Get your patient on Uplinza (Inebilizumab)
Uplinza prior authorization resources
Most recent Uplinza prior authorization forms
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Uplinza patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Hepatitis B virus, quantitative serum immunoglobulins, and tuberculosis screening is required before the first dose. (2.1 )
- Prior to every infusion:
- UPLIZNA must be diluted in 250 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP prior to administration. (2.3 , 2.4 )
- UPLIZNA is administered as an intravenous infusion titrated to completion, approximately 90 minutes. The recommended dose is:
- Initial dose: 300 mg intravenous infusion followed two weeks later by a second 300 mg intravenous infusion.
- Subsequent doses (starting 6 months from the first infusion): single 300 mg intravenous infusion every 6 months. (2.3 )
- Monitor patients closely during the infusion and for at least one hour after completion of the infusion. (2.3 )
Assessments Prior to First Dose of UPLIZNA
Hepatitis B Virus Screening
Prior to initiating UPLIZNA, perform Hepatitis B virus (HBV) screening. UPLIZNA is contraindicated in patients with active HBV confirmed by positive results for surface antigen [HBsAg] and anti-HBV tests. For patients who are negative for HBsAg and positive for HB core antibody [HBcAb+] or are carriers of HBV [HBsAg+], consult liver disease experts before starting and during treatment with UPLIZNA [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ].
Serum Immunoglobulins
Prior to initiating UPLIZNA, perform testing for quantitative serum immunoglobulins. For patients with low serum immunoglobulins, consult immunology experts before initiating treatment with UPLIZNA [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ].
Tuberculosis Screening
Prior to initiating UPLIZNA, evaluate for active tuberculosis and test for latent infection. For patients with active tuberculosis or positive tuberculosis screening without a history of appropriate treatment, consult infectious disease experts before initiating treatment with UPLIZNA [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] .
Vaccinations
Because vaccination with live-attenuated or live vaccines is not recommended during treatment and after discontinuation until B-cell repletion, administer all immunizations according to immunization guidelines at least 4 weeks prior to initiation of UPLIZNA for live or live-attenuated vaccines [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2) ].
Assessment and Premedication Before Every Infusion
Infection Assessment
Prior to every infusion of UPLIZNA, determine whether there is an active infection. In case of active infection, delay infusion of UPLIZNA until the infection resolves [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ].
Premedication
Table 1 shows premedication to administer prior to each infusion of UPLIZNA to reduce the frequency and severity of infusion reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ].
| Type of Premedication | Route of Administration | Examples (or Equivalent) | Administration Time Prior to UPLIZNA Infusion |
|---|---|---|---|
| corticosteroid | intravenous | methylprednisolone 80 mg to 125 mg | 30 minutes |
| antihistamine | oral | diphenhydramine 25 mg to 50 mg | 30 to 60 minutes |
| antipyretic | oral | acetaminophen 500 mg to 650 mg | 30 to 60 minutes |
Recommended Dosage and Administration
NMOSD, IgG4-RD, and gMG
UPLIZNA is administered as an intravenous infusion (see Table 2 ). The recommended dosage is:
- Initial dose: 300 mg intravenous infusion followed 2 weeks later by a second 300 mg intravenous infusion.
- Subsequent doses (starting 6 months from the first infusion): single 300 mg intravenous infusion every 6 months.
Administration
UPLIZNA must be diluted prior to administration [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) ].
Prior to the start of the intravenous infusion, the prepared infusion solution should be at room temperature.
Administer UPLIZNA under the close supervision of an experienced healthcare professional with access to appropriate medical support to manage potential severe reactions such as serious infusion reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ].
Administer the prepared solution intravenously via an infusion pump at an increasing rate to completion, approximately 90 minutes, according to the schedule in Table 2. Administer through an intravenous line containing a sterile, low-protein binding 0.2 or 0.22 micron in-line filter.
| Elapsed Time (minutes) | Infusion Rate (mL/hour) |
|---|---|
| 0-30 | 42 |
| 31-60 | 125 |
| 61 to completion | 333 |
Monitor the patient closely for infusion reactions during and for at least one hour after the completion of the infusion.
Preparation and Storage of Infusion Solution
Preparation
Visually inspect UPLIZNA solution for particulate matter and discoloration [see Dosage Forms and Strengths (3) ]. If the solution is cloudy, discolored, or it contains discrete particulate matter, do not use and contact the manufacturer (1-800-772-6436). Do not shake the vial.
Obtain an intravenous bag containing 250 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP. Do not use other diluents to dilute UPLIZNA.
Withdraw 10 mL of UPLIZNA from each of the 3 vials contained in the carton and transfer a total of 30 mL into the 250 mL intravenous bag. Mix diluted solution by gentle inversion. Do not shake the solution.
Discard the unused portion remaining in the vials.
Storage of Infusion Solution
UPLIZNA does not contain a preservative.
Administer the prepared infusion solution immediately. If not administered immediately, store the infusion solution for a maximum of 24 hours in the refrigerator between 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) or 4 hours at room temperature between 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) prior to the start of the infusion.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Uplinza prescribing information
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
UPLIZNA is a CD19-directed cytolytic antibody indicated for the treatment of:
- Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) in adult patients who are anti-aquaporin-4 (AQP4) antibody positive. (1.1 )
- Immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) in adult patients. (1.2 )
- Generalized myasthenia gravis (gMG) in adult patients who are anti-acetylcholine receptor (AChR) or anti-muscle specific tyrosine kinase (MuSK) antibody positive. (1.2 )
Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder (NMOSD)
UPLIZNA is indicated for the treatment of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) in adult patients who are anti-aquaporin-4 (AQP4) antibody positive.
Immunoglobulin G4-Related Disease (IgG4-RD)
UPLIZNA is indicated for the treatment of Immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) in adult patients.
Generalized Myasthenia Gravis (gMG)
UPLIZNA is indicated for the treatment of generalized myasthenia gravis (gMG) in adult patients who are anti-acetylcholine receptor (AChR) or anti-muscle specific tyrosine kinase (MuSK) antibody positive.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Hepatitis B virus, quantitative serum immunoglobulins, and tuberculosis screening is required before the first dose. (2.1 )
- Prior to every infusion:
- UPLIZNA must be diluted in 250 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP prior to administration. (2.3 , 2.4 )
- UPLIZNA is administered as an intravenous infusion titrated to completion, approximately 90 minutes. The recommended dose is:
- Initial dose: 300 mg intravenous infusion followed two weeks later by a second 300 mg intravenous infusion.
- Subsequent doses (starting 6 months from the first infusion): single 300 mg intravenous infusion every 6 months. (2.3 )
- Monitor patients closely during the infusion and for at least one hour after completion of the infusion. (2.3 )
Assessments Prior to First Dose of UPLIZNA
Hepatitis B Virus Screening
Prior to initiating UPLIZNA, perform Hepatitis B virus (HBV) screening. UPLIZNA is contraindicated in patients with active HBV confirmed by positive results for surface antigen [HBsAg] and anti-HBV tests. For patients who are negative for HBsAg and positive for HB core antibody [HBcAb+] or are carriers of HBV [HBsAg+], consult liver disease experts before starting and during treatment with UPLIZNA [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ].
