Zynrelef prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Zynrelef patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- ZYNRELEF is intended for single-dose administration only (2.1 ). Administer ZYNRELEF via instillation only.
- The toxic effects of local anesthetics are additive. Avoid additional use of local anesthetics within 96 hours following administration of ZYNRELEF (2.1 ).
- ZYNRELEF should only be prepared and administered with the components provided in the ZYNRELEF kit (2.1 ).
- ZYNRELEF is applied without a needle into the surgical site following final irrigation and suction and prior to suturing (2.1 ).
- The recommended dose of ZYNRELEF is up to a maximum dose of 400 mg/12 mg (14 mL) (2.4 ).
- See Full Prescribing Information for important preparation and administration instructions, dose selection, and compatibility considerations (2.2 , 2.3 , 2.4 , 2.5 ).
Important Dosage and Administration Information
ADMINISTER ZYNRELEF VIA INSTILLATION ONLY.
- ZYNRELEF should not be administered via the following routes.
- Epidural
- Intrathecal
- Intravascular
- Intra-articular [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10) , Nonclinical Toxicology (13.2) ]
- Regional nerve blocks
- Pre-incisional or pre-procedural locoregional anesthetic techniques.
- ZYNRELEF is intended for single-dose administration only.
- As there is a potential risk of severe, life-threatening adverse reactions associated with the administration of bupivacaine, ZYNRELEF should be administered in a setting where trained personnel and equipment are available to promptly treat patients who show evidence of neurologic or cardiac toxicity [see Overdosage (10) ] .
- The toxic effects of local anesthetics are additive. Avoid additional use of local anesthetics within 96 hours following administration of ZYNRELEF.
- Avoid intravascular administration of ZYNRELEF. Convulsions and cardiac arrest have occurred following accidental intravascular injection of bupivacaine and other amide-containing products.
- Limit exposure to articular cartilage due to the potential risk of chondrolysis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11) ] .
- ZYNRELEF is a viscous solution supplied as a kit consisting of a single-dose glass vial, and the following sterile components: Luer lock syringe(s), a vented vial spike or vial access needle, Luer lock cone-shaped applicator(s), and syringe tip cap(s). ZYNRELEF should only be prepared and administered with the components provided in the ZYNRELEF kit. See the ZYNRELEF Instructions for Use included in the kit for complete administration instructions with illustrations.
- The contents of the ZYNRELEF vial are sterile. The vial exterior is not sterile. Follow your facility's standard operating procedures regarding aseptic drug preparation.
- Each ZYNRELEF vial contains overfill to compensate for residual amounts that remain in the vial, vented vial spike or vial access needle, Luer lock applicator, and syringe(s) during drug withdrawal and administration.
- ZYNRELEF is applied without a needle into the surgical site after placement of implant(s) (if applicable), following final irrigation and suctioning, and prior to suturing of each layer, when multiple tissue layers are involved.

- When ZYNRELEF comes in contact with moisture in the tissues, it becomes more viscous, allowing it to stay in place.
- ZYNRELEF does not degrade sutures. When tying knots with monofilament sutures, contact with ZYNRELEF may cause knots to loosen or untie due to the viscosity of ZYNRELEF. In vitro studies showed an increase in elasticity with monofilament sutures exposed to ZYNRELEF with unknown clinical significance. Minimize administration of ZYNRELEF near the incision line and wipe off excess ZYNRELEF from the skin prior to suturing. Three (3) or more knots ending in a multi-throw knot (e.g., a Surgeon's knot) are recommended with monofilament sutures. Braided or barbed sutures are recommended, especially for closure of deeper layers.
Preparation Instructions
See the ZYNRELEF Instructions for Use included in the kit for complete administration instructions with illustrations.
- ZYNRELEF is a clear, pale yellow to yellow, viscous liquid. Visually inspect the ZYNRELEF vial for particulate matter and discoloration. Obtain a new vial if particulate matter or discoloration is observed.
- Prepare vial for filling of syringe(s) by attaching vented vial spike or vial access needle.
- Syringe attachment for product withdrawal:
- For vented vial spike, fill syringe with air prior to attaching syringe. Attach syringe to vented vial spike, invert vial and syringe to allow product to fill the vial neck, then push air into vented vial spike prior to withdrawing ZYNRELEF from vial.
- For vial access needle, do not fill syringe with air prior to attaching syringe. Attach syringe to vial access needle, then invert vial and syringe to allow product to fill the vial neck prior to withdrawing ZYNRELEF from vial.
- Withdraw dose of ZYNRELEF into syringe. (The dose volume takes into account the potential residual volume in the components.). Withdrawal time using the vial access needle is faster than the vented vial spike.
Nominal Dose of Bupivacaine / Meloxicam Number of Syringes and LLAs LLA: Luer lock cone-shaped applicator Per Dose Volume to be Withdrawn 60 mg/ 1.8 mg 1 2.3 mL (using 3 mL syringe provided) 200 mg / 6 mg 1 7 mL (using 12 mL syringe provided) 300 mg/ 9 mg 1 10.5 mL (using 12 mL syringe provided) 400 mg/ 12 mg 2 14 mL (using two 12 mL syringes provided, 7 mL ZYNRELEF per syringe) - Repeat steps 1-3 for more than one syringe.
- Prepare product immediately prior to use and apply syringe tip cap if needed until product delivery.
Administration Instructions
Before administration, remove the syringe tip cap and attach the Luer lock cone-shaped applicator to the syringe.
- Using the Luer lock cone-shaped applicator attached to the syringe, apply ZYNRELEF to the tissues within the surgical site as follows:
- For soft tissue procedures, apply ZYNRELEF into the wound prior to closure of each layer within the surgical space.
- For abdominal procedures, apply after closure of the peritoneum (if applicable) and avoid administration below the peritoneum.
- In general for orthopedic procedures, apply ZYNRELEF into the wound and on the periosteum from the proximal to the distal ends of the wound (i.e., beyond the boney repair).
- For total joint arthroplasty, apply ZYNRELEF directly into the joint capsule, onto the periosteum, and the antero-, medial-, and lateral tissues (if applicable), after placement of the component(s).
- For spinal procedures, apply ZYNRELEF after closure of the paraspinal musculature and again after closure of the subcutaneous fascia. ZYNRELEF must not be applied to the dura or spinal cord.
- For soft tissue procedures, apply ZYNRELEF into the wound prior to closure of each layer within the surgical space.
- Only apply ZYNRELEF to the tissue layers below the skin incision and not directly onto the subdermal layer or the skin. Minimize administration of ZYNRELEF near the incision line.
- Use only the amount necessary to coat the tissues, such that ZYNRELEF does not leak from the surgical wound after closure. Wipe off excess ZYNRELEF from the skin prior to or during closure of the wound.
Dosing Instructions
As a general guidance in selecting the proper dosing of ZYNRELEF, the following examples of dosing are provided:
- For soft tissue surgical procedures, such as:
- open inguinal herniorrhaphy: up to 10.5 mL to deliver 300 mg of bupivacaine and 9 mg of meloxicam [see Clinical Studies (14) ] ;
- abdominoplasty: up to 14 mL to deliver 400 mg of bupivacaine and 12 mg of meloxicam [see Clinical Studies (14) ] ;
- Cesarean section: up to 14 mL to deliver 400 mg of bupivacaine and 12 mg of meloxicam [see Clinical Studies (14) ] ;
- augmentation mammoplasty: up to 7 mL per side to deliver total of 400 mg of bupivacaine and 12 mg of meloxicam [see Clinical Studies (14) ] .
- For orthopedic surgical procedures, such as:
- bunionectomy: up to 2.3 mL to deliver 60 mg of bupivacaine and 1.8 mg of meloxicam [see Clinical Studies (14) ] ;
- total knee arthroplasty: up to 14 mL to deliver 400 mg of bupivacaine and 12 mg of meloxicam [see Clinical Studies (14) ] ;
- total shoulder arthroplasty: up to 14 mL to deliver 400 mg of bupivacaine and 12 mg of meloxicam [see Clinical Studies (14) ] ;
- 1- to 3-level spinal surgery: up to 7 mL to deliver 200 mg bupivacaine and 6 mg meloxicam [see Clinical Studies (14) ] .
Compatibility Considerations
- Do not dilute ZYNRELEF.
- ZYNRELEF is a nonaqueous solution. It cannot be mixed with water, saline, or other local anesthetics as the product will become more viscous and difficult to administer.
- When a topical antiseptic such as povidone iodine (e.g., Betadine ® ) is applied, the site should be allowed to dry before a local anesthetic, including ZYNRELEF, is administered into the site.
- When administered in recommended doses and concentrations, ZYNRELEF does not ordinarily produce irritation or tissue damage.
ZYNRELEF is compatible with:
- All components of the ZYNRELEF kit, including syringes, Luer lock cone-shaped applicator, vented vial spike, vial access needle, and syringe tip caps.
- Surgical mesh materials, including polypropylene (Prolene ® ), Gore-tex, and polyester.
- Silicone membranes.
- Bone cement.
- Metal alloys used in surgical implants.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Zynrelef prescribing information
WARNING: RISK OF SERIOUS CARDIOVASCULAR AND GASTROINTESTINAL EVENTS
WARNING: RISK OF SERIOUS CARDIOVASCULAR AND GASTROINTESTINAL EVENTS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) cause an increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction and stroke, which can be fatal. This risk may occur early in treatment and may increase with duration of use (5.1 )
- ZYNRELEF is contraindicated in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery (4 , 5.1 )
- NSAIDs cause an increased risk of serious gastrointestinal (GI) adverse events including bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach or intestines, which can be fatal. These events can occur at any time during use and without warning symptoms. Elderly patients and patients with a prior history of peptic ulcer disease and/or GI bleeding are at greater risk for serious GI events (5.2 )
Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) cause an increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction and stroke, which can be fatal. This risk may occur early in treatment and may increase with duration of use [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
- ZYNRELEF is contraindicated in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
Gastrointestinal Bleeding, Ulceration, and Perforation
- NSAIDs cause an increased risk of serious gastrointestinal (GI) adverse events including bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach or intestines, which can be fatal. These events can occur at any time during use and without warning symptoms. Elderly patients and patients with a prior history of peptic ulcer disease and/or GI bleeding are at greater risk for serious GI events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] .
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ZYNRELEF is indicated in adults for postsurgical analgesia for up to 72 hours after:
- soft tissue surgical procedures
- orthopedic surgical procedures
- foot and ankle procedures
- other orthopedic surgical procedures (e.g., total joint arthroplasty) in which direct exposure to articular cartilage is avoided [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10) ]
Limitations of Use
Safety and efficacy have not been established in highly vascular surgeries, such as intrathoracic, large 4 or more level spinal, and head and neck procedures.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- ZYNRELEF is intended for single-dose administration only (2.1 ). Administer ZYNRELEF via instillation only.
- The toxic effects of local anesthetics are additive. Avoid additional use of local anesthetics within 96 hours following administration of ZYNRELEF (2.1 ).
- ZYNRELEF should only be prepared and administered with the components provided in the ZYNRELEF kit (2.1 ).
- ZYNRELEF is applied without a needle into the surgical site following final irrigation and suction and prior to suturing (2.1 ).
- The recommended dose of ZYNRELEF is up to a maximum dose of 400 mg/12 mg (14 mL) (2.4 ).
- See Full Prescribing Information for important preparation and administration instructions, dose selection, and compatibility considerations (2.2 , 2.3 , 2.4 , 2.5 ).
Important Dosage and Administration Information
ADMINISTER ZYNRELEF VIA INSTILLATION ONLY.
- ZYNRELEF should not be administered via the following routes.
- Epidural
- Intrathecal
- Intravascular
- Intra-articular [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10) , Nonclinical Toxicology (13.2) ]
- Regional nerve blocks
- Pre-incisional or pre-procedural locoregional anesthetic techniques.
- ZYNRELEF is intended for single-dose administration only.
- As there is a potential risk of severe, life-threatening adverse reactions associated with the administration of bupivacaine, ZYNRELEF should be administered in a setting where trained personnel and equipment are available to promptly treat patients who show evidence of neurologic or cardiac toxicity [see Overdosage (10) ] .
- The toxic effects of local anesthetics are additive. Avoid additional use of local anesthetics within 96 hours following administration of ZYNRELEF.
- Avoid intravascular administration of ZYNRELEF. Convulsions and cardiac arrest have occurred following accidental intravascular injection of bupivacaine and other amide-containing products.
- Limit exposure to articular cartilage due to the potential risk of chondrolysis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11) ] .
- ZYNRELEF is a viscous solution supplied as a kit consisting of a single-dose glass vial, and the following sterile components: Luer lock syringe(s), a vented vial spike or vial access needle, Luer lock cone-shaped applicator(s), and syringe tip cap(s). ZYNRELEF should only be prepared and administered with the components provided in the ZYNRELEF kit. See the ZYNRELEF Instructions for Use included in the kit for complete administration instructions with illustrations.
- The contents of the ZYNRELEF vial are sterile. The vial exterior is not sterile. Follow your facility's standard operating procedures regarding aseptic drug preparation.
- Each ZYNRELEF vial contains overfill to compensate for residual amounts that remain in the vial, vented vial spike or vial access needle, Luer lock applicator, and syringe(s) during drug withdrawal and administration.
- ZYNRELEF is applied without a needle into the surgical site after placement of implant(s) (if applicable), following final irrigation and suctioning, and prior to suturing of each layer, when multiple tissue layers are involved.

- When ZYNRELEF comes in contact with moisture in the tissues, it becomes more viscous, allowing it to stay in place.
