Get your patient on Zoryve Cream (Roflumilast)
Zoryve Cream patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Plaque Psoriasis
- Use ZORYVE cream, 0.3%, for the treatment of plaque psoriasis in adult and pediatric patients 6 years of age and older.
Atopic Dermatitis
- Use ZORYVE cream, 0.15%, for the treatment of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in adult and pediatric patients 6 years of age and older.
- Use ZORYVE cream, 0.05%, for the treatment of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in pediatric patients 2 to 5 years of age.
Administration Instructions
- Apply ZORYVE cream to affected areas once daily and rub in completely. Wash hands after application.
- ZORYVE cream is for topical use only and not for ophthalmic, oral, or intravaginal use.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Zoryve Cream prescribing information
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ZORYVE cream is a phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor:
Plaque Psoriasis
- ZORYVE cream, 0.3%, is indicated for the topical treatment of plaque psoriasis, including intertriginous areas, in adult and pediatric patients 6 years of age and older. (1.1 )
Atopic Dermatitis
- ZORYVE cream, 0.15%, is indicated for the topical treatment of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in adult and pediatric patients 6 years of age and older. (1.2 )
- ZORYVE cream, 0.05%, is indicated for the topical treatment of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in pediatric patients 2 to 5 years of age. (1.2 )
Plaque Psoriasis
ZORYVE ® cream, 0.3%, is indicated for topical treatment of plaque psoriasis, including intertriginous areas, in adult and pediatric patients 6 years of age and older.
Atopic Dermatitis
ZORYVE cream, 0.15%, is indicated for topical treatment of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in adult and pediatric patients 6 years of age and older.
ZORYVE cream, 0.05%, is indicated for topical treatment of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in pediatric patients 2 to 5 years of age.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Plaque Psoriasis
- Use ZORYVE cream, 0.3%, for the treatment of plaque psoriasis in adult and pediatric patients 6 years of age and older.
Atopic Dermatitis
- Use ZORYVE cream, 0.15%, for the treatment of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in adult and pediatric patients 6 years of age and older.
- Use ZORYVE cream, 0.05%, for the treatment of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in pediatric patients 2 to 5 years of age.
Administration Instructions
- Apply ZORYVE cream to affected areas once daily and rub in completely. Wash hands after application.
- ZORYVE cream is for topical use only and not for ophthalmic, oral, or intravaginal use.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- Cream, 0.3%: 3 mg of roflumilast per gram of white to off-white cream in 60-gram tubes.
- Cream, 0.15%: 1.5 mg of roflumilast per gram of white to off-white cream in 60-gram tubes.
- Cream, 0.05%: 0.5 mg of roflumilast per gram of white to off-white cream in 60-gram tubes.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are insufficient data available on the use of ZORYVE cream in pregnant women to inform a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. In animal reproduction studies, roflumilast administered orally to pregnant rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis produced no fetal structural abnormalities at doses up to 36 and 31 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD), respectively. Roflumilast induced post-implantation loss in rats at oral doses greater than or equal to 12 times the MRHD. Roflumilast induced stillbirth and decreased pup viability in mice at oral doses 19 and 59 times the MRHD, respectively. Roflumilast has been shown to adversely affect pup post-natal development when dams were treated with an oral dose 59 times the MRHD during pregnancy and lactation periods in mice ( see Data ).
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Labor or Delivery
Avoid using ZORYVE cream during labor and delivery. There are no human studies that have investigated effects of ZORYVE cream on preterm labor or labor at term; however, animal studies showed that oral roflumilast disrupted the labor and delivery process in mice.
Data
Animal Data
In an embryo-fetal development study, pregnant rats were dosed orally during the period of organogenesis with up to 1.8 mg/kg/day roflumilast (36 times the MRHD on a mg/m 2 basis). No evidence of structural abnormalities or effects on survival rates were observed. Roflumilast did not affect embryo-fetal development at a maternal oral dose of 0.2 mg/kg/day (4 times the MRHD on a mg/m 2 basis).
In a fertility and embryo-fetal development study, male rats were dosed orally with up to 1.8 mg/kg/day roflumilast for 10 weeks and females for 2 weeks prior to pairing and throughout the organogenesis period. Roflumilast induced pre- and post-implantation loss at maternal oral doses greater than or equal to 0.6 mg/kg/day (12 times the MRHD on a mg/m 2 basis). Roflumilast did not cause fetal structural abnormalities at maternal oral doses up to 1.8 mg/kg/day (35 times the MRHD on a mg/m 2 basis).
In an embryo-fetal development study in rabbits, pregnant does were dosed orally with 0.8 mg/kg/day roflumilast during the period of organogenesis. Roflumilast did not cause fetal structural abnormalities at the maternal oral doses of 0.8 mg/kg/day (31 times the MRHD on a mg/m 2 basis).
In pre- and post-natal developmental studies in mice, dams were dosed orally with up to 12 mg/kg/day roflumilast during the period of organogenesis and lactation. Roflumilast induced stillbirth and decreased pup viability at maternal oral doses greater than 2 mg/kg/day and 6 mg/kg/day, respectively (19 and 59 times the MRHD on a mg/m 2 basis, respectively). Roflumilast induced delivery retardation in pregnant mice at maternal oral doses greater than 2 mg/kg/day (19 times the MRHD on a mg/m 2 basis). Roflumilast decreased pup rearing frequencies at a maternal oral dose of 6 mg/kg/day during pregnancy and lactation (59 times the MRHD on a mg/m 2 basis). Roflumilast also decreased survival and forelimb grip reflex and delayed pinna detachment in mouse pups at a maternal oral dose of 12 mg/kg/day (116 times the MRHD on a mg/m 2 basis).
Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of roflumilast or its metabolite in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production.
Roflumilast and/or its metabolites are excreted into the milk of lactating rats ( see Data ). When a drug is present in animal milk, it is likely that the drug will be present in human milk. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for ZORYVE cream and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from ZORYVE cream or from the underlying maternal condition.
Clinical Considerations
To minimize potential exposure to the breastfed infant via breast milk, use ZORYVE cream on the smallest area of skin and for the shortest duration possible while breastfeeding. To avoid direct infant exposure, advise breastfeeding women not to apply ZORYVE cream directly to the nipple or areola. If applied to the patient's chest, avoid exposure via direct contact with the infant's skin.
Data
Animal Data
Roflumilast and/or its metabolite concentrations measured 8 hours after an oral dose of 1 mg/kg given to lactating rats were 0.32 and 0.02 mcg/g in the milk and pup liver, respectively. The concentration of roflumilast in animal milk does not necessarily predict the concentration of drug in human milk.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Infertility
In a human spermatogenesis study, oral roflumilast 500 mcg had no effects on semen parameters or reproductive hormones during the 3-month treatment period and the following 3-month off-treatment period.
Pediatric Use
Plaque Psoriasis
The safety and effectiveness of ZORYVE cream, 0.3%, for the topical treatment of plaque psoriasis, including intertriginous areas, have been established in pediatric patients 6 years of age and older. Use of ZORYVE cream, 0.3%, in pediatric patients 6 years of age and older is supported by data from two 8-week, vehicle-controlled, safety and efficacy trials which included 18 subjects 6 to 17 years of age, of whom 11 received ZORYVE cream, 0.3%. Use of ZORYVE cream, 0.3%, in pediatric patients 12 years of age and older is also supported by data from open-label trials of 2- and 24-weeks duration which included 18 subjects 12 to 17 years of age treated with ZORYVE cream, 0.3%. Use of ZORYVE cream, 0.3%, in pediatric patients 6 to less than 12 years of age is also supported by data from one 4-week, open-label, safety and pharmacokinetic (PK) study which included 20 pediatric subjects 6 to less than 12 years of age [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) , Clinical Studies (14.1) ] .
The safety and effectiveness of ZORYVE cream, 0.3%, have not been established in pediatric patients younger than 6 years of age.
Atopic Dermatitis
ZORYVE Cream, 0.15%
The safety and effectiveness of ZORYVE cream, 0.15%, for the topical treatment of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis have been established in pediatric patients 6 years of age and older. Use of ZORYVE cream, 0.15%, in this age group is supported by data from two 4-week, vehicle-controlled, safety and efficacy trials which included 615 subjects 6 to 17 years of age, of whom 406 received ZORYVE cream, 0.15%, [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) , Clinical Studies (14.2) ] . Use of ZORYVE cream, 0.15%, in pediatric patients 6 years of age and older is also supported by data from 481 pediatric subjects treated with ZORYVE cream, 0.15%, in open-label trials, of which 104 were treated for 52 weeks.
In an open-label PK trial in 36 pediatric subjects 2 to 16 years of age, following topical administration of roflumilast cream, 0.15%, once daily for 2 weeks, mean systemic exposure of roflumilast and roflumilast N-oxide in subjects 2 to 5 years of age was approximately 3.2-fold and 5.2-fold higher, respectively, compared to subjects 12 to 16 years of age, and approximately 2-fold and 2.3-fold higher, respectively, compared to subjects 6 to 11 years of age.
The safety and effectiveness of ZORYVE cream, 0.15%, have not been established in pediatric patients younger than 6 years of age.
ZORYVE Cream, 0.05%
The safety and effectiveness of ZORYVE cream, 0.05%, for the topical treatment of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis have been established in pediatric patients 2 to 5 years of age. Use of ZORYVE cream, 0.05%, in this age group is supported by data from one 4-week, vehicle-controlled, safety and efficacy trial which included 652 subjects 2 to 5 years of age, of whom 437 received ZORYVE cream, 0.05%, [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) , Clinical Studies (14.2) ] . Use of ZORYVE cream, 0.05%, in pediatric patients 2 to 5 years of age is also supported by data from 572 pediatric subjects treated with ZORYVE cream, 0.05%, in open-label trials, of whom 353 were treated for 52 weeks.
The safety and effectiveness of ZORYVE cream, 0.05%, have not been established in pediatric patients younger than 2 years of age and older than 6 years of age.
Geriatric Use
There were 184 patients 65 years of age and older in clinical studies for plaque psoriasis and atopic dermatitis [see Clinical Studies (14.1 , 14.2) ] .