Serum Immunoglobulins
Prior to initiating UPLIZNA, perform testing for quantitative serum immunoglobulins. For patients with low serum immunoglobulins, consult immunology experts before initiating treatment with UPLIZNA [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ].
Tuberculosis Screening
Prior to initiating UPLIZNA, evaluate for active tuberculosis and test for latent infection. For patients with active tuberculosis or positive tuberculosis screening without a history of appropriate treatment, consult infectious disease experts before initiating treatment with UPLIZNA [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] .
Vaccinations
Because vaccination with live-attenuated or live vaccines is not recommended during treatment and after discontinuation until B-cell repletion, administer all immunizations according to immunization guidelines at least 4 weeks prior to initiation of UPLIZNA for live or live-attenuated vaccines [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2) ].
Assessment and Premedication Before Every Infusion
Infection Assessment
Prior to every infusion of UPLIZNA, determine whether there is an active infection. In case of active infection, delay infusion of UPLIZNA until the infection resolves [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ].
Premedication
Table 1 shows premedication to administer prior to each infusion of UPLIZNA to reduce the frequency and severity of infusion reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ].
| Type of Premedication | Route of Administration | Examples (or Equivalent) | Administration Time Prior to UPLIZNA Infusion |
|---|---|---|---|
| corticosteroid | intravenous | methylprednisolone 80 mg to 125 mg | 30 minutes |
| antihistamine | oral | diphenhydramine 25 mg to 50 mg | 30 to 60 minutes |
| antipyretic | oral | acetaminophen 500 mg to 650 mg | 30 to 60 minutes |
Recommended Dosage and Administration
NMOSD, IgG4-RD, and gMG
UPLIZNA is administered as an intravenous infusion (see Table 2 ). The recommended dosage is:
- Initial dose: 300 mg intravenous infusion followed 2 weeks later by a second 300 mg intravenous infusion.
- Subsequent doses (starting 6 months from the first infusion): single 300 mg intravenous infusion every 6 months.
Administration
UPLIZNA must be diluted prior to administration [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) ].
Prior to the start of the intravenous infusion, the prepared infusion solution should be at room temperature.
Administer UPLIZNA under the close supervision of an experienced healthcare professional with access to appropriate medical support to manage potential severe reactions such as serious infusion reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ].
Administer the prepared solution intravenously via an infusion pump at an increasing rate to completion, approximately 90 minutes, according to the schedule in Table 2. Administer through an intravenous line containing a sterile, low-protein binding 0.2 or 0.22 micron in-line filter.
| Elapsed Time (minutes) | Infusion Rate (mL/hour) |
|---|---|
| 0-30 | 42 |
| 31-60 | 125 |
| 61 to completion | 333 |
Monitor the patient closely for infusion reactions during and for at least one hour after the completion of the infusion.
Preparation and Storage of Infusion Solution
Preparation
Visually inspect UPLIZNA solution for particulate matter and discoloration [see Dosage Forms and Strengths (3) ]. If the solution is cloudy, discolored, or it contains discrete particulate matter, do not use and contact the manufacturer (1-800-772-6436). Do not shake the vial.
Obtain an intravenous bag containing 250 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP. Do not use other diluents to dilute UPLIZNA.
Withdraw 10 mL of UPLIZNA from each of the 3 vials contained in the carton and transfer a total of 30 mL into the 250 mL intravenous bag. Mix diluted solution by gentle inversion. Do not shake the solution.
Discard the unused portion remaining in the vials.
Storage of Infusion Solution
UPLIZNA does not contain a preservative.
Administer the prepared infusion solution immediately. If not administered immediately, store the infusion solution for a maximum of 24 hours in the refrigerator between 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) or 4 hours at room temperature between 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) prior to the start of the infusion.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Injection: 100 mg/10 mL (10 mg/mL) clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to slightly yellow solution in a single-dose vial.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to UPLIZNA during pregnancy or shortly before conception. Healthcare providers are encouraged to advise their patients to register by contacting the UPLIZNA Pregnancy Registry by calling the coordinating center at 1 (303) 724-4644 or www.upliznapregnancyregistry.com.
Risk Summary
UPLIZNA is a humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody and immunoglobulins are known to cross the placental barrier. There are no adequate data on the developmental risk associated with the use of UPLIZNA in pregnant women. However, transient peripheral B-cell depletion and lymphocytopenia have been reported in infants born to mothers exposed to other B-cell depleting antibodies during pregnancy. B-cell levels in infants following maternal exposure to UPLIZNA have not been studied in clinical trials. The potential duration of B-cell depletion in such infants, and the impact of B-cell depletion on vaccine safety and effectiveness, is unknown [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ].
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
Intravenous administration of inebilizumab-cdon (0, 3, or 30 mg/kg/week) to human CD19 transgenic (huCD19 Tg) male and female mice prior to and during mating and continuing in females through gestation day 15 resulted in no adverse effects on embryofetal development; however, there was a marked reduction in B-cells in fetal blood and liver at both doses tested. These results demonstrate that inebilizumab-cdon crosses the placenta and depletes B-cells in the fetus.
Intravenous administration of inebilizumab-cdon (0, 3, or 30 mg/kg) to huCD19 Tg mice every three days throughout organogenesis and lactation resulted in depletion of B-cells and persistent reductions in immune function (even following repletion of B-cells and lasting into adulthood) in offspring at both doses tested. At the end of the lactation period, plasma inebilizumab-cdon levels in offspring were only slightly lower than those in maternal plasma. A no-effect level for immunotoxicity in the offspring was not identified.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of inebilizumab-cdon in human milk, the effects on a breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Human IgG is excreted in human milk, and the potential for absorption of UPLIZNA to lead to B-cell depletion in the breastfed infant is unknown. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for UPLIZNA and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from UPLIZNA or from the underlying maternal condition.
Females of Reproductive Potential
Contraception
Women of childbearing potential should use contraception while receiving UPLIZNA and for 6 months after the last infusion of UPLIZNA [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatric Use
NMOSD
Clinical studies of UPLIZNA did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients (aged 18 to 64 years of age).
IgG4-RD
Twenty-nine percent (32 out of 112) of patients 65 years of age or older, were treated with UPLIZNA. There were no overall age-related differences in safety or efficacy observed compared to younger patients (aged 18 to 64 years of age).
gMG
Clinical studies of UPLIZNA did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 and older to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients (aged 18 to 64 years of age).
