Xospata prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
120 mg orally once daily. (2.2 )
Patient Selection
Select patients for the treatment of AML with XOSPATA based on the presence of FLT3 mutations in the blood or bone marrow [see Clinical Studies (14 )]. Information on FDA-approved tests for the detection of a FLT3 mutation in AML is available at http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics .
Recommended Dosage
The recommended starting dose of XOSPATA is 120 mg orally once daily with or without food. Response may be delayed. In the absence of disease progression or unacceptable toxicity, treatment for a minimum of 6 months is recommended to allow time for a clinical response.
Do not break or crush XOSPATA tablets. Administer XOSPATA tablets orally about the same time each day. If a dose of XOSPATA is missed or not taken at the usual time, administer the dose as soon as possible on the same day, and at least 12 hours prior to the next scheduled dose. Return to the normal schedule the following day. Do not administer 2 doses within 12 hours.
Dosage Modifications
Assess blood counts and blood chemistries, including creatine phosphokinase, prior to the initiation of XOSPATA, at least once weekly for the first month, once every other week for the second month, and once monthly for the duration of therapy. Perform electrocardiogram (ECG) prior to initiation of treatment with gilteritinib, on days 8 and 15 of cycle 1, and prior to the start of the next two subsequent cycles.
Interrupt dosing or reduce dose for toxicities as per Table 1 .
Adverse Reaction | Recommended Action |
Differentiation Syndrome |
|
Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome |
|
QTc interval greater than 500 msec |
|
QTc interval increased by >30 msec on ECG on day 8 of cycle 1 |
|
Pancreatitis |
|
Other Grade 3or higher toxicity considered related to treatment. |
|

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Xospata prescribing information
WARNING: DIFFERENTIATION SYNDROME
Patients treated with XOSPATA have experienced symptoms of differentiation syndrome, which can be fatal or life-threatening if not treated. Symptoms may include fever, dyspnea, hypoxia, pulmonary infiltrates, pleural or pericardial effusions, rapid weight gain or peripheral edema, hypotension, or renal dysfunction. If differentiation syndrome is suspected, initiate corticosteroid therapy and hemodynamic monitoring until symptom resolution [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 ) and Adverse Reactions (6.1 )] .
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
XOSPATA is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of adult patients who have relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with a FLT3 mutation as detected by an FDA-approved test. (1.1 )
Relapsed or Refractory Acute Myeloid Leukemia
XOSPATA is indicated for the treatment of adult patients who have relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with a FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3) mutation as detected by an FDA-approved test.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
120 mg orally once daily. (2.2 )
Patient Selection
Select patients for the treatment of AML with XOSPATA based on the presence of FLT3 mutations in the blood or bone marrow [see Clinical Studies (14 )]. Information on FDA-approved tests for the detection of a FLT3 mutation in AML is available at http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics .
Recommended Dosage
The recommended starting dose of XOSPATA is 120 mg orally once daily with or without food. Response may be delayed. In the absence of disease progression or unacceptable toxicity, treatment for a minimum of 6 months is recommended to allow time for a clinical response.
Do not break or crush XOSPATA tablets. Administer XOSPATA tablets orally about the same time each day. If a dose of XOSPATA is missed or not taken at the usual time, administer the dose as soon as possible on the same day, and at least 12 hours prior to the next scheduled dose. Return to the normal schedule the following day. Do not administer 2 doses within 12 hours.
Dosage Modifications
Assess blood counts and blood chemistries, including creatine phosphokinase, prior to the initiation of XOSPATA, at least once weekly for the first month, once every other week for the second month, and once monthly for the duration of therapy. Perform electrocardiogram (ECG) prior to initiation of treatment with gilteritinib, on days 8 and 15 of cycle 1, and prior to the start of the next two subsequent cycles.
Interrupt dosing or reduce dose for toxicities as per Table 1 .
Adverse Reaction | Recommended Action |
Differentiation Syndrome |
|
Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome |
|
QTc interval greater than 500 msec |
|
QTc interval increased by >30 msec on ECG on day 8 of cycle 1 |
|
Pancreatitis |
|
Other Grade 3or higher toxicity considered related to treatment. |
|
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets: 40 mg as light yellow, round-shaped, film-coated tablets debossed with the Astellas logo and ‘235’ on the same side.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Lactation: Advise women not to breastfeed. (8.2 )
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings from animal studies (see Data) and its mechanism of action, XOSPATA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1 )] .
There are no available data on XOSPATA use in pregnant women to inform a drug-associated risk of adverse developmental outcomes. In animal reproduction studies, administration of gilteritinib to pregnant rats during organogenesis caused adverse developmental outcomes including embryo-fetal lethality, suppressed fetal growth, and teratogenicity at maternal exposures (AUC 24 ) approximately 0.4 times the AUC 24 in patients receiving the recommended dose ( see Data ). Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
Adverse outcomes in pregnancy occur regardless of the health of the mother or the use of medications. The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2%-4% and 15%-20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In an embryo-fetal development study in rats, pregnant animals received oral doses of gilteritinib of 0, 0.3, 3, 10, and 30 mg/kg/day during the period of organogenesis. Maternal findings at 30 mg/kg/day (resulting in exposures approximately 0.4 times the AUC 24 in patients receiving the recommended dose) included decreased body weight and food consumption. Administration of gilteritinib at the dose of 30 mg/kg/day also resulted in embryo-fetal death (postimplantation loss), decreased fetal body and placental weight, and decreased numbers of ossified sternebrae and sacral and caudal vertebrae, and increased incidence of fetal gross external (anasarca, local edema, exencephaly, cleft lip, cleft palate, short tail, and umbilical hernia), visceral (microphthalmia; atrial and/or ventricular defects; and malformed/absent kidney, and malpositioned adrenal, and ovary), and skeletal (sternoschisis, absent rib, fused rib, fused cervical arch, misaligned cervical vertebra, and absent thoracic vertebra) abnormalities.