Plaque Psoriasis
Of the 576 patients treated with ZORYVE cream, 0.3%, in the 2 controlled clinical studies for plaque psoriasis, 56 (9.7%) were 65 to 74 years of age and 21 (3.7%) were 75 years of age and older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the geriatric and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
Atopic Dermatitis
Of the 885 patients treated with ZORYVE cream, 0.15%, in the 2 controlled clinical studies for atopic dermatitis, 36 (4.1%) were 65 to 74 years of age and 8 (0.9%) were 75 years of age and older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the geriatric and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
Hepatic Impairment
Oral roflumilast 250 mcg once daily for 14 days was studied in subjects with hepatic impairment. The systemic exposure of roflumilast and roflumilast N-oxide were increased in subjects with moderate (Child-Pugh B) hepatic impairment. ZORYVE cream is contraindicated in patients with moderate to severe liver impairment (Child-Pugh B or C). No dosage adjustment is needed in patients with mild (Child-Pugh A) hepatic impairment [see Contraindications (4) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
CONTRAINDICATIONS
ZORYVE cream is contraindicated in patients with moderate to severe liver impairment (Child-Pugh B or C) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (reported in ≥1% of subjects) are:
- Plaque Psoriasis: diarrhea, headache, insomnia, nausea, application site pain, upper respiratory tract infection, and urinary tract infection. (6.1 )
- Atopic Dermatitis: headache, nausea, application site pain, diarrhea, vomiting, upper respiratory tract infection, rhinitis, and conjunctivitis. (6.1 )
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Arcutis Biotherapeutics, Inc. at 1-844-692-6729 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Plaque Psoriasis
Adult and Pediatric Subjects 6 Years of Age and Older
In two multicenter, randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled trials (DERMIS-1 and DERMIS-2), 881 adult and pediatric subjects 6 years of age or older with plaque psoriasis were treated with ZORYVE cream, 0.3%, or vehicle cream once daily for 8 weeks [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ] .
The proportion of subjects who discontinued treatment due to an adverse reaction was 1.0% for subjects treated with ZORYVE cream, 0.3%, and 1.3% for subjects treated with vehicle cream. The most common adverse reaction that led to discontinuation of ZORYVE cream, 0.3%, was application site urticaria (0.3%).
Table 1 presents adverse reactions that occurred in at least 1% of subjects treated with ZORYVE cream, 0.3%, and for which the rate exceeded the rate for vehicle cream.
| Adverse Reaction | ZORYVE Cream, 0.3% (N=576) n (%) | Vehicle Cream (N=305) n (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Diarrhea | 18 (3.1) | 0 (0.0) |
| Headache | 14 (2.4) | 3 (1.0) |
| Insomnia | 8 (1.4) | 2 (0.7) |
| Nausea | 7 (1.2) | 1 (0.3) |
| Application site pain | 6 (1.0) | 1 (0.3) |
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 6 (1.0) | 1 (0.3) |
| Urinary tract infection | 6 (1.0) | 2 (0.7) |
In 594 subjects with plaque psoriasis who continued treatment with ZORYVE cream, 0.3%, for up to 64 weeks in open-label extension trials, the adverse reaction profile was consistent with that observed in vehicle-controlled trials.
Atopic Dermatitis
Adult and Pediatric Subjects 6 Years of Age and Older
In two multicenter, randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled trials (INTEGUMENT-1 and INTEGUMENT-2), 1336 adult and pediatric subjects 6 years of age or older with mild to moderate atopic dermatitis were treated with ZORYVE cream, 0.15%, or vehicle cream once daily for 4 weeks [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ] .
The proportion of subjects who discontinued treatment due to an adverse reaction was 1.6% for subjects treated with ZORYVE cream, 0.15%, and 1.1% for subjects treated with vehicle cream.
Table 2 presents adverse reactions that occurred in at least 1% of subjects treated with ZORYVE cream, 0.15%, and for which the rate exceeded the rate for vehicle cream.
| Adverse Reaction | ZORYVE Cream, 0.15% (N=885) n (%) | Vehicle Cream (N=451) n (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Headache | 26 (2.9) | 4 (0.9) |
| Nausea | 17 (1.9) | 2 (0.4) |
| Application site pain | 13 (1.5) | 3 (0.7) |
| Diarrhea | 13 (1.5) | 2 (0.4) |
| Vomiting | 13 (1.5) | 2 (0.4) |
The adverse reaction of insomnia was reported in fewer than 1% of subjects treated with ZORYVE cream, 0.15%.
Pediatric Subjects 2 to 5 Years of Age
In a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled trial (INTEGUMENT-PED), 652 pediatric subjects 2 to 5 years of age with mild to moderate atopic dermatitis were treated with ZORYVE cream, 0.05%, or vehicle cream once daily for 4 weeks [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ] .
