||
| Apparent clearance at steady state (L/hr) | 4.6 (35%) | 5.6 (35%) | 5.1 (35%) | 6.1 (31%) |
| Terminal half-life at steady state (hr) | 98 (42%) | 58 (42%) | 96 (43%) | 129 (102%) |
| Metabolism | ||||
| Plasma Data from a single radiolabeled ivosidenib dose in healthy subjects. | >92% of total radioactivity as ivosidenib | |||
| Metabolic pathways | ||||
| Major | CYP3A4 | |||
| Minor | N-dealkylation and hydrolytic pathways | |||
| Excretion | ||||
| Urine | 17% (10% as unchanged ivosidenib) | |||
| Feces | 77% (67% as unchanged ivosidenib) | |||
Specific Populations
No clinically significant effects on the pharmacokinetics of ivosidenib were observed based on age (18 years to 89 years), sex, race (White, Asian, Black or African American), body weight (38 to 150 kg), ECOG performance status, mild or moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh A or B) or mild or moderate renal impairment (eGFR ≥30 mL/min/1.73m 2 , MDRD). The pharmacokinetics of ivosidenib in patients with severe renal impairment (eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73m 2 , MDRD) or renal impairment requiring dialysis or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C) is unknown.
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies and Model-Based Approaches
Effect of Strong or Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors on Ivosidenib
Co-administration of 250 mg ivosidenib with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor (200 mg itraconazole once daily for 18 days) increased ivosidenib single-dose AUC by 269% (90% CI: 245%, 295%) with no change in C max in healthy subjects . Co-administration of 500 mg ivosidenib with the moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor fluconazole (dosed to steady-state) increases ivosidenib single-dose AUC by 173% with no change in C max . Co-administration of fluconazole following multiple daily ivosidenib doses is predicted to increase ivosidenib steady-state C max by 152% and AUC by 190% .
Effect of Strong CYP3A4 Inducers on Ivosidenib
Co-administration of ivosidenib with a strong CYP3A4 inducer (600 mg rifampin once daily for 15 days) is predicted to decrease ivosidenib steady-state AUC by 33% .
Effect of Ivosidenib on CYP3A4 Substrates
Ivosidenib induces CYP3A4, including its own metabolism. Co-administration of ivosidenib with CYP3A4 substrates, including certain azole anti-fungal agents, is expected to decrease CYP3A4 substrate steady-state AUC .
Effect of Gastric Acid Reducing Agents on Ivosidenib
No clinically significant ivosidenib pharmacokinetic differences were observed following co-administration with gastric acid reducing agents (e.g., proton pump inhibitors, H2-receptor antagonists, antacids).
In vitro Studies
Metabolic Pathways
Ivosidenib may induce CYP2B6, CYP2C8, and CYP2C9 .
Drug Transporter Systems
Ivosidenib is a substrate for P-glycoprotein (P-gp). Ivosidenib is not a substrate for BCRP or hepatic transporters OATP1B1 and OATP1B3.
Ivosidenib is an inhibitor of OAT3 and P-gp. Ivosidenib does not inhibit BCRP, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OAT1, and OCT2.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies have not been conducted with ivosidenib. Ivosidenib was not mutagenic in an in vitro bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assay. Ivosidenib was not clastogenic in an in vitro human lymphocyte micronucleus assay, or in an in vivo rat bone marrow micronucleus assay. Fertility studies in animals have not been conducted with ivosidenib. In repeat-dose toxicity studies up to 90 days in duration with twice daily oral administration of ivosidenib in rats, uterine atrophy was reported in females at non-tolerated dose levels.
