Phentolamine Mesylate
Phentolamine Mesylate Prescribing Information
Phentolamine Mesylate for Injection, USP is indicated for the prevention or control of hypertensive episodes that may occur in a patient with pheochromocytoma as a result of stress or manipulation during preoperative preparation and surgical excision.
Phentolamine Mesylate for Injection, USP is indicated for the prevention or treatment of dermal necrosis and sloughing following intravenous administration or extravasation of norepinephrine.
Phentolamine Mesylate for Injection, USP is also indicated for the diagnosis of pheochromocytoma by the Phentolamine Mesylate for Injection, USP blocking test.
If the intramuscular test for pheochromocytoma is preferred, preparation is the same as for the intravenous test. Five milligrams of Phentolamine Mesylate for Injection, USP is then dissolved in 1mL of Sterile Water for Injection. The dose for adults is 5 mg intramuscularly; for children, 3 mg. Blood pressure is recorded every 5 minutes for 30-45 minutes following injection. A positive response is indicated when the blood pressure is reduced 35 mmHg systolic and 25 mmHg diastolic, or more, within 20 minutes following injection.
Myocardial infarction, history of myocardial infarction, coronary insufficiency, angina or other evidence suggestive of coronary artery disease; hypersensitivity to phentolamine or related compounds.
Acute and prolonged hypotensive episodes, tachycardia, and cardiac arrhythmias have been reported. In addition, weakness, dizziness, flushing, orthostatic hypotension, nasal stuffiness, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea may occur.
See
Note:
For preoperative reduction of elevated blood pressure, 5 mg of Phentolamine Mesylate for Injection, USP (1mg for children) is injected intravenously or intramuscularly 1 or 2 hours before surgery, and repeated if necessary.
During surgery, Phentolamine Mesylate for Injection, USP (5 mg for adults, 1 mg for children) is administered intravenously as indicated, to help prevent or control paroxysms of hypertension, tachycardia, respiratory depression, convulsions, or other effects of epinephrine intoxication. (Postoperatively, norepinephrine may be given to control the hypotension that commonly follows complete removal of a pheochromocytoma.)
The test is most reliable in detecting pheochromocytoma in patients with sustained hypertension and least reliable in those with paroxysmal hypertension. False-positive tests may occur in patients with hypertension without pheochromocytoma.
The CONTRAINDICATIONS, WARNINGS, and PRECAUTIONSsections should be reviewed. Sedatives, analgesics, and all other medications except those that might be deemed essential (such as digitalis and insulin) are withheld for at least 24 hours, and preferably 48 -72 hours, prior to the test. Antihypertensive drugs are withheld until blood pressure returns to the untreated, hypertensive level. This test is not performed on a patient who is normotensive.
The patient is kept at rest in the supine position throughout the test, preferably in a quiet, darkened room. Injection of Phentolamine Mesylate for Injection, USP is delayed until blood pressure is stabilized, as evidenced by blood pressure readings taken every 10 minutes for at least 30 minutes.
Five milligrams of Phentolamine Mesylate for Injection, USP is dissolved in 1mL of Sterile Water for Injection. The dose for adults is 5 mg; for children, 1 mg.
The syringe needle is inserted into the vein, and injection is delayed until pressor response to venipuncture has subsided.
Phentolamine Mesylate for Injection, USP is injected rapidly. Blood pressure is recorded immediately after injection, at 30-second intervals for the first 3 minutes, and at 60-second intervals for the next 7 minutes.
A positive response, suggestive of pheochromocytoma, is indicated when the blood pressure is reduced more than 35 mmHg systolic and 25 mmHg diastolic. A typical positive response is a reduction in pressure of 60 mmHg systolic and 25 mmHg diastolic. Usually, maximal effect is evident within 2 minutes after injection. A return to preinjection pressure commonly occurs within 15-30 minutes but may occur more rapidly.
If blood pressure decreases to a dangerous level, the patient should be treated as outlined under OVERDOSAGE.
A positive response should always be confirmed by other diagnostic procedures, preferably by measurement of urinary catecholamines or their metabolites.
A negative response is indicated when the blood pressure is elevated, unchanged, or reduced less than 35 mmHg, systolic and 25 mmHg diastolic after injection of Phentolamine Mesylate for Injection, USP. A negative response to this test does not exclude the diagnosis of pheochromocytoma, especially in patients with paroxysmal hypertension in whom the incidence of false-negative responses is high.
If the intramuscular test for pheochromocytoma is preferred, preparation is the same as for the intravenous test. Five milligrams of Phentolamine Mesylate for Injection, USP is then dissolved in 1mL of Sterile Water for Injection. The dose for adults is 5 mg intramuscularly; for children, 3 mg. Blood pressure is recorded every 5 minutes for 30-45 minutes following injection. A positive response is indicated when the blood pressure is reduced 35 mmHg systolic and 25 mmHg diastolic, or more, within 20 minutes following injection.
The test is most reliable in detecting pheochromocytoma in patients with sustained hypertension and least reliable in those with paroxysmal hypertension. False-positive tests may occur in patients with hypertension without pheochromocytoma.
The CONTRAINDICATIONS, WARNINGS, and PRECAUTIONSsections should be reviewed. Sedatives, analgesics, and all other medications except those that might be deemed essential (such as digitalis and insulin) are withheld for at least 24 hours, and preferably 48 -72 hours, prior to the test. Antihypertensive drugs are withheld until blood pressure returns to the untreated, hypertensive level. This test is not performed on a patient who is normotensive.
Phentolamine Mesylate for Injection, USP is an antihypertensive, available in vials for intravenous and intramuscular administration. Each vial contains phentolamine mesylate, USP, 5 mg, and mannitol USP, 25 mg, in sterile, lyophilized form.
Phentolamine Mesylate, USP is 4,5-dihydro-2-[N-(
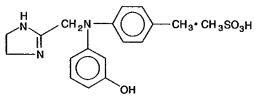
Phentolamine mesylate, USP is a white or off-white, odorless crystalline powder with a molecular weight of 377.46. Its solutions are acid to litmus. It is freely soluble in water and in alcohol, and slightly soluble in chloroform. It melts at about 178°C.