- ZYNRELEF does not degrade sutures. When tying knots with monofilament sutures, contact with ZYNRELEF may cause knots to loosen or untie due to the viscosity of ZYNRELEF. In vitro studies showed an increase in elasticity with monofilament sutures exposed to ZYNRELEF with unknown clinical significance. Minimize administration of ZYNRELEF near the incision line and wipe off excess ZYNRELEF from the skin prior to suturing. Three (3) or more knots ending in a multi-throw knot (e.g., a Surgeon's knot) are recommended with monofilament sutures. Braided or barbed sutures are recommended, especially for closure of deeper layers.
Preparation Instructions
See the ZYNRELEF Instructions for Use included in the kit for complete administration instructions with illustrations.
- ZYNRELEF is a clear, pale yellow to yellow, viscous liquid. Visually inspect the ZYNRELEF vial for particulate matter and discoloration. Obtain a new vial if particulate matter or discoloration is observed.
- Prepare vial for filling of syringe(s) by attaching vented vial spike or vial access needle.
- Syringe attachment for product withdrawal:
- For vented vial spike, fill syringe with air prior to attaching syringe. Attach syringe to vented vial spike, invert vial and syringe to allow product to fill the vial neck, then push air into vented vial spike prior to withdrawing ZYNRELEF from vial.
- For vial access needle, do not fill syringe with air prior to attaching syringe. Attach syringe to vial access needle, then invert vial and syringe to allow product to fill the vial neck prior to withdrawing ZYNRELEF from vial.
- Withdraw dose of ZYNRELEF into syringe. (The dose volume takes into account the potential residual volume in the components.). Withdrawal time using the vial access needle is faster than the vented vial spike.
Nominal Dose of Bupivacaine / Meloxicam Number of Syringes and LLAs LLA: Luer lock cone-shaped applicator Per Dose Volume to be Withdrawn 60 mg/ 1.8 mg 1 2.3 mL (using 3 mL syringe provided) 200 mg / 6 mg 1 7 mL (using 12 mL syringe provided) 300 mg/ 9 mg 1 10.5 mL (using 12 mL syringe provided) 400 mg/ 12 mg 2 14 mL (using two 12 mL syringes provided, 7 mL ZYNRELEF per syringe) - Repeat steps 1-3 for more than one syringe.
- Prepare product immediately prior to use and apply syringe tip cap if needed until product delivery.
Administration Instructions
Before administration, remove the syringe tip cap and attach the Luer lock cone-shaped applicator to the syringe.
- Using the Luer lock cone-shaped applicator attached to the syringe, apply ZYNRELEF to the tissues within the surgical site as follows:
- For soft tissue procedures, apply ZYNRELEF into the wound prior to closure of each layer within the surgical space.
- For abdominal procedures, apply after closure of the peritoneum (if applicable) and avoid administration below the peritoneum.
- In general for orthopedic procedures, apply ZYNRELEF into the wound and on the periosteum from the proximal to the distal ends of the wound (i.e., beyond the boney repair).
- For total joint arthroplasty, apply ZYNRELEF directly into the joint capsule, onto the periosteum, and the antero-, medial-, and lateral tissues (if applicable), after placement of the component(s).
- For spinal procedures, apply ZYNRELEF after closure of the paraspinal musculature and again after closure of the subcutaneous fascia. ZYNRELEF must not be applied to the dura or spinal cord.
- For soft tissue procedures, apply ZYNRELEF into the wound prior to closure of each layer within the surgical space.
- Only apply ZYNRELEF to the tissue layers below the skin incision and not directly onto the subdermal layer or the skin. Minimize administration of ZYNRELEF near the incision line.
- Use only the amount necessary to coat the tissues, such that ZYNRELEF does not leak from the surgical wound after closure. Wipe off excess ZYNRELEF from the skin prior to or during closure of the wound.
Dosing Instructions
As a general guidance in selecting the proper dosing of ZYNRELEF, the following examples of dosing are provided:
- For soft tissue surgical procedures, such as:
- open inguinal herniorrhaphy: up to 10.5 mL to deliver 300 mg of bupivacaine and 9 mg of meloxicam [see Clinical Studies (14) ] ;
- abdominoplasty: up to 14 mL to deliver 400 mg of bupivacaine and 12 mg of meloxicam [see Clinical Studies (14) ] ;
- Cesarean section: up to 14 mL to deliver 400 mg of bupivacaine and 12 mg of meloxicam [see Clinical Studies (14) ] ;
- augmentation mammoplasty: up to 7 mL per side to deliver total of 400 mg of bupivacaine and 12 mg of meloxicam [see Clinical Studies (14) ] .
- For orthopedic surgical procedures, such as:
- bunionectomy: up to 2.3 mL to deliver 60 mg of bupivacaine and 1.8 mg of meloxicam [see Clinical Studies (14) ] ;
- total knee arthroplasty: up to 14 mL to deliver 400 mg of bupivacaine and 12 mg of meloxicam [see Clinical Studies (14) ] ;
- total shoulder arthroplasty: up to 14 mL to deliver 400 mg of bupivacaine and 12 mg of meloxicam [see Clinical Studies (14) ] ;
- 1- to 3-level spinal surgery: up to 7 mL to deliver 200 mg bupivacaine and 6 mg meloxicam [see Clinical Studies (14) ] .
Compatibility Considerations
- Do not dilute ZYNRELEF.
- ZYNRELEF is a nonaqueous solution. It cannot be mixed with water, saline, or other local anesthetics as the product will become more viscous and difficult to administer.
- When a topical antiseptic such as povidone iodine (e.g., Betadine ® ) is applied, the site should be allowed to dry before a local anesthetic, including ZYNRELEF, is administered into the site.
- When administered in recommended doses and concentrations, ZYNRELEF does not ordinarily produce irritation or tissue damage.
ZYNRELEF is compatible with:
- All components of the ZYNRELEF kit, including syringes, Luer lock cone-shaped applicator, vented vial spike, vial access needle, and syringe tip caps.
- Surgical mesh materials, including polypropylene (Prolene ® ), Gore-tex, and polyester.
- Silicone membranes.
- Bone cement.
- Metal alloys used in surgical implants.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
ZYNRELEF (bupivacaine and meloxicam) extended-release solution is a sterile, clear, pale-yellow to yellow, viscous liquid in a single-dose vial containing 29.25 mg/mL bupivacaine and 0.88 mg/mL meloxicam and is available in the following four presentations:
- 14 mL containing 400 mg bupivacaine and 12 mg meloxicam
- 10.5 mL containing 300 mg bupivacaine and 9 mg meloxicam
- 7 mL containing 200 mg bupivacaine and 6 mg meloxicam
- 2.3 mL containing 60 mg bupivacaine and 1.8 mg meloxicam
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Infertility : NSAIDs are associated with reversible infertility. Consider avoidance of ZYNRELEF in women who have difficulties conceiving (8.3 ).
Severe Hepatic Impairment : Only use if benefits are expected to outweigh risks; monitor for signs of worsening liver function (8.6 ).
Severe Renal Impairment : Not recommended (8.7 ).
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no available human data on use of ZYNRELEF in pregnant women to evaluate for a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. However, there are available data on the individual components of ZYNRELEF, bupivacaine and meloxicam.
Bupivacaine
The available data on bupivacaine use in pregnant women for epidural anesthesia (excluding paracervical block) are insufficient to draw conclusions about a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies with bupivacaine in pregnant women. In animal studies, embryo-fetal lethality was noted when bupivacaine was administered subcutaneously to pregnant rabbits during organogenesis at a comparable bupivacaine dose level of 400 mg at the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of ZYNRELEF. Decreased pup survival was observed in a rat pre- and post-natal developmental study (dosing from implantation through weaning) at a comparable bupivacaine dose to the MRHD ( see Data ). Based on animal data, pregnant women should be advised of the potential risks to a fetus.
Meloxicam
Use of NSAIDs, including ZYNRELEF, can cause premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus and fetal renal dysfunction leading to oligohydramnios and, in some cases, neonatal renal impairment. Because of these risks, limit dose and duration of ZYNRELEF use between about 20 and 30 weeks of gestation and avoid ZYNRELEF use at about 30 weeks of gestation and later in pregnancy ( see Clinical Considerations , Data ).
Premature Closure of Fetal Ductus Arteriosus
Use of NSAIDs, including ZYNRELEF, at about 30 weeks gestation or later in pregnancy increases the risk of premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus.
Oligohydramnios/Neonatal Renal Impairment
Use of NSAIDs at about 20 weeks gestation or later in pregnancy has been associated with cases of fetal renal dysfunction leading to oligohydramnios, and in some cases, neonatal renal impairment.
Data from observational studies regarding other potential embryofetal risks of NSAID use in women in the first or second trimesters of pregnancy are inconclusive. In animal reproduction studies, embryofetal death was observed in rats and rabbits treated during the period of organogenesis with meloxicam at oral doses equivalent to 0.8 and 8 times, respectively, the meloxicam dose level of 12 mg at the MRHD of ZYNRELEF. Increased incidence of septal heart defects was observed in rabbits treated throughout embryogenesis with meloxicam at an oral dose equivalent to 97 times the MRHD. In pre- and post-natal reproduction studies, there was an increased incidence of dystocia, delayed parturition, and decreased offspring survival at 0.1 times the MRHD. No malformations were observed in rats and rabbits treated with meloxicam during organogenesis at an oral dose equivalent to 3.2 and 32 times, respectively, the MRHD (see Data ).
Based on animal data, prostaglandins have been shown to have an important role in endometrial vascular permeability, blastocyst implantation, and decidualization. In animal studies, administration of prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors such as meloxicam, resulted in increased pre- and post-implantation loss. Prostaglandins also have been shown to have an important role in fetal kidney development. In published animal studies, prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors have been reported to impair kidney development when administered at clinically relevant doses.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population(s) is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Fetal/Neonatal Adverse Reactions
Meloxicam
Premature Closure of the Fetal Ductus Arteriosus:
Avoid use of NSAIDs in women at about 30 weeks gestation and later in pregnancy, because NSAIDs, including ZYNRELEF, can cause premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus (see Data ) .
Oligohydramnios/Neonatal Renal Impairment:
If an NSAID is necessary at about 20 weeks gestation or later in pregnancy, limit the use to the lowest effective dose and shortest duration possible. Because meloxicam can be detected in plasma beyond 48 hours after administration of ZYNRELEF, consider monitoring with ultrasound for oligohydramnios. If oligohydramnios occurs, follow up according to clinical practice ( see Data ).
Labor or Delivery
Bupivacaine
Bupivacaine is contraindicated in obstetrical paracervical block anesthesia. The use of bupivacaine for obstetrical paracervical block anesthesia has resulted in fetal bradycardia and death [see Contraindications (4) ].
Bupivacaine can rapidly cross the placenta, and when used for epidural, caudal, or pudendal block anesthesia, can cause varying degrees of maternal, fetal, and neonatal toxicity [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ]. The incidence and degree of toxicity depend upon the procedure performed, the type and amount of drug used, and the technique of drug administration. Adverse reactions in the parturient, fetus, and neonate involve alterations of the central nervous system, peripheral vascular tone, and cardiac function.
Meloxicam
There are no studies on the effects of meloxicam during labor or delivery. In animal studies, NSAIDs, including meloxicam, inhibit prostaglandin synthesis, cause delayed parturition, and increase the incidence of stillbirth.
Data
Human Data
Meloxicam
Premature Closure of Fetal Ductus Arteriosus:
Published literature reports that the use of NSAIDs at about 30 weeks of gestation and later in pregnancy may cause premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus.
Oligohydramnios/Neonatal Renal Impairment:
Published studies and postmarketing reports describe maternal NSAID use at about 20 weeks gestation or later in pregnancy associated with fetal renal dysfunction leading to oligohydramnios, and in some cases, neonatal renal impairment. These adverse outcomes are seen, on average, after days to weeks of treatment, although oligohydramnios has been infrequently reported as soon as 48 hours after NSAID initiation. In many cases, but not all, the decrease in amniotic fluid was transient and reversible with cessation of the drug. There have been a limited number of case reports of maternal NSAID use and neonatal renal dysfunction without oligohydramnios, some of which were irreversible. Some cases of neonatal renal dysfunction required treatment with invasive procedures, such as exchange transfusion or dialysis.
Methodological limitations of these postmarketing studies and reports include lack of a control group; limited information regarding dose, duration, and timing of drug exposure; and concomitant use of other medications. These limitations preclude establishing a reliable estimate of the risk of adverse fetal and neonatal outcomes with maternal NSAID use. Because the published safety data on neonatal outcomes involved mostly preterm infants, the generalizability of certain reported risks to the full-term infant exposed to NSAIDs through maternal use is uncertain.
Animal Data
Reproduction studies have not been conducted with ZYNRELEF.
Bupivacaine
Bupivacaine HCl was administered subcutaneously to rats at doses of 4.4, 13.3, and 40 mg/kg and to rabbits at doses of 1.3, 5.8, and 22.2 mg/kg during the period of organogenesis (implantation to closure of the hard palate). The high doses are comparable to the daily MRHD of 400 mg on a mg/m 2 (BSA) basis. No embryo-fetal effects were observed in rats at the high dose which caused increased maternal lethality. An increase in embryo-fetal deaths was observed in rabbits at the high dose in the absence of maternal toxicity with the fetal No Observed Adverse Effect Level representing approximately 0.3 times the MRHD on a BSA basis.
In a rat pre- and post-natal developmental study (dosing from implantation through weaning) conducted at subcutaneous doses of 4.4, 13.3, and 40 mg/kg, decreased pup survival was observed at the high dose. The high dose is comparable to the daily MRHD of 400 mg on a BSA basis.