CLINICAL STUDIES
Newly Diagnosed AML
Newly Diagnosed AML in Combination with Azacitidine
The efficacy of TIBSOVO was evaluated in a randomized (1:1), multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial (Study AG120-C-009, NCT03173248) of 146 adult patients with newly-diagnosed AML with an IDH1 mutation who were 75 years or older, or had comorbidities that precluded the use of intensive induction chemotherapy based on at least one of the following criteria: baseline Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status of 2, severe cardiac or pulmonary disease, hepatic impairment with bilirubin > 1.5 times the upper limit of normal, creatinine clearance < 45 mL/min, or other comorbidity. IDH1 mutations were confirmed centrally using the Abbott RealTi m e™ IDH1 Assay. Local diagnostic tests were permitted for screening and randomization provided a bone marrow or peripheral blood sample was sent for central confirmation. Gene mutation analysis to document IDH1 mutated disease from a bone marrow or peripheral blood sample was conducted for all patients. Patients were randomized to receive either TIBSOVO 500 mg or matched placebo orally once daily on Days 1-28 in combination with azacitidine 75 mg/m 2 /day either subcutaneously or intravenously on Days 1-7 or Days 1-5 and 8-9 of each 28-day cycle beginning on Cycle 1 Day 1. Patients were treated for a minimum of 6 cycles unless they experienced disease progression, unacceptable toxicity or undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Baseline demographic and disease characteristics are shown in Table 13.
| Demographic and Disease Characteristics | TIBSOVO + azacitidine (500 mg daily) N=72 | Placebo + azacitidine N=74 |
|---|---|---|
| ECOG PS: Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status; MPN = Myeloproliferative Neoplasm; MDS = Myelodysplastic syndrome | ||
| Demographics | ||
| Age (Years) Median (Min, Max) | 76 (58, 84) | 76 (45, 94) |
| Age Categories, n (%) | ||
| <65 years | 4 (6) | 4 (5) |
| ≥65 years to <75 years | 29 (40) | 27 (36) |
| ≥75 years | 39 (54) | 43 (58) |
| Sex, n (%) | ||
| Male | 42 (58) | 38 (51) |
| Female | 30 (42) | 36 (49) |
| Race, n (%) | ||
| Asian | 15 (21) | 19 (26) |
| White | 12 (17) | 12 (16) |
| Black or African American | 0 | 2 (3) |
| Other | 1 (1) | 1 (1) |
| Not provided | 44 (61) | 40 (54) |
| Disease Characteristics | ||
| ECOG PS, n (%) | ||
| 0 | 14 (19) | 10 (14) |
| 1 | 32 (44) | 40 (54) |
| 2 | 26 (36) | 24 (32) |
| IDH1 Mutation, n (%) Using confirmatory Abbott RealTi m e IDH1 assay testing results. | ||
| R132C | 45 (63) | 51 (69) |
| R132H | 14 (19) | 12 (16) |
| R132G | 6 (8) | 4 (5) |
| R132L | 3 (4) | 0 |
| R132S | 2 (3) | 6 (8) |
| Wild type | 1 (1) | 0 |
| Missing | 1 (1) | 1 (1) |
| Cytogenetic risk status Cytogenetic risk status: National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines. n (%) | ||
| Favorable | 3 (4) | 7 (9) |
| Intermediate | 48 (67) | 44 (59) |
| Poor | 16 (22) | 20 (27) |
| Other | 3 (4) | 1 (1) |
| Missing | 2 (3) | 2 (3) |
| Transfusion Dependent at Baseline Patients were defined as transfusion dependent at baseline if they received any red blood cell or platelet transfusion within 56 days prior to the first dose of TIBSOVO. , n (%) | 39 (54) | 40 (54) |
| Type of AML, n (%) | ||
| De novo AML | 54 (75) | 53 (72) |
| Secondary AML | 18 (25) | 21 (28) |
| Therapy-related AML | 2 (3) | 1 (1) |
| MDS related | 10 (14) | 12 (16) |
| MPN related | 4 (6) | 8 (11) |
Efficacy was established on the basis of event-free survival (EFS), overall survival (OS), and rate and duration of complete remission (CR). EFS was defined as the time from randomization until treatment failure, relapse from remission, or death from any cause, whichever occurred first. Treatment failure was defined as failure to achieve CR by 24 weeks. The efficacy results are shown in Table 14 and Figure 1.