Table 3 presents adverse reactions that occurred in at least 1% of subjects treated with ZORYVE cream, 0.05%, and for which the rate exceeded the rate for vehicle cream.
| Adverse Reaction | ZORYVE Cream, 0.05% N=437 n (%) | Vehicle Cream N=215 n (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 18 (4.1) | 3 (1.4) |
| Diarrhea | 11 (2.5) | 1 (0.5) |
| Vomiting | 9 (2.1) | 0 |
| Rhinitis | 7 (1.6) | 0 |
| Conjunctivitis | 6 (1.4) | 0 |
| Headache | 5 (1.1) | 0 |
Adult and Pediatric Subjects 2 Years of Age and Older
The long-term safety of ZORYVE cream, 0.15%, and ZORYVE cream, 0.05%, was assessed in an open-label extension trial of 1219 subjects 2 years of age and older with mild to moderate atopic dermatitis who had completed one of the 4-week vehicle-controlled trials. The safety profile observed in the open-label extension trial was generally consistent with the safety profile observed at Week 4.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Co-administration of roflumilast with systemic CYP3A4 inhibitors or dual inhibitors that inhibit both CYP3A4 and CYP1A2 simultaneously may increase roflumilast systemic exposure and may result in increased adverse reactions. If these products are co-administered with ZORYVE cream, weigh the potential for increased adverse reactions against benefit. (7.1 )
- Co-administration of roflumilast with oral contraceptives containing gestodene and ethinyl estradiol may increase roflumilast systemic exposure and may result in increased adverse reactions. If these products are co-administered with ZORYVE cream, weigh the potential for increased adverse reactions against benefit. (7.1 )
Effects of Other Drugs on ZORYVE Cream
Drugs that Inhibit Cytochrome P450 (CYP) Enzymes
No formal drug-drug interaction studies were conducted with ZORYVE cream; however, the co-administration of roflumilast with systemic CYP3A4 inhibitors or dual inhibitors that inhibit both CYP3A4 and CYP1A2 simultaneously may increase roflumilast systemic exposure and may result in increased adverse reactions. If these products are co-administered with ZORYVE cream, weigh the potential for increased adverse reactions against benefit [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Oral Contraceptives Containing Gestodene and Ethinyl Estradiol
The co-administration of roflumilast with oral contraceptives containing gestodene and ethinyl estradiol may increase roflumilast systemic exposure and may result in increased adverse reactions. If these products are co-administered with ZORYVE cream, weigh the potential for increased adverse reactions against benefit [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
DESCRIPTION
ZORYVE (roflumilast) cream is a white to off-white cream for topical use. The active ingredient, roflumilast, is a phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitor.
Roflumilast is described chemically as 3-cyclopropylmethoxy- N -(3,5-dichloropyridin-4-yl)-4-(difluoromethoxy)benzamide. The empirical formula is C 17 H 14 Cl 2 F 2 N 2 O 3, and the molecular weight is 403.21.
The structural formula is represented below:

Roflumilast is practically insoluble in water and hexane, sparingly soluble in ethanol, and freely soluble in acetone.
Each gram of cream, 0.05%, 0.15%, or 0.3%, contains 0.5 mg, 1.5 mg, or 3 mg of roflumilast, respectively, in a cream base containing ceteareth-10 phosphate, cetearyl phosphate, cetostearyl alcohol, diethylene glycol monoethyl ether, hexylene glycol, isopropyl palmitate, methylparaben, propylparaben, purified water, sodium hydroxide, and white petrolatum. Hydrochloric acid may have been added to adjust pH.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Roflumilast and its active metabolite (roflumilast N-oxide) are inhibitors of PDE4. Roflumilast and roflumilast N-oxide inhibition of PDE4 (a major cyclic 3′,5′-adenosine monophosphate [cyclic AMP] metabolizing enzyme) activity leads to accumulation of intracellular cyclic AMP. The specific mechanism(s) by which roflumilast exerts its therapeutic action is not well defined.
Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacodynamics of ZORYVE cream in the treatment of plaque psoriasis and atopic dermatitis are unknown.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Following application of ZORYVE cream, the plasma concentration versus time profile was relatively flat, generally with a peak-to-trough ratio less than 2.
Plaque Psoriasis
The PK of ZORYVE cream, 0.3%, was assessed in 18 adult and 6 pediatric subjects 13 to 16 years of age with plaque psoriasis and a mean ± SD body surface area (BSA) involvement of 26.8 ± 6.80% and 13.0 ± 3.58% in adult and pediatric subjects, respectively. In this study, on average, subjects applied 3 to 6.5 g of ZORYVE cream, 0.3%, once daily for 15 days. Plasma concentrations of roflumilast and roflumilast N-oxide (see Metabolism ) were quantifiable in all but two subjects at Day 15.
In adults, the mean ± SD systemic exposure (AUC 0-24 ) was 72.7 ± 53.1 and 628 ± 648 h∙ng/mL for roflumilast and the N-oxide metabolite, respectively. In pediatric subjects (13 to 16 years of age), the mean ± SD AUC 0-24 was 25.1 ± 24.0 and 140 ± 179 h∙ng/mL for roflumilast and the N-oxide metabolite, respectively.
The PK of ZORYVE cream, 0.3%, was assessed in 10 pediatric subjects (6 to less than 12 years of age) with at least mild plaque psoriasis and a mean ± SD BSA involvement of 10.9 ± 6.56%. The 14-day mean ± SD extrapolated AUC 0-24 was 75.6 ± 87.3 and 693 ± 986 h∙ng/mL for roflumilast and the N-oxide metabolite, respectively. In another study, the PK of ZORYVE cream, 0.3%, was assessed in 9 pediatric subjects (2 to less than 6 years of age) with at least mild plaque psoriasis and a mean ± SD BSA involvement of 9.44 ± 5.57%. The 14-day mean ± SD extrapolated AUC 0-24 was 51.6 ± 29.9 and 539 ± 372 h∙ng/mL for roflumilast and the N-oxide metabolite, respectively.