Single oral administration of [ 14 C] gilteritinib to pregnant rats resulted in transfer of radioactivity to the fetus similar to that observed in maternal plasma on day 14 of gestation. In addition, distribution profiles of radioactivity in most maternal tissues and the fetus on day 18 of gestation were similar to that on day 14 of gestation.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of gilteritinib and/or its metabolites in human milk, the effects on the breastfed child, or the effects on milk production. Following administration of radiolabeled gilteritinib to lactating rats, milk concentrations of radioactivity were higher than radioactivity in maternal plasma at 4 and 24 hours post-dose. In animal studies, gilteritinib and/or its metabolite(s) were distributed to the tissues in infant rats via the milk. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in a breastfed child, advise a lactating woman not to breastfeed during treatment with XOSPATA and for 2 months after the last dose.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
XOSPATA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1 )] .
Pregnancy testing
Pregnancy testing is recommended for females of reproductive potential within seven days prior to initiating XOSPATA treatment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1 )] .
Contraception
Females
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for 6 months after the last dose of XOSPATA.
Males
Advise males of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for 4 months after the last dose of XOSPATA.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatric Use
Of the 319 patients in clinical studies of XOSPATA, 43% were age 65 years or older, and 13% were 75 years or older. No overall differences in effectiveness or safety were observed between patients age 65 years or older and younger patients.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES): Discontinue XOSPATA in patients who develop PRES. (2.3 , 5.2 , 6.1 )
- Prolonged QT Interval: Interrupt and reduce XOSPATA dosage in patients who have a QTcF >500 msec. Correct hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia prior to and during XOSPATA administration. (2.3 , 5.3 , 12.2 , 6.1 )
- Pancreatitis: Interrupt and reduce the dose in patients who develop pancreatitis. (2.3 , 5.4 )
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: XOSPATA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Advise of the potential risk to a fetus and to use effective contraception. (5.5 , 8.1 , 8.3 )
Differentiation Syndrome
Of 319 patients treated with XOSPATA in the clinical trials, 3% experienced differentiation syndrome. Differentiation syndrome is associated with rapid proliferation and differentiation of myeloid cells and may be life-threatening or fatal if not treated. Symptoms and other clinical findings of differentiation syndrome in patients treated with XOSPATA included fever, dyspnea, pleural effusion, pericardial effusion, pulmonary edema, hypotension, rapid weight gain, peripheral edema, rash, and renal dysfunction. Some cases had concomitant acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis. Differentiation syndrome occurred as early as 1 day and up to 82 days after XOSPATA initiation and has been observed with or without concomitant leukocytosis. Of the 11 patients who experienced differentiation syndrome, 9 (82%) recovered after treatment or after dose interruption of XOSPATA.
If differentiation syndrome is suspected, initiate dexamethasone 10 mg IV every 12 hours (or an equivalent dose of an alternative oral or IV corticosteroid) and hemodynamic monitoring until improvement. Taper corticosteroids after resolution of symptoms and administer corticosteroids for a minimum of 3 days. Symptoms of differentiation syndrome may recur with premature discontinuation of corticosteroid treatment. If severe signs and/or symptoms persist for more than 48 hours after initiation of corticosteroids, interrupt XOSPATA until signs and symptoms are no longer severe [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 )] .
Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome
Of 319 patients treated with XOSPATA in the clinical trials, 1% experienced posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) with symptoms including seizure and altered mental status. Symptoms have resolved after discontinuation of XOSPATA. A diagnosis of PRES requires confirmation by brain imaging, preferably magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Discontinue XOSPATA in patients who develop PRES [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 ) and Adverse Reactions (6.1 )] .
Prolonged QT Interval
XOSPATA has been associated with prolonged cardiac ventricular repolarization (QT interval). Of the 317 patients with a post-baseline QTc measurement on treatment with XOSPATA in the clinical trial, 1% were found to have a QTc interval greater than 500 msec and 7% of patients had an increase from baseline QTc greater than 60 msec. Perform electrocardiogram (ECG) prior to initiation of treatment with gilteritinib, on days 8 and 15 of cycle 1, and prior to the start of the next two subsequent cycles. Interrupt and reduce XOSPATA dosage in patients who have a QTcF >500 msec [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 ), Adverse Reactions (6.1 ) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2 )] .
Hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia may increase the QT prolongation risk. Correct hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia prior to and during XOSPATA administration.
Pancreatitis
Of 319 patients treated with XOSPATA in the clinical trials, 4% experienced pancreatitis. Evaluate patients who develop signs and symptoms of pancreatitis. Interrupt and reduce the dose of XOSPATA in patients who develop pancreatitis [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 )] .