Meloxicam
Meloxicam did not cause malformations when administered to pregnant rats during fetal organogenesis at oral doses up to 4 mg/kg/day (3.2 times the meloxicam dose level of 12 mg at the MRHD of ZYNRELEF based on BSA comparison). Administration of meloxicam to pregnant rabbits throughout embryogenesis produced an increased incidence of septal defects of the heart at an oral dose of 60 mg/kg/day (97 times the MRHD based on BSA comparison). The no effect level was 20 mg/kg/day (32 times the MRHD based on BSA comparison). In rats and rabbits, embryolethality occurred at oral meloxicam doses of 1 mg/kg/day and 5 mg/kg/day, respectively (0.8 and 8 times the MRHD, respectively, based on BSA comparison) when administered throughout organogenesis.
Oral administration of meloxicam to pregnant rats during late gestation through lactation increased the incidence of dystocia, delayed parturition, and decreased offspring survival at meloxicam doses of 0.125 mg/kg/day or greater (0.1 times the MRHD based on BSA comparison).
Lactation
Risk Summary
Limited published literature reports that bupivacaine and its primary metabolite, pipecoloxylidine (PPX), are present in human milk at low levels. There are no human data available on whether meloxicam is present in human milk. There is no available information on effects of bupivacaine or meloxicam in the breastfed infant or effects of the drugs on milk production.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for ZYNRELEF and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from ZYNRELEF or from the underlying maternal condition.
Data
Animal Data
Following administration of ZYNRELEF to lactating pigs, bupivacaine and meloxicam were detected in milk, but only bupivacaine was detected in the plasma of piglets allowed to suckle milk from the treated animals. Meloxicam was present in the milk of lactating rats at concentrations higher than those in plasma.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Infertility
Females
Based on the mechanism of action, the use of prostaglandin-mediated NSAIDs, including meloxicam, may delay or prevent rupture of ovarian follicles, which has been associated with reversible infertility in some women. Published animal studies have shown that administration of prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors has the potential to disrupt prostaglandin-mediated follicular rupture required for ovulation. Small studies in women treated with NSAIDs have also shown a reversible delay in ovulation. Consider withdrawal of NSAIDs and avoidance of ZYNRELEF in women who have difficulties conceiving or who are undergoing investigation of infertility.
Males
In a published study, oral administration of meloxicam to male rats for 35 days resulted in decreased sperm count and motility and histopathological evidence of testicular degeneration at 0.8 times the MRHD based on BSA comparison [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1) ] . It is not known if these effects on fertility are reversible. The clinical relevance of these findings is unknown.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of ZYNRELEF in pediatric patients has not been established.
Geriatric Use
Of the total number of patients undergoing various surgical procedures who were exposed to ZYNRELEF in clinical studies (N=1627), 288 patients (17.7%) were ≥ 65 years old, while 83 (5.1%) were ≥75 years old. No overall differences in safety or efficacy were observed between elderly patients and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
Elderly patients, compared to younger patients, are at greater risk for NSAID-associated serious cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, and/or renal adverse reactions, although the applicability of this to a single administration of low-dose meloxicam in ZYNRELEF is uncertain [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 , 5.2 , 5.8) ] .
In clinical studies, differences in various pharmacokinetic parameters have been observed with bupivacaine HCl between elderly and younger patients. Bupivacaine is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to bupivacaine may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in ZYNRELEF dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . Consider reducing the dose of ZYNRELEF for elderly patients.
Hepatic Impairment
Amide-type local anesthetics such as bupivacaine are metabolized primarily in the liver. Patients with severe hepatic disease, because of their inability to metabolize local anesthetics normally, are at a greater risk of developing toxic plasma concentrations, and potentially local anesthetic systemic toxicity.
Because meloxicam is primarily metabolized in the liver and hepatotoxicity may occur, monitor patients with hepatic impairment for signs and symptoms of worsening disease. Meloxicam has not been adequately studied in patients with severe hepatic impairment.
No dose adjustment of ZYNRELEF is necessary in patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment. ZYNRELEF should only be used in patients with severe hepatic impairment if the benefits are expected to outweigh the risks; monitor patients for signs of worsening liver function. Consider increased monitoring for local anesthetic systemic toxicity in subjects with moderate to severe hepatic disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) , and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Renal Impairment
Because bupivacaine and meloxicam and their metabolites are excreted by the kidney, the risk of toxic reactions to these drugs may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. This should be considered when performing dose selection of ZYNRELEF. Consider reducing the dose of ZYNRELEF for patients with mild to moderate renal impairment.
Patients with severe renal disease, may be more susceptible to the potential toxicities of the amide-type local anesthetics. Patients with severe renal impairment have not been studied. The use of ZYNRELEF in patients with severe renal impairment is not recommended. Meloxicam is not dialyzable. When using ZYNRELEF in patients on hemodialysis do not exceed maximum recommended dose or use with other meloxicam-containing products [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Poor Metabolizers of CYP2C9 Substrates
In patients who are known or suspected to be poor CYP2C9 metabolizers based on genotype or previous history/experience with other CYP2C9 substrates (such as warfarin or phenytoin), consider dose reduction, as these patients may have abnormally high plasma levels of meloxicam due to reduced metabolic clearance. Monitor these patients for adverse effects.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
ZYNRELEF is contraindicated in:
- Patients with a known hypersensitivity (e.g., anaphylactic reactions and serious skin reactions) to any local anesthetic agent of the amide-type, NSAIDs, or to any of the other components of ZYNRELEF [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9 , 5.14) ] .
- Patients with a history of asthma, urticaria, or other allergic-type reactions after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs. Severe, sometimes fatal, anaphylactic reactions to NSAIDs have been reported in such patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9) ] .
- Patients undergoing obstetrical paracervical block anesthesia. The use of bupivacaine in this technique has resulted in fetal bradycardia and death [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ] .
- Patients undergoing coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Dose-Related Toxicity : Monitor cardiovascular and respiratory vital signs and patient's state of consciousness after application of ZYNRELEF (5.3 ).
When using ZYNRELEF with other local anesthetics, overall local anesthetic exposure must be considered through 72 hours (5.3 ).
Hepatotoxicity : If abnormal liver tests persist or worsen, perform a clinical evaluation of the patient (5.5 ).
Hypertension : Patients taking some antihypertensive medications may have impaired response to these therapies when taking NSAIDs. Monitor blood pressure (5.6 , 7 ).
Heart Failure and Edema : Avoid use of ZYNRELEF in patients with severe heart failure unless benefits are expected to outweigh risk of worsening heart failure (5.7 ).
Renal Toxicity : Monitor renal function in patients with renal or hepatic impairment, heart failure, dehydration, or hypovolemia. Avoid use of ZYNRELEF in patients with advanced renal disease unless benefits are expected to outweigh risk of worsening renal function (5.8 ).
Anaphylactic Reactions : Seek emergency help if an anaphylactic reaction occurs (5.9 ).
Risk of Joint Cartilage Necrosis and Degeneration with Unapproved Intra-articular Use : Animal studies evaluating the effects of ZYNRELEF following intra-articular administration in the knee joint demonstrated cartilage necrosis and degeneration (5.10 , 13.2 ).
Chondrolysis : Limit exposure to articular cartilage due to the potential risk of chondrolysis (5.11 ).
Methemoglobinemia : Cases of methemoglobinemia have been reported in association with local anesthetic use (5.12 ).
Serious Skin Reactions : NSAIDs, including meloxicam, can cause serious skin adverse reactions. If symptoms present, evaluate clinically (5.14 ).
Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) : If symptoms are present, evaluate clinically (5.15 ).
Fetal Toxicity : Limit use of NSAIDs, including ZYNRELEF, between about 20 to 30 weeks in pregnancy due to the risk of oligohydramnios/fetal renal dysfunction. Avoid use of NSAIDs in women at about 30 weeks gestation and later in pregnancy due to the risks of oligohydramnios/fetal renal dysfunction and premature closure of the ductus arteriosus (5.16 , 8.1 ).
Hematologic Toxicity : Monitor hemoglobin or hematocrit in patients with any signs or symptoms of anemia (5.17 ).
Cardiovascular (CV) Thrombotic Events with NSAID Use
Clinical trials of several COX-2 selective and nonselective NSAIDs of up to three years duration have shown an increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction (MI) and stroke, which can be fatal. Based on available data, it is unclear that the risk for CV thrombotic events is similar for all NSAIDs. The relative increase in serious CV thrombotic events over baseline conferred by NSAID use appears to be similar in those with and without known CV disease or risk factors for CV disease. However, patients with known CV disease or risk factors had a higher absolute incidence of excess serious CV thrombotic events, due to their increased baseline rate. Some observational studies found that this increased risk of serious CV thrombotic events began as early as the first weeks of treatment. The increase in CV thrombotic risk has been observed most consistently at higher doses. The risk of these events following single-dose local application of ZYNRELEF is uncertain.
To minimize the potential risk for an adverse CV event in NSAID-treated patients, do not exceed the recommended dose. Physicians and patients should remain alert for the development of such events following treatment with ZYNRELEF, even in the absence of previous CV symptoms. Inform patients about the signs and symptoms of serious CV events and the steps to take if they occur.
There is no consistent evidence that concurrent use of aspirin mitigates the increased risk of serious CV thrombotic events associated with NSAID use. The concurrent use of aspirin and an NSAID, such as meloxicam, increases the risk of serious gastrointestinal (GI) events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] .
Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) Surgery
Two large, controlled clinical trials of a COX-2 selective NSAID for the treatment of pain in the first 10-14 days following CABG surgery found an increased incidence of myocardial infarction and stroke. ZYNRELEF is contraindicated in the setting of CABG [see Contraindications (4) ] .
Post-MI Patients
Observational studies conducted in the Danish National Registry have demonstrated that patients treated with NSAIDs in the post-MI period were at increased risk of reinfarction, CV-related death, and all-cause mortality beginning in the first week of treatment. In this same cohort, the incidence of death in the first year post-MI was 20 per 100 person years in NSAID-treated patients compared to 12 per 100 person years in non-NSAID exposed patients. Although the absolute rate of death declined somewhat after the first year post-MI, the increased relative risk of death in NSAID users persisted over at least the next four years of follow-up.
Avoid the use of ZYNRELEF in patients with a recent MI unless the benefits are expected to outweigh the risk of recurrent CV thrombotic events. If ZYNRELEF is used in patients with a recent MI, monitor patients for signs of cardiac ischemia. The risk of these events following single-dose local application of ZYNRELEF is uncertain.
Gastrointestinal Bleeding, Ulceration, and Perforation with NSAID Use
NSAIDs, including meloxicam in ZYNRELEF, can cause serious gastrointestinal (GI) adverse events including inflammation, bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, or large intestine, which can be fatal. These serious adverse events can occur at any time, with or without warning symptoms, in patients treated with NSAIDs. Only one in five patients who develop a serious upper GI adverse event on NSAID therapy is symptomatic. Upper GI ulcers, gross bleeding, or perforation caused by NSAIDs occurred in approximately 1% of patients treated for 3 to 6 months, and in about 2 to 4% of patients treated for one year. However, even short-term NSAID therapy is not without risk.
Risk Factors for GI Bleeding, Ulceration, and Perforation
Patients with a prior history of peptic ulcer disease and/or GI bleeding who used NSAIDs have a greater than 10-fold increased risk for developing a GI bleed compared to patients without these risk factors. Other factors that increase the risk of GI bleeding in patients treated with NSAIDs include longer duration of NSAID therapy; concomitant use of oral corticosteroids, aspirin, anticoagulants, or selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs); smoking; use of alcohol; older age; and poor general health status. Most post marketing reports of fatal GI events occurred in elderly or debilitated patients. Additionally, patients with advanced liver disease and/or coagulopathy are at increased risk for GI bleeding.
Strategies to Minimize the GI Risks in NSAID-treated Patients
- Use the recommended dose for each indicated surgical procedure.
- Avoid administration of analgesic doses of more than one NSAID at a time. If additional NSAID medication is indicated in the postoperative period, monitor patients for signs and symptoms of NSAID-related GI adverse reactions.
- Avoid use in patients at higher risk unless benefits are expected to outweigh the increased risk of bleeding. For such patients, as well as those with active GI bleeding, consider alternate therapies other than NSAIDs.
- Remain alert for signs and symptoms of GI ulceration and bleeding following treatment with ZYNRELEF.
- If a serious GI adverse event is suspected, promptly initiate evaluation and treatment.
- In the setting of concomitant use of low-dose aspirin for cardiac prophylaxis, monitor patients more closely for evidence of GI bleeding [see Drug Interactions (7) ] .
Dose-Related Toxicity
The safety and effectiveness of local anesthetics depend on proper dosage, correct technique, adequate precautions, and readiness for emergencies. The toxic effects of local anesthetics are additive. Avoid additional local anesthetic administration within 96 hours following ZYNRELEF instillation. If additional local anesthetic administration with ZYNRELEF cannot be avoided based on clinical need, monitor patients for neurologic and cardiovascular effects related to local anesthetic systemic toxicity. Careful and constant monitoring of cardiovascular and respiratory (adequacy of ventilation) vital signs and the patient's state of consciousness should be performed after administration of ZYNRELEF.
Possible early warning signs of central nervous system (CNS) toxicity are restlessness, anxiety, incoherent speech, lightheadedness, numbness and tingling of the mouth and lips, metallic taste, tinnitus, dizziness, blurred vision, tremors, twitching, CNS depression, or drowsiness. Delay in proper management of dose-related toxicity, underventilation from any cause, and/or altered sensitivity may lead to the development of acidosis, cardiac arrest, and, possibly, death.