Atopic Dermatitis
The PK of ZORYVE cream, 0.15%, was assessed in 12 pediatric subjects 12 to 16 years of age and 13 pediatric subjects 6 to 11 years of age with atopic dermatitis and a mean ± SD BSA involvement of 33.7 ± 14.8% and 43.5 ± 10.5%, respectively. On average, subjects applied 8.2 to 10.5 g of ZORYVE cream, 0.15%, once daily.
In pediatric subjects 12 to 16 years of age, the Day 14 mean ± SD systemic exposure (AUC 0-24 ) was 62.9 ± 53.0 and 336 ± 310 h∙ng/mL for roflumilast and the N-oxide metabolite, respectively. In pediatric subjects 6 to 11 years of age, the Day 14 mean ± SD AUC 0-24 was 102 ± 96.5 and 743 ± 710 h∙ng/mL for roflumilast and the N-oxide metabolite, respectively.
The PK of ZORYVE cream, 0.05%, was assessed in 9 pediatric subjects 2 to 5 years of age with atopic dermatitis and a mean ± SD BSA involvement of 42.4 ± 6.21%. On average, subjects applied 5.2 g of ZORYVE cream, 0.05%, once daily.
In pediatric subjects 2 to 5 years of age, the Day 14 mean ± SD systemic exposure (AUC 0-24 ) was 47.2 ± 27.4 and 338 ± 280 h∙ng/mL for roflumilast and the N-oxide metabolite, respectively.
Distribution
Plasma protein binding of roflumilast and its N-oxide metabolite is approximately 99% and 97%, respectively.
Elimination
The plasma clearance after short-term intravenous infusion of roflumilast is on average about 9.6 L/h. Following topical administration, the half-lives of roflumilast and the N-oxide metabolite were 4.0 and 4.6 days, respectively.
Metabolism
Roflumilast is extensively metabolized via Phase I (cytochrome P450) and Phase II (conjugation) reactions. The N-oxide metabolite is the only major metabolite observed in the plasma of humans. Following oral administration, roflumilast and roflumilast N-oxide account for the majority (87.5%) of total dose administered in plasma. Roflumilast was not detectable in urine, while roflumilast N-oxide was only a trace metabolite (less than 1%). Other conjugated metabolites such as roflumilast N-oxide glucuronide and 4-amino-3,5-dichloropyridine N-oxide were detected in urine.
While roflumilast is 3 times more potent than roflumilast N-oxide at inhibition of the PDE4 enzyme in vitro , the plasma AUC of roflumilast N-oxide on average is approximately 8-fold greater than the plasma AUC of roflumilast following topical administration. A similar ratio was observed following intravenous administration, whereas following oral administration the N-oxide metabolite circulated on average about 10-fold higher than the parent drug.
Specific Populations
Following topical administration, no clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of roflumilast and roflumilast N-oxide were observed based on sex, race, or ethnicity.
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
No studies were conducted with topical roflumilast in subjects with hepatic impairment; however, oral roflumilast 250 mcg once daily for 14 days was studied in subjects with mild to moderate hepatic impairment classified as Child-Pugh A and B (8 subjects in each group). The AUC of roflumilast and roflumilast N-oxide were increased by 51% and 24%, respectively, in Child-Pugh A subjects and by 92% and 41%, respectively, in Child-Pugh B subjects, as compared to age-, weight-, and gender-matched healthy subjects. The C max of roflumilast and roflumilast N-oxide were increased by 3% and 26%, respectively, in Child-Pugh A subjects and by 26% and 40%, respectively, in Child-Pugh B subjects, as compared to healthy subjects [see Contraindications (4) ] .
Patients with Renal Impairment
No studies were conducted with topical roflumilast in subjects with renal impairment. Following oral administration in 12 subjects with severe renal impairment, no clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of roflumilast and roflumilast N-oxide were observed.
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies
No formal drug-drug interaction studies were conducted with roflumilast cream.
Since a major step in roflumilast metabolism is the N-oxidation of roflumilast to roflumilast N-oxide by CYP3A4 and CYP1A2, drug interaction studies were performed with oral roflumilast and systemic inhibitors of CYP3A4 and CYP1A2 [see Drug Interactions (7.1) ] .
Erythromycin: In an open-label crossover study in 16 healthy volunteers, the co-administration of CYP3A4 inhibitor erythromycin (500 mg 3 times daily for 13 days) with a single oral dose of 500 mcg roflumilast resulted in 40% and 70% increase in C max and AUC for roflumilast, respectively, and a 34% decrease and a 4% increase in C max and AUC for roflumilast N-oxide, respectively.
Ketoconazole: In an open-label crossover study in 16 healthy volunteers, the co-administration of a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor ketoconazole (200 mg twice daily for 13 days) with a single oral dose of 500 mcg roflumilast resulted in 23% and 99% increase in C max and AUC for roflumilast, respectively, and a 38% reduction and 3% increase in C max and AUC for roflumilast N-oxide, respectively.
Fluvoxamine: In an open-label crossover study in 16 healthy volunteers, the co-administration of dual CYP 3A4/1A2 inhibitor fluvoxamine (50 mg daily for 14 days) with a single oral dose of 500 mcg roflumilast showed a 12% and 156% increase in roflumilast C max and AUC along with a 210% decrease and 52% increase in roflumilast N-oxide C max and AUC, respectively.