CONTRAINDICATIONS
UPLIZNA is contraindicated in patients with:
- A history of a life-threatening infusion reaction to UPLIZNA [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- Active hepatitis B infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
- Active or untreated latent tuberculosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Infusion reactions: Administer premedications prior to infusion. (2.2 ) Management recommendations for infusion reactions depend on the type and severity of the reaction. Permanently discontinue UPLIZNA if a life-threatening or disabling infusion reaction occurs. (5.1 )
- Infections: Serious, including life-threatening and fatal infections, have occurred in patients treated with B-cell depleting therapies, including UPLIZNA. Delay UPLIZNA administration in patients with an active infection until the infection is resolved. Vaccination with live-attenuated or live vaccines is not recommended during treatment and after discontinuation, until B-cell repletion. (5.2 )
- Immunoglobulin levels: Monitor the level of immunoglobulins at the beginning, during, and after discontinuation of treatment with UPLIZNA until B-cell repletion. Consider discontinuing UPLIZNA if a patient develops a serious opportunistic infection or recurrent infections if immunoglobulin levels indicate immune compromise. (5.3 )
- Fetal Risk: May cause fetal harm based on animal data. Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus and to use an effective method of contraception during treatment and for 6 months after stopping UPLIZNA. (5.4 , 8.1 )
Infusion Reactions
UPLIZNA can cause infusion reactions, including anaphylaxis. Symptoms of infusion reactions can include headache, nausea, somnolence, dyspnea, fever, myalgia, rash, or palpitations. Infusion reactions were observed in 9.3%, 7.4%, and 10.1% of patients treated with UPLIZNA during the randomized controlled periods of Study 1 in patients with NMOSD, Study 2 in patients with IgG4-RD, and Study 3 in patients with gMG, respectively. Infusion reactions were most common with the first infusion but were also observed during subsequent infusions.
Reducing the Risk of Infusion Reactions and Managing Infusion Reactions
Administer pre-medication with a corticosteroid, an antihistamine, and an antipyretic [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) ].
Management recommendations for infusion reactions depend on the type and severity of the reaction . For life-threatening infusion reactions, immediately and permanently stop UPLIZNA and administer appropriate supportive treatment. For less severe infusion reactions, management may involve temporarily stopping the infusion, reducing the infusion rate, and/or administering symptomatic treatment.
Infections
Serious, including life-threatening or fatal, bacterial, fungal, and new or reactivated viral infections have been observed during and following completion of treatment with B-cell depleting therapies, including UPLIZNA.
The most common infections reported by UPLIZNA-treated patients in the randomized and open-label clinical trial periods for NMOSD included urinary tract infection (20%), nasopharyngitis (13%), upper respiratory tract infection (8%), and influenza (7%). In the IgG4-RD randomized controlled and open-label periods, the most common infections reported by UPLIZNA-treated patients were upper respiratory tract infection (11%), nasopharyngitis (10%), urinary tract infection (9%), and influenza (6%). In the gMG randomized controlled period, the most common infections reported by UPLIZNA-treated patients were urinary tract infection (7%) and nasopharyngitis (7%).
Delay UPLIZNA administration in patients with an active infection until the infection is resolved.
Possible Increased Risk of Immunosuppressant Effects with Other Immunosuppressants
If combining UPLIZNA with another immunosuppressive therapy, consider the potential for increased immunosuppressive effects.
Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Reactivation
HBV reactivation has been observed with the use of B-cell depleting therapies, including UPLIZNA. Fulminant hepatitis, hepatic failure, and death caused by HBV reactivation have occurred in patients treated with B-cell depleting therapies.
HBV reactivation was observed in a patient treated with UPLIZNA during the gMG clinical trial, and has also been observed in the postmarketing setting. Patients with active or chronic HBV infection were excluded from clinical trials.
Perform HBV screening in all patients before initiation of treatment with UPLIZNA. Do not administer UPLIZNA to patients with active HBV infection confirmed by positive results for HBsAg and anti-HB tests. For patients who are negative for HBsAg and positive for HBcAb, or who are carriers of HBV (i.e., HBsAg+), consult liver disease experts before starting and during treatment with UPLIZNA.
Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML)
PML is an opportunistic viral infection of the brain caused by the JC virus that typically only occurs in patients who are immunocompromised, and that usually leads to death or severe disability. Although no confirmed cases of PML were identified in UPLIZNA clinical trials, JC virus infection resulting in PML has been observed in patients treated with other B-cell depleting antibodies and other therapies that affect immune competence. In UPLIZNA clinical trials one subject died following the development of new brain lesions for which a definitive diagnosis could not be established, though the differential diagnosis included an atypical NMOSD relapse, PML, or acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. At the first sign or symptom suggestive of PML, withhold UPLIZNA and perform an appropriate diagnostic evaluation. MRI findings may be apparent before clinical signs or symptoms. Typical symptoms associated with PML are diverse, progress over days to weeks, and include progressive weakness on one side of the body or clumsiness of limbs, disturbance of vision, and changes in thinking, memory, and orientation leading to confusion and personality changes.
Tuberculosis
Patients should be evaluated for tuberculosis risk factors and tested for latent infection prior to initiating UPLIZNA. Consider anti-tuberculosis therapy prior to initiation of UPLIZNA in patients with a history of latent active tuberculosis in whom an adequate course of treatment cannot be confirmed, and for patients with a negative test for latent tuberculosis but having risk factors for tuberculosis infection. Consult infectious disease experts regarding whether initiating anti-tuberculosis therapy is appropriate before starting treatment.
Vaccinations
Administer all immunizations according to immunization guidelines at least 4 weeks prior to initiation of UPLIZNA. The safety of immunization with live or live-attenuated vaccines following UPLIZNA therapy has not been studied, and vaccination with live-attenuated or live vaccines is not recommended during treatment and until B-cell repletion.
Vaccination of Infants Born to Mothers Treated with UPLIZNA During Pregnancy
In infants of mothers exposed to UPLIZNA during pregnancy, do not administer live or live-attenuated vaccines before confirming recovery of B-cell counts in the infant. Depletion of B-cells in these exposed infants may increase the risks from live or live-attenuated vaccines. Non-live vaccines, as indicated, may be administered prior to recovery from B-cell and immunoglobulin level depletion, but consultation with a qualified specialist should be considered to assess whether a protective immune response was mounted [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ].
Reduction in Immunoglobulins
There may be a progressive and prolonged hypogammaglobulinemia or decline in the levels of total and individual immunoglobulins such as immunoglobulins G and M (IgG and IgM) with continued UPLIZNA treatment [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ]. Monitor the levels of quantitative serum immunoglobulins during treatment with UPLIZNA, especially in patients with opportunistic or recurrent infections, and until B-cell repletion after discontinuation of therapy. Consider discontinuing UPLIZNA therapy if a patient with low immunoglobulin G or M develops a serious opportunistic infection or recurrent infections, or if prolonged hypogammaglobulinemia requires treatment with intravenous immunoglobulins.
