Dosage & Administration
By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Vanflyta Prescribing Information
- VANFLYTA prolongs the QT interval in a dose- and concentration-related manner[see. Prior to VANFLYTA administration and periodically, monitor for hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia, and correct deficiencies. Perform ECGs to monitor the QTc at baseline, weekly during induction and consolidation therapy, weekly for at least the first month of maintenance, and periodically thereafter]
12.2 PharmacodynamicsThe exposure-response relationship and time course of pharmacodynamic response for the safety and effectiveness of quizartinib have not been fully characterized.
Cardiac ElectrophysiologyIn vitro studies have shown that quizartinib is a predominant inhibitor of the slow delayed rectifier potassium current, IKs.
The exposure-response analysis predicted a concentration-dependent QTcF interval median prolongation of 18 and 24 ms [upper bound of 2-sided 90% confidence interval (CI): 21 and 27 ms] at the median steady-state Cmaxof quizartinib at the 26.5 mg and 53 mg dose level during maintenance therapy
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)and Drug Interactions (7)].[seeand2.3 Monitoring and Dosage Modifications for Adverse ReactionsInitiate VANFLYTA only if QTcF is less than or equal to 450 ms
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].During induction and consolidation, perform ECGs prior to initiation and then once weekly during VANFLYTA treatment or more frequently as clinically indicated
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].During maintenance, perform ECGs prior to initiation, once weekly for at least the first month following dose initiation and escalation, and thereafter as clinically indicated. Escalate the dose only if QTcF is less than or equal to 450 ms
[see Dosage and Administration (2.2)and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].Correct electrolyte abnormalities (hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia), and if possible, avoid concomitant administration of drugs that prolong the QT interval
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].For recommended dosage modifications due to adverse reactions, see Table 2. For dosage adjustments due to adverse reactions, see Table 3.
Table 2: Recommended Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)and Adverse Reactions (6.1)] Adverse Reaction Recommended Action Grades are in accordance with National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events version 4.03 (NCI CTCAE v4.03). QTcF between 450 ms and 480 ms (Grade 1) - Continue VANFLYTA dose.
QTcF between 481 ms and 500 ms (Grade 2) - Reduce the dose of VANFLYTA (see Table 3) without interruption.
- Resume VANFLYTA at the previous dose in the next cycle if QTcF has decreased to less than 450 ms. Monitor the patient closely for QT prolongation during the first cycle at the increased dose.
QTcF greater than 500 ms (Grade 3) - Interrupt VANFLYTA.
- Resume VANFLYTA at a reduced dose (see Table 3) when QTcF returns to less than 450 ms.
- Maintain the 26.5 mg once daily dose during maintenance if QTcF greater than 500 ms was observed during induction or consolidation.
Recurrent QTcF greater than 500 ms (Grade 3) - Permanently discontinue VANFLYTA if QTcF greater than 500 ms recurs despite appropriate dose reduction and correction/elimination of other risk factors (e.g., serum electrolyte abnormalities, concomitant QT prolonging medications).
Torsades de pointes, polymorphic ventricular tachycardia, signs/symptoms of life-threatening arrhythmia (Grade 4) - Permanently discontinue VANFLYTA.
Grade 3 or 4 non-hematologic adverse reactions - Interrupt VANFLYTA.
- Resume treatment at the previous dose if adverse reaction improves to Grade 1 or less.
- Resume treatment at a reduced dose (see Table 3) if adverse reaction improves to Grade 2.
- Discontinue if Grade 3 or 4 adverse reaction persists beyond 28 days.
Grade 3 or 4 hypokalemia (<3 mmol/L) or hypomagnesemia (<0.4 mmol/L or <0.9 mg/dL) - Interrupt VANFLYTA.
- Correct hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia according to institutional guidelines.
- VANFLYTA may be restarted at the previous dose when the adverse reaction improves to Grade 2 or less without symptoms.
Grade 4 neutropenia or thrombocytopenia after achieving remissionRecommend bone marrow evaluation. - Reduce VANFLYTA dose (see Table 3).
Table 3: Recommended Dosage Adjustments for Adverse Reactions for VANFLYTA Current Dosage Modified Dosage 53 mg once daily 35.4 mg once daily 35.4 mg once daily 26.5 mg once daily 26.5 mg once daily Interrupt 17.7 mg once daily Interrupt ].5.1 QT Prolongation, Torsades de Pointes, and Cardiac ArrestVANFLYTA prolongs the QT interval in a dose- and concentration-dependent manner. The mechanism of QTc interval prolongation is via inhibition of the slow delayed rectifier potassium current, IKs, as compared to all other medications that prolong the QTc interval, which is via the rapid delayed rectifier potassium current, IKr. Therefore, the level of QTc prolongation with VANFLYTA that predicts the risk of cardiac arrhythmias is unclear. Inhibition of IKsand IKrmay leave patients with limited reserve leading to a higher risk of QT prolongation and serious cardiac arrhythmias, including fatal outcomes
[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. Torsades de pointes, ventricular fibrillation, cardiac arrest, and sudden death have occurred in patients treated with VANFLYTA.Of the 1,081 patients with AML treated with VANFLYTA in clinical trials, torsades de pointes occurred in approximately 0.2% of patients, cardiac arrest occurred in 0.6%, including 0.4% with a fatal outcome, and 0.1% of patients experienced ventricular fibrillation
[see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. These severe cardiac arrhythmias occurred predominantly during the induction phase.Of the 265 patients with newly diagnosed FLT3-ITD-positive AML treated with VANFLYTA in combination with chemotherapy in the clinical trial, 2.3% were found to have a QTcF greater than 500 ms and 10% of patients had an increase from baseline QTcF greater than 60 ms. The clinical trial excluded patients with a QTcF ≥450 ms or other factors that increased the risk of QT prolongation or arrhythmic events (e.g., NYHA Class III or IV congestive heart failure, hypokalemia, family history of long QT interval syndrome). Therefore, avoid use in patients who are at significant risk of developing torsades de pointes, including uncontrolled or significant cardiac disease, recent myocardial infarction, heart failure, unstable angina, bradyarrhythmias, tachyarrhythmias, uncontrolled hypertension, high-degree atrioventricular block, severe aortic stenosis, or uncontrolled hypothyroidism.