Enoxacin: In an open-label crossover study in 16 healthy volunteers, the co-administration of dual CYP 3A4/1A2 inhibitor enoxacin (400 mg twice daily for 12 days) with a single oral dose of 500 mcg roflumilast resulted in an increased C max and AUC of roflumilast by 20% and 56%, respectively. Roflumilast N-oxide C max was decreased by 14% while roflumilast N-oxide AUC was increased by 23%.
Cimetidine: In an open-label crossover study in 16 healthy volunteers, the co-administration of a dual CYP 3A4/1A2 inhibitor cimetidine (400 mg twice daily for 7 days) with a single oral dose of 500 mcg roflumilast resulted in a 46% and 85% increase in roflumilast C max and AUC; and a 4% decrease in C max and 27% increase in AUC for roflumilast N-oxide, respectively.
Oral Contraceptives Containing Gestodene and Ethinyl Estradiol: In an open-label crossover study in 20 healthy adult volunteers, co-administration of a single oral dose of roflumilast with repeated doses of a fixed combination oral contraceptive containing 0.075 mg gestodene and 0.03 mg ethinyl estradiol to steady state caused a 38% increase and 12% decrease in C max of roflumilast and roflumilast N-oxide, respectively. Roflumilast and roflumilast N-oxide AUCs were increased by 51% and 14%, respectively.
In Vitro Studies
Cytochrome P450 (CYP) Enzymes: In vitro studies suggest that the biotransformation of roflumilast to its N-oxide metabolite is mediated by CYP1A2 and 3A4. Based on further in vitro results in human liver microsomes, roflumilast and roflumilast N-oxide in therapeutic plasma concentrations do not inhibit CYP1A2, 2A6, 2B6, 2C8, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, 2E1, 3A4/5, or 4A9/11; therefore, there is a low probability of relevant interactions with substances metabolized by these P450 enzymes. In addition, in vitro studies demonstrated no induction of the CYP1A2, 2A6, 2C9, 2C19, or 3A4/5 and only a weak induction of CYP2B6 by roflumilast.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term studies were conducted in hamsters and mice with roflumilast to evaluate its carcinogenic potential. In 2-year oral gavage carcinogenicity studies, roflumilast treatment resulted in dose-related, statistically significant increases in the incidence of undifferentiated carcinomas of nasal epithelium in hamsters at doses greater than or equal to 8 mg/kg/day (12 times the MRHD on an AUC basis). The tumorigenicity of roflumilast appears to be attributed to a reactive metabolite of 4-amino-3,5-dichloropyridine N-oxide (ADCP N-oxide). No evidence of tumorigenicity was observed in mice at roflumilast oral doses up to 12 and 18 mg/kg/day in females and males, respectively (11 and 17 times the MRHD, respectively, on an AUC basis).
In a 2-year dermal mouse carcinogenicity study, no evidence of carcinogenicity was observed at topical doses of roflumilast cream up to 1% applied at 2 mL/kg/day (4 times the MRHD on an AUC basis).
Roflumilast tested positive in an in vivo mouse micronucleus test, but negative in the following assays: the Ames test, an in vitro chromosome aberration assay in human lymphocytes, an in vitro HPRT assay with V79 cells, an in vitro micronucleus test with V79 cells, a DNA adduct formation assay in rat nasal mucosa, liver, and testes, and an in vivo mouse bone marrow chromosome aberration assay. Roflumilast N-oxide was negative in the Ames test and an in vitro micronucleus test with V79 cells.
In a fertility study, oral roflumilast decreased fertility rates in male rats at 1.8 mg/kg/day (35 times the MRHD on a mg/m 2 basis). The male rats also showed increases in the incidence of tubular atrophy, degeneration in the testis, and spermiogenic granuloma in the epididymides. No effect on rat fertility rate or male reproductive organ morphology was observed at 0.6 mg/kg/day (12 times the MRHD on a mg/m 2 basis). In a female fertility study, no effect on fertility was observed up to the highest roflumilast dose of 1.5 mg/kg/day in rats (29 times the MRHD on a mg/m 2 basis).
CLINICAL STUDIES
Plaque Psoriasis
Adult and Pediatric Subjects 6 Years of Age and Older
Two multicenter, randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled trials (DERMIS-1 [NCT04211363] and DERMIS-2 [NCT04211389]) enrolled a total of 881 adult and pediatric subjects 6 years of age or older with mild to severe plaque psoriasis. Subjects were randomized 2:1 to receive ZORYVE cream, 0.3%, or vehicle cream applied topically once daily for 8 weeks. The median age of the trial population was 47 years (range 6 to 88 years of age). The trial population was 64% male and 36% female; 82.3% were White, 7.1% Asian, 3.6% Black or African American, 0.9% Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander, 0.7% American Indian or Alaska Native, 0.5% more than one race, 3.3% other races, and 1.6% with missing racial information. For ethnicity, 75.7% of subjects identified as Not Hispanic or Latino, 24.1% identified as Hispanic or Latino, and 0.2% were unknown. The median body surface area (BSA) affected of the trial population was 5.5% (range 2% to 20%). At baseline, 16% of subjects had an Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) score of 2 (mild), 76% had an IGA score of 3 (moderate), and 8% had an IGA score of 4 (severe). One hundred seventy-nine (20%) subjects had a baseline intertriginous IGA (I-IGA) score of 2 or higher (mild), and 678 (77%) subjects had a baseline Worst Itch Numeric Rating Scale (WI-NRS) score of 4 or higher on a scale of 0 to 10.