| Endpoint | TIBSOVO (500 mg daily) + azacitidine N=72 | Placebo + azacitidine N=74 |
|---|---|---|
| Abbreviations: EFS = Event free survival; CI: confidence interval; OS = Overall survival; CR = Complete remission; CRh = Complete remission with partial hematologic recovery; NE = Not estimable. | ||
| The 2-sided p-value boundaries for EFS, OS, CR, and CR+CRh are 0.0095, 0.0034, 0.0174, and 0.0174, respectively. | ||
| EFS , events (%) | 47 (65) | 62 (84) |
| Treatment Failure | 43 (60) | 59 (80) |
| Relapse | 3 (4) | 2 (3) |
| Death | 1 (1) | 1 (1) |
| Hazard ratio Hazard ratio is estimated using a Cox's proportional hazards model stratified by the randomization stratification factors (AML status and geographic region) with Placebo+ azacitidine as the denominator. (95% CI) | 0.35 (0.17, 0.72) | |
| p-value Two-sided p-value is calculated from the log-rank test stratified by the randomization stratification factors (AML status and geographic region). | 0.0038 | |
| OS events (%) | 28 (39) | 46 (62) |
| Median OS (95% CI) months | 24.0 (11.3, 34.1) | 7.9 (4.1, 11.3) |
| Hazard ratio(95% CI) | 0.44 (0.27, 0.73) | |
| p-value | 0.0010 | |
| CR, n (%) | 34 (47) | 11 (15) |
| 95% CI CI of percentage is calculated with the Clopper and Pearson (exact Binomial) method. | (35, 59) | (8, 25) |
| Risk difference Mantel-Haenszel estimate of risk difference in percentage between TIBSOVO + azacitidine and Placebo+ azacitidine is calculated. (95% CI), (%) | 31 (17, 46) | |
| p-value Two-sided p-value is calculated from the Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel test stratified by the randomization stratification factors (AML status and geographic region). | <0.0001 | |
| Median duration of CR (95% CI), months | NE (13.0, NE) | 11.2 (3.2, NE) |
| CR +CRh , n (%) | 37 (51) | 13 (18) |
| 95% CI | (39, 63) | (10, 28) |
| Risk difference(95% CI), (%) | 33 (18, 47) | |
| p-value | <0.0001 | |
| Median duration of CR + CRh (95% CI), months | NE (13.0, NE) | 9.2 (5.8, NE) |
Figure 1: Kaplan-Meier Curve for Overall Survival in AG120-C-009
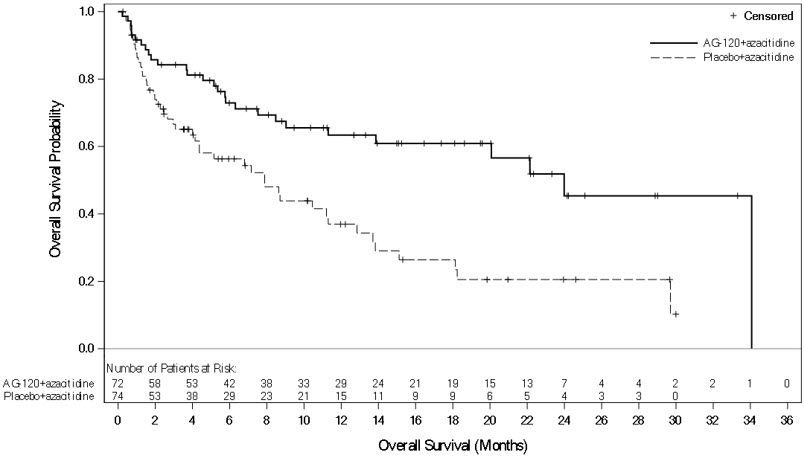
The median time to first CR for TIBSOVO with azacitidine was 4 months (range, 1.7 to 11.9 months).
The median time to first CR + CRh for TIBSOVO with azacitidine was 4 months (range, 1.7 to 11.9 months).