Do not initiate treatment with VANFLYTA if the QTcF interval is greater than 450 ms. Do not use VANFLYTA in patients with severe hypokalemia, severe hypomagnesemia, long QT syndrome, or in patients with a history of ventricular arrhythmias or torsades de pointes
[see Contraindications (4)].Perform an ECG and correct electrolyte abnormalities prior to initiation of treatment with VANFLYTA. During induction and consolidation, perform an ECG prior to initiation and then once weekly during VANFLYTA treatment or more frequently as clinically indicated. During maintenance, perform ECGs prior to initiation, once weekly for at least the first month following dose initiation and escalation, and as clinically indicated thereafter. Do not escalate the dose if QTcF is greater than 450 ms
[see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].Perform ECG monitoring of the QT interval more frequently in patients who are at significant risk of developing QT interval prolongation and torsades de pointes, or following dose escalation.
Monitor and correct hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia prior to and during treatment with VANFLYTA. Maintain electrolytes in the normal range. Monitor electrolytes and ECGs more frequently in patients who experience diarrhea or vomiting.
Monitor patients more frequently with ECGs if coadministration of VANFLYTA with drugs known to prolong the QT interval is required
[see Drug Interactions (7)].Reduce the VANFLYTA dose when used concomitantly with strong CYP3A inhibitors, as they may increase quizartinib exposure
[see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].Reduce VANFLYTA if QTc increases to greater than 480 ms and less than 500 ms. Interrupt and reduce VANFLYTA if QTc increases to greater than 500 ms. Permanently discontinue VANFLYTA in patients who develop recurrent QTc greater than 500 ms or QTc interval prolongation with signs or symptoms of life-threatening arrhythmia
[see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].VANFLYTA is available only through a restricted program under a REMS
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. - Torsades de pointes and cardiac arrest have occurred in patients receiving VANFLYTA. Do not administer VANFLYTA to patients with severe hypokalemia, severe hypomagnesemia, or long QT syndrome[see.and
4 CONTRAINDICATIONSVANFLYTA is contraindicated in patients with severe hypokalemia, severe hypomagnesemia, long QT syndrome, or in patients with a history of ventricular arrhythmias or torsades de pointes
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].Contraindicated in patients with severe hypokalemia, severe hypomagnesemia, long QT syndrome, or in patients with a history of ventricular arrhythmias or torsades de pointes.
]5.1 QT Prolongation, Torsades de Pointes, and Cardiac ArrestVANFLYTA prolongs the QT interval in a dose- and concentration-dependent manner. The mechanism of QTc interval prolongation is via inhibition of the slow delayed rectifier potassium current, IKs, as compared to all other medications that prolong the QTc interval, which is via the rapid delayed rectifier potassium current, IKr. Therefore, the level of QTc prolongation with VANFLYTA that predicts the risk of cardiac arrhythmias is unclear. Inhibition of IKsand IKrmay leave patients with limited reserve leading to a higher risk of QT prolongation and serious cardiac arrhythmias, including fatal outcomes
[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. Torsades de pointes, ventricular fibrillation, cardiac arrest, and sudden death have occurred in patients treated with VANFLYTA.Of the 1,081 patients with AML treated with VANFLYTA in clinical trials, torsades de pointes occurred in approximately 0.2% of patients, cardiac arrest occurred in 0.6%, including 0.4% with a fatal outcome, and 0.1% of patients experienced ventricular fibrillation
[see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. These severe cardiac arrhythmias occurred predominantly during the induction phase.Of the 265 patients with newly diagnosed FLT3-ITD-positive AML treated with VANFLYTA in combination with chemotherapy in the clinical trial, 2.3% were found to have a QTcF greater than 500 ms and 10% of patients had an increase from baseline QTcF greater than 60 ms. The clinical trial excluded patients with a QTcF ≥450 ms or other factors that increased the risk of QT prolongation or arrhythmic events (e.g., NYHA Class III or IV congestive heart failure, hypokalemia, family history of long QT interval syndrome). Therefore, avoid use in patients who are at significant risk of developing torsades de pointes, including uncontrolled or significant cardiac disease, recent myocardial infarction, heart failure, unstable angina, bradyarrhythmias, tachyarrhythmias, uncontrolled hypertension, high-degree atrioventricular block, severe aortic stenosis, or uncontrolled hypothyroidism.
Do not initiate treatment with VANFLYTA if the QTcF interval is greater than 450 ms. Do not use VANFLYTA in patients with severe hypokalemia, severe hypomagnesemia, long QT syndrome, or in patients with a history of ventricular arrhythmias or torsades de pointes
[see Contraindications (4)].Perform an ECG and correct electrolyte abnormalities prior to initiation of treatment with VANFLYTA. During induction and consolidation, perform an ECG prior to initiation and then once weekly during VANFLYTA treatment or more frequently as clinically indicated. During maintenance, perform ECGs prior to initiation, once weekly for at least the first month following dose initiation and escalation, and as clinically indicated thereafter. Do not escalate the dose if QTcF is greater than 450 ms
[see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].Perform ECG monitoring of the QT interval more frequently in patients who are at significant risk of developing QT interval prolongation and torsades de pointes, or following dose escalation.
Monitor and correct hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia prior to and during treatment with VANFLYTA. Maintain electrolytes in the normal range. Monitor electrolytes and ECGs more frequently in patients who experience diarrhea or vomiting.
