Xphozah
(Tenapanor)Dosage & Administration
By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Xphozah Prescribing Information
XPHOZAH is indicated to reduce serum phosphorus in adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD) on dialysis as add-on therapy in patients who have an inadequate response to phosphate binders or who are intolerant of any dose of phosphate binder therapy.
- Recommended dosage: 30 mg orally twice daily before the morning and evening meals ().
2.1 Recommended DosageThe recommended dosage is 30 mg orally twice daily before the morning and evening meals. Monitor serum phosphorus and adjust the dosage as needed to manage gastrointestinal tolerability.
- Manage serum phosphorus levels and tolerability with dosage adjustments ().
2.1 Recommended DosageThe recommended dosage is 30 mg orally twice daily before the morning and evening meals. Monitor serum phosphorus and adjust the dosage as needed to manage gastrointestinal tolerability.
- Take just prior to the first and last meals of the day ().
2.2 Administration Instructions- Instruct patients to take XPHOZAH just prior to the first and last meals of the day[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
- Instruct patients not to take XPHOZAH right before a hemodialysis session, and instead take right before the next meal following dialysis, as patients may experience diarrhea after taking XPHOZAH[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Instruct patients who miss a dose to skip the missed dose and take the next dose at the regular time.
- Instruct patients to take XPHOZAH just prior to the first and last meals of the day
- Instruct patients not to take right before a hemodialysis session, and instead take right before the next meal following dialysis ().
2.2 Administration Instructions- Instruct patients to take XPHOZAH just prior to the first and last meals of the day[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
- Instruct patients not to take XPHOZAH right before a hemodialysis session, and instead take right before the next meal following dialysis, as patients may experience diarrhea after taking XPHOZAH[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Instruct patients who miss a dose to skip the missed dose and take the next dose at the regular time.
- Instruct patients to take XPHOZAH just prior to the first and last meals of the day
XPHOZAH tablets available as:
10 mg tenapanor supplied as a yellow, oval, biconvex film-coated tablet debossed with "
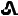 " on one side and "T10" on the other side.
" on one side and "T10" on the other side.20 mg tenapanor supplied as a brown, oval, biconvex film-coated tablet debossed with "
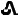 " on one side and "T20" on the other side.
" on one side and "T20" on the other side.30 mg tenapanor supplied as a red, oval, biconvex film-coated tablet debossed with "
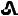 " on one side and "T30" on the other side.
" on one side and "T30" on the other side.
Tenapanor is essentially non-absorbed systemically, with plasma concentrations below the limit of quantification (less than 0.5 ng/mL) following oral administration
Tenapanor is minimally absorbed following repeated twice daily oral administration. Plasma concentrations of tenapanor were below the limit of quantitation (less than 0.5 ng/mL) in the majority of samples from subjects following single and repeated oral administration of tenapanor 30 mg twice daily. Therefore, standard pharmacokinetic parameters such as area under the curve (AUC), maximum concentration (Cmax), and half-life (t1/2) could not be determined.
Plasma protein binding of tenapanor and its major metabolite, M1, is approximately 99% and 97%, respectively
Tenapanor is metabolized primarily by CYP3A4/5 and low levels of its major metabolite, M1, are detected in plasma. The Cmaxof M1 is approximately 3 ng/mL after a single dose of XPHOZAH 30 mg and 14 ng/mL at steady state following repeated dosing of XPHOZAH 30 mg twice daily in healthy subjects. Based on a cross-study comparison, the steady state plasma concentration of M1 in CKD patients on dialysis (eGFR less than 15 mL/min/1.73 m2) was not notably different from those of healthy subjects given similar doses of XPHOZAH.
Following administration of a single 15 mg radiolabeled14C- XPHOZAH dose to healthy subjects, approximately 70% of the radioactivity was excreted in feces through 120 hours post-dose (79% through 240 hours post-dose), mostly as the parent drug accounting for 65% of dose within 144 hours post-dose. Approximately 9% of the administered dose was recovered in urine, primarily as metabolites. M1 is excreted in urine unchanged accounting for 1.5% of dose within 144 hours post-dose.
Tenapanor and M1 did not inhibit CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, and CYP2D6
Tenapanor and M1 did not induce CYP1A2 and CYP2B6 in vitro.
No significant inhibition or induction of CYP3A4 enzyme using midazolam as a substrate was observed when XPHOZAH 50 mg was administered twice a day for 13 days in healthy subjects.
