Hydroxyzine Hydrochloride - Hydroxyzine Hydrochloride solution
(Hydroxyzine Hydrochloride)Hydroxyzine Hydrochloride - Hydroxyzine Hydrochloride solution Prescribing Information
For symptomatic relief of anxiety and tension associated with psychoneurosis and as an adjunct in organic disease states in which anxiety is manifested.
Useful in the management of pruritus due to allergic conditions such as chronic urticaria and atopic and contact dermatoses, and in histamine-mediated pruritus.
As a sedative when used as premedication and following general anesthesia,
The effectiveness of hydroxyzine as an antianxiety agent for long term use, that is more than 4 months, has not been assessed by systematic clinical studies. The physician should reassess periodically the usefulness of the drug for the individual patient.
For symptomatic relief of anxiety and tension associated with psychoneurosis and as an adjunct in organic disease states in which anxiety is manifested: in adults, 50–100 mg q.i.d.; children under 6 years, 50 mg daily in divided doses and over 6 years, 50–100 mg daily in divided doses.
For use in the management of pruritus due to allergic conditions such as chronic urticaria, and atopic and contact dermatoses, and in histamine-mediated pruritus: in adults, 25 mg t.i.d. or q.i.d.; children under 6 years, 50 mg daily in divided doses; and over 6 years, 50–100 mg daily in divided doses.
As a sedative when used as a premedication and following general anesthesia: 50–100 mg in adults, and 0.6 mg/kg in children.
When treatment is initiated by the intramuscular route of administration, subsequent doses may be administered orally.
As with all medications, the dosage should be adjusted according to the patient's response to therapy.
Oral hydroxyzine hydrochloride is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to hydroxyzine hydrochloride products, and in patients with known hypersensitivity to cetirizine hydrochloride or levocetirizine hydrochloride.
Hydroxyzine is contraindicated in patients with a prolonged QT interval.
Hydroxyzine, when administered to the pregnant mouse, rat, and rabbit, induced fetal abnormalities in the rat and mouse at doses substantially above the human therapeutic range. Clinical data in human beings are inadequate to establish safety in early pregnancy. Until such data are available, hydroxyzine is contraindicated in early pregnancy.
Hydroxyzine is contraindicated for patients who have shown a previous hypersensitivity to it.
Side effects reported with the administration of hydroxyzine hydrochloride are usually mild and transitory in nature.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact PAI Pharma at 1-800-845-8210 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
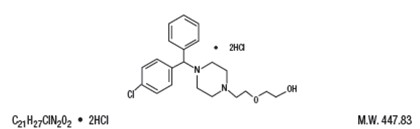
Hydroxyzine hydrochloride is designated chemically as ( ±)2-[2-[4-(
Inactive Ingredients for Hydroxyzine Hydrochloride Oral Solution, USP (Syrup) are: alcohol 0.5% (v/v), citric acid anhydrous, purified water, sodium benzoate, sodium citrate, sucrose. It may also contain sodium hydroxide for pH adjustment. The pH range is between 4.0 and 4.8.
Hydroxyzine hydrochloride is unrelated chemically to the phenothiazines, reserpine, meprobamate, or the benzodiazepines.
Hydroxyzine is not a cortical depressant, but its action may be due to a suppression of activity in certain key regions of the subcortical area of the central nervous system. Primary skeletal muscle relaxation has been demonstrated experimentally. Bronchodilator activity, and antihistaminic and analgesic effects have been demonstrated experimentally and confirmed clinically. An antiemetic effect, both by the apomorphine test and the veriloid test, has been demonstrated. Pharmacological and clinical studies indicate that hydroxyzine in therapeutic dosage does not increase gastric secretion or acidity and in most cases has mild antisecretory activity. Hydroxyzine is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and its clinical effects are usually noted within 15 to 30 minutes after oral administration.