Tlando
(Testosterone Undecanoate)Dosage & Administration
By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Tlando Prescribing Information
| Boxed Warnings, Blood Pressure Increases | Removed 07/2025 |
Indications and Usage, Limitations of Use (TLANDO is indicated for testosterone replacement therapy in adult males for conditions associated with a deficiency or absence of endogenous testosterone:
TLANDO is an androgen indicated for testosterone replacement therapy in adult males for conditions associated with a deficiency or absence of endogenous testosterone . Limitations of Use
| 07/2025 |
| Contraindications, Men with “age related hypogonadism” (4) | Removed 07/2025 |
Warnings and Precautions, Venous Thromboembolism (There have been post marketing reports of venous thromboembolic events, including deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE), in patients using testosterone replacement products such as TLANDO. In the Testosterone Replacement therapy for Assessment of long-term Vascular Events and efficacy ResponSE in hypogonadal men (TRAVERSE) Study, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, cardiovascular (CV) outcomes study, compared to placebo, topical testosterone gel was associated with a numerically higher incidence of VTE (1.7% vs 1.2%) which included DVT (0.6% vs 0.5%) and PE events (0.9% vs 0.5%)[see Adverse Reactions ]. Evaluate patients who report symptoms of pain, edema, warmth, and erythema in the lower extremity for DVT and those who present with acute shortness of breath for PE. If a venous thromboembolic event is suspected, discontinue TLANDO and initiate appropriate workup and management [see Adverse Reactions ] . | 07/2025 |
Warnings and Precautions, Blood Pressure Increases (TLANDO can increase blood pressure. Based on ambulatory blood pressure monitoring in Study 18-001, TLANDO increased mean systolic/diastolic BP by 4.3/1.4 mmHg from baseline after 4 months of treatment. In patients with hypertension on antihypertensive therapy, TLANDO increased the mean systolic/diastolic BP by 4.8/1.6 mm Hg from baseline.[see Adverse Reactions ] . Blood pressure increases can increase cardiovascular (CV) risk over time.The CV risk associated with topical testosterone gel was evaluated in TRAVERSE, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, CV outcomes study in men with a history of CV disease or multiple CV risk factors. In TRAVERSE, topical testosterone gel increased mean systolic blood pressure by 1.0 mmHg from baseline to 36 months, whereas a mean decrease from baseline of 0.5 mmHg was observed in the placebo group at this timepoint, for a mean between group difference of 1.5 mmHg. However, the incidences of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), including cardiovascular death, non-fatal myocardial infarction [MI] and non-fatal stroke, were similar between treatment groups (7% for topical testosterone gel vs 7.3% for placebo)[See Adverse Reactions ]. Monitor BP periodically in men using TLANDO, especially men with hypertension. TLANDO is not recommended for use in patients with uncontrolled hypertension. | 07/2025 |
| Warnings and Precautions, Cardiovascular Risk (5.4) | Removed 07/2025 |
TLANDO is indicated for testosterone replacement therapy in adult males for conditions associated with a deficiency or absence of endogenous testosterone:
- Primary hypogonadism (congenital or acquired): testicular failure due to conditions such as cryptorchidism, bilateral torsion, orchitis, vanishing testis syndrome, orchiectomy, Klinefelter's syndrome, chemotherapy, or toxic damage from alcohol or heavy metals. These men usually have low serum testosterone concentrations and gonadotropins (follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH)) above the normal range [see Dosage and Administration (
2.2 Confirmation of Hypogonadism Before Initiation of TLANDOPrior to initiating TLANDO, confirm the diagnosis of hypogonadism by ensuring that serum testosterone concentrations have been measured in the morning on at least two separate days and that these serum testosterone concentrations are below the normal range.
)]. - Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (congenital or acquired): gonadotropin or luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) deficiency or pituitary-hypothalamic injury from tumors, trauma, or radiation. These men have low testosterone serum concentrations but have gonadotropins in the normal or low range [see Dosage and Administration (
2.2 Confirmation of Hypogonadism Before Initiation of TLANDOPrior to initiating TLANDO, confirm the diagnosis of hypogonadism by ensuring that serum testosterone concentrations have been measured in the morning on at least two separate days and that these serum testosterone concentrations are below the normal range.
)].
Safety and efficacy of TLANDO in males less than 18 years old have not been established
[see Use in Specific Populations (.)]8.4 Pediatric UseThe safety and effectiveness of TLANDO in pediatric patients less than 18 years old have not been established. Improper use may result in acceleration of bone age and premature closure of epiphyses.
- Safetyand efficacy of TLANDO in men with “age-related hypogonadism” (also referred to as “late-onset hypogonadism”) have not been established[see Use in Specific Populations (.)]
8.5 Geriatric UseThere have not been sufficient numbers of geriatric patients in controlled clinical studies with TLANDO to determine whether efficacy or safety in those over 65 years of age differs from younger subjects. Of the 95 patients enrolled in Study 16-002, the 24-day major safety and effectiveness study utilizing TLANDO, 16 (16.8%) were over 65 years of age. Additionally, there is insufficient long-term safety data in geriatric patients utilizing TLANDO to assess the potentially increased risk of cardiovascular disease and prostate cancer.
Geriatric patients treated with androgens may also be at risk for worsening of signs and symptoms of BPH and hypertension
[seeWarnings and Precautions ].
- Prior to initiating TLANDO, confirm the diagnosis of hypogonadism by ensuring that serum testosterone concentrations have been measured in the morning on at least two separate days and that these serum testosterone concentrations are below the normal range ().
2.2 Confirmation of Hypogonadism Before Initiation of TLANDOPrior to initiating TLANDO, confirm the diagnosis of hypogonadism by ensuring that serum testosterone concentrations have been measured in the morning on at least two separate days and that these serum testosterone concentrations are below the normal range.