Monotherapy in Newly Diagnosed AML
The efficacy of TIBSOVO was evaluated in an open-label, single-arm, multicenter clinical trial (Study AG120-C-001, NCT02074839) that included 28 adult patients with newly diagnosed AML with an IDH1 mutation. IDH1 mutations were identified by a local or central diagnostic test and confirmed retrospectively using the Abbott RealTi m e™ IDH1 Assay. The cohort included patients who were age 75 years or older or who had comorbidities that precluded the use of intensive induction chemotherapy based on at least one of the following criteria: baseline ECOG performance status of ≥ 2, severe cardiac or pulmonary disease, hepatic impairment with bilirubin > 1.5 times the upper limit of normal, or creatinine clearance < 45 mL/min. TIBSOVO was given orally at a starting dose of 500 mg daily until disease progression, development of unacceptable toxicity, or undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Two (7%) of the 28 patients went on to stem cell transplantation following TIBSOVO treatment.
The baseline demographic and disease characteristics are shown in Table 15.
| Demographic and Disease Characteristics | TIBSOVO (500 mg daily) N=28 | |
|---|---|---|
| ECOG PS: Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status. ELN: European Leukemia Net | ||
| Demographics | ||
| Age (Years) Median (Min, Max) | 77 (64, 87) | |
| Age Categories, n (%) | ||
| <65 years | 1 (4) | |
| ≥65 years to <75 years | 8 (29) | |
| ≥75 years | 19 (68) | |
| Sex, n (%) | ||
| Male | 15 (54) | |
| Female | 13 (46) | |
| Race, n (%) | ||
| White | 24 (86) | |
| Black or African American | 2 (7) | |
| Asian | 0 | |
| Native Hawaiian/Other Pacific Islander | 0 | |
| Other/Not provided | 2 (7) | |
| Disease Characteristics | ||
| ECOG PS, n (%) | ||
| 0 | 6 (21) | |
| 1 | 16 (57) | |
| 2 | 5 (18) | |
| 3 | 1 (4) | |
| IDH1 Mutation, n (%) Using confirmatory Abbott RealTi m e IDH1 assay testing results. | ||
| R132C | 24 (86) | |
| R132H | 2 (7) | |
| R132G | 1 (4) | |
| R132L | 1 (4) | |
| R132S | 0 | |
| ELN Risk Category, n (%) | ||
| Favorable | 0 | |
| Intermediate | 9 (32) | |
| Adverse | 19 (68) | |
| Transfusion Dependent at Baseline Patients were defined as transfusion dependent at baseline if they received any transfusion occurring within 56 days prior to the first dose of TIBSOVO. , n (%) | 17 (61) | |
| Type of AML, n (%) | ||
| De novo AML | 6 (21) | |
| AML-MRC AML with myelodysplasia-related changes. | 19 (68) | |
| Therapy-related AML | 3 (11) | |
| Prior Hypomethylating Agent for Antecedent | ||
| Hematologic Disorder | 13 (46) | |
Efficacy was established on the basis of the rate of complete remission (CR) or complete remission with partial hematologic recovery (CRh), the duration of CR+CRh, and the rate of conversion from transfusion dependence to transfusion independence. The efficacy results are shown in Table 16. The median follow-up was 8.1 months (range, 0.6 to 40.9 months) and median treatment duration was 4.3 months (range, 0.3 to 40.9 months).