Monitor patients more frequently with ECGs if coadministration of VANFLYTA with drugs known to prolong the QT interval is required
[see Drug Interactions (7)].Reduce the VANFLYTA dose when used concomitantly with strong CYP3A inhibitors, as they may increase quizartinib exposure
[see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].Reduce VANFLYTA if QTc increases to greater than 480 ms and less than 500 ms. Interrupt and reduce VANFLYTA if QTc increases to greater than 500 ms. Permanently discontinue VANFLYTA in patients who develop recurrent QTc greater than 500 ms or QTc interval prolongation with signs or symptoms of life-threatening arrhythmia
[see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].VANFLYTA is available only through a restricted program under a REMS
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. - Do not initiate treatment with VANFLYTA or escalate the VANFLYTA dose if the QT interval corrected by Fridericia's formula (QTcF) is greater than 450 ms[see.and
2.3 Monitoring and Dosage Modifications for Adverse ReactionsInitiate VANFLYTA only if QTcF is less than or equal to 450 ms
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].During induction and consolidation, perform ECGs prior to initiation and then once weekly during VANFLYTA treatment or more frequently as clinically indicated
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].During maintenance, perform ECGs prior to initiation, once weekly for at least the first month following dose initiation and escalation, and thereafter as clinically indicated. Escalate the dose only if QTcF is less than or equal to 450 ms
[see Dosage and Administration (2.2)and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].Correct electrolyte abnormalities (hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia), and if possible, avoid concomitant administration of drugs that prolong the QT interval
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].For recommended dosage modifications due to adverse reactions, see Table 2. For dosage adjustments due to adverse reactions, see Table 3.
Table 2: Recommended Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)and Adverse Reactions (6.1)] Adverse Reaction Recommended Action Grades are in accordance with National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events version 4.03 (NCI CTCAE v4.03). QTcF between 450 ms and 480 ms (Grade 1) - Continue VANFLYTA dose.
QTcF between 481 ms and 500 ms (Grade 2) - Reduce the dose of VANFLYTA (see Table 3) without interruption.
- Resume VANFLYTA at the previous dose in the next cycle if QTcF has decreased to less than 450 ms. Monitor the patient closely for QT prolongation during the first cycle at the increased dose.
QTcF greater than 500 ms (Grade 3) - Interrupt VANFLYTA.
- Resume VANFLYTA at a reduced dose (see Table 3) when QTcF returns to less than 450 ms.
- Maintain the 26.5 mg once daily dose during maintenance if QTcF greater than 500 ms was observed during induction or consolidation.
Recurrent QTcF greater than 500 ms (Grade 3) - Permanently discontinue VANFLYTA if QTcF greater than 500 ms recurs despite appropriate dose reduction and correction/elimination of other risk factors (e.g., serum electrolyte abnormalities, concomitant QT prolonging medications).
Torsades de pointes, polymorphic ventricular tachycardia, signs/symptoms of life-threatening arrhythmia (Grade 4) - Permanently discontinue VANFLYTA.
Grade 3 or 4 non-hematologic adverse reactions - Interrupt VANFLYTA.
- Resume treatment at the previous dose if adverse reaction improves to Grade 1 or less.
- Resume treatment at a reduced dose (see Table 3) if adverse reaction improves to Grade 2.
- Discontinue if Grade 3 or 4 adverse reaction persists beyond 28 days.
Grade 3 or 4 hypokalemia (<3 mmol/L) or hypomagnesemia (<0.4 mmol/L or <0.9 mg/dL) - Interrupt VANFLYTA.
- Correct hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia according to institutional guidelines.
- VANFLYTA may be restarted at the previous dose when the adverse reaction improves to Grade 2 or less without symptoms.
Grade 4 neutropenia or thrombocytopenia after achieving remissionRecommend bone marrow evaluation. - Reduce VANFLYTA dose (see Table 3).
Table 3: Recommended Dosage Adjustments for Adverse Reactions for VANFLYTA Current Dosage Modified Dosage 53 mg once daily 35.4 mg once daily 35.4 mg once daily 26.5 mg once daily 26.5 mg once daily Interrupt 17.7 mg once daily Interrupt ]5.1 QT Prolongation, Torsades de Pointes, and Cardiac ArrestVANFLYTA prolongs the QT interval in a dose- and concentration-dependent manner. The mechanism of QTc interval prolongation is via inhibition of the slow delayed rectifier potassium current, IKs, as compared to all other medications that prolong the QTc interval, which is via the rapid delayed rectifier potassium current, IKr. Therefore, the level of QTc prolongation with VANFLYTA that predicts the risk of cardiac arrhythmias is unclear. Inhibition of IKsand IKrmay leave patients with limited reserve leading to a higher risk of QT prolongation and serious cardiac arrhythmias, including fatal outcomes
[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. Torsades de pointes, ventricular fibrillation, cardiac arrest, and sudden death have occurred in patients treated with VANFLYTA.Of the 1,081 patients with AML treated with VANFLYTA in clinical trials, torsades de pointes occurred in approximately 0.2% of patients, cardiac arrest occurred in 0.6%, including 0.4% with a fatal outcome, and 0.1% of patients experienced ventricular fibrillation
[see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. These severe cardiac arrhythmias occurred predominantly during the induction phase.Of the 265 patients with newly diagnosed FLT3-ITD-positive AML treated with VANFLYTA in combination with chemotherapy in the clinical trial, 2.3% were found to have a QTcF greater than 500 ms and 10% of patients had an increase from baseline QTcF greater than 60 ms. The clinical trial excluded patients with a QTcF ≥450 ms or other factors that increased the risk of QT prolongation or arrhythmic events (e.g., NYHA Class III or IV congestive heart failure, hypokalemia, family history of long QT interval syndrome). Therefore, avoid use in patients who are at significant risk of developing torsades de pointes, including uncontrolled or significant cardiac disease, recent myocardial infarction, heart failure, unstable angina, bradyarrhythmias, tachyarrhythmias, uncontrolled hypertension, high-degree atrioventricular block, severe aortic stenosis, or uncontrolled hypothyroidism.
Do not initiate treatment with VANFLYTA if the QTcF interval is greater than 450 ms. Do not use VANFLYTA in patients with severe hypokalemia, severe hypomagnesemia, long QT syndrome, or in patients with a history of ventricular arrhythmias or torsades de pointes
[see Contraindications (4)].Perform an ECG and correct electrolyte abnormalities prior to initiation of treatment with VANFLYTA. During induction and consolidation, perform an ECG prior to initiation and then once weekly during VANFLYTA treatment or more frequently as clinically indicated. During maintenance, perform ECGs prior to initiation, once weekly for at least the first month following dose initiation and escalation, and as clinically indicated thereafter. Do not escalate the dose if QTcF is greater than 450 ms
[see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].Perform ECG monitoring of the QT interval more frequently in patients who are at significant risk of developing QT interval prolongation and torsades de pointes, or following dose escalation.
