Ampicillin - Ampicillin Sodium injection, Powder, For Solution
(Ampicillin Sodium)Ampicillin - Ampicillin Sodium injection, Powder, For Solution Prescribing Information
Ampicillin for Injection, USP is indicated in the treatment of infections caused by susceptible strains of the designated organisms in the following conditions:
Bacteriology studies to determine the causative organisms and their susceptibility to ampicillin should be performed. Therapy may be instituted prior to obtaining results of susceptibility testing.
It is advisable to reserve the parenteral form of this drug for moderately severe and severe infections and for patients who are unable to take the oral forms. A change to oral ampicillin may be made as soon as appropriate.
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Ampicillin for Injection, USP and other antibacterial drugs, Ampicillin for Injection, USP should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
Indicated surgical procedures should be performed.
Infections of the respiratory tract and soft tissues.
Patients weighing 40 kg (88 lbs) or more: 250 mg to 500 mg every 6 hours.
Patients weighing less than 40 kg (88 lbs): 25 to 50 mg/kg/day in equally divided doses at 6- to 8- hour intervals.
Infections of the gastrointestinal and genitourinary tracts (including those caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae in females).
Patients weighing 40 kg (88 lbs) or more: 500 mg every 6 hours.
Patients weighing less than 40 kg (88 lbs): 50 mg/kg/day in equally divided doses at 6- to 8- hour intervals.
In the treatment of chronic urinary tract and intestinal infections, frequent bacteriological and clinical appraisal is necessary. Smaller doses than those recommended above should not be used. Higher doses should be used for stubborn or severe infections. In stubborn infections, therapy may be required for several weeks. It may be necessary to continue clinical and/or bacteriological follow-up for several months after cessation of therapy.
Urethritis in males due to
In the treatment of complications of gonorrheal urethritis, such as prostatitis and epididymitis, prolonged and intensive therapy is recommended. Cases of gonorrhea with a suspected primary lesion of syphilis should have darkfield examinations before receiving treatment. In all other cases where concomitant syphilis is suspected, monthly serological tests should be made for a minimum of four months. The doses for the preceding infections may be given by either the intramuscular or intravenous route. A change to oral ampicillin may be made when appropriate.
A history of a previous hypersensitivity reaction to any of the penicillins is a contraindication.
As with other penicillins, it may be expected that untoward reactions will be essentially limited to sensitivity phenomena. They are more likely to occur in individuals who have previously demonstrated hypersensitivity to penicillins and in those with a history of allergy, asthma, hay fever, or urticaria.
The following adverse reactions have been reported as associated with the use of ampicillin:
Glossitis, stomatitis, black "hairy" tongue, nausea, vomiting, enterocolitis, pseudomembranous colitis, and diarrhea. (These reactions are usua
Skin rashes and urticaria have been reported frequently. A few cases of exfoliative dermatitis and erythema multiforme have been reported. Anaphylaxis is the most serious reaction experienced and has usually been associated with the parenteral dosage form.
The concurrent administration of allopurinol and ampicillin increases substantially the incidence of skin rashes in patients receiving both drugs as compared to patients receiving ampicillin alone. It is not known whether this potentiation of ampicillin rashes is due to allopurinol or the hyperuricemia present in these patients.
Ampicillin for Injection, USP the monosodium salt of [2S-[2α, 5α, 6β(S*)]]-6- [(aminophenylacetyl)amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2- carboxylic acid, is a synthetic penicillin for intravenous use. The pharmacy bulk package contains sterile ampicillin sodium equivalent to 10 grams ampicillin. It is an antibacterial agent with a broad spectrum of bactericidal activity against both penicillin-susceptible Gram-positive organisms and many common Gram-negative pathogens.
Ampicillin for Injection, USP is a dry, white to off-white powder. The reconstituted solution is clear, colorless and free from visible particulates.
Each Pharmacy Bulk Package bottle contains ampicillin sodium equivalent to 10 grams of ampicillin. The sodium content is 65.8 mg (2.9 mEq) per one gram ampicillin.
A pharmacy bulk package is a container of a sterile preparation for parenteral use that contains many single doses. The contents of this pharmacy bulk package are intended for use by a pharmacy admixture service for addition to suitable parenteral fluids in the preparation of admixtures for intravenous infusion. (See
This Pharmacy Bulk Package glass bottle contains ampicillin sodium equivalent to 10 grams of ampicillin. It is designed for use in the pharmacy in preparing IV admixtures using aseptic technique in a laminar flow hood.
a) Add 94 mL Sterile Water for Injection USP. The resulting solution will contain 100 milligrams ampicillin activity per mL, and is stable up toONE hourat room temperature.b) Dilute further withinONE hourto a concentration of 5 mg to 10 mg per mL. See Table for suitable fluid. Use promptly. This chemical stability information in no way indicates that it would be acceptable practice to use this product well after preparation time. Good professional practice suggests that compounded admixtures should be administered as soon after preparation as is feasible.c) Using aseptic technique under a laminar flow hood, the closure should be penetrated only one time after reconstitution using a suitable sterile dispensing set; which allows measured dispensing of the contents. Use of a syringe and needle is not recommended as it may cause leakage.d) After entry, use entire contents of bottle promptly. The entire contents of the Pharmacy Bulk Package must be dispensed withinONE hourof reconstitution. This time limit should begin with the introduction of solvent or diluent into the Pharmacy Bulk Package.
Use of this product is restricted to a suitable work area, such as a laminar flow hood. Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
It has the following molecular structure:
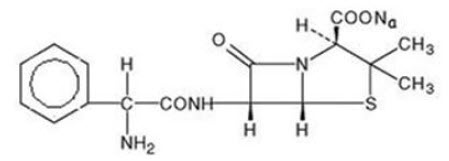
The molecular formula is C16H18N3NaO4S, and the molecular weight is 371.39. The pH range of the reconstituted solution is 8 to 10.