Risk of Use in Patients with Impaired Cardiovascular Function
Patients with impaired cardiovascular function (e.g., hypotension, heart block) may be less able to compensate for functional changes associated with the prolongation of AV conduction produced by ZYNRELEF. Monitor patients closely for blood pressure, heart rate, and ECG changes.
Hepatotoxicity
Local Anesthetics, Including Bupivacaine
Because amide-type local anesthetics such as bupivacaine are metabolized by the liver, these drugs should be used cautiously in patients with hepatic disease. Patients with severe hepatic disease, because of their inability to metabolize local anesthetics normally, are at a greater risk of developing toxic plasma concentrations.
NSAIDs
Elevations of ALT or AST (three or more times the upper limit of normal [ULN]) have been reported in approximately 1% of NSAID-treated patients in clinical trials. In addition, rare, sometimes fatal, cases of severe hepatic injury, including fulminant hepatitis, liver necrosis, and hepatic failure have been reported.
Elevations of ALT or AST (less than three times ULN) may occur in up to 15% of patients treated with NSAIDs including meloxicam. The risk of these events following single-dose local application of ZYNRELEF is uncertain.
Inform patients of the warning signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity (e.g., nausea, fatigue, lethargy, diarrhea, pruritus, jaundice, right upper quadrant tenderness, and "flu-like" symptoms). If clinical signs and symptoms consistent with liver disease develop, or if systemic manifestations occur (e.g., eosinophilia, rash, etc.), perform a clinical evaluation of the patient [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Hypertension
NSAIDs, including meloxicam in ZYNRELEF, can lead to new onset of hypertension or worsening of preexisting hypertension, either of which may contribute to the increased incidence of CV events. Patients taking angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, thiazide diuretics, or loop diuretics may have impaired response to these therapies when taking NSAIDs [see Drug Interactions (7) ] .
Monitor blood pressure (BP) after administration of ZYNRELEF.
Heart Failure and Edema
The Coxib and traditional NSAID Trialists' Collaboration meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials demonstrated an approximately two-fold increase in hospitalizations for heart failure in COX-2 selective-treated patients and nonselective NSAID-treated patients compared to placebo-treated patients. In a Danish National Registry study of patients with heart failure, NSAID use increased the risk of MI, hospitalization for heart failure, and death.
Additionally, fluid retention and edema have been observed in some patients treated with NSAIDs. Use of meloxicam may blunt the CV effects of several therapeutic agents used to treat these medical conditions (e.g., diuretics, ACE inhibitors, or angiotensin receptor blockers [ARBs]) [see Drug Interactions (7) ] . The risk of these events following single-dose local application of ZYNRELEF is uncertain.
Avoid the use of ZYNRELEF in patients with severe heart failure unless the benefits are expected to outweigh the risk of worsening heart failure. If ZYNRELEF is used in patients with severe heart failure, monitor patients for signs of worsening heart failure.
Renal Toxicity and Hyperkalemia
Renal Toxicity
ZYNRELEF is a single-use product that contains an NSAID. Long-term administration of NSAIDs has resulted in renal papillary necrosis, renal insufficiency, acute renal failure, and other renal injury.
Renal toxicity has also been seen in patients in whom renal prostaglandins have a compensatory role in the maintenance of renal perfusion. In these patients, administration of an NSAID may cause a dose-dependent reduction in prostaglandin formation and, secondarily, in renal blood flow, which may precipitate overt renal decompensation. Patients at greatest risk of this reaction are those with impaired renal function, dehydration, hypovolemia, heart failure, liver dysfunction, those taking diuretics and ACE inhibitors or ARBs, and the elderly. Discontinuation of NSAID therapy is usually followed by recovery to the pretreatment state.
The renal effects of meloxicam may hasten the progression of renal dysfunction in patients with preexisting renal disease. Because some meloxicam metabolites are excreted by the kidney, monitor patients for signs of worsening renal function.
Correct volume status in dehydrated or hypovolemic patients prior to initiating ZYNRELEF. Monitor renal function in patients with renal or hepatic impairment, heart failure, dehydration, or hypovolemia during use of ZYNRELEF [see Drug Interactions (7) ] . Avoid the use of ZYNRELEF in patients with advanced renal disease unless the benefits are expected to outweigh the risk of worsening renal function. If ZYNRELEF is used in patients with advanced renal disease, monitor patients for signs of worsening renal function [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Hyperkalemia
Increases in serum potassium concentration, including hyperkalemia, have been reported with use of NSAIDs, even in some patients without renal impairment. In patients with normal renal function, these effects have been attributed to a hyporeninemic-hypoaldosteronism state.
Anaphylactic Reactions
NSAIDs
Meloxicam, contained in ZYNRELEF, has been associated with anaphylactic reactions in patients with and without known hypersensitivity to meloxicam and in patients with aspirin-sensitive asthma [see Contraindications (4) ] .
Seek emergency help if an anaphylactic reaction occurs.
Risk of Joint Cartilage Necrosis with Unapproved Intra-articular Use
The safety and effectiveness of intra-articular use of ZYNRELEF in orthopedic surgical procedures other than for foot and ankle procedures have not been established, and ZYNRELEF is not approved for use via other intra-articular administration routes. Animal studies evaluating the effects of ZYNRELEF following intra-articular administration in the knee joint demonstrated cartilage necrosis and degeneration [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.2) ] .
Chondrolysis
Limit exposure to articular cartilage due to the potential risk of chondrolysis.
Intra-articular infusions of local anesthetics, following arthroscopic and other surgical procedures is an unapproved use, and there have been post marketing reports of chondrolysis in patients receiving such infusions. The majority of reported cases of chondrolysis have involved the shoulder joint; cases of glenohumeral chondrolysis have been described in pediatric patients and adult patients following intra-articular infusions of local anesthetics with and without epinephrine for periods of 48 to 72 hours. There is insufficient information to determine whether shorter infusion periods are associated with chondrolysis. The time of onset of symptoms, such as joint pain, stiffness, and loss of motion can be variable, but may begin as early as the 2 nd month after surgery. Currently, there is no effective treatment for chondrolysis; patients who have experienced chondrolysis have required additional diagnostic and therapeutic procedures and some required arthroplasty or shoulder replacement.
Methemoglobinemia
Cases of methemoglobinemia have been reported in association with local anesthetic use. Although all patients are at risk for methemoglobinemia, patients with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, congenital or idiopathic methemoglobinemia, cardiac or pulmonary compromise, infants under 6 months of age, and concurrent exposure to oxidizing agents or their metabolites are more susceptible to developing clinical manifestations of the condition. If local anesthetics must be used in these patients, close monitoring for symptoms and signs of methemoglobinemia is recommended. Signs of methemoglobinemia may occur immediately or may be delayed some hours after exposure, and are characterized by a cyanotic skin discoloration and/or abnormal coloration of the blood.
Methemoglobin levels may continue to rise; therefore, immediate treatment is required to avert more serious central nervous system and cardiovascular adverse effects, including seizures, coma, arrhythmias, and death. Discontinue any oxidizing agents. Depending on the severity of the signs and symptoms, patients may respond to supportive care, i.e., oxygen therapy, hydration. A more severe clinical presentation may require treatment with methylene blue, exchange transfusion, or hyperbaric oxygen.
Exacerbation of Asthma Related to Aspirin Sensitivity
A subpopulation of patients with asthma may have aspirin-sensitive asthma, which may include: chronic rhinosinusitis complicated by nasal polyps; severe, potentially fatal bronchospasm; and/or intolerance to aspirin and other NSAIDs. Because cross-reactivity between aspirin and other NSAIDs has been reported in such aspirin-sensitive patients, NSAIDs are contraindicated in patients with this form of aspirin sensitivity [see Contraindications (4) ] . When ZYNRELEF is used in patients with preexisting asthma (without known aspirin sensitivity), monitor patients for exacerbation of asthma symptoms.
Serious Skin Reactions
NSAIDs, including meloxicam, can cause serious skin adverse reactions such as exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), which can be fatal. NSAIDs can also cause fixed drug eruption (FDE). FDE may present as a more severe variant known as generalized bullous fixed drug eruption (GBFDE), which can be life-threatening. These serious events may occur without warning. Inform patients about the signs and symptoms of serious skin reactions.
ZYNRELEF is contraindicated in patients with previous serious skin reactions to NSAIDs [see Contraindications (4) ] .
Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS)
Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) has been reported in patients taking NSAIDs such as ZYNRELEF. Some of these events have been fatal or life-threatening. DRESS typically, although not exclusively, presents with fever, rash, lymphadenopathy, and/or facial swelling. Other clinical manifestations may include hepatitis, nephritis, hematological abnormalities, myocarditis, or myositis. Sometimes symptoms of DRESS may resemble an acute viral infection. Eosinophilia is often present. Because this disorder is variable in its presentation, other organ systems not noted here may be involved. It is important to note that early manifestations of hypersensitivity, such as fever or lymphadenopathy, may be present even though rash is not evident. If such signs or symptoms are present, evaluate the patient immediately and treat as clinically indicated.
Fetal Toxicity
Premature Closure of Fetal Ductus Arteriosus
Avoid use of NSAIDs, including ZYNRELEF, in pregnant women at about 30 weeks gestation and later. NSAIDs, including ZYNRELEF, increase the risk of premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus at approximately this gestational age.
Oligohydramnios/Neonatal Renal Impairment
Use of NSAIDs, including ZYNRELEF, at about 20 weeks gestation or later in pregnancy may cause fetal renal dysfunction leading to oligohydramnios and, in some cases, neonatal renal impairment. These adverse outcomes are seen, on average, after days to weeks of treatment, although oligohydramnios has been infrequently reported as soon as 48 hours after NSAID initiation. Oligohydramnios is often, but not always, reversible with treatment discontinuation. Complications of prolonged oligohydramnios may, for example, include limb contractures and delayed lung maturation. In some postmarketing cases of impaired neonatal renal function, invasive procedures such as exchange transfusion or dialysis were required.
If NSAID treatment is necessary between about 20 weeks and 30 weeks gestation, limit ZYNRELEF use to the lowest effective dose. Because meloxicam can be detected in plasma beyond 48 hours after administration of ZYNRELEF, consider ultrasound monitoring for oligohydramnios. If oligohydramnios occurs, follow up according to clinical practice [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ] .
Hematologic Toxicity
Anemia has occurred in NSAID-treated patients. This may be due to occult or gross blood loss, fluid retention, or an incompletely described effect on erythropoiesis. If a patient treated with ZYNRELEF has any signs or symptoms of anemia, monitor hemoglobin or hematocrit.
NSAIDs, including meloxicam, may increase the risk of bleeding events. Co-morbid conditions such as coagulation disorders or concomitant use of warfarin, other anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents (e.g., aspirin), serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) may increase this risk. Monitor these patients for signs of bleeding [see Drug Interactions (7) ] .
Masking of Inflammation and Fever
The pharmacological activity of ZYNRELEF in reducing inflammation, and possibly fever, may diminish the utility of diagnostic signs in detecting infections.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions have been associated with bupivacaine HCl or meloxicam and are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Cardiovascular System Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 , 5.4) ]
- Gastrointestinal Bleeding, Ulceration, and Perforation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
- Dose-Related Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ]
- Hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ]
- Heart Failure and Edema [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ]
- Renal Toxicity and Hyperkalemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) ]
- Anaphylactic Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9) ]
- Chondrolysis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11) ]
- Methemoglobinemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12) ]
- Exacerbation of Asthma Related to Aspirin Sensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13) ]
- Serious Skin Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14) ]
- Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Toxicity (DRESS) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.15) ]
- Fetal Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.16) ]
- Hematologic Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.17) ]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical studies are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical studies of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of ZYNRELEF has been evaluated in a total of 1627 patients undergoing various surgical procedures across 14 clinical studies including 7 randomized, double-blind, bupivacaine- and placebo-controlled and saline placebo-controlled studies designed to investigate ZYNRELEF to reduce postoperative pain for 72 hours and the need for opioid analgesics, of whom 1183 received ZYNRELEF by instillation. Patients treated with ZYNRELEF ranged in age from 18 to 85 years (median age 51 years), with 53.0% female, 82.1% White, 13.7% African-American, and 4.3% all other races.
Common Adverse Reactions
The safety of ZYNRELEF has been evaluated in 1064 patients who received ZYNRELEF in single doses up to 400 mg/12 mg via instillation into the surgical site, including 533 patients undergoing a soft tissue surgical procedure (herniorrhaphy, abdominoplasty, augmentation mammoplasty, or Cesarean section) and 531 patients undergoing an orthopedic surgical procedure (bunionectomy, total knee arthroplasty, total shoulder arthroplasty, or lumbar spinal surgery). The most common adverse reactions (incidence greater than or equal to 5% and higher than placebo) following ZYNRELEF administration among patients undergoing soft tissue procedures was vomiting and among patients undergoing orthopedic procedures were constipation and headache.
The safety of ZYNRELEF as part of a scheduled, non-opioid multimodal analgesic regimen including 1 or more other NSAIDs has been evaluated in a total of 473 patients undergoing soft tissue procedures or orthopedic procedures. NSAIDs included ibuprofen, ketorolac, and celecoxib. In these studies, the most common adverse reactions (incidence of greater than or equal to 2%) potentially associated with NSAIDs were pruritus and postoperative anemia. Rare but clinically serious NSAID-related adverse events, including peptic ulcer hemorrhage, gastritis requiring hospitalization, hematemesis and melena, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, and increased hepatic enzymes, were observed in subjects with predisposing risk factors (i.e., concomitant comorbidities and/or on concomitant medications such as anticoagulant and/or antiplatelet medications) that increased the risk for NSAID-related gastrointestinal toxicity.