Monitor and correct hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia prior to and during treatment with VANFLYTA. Maintain electrolytes in the normal range. Monitor electrolytes and ECGs more frequently in patients who experience diarrhea or vomiting.
Monitor patients more frequently with ECGs if coadministration of VANFLYTA with drugs known to prolong the QT interval is required
[see Drug Interactions (7)].Reduce the VANFLYTA dose when used concomitantly with strong CYP3A inhibitors, as they may increase quizartinib exposure
[see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].Reduce VANFLYTA if QTc increases to greater than 480 ms and less than 500 ms. Interrupt and reduce VANFLYTA if QTc increases to greater than 500 ms. Permanently discontinue VANFLYTA in patients who develop recurrent QTc greater than 500 ms or QTc interval prolongation with signs or symptoms of life-threatening arrhythmia
[see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].VANFLYTA is available only through a restricted program under a REMS
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. - Monitor ECGs more frequently if concomitant use of drugs known to prolong the QT interval is required[see.and
2.3 Monitoring and Dosage Modifications for Adverse ReactionsInitiate VANFLYTA only if QTcF is less than or equal to 450 ms
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].During induction and consolidation, perform ECGs prior to initiation and then once weekly during VANFLYTA treatment or more frequently as clinically indicated
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].During maintenance, perform ECGs prior to initiation, once weekly for at least the first month following dose initiation and escalation, and thereafter as clinically indicated. Escalate the dose only if QTcF is less than or equal to 450 ms
[see Dosage and Administration (2.2)and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].Correct electrolyte abnormalities (hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia), and if possible, avoid concomitant administration of drugs that prolong the QT interval
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].For recommended dosage modifications due to adverse reactions, see Table 2. For dosage adjustments due to adverse reactions, see Table 3.
Table 2: Recommended Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)and Adverse Reactions (6.1)] Adverse Reaction Recommended Action Grades are in accordance with National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events version 4.03 (NCI CTCAE v4.03). QTcF between 450 ms and 480 ms (Grade 1) - Continue VANFLYTA dose.
QTcF between 481 ms and 500 ms (Grade 2) - Reduce the dose of VANFLYTA (see Table 3) without interruption.
- Resume VANFLYTA at the previous dose in the next cycle if QTcF has decreased to less than 450 ms. Monitor the patient closely for QT prolongation during the first cycle at the increased dose.
QTcF greater than 500 ms (Grade 3) - Interrupt VANFLYTA.
- Resume VANFLYTA at a reduced dose (see Table 3) when QTcF returns to less than 450 ms.
- Maintain the 26.5 mg once daily dose during maintenance if QTcF greater than 500 ms was observed during induction or consolidation.
Recurrent QTcF greater than 500 ms (Grade 3) - Permanently discontinue VANFLYTA if QTcF greater than 500 ms recurs despite appropriate dose reduction and correction/elimination of other risk factors (e.g., serum electrolyte abnormalities, concomitant QT prolonging medications).
Torsades de pointes, polymorphic ventricular tachycardia, signs/symptoms of life-threatening arrhythmia (Grade 4) - Permanently discontinue VANFLYTA.
Grade 3 or 4 non-hematologic adverse reactions - Interrupt VANFLYTA.
- Resume treatment at the previous dose if adverse reaction improves to Grade 1 or less.
- Resume treatment at a reduced dose (see Table 3) if adverse reaction improves to Grade 2.
- Discontinue if Grade 3 or 4 adverse reaction persists beyond 28 days.
Grade 3 or 4 hypokalemia (<3 mmol/L) or hypomagnesemia (<0.4 mmol/L or <0.9 mg/dL) - Interrupt VANFLYTA.
- Correct hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia according to institutional guidelines.
- VANFLYTA may be restarted at the previous dose when the adverse reaction improves to Grade 2 or less without symptoms.
Grade 4 neutropenia or thrombocytopenia after achieving remissionRecommend bone marrow evaluation. - Reduce VANFLYTA dose (see Table 3).
Table 3: Recommended Dosage Adjustments for Adverse Reactions for VANFLYTA Current Dosage Modified Dosage 53 mg once daily 35.4 mg once daily 35.4 mg once daily 26.5 mg once daily 26.5 mg once daily Interrupt 17.7 mg once daily Interrupt ]5.1 QT Prolongation, Torsades de Pointes, and Cardiac ArrestVANFLYTA prolongs the QT interval in a dose- and concentration-dependent manner. The mechanism of QTc interval prolongation is via inhibition of the slow delayed rectifier potassium current, IKs, as compared to all other medications that prolong the QTc interval, which is via the rapid delayed rectifier potassium current, IKr. Therefore, the level of QTc prolongation with VANFLYTA that predicts the risk of cardiac arrhythmias is unclear. Inhibition of IKsand IKrmay leave patients with limited reserve leading to a higher risk of QT prolongation and serious cardiac arrhythmias, including fatal outcomes
[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. Torsades de pointes, ventricular fibrillation, cardiac arrest, and sudden death have occurred in patients treated with VANFLYTA.Of the 1,081 patients with AML treated with VANFLYTA in clinical trials, torsades de pointes occurred in approximately 0.2% of patients, cardiac arrest occurred in 0.6%, including 0.4% with a fatal outcome, and 0.1% of patients experienced ventricular fibrillation
[see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. These severe cardiac arrhythmias occurred predominantly during the induction phase.Of the 265 patients with newly diagnosed FLT3-ITD-positive AML treated with VANFLYTA in combination with chemotherapy in the clinical trial, 2.3% were found to have a QTcF greater than 500 ms and 10% of patients had an increase from baseline QTcF greater than 60 ms. The clinical trial excluded patients with a QTcF ≥450 ms or other factors that increased the risk of QT prolongation or arrhythmic events (e.g., NYHA Class III or IV congestive heart failure, hypokalemia, family history of long QT interval syndrome). Therefore, avoid use in patients who are at significant risk of developing torsades de pointes, including uncontrolled or significant cardiac disease, recent myocardial infarction, heart failure, unstable angina, bradyarrhythmias, tachyarrhythmias, uncontrolled hypertension, high-degree atrioventricular block, severe aortic stenosis, or uncontrolled hypothyroidism.