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings in animals and its mechanism of action, XOSPATA can cause embryo-fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. In animal reproduction studies, administration of gilteritinib to pregnant rats during organogenesis caused embryo-fetal lethality, suppressed fetal growth and teratogenicity at maternal exposures (AUC 24 ) approximately 0.4 times the AUC 24 in patients receiving the recommended dose. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with XOSPATA and for 6 months after the last dose of XOSPATA. Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with XOSPATA and for 4 months after the last dose of XOSPATA. Pregnant women, patients becoming pregnant while receiving XOSPATA or male patients with pregnant female partners should be apprised of the potential risk to the fetus [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1 , 8.3 ) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.1 )] .
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Differentiation syndrome [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )]
- Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 )]
- Prolonged QT interval [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 )]
- Pancreatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4 )]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety profile of XOSPATA is based on 319 patients with relapsed or refractory AML treated with gilteritinib 120 mg daily in three clinical trials. The median duration of exposure to XOSPATA was 3.6 months (range 0.1 to 43.4 months).
Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 2% of patients receiving XOSPATA. These included cardiac arrest (1%) and one case each of differentiation syndrome and pancreatitis. The most frequent (≥5%) nonhematological serious adverse reactions reported in patients were fever (13%), dyspnea (9%), renal impairment (8%), transaminase increased (6%) and noninfectious diarrhea (5%).
Of the 319 patients, 91 (29%) required a dose interruption due to an adverse reaction; the most common adverse reactions leading to dose interruption were aspartate aminotransferase increased (6%), alanine aminotransferase increased (6%) and fever (4%). Twenty patients (6%) required a dose reduction due to an adverse reaction. Twenty-two (7%) discontinued XOSPATA treatment permanently due to an adverse reaction. The most common (>1%) adverse reactions leading to discontinuation were aspartate aminotransferase increased (2%) and alanine aminotransferase increased (2%).
Overall, for the 319 patients, the most frequent (≥10%) all-grade nonhematological adverse reactions reported in patients were transaminase increased (51%), myalgia/arthralgia (50%), fatigue/malaise (44%), fever (41%), mucositis (41%), edema (40%), rash (36%), noninfectious diarrhea (35%), dyspnea (35%), nausea (30%), cough (28%), constipation (28%), eye disorders (25%), headache (24%), dizziness (22%), hypotension (22%), vomiting (21%), renal impairment (21%), abdominal pain (18%), neuropathy (18%), insomnia (15%) and dysgeusia (11%). The most frequent (≥5%) grade ≥3 nonhematological adverse reactions reported in patients were transaminase increased (21%), dyspnea (12%), hypotension (7%), mucositis (7%), myalgia/arthralgia (7%), and fatigue/malaise (6%). Shifts to grades 3-4 nonhematologic laboratory abnormalities included phosphate decreased 42/309 (14%), alanine aminotransferase increased 41/317 (13%), sodium decreased 37/314 (12%), aspartate aminotransferase increased 33/317 (10%), calcium decreased 19/312 (6%), creatine kinase increased 20/317 (6%), triglycerides increased 18/310 (6%), creatinine increased 10/316 (3%), and alkaline phosphatase increased 5/317 (2%).
Adverse reactions reported in the first 30 days of therapy on the ADMIRAL Study [see Clinical Studies (14 )] are shown in Tables 2 and 3 , according to whether patients were preselected for high intensity or low intensity chemotherapy.
Adverse Reaction | Any Grade n (%) | Grade ≥3 n (%) | ||
XOSPATA (120 mg daily) n=149 | Chemotherapy n=68 | XOSPATA (120 mg daily) n=149 | Chemotherapy n=68 | |
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||||
Myalgia/arthralgia Grouped terms: arthralgia, back pain, bone pain, flank pain, limb discomfort, medial tibial stress syndrome, myalgia, muscle twitching, musculoskeletal discomfort, musculoskeletal pain, muscle spasms, neck pain, non-cardiac chest pain, pain and pain in extremity | 56 (38) | 20 (29) | 1 (1) | 3 (4) |
Investigations | ||||
Transaminase increased Grouped terms: aspartate aminotransferase increased, alanine aminotransferase increased, blood alkaline phosphatase increased, gamma-glutamyltransferase increased, hepatic enzyme increased, hepatic function abnormal, hepatoxicity, liver function test increased and transaminases increased | 46 (31) | 11 (16) | 15 (10) | 5 (7) |
General disorders and administration site conditions | ||||
Fatigue/malaise Grouped terms: asthenia, fatigue, lethargy and malaise | 36 (24) | 9 (13) | 1 (1) | 2 (3) |