Adverse Reactions Reported in Phase 3 and 2b Placebo-controlled Trials
Three randomized, bupivacaine-controlled and saline placebo-controlled studies were conducted in patients undergoing bunionectomy (STUDY 1, Table 1 and Table 2), open inguinal herniorrhaphy (STUDY 2, Table 3), and total knee arthroplasty (STUDY 3, Table 4). The bunionectomy procedures in STUDY 1 were performed under regional anesthesia, a lidocaine Mayo block, and intravenous sedation. The herniorrhaphy procedures in STUDY 2 were performed under general anesthesia. The total knee arthroplasty procedures in STUDY 3 were performed under either general or spinal anesthesia. Patients in STUDY 1 and STUDY 2 were allowed opioid rescue with intravenous (IV) morphine and oral oxycodone, and/or non-opioid rescue with oral acetaminophen. Patients in STUDY 3 were pretreated with oral pregabalin and acetaminophen, and allowed opioid rescue with IV morphine and oral oxycodone postoperatively.
| Preferred Term | Saline Placebo (N=101), % | Bupivacaine HCl 50 mg (N=154), % | ZYNRELEF 60 mg/1.8 mg (N=157), % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dizziness | 18 | 23 | 22 |
| Incision site edema | 13 | 14 | 17 |
| Headache | 10 | 13 | 14 |
| Incision site erythema | 8 | 12 | 13 |
| Bradycardia | 6 | 8 | 8 |
| Impaired healing | 1 | 4 | 6 |
| Muscle twitching | 5 | 5 | 6 |
In STUDY 1, bone healing was assessed by X-ray on Days 28 and 42. There was no clinically meaningful difference in bone healing between treatment groups. A total of 4 subjects had delayed bone healing: 1 in the ZYNRELEF group, 1 in the saline placebo group, and 2 in the bupivacaine HCl group.
The incidence of local inflammatory adverse events was higher in the ZYNRELEF group than in either control group (Table 2).
| Saline Placebo (N=101), % | Bupivacaine HCl 50 mg (N=154), % | ZYNRELEF 60 mg/1.8 mg (N=157), % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Incision site edema | 13 | 14 | 17 |
| Incision site erythema | 8 | 12 | 13 |
| Impaired healing | 1 | 4 | 6 |
| Incision site cellulitis | 1 | 1 | 4 |
| Wound dehiscence | 2 | 1 | 4 |
| Incision site infection | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| Preferred Term | Saline Placebo (N=82), % | Bupivacaine HCl 75 mg (N=173), % | ZYNRELEF 300 mg/9 mg (N=163), % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Headache | 12 | 14 | 13 |
| Bradycardia | 7 | 9 | 9 |
| Dysgeusia | 4 | 12 | 9 |
| Skin odor abnormal All TEAEs of skin odor abnormal were recorded at a single site. | 1 | 1 | 8 |
| Preferred Term | Saline Placebo (N=53), % | Bupivacaine HCl 125 mg (N=55), % | ZYNRELEF 400 mg/12 mg (N=58), % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nausea | 47 | 55 | 50 |
| Constipation | 23 | 33 | 24 |
| Vomiting | 19 | 27 | 26 |
| Hypertension | 15 | 13 | 19 |
| Pyrexia | 4 | 15 | 14 |
| Leukocytosis | 0 | 2 | 7 |
| Pruritis | 2 | 5 | 7 |
| Headache | 0 | 7 | 7 |
| Anemia | 2 | 0 | 5 |
| Hyperhidrosis | 4 | 0 | 5 |
| Hypotension | 4 | 2 | 5 |
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of ZYNRELEF or other products containing NSAIDs. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
ZYNRELEF
Injury, Poisoning, and Procedural Complications: Wound necrosis, Wound dehiscence.
Surgical and Medical Procedures: Post-procedural drainage.
NSAIDs
Skin and Appendages: Exfoliative dermatitis, SJS, TEN, and FDE [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14) ] .
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Drugs that Interfere with Hemostasis (e.g., warfarin, aspirin, SSRIs/SNRIs) : Monitor patients for bleeding who are concomitantly taking ZYNRELEF with drugs that interfere with hemostasis (7.2 ).
ACE Inhibitors, Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs), or Beta-Blockers : Concomitant use with ZYNRELEF may diminish the antihypertensive effect of these drugs. Monitor blood pressure (7.2 ).
ACE Inhibitors and ARBs : Concomitant use with ZYNRELEF in elderly, volume-depleted, or those with renal impairment may result in deterioration of renal function. In such high-risk patients, monitor for signs of worsening renal function (7.2 ).
Diuretics : NSAIDs can reduce natriuretic effect of furosemide and thiazide diuretics. Monitor patients to assure diuretic efficacy including antihypertensive effect (7.2 ).
Bupivacaine Drug Interactions
In clinical studies, other local anesthetics (including ropivacaine and lidocaine) have been administered before, during, or after application of ZYNRELEF without evidence of local anesthetic systemic toxicity. Administration of ZYNRELEF with other formulations of local anesthetics, including bupivacaine liposome injectable suspension, has not been studied [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ] .
The toxic effects of local anesthetics are additive. Avoid additional use of local anesthetics within 96 hours following administration of ZYNRELEF. If co-administration cannot be avoided, monitor patients for neurologic and cardiovascular effects related to local anesthetic systemic toxicity [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) , Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Overdosage (10) ] .
Patients who are administered local anesthetics may be at increased risk of developing methemoglobinemia when concurrently exposed to the following drugs, which could include other local anesthetics (Table 5).
| Class | Examples |
|---|---|
| Nitrates/Nitrites | nitric oxide, nitroglycerin, nitroprusside, nitrous oxide |
| Local anesthetics | articaine, benzocaine, bupivacaine, lidocaine, mepivacaine, prilocaine, procaine, ropivacaine, tetracaine |
| Antineoplastic agents | cyclophosphamide, flutamide, hydroxyurea, ifosfamide, rasburicase |
| Antibiotics | dapsone, nitrofurantoin, para-aminosalicylic acid, sulfonamides |
| Antimalarials | chloroquine, primaquine |
| Anticonvulsants | phenobarbital, phenytoin, sodium valproate |
| Other drugs | acetaminophen, metoclopramide, quinine, sulfasalazine |
Meloxicam Drug Interactions
See Table 6 for clinically significant drug interactions with meloxicam.
| Drugs that Interfere with Hemostasis | |
| Clinical Impact: | Meloxicam and anticoagulants such as warfarin have a synergistic effect on bleeding. The concomitant use of meloxicam and anticoagulants have an increased risk of serious bleeding compared to the use of either drug alone. Serotonin release by platelets plays an important role in hemostasis. Case-control and cohort epidemiological studies showed that concomitant use of drugs that interfere with serotonin reuptake and an NSAID may potentiate the risk of bleeding more than an NSAID alone. |
| Intervention: | Monitor patients with concomitant use of ZYNRELEF with anticoagulants (e.g., warfarin), antiplatelet agents (e.g., aspirin), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), and serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) for signs of bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.17)] . |
| Aspirin | |
| Clinical Impact: | In a clinical study, the concomitant use of an NSAID and aspirin was associated with a significantly increased incidence of GI adverse reactions as compared to use of the NSAID alone [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] . |
| Intervention: | If aspirin is indicated in the postoperative period, monitor patients for signs and symptoms of GI bleeding [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . |
| ACE Inhibitors, Angiotensin Receptor Blockers, or Beta-Blockers | |
| Clinical Impact: | NSAIDs may diminish the antihypertensive effect of angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), or beta-blockers (including propranolol). In patients who are elderly, volume-depleted (including those on diuretic therapy), or have renal impairment, coadministration of an NSAID with ACE inhibitors or ARBs may result in deterioration of renal function, including possible acute renal failure. These effects are usually reversible. |
| Intervention: | During concomitant use of ZYNRELEF and ACE inhibitors, ARBs, or beta-blockers, monitor blood pressure to ensure that the desired blood pressure is obtained. During concomitant use of ZYNRELEF and ACE inhibitors or ARBs in patients who are elderly, volume-depleted, or have impaired renal function, monitor for signs of worsening renal function [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ] . When these drugs are administered concomitantly, patients should be adequately hydrated. Assess renal function at the beginning of the concomitant treatment and periodically thereafter. |
| Diuretics | |
| Clinical Impact: | Clinical studies, as well as post-marketing observations, showed that NSAIDs have reduced the natriuretic effect of loop diuretics (e.g., furosemide) and thiazide diuretics in some patients. This effect has been attributed to the NSAID inhibition of renal prostaglandin synthesis. However, studies with furosemide agents and meloxicam have not demonstrated a reduction in natriuretic effect. Furosemide single and multiple dose pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics are not affected by multiple doses of meloxicam. |
| Intervention: | During concomitant use of ZYNRELEF with diuretics, observe patients for signs of worsening renal function, in addition to assuring diuretic efficacy including antihypertensive effects. |
| Digoxin | |
| Clinical Impact: | The concomitant use of NSAIDS with digoxin has been reported to increase the serum concentration and prolong the half-life of digoxin. |
| Intervention: | During concomitant use of ZYNRELEF and digoxin, monitor serum digoxin levels. |
| Lithium | |
| Clinical Impact: | NSAIDs have produced elevations in plasma lithium levels and reductions in renal lithium clearance. The mean minimum lithium concentration increased 15%, and the renal clearance decreased by approximately 20%. This effect has been attributed to NSAID inhibition of renal prostaglandin synthesis [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . |
| Intervention: | Monitor patients on lithium for signs of lithium toxicity. |
| Methotrexate | |
| Clinical Impact: | Concomitant use of NSAIDs and methotrexate may increase the risk for methotrexate toxicity (e.g., neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, renal dysfunction). |
| Intervention: | During concomitant use of ZYNRELEF and methotrexate, monitor patients for methotrexate toxicity. |
| Cyclosporine | |
| Clinical Impact: | Concomitant use of NSAIDs and cyclosporine may increase cyclosporine's nephrotoxicity. |
| Intervention: | During concomitant use of ZYNRELEF and cyclosporine, monitor patients for signs of worsening renal function. |
| NSAIDs and Salicylates | |
| Clinical Impact: | Concomitant use of meloxicam with other NSAIDs or salicylates (e.g., diflunisal, salsalate) increases the risk of GI toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] . |
| Intervention: | If additional NSAID or salicylate medication is indicated in the postoperative period, monitor patients for signs and symptoms of GI toxicity [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . |
| Pemetrexed | |
| Clinical Impact: | Concomitant use of NSAIDs and pemetrexed may increase the risk of pemetrexed-associated myelosuppression, renal, and GI toxicity (see the pemetrexed prescribing information). |
| Intervention: | During concomitant use of ZYNRELEF and pemetrexed, in patients with renal impairment whose creatinine clearance ranges from 45 to 79 mL/min, monitor for myelosuppression, renal and GI toxicity. Patients taking meloxicam should interrupt dosing for at least five days before, the day of, and two days following pemetrexed administration. In patients with creatinine clearance below 45 mL/min, the concomitant administration of meloxicam with pemetrexed is not recommended. |
DESCRIPTION
ZYNRELEF (bupivacaine and meloxicam) extended-release solution, for soft tissue or periarticular instillation use, contains bupivacaine, an amide local anesthetic, and meloxicam, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID).
Bupivacaine
Bupivacaine is a white to off-white crystalline powder, crystals, or granules. The chemical name for bupivacaine is (±)-1-butyl- N -(2,6-dimethylphenyl)piperidine-2-carboxamide, and its empirical formula is C 18 H 28 N 2 O. The molecular weight of bupivacaine is 288.4. Bupivacaine is sparingly soluble in water and freely soluble in alcohol. Bupivacaine has a log P ow of 1.82 and a pKa of 8.1. Bupivacaine has the following structural formula:

Meloxicam
Meloxicam is a pale yellow solid, practically insoluble in water, with higher solubility observed in strong acids and bases. It is very slightly soluble in methanol. Meloxicam has an apparent partition coefficient (log P) app = 0.1 in n -octanol/buffer pH 7.4. Meloxicam has pKa values of 1.1 and 4.2. Meloxicam is chemically designated as 4-hydroxy-2-methyl- N -(5-methyl-2-thiazolyl)-2 H -1,2-benzothiazine-3-carboxamide-1,1-dioxide. The molecular weight is 351.4. Its empirical formula is C 14 H 13 N 3 O 4 S 2 and it has the following structural formula:

ZYNRELEF is a sterile, clear, pale yellow to yellow, viscous liquid provided in single-dose vials (10 mL or 20 mL) for instillation into the surgical site. Each mL of the solution contains active ingredients bupivacaine 29.25 mg and meloxicam 0.88 mg; and inactive ingredients tri(ethylene glycol) poly(orthoester) (730 mg), triacetin (293 mg), dimethyl sulfoxide (117 mg), and maleic acid (0.59 mg).
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
ZYNRELEF is a fixed-dose combination of bupivacaine and meloxicam.
Bupivacaine
Local anesthetics block the generation and the conduction of nerve impulses presumably by increasing the threshold for electrical excitation in the nerve, by slowing the propagation of the nerve impulse, and by reducing the rate of rise of the action potential. In general, the progression of anesthesia is related to the diameter, myelination, and conduction velocity of affected nerve fibers. Clinically, the order of loss of nerve function is as follows: (1) pain, (2) temperature, (3) touch, (4) proprioception, and (5) skeletal muscle tone.
Meloxicam
The mechanism of action of meloxicam, like that of other NSAIDs, is not completely understood but involves inhibition of cyclooxygenase (COX-1 and COX-2).