Do not initiate treatment with VANFLYTA if the QTcF interval is greater than 450 ms. Do not use VANFLYTA in patients with severe hypokalemia, severe hypomagnesemia, long QT syndrome, or in patients with a history of ventricular arrhythmias or torsades de pointes
[see Contraindications (4)].Perform an ECG and correct electrolyte abnormalities prior to initiation of treatment with VANFLYTA. During induction and consolidation, perform an ECG prior to initiation and then once weekly during VANFLYTA treatment or more frequently as clinically indicated. During maintenance, perform ECGs prior to initiation, once weekly for at least the first month following dose initiation and escalation, and as clinically indicated thereafter. Do not escalate the dose if QTcF is greater than 450 ms
[see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].Perform ECG monitoring of the QT interval more frequently in patients who are at significant risk of developing QT interval prolongation and torsades de pointes, or following dose escalation.
Monitor and correct hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia prior to and during treatment with VANFLYTA. Maintain electrolytes in the normal range. Monitor electrolytes and ECGs more frequently in patients who experience diarrhea or vomiting.
Monitor patients more frequently with ECGs if coadministration of VANFLYTA with drugs known to prolong the QT interval is required
[see Drug Interactions (7)].Reduce the VANFLYTA dose when used concomitantly with strong CYP3A inhibitors, as they may increase quizartinib exposure
[see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].Reduce VANFLYTA if QTc increases to greater than 480 ms and less than 500 ms. Interrupt and reduce VANFLYTA if QTc increases to greater than 500 ms. Permanently discontinue VANFLYTA in patients who develop recurrent QTc greater than 500 ms or QTc interval prolongation with signs or symptoms of life-threatening arrhythmia
[see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].VANFLYTA is available only through a restricted program under a REMS
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. - Reduce the VANFLYTA dose when used concomitantly with strong CYP3A inhibitors, as they may increase quizartinib exposure[see.and
2.4 Dosage Modifications for Strong CYP3A InhibitorsReduce the dosage of VANFLYTA when used concomitantly with strong CYP3A inhibitors as shown in Table 4. If the current dosage is 17.7 mg once daily, interrupt VANFLYTA treatment for the duration of strong CYP3A inhibitor use. After discontinuation of a strong CYP3A inhibitor for 5 half-lives, resume the VANFLYTA dose that was taken before initiating the strong inhibitor
[see Drug Interactions (7)].Table 4: Dosage Adjustments for Concomitant Use with Strong CYP3A Inhibitors Current Dosage Modified Dosage 53 mg once daily 26.5 mg once daily 35.4 mg once daily 17.7 mg once daily 26.5 mg once daily 17.7 mg once daily ]5.1 QT Prolongation, Torsades de Pointes, and Cardiac ArrestVANFLYTA prolongs the QT interval in a dose- and concentration-dependent manner. The mechanism of QTc interval prolongation is via inhibition of the slow delayed rectifier potassium current, IKs, as compared to all other medications that prolong the QTc interval, which is via the rapid delayed rectifier potassium current, IKr. Therefore, the level of QTc prolongation with VANFLYTA that predicts the risk of cardiac arrhythmias is unclear. Inhibition of IKsand IKrmay leave patients with limited reserve leading to a higher risk of QT prolongation and serious cardiac arrhythmias, including fatal outcomes
[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. Torsades de pointes, ventricular fibrillation, cardiac arrest, and sudden death have occurred in patients treated with VANFLYTA.Of the 1,081 patients with AML treated with VANFLYTA in clinical trials, torsades de pointes occurred in approximately 0.2% of patients, cardiac arrest occurred in 0.6%, including 0.4% with a fatal outcome, and 0.1% of patients experienced ventricular fibrillation
[see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. These severe cardiac arrhythmias occurred predominantly during the induction phase.Of the 265 patients with newly diagnosed FLT3-ITD-positive AML treated with VANFLYTA in combination with chemotherapy in the clinical trial, 2.3% were found to have a QTcF greater than 500 ms and 10% of patients had an increase from baseline QTcF greater than 60 ms. The clinical trial excluded patients with a QTcF ≥450 ms or other factors that increased the risk of QT prolongation or arrhythmic events (e.g., NYHA Class III or IV congestive heart failure, hypokalemia, family history of long QT interval syndrome). Therefore, avoid use in patients who are at significant risk of developing torsades de pointes, including uncontrolled or significant cardiac disease, recent myocardial infarction, heart failure, unstable angina, bradyarrhythmias, tachyarrhythmias, uncontrolled hypertension, high-degree atrioventricular block, severe aortic stenosis, or uncontrolled hypothyroidism.
Do not initiate treatment with VANFLYTA if the QTcF interval is greater than 450 ms. Do not use VANFLYTA in patients with severe hypokalemia, severe hypomagnesemia, long QT syndrome, or in patients with a history of ventricular arrhythmias or torsades de pointes
[see Contraindications (4)].Perform an ECG and correct electrolyte abnormalities prior to initiation of treatment with VANFLYTA. During induction and consolidation, perform an ECG prior to initiation and then once weekly during VANFLYTA treatment or more frequently as clinically indicated. During maintenance, perform ECGs prior to initiation, once weekly for at least the first month following dose initiation and escalation, and as clinically indicated thereafter. Do not escalate the dose if QTcF is greater than 450 ms
[see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].Perform ECG monitoring of the QT interval more frequently in patients who are at significant risk of developing QT interval prolongation and torsades de pointes, or following dose escalation.
Monitor and correct hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia prior to and during treatment with VANFLYTA. Maintain electrolytes in the normal range. Monitor electrolytes and ECGs more frequently in patients who experience diarrhea or vomiting.
Monitor patients more frequently with ECGs if coadministration of VANFLYTA with drugs known to prolong the QT interval is required
[see Drug Interactions (7)].Reduce the VANFLYTA dose when used concomitantly with strong CYP3A inhibitors, as they may increase quizartinib exposure
[see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].Reduce VANFLYTA if QTc increases to greater than 480 ms and less than 500 ms. Interrupt and reduce VANFLYTA if QTc increases to greater than 500 ms. Permanently discontinue VANFLYTA in patients who develop recurrent QTc greater than 500 ms or QTc interval prolongation with signs or symptoms of life-threatening arrhythmia
[see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].VANFLYTA is available only through a restricted program under a REMS
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. - Because of the risk of QT prolongation, VANFLYTA is available only through a restricted program under a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) called the VANFLYTA REMS[see.]