Fetal Risk
Based on animal data, UPLIZNA can cause fetal harm due to B-cell lymphopenia and reduce antibody response in offspring exposed to UPLIZNA even after B-cell repletion. Transient peripheral B-cell depletion and lymphocytopenia have been reported in infants born to mothers exposed to other B-cell depleting antibodies during pregnancy. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception while receiving UPLIZNA and for at least 6 months after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ] .
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Infusion Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
- Reduction in Immunoglobulins [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adverse Reactions
NMOSD
The safety of UPLIZNA was evaluated in Study 1, in which 161 patients were exposed to UPLIZNA at the recommended dosage regimen during the randomized, controlled treatment period; during which 52 patients received placebo [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) and Clinical Studies (14) ] . Subsequently, 198 patients were exposed to UPLIZNA during an open-label treatment period.
Two-hundred and eight patients in the randomized and open-label treatment periods had a total of 324 person-years of exposure to UPLIZNA, including 165 patients with exposure for at least 6 months and 128 with exposure for one year or more.
Table 3 lists adverse reactions that occurred in at least 5% of patients treated with UPLIZNA and at a greater incidence than in patients who received placebo in Study 1. The most common adverse reactions (incidence of at least 10% in patients treated with UPLIZNA and at a greater incidence than placebo) were urinary tract infection and arthralgia.
| Adverse Reactions | UPLIZNA N = 161 % | Placebo N = 52 % |
|---|---|---|
| Urinary tract infection | 11 | 10 |
| Arthralgia | 10 | 4 |
| Headache | 8 | 8 |
| Back pain | 7 | 4 |
Across both the randomized and open-label treatment in Study 1, the most common adverse reactions (greater than 10%) were urinary tract infection (20%), nasopharyngitis (13%), infusion reaction (12%), arthralgia (11%), and headache (10%).
IgG4-RD
The safety of UPLIZNA was evaluated in Study 2, in which 68 patients were exposed to UPLIZNA at the recommended dosage regimen during the randomized, controlled treatment period; during which 67 patients received placebo [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) and Clinical Studies (14) ] .
Table 4 lists adverse reactions that occurred in at least 5% of patients treated with UPLIZNA and at a greater incidence than in patients who received placebo in Study 2. The most common adverse reactions (incidence of at least 10% in patients treated with UPLIZNA and at a greater incidence than placebo) were urinary tract infection and lymphopenia.
| Adverse Reactions | UPLIZNA N = 68 % | Placebo N = 67 % |
|---|---|---|
| Lymphopenia | 19 Lymphopenia includes both lymphopenia and lymphocyte count decreased. | 9 |
| Urinary tract infection | 12 | 6 |
| Pyrexia | 9 | 5 |
| Neutropenia | 6 | 5 |
| Myalgia | 6 | 0 |
Additional adverse reactions during the randomized controlled period in Study 2 were infusion related reactions, influenza, and pneumonia.
gMG
The safety of UPLIZNA was evaluated in Study 3, in which 119 patients were exposed to UPLIZNA at the recommended dosage regimen and 119 patients received placebo during the randomized, placebo-controlled treatment period. The randomized controlled treatment period was 52 weeks for patients who were anti-AChR antibody positive (n=95 each group) and 26 weeks for patients who were anti-MuSK antibody positive (n=24 each group) [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) and Clinical Studies (14) ] . References to adverse reaction frequency in the overall population in the randomized controlled period of Study 3 are reflective of 52-week data for the anti-AChR antibody positive population, and 26-week data for the anti-MuSK antibody positive population that were available at the time of the primary analysis.
Table 5 lists adverse reactions that occurred in at least 5% of patients treated with UPLIZNA and at a greater incidence than in patients who received placebo in Study 3. The most common adverse reactions (incidence of at least 10% in patients treated with UPLIZNA and at a greater incidence than placebo) were headache and infusion-related reaction.
| Adverse Reactions Based on the overall randomized controlled period, comprised of 52 weeks for the anti-AChR antibody positive population and 26 weeks for the anti-MuSK antibody positive population | UPLIZNA N = 119 % | Placebo N = 119 % |
|---|---|---|
| Headache | 15 | 7 |
| Infusion-related reaction Infusion-related reaction was defined as any sign or symptom experienced by patients during the infusion of study drug, or any adverse event occurring within 24 hours of study drug administration for which an alternative explanation was not evident. | 10 | 6 |
| Nasopharyngitis | 7 | 3 |
| Cough | 7 | 3 |
| Urinary tract infection | 7 | 3 |
Laboratory Abnormalities
Decreased Immunoglobulins
NMOSD
At the end of the 6.5-month randomized, controlled period, relative to baseline, the total immunoglobulin level was reduced approximately 8% from baseline for patients treated with UPLIZNA as compared to an increase of 6% in patients treated with placebo. The mean decreases from baseline in immunoglobulin G (IgG) and immunoglobulin M (IgM) were approximately 4% and 32%, respectively, in patients treated with UPLIZNA, whereas IgG was increased by 6% and IgM was increased by approximately 13% in placebo-treated patients. The proportion of patients treated with UPLIZNA who had IgG levels below the lower limit of normal at year 1 was 7% and at year 2 was 13%. The proportion of patients treated with UPLIZNA who had IgM levels below the lower limit of normal at year 1 was 31% and at year 2 was 42%.
IgG4-RD
At the end of the 12-month randomized, controlled period, relative to baseline, the total immunoglobulin level was reduced approximately 12% from baseline for patients treated with UPLIZNA as compared to an increase of 21% in patients treated with placebo. The mean decreases from baseline in IgG and IgM were approximately 9% and 32%, respectively, in patients treated with UPLIZNA, whereas IgG was increased by 26% and IgM was increased by approximately 3% in placebo-treated patients.
gMG
At the end of the 26-week randomized, controlled period, relative to baseline, the total immunoglobulin level was reduced approximately 13% from baseline for patients treated with UPLIZNA as compared to an increase of 15% in patients treated with placebo. The mean decreases from baseline in IgG and IgM were approximately 8% and 30%, respectively, in patients treated with UPLIZNA, whereas IgG was increased by 18% and IgM was increased by approximately 5% in placebo-treated patients. The proportion of patients treated with UPLIZNA who had IgG and IgM levels below the lower limit of normal at the end of the 26-week randomized, controlled period was 29% and 16%, respectively, compared to 8% and 4%, respectively, in the placebo group.
Decreased Neutrophil Counts
NMOSD
Neutrophil counts between 1.0-1.5 × 10 9 /L were observed in 7% of UPLIZNA-treated patients versus 2% of patients who received placebo. Neutrophil counts between 0.5-1.0 × 10 9 /L were observed in 2% of patients treated with UPLIZNA compared to no patients who received placebo. At the end of the 6.5-month randomized, controlled period, the proportion of patients with a neutrophil count below the limit of normal was 12% for patients treated with UPLIZNA compared to 4% for patients who received placebo.