The primary endpoint was the proportion of subjects who achieved IGA treatment success at Week 8 (Table 4). Success was defined as a score of "Clear" (0) or "Almost Clear" (1), plus a 2-grade improvement from baseline.
| DERMIS-1 | DERMIS-2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZORYVE Cream, 0.3% | Vehicle Cream | ZORYVE Cream, 0.3% | Vehicle Cream | |
| Subjects randomized | N=286 | N=153 | N=290 | N=152 |
| Abbreviations: CI = Confidence Interval | ||||
| IGA success | 41.5% | 5.8% | 36.7% | 7.1% |
| Difference from vehicle (95% CI) Treatment difference and 95% CI are based on the CMH method stratified by site, baseline IGA, and baseline intertriginous involvement. | 39.7% (32.4%, 47.0%) | 29.5% (21.5%, 37.6%) | ||
Secondary endpoints included the proportion of subjects that achieved I-IGA success at Week 8 and WI-NRS success sequentially at Weeks 8, 4, and 2 (see Figure 1 ). WI-NRS success was defined as a reduction of at least 4 points from baseline in subjects with a baseline WI-NRS score of at least 4.
| Figure 1: WI-NRS Success WI-NRS success is a reduction of at least 4 points in subjects with a WI-NRS score of 4 or higher at baseline. Over Time in Adult and Pediatric Subjects 12 Years of Age and Older with Mild to Severe Plaque Psoriasis in Trials DERMIS-1 and DERMIS-2 |
|---|
| † The treatment difference at Week 2 in DERMIS-1 was not statistically significant. |
|
Among subjects with an I-IGA score of at least 2 (mild) at baseline (approximately 22% of subjects in DERMIS-1 and 19% in DERMIS-2), there was a higher percentage of subjects who achieved I-IGA success at Week 8 in the group who received ZORYVE cream, 0.3%, compared to the group who received vehicle cream (DERMIS-1: 71.5% vs. 13.8%; DERMIS-2: 67.5% vs. 17.4%).
Atopic Dermatitis
Adult and Pediatric Subjects 6 Years of Age and Older
Two multicenter, randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled trials (INTEGUMENT-1 [NCT04773587] and INTEGUMENT-2 [NCT04773600]) enrolled a total of 1337 adult and pediatric subjects 6 years of age and older (615 subjects were 6 to 17 years of age) with mild to moderate atopic dermatitis. Subjects were randomized 2:1 to receive ZORYVE cream, 0.15%, or vehicle cream applied once daily for 4 weeks. The median age of the trial population was 20 years (range 6 to 91 years of age). The trial population was 57% female; 59.5% were White, 20.3% Black or African American, 13.2% Asian, 3.4% other races, 2.8% more than one race, 0.6% American Indian or Alaska Native, and 0.1% Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander. For ethnicity, 82.8% of subjects identified as Not Hispanic or Latino, 16.6% identified as Hispanic or Latino, and 0.6% were unknown. At baseline, subjects had a mean affected BSA of 14% (range of 3% to 88%), and 42% had facial involvement. At baseline, 24% of subjects had a validated Investigator Global Assessment for Atopic Dermatitis (vIGA-AD) score of 2 (mild), and 76% had a vIGA-AD score of 3 (moderate). Eight hundred thirteen (60.8%) subjects 12 years of age and older had a baseline WI-NRS score of 4 or higher on a scale of 0 to 10.
The primary endpoint was the proportion of subjects who achieved vIGA-AD treatment success at Week 4 (Table 5). Success was defined as a score of "Clear" (0) or "Almost Clear" (1), plus a 2-grade improvement from baseline.
Secondary endpoints included the proportion of subjects that achieved vIGA-AD success at Weeks 2 and 1 (Figure 2) and WI-NRS success at Weeks 4, 2, and 1 (Table 6, Figure 3). WI-NRS success was defined as a reduction of at least 4 points from baseline in subjects 12 years of age or older with a baseline WI-NRS score of at least 4.
