Acyclovir
Acyclovir Prescribing Information
Acyclovir ointment 5% is indicated in the management of initial genital herpes and in limited nonlifethreatening mucocutaneous HSV infections in immune compromised patients.
Apply sufficient quantity to adequately cover all lesions every 3 hours, 6 times per day for 7 days. The dose size per application will vary depending upon the total lesion area but should approximate a one-half inch ribbon of ointment per 4 square inches of surface area. A finger cot or rubber glove should be used when applying acyclovir ointment to prevent autoinoculation of other body sites and transmission of infection to other persons.
Acyclovir ointment 5% is contraindicated in patients who develop hypersensitivity to the components of the formulation.
In the controlled clinical trials, mild pain (including transient burning and stinging) was reported by about 30% of patients in both the active and placebo arms; treatment was discontinued in 2 of these patients. Local pruritus occurred in 4% of these patients. In all studies, there was no significant difference between the drug and placebo group in the rate or type of reported adverse reactions nor were there any differences in abnormal clinical laboratory findings.
Acyclovir is a synthetic nucleoside analogue active against herpes viruses. Acyclovir ointment, USP 5% is a formulation for topical administration. Each gram of acyclovir ointment 5% contains 50 mg of acyclovir, USP in a polyethylene glycol (PEG) base.
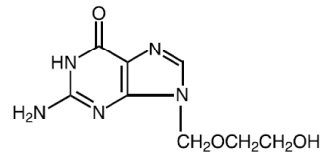
Acyclovir is a white to off-white, crystalline powder with the molecular formula C8H11N5O3 and a molecular weight of 225. The maximum solubility in water at 37°C is 2.5 mg/mL. The pka's of acyclovir are 2.27 and 9.25.
The chemical name of acyclovir is 2-amino-1,9-dihydro-9-[(2-hydroxyethoxy)methyl]-6
Two clinical pharmacology studies were performed with acyclovir ointment 5% in immune compromised adults at risk of developing mucocutaneous HSV infections or with localized varicella-zoster infections. These studies were designed to evaluate the dermal tolerance, systemic toxicity, and percutaneous absorption of acyclovir.
In one of these studies, which included 16 inpatients, the complete ointment or its vehicle were randomly administered in a dose of 1-cm strips (25 mg acyclovir) 4 times a day for 7 days to an intact skin surface area of 4.5 square inches. No local intolerance, systemic toxicity, or contact dermatitis were observed. In addition, no drug was detected in blood and urine by radioimmunoassay (sensitivity, 0.01 mcg/mL).
The other study included 11 patients with localized varicella zoster infections. In this uncontrolled study, acyclovir was detected in the blood of 9 patients and in the urine of all patients tested. Acyclovir levels in plasma ranged from <0.01 to 0.28 mcg/mL in 8 patients with normal renal function, and from <0.01 to 0.78 mcg/mL in 1 patient with impaired renal function. Acyclovir excreted in the urine ranged from <0.02% to 9.4% of the daily dose. Therefore, systemic absorption of acyclovir after topical application is minimal.