IgG4-RD
During the 12-month randomized, controlled period, neutrophil counts between 1.0-1.5 × 10 9 /L were observed in 8% of UPLIZNA-treated patients versus 3% of patients who received placebo. Neutrophil counts between 0.5-1.0 × 10 9 /L were observed in 2% of patients treated with placebo compared to no patients who received UPLIZNA.
gMG
During the 26-week randomized, controlled period, neutrophil counts between 1.0-1.5 × 10 9 /L were observed in 3% of patients who received placebo compared to no patients who received UPLIZNA. Neutrophil counts between 0.5-1.0 × 10 9 /L were observed in 1% of patients treated with UPLIZNA compared to no patients who received placebo.
Decreased Lymphocyte Counts
NMOSD
A reduction in lymphocyte counts was observed more frequently in patients treated with UPLIZNA compared to those who received placebo. At the end of the 6.5-month randomized, controlled period, the proportion of patients with a lymphocyte count below the limit of normal was 5% for patients treated with UPLIZNA compared to 4% for patients who received placebo.
IgG4-RD
A reduction in lymphocyte counts was observed more frequently in patients treated with UPLIZNA compared to those who received placebo. During the 12-month randomized, controlled period, the proportion of patients with a lymphocyte count below the limit of normal was 42% for patients treated with UPLIZNA compared to 36% for patients who received placebo.
gMG
A reduction in lymphocyte counts was observed more frequently in patients treated with UPLIZNA compared to those who received placebo. During the 26-week randomized, controlled period, the proportion of patients with a lymphocyte count below the limit of normal was 35% for patients treated with UPLIZNA compared to 31% for patients who received placebo.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Immunosuppressive or Immune-Modulating Therapies
Concomitant usage of UPLIZNA with immunosuppressant drugs, including systemic corticosteroids, may increase the risk of infection. Consider the risk of additive immune system effects when co-administering immunosuppressive therapies with UPLIZNA.
DESCRIPTION
Inebilizumab-cdon is a CD19-directed humanized afucosylated IgG1 monoclonal antibody produced by recombinant DNA technology in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell suspension culture. The molecular weight is approximately 149 kDa.
UPLIZNA (inebilizumab-cdon) injection is a sterile, preservative-free, clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to slightly yellow solution, free from visible particles, for intravenous use.
Each single-dose vial contains 100 mg of inebilizumab in 10 mL of solution. Each mL contains 10 mg of inebilizumab-cdon, L-histidine (1.4 mg), L-histidine hydrochloride monohydrate (2.3 mg), polysorbate 80 (0.1 mg), sodium chloride (4.1 mg), α,α-trehalose dihydrate (40.1 mg), and Water for Injection, USP and a pH of 6.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
The mechanism by which inebilizumab-cdon exerts its therapeutic effects in NMOSD, IgG4-RD, and gMG is presumed to involve binding to CD19, a cell surface antigen presents on pre-B and mature B lymphocytes. Following cell surface binding to B lymphocytes, inebilizumab-cdon results in antibody-dependent cellular cytolysis.
Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacodynamics of UPLIZNA were assessed with an assay for CD20+ B-cells, since UPLIZNA can interfere with the CD19+ B-cell assay. Treatment with UPLIZNA reduces CD20+ B-cell counts in blood by 8 days after infusion.
In Study 1 [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ] , CD20+ B-cell counts were reduced below the lower limit of normal by 4 weeks in 100% of patients treated with UPLIZNA and remained below the lower limit of normal in 94% of patients for 28 weeks after initiation of treatment.
In Study 2 [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ], CD20+ B-cell counts were reduced below the lower limit of normal by week 2 in 100% of patients treated with UPLIZNA and remained below the lower limit of normal in 85% of patients for up to 52 weeks after initiation of treatment.
In Study 3 [see Clinical Studies (14.3) ] , CD20+ B-cell counts were reduced below the lower limit of normal by week 4 in ≥ 99% of patients in the overall population (anti-AChR antibody positive and anti-MuSK antibody positive patients) treated with UPLIZNA. B-cell counts remained below the lower limit of normal in ≥ 96% of patients treated with UPLIZNA in the anti-AChR antibody positive population for 52 weeks after initiation of treatment, and in > 96% of patients treated with UPLIZNA in the anti-MuSK antibody positive population for 26 weeks after initiation of treatment.
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of inebilizumab-cdon in patients with NMOSD, IgG4-RD, and gMG was similar, and was biphasic with a mean terminal half-life of 18 days.
In patients with NMOSD, the mean maximum concentration was 108 µg/mL (following the second 300 mg dose on day 15), and the cumulative AUC of the 26-week treatment period in which NMOSD patients received two intravenous administrations 2 week apart was 2980 µg∙d/mL.
In patients with IgG4-RD, the mean maximum concentration was 127 µg/mL (following the second 300 mg dose on day 15), and the cumulative AUC of the 52-week treatment period in which IgG4-RD patients received two intravenous administrations 2 weeks apart, followed by a third dose at week 26 was 4290 µg×d/mL.
In patients with gMG, the mean maximum concentration was 139 µg/mL (following the second 300 mg dose on day 15) for the overall population. The cumulative AUC of the 52-week treatment period in which anti-AChR antibody positive patients (n = 84) received two intravenous administrations 2 weeks apart, followed by a third dose at week 26 was 4240 µg×d/mL. The cumulative AUC of the 26-week treatment period in which anti-MuSK antibody positive patients (n = 17) received two intravenous administrations 2 weeks apart was 3740 µg×d/mL.
Distribution
Based on population pharmacokinetic analysis, the estimated typical central and peripheral volume of distribution of inebilizumab-cdon was 2.95 L and 2.57 L, respectively.
Metabolism
Inebilizumab-cdon is a humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody that is degraded by proteolytic enzymes widely distributed in the body.
Elimination
The results of population pharmacokinetic analysis indicated that the estimated inebilizumab-cdon systemic clearance of the first-order elimination pathway was 0.19 L/day. At low exposure levels, inebilizumab-cdon was likely subject to the receptor (CD19)-mediated clearance, which decreased with time presumably because of the depletion of B-cells by UPLIZNA treatment.
Specific Populations
Gender, Race, Geriatric Use
A population pharmacokinetic analysis indicated that there was no significant effect of gender, race, and age on inebilizumab-cdon clearance.
Renal/Hepatic Impairment
No formal clinical studies have been conducted to investigate the effect of renal impairment or hepatic impairment on inebilizumab-cdon pharmacokinetic parameters.
Drug Interaction Studies
Cytochrome P450 enzymes and transporters are not involved in the clearance of inebilizumab-cdon; therefore, the potential risk of interactions between UPLIZNA and concomitant medications that are substrates, inducers, or inhibitors of cytochrome P450 enzymes and transporters is low.