| INTEGUMENT-1 | INTEGUMENT-2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZORYVE Cream, 0.15% | Vehicle Cream | ZORYVE Cream, 0.15% | Vehicle Cream | |
| Abbreviations: CI = Confidence Interval | ||||
| Subjects randomized | N=433 | N=221 | N=451 | N=232 |
| vIGA-AD success | 32.0% | 15.2% | 28.9% | 12.0% |
| Difference from vehicle (95% CI) The difference in percent and related 95% CIs are Mantel-Haenszel estimates stratified by pooled study site and vIGA-AD randomization strata. | 17.4% (11.09%, 23.75%) | 16.5% (10.61%, 22.42%) | ||
| Figure 2: vIGA-AD Success vIGA-AD success was defined as a vIGA-AD score of "Clear" (0) or "Almost Clear" (1), plus a 2-grade vIGA-AD score improvement from baseline at Week 4 (Multiple Imputation). Over Time in Adult and Pediatric Subjects 6 Years of Age and Older with Mild to Moderate Atopic Dermatitis in Trials INTEGUMENT-1 and INTEGUMENT-2 |
|---|
| † The treatment difference at Week 1 in INTEGUMENT-2 was not statistically significant. |
|
| INTEGUMENT-1 | INTEGUMENT-2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZORYVE Cream, 0.15% | Vehicle Cream | ZORYVE Cream, 0.15% | Vehicle Cream | |
| Abbreviations: CI = Confidence Interval | ||||
| Subjects randomized | N=433 | N=221 | N=451 | N=232 |
| Subjects ≥12 years randomized with baseline WI-NRS ≥4 | N=278 | N=135 | N=264 | N=136 |
| WI-NRS success | 33.6% | 20.7% | 30.2% | 12.4% |
| Difference from vehicle (95% CI) The difference in percent and related 95% CIs are Mantel-Haenszel estimates stratified by pooled study site and vIGA-AD randomization strata. | 13.3% (4.01%, 22.60%) | 15.0% (6.52%, 23.54%) | ||
| Figure 3: WI-NRS Success WI-NRS success in subjects 12 years of age or older is a reduction of at least 4 points in subjects with a WI-NRS score of 4 or higher at baseline. Over Time in Adult and Pediatric Subjects 12 Years of Age and Older with Mild to Moderate Atopic Dermatitis in Trials INTEGUMENT-1 and INTEGUMENT-2 |
|---|
|
Pediatric Subjects 2 to 5 Years of Age
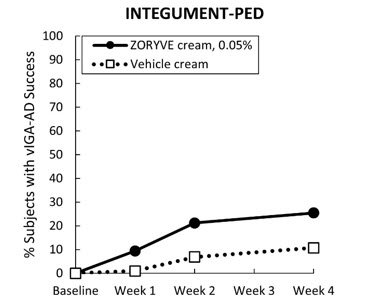
A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled trial (INTEGUMENT-PED [NCT04845620]) enrolled a total of 652 pediatric subjects 2 to 5 years of age with mild to moderate atopic dermatitis. Subjects were randomized 2:1 to receive ZORYVE cream, 0.05%, or vehicle cream applied once daily for 4 weeks. The median age of the trial population was 3 years (range 2 to 5 years of age). The trial population was 52% male; 69.1% were White, 15.4% Black or African American, 8.3% Asian, 1.8% other races, 4.9% more than one race, and 0.5% American Indian or Alaska Native. For ethnicity, 82.2% of subjects identified as Not Hispanic or Latino, 17.4% identified as Hispanic or Latino, and 0.5% were unknown. At baseline, subjects had a mean affected BSA of 22% (range of 3% to 82%), and 53% had facial involvement. At baseline, 22% of subjects had a validated Investigator Global Assessment for Atopic Dermatitis (vIGA-AD) score of 2 (mild), and 78% had a vIGA-AD score of 3 (moderate).
The primary endpoint was the proportion of subjects who achieved vIGA-AD treatment success at Week 4 (Table 7). Success was defined as a score of "Clear" (0) or "Almost Clear" (1), plus a 2-grade improvement from baseline. Secondary endpoints included the proportion of subjects that achieved vIGA-AD success at Weeks 1 and 2 (Figure 4).
| INTEGUMENT-PED | ||
|---|---|---|
| ZORYVE Cream, 0.05% | Vehicle Cream | |
| Subjects randomized | N=436 | N=215 |
| Abbreviations: CI = Confidence Interval | ||
| vIGA-AD success | 25.4% | 10.7% |
| Difference from vehicle (95% CI) The difference in percent and related 95% CIs are Mantel-Haenszel estimates stratified by pooled study site and vIGA-AD randomization strata. | 14.9% (9.04%, 20.79%) | |
| Figure 4: vIGA-AD Success vIGA-AD success was defined as a vIGA-AD score of "Clear" (0) or "Almost Clear" (1), plus a 2-grade vIGA-AD score improvement from baseline at Week 4 (Multiple Imputation). Over Time in Pediatric Subjects 2 to 5 Years of Age with Mild to Moderate Atopic Dermatitis in Trial INTEGUMENT-PED |
|
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
ZORYVE (roflumilast) cream is a white to off-white cream supplied as follows:
- Cream, 0.3%: 3 mg of roflumilast per gram supplied in 60-gram aluminum tubes (NDC 80610-130-60).
- Cream, 0.15%: 1.5 mg of roflumilast per gram supplied in 60-gram aluminum tubes (NDC 80610-115-60).
- Cream, 0.05%: 0.5 mg of roflumilast per gram supplied in 60-gram aluminum tubes (NDC 80610-105-60).
Storage and Handling
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C and 30°C (59°F and 86°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature]
Mechanism of Action
Roflumilast and its active metabolite (roflumilast N-oxide) are inhibitors of PDE4. Roflumilast and roflumilast N-oxide inhibition of PDE4 (a major cyclic 3′,5′-adenosine monophosphate [cyclic AMP] metabolizing enzyme) activity leads to accumulation of intracellular cyclic AMP. The specific mechanism(s) by which roflumilast exerts its therapeutic action is not well defined.