Fever | 25 (17) | 21 (31) | 2 (1) | 4 (6) |
Edema Grouped terms: edema, edema peripheral, face edema, fluid overload, generalized edema, hypervolemia, localized edema, periorbital edema and swelling face | 20 (13) | 13 (19) | 0 | 0 |
Gastrointestinal disorders | ||||
Constipation | 29 (20) | 10 (15) | 0 | 0 |
Mucositis Grouped terms: aphthous ulcer, colitis, enteritis, esophageal pain, gingival pain, large intestinal ulcer, laryngeal inflammation, lip blister, lip ulceration, mouth hemorrhage, mouth ulceration, mucosal inflammation, oral discomfort, oral pain, oropharyngeal pain, proctalgia, stomatitis, swollen tongue, tongue discomfort and tongue ulceration | 18 (12) | 30 (44) | 0 | 5 (7) |
Nausea | 23 (15) | 26 (38) | 0 | 0 |
Abdominal pain Grouped terms: abdominal discomfort, abdominal pain, abdominal pain lower, abdominal pain upper and gastrointestinal pain | 16 (11) | 16 (24) | 0 | 0 |
Blood and lymphatic system disorder | ||||
Febrile neutropenia | 26 (17) | 30 (44) | 26 (17) | 30 (44) |
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||||
Rash Grouped terms: acne, dermatitis bullous, dermatitis contact, drug eruption, eczema asteatotic, erythema, hyperkeratosis, lichenoid keratosis, palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome, rash, rash maculo-papular, rash papular, skin exfoliation, skin lesion and skin hyperpigmentation | 23 (15) | 21 (31) | 1 (1) | 2 (3) |
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | ||||
Dyspnea Grouped terms: acute respiratory distress syndrome, dyspnea, dyspnea exertional, hypoxia, pulmonary edema, respiratory failure, tachypnea and wheezing | 20 (13) | 9 (13) | 1 (1) | 6 (9) |
Cough | 18 (12) | 5 (7) | 1 (1) | 0 |
Nervous system disorders | ||||
Neuropathy Grouped terms: hyperesthesia, hypoesthesia, neuralgia, neuropathy peripheral, peripheral sensory neuropathy and paresthesia | 19 (13) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Dizziness Grouped terms: coordination abnormal and dizziness | 17 (11) | 2 (3) | 0 | 0 |
Headache | 17 (11) | 12 (18) | 0 | 0 |
Adverse Reaction | Any Grade n (%) | Grade ≥3 n (%) | ||
XOSPATA (120 mg daily) n=97 | Chemotherapy n=41 | XOSPATA (120 mg daily) n=97 | Chemotherapy n=41 | |
Investigations | ||||
Transaminase increased Grouped terms: aspartate aminotransferase increased, alanine aminotransferase increased, blood alkaline phosphatase increased and transaminases increased | 35 (36) | 6 (15) | 9 (9) | 1 (2) |
Blood and lymphatic system disorder | ||||
Febrile neutropenia | 26 (27) | 5 (12) | 25 (26) | 5 (12) |
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||||
Myalgia/arthralgia Grouped terms: arthralgia, arthritis, back pain, limb discomfort, myalgia, muscle contracture, muscle spasms, myositis, non-cardiac chest pain, pain, pain in extremity and polyarthritis | 21 (22) | 7 (17) | 2 (2) | 0 |
General disorders and administration site conditions | ||||
Fatigue/malaise Grouped terms: asthenia, fatigue and malaise | 20 (21) | 9 (22) | 4 (4) | 1 (2) |
Edema Grouped terms: edema, face edema, localized edema, edema peripheral, peripheral swelling, periorbital edema, scrotal edema and swelling face | 19 (20) | 5 (12) | 1 (1) | 0 |
Fever | 11 (11) | 7 (17) | 0 | 0 |
Gastrointestinal disorders | ||||
Mucositis Grouped terms: colitis, mouth hemorrhage, mouth ulceration, mucosal inflammation, oropharyngeal pain, proctalgia, stomatitis, tongue discomfort and tongue ulceration | 19 (20) | 7 (17) | 1 (1) | 1 (2) |
Constipation | 13 (13) | 5 (12) | 1 (1) | 0 |
Diarrhea | 12 (12) | 2 (5) | 0 | 0 |
Nausea | 10 (10) | 7 (17) | 0 | 0 |
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | ||||
Dyspnea Grouped terms: acute respiratory failure, dyspnea, hypoxia and respiratory failure | 11 (11) | 2 (5) | 3 (3) | 2 (5) |
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||||
Rash Grouped terms: dermatitis acneiform, dermatitis bullous, dermatitis exfoliative, erythema, rash, rash maculo-papular, rash papular, rosacea and skin ulcer | 10 (10) | 2 (5) | 2 (2) | 0 |
Other clinically significant adverse reactions occurring in ≤10% of patients included: electrocardiogram QT prolonged (9%), hypersensitivity• (8%), pancreatitis• (5%), cardiac failure• (4%), pericardial effusion (4%), acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis (3%), differentiation syndrome (3%), pericarditis/myocarditis• (2%), large intestine perforation (1%), and posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (1%).
•Grouped terms: cardiac failure (cardiac failure, cardiac failure congestive, cardiomegaly, cardiomyopathy, chronic left ventricular failure, and ejection fraction decreased), hypersensitivity (anaphylactic reaction, angioedema, dermatitis allergic, drug hypersensitivity, erythema multiforme, hypersensitivity, and urticaria), pancreatitis (amylase increased, lipase increased, pancreatitis, pancreatitis acute), pericarditis/myocarditis (myocarditis, pericardial hemorrhage, pericardial rub, and pericarditis).
Selected post-baseline laboratory values that were observed in patients with relapsed or refractory AML are shown in Table 4 .