Immunogenicity
The observed incidence of anti-drug antibodies is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Differences in assay methods preclude meaningful comparisons of the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in the studies described below with the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in other studies, including those of UPLIZNA.
In Study 1, treatment-emergent antibodies (those that appeared or significantly increased from baseline after administration of UPLIZNA), were detected in 5.6% patients receiving UPLIZNA. Although these data do not demonstrate an impact of anti-inebilizumab-cdon antibody development on the efficacy or safety of UPLIZNA in these patients, the available data are too limited to make definitive conclusions.
In Study 2, the incidence of treatment-emergent anti-inebilizumab-cdon antibodies was 8.8% (6/68) of patients receiving UPLIZNA during the 52-week randomized controlled period. Neutralizing antibodies were not directly assessed. There was no identified clinically significant effect of anti--inebilizumab--cdon antibodies on pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, safety or effectiveness of UPLIZNA.
In Study 3, treatment-emergent anti-inebilizumab-cdon antibodies were detected in 0.8% (1/119) of patients receiving UPLIZNA during the randomized controlled period. Neutralizing antibodies were not directly assessed. The available data are too limited to make definitive conclusions regarding the impact of anti-inebilizumab-cdon antibodies on pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, safety, or effectiveness of UPLIZNA.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
No studies have been conducted to assess the carcinogenic potential of inebilizumab-cdon.
Mutagenesis
No studies have been conducted to assess the genotoxic potential of inebilizumab-cdon.
Impairment of Fertility
Intravenous administration of inebilizumab-cdon (0, 3, or 30 mg/kg/week) to human CD19 transgenic male and female mice prior to and during mating and continuing in females through gestation day 15 resulted in reduced fertility at both doses tested. A no-effect dose for adverse effects on fertility was not identified.
CLINICAL STUDIES
Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder (NMOSD)
The efficacy of UPLIZNA for the treatment of NMOSD was established in Study 1 (NCT02200770), a randomized (3:1), double-blind, placebo-controlled trial that enrolled 213 patients with NMOSD who were anti-AQP4 antibody positive and 17 who were anti-AQP4 antibody negative.
Patients met the following eligibility criteria:
- A history of one or more relapses that required rescue therapy within the year prior to screening, or 2 or more relapses that required rescue therapy in 2 years prior to screening.
- Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) score of 7.5 or less. Patients with an EDSS score of 8.0 were eligible if they were deemed capable of participating.
- Patients were excluded if previously treated with immunosuppressant therapies within an interval specified for each such therapy.
The use of immunosuppressants during the blinded phase of the trial was prohibited.
The use of oral or intravenous corticosteroids during the blinded phase of the trial was prohibited, with the exception of premedication for investigational treatment and treatment for a relapse.
Of the 213 enrolled anti-AQP4 antibody positive patients, a total of 161 were randomized to receive treatment with UPLIZNA, and 52 were randomized to receive placebo.
The baseline demographic and disease characteristics were balanced between the treatment groups. Females accounted for 94% of the study population. Fifty-two percent of patients were White, 21% Asian, and 9% Black or African American. The mean age was 43 years (range 18 to 74 years). The mean EDSS score was 4.0. The number of relapses in the two years prior to randomization was 2 or more in 83% of the patients.
UPLIZNA was administered according to the recommended dosage regimen [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) ].
All potential relapses were evaluated by a blinded, independent, adjudication committee, who determined whether the relapse met protocol-defined criteria. Patients who experienced an adjudicated relapse in the randomized-controlled period (RCP), or who completed the Day 197 visit without a relapse, exited the RCP.
The primary efficacy endpoint was the time to the onset of the first adjudicated relapse on or before Day 197.
The time to the first adjudicated relapse was significantly longer in patients treated with UPLIZNA compared to patients who received placebo (relative risk reduction 73%; hazard ratio: 0.272; p < 0.0001). In the anti-AQP4 antibody positive population there was a 77.3% relative reduction (hazard ratio: 0.227, p < 0.0001). There was no evidence of a benefit in patients who were anti-AQP4 antibody negative.
| Treatment Group | ||
|---|---|---|
| UPLIZNA N = 161 | Placebo N = 52 | |
| Time to Adjudication Committee-Determined Relapse (Primary Efficacy Endpoint) | ||
| Number (%) of patients with relapse | 18 (11.2%) | 22 (42.3%) |
| Hazard ratio (95% CI) Cox regression method, with placebo as the reference group. | 0.227 (0.121, 0.423) | |
| p-value | < 0.0001 | |
| Note: Numbers of patients at risk are shown at each time point. |
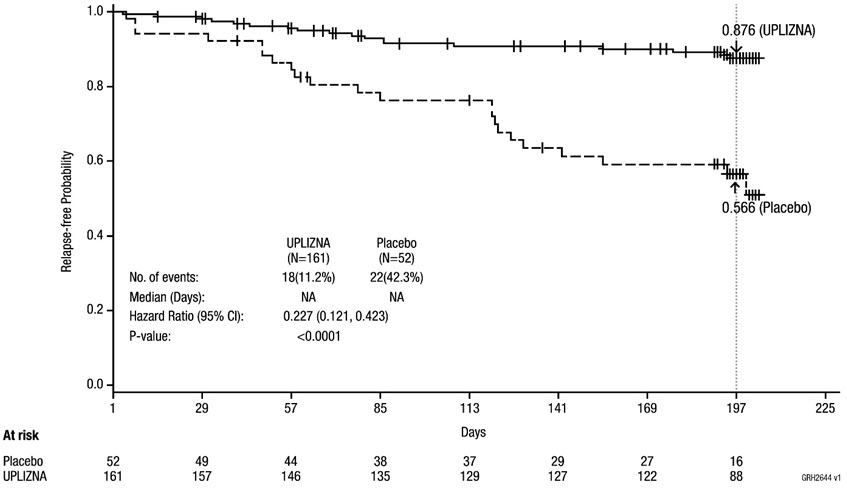 |
Compared to placebo-treated patients, patients treated with UPLIZNA who were anti-AQP4 antibody positive had reduced annualized rates of hospitalizations (0.11 for UPLIZNA versus 0.50 for placebo).
Immunoglobulin G4-Related Disease (IgG4-RD)
The efficacy of UPLIZNA for the treatment of IgG4-RD was established in Study 2 (NCT04540497), a randomized, double-blind, multicenter, 52-week placebo-controlled trial that enrolled 135 adult patients who met the following eligibility criteria:
- Newly diagnosed or recurrent IgG4-RD that required glucocorticoid (GC) treatment at screening.
- Confirmed history of organ involvement at any time in the course of disease.
The concomitant use of biologic and non-biologic immunosuppressive agents was prohibited during the blinded phase of the trial. Of the 135 enrolled IgG4-RD patients, 68 patients were randomized to receive UPLIZNA and 67 were randomized to receive placebo. The baseline demographic and disease characteristics were generally balanced between the treatment groups. Females accounted for 35% of the study population. Thirty-nine percent of patients were White, 47% Asian, and 1% Black or African American. The mean age was 58 years (range 24 to 80 years). The median disease duration was 0.9 years. Forty-six percent of patients were newly diagnosed with IgG4-RD and 54% had recurrent disease.