5.2 VANFLYTA REMSVANFLYTA is available only through a restricted distribution program under a REMS called the VANFLYTA REMS because of the serious risk of QT prolongation, torsades de pointes, and cardiac arrest
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].Notable requirements of the VANFLYTA REMS include the following:
- Prescribers must be certified in the VANFLYTA REMS by enrolling and completing training.
- Prescribers must counsel patients receiving VANFLYTA about the risk of QT prolongation, torsades de pointes, and cardiac arrest, and provide patients with a Patient Wallet Card.
- Pharmacies that dispense VANFLYTA must be certified with the VANFLYTA REMS and must verify prescribers are certified through the VANFLYTA REMS.
Further information about the VANFLYTA REMS is available at www.VANFLYTAREMS.com or by telephone at 1-855-212-6670.
VANFLYTA is indicated in combination with standard cytarabine and anthracycline induction and cytarabine consolidation, and as maintenance monotherapy following consolidation chemotherapy, for the treatment of adult patients with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia (AML) that is FLT3 internal tandem duplication (ITD)-positive as detected by an FDA-approved test
Select patients for the treatment of AML with VANFLYTA based on the presence of FLT3-ITD mutation positivity
The efficacy of VANFLYTA in combination with chemotherapy was evaluated in QuANTUM-First (NCT02668653), a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of 539 patients with newly diagnosed FLT3-ITD positive AML. FLT3-ITD status was determined prospectively with a clinical trial assay and verified retrospectively using the companion diagnostic LeukoStrat®CDx
Patients were stratified by age (<60 versus ≥60 years), white blood cell count at diagnosis (<40×109/L versus ≥40×109/L), and region (North America, Europe versus Asia, other regions). Patients were randomized (1:1) to receive VANFLYTA (n=268) or placebo (n=271) in combination with induction and consolidation therapy and as maintenance monotherapy according to the initial assignment, as follows: a)
The two treatment groups were generally balanced with respect to baseline demographics and disease characteristics. Of the 539 randomized patients, the median age was 56 years (range 20-75 years); 46% were male; 60% were White, 29% were Asian, 1% were Black, and 10% were other races. Eighty-four percent had an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) baseline performance status of 0 or 1. The majority of the patients (72%) had intermediate risk cytogenetics at baseline. FLT3-ITD variant allelic frequency (VAF) was 3-25% in 36% of patients, >25-50% in 52% of patients, and >50% in 12% of patients. NPM1 mutations were identified in 52% of patients.
A second course of induction was administered to 20% of the patients, 65% initiated at least one cycle of consolidation, and 39% initiated maintenance. Among the patients who entered maintenance, 64% completed at least 12 cycles, 36% completed at least 24 cycles, and 16% completed all 36 planned cycles of maintenance. Twenty-nine percent (157/539) of the patients underwent HSCT in first complete remission (CR). The overall rate of HSCT (including the following settings: first CR, induction failure, or salvage after relapse) was 54% (144/268) in the VANFLYTA plus standard chemotherapy arm versus 47% (128/271) in the placebo plus standard chemotherapy arm. All patients were followed for survival.
Efficacy was established on the basis of overall survival (OS), measured from the date of randomization until death by any cause. The primary analysis was conducted after a minimum follow-up of 24 months after the randomization of the last patient. The study demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in OS for the VANFLYTA arm [hazard ratio (HR) 0.78; 95% CI: 0.62, 0.98; 2-sided p=0.0324] (see Figure 1).
| Figure 1: Kaplan-Meier Curve for Overall Survival in QuANTUM-First |
|---|
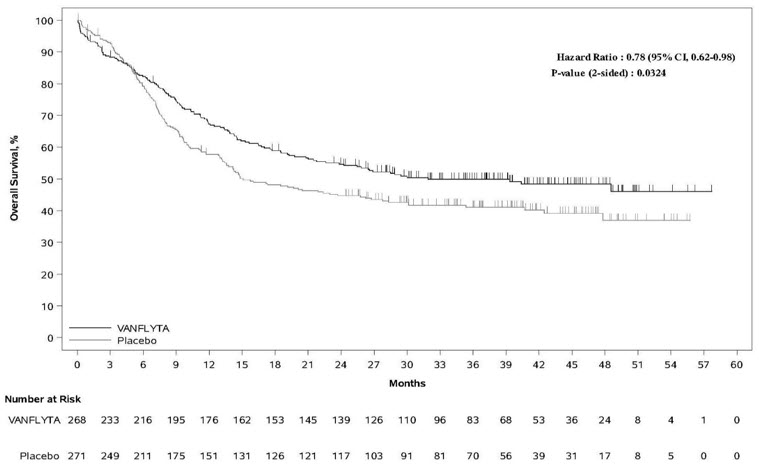 |
In an exploratory subgroup analysis of the 89/208 (43%) of patients who received maintenance therapy with VANFLYTA or placebo following consolidation chemotherapy, the OS HR was 0.40 (95% CI: 0.19, 0.84). Of 119/208 (57%) of patients who received maintenance therapy with VANFLYTA or placebo following HSCT, the OS HR was 1.62 (95% CI: 0.62, 4.22).
The CR rate in the VANFLYTA arm was 55% (95% CI: 48.7, 60.9) with a median duration of CR of 38.6 months (95% CI: 21.9, NE), and the CR rate in the placebo arm was 55% (95% CI: 49.2, 61.4) with a median duration of CR of 12.4 months (95% CI: 8.8, 22.7).

- Take VANFLYTA tablets orally once daily with or without food at approximately the same time each day. ()
2.2 Recommended Dosage- A treatment course consists of up to 2 cycles of VANFLYTA in combination with induction cytarabine and anthracycline, up to 4 cycles of VANFLYTA in combination with high-dose cytarabine consolidation, and up to 36 cycles of VANFLYTA as maintenance therapy[see Clinical Studies (14)]or until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. VANFLYTA maintenance therapy should be initiated following consolidation chemotherapy upon blood count recovery of absolute neutrophil count >500/mm3and platelet count >50,000/mm3.