Pre-selected High Intensity Chemotherapy Subgroup | Pre-selected Low Intensity Chemotherapy Subgroup | |||
XOSPATA (120 mg daily) | Chemotherapy | XOSPATA (120 mg daily) | Chemotherapy | |
Alanine aminotransferase increased | 7/149 (5%) | 1/66 (2%) | 7/95 (7%) | 1/41 (2%) |
Alkaline phosphatase increased | 1/149 (1%) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Aspartate aminotransferase increased | 8/149 (5%) | 2/65 (3%) | 5/95 (5%) | 0 |
Calcium decreased | 2/149 (1%) | 3/65 (5%) | 3/94 (3%) | 0 |
Creatine kinase increased | 1/149 (1%) | 0 | 1/95 (1%) | 0 |
Phosphatase decreased | 4/144 (3%) | 6/65 (9%) | 4/93 (4%) | 3/38 (8%) |
Sodium decreased | 7/148 (5%) | 5/65 (8%) | 6/93 (6%) | 2/41 (5%) |
Triglycerides increased | 1/146 (1%) | 0 | 2/94 (2%) | 0 |
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Combined P-gp and Strong CYP3A Inducers: Avoid concomitant use. (7.1 )
- Strong CYP3A Inhibitors: Consider alternative therapies. If the concomitant use of strong CYP3A inhibitors cannot be avoided, monitor patients more frequently for XOSPATA adverse reactions. (2.3 , 7.1 )
- P-gp, BCRP, OCT1 Substrates: Decrease the dose of the substrates when coadministered with gilteritinib and as clinically indicated. (7.2 )
7.1 Effect of Other Drugs on XOSPATA
Combined P-gp and Strong CYP3A Inducers
Concomitant use of XOSPATA with a combined P-gp and strong CYP3A inducer decreases gilteritinib exposure which may decrease XOSPATA efficacy [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] . Avoid concomitant use of XOSPATA with combined P-gp and strong CYP3A inducers.
Strong CYP3A Inhibitors
Concomitant use of XOSPATA with a strong CYP3A inhibitor increases gilteritinib exposure [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] . Consider alternative therapies that are not strong CYP3A inhibitors. If the concomitant use of these inhibitors is considered essential for the care of the patient, monitor patient more frequently for XOSPATA adverse reactions. Interrupt and reduce XOSPATA dosage in patients with serious or life-threatening toxicity [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 )] .
Effect of XOSPATA on Other Drugs
Drugs that Target 5HT2B Receptor or Sigma Nonspecific Receptor
Concomitant use of gilteritinib may reduce the effects of drugs that target the 5HT 2B receptor or the sigma nonspecific receptor (e.g., escitalopram, fluoxetine, sertraline). Avoid concomitant use of these drugs with XOSPATA unless their use is considered essential for the care of the patient [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] .
P-gp, BCRP, and OCT1 Substrates
Based on in vitro data, gilteritinib is a P-gp, breast cancer resistant protein (BCRP), and organic cation transporter 1 (OCT1) inhibitor. Coadministration of gilteritinib may increase the exposure of P-gp, BCRP, and OCT1 substrates, which may increase the incidence and severity of adverse reactions of these substrates [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )].
For P-gp, BCRP, or OCT1 substrates where small concentration changes may lead to serious adverse reactions, decrease the dose or modify the dosing frequency of such substrate and monitor for adverse reactions as recommended in the respective prescribing information.
DESCRIPTION
Gilteritinib is a kinase inhibitor. The chemical name is 2-Pyrazinecarboxamide, 6-ethyl-3-[[3-methoxy-4-[4-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-1-piperidinyl] phenyl] amino]-5-[(tetrahydro-2 H -pyran-4-yl) amino]-, (2 E )-2-butenedioate (2:1). The molecular weight is 1221.50 and the molecular formula is (C 29 H 44 N 8 O 3 ) 2 ·C 4 H 4 O 4 . The structural formula is:
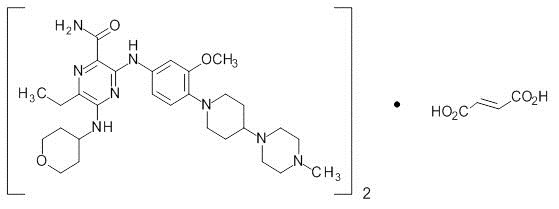
Gilteritinib fumarate is a light yellow to yellow powder or crystals that is sparingly soluble in water and very slightly soluble in anhydrous ethanol.
XOSPATA (gilteritinib) is provided as a tablet for oral administration. Each tablet contains 40 mg of gilteritinib active ingredient as free base (corresponding to 44.2 mg gilteritinib fumarate). The inactive ingredients are ferric oxide, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose, low-substituted hydroxypropyl cellulose, mannitol, magnesium stearate, polyethylene glycol, talc, and titanium dioxide.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Gilteritinib is a small molecule that inhibits multiple receptor tyrosine kinases, including FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3). Gilteritinib demonstrated the ability to inhibit FLT3 receptor signaling and proliferation in cells exogenously expressing FLT3 including FLT3-ITD, tyrosine kinase domain mutations (TKD) FLT3-D835Y and FLT3-ITD-D835Y, and it induced apoptosis in leukemic cells expressing FLT3-ITD.
Pharmacodynamics
In patients with relapsed or refractory AML administered gilteritinib 120 mg, substantial (>90%) inhibition of FLT3 phosphorylation was rapid (within 24 hours after first dose) and sustained, as characterized by an ex vivo plasma inhibitory activity (PIA) assay.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
The effect of XOSPATA 120 mg once a day on the QTc interval has been evaluated in patients, which showed an absence of large mean increases (i.e., 20 msec) in the QTc interval.
Of 317 patients with a post-baseline QTc measurement on treatment with gilteritinib at 120 mg in clinical trials, 4 patients (1.3%) experienced a QTcF >500 msec. Additionally, across all doses 2.3% of patients with relapse/refractory AML had a maximum post-baseline QTcF interval >500 msec [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 )].