Patients were at a uniform 20 mg per day dose of glucocorticoids at the time of randomization and then began a prespecified taper of 5 mg dose every two weeks until discontinuation at the end of 8 weeks. The use of glucocorticoids during the trial was permitted for premedication for investigational treatment, treatment for a relapse and in certain situations other than an IgG4-RD flare. UPLIZNA was administered according to the recommended dosage regimen [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) ].
Disease flare was defined as new/worsening signs or symptoms that were positively adjudicated and warranted treatment by the investigator. All potential flares were assessed by the investigator and subsequently reviewed by a blinded, independent, adjudication committee, who determined whether the flare met one or more of the protocol-defined, organ-specific flare diagnostic criteria.
The primary efficacy endpoint was the time to First Treated and Adjudication Committee (AC)-determined IgG4-RD flare within the 52-week RCP. The time to the First Treated and AC determined IgG4-RD flare was significantly longer in the UPLIZNA group, compared with the placebo group (Figure 2). UPLIZNA reduced the risk of treated and AC-determined IgG4-RD flare by 87%, compared with placebo (hazard ratio: 0.13; p < 0.0001) (see Table 6 ).
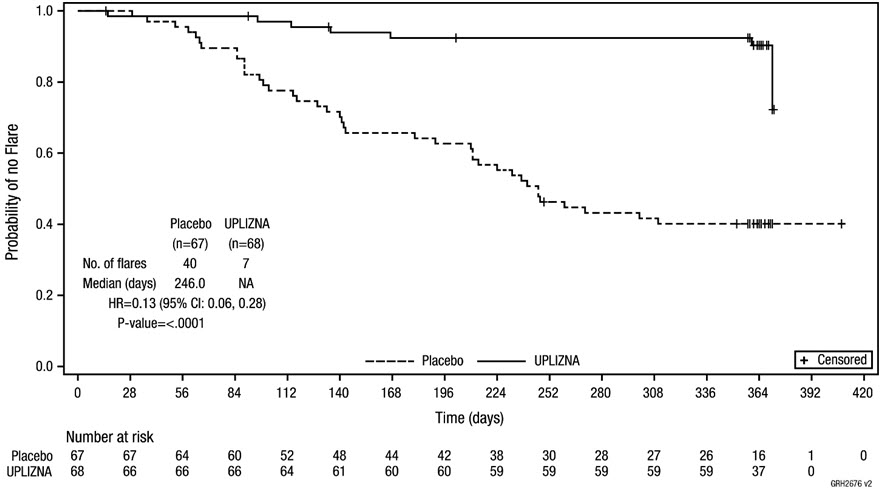 |
Patients who did not complete the RCP and who did not have a treated and AC-determined flare during the RCP were censored at the time of discontinuation.
| Treatment Group | ||
|---|---|---|
| UPLIZNA N = 68 | Placebo N = 67 | |
| Time to The First Treated and AC-Determined IgG4-RD Flare (Primary Efficacy Endpoint) | ||
| Number of subjects with a IgG4-RD flare | 7 (10.3%) | 40 (59.7%) |
| Hazard ratio (95% CI) Based on Cox regression method, with placebo as the reference group. | 0.13 (0.06, 0.28) | |
| p-value | < 0.0001 | |
| Annualized Flare Rate for Treated and AC-Determined IgG4-RD Flares | 0.10 | 0.71 |
| Rate ratio (95% CI) Estimated from the negative binomial regression, with placebo as the reference group. | 0.14 (0.06, 0.31) | |
| p-value | < 0.0001 | |
| Proportion of Subjects Achieving Treatment-free, Flare-Free Complete Remission at Week 52 Defined as the lack of evident disease activity (IgG4-RD RI = 0 or investigator's decision) at Week 52, no AC-determined flare during the RCP, and no treatment for flare or disease control except the required 8-week GC taper. | 39 (57.4%) | 15 (22.4%) |
| Difference (95% CI) Based on logistic regression model, with placebo as the reference group. | 35.0% (19.5%, 50.5%) | |
| p-value | < 0.0001 | |
| Proportion of Subjects Achieving Corticosteroid-free, Flare-Free and Complete Remission at Week 52 Defined as the lack of evident disease activity (IgG4-RD RI = 0 or investigator's decision) at Week 52, no AC-determined flare during the RCP, and no corticosteroid treatment for flare or disease control except the required 8-week GC taper. | 40 (58.8%) | 15 (22.4%) |
| Difference (95% CI) | 36.5% (21.0%, 51.9%) | |
| p-value | < 0.0001 | |
For all patients in the trial, the mean (SD) total GC use for IgG4-RD control per patient other than the planned GC taper was lower in the UPLIZNA-treated group compared with the placebo-treated group, with a mean (SD) of 118.25 (438.97) mg prednisone equivalent versus 1384.53 (1723.26) mg prednisone equivalent, respectively during the RCP. Forty-two (62.7%) placebo-treated patients and 7 (10.3%) UPLIZNA-treated patients received GC for IgG4-RD control other than the planned GC taper. The mean (SD) total GC use per patient for the 42 placebo-treated patients was 2202.76 (1709) mg prednisone equivalent and for the 7 UPLIZNA-treated patients was 1148.71 (878) mg prednisone equivalent.
Generalized Myasthenia Gravis (gMG)
The efficacy of UPLIZNA for the treatment of gMG in adult patients who are anti-acetylcholine receptor (AChR) or anti-muscle specific tyrosine kinase (MuSK) antibody positive was established in Study 3 (NCT04524273), a randomized, double-blind, multicenter, placebo-controlled trial. The randomized, controlled treatment period was 52 weeks for the anti-AChR antibody positive population and 26 weeks for the anti-MuSK antibody positive population. The primary analysis was conducted after week 26 in both populations. UPLIZNA was administered according to the recommended dosage regimen [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) ] .
Patients met the following eligibility criteria:
- Presence of autoantibodies against AChR or MuSK
- Myasthenia Gravis Foundation of America (MGFA) Clinical Classification Class II to IV
- Myasthenia Gravis-Activities of Daily Living (MG-ADL) score between 6 and 10 with > 50% of this score attributed to non-ocular items or an MG-ADL score ≥ 11
- Quantitative Myasthenia Gravis (QMG) score of ≥ 11
- On a stable dose of a corticosteroid or a specified non-steroidal immunosuppressive therapy, or a combination of both prior to randomization.
In Study 3, a total of 238 patients with gMG were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive UPLIZNA or placebo. The majority of patients, 80% (n=190) were anti-AChR antibody positive and 20% (n=48) were anti-MuSK antibody positive.