| Endpoint | TIBSOVO (500 mg daily) N=28 |
|---|---|
| CI: confidence interval, NE: not estimable | |
| CR CR (complete remission) was defined as <5% blasts in the bone marrow, no evidence of disease, and full recovery of peripheral blood counts (platelets >100,000/microliter and absolute neutrophil counts [ANC] >1,000/microliter). n (%) | 8 (28.6) |
| 95% CI | (13.2, 48.7) |
| Median DOCR DOCR (duration of CR), DOCRh (duration of CRh), and DOCR+CRh (duration of CR+CRh) was defined as time since first response of CR, CRh or CR/CRh, respectively, to relapse or death, whichever is earlier. + indicates censored observation. (months) | NE The median durations of CR and CR+CRh were not estimable, with 5 patients (41.7%) who achieved CR or CRh remaining on TIBSOVO treatment (treatment duration range: 20.3 to 40.9 months). |
| 95% CI | (4.2, NE) |
| CRh CRh (complete remission with partial hematological recovery) was defined as <5% blasts in the bone marrow, no evidence of disease, and partial recovery of peripheral blood counts (platelets >50,000/microliter and ANC >500/microliter). n (%) | 4 (14.3) |
| 95% CI | (4.0, 32.7) |
| Observed DOCRh(months) | 2.8, 4.6, 8.3, 15.7+ |
| CR+CRh n (%) | 12 (42.9) |
| 95% CI | (24.5, 62.8) |
| Median DOCR+CRh(months) | NE |
| 95% CI | (4.2, NE) |
For patients who achieved a CR or CRh, the median time to CR or CRh was 2.8 months (range, 1.9 to 12.9 months). Of the 12 patients who achieved a best response of CR or CRh, 11 (92%) achieved a first response of CR or CRh within 6 months of initiating TIBSOVO.
Among the 17 patients who were dependent on red blood cell (RBC) and/or platelet transfusions at baseline, 7 (41.2%) became independent of RBC and platelet transfusions during any 56-day post-baseline period. Of the 11 patients who were independent of both RBC and platelet transfusions at baseline, 6 (54.5%) remained transfusion independent during any 56-day post-baseline period.
Relapsed or Refractory AML
The efficacy of TIBSOVO was evaluated in an open-label, single-arm, multicenter clinical trial (Study AG120-C-001, NCT02074839) of 174 adult patients with relapsed or refractory AML with an IDH1 mutation. IDH1 mutations were identified by a local or central diagnostic test and confirmed retrospectively using the Abbott RealTi m e™ IDH1 Assay. TIBSOVO was given orally at a starting dose of 500 mg daily until disease progression, development of unacceptable toxicity, or undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Twenty-one (12%) of the 174 patients went on to stem cell transplantation following TIBSOVO treatment.
The baseline demographic and disease characteristics are shown in Table 17.
| Demographic and Disease Characteristics | TIBSOVO (500 mg daily) N=174 |
|---|---|
| ECOG PS: Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status. | |
| Demographics | |
| Age (Years) Median (Min, Max) | 67 (18, 87) |
| Age Categories, n (%) | |
| <65 years | 63 (36) |
| ≥65 years to <75 years | 71 (41) |
| ≥75 years | 40 (23) |
| Sex, n (%) | |
| Male | 88 (51) |
| Female | 86 (49) |
| Race, n (%) | |
| White | 108 (62) |
| Black or African American | 10 (6) |
| Asian | 6 (3) |
| Native Hawaiian/Other Pacific Islander | 1 (1) |
| Other/Not provided | 49 (28) |
| Disease Characteristics | |
| ECOG PS, n (%) | |
| 0 | 36 (21) |
| 1 | 97 (56) |
| 2 | 39 (22) |
| 3 | 2 (1) |
| IDH1 Mutation, n (%) Using confirmatory Abbott RealTi m e IDH1 assay testing results. | |
| R132C | 102 (59) |
| R132H | 43 (25) |
| R132G | 12 (7) |
| R132S | 10 (6) |
| R132L | 7 (4) |
| Cytogenetic Risk Status, n (%) | |
| Intermediate | 104 (60) |
| Poor | 47 (27) |
| Missing/Unknown | 23 (13) |
| Relapse Type | |
| Primary refractory | 64 (37) |
| Refractory relapse | 45 (26) |
| Untreated relapse | 65 (37) |
| Relapse Number | |
| 0 | 64 (37) |
| 1 | 83 (48) |
| 2 | 21 (12) |
| ≥3 | 6 (3) |
| Prior Stem Cell Transplantation for AML, n (%) | 40 (23) |
| Transfusion Dependent at Baseline Patients were defined as transfusion dependent at baseline if they received any transfusion occurring within 56 days prior to the first dose of TIBSOVO. , n (%) | 110 (63) |
| Median Number of Prior Therapies (Min, Max) | 2 (1, 6) |
| Type of AML, n (%) | |
| De novo AML | 116 (67) |
| Secondary AML | 58 (33) |
Efficacy was established on the basis of the rate of complete remission (CR) plus complete remission with partial hematologic recovery (CRh), the duration of CR+CRh, and the rate of conversion from transfusion dependence to transfusion independence. The efficacy results are shown in Table 18. The median follow-up was 8.3 months (range, 0.2 to 39.5 months) and median treatment duration was 4.1 months (range, 0.1 to 39.5 months).