- Recommended dosage is 225 mg orally twice daily with food ().
2.3 Recommended DosageThe recommended dosage of TLANDO is 225 mg (taken as two 112.5 mg capsules), orally twice daily, once in the morning and once in the evening. Take with food.
Monitoring for Continued Use or DiscontinuationMonitor serum testosterone (8 to 9 hours after the morning dose) 3 to 4 weeks after initiating TLANDO, and periodically thereafter. Based on serum testosterone measurements, determine if TLANDO should be continued or discontinued:
- Serum testosterone 300 - 1080 ng/dL: continue TLANDO
- Serum testosterone < 300 ng/dL: discontinue TLANDO
- Serum testosterone > 1080 ng/dL: discontinue TLANDO
- Monitor serum testosterone after initiating TLANDO to determine if TLANDO should be continued or discontinued ().
2.3 Recommended DosageThe recommended dosage of TLANDO is 225 mg (taken as two 112.5 mg capsules), orally twice daily, once in the morning and once in the evening. Take with food.
Monitoring for Continued Use or DiscontinuationMonitor serum testosterone (8 to 9 hours after the morning dose) 3 to 4 weeks after initiating TLANDO, and periodically thereafter. Based on serum testosterone measurements, determine if TLANDO should be continued or discontinued:
- Serum testosterone 300 - 1080 ng/dL: continue TLANDO
- Serum testosterone < 300 ng/dL: discontinue TLANDO
- Serum testosterone > 1080 ng/dL: discontinue TLANDO
Capsules: 112.5 mg, white opaque body imprinted with “112” in black ink and grey opaque cap, banded with a colorless gelatin band.
Geriatric Patients: Geriatric patients treated with androgens may also be at risk for worsening of signs and symptoms of BPH and hypertension (
There have not been sufficient numbers of geriatric patients in controlled clinical studies with TLANDO to determine whether efficacy or safety in those over 65 years of age differs from younger subjects. Of the 95 patients enrolled in Study 16-002, the 24-day major safety and effectiveness study utilizing TLANDO, 16 (16.8%) were over 65 years of age. Additionally, there is insufficient long-term safety data in geriatric patients utilizing TLANDO to assess the potentially increased risk of cardiovascular disease and prostate cancer.
Geriatric patients treated with androgens may also be at risk for worsening of signs and symptoms of BPH and hypertension
TLANDO is contraindicated in:
- Patients with carcinoma of the breast or known or suspected carcinoma of the prostate [seeWarnings and Precautions (.)]
5.3 Worsening of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) and Potential Risk of Prostate Cancer- Patients with BPH treated with androgens are at an increased risk for worsening of signs and symptoms of BPH. Monitor patients with BPH for worsening signs and symptoms.
- Patients treated with androgens may be at increased risk for prostate cancer. Evaluate patients for prostate cancer, including measurement of prostate specific antigen (PSA), prior to initiating and during treatment with androgens[see Contraindications (4)].
- Women who are pregnant. Testosterone can cause virilization of the female fetus when administered to a pregnant woman [seeUse in Specific Populations (.)]
8.1 PregnancyRisk SummaryTLANDO is contraindicated in pregnant women and not indicated for use in females
[see Contraindications ]. Testosterone is teratogenic and may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman based on data from animal studies (see Data) and its mechanism of action[see Clinical Pharmacology]. Exposure of a female fetus to androgens may result in varying degrees of virilization. In animal developmental studies, exposure to testosterone in utero resulted in hormonal and behavioral changes in offspring and structural impairments of reproductive tissues in female and male offspring. These studies did not meet current standards for nonclinical development toxicity studies.DataAnimal DataIn developmental studies conducted in rats, rabbits, pigs, sheep and rhesus monkeys, pregnant animals received intramuscular injection of testosterone during the period of organogenesis. Testosterone treatment at doses that were comparable to those used for testosterone replacement therapy resulted in structural impairments in both female and male offspring. Structural impairments observed in females included increased anogenital distance, phallus development, empty scrotum, no external vagina, intrauterine growth retardation, reduced ovarian reserve, and increased ovarian follicular recruitment. Structural impairments seen in male offspring included increased testicular weight, larger seminal tubular lumen diameter, and higher frequency of occluded tubule lumen. Increased pituitary weight was seen in both sexes.
Testosterone exposure in utero also resulted in hormonal and behavioral changes in offspring. Hypertension was observed in pregnant females and offspring in rats exposed to doses approximately twice those used for testosterone replacement therapy. - Known hypersensitivity to testosterone undecanoate or any of TLANDO’s ingredients [see Description ()].
11 DESCRIPTIONTLANDO (testosterone undecanoate) capsules contain 112.5 mg testosterone undecanoate, an ester of testosterone, for oral administration. Testosterone, an androgen, is formed by cleavage of the ester side chain of testosterone undecanoate.
The chemical name of testosterone undecanoate is 17β-undecanoyloxy-4-androsten-3-one. It has an empirical formula of C30H48O3and a molecular weight of 456.7. The structural formula is:
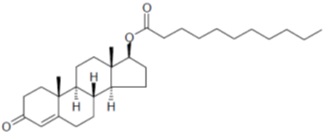
Testosterone undecanoate is a white to off-white crystalline substance.
The inactive ingredients in TLANDO capsules are ascorbyl palmitate, glyceryl monolinoleate, polyethylene glycol 8000, and polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil. The capsule shell contains black iron oxide, gelatin, and titanium dioxide. The capsule is imprinted with black ink that contains ammonium hydroxide, black iron oxide, propylene glycol, and shellac.

Structure