- See Table 1for the recommended dosage of VANFLYTA by phase of therapy.
Table 1: VANFLYTA Dosage Regimen VANFLYTA Initiation InductionPatients can receive up to 2 cycles of induction. ConsolidationPatients can receive up to 4 cycles of consolidation. Maintenance Starting on Day 8
(for 7 + 3 regimen)For 5 + 2 regimen as the second induction cycle, VANFLYTA will be given on Days 6 to 19.Starting on Day 6 Starting on Day 1 Dose35.4 mg orally once daily 35.4 mg orally once daily - Administer 26.5 mg orally once daily Days 1 through 14 of the first cycle if QTcF is less than or equal to 450 ms.
- Increase the dose to 53 mg once daily on Day 15 of the first cycle if QTcF is less than or equal to 450 ms. Maintain the 26.5 mg once daily dose if QTcF greater than 500 ms was observed during induction or consolidation.
Duration
(28-day cycles)Two weeks in each cycle (Days 8 to 21) Two weeks in each cycle (Days 6 to 19) - Once daily with no break between cycles for up to 36 cycles
For patients who proceed to hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), VANFLYTA should be stopped 7 days before the start of a conditioning regimen.
Administer VANFLYTA orally with or without food at approximately the same time each day. Swallow tablets whole. Do not cut, crush, or chew the tablets. If a dose of VANFLYTA is vomited, do not administer a replacement dose; wait until the next scheduled dose is due. If a dose of VANFLYTA is missed or not taken at the usual time, administer the dose as soon as possible on the same day and return to the usual schedule the following day. The patient should not take two doses on the same day.
- A treatment course consists of up to 2 cycles of VANFLYTA in combination with induction cytarabine and anthracycline, up to 4 cycles of VANFLYTA in combination with high-dose cytarabine consolidation, and up to 36 cycles of VANFLYTA as maintenance therapy
- See Full Prescribing Information for recommended VANFLYTA dosage regimen and dosage modifications. (,
2.2 Recommended Dosage- A treatment course consists of up to 2 cycles of VANFLYTA in combination with induction cytarabine and anthracycline, up to 4 cycles of VANFLYTA in combination with high-dose cytarabine consolidation, and up to 36 cycles of VANFLYTA as maintenance therapy[see Clinical Studies (14)]or until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. VANFLYTA maintenance therapy should be initiated following consolidation chemotherapy upon blood count recovery of absolute neutrophil count >500/mm3and platelet count >50,000/mm3.
- See Table 1for the recommended dosage of VANFLYTA by phase of therapy.
Table 1: VANFLYTA Dosage Regimen VANFLYTA Initiation InductionPatients can receive up to 2 cycles of induction. ConsolidationPatients can receive up to 4 cycles of consolidation. Maintenance Starting on Day 8
(for 7 + 3 regimen)For 5 + 2 regimen as the second induction cycle, VANFLYTA will be given on Days 6 to 19.Starting on Day 6 Starting on Day 1 Dose35.4 mg orally once daily 35.4 mg orally once daily - Administer 26.5 mg orally once daily Days 1 through 14 of the first cycle if QTcF is less than or equal to 450 ms.
- Increase the dose to 53 mg once daily on Day 15 of the first cycle if QTcF is less than or equal to 450 ms. Maintain the 26.5 mg once daily dose if QTcF greater than 500 ms was observed during induction or consolidation.
Duration
(28-day cycles)Two weeks in each cycle (Days 8 to 21) Two weeks in each cycle (Days 6 to 19) - Once daily with no break between cycles for up to 36 cycles
For patients who proceed to hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), VANFLYTA should be stopped 7 days before the start of a conditioning regimen.
Administer VANFLYTA orally with or without food at approximately the same time each day. Swallow tablets whole. Do not cut, crush, or chew the tablets. If a dose of VANFLYTA is vomited, do not administer a replacement dose; wait until the next scheduled dose is due. If a dose of VANFLYTA is missed or not taken at the usual time, administer the dose as soon as possible on the same day and return to the usual schedule the following day. The patient should not take two doses on the same day.
,2.3 Monitoring and Dosage Modifications for Adverse ReactionsInitiate VANFLYTA only if QTcF is less than or equal to 450 ms
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].During induction and consolidation, perform ECGs prior to initiation and then once weekly during VANFLYTA treatment or more frequently as clinically indicated
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].During maintenance, perform ECGs prior to initiation, once weekly for at least the first month following dose initiation and escalation, and thereafter as clinically indicated. Escalate the dose only if QTcF is less than or equal to 450 ms
[see Dosage and Administration (2.2)and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].Correct electrolyte abnormalities (hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia), and if possible, avoid concomitant administration of drugs that prolong the QT interval
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].For recommended dosage modifications due to adverse reactions, see Table 2. For dosage adjustments due to adverse reactions, see Table 3.
Table 2: Recommended Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)and Adverse Reactions (6.1)] Adverse Reaction Recommended Action Grades are in accordance with National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events version 4.03 (NCI CTCAE v4.03). QTcF between 450 ms and 480 ms (Grade 1) - Continue VANFLYTA dose.
QTcF between 481 ms and 500 ms (Grade 2) - Reduce the dose of VANFLYTA (see Table 3) without interruption.
- Resume VANFLYTA at the previous dose in the next cycle if QTcF has decreased to less than 450 ms. Monitor the patient closely for QT prolongation during the first cycle at the increased dose.
QTcF greater than 500 ms (Grade 3) - Interrupt VANFLYTA.
- Resume VANFLYTA at a reduced dose (see Table 3) when QTcF returns to less than 450 ms.
- Maintain the 26.5 mg once daily dose during maintenance if QTcF greater than 500 ms was observed during induction or consolidation.
Recurrent QTcF greater than 500 ms (Grade 3) - Permanently discontinue VANFLYTA if QTcF greater than 500 ms recurs despite appropriate dose reduction and correction/elimination of other risk factors (e.g., serum electrolyte abnormalities, concomitant QT prolonging medications).