In the overall study population, 61% of the patients were female. Fifty-three percent of patients were White, 42% were Asian, and 2% were Black or African American. The mean age was 47.5 years (range 18 to 82 years). Mean MG-ADL score at baseline was 9.1 and mean QMG score at baseline was 17.0. At baseline, approximately 79% of patients received acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, 64% of patients received corticosteroids only, 7% of patients received non-steroidal immunosuppressive therapy only, and 29% of patients received corticosteroids and 1 non-steroidal immunosuppressive therapy.
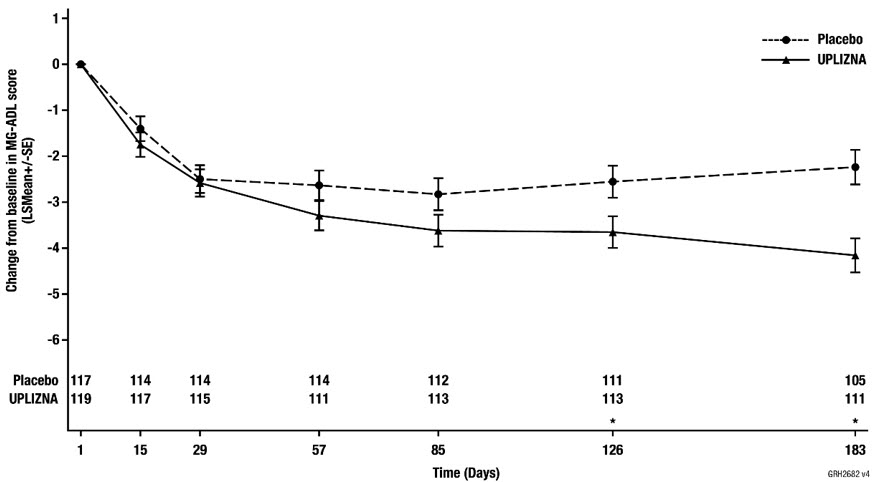
The efficacy of UPLIZNA was measured using MG-ADL scale, which assesses the impact of gMG on daily functions of 8 signs or symptoms that are typically affected in gMG. Each item is assessed on a 4-point scale, where a score of 0 represents normal function and a score of 3 represents loss of ability to perform that function. The total MG-ADL score ranges from 0 to 24, with higher scores indicating more impairment.
The primary efficacy endpoint was the change from baseline in the MG-ADL score at week 26, in the overall population. A statistically significant difference favoring UPLIZNA was observed in the mean change from baseline in MG-ADL total score (−4.2 points in the UPLIZNA-treated group compared to −2.2 points for placebo, difference of −1.9, 95% CI: −2.9, −1.0; p-value < 0.0001).
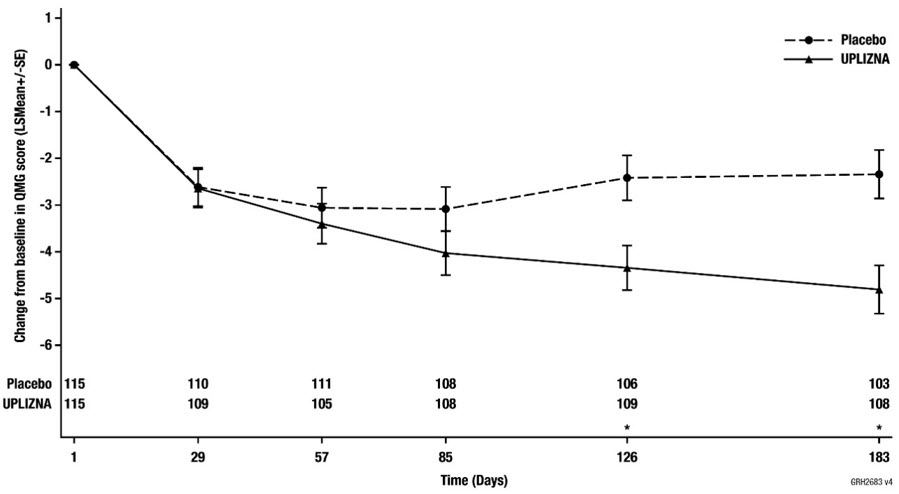
The secondary endpoint was the change from baseline in the QMG score at week 26 in the overall population. The QMG score is a 13-item categorical grading system that assesses muscle weakness. Each item is assessed on a 4-point scale where a score of 0 represents no weakness and a score of 3 represents severe weakness. A total possible score ranges from 0 to 39, where higher scores indicate more severe impairment.
A statistically significant difference favoring UPLIZNA was observed in the mean change from baseline in QMG total score in the overall population (-4.8 points in the UPLIZNA-treated group compared to -2.3 for placebo, difference -2.5, 95% CI: -3.8, -1.2; p-value = 0.0002).
Secondary endpoints also included change in MG-ADL and QMG scores in the anti-AChR antibody positive and anti-MuSK antibody positive populations.
The results of the primary and secondary endpoints are presented in Table 8, Figure 3, and Figure 4.
| Overall Population (Primary) | Anti-AChR-Ab+ Population | Anti-MuSK-Ab+ Population | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UPLIZNA N = 119 | Placebo N = 117 | UPLIZNA N = 95 | Placebo N = 93 | UPLIZNA N = 24 | Placebo N = 24 | |
| Ab+ = antibody positive; CI = confidence interval; LS = least square; NS = not significant | ||||||
| MG-ADL Score | ||||||
| LS Mean | -4.2 | -2.2 | -4.2 | -2.4 | -3.9 | -1.7 |
| Difference | -1.9 | -1.8 | -2.2 | |||
| 95% CI | (-2.9, -1.0) | (-2.9, -0.7) | (-4.2, -0.2) | |||
| p-value | <0.0001 | 0.0015 | 0.0297 | |||
| QMG Score | ||||||
| LS Mean | -4.8 | -2.3 | -4.4 | -2.0 | -5.2 | -3.0 |
| Difference | -2.5 | -2.5 | -2.3 | |||
| 95% CI | (-3.8, -1.2) | (-3.9, -1.0) | (-5.3, 0.7) | |||
| p-value | 0.0002 | 0.0011 | NS | |||
 |
 |
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
UPLIZNA (inebilizumab-cdon) injection is a clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to slightly yellow solution supplied as:
- One carton containing three 100 mg/10 mL single-dose vials – NDC 75987-150-03
Storage and Handling
- Store in a refrigerator at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) in original carton to protect from light.
- Do not freeze.
- Do not shake.
- Store vials upright.
Mechanism of Action
The mechanism by which inebilizumab-cdon exerts its therapeutic effects in NMOSD, IgG4-RD, and gMG is presumed to involve binding to CD19, a cell surface antigen presents on pre-B and mature B lymphocytes. Following cell surface binding to B lymphocytes, inebilizumab-cdon results in antibody-dependent cellular cytolysis.