| Endpoint | TIBSOVO (500 mg daily) N=174 |
|---|---|
| CI: confidence interval | |
| CR CR (complete remission) was defined as <5% blasts in the bone marrow, no evidence of disease, and full recovery of peripheral blood counts (platelets >100,000/microliter and absolute neutrophil counts [ANC] >1,000/microliter). n (%) | 43 (24.7) |
| 95% CI | (18.5, 31.8) |
| Median DOCR DOCR (duration of CR), DOCRh (duration of CRh), and DOCR+CRh (duration of CR+CRh) was defined as time since first response of CR, CRh or CR/CRh, respectively, to relapse or death, whichever is earlier. (months) | 10.1 |
| 95% CI | (6.5, 22.2) |
| CRh CRh (complete remission with partial hematological recovery) was defined as <5% blasts in the bone marrow, no evidence of disease, and partial recovery of peripheral blood counts (platelets >50,000/microliter and ANC >500/microliter). n (%) | 14 (8.0) |
| 95% CI | (4.5, 13.1) |
| Median DOCRh(months) | 3.6 |
| 95% CI | (1, 5.5) |
| CR+CRh CR+CRh rate appeared to be consistent across all baseline demographic and baseline disease characteristics with the exception of number of prior regimens. n (%) | 57 (32.8) |
| 95% CI | (25.8, 40.3) |
| Median DOCR+CRh(months) | 8.2 |
| 95% CI | (5.6, 12) |
For patients who achieved a CR or CRh, the median time to CR or CRh was 2 months (range, 0.9 to 5.6 months). Of the 57 patients who achieved a best response of CR or CRh, all achieved a first response of CR or CRh within 6 months of initiating TIBSOVO.
Among the 110 patients who were dependent on red blood cell (RBC) and/or platelet transfusions at baseline, 41 (37.3%) became independent of RBC and platelet transfusions during any 56-day post-baseline period. Of the 64 patients who were independent of both RBC and platelet transfusions at baseline, 38 (59.4%) remained transfusion independent during any 56-day post-baseline period.
Relapsed or Refractory MDS
The efficacy of TIBSOVO was evaluated in an open-label, single-arm, multicenter study (study AG120-C-001, NCT02074839) of 18 adult patients with relapsed or refractory MDS with an IDH1 mutation. IDH1 mutations were detected in peripheral blood or bone marrow by a local or central diagnostic test and confirmed retrospectively using the Abbott RealTi m e™ IDH1 Assay. TIBSOVO was given orally at a starting dose of 500 mg daily continuous for 28-day cycles until disease progression, development of unacceptable toxicity, or undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. One (6%) of the 18 patients went on to stem cell transplantation following TIBSOVO treatment.
The baseline demographic and disease characteristics are shown in Table 19.