No significant effect on PepT1 activity using cefadroxil as a substrate was observed when tenapanor 50 mg was administered twice a day for 12 days in healthy subjects.
No significant effect on P-gp and CYP2C9 activity using digoxin and warfarin as a substrate was observed when tenapanor 30 mg was administered twice a day for 12 days in healthy subjects.
Following co-administration of a single dose of XPHOZAH 50 mg with repeated doses of itraconazole 200 mg, a CYP3A4 inhibitor, the mean AUC and Cmaxof M1 was decreased 50% in healthy subjects. Plasma concentrations of tenapanor were mostly below the limit of quantitation (less than 0.5 ng/mL) after co-administration of itraconazole.
Following administration of a single 20 mg enalapril dose with tenapanor (30 mg BID) at steady state, the mean AUC and Cmaxof enalapril was decreased by 64% and 69%, respectively, in healthy subjects. The mean AUC and Cmaxof enalaprilat was decreased by 52% and 68%, respectively, in healthy subjects.
Tenapanor inhibited OATP2B1, but is not an inhibitor of P-gp, BCRP, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, and PEPT1. M1 did not inhibit P-gp, BCRP, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OAT1, OAT3, OCT2, MATE1, and MATE2-K.
Tenapanor is not a substrate of P-gp, BCRP, OATP1B1, and OATP1B3. M1 is a substrate of P-gp
In vitro studies indicated the potential for tenapanor to bind to sevelamer carbonate but did not suggest the potential to bind to calcium carbonate or calcium acetate. In a clinical study, there did not appear to be a pharmacodynamic interaction between sevelamer carbonate (800 mg TID) and tenapanor (14 mg BID).
The available data on XPHOZAH exposure from a small number of pregnant women have not identified any drug associated risk for major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. In reproduction studies with tenapanor in pregnant rats and rabbits, no adverse fetal effects were observed in rats at 0.2 times the maximum recommended human dose and in rabbits at doses up to 15 times the maximum recommended human dose (based on body surface area)
The carcinogenic potential of tenapanor was assessed in a 6-month carcinogenicity study in Tg rasH2 mice and in a 2-year carcinogenicity study in rats. Tenapanor was not tumorigenic at oral doses up to 100 mg/kg/day (approximately 7.5 times the recommended human dose, based on the body surface area) in male mice and 800 mg/kg/day (approximately 65 times the maximum recommended human dose, based on the body surface area) for female mice. Tenapanor was not tumorigenic in male and female rats at oral doses up to 5 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.8 times the recommended human dose, based on the body surface area). The major metabolite of tenapanor, M1, was not tumorigenic in Tg rasH2 mice at oral doses up to 165 mg/kg/day (approximately 13.3 times the maximum recommended human dose, based on the body surface area).
Tenapanor was not genotoxic in the in vitro bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assays, an in vitro chromosomal aberration assay in cultured human peripheral blood lymphocytes or the in vivo micronucleus assays in mice and rats. The M1 metabolite of tenapanor was not genotoxic in the Ames assay and in an in vitro micronucleus assay using L5178Y cells.
Tenapanor had no effect on fertility or reproductive function in male rats at oral doses up to 10 mg/kg/day (approximately 1.6 times the recommended human dose, based on the body surface area) and in female mice at oral doses up to 50 mg/kg/day (approximately 4 times the recommended human dose, based on the body surface area).
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for women with CKD on dialysis with hyperphosphatemia is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the United States general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
XPHOZAH is contraindicated in patients under 6 years of age because of the risk of diarrhea and serious dehydration
Diarrhea was the most common adverse reaction in XPHOZAH-treated patients with CKD on dialysis
Of 1010 adult patients with CKD on dialysis randomized and treated in two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized withdrawal clinical trials for XPHOZAH (TEN-02-201 and TEN-02-301) as well as a third randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (TEN-02-202) for XPHOZAH in combination with phosphate binders, 282 (28%) were 65 years of age and older. Clinical studies of XPHOZAH did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 and older to determine whether they respond differently than younger patients.
XPHOZAH is contraindicated in patients with known or suspected mechanical gastrointestinal obstruction.
Patients may experience severe diarrhea (
Diarrhea was the most common adverse reaction in XPHOZAH-treated patients with CKD on dialysis