Meloxicam is a potent inhibitor of prostaglandin synthesis in vitro. Prostaglandins sensitize afferent nerves and potentiate the action of bradykinin in inducing pain in animal models. Prostaglandins are mediators of inflammation. Because meloxicam is an inhibitor of prostaglandin synthesis, its mode of action may be due to a decrease of prostaglandins in peripheral tissues.
Pharmacodynamics
Additional pharmacodynamic data in clinical studies
Additional pharmacodynamic data for ZYNRELEF was evaluated in patients undergoing abdominoplasty, Cesarean section, total shoulder arthroplasty, and 1- to 3-level lumbar spinal surgery. Refer to Dosage and Administration for specific doses used for each study [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) ] .
Contribution of Meloxicam and Bupivacaine to Activity of ZYNRELEF
The contribution of each active ingredient in ZYNRELEF was demonstrated in Phase 2 double-blind, randomized, active- and placebo-controlled clinical studies in subjects undergoing herniorrhaphy or bunionectomy, utilizing ZYNRELEF and formulations of meloxicam alone or bupivacaine alone in the ZYNRELEF vehicle. In both studies, meloxicam alone demonstrated negligible local analgesia and bupivacaine alone demonstrated greater analgesia compared with placebo through 24 hours post surgery, despite exposure to bupivacaine for approximately 72 hours. Compared with bupivacaine alone in both studies, ZYNRELEF (at the same bupivacaine doses) demonstrated greater and longer analgesia through 24, 48, and 72 hours.
Effect on Cardiac Repolarization
The effect of ZYNRELEF on cardiac repolarization as assessed by the QTc interval was evaluated following a single administration in patients undergoing surgical procedures. ZYNRELEF, at single doses up to the maximum recommended dose, did not demonstrate an effect on the QTc interval.
Bupivacaine
Systemic absorption of local anesthetics, including bupivacaine, produces effects on the cardiovascular and central nervous systems (CNS), which can be serious at toxic blood concentrations [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ] . At blood concentrations achieved with normal therapeutic doses, manifestations of CNS stimulation and depression or changes in cardiac conduction, excitability, refractoriness, contractility, and peripheral vascular resistance are minimal. Clinical reports and animal research suggest that cardiovascular changes are more likely to occur after unintended intravascular injection of bupivacaine.
Pharmacokinetics
The instillation of ZYNRELEF into the surgical site results in systemic plasma levels of bupivacaine and meloxicam for up to the duration as described in Table 7 for soft tissue surgical procedures and Table 8 for orthopedic surgical procedures. Systemic plasma levels of bupivacaine or meloxicam following application of ZYNRELEF do not correlate with local efficacy.
Absorption
The rate of systemic absorption of bupivacaine or meloxicam from ZYNRELEF is dependent upon the total dose of drug administered and the vascularity of the administration site.
Pharmacokinetic parameters of bupivacaine and meloxicam after single dose administration by instillation of ZYNRELEF were evaluated following multiple surgical procedures.
Descriptive statistics of pharmacokinetic parameters of representative ZYNRELEF doses are provided in Table 7 for soft tissue surgical procedures and Table 8 for orthopedic surgical procedures.
| Active Ingredient | Parameter | Herniorrhaphy: 300 mg/9 mg ZYNRELEF (N=16) | Abdominoplasty: 400 mg/12 mg ZYNRELEF (N=22) | Augmentation Mammoplasty: 400 mg/12 mg ZYNRELEF (N=49) | Cesarean Section: 400 mg/12 mg ZYNRELEF (N=11) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Note: Arithmetic mean (standard deviation) except T max where it is median (min, max). Doses of ZYNRELEF are shown as bupivacaine dose (mg)/meloxicam dose (mg). | |||||
| NS = not sampled; NR= not reported, since the terminal elimination phase was not adequately characterized in sufficient number of patients. | |||||
| Bupivacaine | C max (ng/mL) | 271 (147) | 382 (149) | 710 (246) | 291 (70) |
| T max (h) | 18 (3, 30) | 31 (20, 54) | 3.6 (1.3, 35) | 24 (1.1, 48) | |
| AUC (0-t) AUC (0-t) : 0 to 120 h post-dose for herniorrhaphy, augmentation mammoplasty, and Cesarean section; 0 to 144 h post-dose for abdominoplasty. (h×ng/mL) | 15174 (8545) | 24411 (10072) | 27363 (9227) | 17923 (5069) | |
| AUC (inf) (h×ng/mL) | 15524 (8921) | 24930 (10105) | 31072 (17998) | 17983 (5065) | |
| t ½ (h) | 16 (9) | 20 (8) | 25 (20) | 10 (2) | |
| C 72h (ng/mL) | 96 (75) | 202 (118) | 149 (68) N=48; | 127 (56) | |
| C 96h (ng/mL) | 37 (43) | 86 (52) N=21; | NS | 27 (16) | |
| C 144h (ng/mL) | NS | 16 (11) | NS | 0.8 (1.0) N=10 | |
| Meloxicam | C max (ng/mL) | 225 (96) | 116 (62) | 527 (149) | 114 (49) |
| T max (h) | 54 (24, 96) | 24 (4.0, 72) | 20 (5.6, 49) | 60 (8.5, 73) | |
| AUC (0-t) (h×ng/mL) | 18721 (7923) | 7924 (4197) | 30499 (9460) | 9710 (4560) | |
| AUC (inf) (h×ng/mL) | NR | 8304 (4422) | 41809 (38414) | 9778 (4592) | |
| t ½ (h) | NR | 21 (9) | 42 (70) | 21 (9) | |
| C 72h (ng/mL) | 197 (95) | 70 (44) | 214 (105) | 86 (43) | |
| C 96h (ng/mL) | 146 (86) | 33 (25) | NS | 48 (32) | |
| C 144h (ng/mL) | NS | 7.1 (10) | NS | 11 (12) | |
| Active Ingredient | Parameter | Bunionectomy: 60 mg/1.8 mg ZYNRELEF (N=17) | Total Knee Arthroplasty: 400 mg/12 mg ZYNRELEF (N=53) | Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: 400 mg/12 mg ZYNRELEF (N=20) | 1-Level Spinal Surgery: 92 mg/2.8 mg ZYNRELEF (N=13) | 2- or 3-Level Spinal Surgery: 191 mg/5.7 mg ZYNRELEF (N=13) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Note: Arithmetic mean (standard deviation) except T max where it is median (min, max). Doses of ZYNRELEF are shown as bupivacaine dose (mg)/meloxicam dose (mg). For spinal surgery, ZYNRELEF mean doses for single-level and multilevel surgeries are shown; individual doses ranged from 45 mg/1.4 mg to 248 mg/7.4 mg. | ||||||
| NS = not sampled. | ||||||
| Bupivacaine | C max (ng/mL) | 54 (33) | 695 (411) | 372 (165) | 95 (105) | 163 (67) |
| T max (h) | 3.0 (1.6, 24) | 21 (4, 59) | 20 (1.8, 48) | 23 (1.9, 38) | 24 (4.1, 69) | |
| AUC (0-t) AUC (0-t) : 0 to 120 h post-dose for bunionectomy and lumbar spinal decompression; 0 to 144 h post-dose for total knee arthroplasty and total shoulder arthroplasty. (h×ng/mL) | 1681 (1154) | 35889 (28399) | 21132 (12331) | 4467 (4977) | 8488 (4086) | |
| AUC (inf) (h×ng/mL) | 1718 (1211) | 38173 (29401) N=50; | 21193 (12329) | 5535 (6091) N=12; | 8659 (4288) N=11; | |
| t ½ (h) | 15 (8) | 17 (7) | 10 (3) | 25 (25) | 14 (5) | |
| C 72h (ng/mL) | 5.0 (5.3) | 227 (283) | 145 (117) | 34 (48) | 61 (49) | |
| C 96h (ng/mL) | 1.7 (2.9) N=16; | NS | 30 (32) | 5.2 (7.3) | 24 (27) | |
| C 144h (ng/mL) | NS | 5.3 (21) N=32; | 1.1 (2.2) N=19; | NS | NS | |
| Meloxicam | C max (ng/mL) | 26 (14) | 275 (134) | 248 (125) N=18; | 53 (41) N=13; | 90 (36) |
| T max (h) | 18 (8, 60) | 36 (12, 72) | 57 (12, 72) | 18 (12, 72) | 43 (23, 69) | |
| AUC (0-t) (h×ng/mL) | 1621 (927) | 19525 (12259) | 22292 (12250) | 3556 (2665) | 6269 (3133) | |
| AUC (inf) (h×ng/mL) | 2079 (1631) | 25673 (17666) N=35; | 24133 (15285) N=17; | 3826 (3890) | 8265 (5874) N=10; | |
| t ½ (h) | 33 (36) | 42 (37) | 29 (11) | 35 (15) | 38 (22) | |
| C 72h (ng/mL) | 13 (9) | 202 (120) | 228 (131) | 44 (44) | 69 (37) | |
| C 96h (ng/mL) | 7.7 (5.8) N=15; | NS | 158 (126) | 21 (23) | 43 (28) | |
| C 144h (ng/mL) | NS | 28 (37) N=28 | 52 (56) | NS | NS | |
Distribution
After bupivacaine and meloxicam have been released from ZYNRELEF and are absorbed systemically, their distribution is expected to be the same as for other bupivacaine HCl solution formulations or meloxicam oral formulation.
Bupivacaine
Local anesthetics including bupivacaine are distributed to some extent to all body tissues, with high concentrations found in highly perfused organs such as the liver, lungs, heart, and brain. Local anesthetics are bound to plasma proteins in varying degrees. Generally, the lower the plasma concentration of drug, the higher the percentage of drug bound to plasma proteins.
Local anesthetics including bupivacaine appear to cross the placenta by passive diffusion. The rate and degree of diffusion is governed by (1) the degree of plasma protein binding, (2) the degree of ionization, and (3) the degree of lipid solubility. Fetal/maternal ratios of local anesthetics appear to be inversely related to the degree of plasma protein binding, because only the free, unbound drug is available for placental transfer. Bupivacaine with a high protein binding capacity (95%) has a low fetal/maternal ratio (0.2 to 0.4). The extent of placental transfer is also determined by the degree of ionization and lipid solubility of the drug. Lipid soluble, non-ionized drugs, such as bupivacaine, readily enter the fetal blood from the maternal circulation.
Meloxicam
Meloxicam is ~99.4% bound to human plasma proteins (primarily albumin) within the therapeutic dose range of oral meloxicam. The fraction of protein binding is independent of drug concentration, over the clinically relevant concentration range, but decreases to ~99% in patients with renal disease. Meloxicam penetration into human red blood cells, after oral dosing, is less than 10%. Following a radiolabeled dose, over 90% of the radioactivity detected in the plasma was present as unchanged meloxicam. Meloxicam concentrations in synovial fluid, after a single oral dose, range from 40% to 50% of those in plasma. The free fraction in synovial fluid is 2.5 times higher than in plasma, due to the lower albumin content in synovial fluid as compared to plasma. The significance of this penetration is unknown.
Elimination
Metabolism
Bupivacaine
Amide-type local anesthetics such as bupivacaine are metabolized primarily in the liver via conjugation with glucuronic acid. Pipecoloxylidine is the major metabolite of bupivacaine. The elimination of drug from tissue distribution depends largely upon the ability of plasma protein binding sites in the circulation to carry it to the liver where it is metabolized [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) ] .
Meloxicam
Meloxicam is extensively metabolized in the liver. Meloxicam metabolites include 5'-carboxy meloxicam (60% of dose), from P450 mediated metabolism formed by oxidation of an intermediate metabolite 5'‑hydroxymethyl meloxicam which is also excreted to a lesser extent (9% of dose). In vitro studies indicate that CYP2C9 (cytochrome P450 metabolizing enzyme) plays an important role in this metabolic pathway with a minor contribution of the CYP3A4 isozyme. Patients' peroxidase activity is probably responsible for the other two metabolites which account for 16% and 4% of the administered dose, respectively. The four metabolites are not known to have any in vivo pharmacological activity.
Excretion
After bupivacaine and meloxicam have been released from ZYNRELEF and are absorbed systemically, their excretion is expected to be the same as for other bupivacaine HCl solution formulations or meloxicam oral formulations.
Bupivacaine
The kidney is the main excretory organ for most local anesthetics and their metabolites. Urinary excretion is affected by urinary perfusion and factors affecting urinary pH. Only 6% of bupivacaine is excreted unchanged in the urine.
When administered in recommended doses and concentrations, bupivacaine HCl does not ordinarily produce irritation or tissue damage. The mean apparent terminal half-life (t 1/2 ) for bupivacaine from ZYNRELEF is approximately 10 to 25 hours.
Meloxicam
Meloxicam excretion is predominately in the form of metabolites, and occurs to equal extents in the urine and feces. Following oral meloxicam, only traces of the unchanged parent compound are excreted in the urine (0.2%) and feces (1.6%). The extent of the urinary excretion was confirmed for unlabeled multiple 7.5 mg oral meloxicam doses: 0.5%, 6%, and 13% of the dose were found in urine in the form of meloxicam, and the 5'-hydroxymethyl and 5'-carboxy metabolites, respectively. There is significant biliary and/or enteral secretion of the drug. This was demonstrated when oral administration of cholestyramine following a single IV dose of meloxicam decreased the AUC of meloxicam by 50%.
The mean apparent terminal half-life (t 1/2 ) for meloxicam from ZYNRELEF is approximately 21 to 42 hours.