Pharmacokinetics
The following pharmacokinetic parameters were observed following administration of gilteritinib 120 mg once daily, unless otherwise specified.
Gilteritinib exposure (C max and AUC 24 ) increases proportionally with once daily doses ranging from 20 mg to 450 mg (0.17 to 3.75 times the recommended dosage) in patients with relapsed or refractory AML. Gilteritinib mean (±SD) steady-state C max is 374 ng/mL (±190) and AUC 24 is 6943 ng•hr/mL (±3221). Steady-state plasma levels are reached within 15 days of dosing with an approximate 10-fold accumulation.
Absorption
The time to maximum gilteritinib concentration (t max ) observed is approximately between 4 and 6 hours post dose in the fasted state.
Effect of Food
In healthy adults administered a single gilteritinib 40 mg dose (0.3 times the recommended dosage), gilteritinib C max decreased by 26% and AUC decreased by less than 10% when co-administered with a high-fat meal (approximately 800 to 1,000 total calories with 500 to 600 fat calories, 250 carbohydrate calories, 150 protein calories) compared to a fasted state. Median t max was delayed 2 hours when gilteritinib was administered with a high-fat meal.
Distribution
The population mean (%CV) estimates of apparent central and peripheral volume of distribution were 1092 L (9.22%) and 1100 L (4.99%), respectively, which may indicate extensive tissue distribution. In vivo , gilteritinib is approximately 94% bound to human plasma proteins. In vitro , gilteritinib is primarily bound to human serum albumin.
Elimination
The estimated half-life of gilteritinib is 113 hours, and the estimated apparent clearance is 14.85 L/h.
Metabolism
Gilteritinib is primarily metabolized via CYP3A4 in vitro . At steady state, the primary metabolites in humans include M17 (formed via N-dealkylation and oxidation), M16 and M10 (both formed via N‑dealkylation). None of these 3 metabolites exceeded 10% of overall parent exposure.
Excretion
After a single radiolabeled dose, gilteritinib is excreted in feces with 64.5% of the total administered dose recovered in feces. Of the total radiolabeled dose of gilteritinib, 16.4% was recovered in urine as unchanged drug and metabolites.
Specific Populations
Age (20-87 years), sex, race, mild (Child-Pugh Class A) or moderate (Child-Pugh Class B) hepatic impairment and mild (creatinine clearance (CLCr) 50-80 mL/min) or moderate (CLCr 30-50 mL/min) renal impairment do not have clinically meaningful effects on the pharmacokinetics of gilteritinib.
The effect of severe hepatic (Child-Pugh Class C) or severe renal impairment (CLCr ≤ 29 mL/min) on gilteritinib pharmacokinetics is unknown.
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies
Combined P-gp and Strong CYP3A Inducers :
Gilteritinib C max decreased approximately 30% and AUC decreased approximately 70% when co-administered with rifampin (a combined P-gp and strong CYP3A inducer).
Strong CYP3A Inhibitors :
Gilteritinib C max increased approximately 20% and AUC increased approximately 120% when co-administered with itraconazole (a strong CYP3A inhibitor).
Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors :
Gilteritinib C max increased approximately 16% and AUC increased approximately 40% when co-administered with fluconazole (a moderate CYP3A inhibitor).
CYP3A Substrates :
Midazolam (a CYP3A substrate) C max and AUC increased approximately 10% when co-administered with gilteritinib.
MATE1 Substrates :
Cephalexin (a MATE1 substrate) C max and AUC decreased by less than 10% when co-administered with gilteritinib.
In Vitro Studies
Gilteritinib inhibits human 5HT 2B receptor or sigma nonspecific receptors, which may reduce the effects of drugs that target these receptors such as escitalopram, fluoxetine and sertraline.
Gilteritinib is a substrate of P-gp and BCRP. Gilteritinib inhibits BCRP, P-gp and OCT1 at clinically relevant concentrations.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies have not been performed with gilteritinib.
Gilteritinib was not mutagenic in a bacterial mutagenesis (Ames) assay and was not clastogenic in a chromosome aberration test assay in Chinese hamster lung cells. Gilteritinib was positive for the induction of micronuclei in mouse bone marrow cells from 65 mg/kg (195 mg/m 2 ) the mid dose tested (approximately 2.6 times the recommended human dose of 120 mg).
The effect of XOSPATA on human fertility is unknown. Administration of 10 mg/kg/day gilteritinib in the 4-week study in dogs (12 days of dosing) resulted in degeneration and necrosis of germ cells and spermatid giant cell formation in the testis as well as single cell necrosis of the epididymal duct epithelia of the epididymal head.
Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
In the 13-week oral repeated dose toxicity studies in rats and dogs, target organs of toxicity included the eye and kidney.
CLINICAL STUDIES
Relapsed or Refractory Acute Myeloid Leukemia
The efficacy of XOSPATA was assessed in the ADMIRAL Trial (NCT02421939 ) , which included adult patients with relapsed or refractory AML having a FLT3 ITD, D835, or I836 mutation by the LeukoStrat ® CDx FLT3 Mutation Assay. XOSPATA was given orally at a starting dose of 120 mg daily until unacceptable toxicity or lack of clinical benefit.