Torsades de pointes, polymorphic ventricular tachycardia, signs/symptoms of life-threatening arrhythmia (Grade 4) - Permanently discontinue VANFLYTA.
Grade 3 or 4 non-hematologic adverse reactions - Interrupt VANFLYTA.
- Resume treatment at the previous dose if adverse reaction improves to Grade 1 or less.
- Resume treatment at a reduced dose (see Table 3) if adverse reaction improves to Grade 2.
- Discontinue if Grade 3 or 4 adverse reaction persists beyond 28 days.
Grade 3 or 4 hypokalemia (<3 mmol/L) or hypomagnesemia (<0.4 mmol/L or <0.9 mg/dL) - Interrupt VANFLYTA.
- Correct hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia according to institutional guidelines.
- VANFLYTA may be restarted at the previous dose when the adverse reaction improves to Grade 2 or less without symptoms.
Grade 4 neutropenia or thrombocytopenia after achieving remissionRecommend bone marrow evaluation. - Reduce VANFLYTA dose (see Table 3).
Table 3: Recommended Dosage Adjustments for Adverse Reactions for VANFLYTA Current Dosage Modified Dosage 53 mg once daily 35.4 mg once daily 35.4 mg once daily 26.5 mg once daily 26.5 mg once daily Interrupt 17.7 mg once daily Interrupt )2.4 Dosage Modifications for Strong CYP3A InhibitorsReduce the dosage of VANFLYTA when used concomitantly with strong CYP3A inhibitors as shown in Table 4. If the current dosage is 17.7 mg once daily, interrupt VANFLYTA treatment for the duration of strong CYP3A inhibitor use. After discontinuation of a strong CYP3A inhibitor for 5 half-lives, resume the VANFLYTA dose that was taken before initiating the strong inhibitor
[see Drug Interactions (7)].Table 4: Dosage Adjustments for Concomitant Use with Strong CYP3A Inhibitors Current Dosage Modified Dosage 53 mg once daily 26.5 mg once daily 35.4 mg once daily 17.7 mg once daily 26.5 mg once daily 17.7 mg once daily - A treatment course consists of up to 2 cycles of VANFLYTA in combination with induction cytarabine and anthracycline, up to 4 cycles of VANFLYTA in combination with high-dose cytarabine consolidation, and up to 36 cycles of VANFLYTA as maintenance therapy
Tablets:
- 17.7 mg quizartinib, white, round, film-coated, debossed with "DSC511"
- 26.5 mg quizartinib, yellow, round, film-coated, debossed with "DSC512"
Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. (
There are no data on the presence of quizartinib or its metabolites in human milk, or the effects on the breastfed child or milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in a breastfed child, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with VANFLYTA and for one month after the last dose.
VANFLYTA is contraindicated in patients with severe hypokalemia, severe hypomagnesemia, long QT syndrome, or in patients with a history of ventricular arrhythmias or torsades de pointes
VANFLYTA prolongs the QT interval in a dose- and concentration-dependent manner. The mechanism of QTc interval prolongation is via inhibition of the slow delayed rectifier potassium current, IKs, as compared to all other medications that prolong the QTc interval, which is via the rapid delayed rectifier potassium current, IKr. Therefore, the level of QTc prolongation with VANFLYTA that predicts the risk of cardiac arrhythmias is unclear. Inhibition of IKsand IKrmay leave patients with limited reserve leading to a higher risk of QT prolongation and serious cardiac arrhythmias, including fatal outcomes
Of the 1,081 patients with AML treated with VANFLYTA in clinical trials, torsades de pointes occurred in approximately 0.2% of patients, cardiac arrest occurred in 0.6%, including 0.4% with a fatal outcome, and 0.1% of patients experienced ventricular fibrillation
Of the 265 patients with newly diagnosed FLT3-ITD-positive AML treated with VANFLYTA in combination with chemotherapy in the clinical trial, 2.3% were found to have a QTcF greater than 500 ms and 10% of patients had an increase from baseline QTcF greater than 60 ms. The clinical trial excluded patients with a QTcF ≥450 ms or other factors that increased the risk of QT prolongation or arrhythmic events (e.g., NYHA Class III or IV congestive heart failure, hypokalemia, family history of long QT interval syndrome). Therefore, avoid use in patients who are at significant risk of developing torsades de pointes, including uncontrolled or significant cardiac disease, recent myocardial infarction, heart failure, unstable angina, bradyarrhythmias, tachyarrhythmias, uncontrolled hypertension, high-degree atrioventricular block, severe aortic stenosis, or uncontrolled hypothyroidism.
Do not initiate treatment with VANFLYTA if the QTcF interval is greater than 450 ms. Do not use VANFLYTA in patients with severe hypokalemia, severe hypomagnesemia, long QT syndrome, or in patients with a history of ventricular arrhythmias or torsades de pointes
Perform an ECG and correct electrolyte abnormalities prior to initiation of treatment with VANFLYTA. During induction and consolidation, perform an ECG prior to initiation and then once weekly during VANFLYTA treatment or more frequently as clinically indicated. During maintenance, perform ECGs prior to initiation, once weekly for at least the first month following dose initiation and escalation, and as clinically indicated thereafter. Do not escalate the dose if QTcF is greater than 450 ms
Perform ECG monitoring of the QT interval more frequently in patients who are at significant risk of developing QT interval prolongation and torsades de pointes, or following dose escalation.
Monitor and correct hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia prior to and during treatment with VANFLYTA. Maintain electrolytes in the normal range. Monitor electrolytes and ECGs more frequently in patients who experience diarrhea or vomiting.
Monitor patients more frequently with ECGs if coadministration of VANFLYTA with drugs known to prolong the QT interval is required
Reduce the VANFLYTA dose when used concomitantly with strong CYP3A inhibitors, as they may increase quizartinib exposure
Reduce VANFLYTA if QTc increases to greater than 480 ms and less than 500 ms. Interrupt and reduce VANFLYTA if QTc increases to greater than 500 ms. Permanently discontinue VANFLYTA in patients who develop recurrent QTc greater than 500 ms or QTc interval prolongation with signs or symptoms of life-threatening arrhythmia
VANFLYTA is available only through a restricted program under a REMS