Specific Populations
Effect of Age, Sex, Race, and Ethnicity on Pharmacokinetics
Based on the population pharmacokinetic analysis, age, sex, race, and ethnicity do not have a clinically meaningful effect on the pharmacokinetics of bupivacaine and meloxicam in ZYNRELEF [see Use in Special Populations (8.5) ] .
Hepatic Impairment
After bupivacaine and meloxicam have been released from ZYNRELEF and are absorbed systemically, the effects of hepatic impairment are expected to be the same as for other bupivacaine and meloxicam formulations [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ] .
Bupivacaine
Various pharmacokinetic parameters of the local anesthetics can be significantly altered by the presence of hepatic disease. Patients with hepatic disease, especially those with severe hepatic disease, may be more susceptible to the potential toxicities of the amide-type local anesthetics [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) ] .
Meloxicam
Following a single 15 mg dose of oral meloxicam there was no marked difference in plasma concentrations in patients with mild (Child-Pugh Class I) or moderate (Child-Pugh Class II) hepatic impairment compared to healthy volunteers. Protein binding of oral meloxicam was not affected by hepatic impairment. No dosage adjustment of ZYNRELEF is necessary in patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment. Patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class III) have not been adequately studied [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) ] .
Renal Impairment
After bupivacaine and meloxicam have been released from ZYNRELEF and are absorbed systemically, the effects of renal impairment are expected to be the same as for other bupivacaine and meloxicam formulations.
Bupivacaine
Various pharmacokinetic parameters of the local anesthetics can be significantly altered by the presence of renal disease, factors affecting urinary pH, and renal blood flow [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) and Use in Specific Populations (8.7) ] .
Meloxicam
Meloxicam pharmacokinetics with oral meloxicam have been investigated in patients with mild and moderate renal impairment. Following oral meloxicam, total drug plasma concentrations of meloxicam decreased and total clearance of meloxicam increased with the degree of renal impairment while free AUC values were similar in all groups. The higher meloxicam clearance in patients with renal impairment may be due to increased fraction of unbound meloxicam which is available for hepatic metabolism and subsequent excretion. No dosage adjustment of ZYNRELEF is necessary in patients with mild to moderate renal impairment. Patients with severe renal impairment have not been adequately studied. The use of ZYNRELEF in patients with severe renal impairment is not recommended [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) and Use in Specific Populations (8.7) ] .
Hemodialysis: Following a single oral dose of meloxicam, the free C max plasma concentrations were higher in patients with renal failure on chronic hemodialysis (1% free fraction) in comparison to healthy volunteers (0.3% free fraction). Hemodialysis did not lower the total drug concentration in plasma. Meloxicam is not dialyzable [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7) ] .
Drug Interaction Studies
Aspirin: When NSAIDs were administered with aspirin, the protein binding of NSAIDs were reduced, although the clearance of free NSAID was not altered. The clinical significance of this interaction is not known. See Table 6 for clinically significant drug interactions of NSAIDs with aspirin [see Drug Interactions (7) ] .
Cholestyramine : Pretreatment for four days with cholestyramine significantly increased the clearance of oral meloxicam by 50%. This resulted in a decrease in t 1/2 , from 19.2 hours to 12.5 hours, and a 35% reduction in AUC. This suggests the existence of a recirculation pathway for oral meloxicam in the gastrointestinal tract. The clinical relevance of this interaction has not been established.
Cimetidine : Concomitant administration of 200 mg cimetidine four times daily did not alter the single-dose pharmacokinetics of 30 mg oral meloxicam.
Digoxin : Oral meloxicam 15 mg once daily for 7 days did not alter the plasma concentration profile of digoxin after β-acetyldigoxin administration for 7 days at clinical doses. In vitro testing found no protein binding drug interaction between digoxin and meloxicam.
Lithium : In a study conducted in healthy patients, mean pre-dose lithium concentration and AUC were increased by 21% in patients receiving lithium doses ranging from 804 to 1072 mg twice daily with oral meloxicam 15 mg QD every day as compared to patients receiving lithium alone [see Drug Interactions (7) ] .
Methotrexate: A study in 13 rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients evaluated the effects of multiple doses of meloxicam on the pharmacokinetics of methotrexate taken once weekly. Meloxicam did not have a significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of single doses of methotrexate. In vitro, methotrexate did not displace meloxicam from its human serum binding sites.
Warfarin : The effect of oral meloxicam on the anticoagulant effect of warfarin was studied in a group of healthy patients receiving daily doses of warfarin that produced an INR (International Normalized Ratio) between 1.2 and 1.8. In these patients, oral meloxicam did not alter warfarin pharmacokinetics and the average anticoagulant effect of warfarin as determined by prothrombin time. However, one patient showed an increase in INR from 1.5 to 2.1. Caution should be used when administering oral meloxicam with warfarin since patients on warfarin may experience changes in INR and an increased risk of bleeding complications when a new medication is introduced.
Pharmacogenomics
CYP2C9 activity is reduced in individuals with genetic variants such as CYP2C9•2 and CYP2C9•3 polymorphisms. Limited data from three published reports showed that meloxicam AUC was substantially higher in individuals with reduced CYP2C9 activity, particularly in poor metabolizers (e.g., •3/•3), compared to normal metabolizers (•1/•1). The frequency of CYP2C9 poor metabolizer genotypes varies based on racial/ethnic background but is generally present in <5% of the population.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, and Impairment of Fertility
The maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of ZYNRELEF is 400 mg and 12 mg of bupivacaine and meloxicam, respectively.
Carcinogenesis
Bupivacaine
Long-term studies in animals to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of ZYNRELEF or bupivacaine have not been conducted.
Meloxicam
There was no increase in tumor incidence in long-term carcinogenicity studies in rats (104 weeks) or mice (99 weeks) administered meloxicam at oral doses up to 0.8 mg/kg/day in rats and up to 8.0 mg/kg/day in mice (up to 0.6 and 3.2 times, respectively, the meloxicam dose level of 12 mg at the MRHD of ZYNRELEF based on BSA comparison).
Mutagenesis
Bupivacaine
The mutagenic potential of bupivacaine has not been determined.
Meloxicam
Meloxicam was not mutagenic in an Ames assay, or clastogenic in a chromosome aberration assay with human lymphocytes and an in vivo micronucleus test in mouse bone marrow.
Impairment of Fertility
Bupivacaine
The effect of ZYNRELEF and bupivacaine on fertility has not been determined.
Meloxicam
Meloxicam did not impair male and female fertility in rats at oral doses up to 9 mg/kg/day in males and 5 mg/kg/day in females (up to 7.3 and 4 times, respectively, the MRHD based on BSA comparison).
In a published study, oral administration of 1 mg/kg (0.8 times the MRHD) meloxicam to male rats for 35 days resulted in decreased sperm count and motility and histopathological evidence of testicular degeneration. The clinical relevance of these findings is unknown.
Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Necrosis and degeneration of cartilage and chondrocytes were observed following intra-articular injection of a single dose of ZYNRELEF in the knee joint of rabbits. Cartilage degeneration was also observed following intra-articular injection of a single dose of ZYNRELEF in the knee joints of dogs.
CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of ZYNRELEF was established in 3 double-blind, controlled studies in patients undergoing bunionectomy (Study 1), unilateral open inguinal herniorrhaphy (Study 2), and total knee arthroplasty (Study 3). Refer to 12.2 for additional supportive pharmacodynamic data for ZYNRELEF [see Pharmacodynamics (12.2) ].
Based on the extrapolation of efficacy of ZYNRELEF across the 3 double-blind, controlled studies in patients undergoing bunionectomy, unilateral open inguinal herniorrhaphy, and total knee arthroplasty, and the pharmacokinetic profiles across surgical procedures with varied characteristics, such as anatomic location, tissue type, length and depth of surgical area, and vascularity, the pharmacokinetic profile and effectiveness of ZYNRELEF are not expected to be clinically significantly different when ZYNRELEF is administered at an appropriate dose in other soft tissue and orthopedic surgical procedures [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) , Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Study 1
In this multicenter, double-blind, parallel-group, active- and placebo-controlled clinical trial (NCT03295721), 412 patients undergoing unilateral simple bunionectomy with a lidocaine Mayo block were randomized to 1 of the following 3 treatment groups in a 3:3:2 ratio (respectively): ZYNRELEF 60 mg/1.8 mg, bupivacaine HCl 50 mg, or saline placebo. The mean patient age was 47 years (range 18 to 77) and patients were predominantly female (86%). ZYNRELEF was applied directly into the surgical site, using the cone-shaped applicator, at the end of the procedure, after final irrigation and suction but prior to closure. Bupivacaine HCl and saline placebo were administered by injection and instillation, respectively. Pain intensity was rated by patients using an 11-point numeric rating scale (NRS) out to 72 hours post-dose. Postoperatively, there was no scheduled pain medication regimen; however, patients were allowed rescue medication as needed, and included oxycodone 10 mg orally every 4 hours, morphine 10 mg IV every 2 hours, and/or acetaminophen 1000 mg orally every 6 hours. The primary endpoint was the mean area under the curve (AUC) of the NRS pain intensity scores (cumulative pain scores) with activity over the 72-hour period for the ZYNRELEF treatment group compared to the saline placebo treatment group. Secondary endpoints included mean AUC of NRS pain intensity scores over the 72-hour period for the ZYNRELEF treatment group compared to the bupivacaine HCl treatment group, proportion of patients who did not receive opioid analgesia, and total opioid consumption.
Patients treated with ZYNRELEF demonstrated a significant reduction in pain intensity compared to those treated with either bupivacaine HCl or saline placebo for up to 72 hours (Figure 1). A significant proportion of patients treated with ZYNRELEF did not receive opioid analgesia (29%) over 72 hours compared to those treated with either bupivacaine HCl (11%) or saline placebo (2%).
Figure 1. Mean Pain Intensity with Activity Over 72 Hours for STUDY 1 (Bunionectomy)

Study 2
In this multicenter, double-blind, parallel-group, active- and placebo-controlled clinical trial (NCT03237481), 418 patients undergoing unilateral open inguinal herniorrhaphy with mesh under general anesthesia were randomized to 1 of the following 3 treatment groups in a 2:2:1 ratio (respectively): ZYNRELEF 300 mg/9 mg, bupivacaine HCl 75 mg, or saline placebo. The mean patient age was 49 years (range 18 to 83) and patients were predominantly male (94%). ZYNRELEF was applied directly into the surgical site, using the cone-shaped applicator, at the end of the procedure, following irrigation and suction of each fascial layer but prior to closure. Bupivacaine HCl and saline placebo were administered by injection and instillation, respectively. Pain intensity was rated by patients using an 11-point NRS out to 72 hours post-dose. Postoperatively, there was no scheduled pain medication regimen; however, patients were allowed rescue medication as needed, which included oxycodone 10 mg orally every 4 hours, morphine 10 mg IV every 2 hours, and/or acetaminophen 1000 mg orally every 6 hours. The primary endpoint was the mean AUC of the NRS pain intensity scores (cumulative pain scores) with activity over the 72-hour period for the ZYNRELEF treatment group compared to the saline placebo treatment group. Secondary endpoints included mean AUC of NRS pain intensity scores over the 72-hour period for the ZYNRELEF treatment group compared to the bupivacaine HCl treatment group, proportion of patients who did not receive opioid analgesia, and total opioid consumption.
Patients treated with ZYNRELEF demonstrated a statistically significant reduction in pain intensity compared to those treated with either bupivacaine HCl or saline placebo for up to 72 hours (Figure 2). A significant proportion of patients treated with ZYNRELEF did not receive opioid analgesia (51%) over 72 hours compared to those treated with either bupivacaine HCl (40%) or saline placebo (22%). A significant reduction in total opioid consumption over 72 hours was also observed for patients treated with ZYNRELEF (median consumption 0 mg) compared to those treated with either bupivacaine HCl (7.3 mg) or saline placebo (11.3 mg).
Figure 2. Mean Pain Intensity with Activity Over 72 Hours for STUDY 2 (Herniorrhaphy)

Study 3
In this multicenter, double-blind, parallel-group, active- and placebo-controlled clinical study (NCT03015532), 222 patients undergoing primary unilateral total knee arthroplasty under general anesthesia were randomized to one of the following treatment groups in a 1:1:1:1 ratio; ZYNRELEF 400 mg/12 mg, ZYNRELEF 400 mg/12 mg plus ropivacaine 50 mg (injected into the posterior capsule), bupivacaine HCl 125 mg, or saline placebo. The mean age was 62 years (range 33 to 85) and 51% of patients were female.
ZYNRELEF was administered, using the cone-shaped applicator, onto the posterior capsule, the anteromedial tissues and periosteum, and the anterolateral tissues and periosteum after cementation of the components. Preoperatively, patients were administered pregabalin 150 mg as a single oral dose and acetaminophen up to 1 g IV. Pain intensity was rated by the patients using an 11-point NRS out to 72 hours post-dose. Postoperatively, there was no scheduled pain medication regimen, and patients were allowed only opioid rescue medication as needed (10 mg oxycodone orally every 4 hours, and/or 10-15 mg morphine IV every 2 hours). The primary endpoint was the AUC of the NRS pain intensity scores (cumulative pain scores) at rest collected over the first 48 hours.
Patients treated with ZYNRELEF demonstrated a significant reduction in pain intensity compared to patients treated with saline placebo for the first 48-hour and 72-hour postoperative periods (Figure 3). There were two patients who did not receive opioid analgesia over 72 hours; one in the ZYNRELEF 400 mg/12 mg + ropivacaine treatment group and one in the bupivacaine HCl treatment group.