First Interim Analysis
The efficacy of XOSPATA was established on the basis of the rate of complete remission (CR)/CR with partial hematological recovery (CRh), the duration of CR/CRh (DOR), and the rate of conversion from transfusion dependence to transfusion independence at the first interim analysis in the ADMIRAL trial (n=138). The median follow-up was 4.6 months (95% CI: 2.8, 15.8). Fourteen patients were still in remission at the time of the first interim DOR analysis. The efficacy results are shown in Table 5 . For patients who achieved a CR/CRh, the median time to first response was 3.6 months (range, 0.9 to 9.6 months). The CR/CRh rate was 29 of 126 in patients with FLT3-ITD or FLT3-ITD/TKD and 0 of 12 in patients with FLT3-TKD only.
Among the 106 patients who were dependent on red blood cell (RBC) and/or platelet transfusions at baseline, 33 (31.1%) became independent of RBC and platelet transfusions during any 56-day post-baseline period. For the 32 patients who were independent of both RBC and platelet transfusions at baseline, 17 (53.1%) remained transfusion-independent during any 56-day post-baseline period.
Remission Rate | XOSPATA N=138 |
CR CR was defined as an absolute neutrophil count ≥1.0 x 10 9 /L, platelets ≥100 x 10 9 /L, normal marrow differential with <5% blasts, must have been red blood cells, platelet transfusion independent and no evidence of extramedullary leukemia. /CRh CRh was defined as marrow blasts <5%, partial hematologic recovery absolute neutrophil count ≥0.5 x 10 9 /L and platelets ≥50 x 10 9 /L, no evidence of extramedullary leukemia and could not have been classified as CR. n/N (%) | 29/138 (21) |
95% CI The 95% CI rate was calculated using the exact method based on binomial distribution. | 14.5, 28.8 |
Median DOR DOR was defined as the time from the date of either first CR or CRh until the date of a documented relapse of any type. Deaths were counted as events. (months) | 4.6 |
Range (months) | 0.1 to 15.8 Response was ongoing. |
CR n/N (%) | 16/138 (11.6) |
95% CI | 6.8, 18.1 |
Median DOR(months) | 8.6 |
Range (months) | 1 to 13.8 |
CRh n/N (%) | 13/138 (9.4) |
95% CI | 5.1, 15.6 |
Median DOR(months) | 2.9 |
Range (months) | 0.1 to 15.8 |
CI: confidence interval; NE: not estimable; NR: not reached; Only responses prior to HSCT were included in response rate. | |
Final Analysis
The final analysis of the ADMIRAL trial included 371 adult patients randomized 2:1 to receive XOSPATA 120 mg once daily (n=247) over continuous 28-day cycles or a prespecified chemotherapy regimen (n=124). Randomization was stratified by response to first-line AML therapy and prespecified chemotherapy. The prespecified chemotherapy regimens included high intensity combinations (MEC and FLAG-IDA) and low intensity regimens (LDAC and AZA).
The demographic and disease characteristics of the randomized patients are shown in Table 6 .
Demographic and Disease Characteristics | Xospata (120 mg daily) N=247 | Chemotherapy N=124 |
Demographics | ||
Median Age (Years) (Range) | 62 (20, 84) | 62 (19, 85) |
Age Categories, n (%) | ||
<65 years | 141 (57) | 75 (60) |
≥65 years | 106 (43) | 49 (40) |
Sex, n (%) | ||
Male | 116 (47) | 54 (44) |
Female | 131 (53) | 70 (57) |
Race, n (%) | ||
White | 145 (59) | 75 (60) |
Asian | 69 (28) | 33 (27) |
Black or African American | 14 (6) | 7 (6) |
Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander | 1 (0.4) | 0 |
Other | 5 (2) | 1 (0.8) |
Unknown/Missing | 13 (5) | 8 (6) |
Baseline ECOG PS, n (%) | ||
0-1 | 206 (83) | 105 (85) |
≥2 | 41 (17) | 19 (15) |
Disease Characteristics | ||
Untreated relapse AML, n (%) | 151 (61) | 74 (60) |
Primary refractory AML, n (%) | 96 (39) | 49 (40) |
Refractory relapse AML, n (%) | 0 | 1 (0.8) |
Number of Relapses, n (%) | ||
0 | 96 (39) | 49 (40) |
1 | 149 (60) | 74 (60) |
2 or more | 2 (0.8) | 1 (0.8) |
Median number of relapses (Range) | 1 (0, 2) | 1 (0, 2) |
Transfusion Dependent at Baseline, n (%) Patients were defined as transfusion dependent at baseline if they were dosed and received any red blood cell or platelet transfusions within the 56-day baseline period. | 197 (80) | 97 (89) |
FLT3 Mutation Status, n (%) | ||
ITD alone | 215 (87) | 113 (91) |
TKD alone | 21 (9) | 10 (8) |
ITD and TKD | 7 (3) | 0 |
Prior Use of FLT3 Inhibitor Prior use of FLT3 inhibitor is defined as “Yes” if patients received prior AML therapy of midostaurin, sorafenib or quizartinib; otherwise, prior use of FLT3 inhibitor was assigned as “No.” , n (%) | ||
No | 215 (87) | 110 (89) |
Yes | 32 (13) | 14 (11) |
Prespecified Chemotherapy | ||
High Intensity | 149 (60) | 75 (60) |
MEC MEC: mitoxantrone 8 mg/m 2 , etoposide 100 mg/m 2 and cytarabine 1000 mg/m 2 once daily by IV for 5 days | 33 (27) | |
FLAG-IDA FLAG-IDA: granulocyte colony-stimulating factor 300 mcg/m 2 once daily by SC days 1 to 5, fludarabine 30 mg/m 2 once daily by IV days 2 through 6, cytarabine 2000 mg/m 2 once daily by IV for days 2 through 6, idarubicin 10 mg/m 2 once daily by IV days 2 through 4 | 42 (34) | |
Low Intensity | 98 (40) | 49 (40) |
LDAC LDAC: cytarabine 20 mg twice daily by subcutaneous (SC) or intravenous (IV) for 10 days | 17 (14) | |
AZA AZA: azacitidine 75 mg/m 2 once daily by SC or IV for 7 days | 32 (26) | |
| ||
The final analysis included an assessment of OS, measured from the date of randomization until death by any cause. At the time of analysis, median follow-up was 17.8 months (range, 14.9 to 19.1). Patients randomized to the XOSPATA arm had significantly longer survival compared to the chemotherapy arm (HR 0.64; 95% CI: 0.49 – 0.83; 1-sided p-value: 0.0004). Figure 1 and Table 7 show the results of the OS analysis.