| Demographic and Disease Characteristics | TIBSOVO (500 mg daily) N=18 |
|---|---|
| ECOG PS: Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status. | |
| Demographics | |
| Age (Years) Median (Min, Max) | 74 (61, 82) |
| Age Categories, n (%) | |
| <65 years | 3 (17) |
| ≥65 years to <75 years | 7 (39) |
| ≥75 years | 8 (44) |
| Sex, n (%) | |
| Male | 14 (78) |
| Female | 4 (22) |
| Race, n (%) | |
| White | 14 (78) |
| Black or African American | 1 (6) |
| Not Reported | 3 (17) |
| Disease Characteristics | |
| ECOG PS, n (%) | |
| 0 | 5 (28) |
| 1 | 10 (56) |
| 2 | 3 (17) |
| IDH1 Mutation, n (%) Using confirmatory Abbott RealTi m e IDH1 assay testing results. | |
| R132C | 9 (50) |
| R132H | 5 (28) |
| R132G | 2 (11) |
| R132L | 1 (6) |
| R132S | 1 (6) |
| Cytogenetic Risk Status, n (%) | |
| Good | 4 (22) |
| Intermediate | 8 (44) |
| Poor | 5 (28) |
| Missing | 1 (6) |
| Baseline Bone Marrow Blasts, n (%) | |
| < 5% | 7 (39) |
| ≥ 5% | 11 (61) |
| Prior Therapies | |
| Intensive chemotherapy | 3 (17) |
| Non-intensive chemotherapy | 15 (83) |
| 1 line of HMA-based therapy | 14 (78) |
| 2 lines of HMA-based therapy | 1 (6) |
Efficacy was established on the basis of the rate of complete remission (CR) or partial remission (PR) as per the 2006 International Working Group response criteria for MDS, the duration of CR+PR, and the rate of conversion from transfusion dependence to transfusion independence. All observed responses were CRs. The efficacy results are shown in Table 20. The median follow-up was 27.1 months (range 3.7 to 88.7 months) and median duration of exposure to TIBSOVO was 8.3 months (range 3.3 to 78.8 months).
| Endpoint | TIBSOVO (500 mg daily) N=18 |
|---|---|
| CI: confidence interval, CR: complete remission, NE: not estimable, derived based on Kaplan-Meier method. | |
| CR CR responders with baseline bone marrow blast < 5% was 43% (3/7). n (%) | 7 (38.9) |
| 95% CI | (17.3, 64.3) |
| DOCR Duration of CR (DOCR) = date of first documented CR (lasted at least 4 weeks) to date of first documented confirmed relapse or death, whichever is earlier. (months) median (range) | NE (1.9, 80.8+ + indicates censored observation. ) |
For patients who achieved a CR, the median time to CR was 1.9 months (range, 1.0 to 5.6 months).
Among the 9 patients who were dependent on red blood cell (RBC) and/or platelet transfusions at baseline, 6 (67%) became independent of RBC and platelet transfusions during any 56-day post-baseline period. Of the 9 patients who were independent of both RBC and platelet transfusions at baseline, 7 (78%) remained transfusion independent during any 56-day post-baseline period.
Locally Advanced or Metastatic Cholangiocarcinoma
The efficacy of TIBSOVO was evaluated in a randomized (2:1), multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial (Study AG120-C-005, NCT02989857) of 185 adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma with an IDH1 mutation whose disease had progressed following at least 1 but not more than 2 prior regimens, including at least one gemcitabine- or 5-FU-containing regimen. Patients were randomized to receive either TIBSOVO 500 mg orally once daily or matched placebo until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Randomization was stratified by number of prior therapies (1 or 2). Eligible patients who were randomized to placebo were allowed to cross over to receive TIBSOVO after documented radiographic disease progression. Patients with IDH1 mutations were selected using a central diagnostic next generation sequencing assay. Tumor imaging assessments were performed every 6 weeks for the first 8 assessments and every 8 weeks thereafter.
The major efficacy outcome measure was Progression Free Survival (PFS) as determined by independent review committee (IRC) according to Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) v1.1.
The median age was 62 years (range: 33 to 83); 63% were female; 57% were White, 12% Asian, 1.1% Black, 0.5% Native Hawaiian/Other Pacific Islander, 0.5% American Indian or Alaska Native, 28% race missing/not reported; and 37% had an ECOG performance status of 0 (37%) or 1 (62%). All patients received at least 1 prior line of systemic therapy and 47% received two prior lines. Most patients had intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (91%) at diagnosis and 92% had metastatic disease. Across both arms, 70% patients had an R132C mutation, 15% had an R132L mutation, 12% had an R132G mutation, 1.1% had an R132H mutation, and 1.6% had an R132S mutation.