Figure 3. Mean Pain Intensity at Rest Over 72 Hours for STUDY 3 (Total Knee Arthroplasty)

HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
ZYNRELEF ® (bupivacaine and meloxicam) extended-release solution is a clear, pale-yellow to yellow viscous liquid available in 4 presentations. Each single-dose glass vial is filled with a solution of 29.25 mg/mL bupivacaine and 0.88 mg/mL meloxicam. Each presentation described below is supplied in the ZYNRELEF kit containing a vial (packaged in an individual carton) along with sterile, individually packaged components for administration.
| Product Presentation (Kit Supplied with Vial Access Needle) | Vial Access Needle Provided | Luer Lock Syringe(s) Provided | Luer Lock Applicator(s) Provided | Syringe Tip Cap(s) Provided | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NDC | Bupivacaine/Meloxicam | Net Quantity Volume Each ZYNRELEF vial contains overfill to compensate for residual amounts that remain in the vial, vial access needle, Luer lock applicator, and syringe(s) during drug withdrawal and administration | ||||
| 47426-501-02 | 400 mg/12 mg | 14 mL | 1 × 20 mL | 2 × 12 mL | 2 | 2 |
| 47426-502-02 | 300 mg/9 mg | 10.5 mL | 1 × 20 mL | 1 × 12 mL | 1 | 1 |
| 47426-503-01 | 200 mg/6 mg | 7 mL | 1 × 10 mL | 1 × 12 mL | 1 | 1 |
| 47426-504-01 | 60 mg/1.8 mg | 2.3 mL | 1 × 10 mL | 1 × 3 mL | 1 | 1 |
| Product Presentation (Kit Supplied with Vented Vial Spike) | Vented Vial Spike Provided | Luer Lock Syringe(s) Provided | Luer Lock Applicator(s) Provided | Syringe Tip Cap(s) Provided | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NDC | Bupivacaine/Meloxicam | Net Quantity Volume Each ZYNRELEF vial contains overfill to compensate for residual amounts that remain in the vial, vented vial spike, Luer lock applicator, and syringe(s) during drug withdrawal and administration | ||||
| 47426-301-02 | 400 mg/12 mg | 14 mL | 1 | 2 × 12 mL | 2 | 2 |
| 47426-302-02 | 300 mg/9 mg | 10.5 mL | 1 | 1 × 12 mL | 1 | 1 |
| 47426-303-01 | 200 mg/6 mg | 7 mL | 1 | 1 × 12 mL | 1 | 1 |
| 47426-304-01 | 60 mg/1.8 mg | 2.3 mL | 1 | 1 × 3 mL | 1 | 1 |
The following replacement components are individually supplied separate from the kit:
- Carton containing 5 vented vial spikes
- Carton containing 10 Luer lock applicators
- Carton containing 10 sterile 3 mL Luer lock syringes
- Carton containing 8 sterile 12 mL Luer lock syringes
- Carton containing 8 sterile 10 mL vial access needles
- Carton containing 6 sterile 20 mL vial access needles
Storage
Store ZYNRELEF kits at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) with excursions permitted between 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Protect from moisture and light.
If ZYNRELEF vials are removed from the kit, store them at controlled room temperature. Protect from light during storage.
Instructions For Use
ZYNRELEF ® (bupivacaine and meloxicam) extended-release solution, for instillation use
| 400 mg bupivacaine and 12 mg meloxicam Each mL contains 29.25 mg bupivacaine and 0.88 mg meloxicam |
Intended Use
ZYNRELEF is indicated in adults to produce postsurgical analgesia for up to 72 hours after soft tissue, foot and ankle, and other orthopedic procedures in which direct exposure to articular cartilage is avoided.
Limitations of Use
Safety and efficacy have not been established in highly vascular surgeries, such as intrathoracic, large 4 or more level spinal, and head and neck procedures.
Dose Information
A single-dose application of a viscous solution administered directly via a needle-free syringe to coat the affected tissue within the surgical site prior to suturing. Two syringes are provided to aid in application.
Preparing the Product
Only withdraw 7 mL of ZYNRELEF into each syringe. This product does not require mixing. During preparation, do not mix with water, saline or other local anesthetics. Preparation is typically done in the Operating Room. Follow your facility's standard operating procedures regarding aseptic and sterile preparation and disposal of unused contents in the vial.
Storing the Product
ZYNRELEF kit should be stored at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) with excursions permitted between 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature], protected from light and moisture.
For Operating Room Preparation
It is recommended that a 2-person team prepare this product: one sterile person and one non-sterile person. If product is prepared in advance of surgery, blue syringe tip caps ➍ may be used to cap the syringe until ready for application. Before administration, remove the blue syringe tip cap and attach the Luer lock applicator ➌.
The ZYNRELEF Kit Contents
Use only the components listed below supplied for use with ZYNRELEF.
- Vented Vial Spike (sterile)
- 12 mL Luer Lock Syringe (sterile) (2×)
- Luer Lock Applicator (sterile) (2×)
- Blue Tip Caps (sterile) (2×) (preparation in advance)
- 14 mL ZYNRELEF Vial (contents sterile, exterior not sterile)

| Preparation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
① Prepare Components | ② Prepare Vial
| ③ Remove Protective Sheath
| ④ Attach Vented Vial Spike | |
⑤ Prepare Syringe | ⑥ Prepare for Withdrawal | ⑦ Withdraw Product
| ⑧ Repeat With Second Syringe
| |
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I attempt to do the entire preparation process on my own?It is recommended that this be done as a 2-person team to maintain sterility.
Is there any way to speed up the withdrawal time?The withdrawal time is faster when the vial is at the upper end of the recommended storage conditions (25°C or 77°F). Do not dilute this product in any way.
What if I touch the aluminum collar when attaching the vented vial spike adapter?Replace your sterile gloves and continue with next steps.
Do I have to wait until the vial is inverted to push in air?Proper insertion of air after inverting the vial improves withdrawal time.
Do I need to dilute this product to expand the volume?No. The product should not be diluted.
Can I pour this product in a sterile cup?No, you will be unable to pull an effective dose from the sterile cup due to the thick nature of the product.
What should I do if I drop a syringe or any of the other components?Use replacement kit components that are individually supplied separate from the kit.
Administration Information
Please familiarize yourself with this information before you use this product for the first time.
ZYNRELEF should only be administered with the syringe and Luer lock applicator provided in the ZYNRELEF kit.
Administration
- 1.000000000000000e+00 ADMINISTER ZYNRELEF VIA INSTILLATION ONLY.
- 2.000000000000000e+00 ZYNRELEF should not be administered via the following routes:
- Epidural
- Intrathecal
- Intravascular
- Intra-articular
- Regional nerve blocks
- Pre-incisional or pre-procedural locoregional anesthetic techniques
- 3.000000000000000e+00 ZYNRELEF is applied without a needle into the surgical site following final irrigation and suction and prior to suturing.

Only apply ZYNRELEF after final irrigation and suction of each layer before closing, if multiple tissue layers are involved. - 4.000000000000000e+00 Using the Luer lock applicator attached to the syringe, apply ZYNRELEF to the tissues within the surgical site that could result in pain generation.
- 5.000000000000000e+00 Use a sufficient amount to coat the tissues. For small spaces, ensure there is not an excess that could be expressed from the site during closure.
- 6.000000000000000e+00 Only apply ZYNRELEF to the tissue layers below the skin incision and not directly onto the skin.
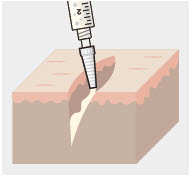
- 7.000000000000000e+00 ZYNRELEF does not degrade sutures.

When tying knots with monofilament sutures, contact with ZYNRELEF may cause knots to loosen or untie due to the viscosity of ZYNRELEF. In vitro studies showed an increase in elasticity with monofilament sutures exposed to ZYNRELEF with unknown clinical significance. Minimize administration of ZYNRELEF near the incision line and wipe off excess ZYNRELEF from the skin prior to suturing. Three or more knots ending in a multi-throw knot (e.g. a Surgeon's knot) are recommended with monofilament sutures. Braided or barbed sutures are recommended, especially for closure of deeper layers.
Important Information
- A. The amount of ZYNRELEF required depends upon the surgical area of tissue to be treated.
- B. ZYNRELEF spreads easily and covers a large area.
- C. Diluting ZYNRELEF is not needed for efficacy.

ZYNRELEF cannot be mixed with water, saline, or other local anesthetics as the product will become very viscous and difficult to administer. - D. When ZYNRELEF comes in contact with moisture in the tissues, it becomes more viscous, allowing it to stay in place.
- E. Avoid additional use of local anesthetics within 96 hours following administration of ZYNRELEF.

Overall local anesthetic exposure must be considered.
HERON THERAPEUTICS
Mechanism of Action
ZYNRELEF is a fixed-dose combination of bupivacaine and meloxicam.
Bupivacaine
Local anesthetics block the generation and the conduction of nerve impulses presumably by increasing the threshold for electrical excitation in the nerve, by slowing the propagation of the nerve impulse, and by reducing the rate of rise of the action potential. In general, the progression of anesthesia is related to the diameter, myelination, and conduction velocity of affected nerve fibers. Clinically, the order of loss of nerve function is as follows: (1) pain, (2) temperature, (3) touch, (4) proprioception, and (5) skeletal muscle tone.
Meloxicam
The mechanism of action of meloxicam, like that of other NSAIDs, is not completely understood but involves inhibition of cyclooxygenase (COX-1 and COX-2).
Meloxicam is a potent inhibitor of prostaglandin synthesis in vitro. Prostaglandins sensitize afferent nerves and potentiate the action of bradykinin in inducing pain in animal models. Prostaglandins are mediators of inflammation. Because meloxicam is an inhibitor of prostaglandin synthesis, its mode of action may be due to a decrease of prostaglandins in peripheral tissues.
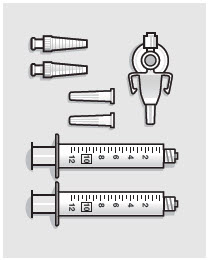 STERILE Open all components onto sterile field. Note: Prepare all syringe(s) provided in kit.
STERILE Open all components onto sterile field. Note: Prepare all syringe(s) provided in kit.  Do not substitute any of the components.
Do not substitute any of the components.  Only withdraw 7 mL of ZYNRELEF into each syringe. Note: Vial contains overfill to account for amount that remains in the vial, vented vial spike, Luer lock applicator, and syringe(s) during drug withdrawal and administration.
Only withdraw 7 mL of ZYNRELEF into each syringe. Note: Vial contains overfill to account for amount that remains in the vial, vented vial spike, Luer lock applicator, and syringe(s) during drug withdrawal and administration. 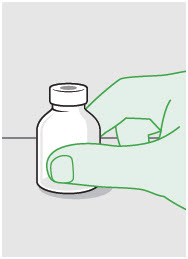 NON-STERILE
NON-STERILE  Do not remove the stopper or attempt to pour the vial contents.
Do not remove the stopper or attempt to pour the vial contents. 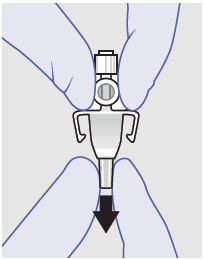 STERILE
STERILE 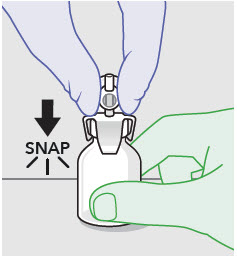 STERILE Push the spike through the septum of the vial until it "snaps" into place.
STERILE Push the spike through the septum of the vial until it "snaps" into place.  Hold the vented vial spike by the adapter neck to maintain sterility of the vented vial spike and sterile person. NON-STERILE Hold the vial in place while sterile person attaches spike. Note: Place the vial on a firm, flat surface and hold in place while the sterile person attaches the spike.
Hold the vented vial spike by the adapter neck to maintain sterility of the vented vial spike and sterile person. NON-STERILE Hold the vial in place while sterile person attaches spike. Note: Place the vial on a firm, flat surface and hold in place while the sterile person attaches the spike. 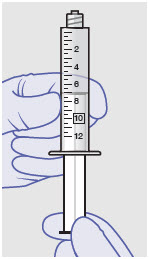 STERILE Fill the syringe with 7 mL of air before attaching to the vented vial spike.
STERILE Fill the syringe with 7 mL of air before attaching to the vented vial spike.  Air from syringe will be pushed into the vial at Step 7 after the vial has been inverted and product has filled the neck of the vial.
Air from syringe will be pushed into the vial at Step 7 after the vial has been inverted and product has filled the neck of the vial. 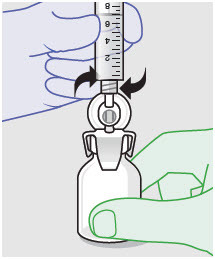 STERILE Attach the air-filled syringe to the vented vial spike. Note: Avoid pushing or pumping the plunger rod up and down at any point in the withdrawal process. NON-STERILE Hold the vial in place until the syringe is attached.
STERILE Attach the air-filled syringe to the vented vial spike. Note: Avoid pushing or pumping the plunger rod up and down at any point in the withdrawal process. NON-STERILE Hold the vial in place until the syringe is attached. 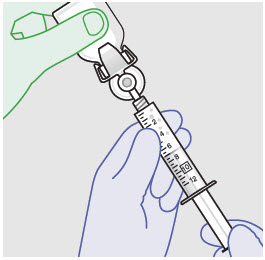 STERILE
STERILE 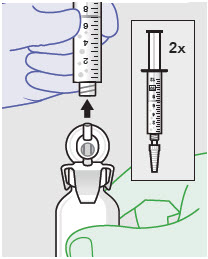 STERILE
STERILE