Exploratory subgroup analyses demonstrated that the hazard ratio for survival was 0.66 (95% CI: 0.47 – 0.93) for patients in the high intensity chemotherapy stratum and 0.56 (95% CI: 0.38 – 0.84) for patients in the low intensity chemotherapy stratum. The CR rates are shown in Table 7 . For patients on XOSPATA and chemotherapy arms, the CR rates were 15.4% (95% CI: 10% – 22.3%) and 16% (95% CI: 8.6% – 26.3%), respectively, for patients in the high intensity chemotherapy stratum, and 12.2% (95% CI: 6.5% – 20.4%) and 2% (95% CI 0.1% – 10.9%), respectively, for patients in the low intensity chemotherapy stratum.
| CI: confidence interval; Only responses prior to HSCT were included in response rate. | ||
XOSPATA N=247 | Chemotherapy N=124 | |
Overall Survival | ||
Deaths, n (%) | 171 (69.2%) | 90 (72.6%) |
Median in months (95% CI) | 9.3 (7.7, 10.7) | 5.6 (4.7, 7.3) |
Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.64 (0.49, 0.83) | |
p-value (1-sided) | 0.0004 | |
Complete Remission | ||
CR, n (%) | 35 (14.2%) | 13 (10.5%) |
(95% CI The 95% CI rate was calculated using the exact method based on binomial distribution. ) | (10.1, 19.2) | (5.7, 17.3) |
Median DOR DOR was defined as the time from the date of first remission until the date of a documented relapse. (range) (months) | 14.8 (0.6 to 23.1+) | 1.8 (<0.1+ to 1.8) |
Figure 1: Kaplan-Meier Plot of Overall Survival in ADMIRAL Trial
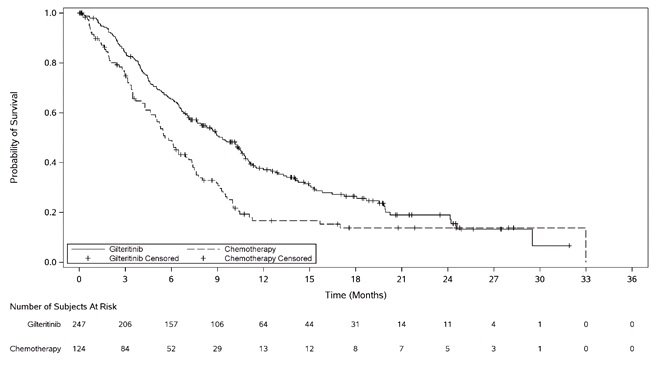
In the final analysis, the CR/CRh rate in the gilteritinib arm was 22.6% (55/243) and the DOR was 7.4 months (range, <0.1+ to 23.1+). For patients who achieved a CR/CRh, the median time to first response was 2 months (range, 0.9 to 9.6 months). The CR/CRh rate was 49 of 215 in patients with FLT3-ITD only, 3 of 7 in patients with FLT3-ITD/TKD and 3 of 21 in patients with FLT3-TKD only.
Among the 197 patients who were dependent on red blood cell (RBC) and/or platelet transfusions at baseline, 68 (34.5%) became independent of RBC and platelet transfusions during any 56-day post-baseline period. For the 49 patients who were independent of both RBC and platelet transfusions at baseline, 29 (59.2%) remained transfusion-independent during any 56-day post-baseline period
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
XOSPATA (gilteritinib) 40 mg tablets are supplied as light yellow, round-shaped, film-coated tablets debossed with the Astellas logo and ‘235’ on the same side. XOSPATA tablets are available in the following package size:
- Bottles of 90 tablets with Child Resistant Closure (NDC 0469-1425-90)
Storage
Store XOSPATA tablets at 20ºC to 25ºC (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15ºC to 30ºC (59°F to 86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Keep in original container until dispensed. Protect from light, moisture and humidity.
Mechanism of Action
Gilteritinib is a small molecule that inhibits multiple receptor tyrosine kinases, including FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3). Gilteritinib demonstrated the ability to inhibit FLT3 receptor signaling and proliferation in cells exogenously expressing FLT3 including FLT3-ITD, tyrosine kinase domain mutations (TKD) FLT3-D835Y and FLT3-ITD-D835Y, and it induced apoptosis in leukemic cells expressing FLT3-ITD.