The efficacy results are shown in Table 21 and Figure 2. The study demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in PFS.
| Endpoint | TIBSOVO (500 mg daily) | Placebo |
|---|---|---|
| IRC: Independent Review Committee; CI: Confidence Interval | ||
| Progression-Free Survival by IRC Assessment | N=124 | N=61 |
| Events, n (%) | 76 (61) | 50 (82) |
| Progressive Disease | 64 (52) | 44 (72) |
| Death | 12 (10) | 6 (10) |
| Hazard ratio (95% CI) Hazard ratio is calculated from stratified Cox regression model. Stratified by number of prior lines of therapy. | 0.37 (0.25, 0.54) | |
| p-value P-value is calculated from the one-sided stratified log-rank test. Stratified by number of prior lines of therapy. | <0.0001 | |
| Objective Response Rate, n (%) | 3 (2.4) | 0 |
| Overall Survival OS results are based on the final analysis of OS (based on 150 deaths) which occurred 16 months after the final analysis of PFS. The median OS (95% CI) for TIBSOVO was 10.3 (7.8, 12.4) months; and placebo was 7.5 (4.8, 11.1) months without adjusting for crossover. In the analysis of OS, 70% of the patients randomized to placebo had crossed over to receive TIBSOVO after radiographic disease progression. | N=126 | N=61 |
| Deaths, n (%) | 100 (79) | 50 (82) |
| Hazard ratio (95% CI) | 0.79 (0.56, 1.12) | |
| p-value | 0.093 | |
Figure 2: Kaplan-Meier Plot of Progression-Free Survival per Independent Review Committee - Before Crossover (ITT)
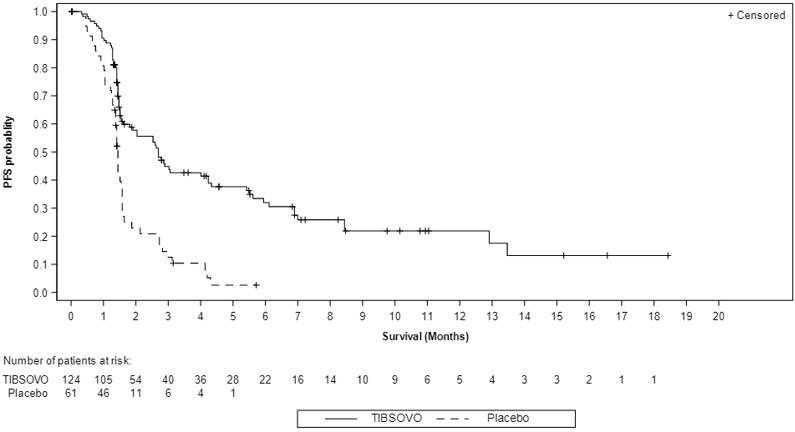
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
250 mg tablet: Blue oval-shaped film-coated tablet debossed "IVO" on one side and "250" on the other side.
- 60-count bottles of 250 mg tablets with a desiccant canister (NDC 72694-617-60)
Storage
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Mechanism of Action
Ivosidenib is a small molecule inhibitor that targets the mutant isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH1) enzyme. In patients with AML, susceptible IDH1 mutations are defined as those leading to increased levels of 2-hydroxyglutarate (2-HG) in the leukemia cells and where efficacy is predicted by 1) clinically meaningful remissions with the recommended dose of ivosidenib and/or 2) inhibition of mutant IDH1 enzymatic activity at concentrations of ivosidenib sustainable at the recommended dosage according to validated methods. The most common of such mutations in patients with AML are R132H and R132C substitutions.
Ivosidenib was shown to inhibit selected IDH1 R132 mutants at much lower concentrations than wild-type IDH1 in vitro. Inhibition of the mutant IDH1 enzyme by ivosidenib led to decreased 2-HG levels and induced myeloid differentiation in vitro and in vivo in mouse xenograft models of IDH1-mutated AML. In blood samples from patients with AML with mutated IDH1, ivosidenib decreased 2-HG levels ex-vivo, reduced blast counts, and increased percentages of mature myeloid cells.
In a patient-derived xenograft intra-hepatic cholangiocarcinoma mouse model with IDH1 R132C, ivosidenib reduced 2-HG levels.